Potential Use of Dimocarpus longan Seeds as a Flocculant in Landfill Leachate Treatment
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Leachate Sampling and Characterization
2.2. Preparation of Dimocarpus Longan Seed Powder (LSP)
2.3. Coagulation–Flocculation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characteristics of Leachate
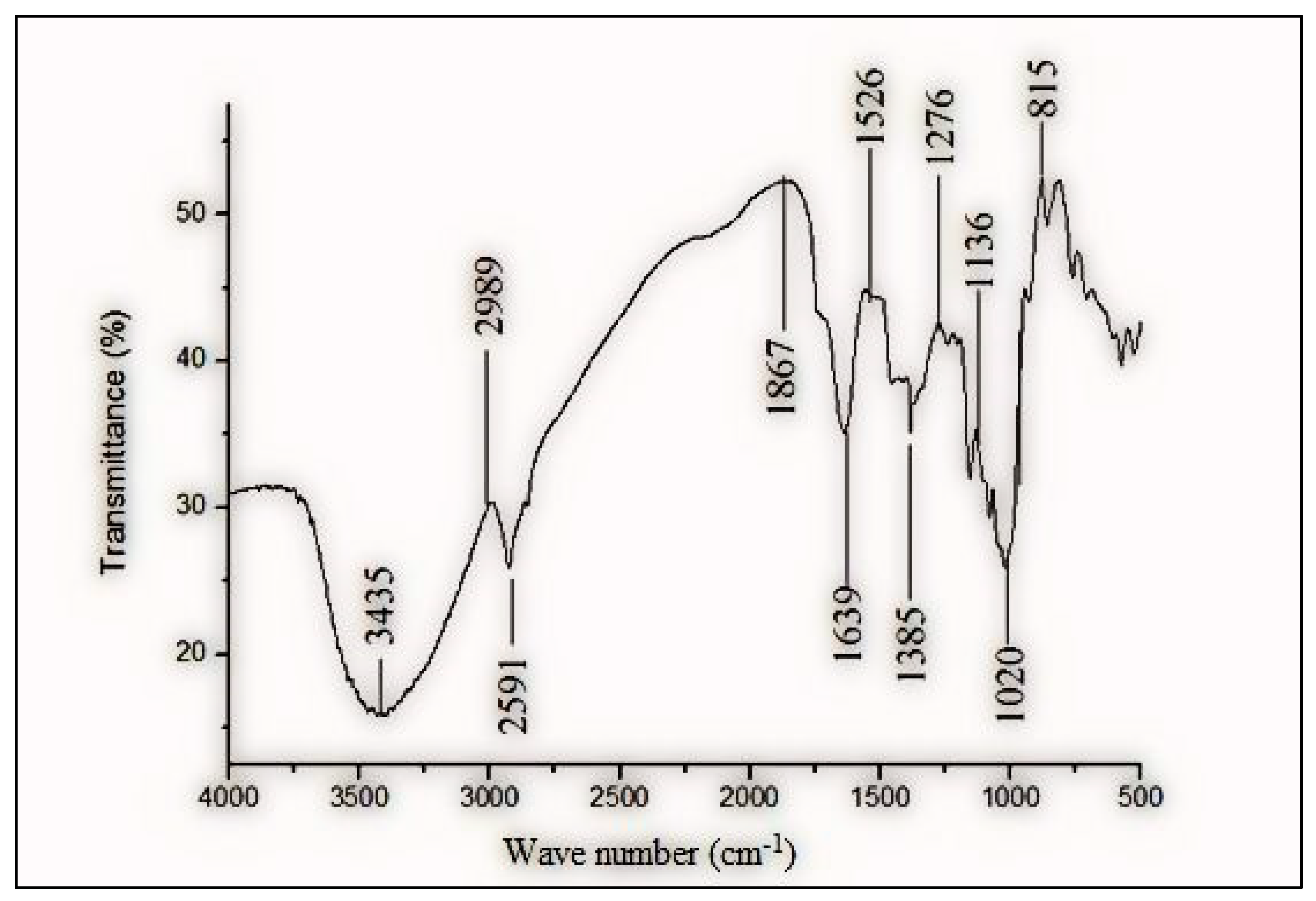
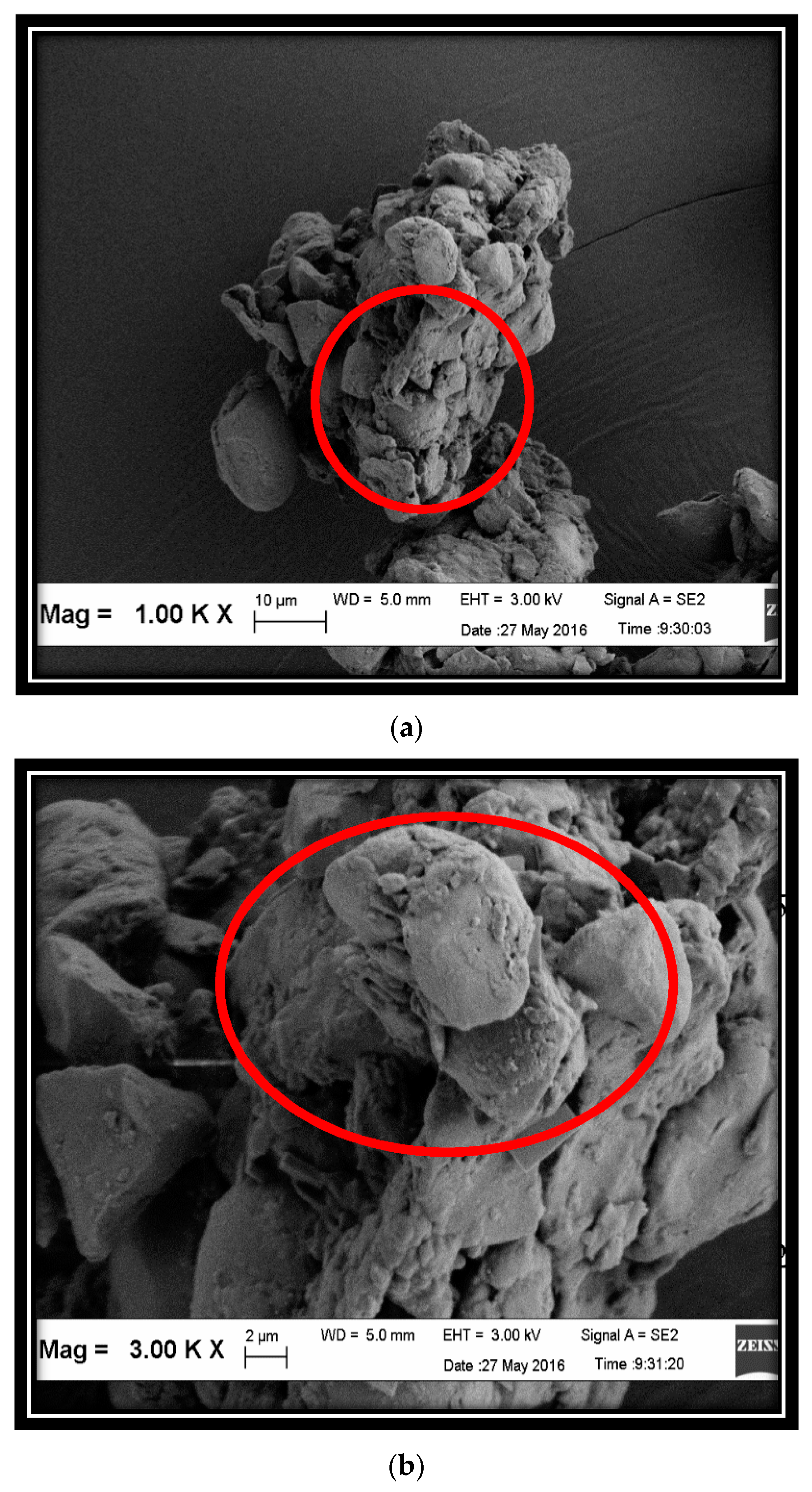
3.2. Characteristics of LSP
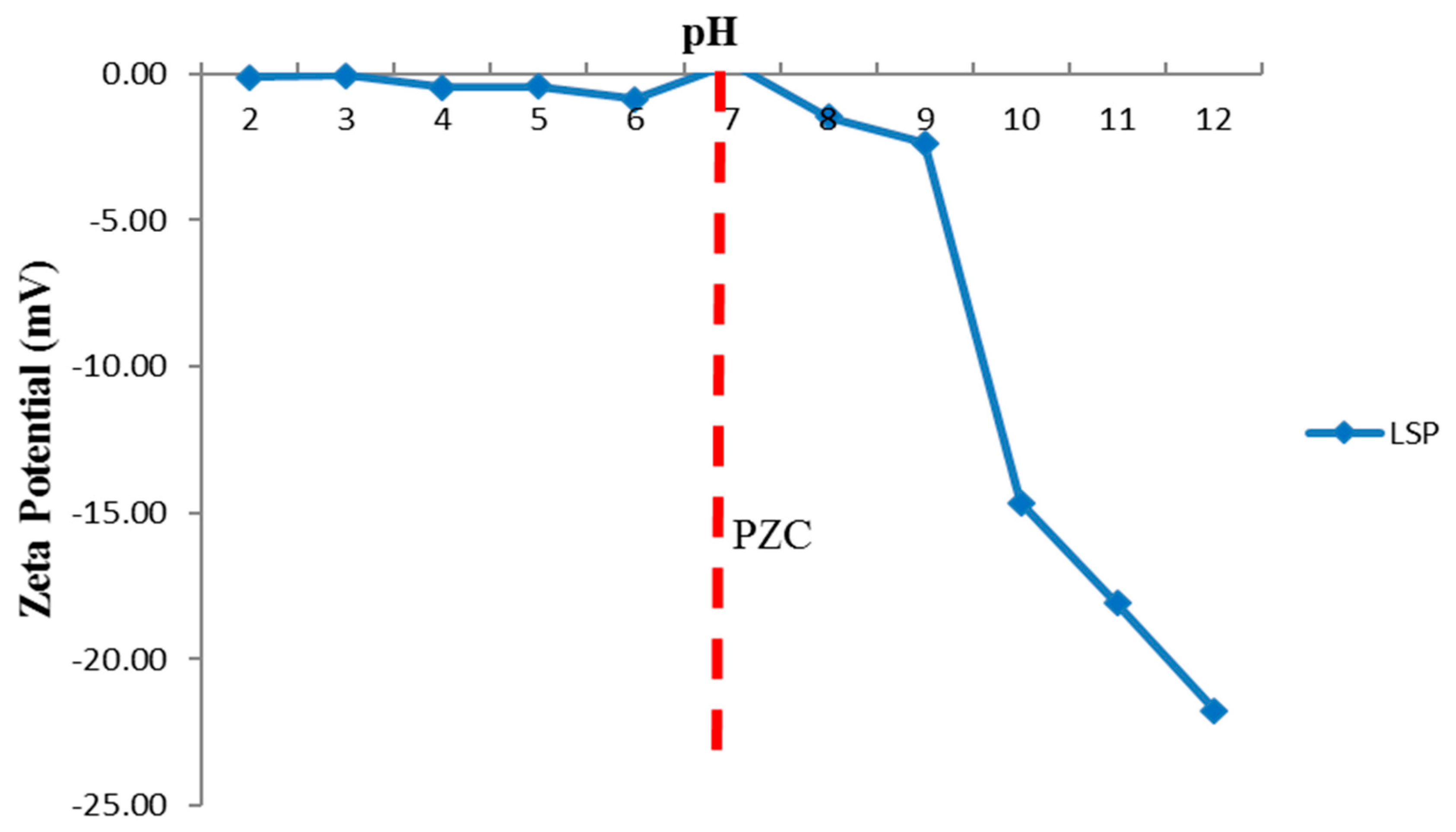
3.3. Determination of Zeta Potential and Particle Size od LSP as a Function of pH
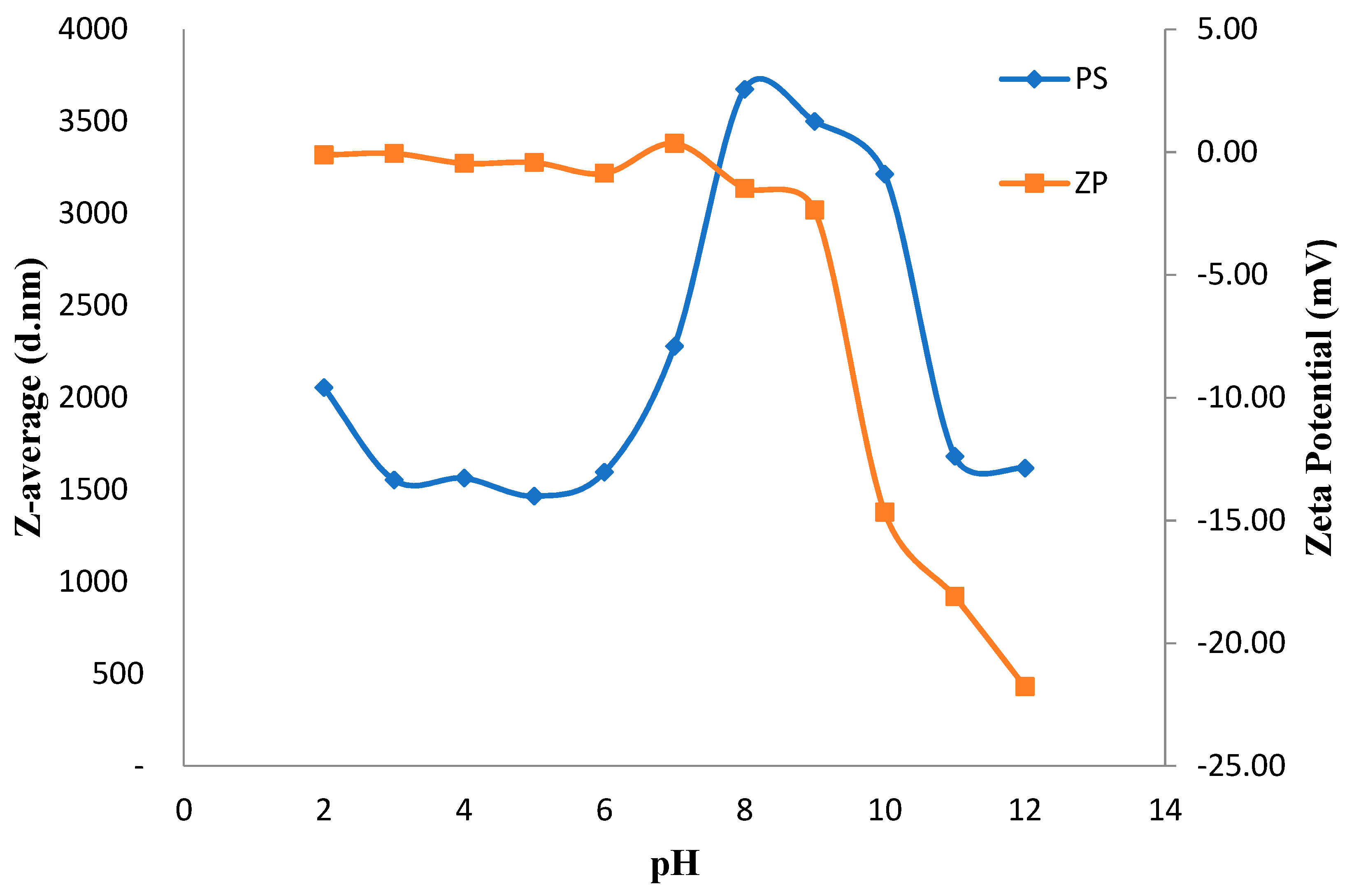
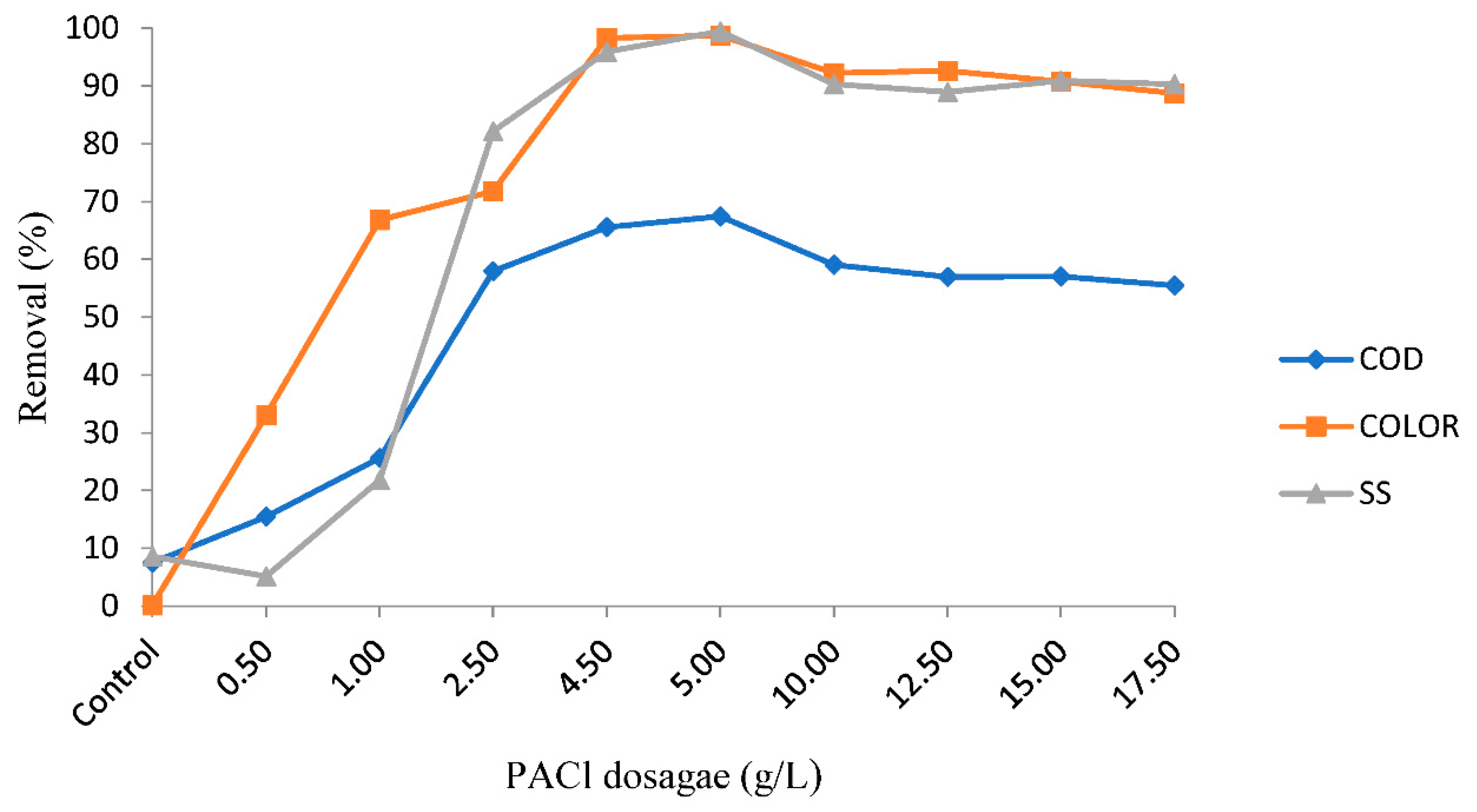
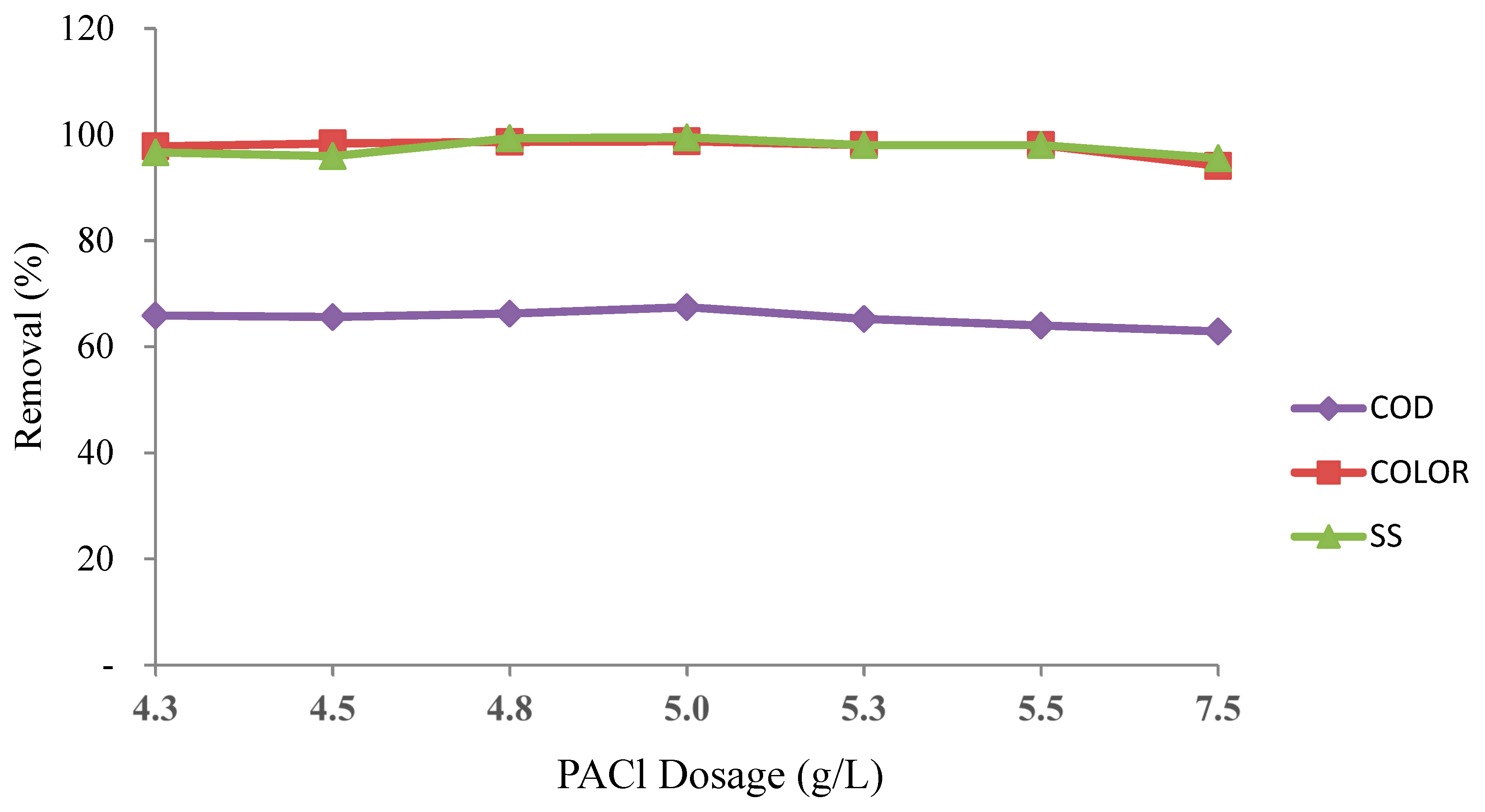
3.4. PACl as a Main Coagulant (Optimum pH and Dosage)
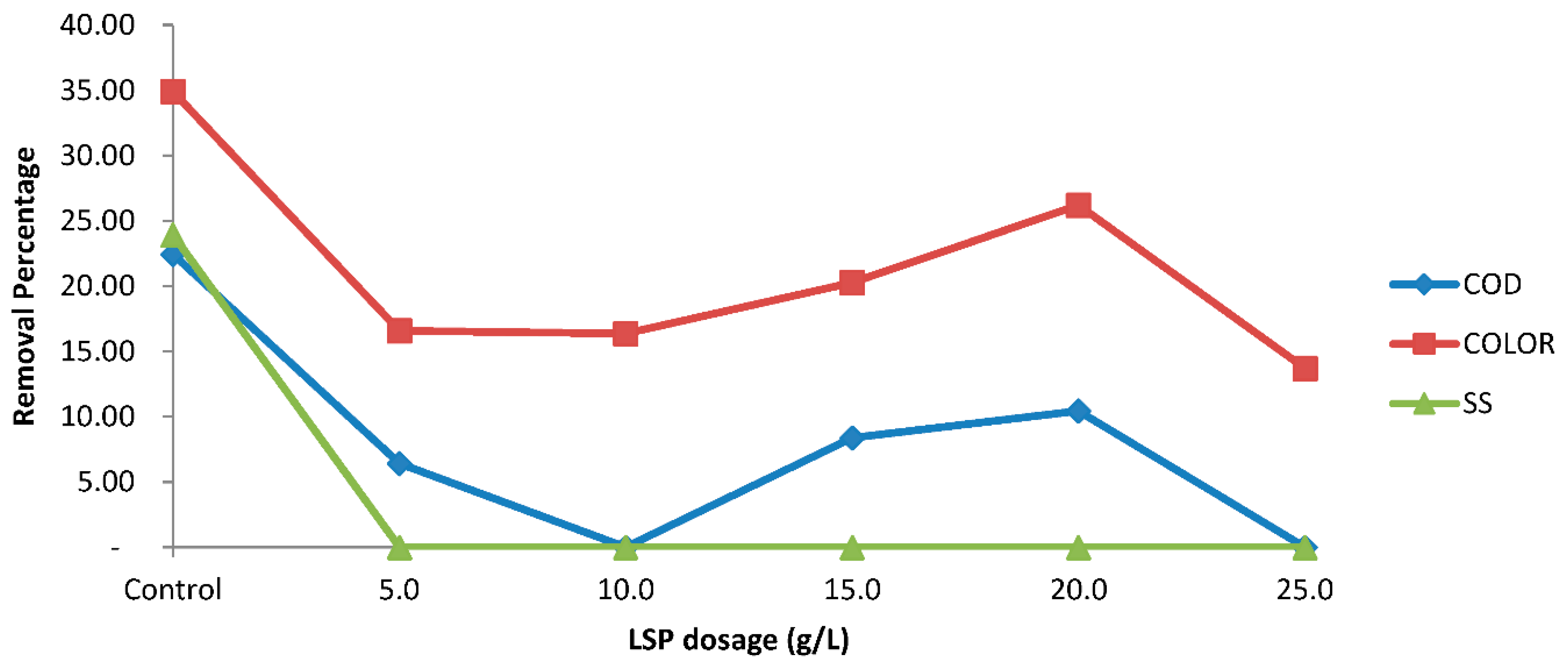
3.5. Removal Efficiency of SS, Color, and COD Using LSP
3.6. PACl as the Main Coagulant with LSP as a Coagulant Aid
3.7. Coagulant Cost Estimation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zamri, M.F.M.A.; Kamaruddin, M.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Aziz, H.A.; Foo, K.Y. Semi-aerobic stabilized landfill leachate treatment by ion exchange resin: Isotherm and kinetic study. Appl. Water Sci. 2017, 7, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Alias, S.; Adlan, M.N.; Asaari, A.; Zahari, M.S. Colour removal from landfill leachate by coagulation and flocculation processes. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Chu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Wang, H.; Long, Y.; Shen, D. Removal of phthalic acid diesters through a municipal solid waste landfill leachate treatment process. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2018, 20, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Adlan, M.N.; Adnan, N.H.; Alias, S. Physico-chemical removal of iron from semi-aerobic landfill leachate by limestone filter. Waste Manag. 2004, 24, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.-P.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, Y.-J.; Deng, N.-S.; Tao, T.; Zhuo, K. Landfill leachate treatment by a coagulation–photooxidation process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2002, 95, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gong, B.; Lin, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J. Robustness and microbial consortia succession of simultaneous partial nitrification, ANAMMOX and denitrification (SNAD) process for mature landfill leachate treatment under low temperature. Biochem. Eng. J. 2018, 132, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulikowska, D.; Klimiuk, E. The effect of landfill age on municipal leachate composition. Bioresour. Technol. 2008, 99, 5981–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umar, M.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S. Trends in the use of Fenton, electro-Fenton and photo-Fenton for the treatment of landfill leachate. Waste Manag. 2010, 30, 2113–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agamuthu, P.; Fauziah, S. Solid waste landfilling: Environmental factors and health. In Proceedings of the EU-Asia Solid Waste Management Conference, Perak, Malaysia, 28–29 October 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dia, O.; Drogui, P.; Buelna, G.; Dubé, R. Hybrid process, electrocoagulation-biofiltration for landfill leachate treatment. Waste Manag. 2018, 75, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uygur, A.; Kargı, F. Biological nutrient removal from pre-treated landfill leachate in a sequencing batch reactor. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 71, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, D.-H.; Chung, Y.-C.; Chang, W.-S. Use of coagulant and zeolite to enhance the biological treatment efficiency of high ammonia leachate. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2002, 37, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, H.A.; Daud, Z.; Adlan, M.N.; Hung, Y.-T. The use of polyaluminium chloride for removing colour, COD and ammonia from semi-aerobic leachate. Int. J. Environ. Eng. 2009, 1, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Huqe, A.; Mohajeri, S. Effects of ion exchange resins in different mobile ion forms on semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 61, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hamadani, Y.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Umar, M.; Bashir, M.J.; Adlan, M.N. Application of psyllium husk as coagulant and coagulant aid in semi-aerobic landfill leachate treatment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 190, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postacchini, L.; Ciarapica, F.E.; Bevilacqua, M. Environmental assessment of a landfill leachate treatment plant: Impacts and research for more sustainable chemical alternatives. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 183, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S. New sequential treatment for mature landfill leachate by cationic/anionic and anionic/cationic processes: Optimization and comparative study. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 186, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onay, T.T.; Pohland, F.G. In situ nitrogen management in controlled bioreactor landfills. Water Res. 1998, 32, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, L.-C.; Chang, J.-E.; Chung, C.-T. Electrochemical oxidation combined with physical–chemical pretreatment processes for the treatment of refractory landfill leachate. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2001, 18, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishak, A.R.; Hamid, F.S.; Mohamad, S.; Tay, K.S. Stabilized landfill leachate treatment by coagulation-flocculation coupled with UV-based sulfate radical oxidation process. Waste Manag. 2018, 76, 575–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by hydrolysing metal salts. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, T.A.; Lo, W.-H.; Chan, G.Y. Physico-chemical treatments for removal of recalcitrant contaminants from landfill leachate. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 129, 80–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amokrane, A.; Comel, C.; Veron, J. Landfill leachates pretreatment by coagulation-flocculation. Water Res. 1997, 31, 2775–2782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Pang, Y.; Li, X.; Chen, F.; Liao, X.; Lei, M.; Song, Y. Landfill leachate treatment by coagulation/flocculation combined with microelectrolysis-Fenton processes. Environ. Technol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaszuba, M.; Corbett, J.; Watson, F.M.; Jones, A. High-concentration zeta potential measurements using light-scattering techniques. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2010, 368, 4439–4451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R. Treatment of Landfill Leachate in Coagulation-Flocculation Method by Using Micro Zeolite and Micro Sand. Ph.D. Thesis, Faculty of Civil Engineering, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Parit Raja, Malaysia, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Fosso-Kankeu, E.; Waanders, F.; Mulaba-Bafubiandi, A.; Mishra, A. Flocculation performances of polymers and nanomaterials for the treatment of industrial wastewaters. Smart Mater. Waste Water Appl. 2016, 7, 213–235. [Google Scholar]
- Jadhav, M.V.; Mahajani, Y. A comparative study of natural coagulants in flocculation of local clay suspensions of varied turbidities. Int. J. Civ. Environ. Eng. 2013, 35, 26–39. [Google Scholar]
- Santos, T.R.; Silva, M.F.; Nishi, L.; Vieira, A.M.; Klein, M.R.; Andrade, M.B.; Vieira, M.F.; Bergamasco, R. Development of a magnetic coagulant based on Moringa oleifera seed extract for water treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 7692–7700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meraz, K.A.S.; Vargas, S.M.P.; Maldonado, J.T.L.; Bravo, J.M.C.; Guzman, M.T.O.; Maldonado, E.A.L. Eco-friendly innovation for nejayote coagulation–flocculation process using chitosan: Evaluation through zeta potential measurements. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 284, 536–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.; Xu, L.; Wu, P.; Xie, H.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, F.; Wei, X. Polyphenols from longan seeds and their radical-scavenging activity. Food Chem. 2009, 116, 433–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, Y.Y.; Barlow, P.J. Isolation and structure elucidation of phenolic compounds from longan (Dimocarpus longan Lour.) seed by high-performance liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2005, 1085, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangkadilok, N.; Sitthimonchai, S.; Worasuttayangkurn, L.; Mahidol, C.; Ruchirawat, M.; Satayavivad, J. Evaluation of free radical scavenging and antityrosinase activities of standardized longan fruit extract. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007, 45, 328–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.; Jain, P.; Saleem, S.; Rao, K. Extraction and Purification of Total Phenolic Content from seeds of Dimocarpus longan fruit. Res. Rev. J. Pharm. 2018, 4, 19–21. [Google Scholar]
- Katayon, S.; Noor, M.M.M.; Asma, M.; Ghani, L.A.; Thamer, A.; Azni, I.; Ahmad, J.; Khor, B.; Suleyman, A. Effects of storage conditions of Moringa oleifera seeds on its performance in coagulation. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 1455–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zawawi, M.H.; Abustan, I. Detection of groundwater aquifer using resistivity imaging profiling at Beriah Landfill Site, Perak, Malaysia. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 250–253, 1852–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APAH. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Waste Water, 21st ed.; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Makhtar, S.M.Z.; Ab Wahab, M.; Selimin, M.T.; Mohamed, N.C. Landfill Leachate Treatment by a Coagulation–Photocatalytic Process. In Proceedings of the 2011 International Conference on Environment and Industrial Innovation (ICEII 2011), Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 4–5 June 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.C.; Tiau, Y. Zeta Potential; Mercel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Salem, Z.; Hamouri, K.; Djemaa, R.; Allia, K. Evaluation of landfill leachate pollution and treatment. Desalination 2008, 220, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, M.J.K.; Aziz, H.A.; Yusoff, M.S.; Adlan, M.N. Application of response surface methodology (RSM) for optimization of ammoniacal nitrogen removal from semi-aerobic landfill leachate using ion exchange resin. Desalination 2010, 254, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awang, N.A.; Aziz, H.A. Hibiscus rosa-sinensis leaf extract as coagulant aid in leachate treatment. Appl. Water Sci. 2012, 2, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamali, H.A.; Mahvi, A.H.; Nabizadeh, R.; Vaezi, F.; Omrani, G.A. Combination of coagulation–flocculation and ozonation processes for treatment of partially stabilized landfill leachate of Tehran. World Appl. Sci. J. 2009, 5, 9–15. [Google Scholar]
- Baghvand, A.; Zand, A.D.; Mehrdadi, N.; Karbassi, A. Optimizing coagulation process for low to high turbidity waters using aluminum and iron salts. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 6, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.M.; Daud, Z.; Latif, A.A.A. Treatment of Leachate by coagulation-flocculation using different coagulants and polymer: A review. Int. J. Adv. Sci. Eng. Inf. Technol. 2012, 2, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, T.; Cao, T.; Szilagyi, I.; Borkovec, M.; Trefalt, G. Aggregation and Charging of Sulfate and Amidine Latex Particles in the Presence of Oxyanions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 524, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abood, A.R.; Bao, J.; Abudi, Z.N.; Zheng, D.; Gao, C. Pretreatment of nonbiodegradable landfill leachate by air stripping coupled with agitation as ammonia stripping and coagulation–flocculation processes. Clean Technol. Environ. Policy 2013, 15, 1069–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


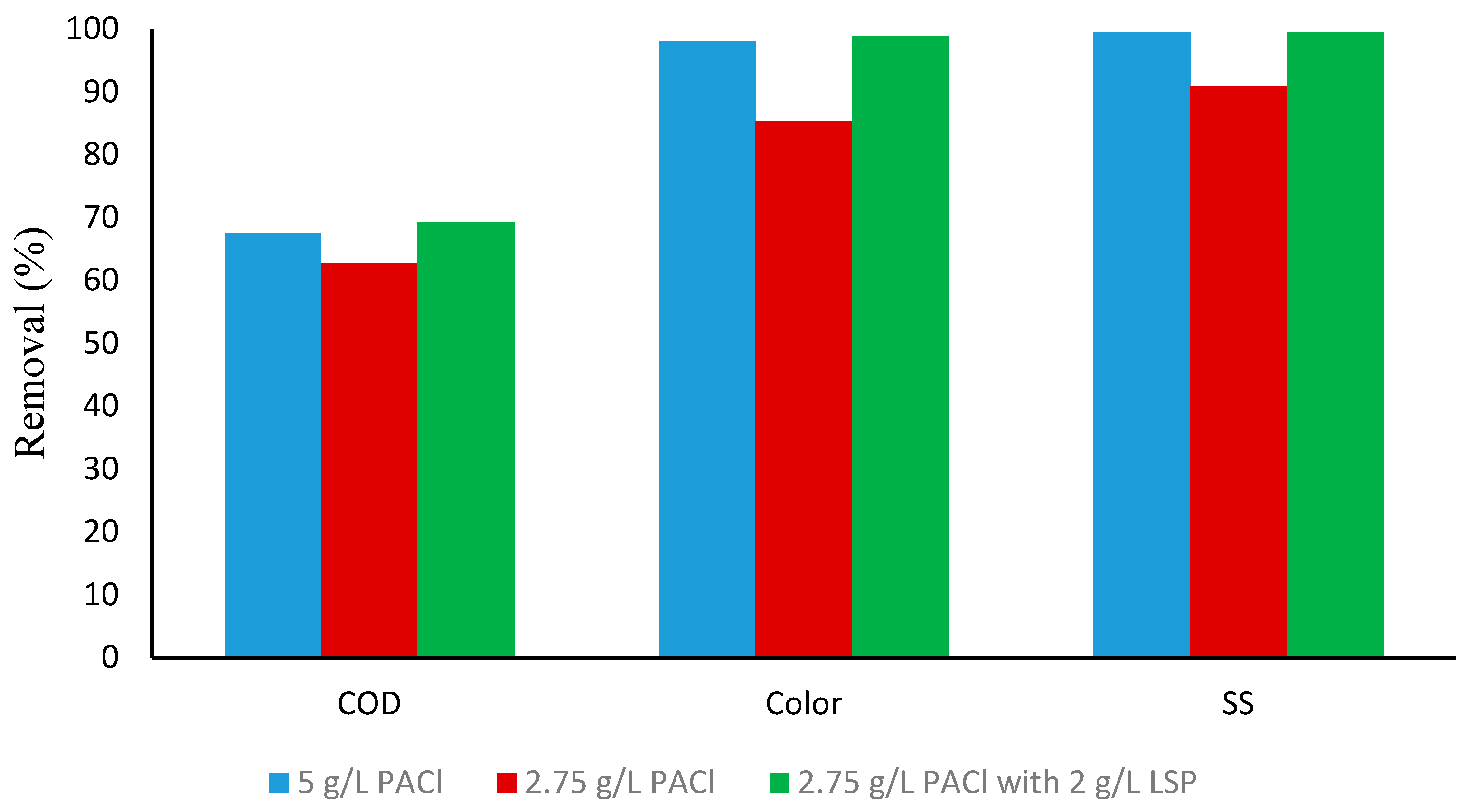
| Parameter | Min | Max | Average | Std. Dev. | Standard |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pH | 7.89 | 8.72 | 8.28 | 0.22 | 6.0–9.0 |
| Residual conductivity (µS/cm) | 814.00 | 966.00 | 880.94 | 51.19 | - |
| Particle size, d (µm) | 0.45 | 94.66 | 61.15 | 23.36 | - |
| COD (mg/L) | 3016.67 | 3055.00 | 3036.82 | 14.34 | 400 |
| BOD5 (mg/L) | 107.33–176 | 130.92 | 48.55 | 20 | |
| Turbidity (NTU) | 228.75 | 337.50 | 306.25 | 34.59 | - |
| Suspended solids (mg/L) | 591.67 | 866.67 | 745.00 | 99.67 | 50 |
| Manganese (mg/L) | 4.17 | 7.50 | 5.83 | 1.49 | 0.2 |
| Iron (mg/L) | 4.00 | 4.92 | 4.47 | 0.35 | 5.0 |
| Copper (mg/L) | 3.00 | 5.08 | 4.00 | 0.61 | 0.2 |
| Zinc (mg/L) | 0.83 | 1.75 | 1.15 | 0.26 | 2.0 |
| Ammonia-nitrogen (mg/L) | 737.50 | 875.00 | 794.00 | 47.82 | 5.0 |
| Phosphate (mg/L) | 43.75 | 62.50 | 53.25 | 6.28 | - |
| Color (PtCO) | 4525.00 | 7150.00 | 5517.50 | 794.75 | 100 ADMI |
| Coagulant | Price of Chemical (RM) | Optimum Concentration Used | Amount of Chemical to Treat 1 m3 of Leachate/Day | The Cost to Treat 1 m3 of Leachate (RM) * | Total (RM) * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5000 mg/L PACl | 300/L | 13 mL/500 mL | 26 L | 7800 | 7800 |
| 2750 mg/L PACl | 300/L | 7.6 mL/500 mL | 15.2 L | 4560 | 4646 |
| 2000 mg/L LSP | 4.30/kg | 10 g/500 mL | 20 kg | 86 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziz, H.A.; Rahim, N.A.; Ramli, S.F.; Alazaiza, M.Y.D.; Omar, F.M.; Hung, Y.-T. Potential Use of Dimocarpus longan Seeds as a Flocculant in Landfill Leachate Treatment. Water 2018, 10, 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111672
Aziz HA, Rahim NA, Ramli SF, Alazaiza MYD, Omar FM, Hung Y-T. Potential Use of Dimocarpus longan Seeds as a Flocculant in Landfill Leachate Treatment. Water. 2018; 10(11):1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111672
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziz, Hamidi Abdul, Nor Aini Rahim, Siti Fatihah Ramli, Motasem Y. D. Alazaiza, Fatehah Mohd Omar, and Yung-Tse Hung. 2018. "Potential Use of Dimocarpus longan Seeds as a Flocculant in Landfill Leachate Treatment" Water 10, no. 11: 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111672
APA StyleAziz, H. A., Rahim, N. A., Ramli, S. F., Alazaiza, M. Y. D., Omar, F. M., & Hung, Y.-T. (2018). Potential Use of Dimocarpus longan Seeds as a Flocculant in Landfill Leachate Treatment. Water, 10(11), 1672. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111672







