Abstract
Municipal wastewater sludge was produced by chemical coagulation of synthetic wastewater (sww) based on Synthene Scarlet P3GL disperse dye and real municipal wastewater (nww), coagulated by commercial coagulants PAX (prepolymerised aluminum coagulant) and PIX (a ferric coagulant based on Fe2(SO4)3). An attempt was made to correlate the sludge’s dewatering capacity (in terms of capillary suction time—CST) with operation parameters for wastewater treatment, size distribution and specific surface area of the sludge particles. It was found that the presence of phosphate ions in the system facilitates the removal efficiency of the above-mentioned dye (L) due to the interaction between the dye molecules and H2PO4− ions. Unlike sww, negatively charged organic substances (sorg) in nww are directly adsorbed on the surface of colloidal particles {Fe(OH)3} and {Al(OH)3} (prtc). It was also discovered that an increase in the dose of a coagulant led to an increase of CST for sww sludge and to a decrease of CST for nww sludge. It has been suggested that flocs composed of spherical {Al(OH)3} units possessed more internal space for water than aggregates consisting of rod-shaped {Fe(OH)3} units and, consequently, it is more difficult to remove water from Al-sww sludge than from Fe-sww. The results obtained showed that smaller particles dominate in sww sludge, while larger particles are prevalent in nww sludge. To explain this distinct difference in the size distribution of particles in sludge obtained with the use of Al3+ and Fe3+, simple models of aggregation and agglomeration-flocculation processes (aaf) of treated wastewater have been proposed. Except for PIX in nww, the analyzed particles of the investigated types of sludge were characterized by similar specific surface area (Sps), regardless of the kind of sludge or the applied coagulant. Slightly larger, negatively-charged sorg bridges, anchored directly on the surface of positive prtc are more effective in closing the structure of nww sludge than small L bridges of the dye molecules anchored on the surface of prtc via H2PO4−. All the discovered aspects could lead to improved performance of wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) by increasing the efficiency of sludge dewatering.
1. Introduction
Chemical coagulation is the second step in wastewater treatment [1,2]. This process has a significant influence on the properties and structure of the resulting sludge [3,4,5,6,7]. The pH of sludge decreases during chemical coagulation because Fe3+ or Al3+ undergoes cationic hydrolysis and its first stage can be described as follows:
Fe3+ (Al3+) + HOH = FeOH2+ (AlOH2+) + H+
Positively-charged, colloidal particles {Fe(OH)3} and/or {Al(OH)3}, described further as prtc (colloidal particles), are formed during the subsequent reactions which occur in wastewater [1,8]. These particles act as adsorbents [9] in the processes of aggregation and agglomeration-flocculation (aaf) of pollutants from wastewater. The surface charge of prtc is neutralized by negatively-charged components such as H2PO4−, or by negatively-charged colloids, called sorg (organic substances). The removal of neutral or positively-charged pollutants takes place during the so-called flocculation [1,5,10]. This mechanism dominates also in the case of wastewater treatment by electrocoagulation [11,12,13], particularly during recirculating electrolysis of wastewater [14].
The quantity and quality of municipal wastewater sludge are indicators for the wastewater treatment performance and, on the other hand, determine the possibilities for further utilization of sludge [15]. For practical and technological reasons, the dewatering capability of sludge is extremely important [16]. This property of municipal wastewater sludge very much depends on the type and dose of inorganic coagulant added to the wastewater [17,18,19]. The structure of sludge flocs, as well as their physical and chemical characteristics, determine the efficiency of the dewatering process of municipal wastewater sludge [16,20]. Under laboratory conditions, so-called capillary suction time (CST) is a measure of the sludge’s dewatering capacity [21]. Reproducibility and precision of CST measurements [22,23] are important, both for theoretical considerations [24] and in practice, e.g., for determination of an appropriate dose of an inorganic flocculant [25].
Probably the most important effect of flocs on the structure of municipal wastewater sludge is through aggregation and agglomeration-flocculation (aaf) processes [26,27,28,29]. Numerous papers have been published, including information about measurements, modeling and characterization of the structure of municipal wastewater sludge [30,31,32,33]. Often, the so-called fractal dimension D becomes a specific research instrument [34,35]. For self-similar objects, e.g., sludge floc-aggregates whose structure does not depend on a change in the scale, D is defined as follows:
where M is the mass comprised in a sphere of the diameter R [34].
M(R)~RD
The value of D, either determined experimentally or calculated theoretically, has been used in many theoretical considerations, e.g., in kinetic calculations [36], and also in practical solutions, e.g., for the filtration of excessive active sludge [37]. The structure and properties of municipal wastewater sludge can also be examined directly through the determination of the distribution of the sizes of particles and their specific surface [38,39,40].
Since it is suspected that there is an interpretable correlation between the structure of municipal wastewater sludge and the value of CST corresponding to the sludge, this paper analyzes the observed correlations and proposes simple models of aaf processes for chemically-coagulated synthetic and real municipal wastewater.
The consecutive stages presented and considered in this article are based on:
- (a)
- results of traditional jar tests,
- (b)
- CST measurements,
- (c)
- determination of the volumetric dimension (Dv) and respectively of the specific surface area (Sps).
2. Materials and Methods
Synthetic dyeing wastewater (sww) and real municipal wastewater (nww) originating from a wastewater treatment plant in Reszel (North-Eastern Poland) were investigated. The municipal wastewater had the following parameters: suspended solids: SS (mg/L) = 250–800; total phosphorus: P (mg/L) = 9–13.5, chemical oxygen demand: COD (mgO2/L) = 600–1800; turbidity: TU = 80–160 NTU; and pH = 6.6–7.8. In turn, each 1 L of sww contained 31.3 mg H2PO4− (10 mg P) and 50 mg disperse dye (L) (Synthene Scarlet P3GL) produced by the Boruta-Zachem Chemical Company, from Zgierz (Poland). Therefore, the composition of synthetic dyeing wastewater (31.3 mg H2PO4− + 50 mg disperse dye/L) is a result of the synergy effect of both components; a mixture of dye and municipal wastewaters is susceptible on coagulation and/or electrocoagulation, which has been proved and explained by previous studies [41]. It was experimentally demonstrated that in the absence of P-PO4 it is impossible to remove even a small amount of dye L by chemical coagulation of its aqueous solution. However, coagulation of L solution proceeds effectively and efficiently in the presence of phosphate ions [42] and for this reason we decided to use this composition of synthetic wastewater in the present study.
The sludge samples submitted for further tests were obtained in wastewater coagulation by: (a) PIX 113, a ferric coagulant (based on Fe2(SO4)3) widely used in Poland, and (b) PAX 18, pre-polymerised aluminum coagulant, an alternative to PIX. Both coagulants were produced by Kemipol, the Polish branch of the Kemira Chemicals in Gdansk, Poland. By adding the above-mentioned coagulants to the wastewaters, many intermediate polymeric species such as (Al(OH)3)n, (Fe(OH)3)m or (Fe(OH)2)p are produced, being responsible for colloidal sorption on their surfaces of pollutants from wastewaters.
In sww, the dye concentration was determined spectrophotometrically at a wavelength λ = 460 nm, while P-PO4 was assayed according to the standard method (λ = 690 nm) using a HACH DR 3900 instrument (Hach Company, Loveland, CO, USA) with 13 mm standard cell tests.
After 30 min of sedimentation, followed by decantation, 25.0 cm3 of separated sludge was collected in order to determine capillary suction time CST [21,22,23], which is a measurement of the dewaterability of sludge. In CST measurements, a new prototype developed in the University of Warmia and Mazury in Olsztyn, Poland (DWTEST—Dewatering tester, schematically illustrated in Figure 1), was used.
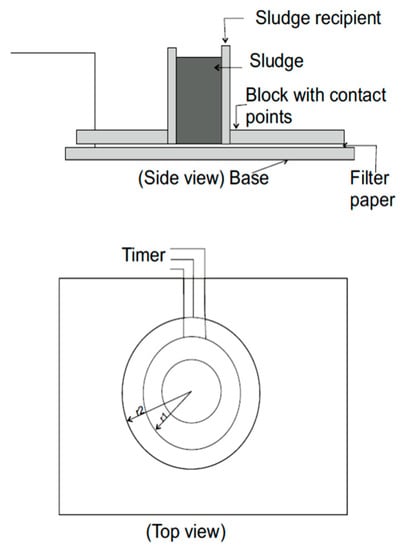
Figure 1.
The schematic diagrame of a new DWTEST prototype for measurement of the capillary suction time (CST).
In each case, 25 cm3 of separated sludge was applied onto a Whatman filter paper disc, while pressing the appropriate button on the apparatus. After several dozen seconds, the value of measured time corresponding to the flow of the liquid between electrodes in the measuring cell was displayed. The measurements were always repeated three times and the values for standard deviation (SD) (s) are indicated in the graphs. The results of CST measurements are presented in the graphical form in dependence of coagulant dose CST = f(mg Al or Fe/L).
Particle size distribution of the sludge was determined by measurement of laser light dispersion using a Mastersizer 3000 unit, Malvern Instruments, Malvern, United Kingdom [43]. Sludge samples were instilled to a measuring cell until an obscuration of 5–15% was achieved. The refractive indices for water and wastewater were 1.33 and 3.80, respectively. The particle size distribution was used to determine the mean particle size D(3,2) (μm) and available surface area (Sps) of particles in the sludge (m2/g). Mean particle size is defined as [43]:
where ni is the number of particles of diameter di.
D(3,2) = nidi3/Σnidi2
Volumetric dimensions Dv10, Dv50 and Dv90 denoting the maximum particle diameter below which particles account for 10%, 50% and 90% of the volume of the analyzed sludge, respectively, were also calculated. The results represent the mean values of three replications for each type of sludge evaluated.
3. Results and Discussion
The results of the laboratory tests are presented in Table 1 and Table 2 and some of them in Figure 2. The mean values from three repetitions were used for plotting the graphs and SD values (in % or s) were marked in each case.

Table 1.
The specific surface area (Sps) and volumetric dimension (Dv) values, for sludge particles illustrated in Figure 8.

Table 2.
Number of units in a statistical floc of the analyzed sludge.
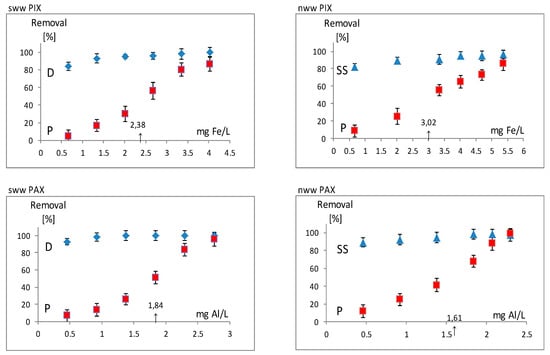
Figure 2.
Synthetic wastewater (sww) and real municipal wastewater (nww) coagulated by PIX and PAX.
The initial (o) and final (f) values of the pH, concentration of total phosphorus (P), chemical oxygen demand (COD) and suspended solids (SS) are presented for both PIX and PAX coagulants used for treatment of both sww and nww:
PIX-sww: pHo = 5.2 → pHf = 4.75 PAX-sww: pHo = 5.2 → pHf = 5.0
PIX-nww: SSo = 750, Po = 11.40; CODo = 1690 → CODf = 360 (mgO2/L);
pHo = 7.53 → pHf = 6.84
PAX-nww: SSo = 440, Po = 9.75; CODo = 1190 → CODf = 313 (mgO2/L);
pHo = 7.80 → pHf = 7.14
Courses of all four dependences, where Removal = f(coagulant dose), showed that the highest dose of both aluminum ions and ferric ions ensured 100% removal of L from sww and SS from nww. Under these conditions, PIX removed 86–87%, and PAX 96–99% of phosphorus (P) from both sww and nww. Because the limit of P allowed in the effluents according to Polish legislation for wastewater treatment plants (WTTP) is 5 mg P/L, the sludge analyzed in our research was precipitated under conditions ensuring 50% removal of P from treated wastewater. It can be assumed that primary coagulation of municipal wastewater in Poland is sufficient to obtain the required P level in effluent, principally owing to the mentioned 50% coagulation of phosphorus compounds. In all of the four diagrams seen in Figure 2, an arrow on the x-axis indicates the numerical value of the dose of a coagulant (fes, fen, als, aln) adequate for attaining 50% of phosphorus removal from sww and nww. When these doses are added, i.e., to sww: fes = 2.38 mg Fe/L ≡ 0.0425 mmol Fe/L and als =1.84 mg Al/L ≡ 0.068 mmol Al/L; and to nww: fen = 3.02 mg Fe/L ≡ 0.054 mmol Fe/L and aln = 1.61 mg Al/L ≡ 0.060 mmol Al/L, sediments were obtained, which were subsequently tested to determine CST, Sps and Dv (Table 1) as well as percentage shares of particular particle sizes.
During the coagulation process of sww, the presence of phosphate ions in the system made it possible to effectively remove the dye from the liquid phase of wastewater. Phosphate anions are adsorbed on positively-charged colloidal particles {Fe(OH)3} and/or {Al(OH)3} (prtc), creating units of the type:
{Fe(OH)3} − (H2PO4−)c and {Al(OH)3} − (H2PO4−)d
As the negative sorbate (phosphate) accumulates on prtc, the positive potential of the systems in Formulas (4) decreases and mutual repulsive forces weaken between particles, which determine the direction, range and intensity of Brownian motions. Thus, the stability of the colloidal system decreases, while the probability of collisions between particles rises and finally an aaf process may occur.
In practice, an aqueous solution of phosphate ions undergoes coagulation (both precipitation and adsorption) and almost all phosphates could be transferred into municipal wastewater sludge.
As mentioned at the beginning of the Materials and Methods Section, in the absence of P-PO4 it was impossible to remove even a small amount of a dye directly, by chemical coagulation of a water solution of L, whereas the coagulation or electro-coagulation of L [42] proceeded efficiently only when “supported” by phosphate ions. To explain the reasons for this phenomenon, the following simple model of adsorption of a dye particle to systems is proposed in Formulas (5) and (6):
{Fe(OH)3} − (H2PO4−)c − L
{Al(OH)3} − (H2PO4−)d − L
This model assumes a slightly positive surface charge of a dye molecule, which repels it from a positive prtc while attracting it to prtc centers absorbing H2PO4−. It is thus based on the assumption that dye molecules can be adsorbed to units, Formulas (4), by forming bridges with the help of previously adsorbed H2PO4− ions (Formulas (5) and (6)). Although the occurrence of dye molecules, bridged on the surface of prtc with the help of H2PO4− slightly decreases the process of neutralization of the system’s surface, it also causes the growth of its mass and size, which is conducive to destabilization of prtc and leads to aaf. Thus, in laboratory practice, slightly more coagulant is used to achieve destabilization of a mixture of dye and H2PO4− than for a solution containing only H2PO4−.
Figure 3a shows volumetric proportions for a spherical colloidal particle {Al(OH)3} (sized from 86 to 206 μm, for which the diameter was assumed to be around 165 nm [44], which in fact, has a rather corrugated surface), a molecule of the dye (having an estimated 1 mole ≈ 500 g and a size of about 10 nm) and a H2PO4− ion (with a diameter of 1.2 nm). In the subsequent models presented in this paper (Figure 3b), for better clarity of the visualization, rod-shaped particles {Fe(OH)3} [45] and spherical particles {Al(OH)3} [44] are presented in appropriately diminished sizes, which is highlighted by using a broken line to draw their contours.
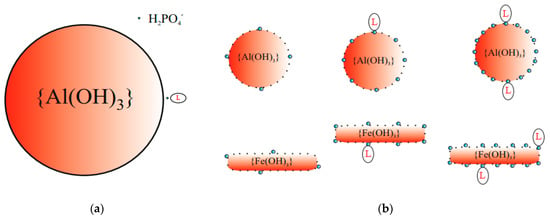
Figure 3.
Schematic diagrams of interactions between colloidal particles and a dye molecule and H2PO4− ion, respectively: (a) Approximate proportions between sizes of: colloidal particle {Al(OH)3}, dye L molecule and H2PO4− ion; (b) schemes of structures for Formulas (4) and (5) responsible for adsorption of H2PO4− and L from sww on the surface of colloidal particles (prtc).
As expected, amounts of mg Fe/L from PIX (fes and fen) needed to remove 50% of P were higher than the respective amounts of mg Al/L from PAX (als and aln). Simultaneously, the same amounts expressed in mmol/L were higher for PAX than for PIX. In Poland PIX, rather than PAX, is a more popular coagulant in urban wastewater treatment plants (despite being less efficient) because of its much lower price per 1 kg of coagulant.
Slightly more mg/L PIX was applied to remove 50% P from nww than from sww. Most probably, a part of the PIX dose in nww had been sacrificed to remove 1.330 mg/L sorg denoted as COD; CODo = 1690 → CODf = 360 mgO2/L (Figure 2). Meanwhile, the same sample was characterized by a slightly higher concentration of phosphorus (Po = 11.4 → Pf = 0.64 mg/L) and SSo (750 mg/L) than the sample treated by PAX (Po = 9.75 → Pf = 0.22 mg/L, SSo = 440 mg/L). For nww a slightly lower dose of PAX in mg/L, than from sww, was needed to remove 50% of phosphorus, which was most probably a consequence of lower consumption of the coagulant for removing just 887 mgO2/L COD from nww (CODo = 1190 → CODf = 313 mgO2/L) at an approximately similar efficiency as PIX in the removal of L from sww.
Figure 4 contains a schematic representation of the removal of phosphorus as well as sorg from nww using PIX and PAX, respectively. Unlike L being bridged in sww by H2PO4−, negatively charged sorg in nww are directly adsorbed on the surface of prtc. The schemas shown in Figure 4 also account for the hydrophilic properties of wastewater sol (sorg), marking in yellow the water molecules which stabilize this sol. Because of the negative charge of sorg here (nww), fewer H2PO4− are adsorbed on the surface of prtc (only 7 H2PO4− ions in the schema in Figure 4), compared to the respective surfaces of prtc formed during sww coagulation.
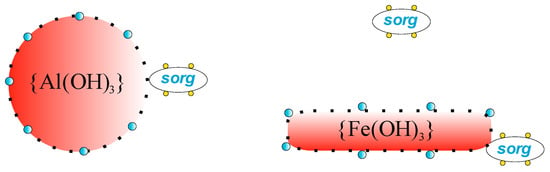
Figure 4.
Schemas of structures responsible for adsorption of H2PO4− and organic substances (sorg) from nww on the surface of prtc.
The following graphs in Figure 5 show the process of dewatering sww and nww, presented in the form of CST = f(dose of coagulant) relationships.
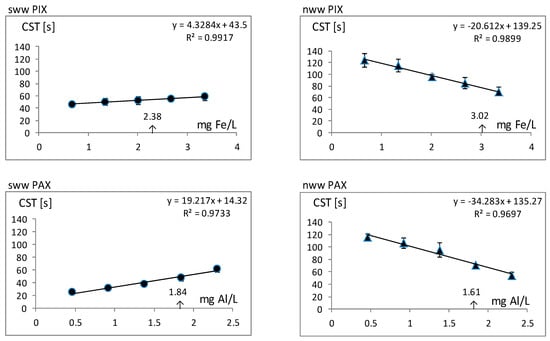
Figure 5.
Dewatering of sludge obtained from sww and nww coagulated with PIX and PAX.
In both cases, the doses of coagulants (0.67 to 3.35 mg Fe/L and 0.46 to 2.3 mg Al/L) are within the range of doses used in the coagulation tests illustrated in Figure 2. According to Figure 5, the low values of SD (s), show a high repeatability of the measurements for capillary suction time CST, carried out by DWTEST instrument. For sww wastewater, the tendency of the relationship CSTsww = f(dose of coagulant) demonstrates a linear increase in CST, when the dose of coagulant is increased. Conversely, the increase in the dose of added coagulate to nww causes a linear decrease in CSTnww. The high values of the regression correlation coeficient R2, (which are ranged between 0.9697 and 0.9917), provide the linear character confirmation for the regression relationship CST = f(dose of coagulant). For fes, the CSTsww was 53.5 s, and for als it was 58 s.
With increasing doses of coagulant, CSTsww increased from 46 to 58 s for PIX and over a slightly wider range from 25 to 61 s for PAX. Undoubtedly, the structure of sww sludge obtained with PIX is different from the structure of sludge achieved with PAX, although the mechanism of bridging particular units is similar. As the dose of a coagulant increased, the share of these units in structures of sludge increased, which may have led to the blocking of water molecules in sludge flocs and a subsequent increase in CST. It is known that micelles {Fe(OH)3}n and {Al(OH)3}n differ from each other in shape and dimension [44,45]. The regression equations (Figure 5) allow the CST to be easily calculated for an identical dose of both coagulants, which is 0.05 mmol/L (within the range of fes = 0.045 and als = 0.068): CSTFe = 55.5 s, and CSTAl = 40.3 s. The next calculation can be made for the same dose of both coagulants, equal to 0.1 mmol/L. Here, CSTFe = 67.7 s, and CSTAl = 66.2 s, which almost the same. By extrapolating the CST values to higher coagulant doses, it can be hypothesized that sww sludge with PIX binds water more effectively at lower Fe doses, while sww sludge with PAX binds water more effectively at higher Al doses. Due to the small number of components in sww sludge as described in Formula (7):
the only explanation of the CST = f(dose of coagulant) is the structure of this sludge.
water + dye + KH2PO4 + prtc
The structures illustrated in Figure 6 schematically describe the progressing aaf processes. It is clear that repulsion, as well as the intensity and scope of Brownian motions, decrease as the dose of a coagulant increases. The network of bridging and connections grows in the emerging aggregates-flocs of sediment sww. The schemas in Figure 6 may illustrate the destabilization of a single cluster (previously presented in Figure 3) due to the formation of appropriate dimers, in which a dye molecule most probably can bridge two prtc partly destabilized by H2PO4−. At an increasing dose of a coagulant, these structures are most probably bridging, thus binding water in the internal spaces of agglomerate-flocs. It is known that rod-shaped colloidal particles, e.g., {Fe(OH)3}, coagulate more rapidly than spherical units {Al(OH)3}. However, the aggregation of many “rods” ultimately leads to the formation of a spherical aggregate-floc. Most probably, spherical aggregates composed of spherical units {Al(OH)3} leave more internal space for water than other spherical aggregates composed of rod-shaped {Fe(OH)3}, which is why it is more difficult to remove water from Al-sww (longer CST) than from Fe-sww (shorter CST).
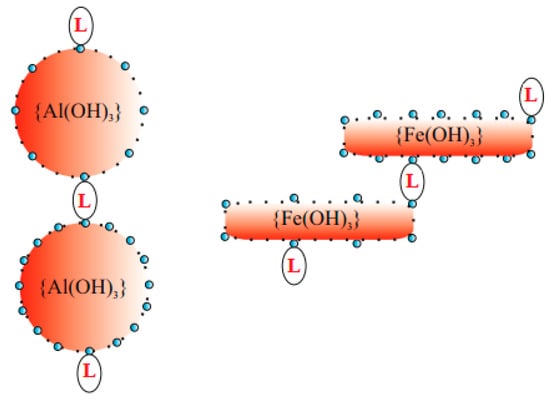
Figure 6.
Schema of the progress of aaf sww.
As mentioned above, in contrast to sww sludge, an increase in the dose of a coagulant (both PIX and PAX) added to nww caused a linear decrease CSTnww. The CSTsww for fen was 77 s, and for aln it was 80 s. As the dose of a coagulant increased, the CSTnww decreased from 124 to 70 s for PIX, and from 115 to 54 s for PAX. In comparison with sww, in this case the variation of CST values for sludge obtained with PIX and PAX was distinctly smaller. From an appropriate regression equation (Figure 5), for identical doses of both coagulants (0.05 mmol/L), the following values of CST were calculated: CSTFe = 81.5 s and CSTAl = 89 s. Analogously to sww tests, the subsequent calculations were made for the same dose of the coagulants equal to 0.1 mmol/L. The results were CSTFe = 23.8 s and CSTAl = 42.7 s, which means that CSTAl is distinctly higher than CSTFe. When extrapolating CST values to higher coagulant doses, it appears that at higher coagulant doses nww sludge with PAX may bind water more effectively than nww sludge with PIX. Compared to sww, nww sludge is a much more complex, multi-component system. From this point of view, the most significant constituent of nww sludge is sorg. Most probably, the participation of sorg in the aaf process, leading to the formation of nww sludge, is responsible for the negative regression of the course of the CST = f(dose of coagulant) function.
Figure 7 shows a suggested schema of the aaf processes occurring during nww coagulation. Similarly to sww, an increase in the dose of a coagulant leads to a decrease in repulsion as well as the intensity and scope of Brownian motions in the system. The network of branches and connections in the sww sludge is expanding. The schema in Figure 7 may illustrate the destabilization of a single unit from Figure 4 through the formation of appropriate dimers, in which sorg most probably bridges two prtc partly destabilized by H2PO4−. At an increasing dose of the coagulant, these structures most probably begin to branch, binding water in internal spaces within agglomerates-flocs. Organic compounds, sorg, which in total constitute so-called the “negative wastewater colloid” of nww, are classified as hydrophilic colloids, stabilized by the hydration shell of water molecules. As the negative wastewater colloid is progressively destabilized, and the aaf processes are in progress, the concentration of sorg decreases and water molecules released from the hydration shell become “available”, which leads to a decrease in CST. The increasing difference in the values of CSTFe and CSTAl at increasing doses of a coagulant can be explained in this case as for sww. Gradually branching (Figure 7) structures containing spherical {Al(OH)3} units absorbing components of nww block the “inner-network” water more effectively than rod-shaped units with {Fe(OH)3}.
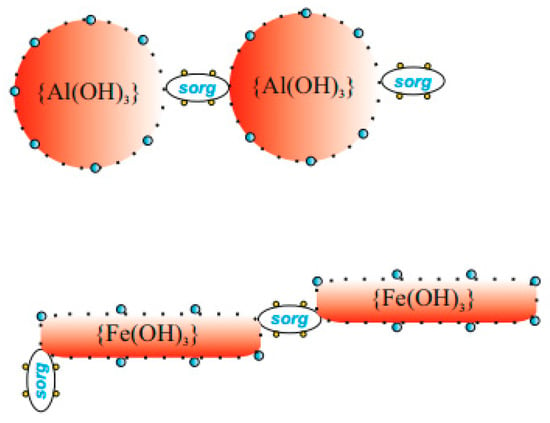
Figure 7.
Schema of the progress of aaf processes in nww.
Figure 8 shows the percentages of specific size classes of particles in sludge obtained in the coagulation of sww and nww; using a) fes and als, and b) fen and aln. For both coagulants and in both types of wastewater, two classes of sludge particle size can be distinguished. The sww type of sludge is dominated by particles of a smaller size: 3–40 μm, but with a maximum of 3.72% at 12.7 μm for PIX, and 5–75 μm with a maximum of 6.38% at 24.1 μm for PAX. On the other hand, nww is dominated by sludge particles larger in size, in the range of 45–1300 μm for both coagulants. For the very low doses of a coagulant applied, the dominant size of nww sludge particles within the first range of sizes is difficult to define. For both coagulants, about 3.5% of sludge particles are sized about 130 μm, and are located within the second range.
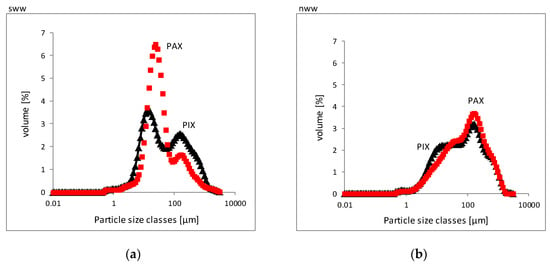
Figure 8.
Sizes of flocs of sludge obtained from sww and nww coagulated with the help of: (a) fes and als, (b) fen and aln.
Distributions of sludge particle size classes were very similar to the ones achieved for nww which were obtained in real municipal wastewater coagulated with the minimal doses of PIX (13.55 mg Fe/L) and PAX (2.45 mg Al/L), respectively [40]. It can be observed that these doses were much higher than the doses used in this study (3.02 mg Fe/L and 1.61 mg Al/L, respectively).
At the lower coagulant dose, larger size particles > 100 μm were prevalent as well. On the other hand, distributions of sludge particle classes similar to the ones identified in sww have also been recorded previously [39] in sludge obtained from synthetic wastewater coagulated with minimal doses of PIX (6.5% of particles about 4 μm in size) and PAX (10% of particles about 10 μm in size). Certain similarities and differences in particle size classes between sww and nww sludge discussed here are most probably a consequence of very low doses of coagulant; in this study, a coagulant dose was high enough to remove only 50% of P. Development of this issue will be completed by using the values Sps and Dv, which are collected in Table 1.
Table 1 presents Sps and Dv (including SD values) for particles of sludge obtained in the conditions illustrated in Figure 2 and Figure 5 and specified in Figure 6 and Figure 7.
The values of Sps (ranged between 283 and 355 m2/g), were similar to the Sps values of 260–360 m2/g, achieved for sludge obtained at coagulation of real municipal wastewater [40]. It is note worthy that such Sps values were obtained for all doses (i.e., minimal, optimal and maximal) of each coagulant PIX and PAX, respectively. Dv90 sww (Table 1), was slightly higher than Dv90 nww, which means that the applied doses of both coagulants formed slightly more uniform/homogenous particles in nww sludge than in sww sludge. It may also be suggested that the overall diversity of structures of the particles in sww sludge is higher than the diversity of particles in nww sludge.
Figure 9 contains a schematic presentation of the development of flocs in sww and nww sludge obtained with PIX. The low Dv90 value for nww indicated a generally higher uniformity of flocs in sludge built on sorg bridges than in sludge built on D bridges. The Dv90-based floc uniformity concept generally indicates the upper limit for the diameter and thus, within the specified range, limits the degree of raggedness or branching of these objects.
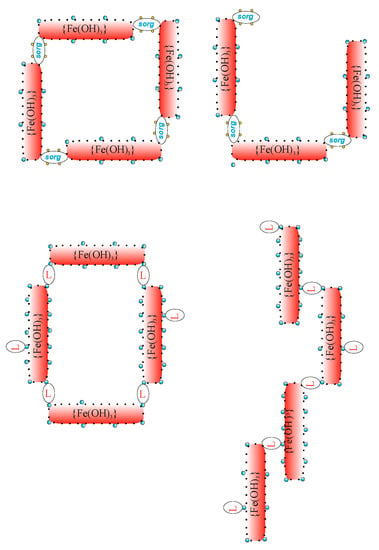
Figure 9.
Schemas of more homogenous structures of nww sludge (Dv90 = 537 μm) and less homogenous sww sludge (Dv90 = 702 μm) obtained after coagulation with PIX.
Since it is not an easy task to illustrate this problem, the objects presented in Figure 9 to a large extent are schematic representations. It seems likely that slightly larger, negatively charged sorg bridges, anchored directly on the surface of positive prtc more effectively close the sludge structures than the smaller L bridges anchored on the prtc surface by the HPO4−, because L is rather unattractive for positive prtc.
Thus, the left part of Figure 9 shows the closed, and the right part shows the partly open, structure of two aggregates of nww sludge, similar in size, and an analogous, closed and completely open structure of two aggregates of sww sludge. For such structures, Dv90 of nww would be lower than Dv90 of sww, represented by the “open aggregate” in the lower, right-hand corner of Figure 9. At the same time, the higher Dv90 value of sww sludge may generally indicate greater structural differentiation in sww sludge than in nww sludge.
Unquestionably, the progress of aaf processes is a direct consequence of the primary process forming the units illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure 4. Due to a large deficit of the coagulant (an amount needed to remove just 50% of P), the conditions applied in this study can be referred to as “sub-stoichiometric”. In line with the Langmuir’s theory of adsorption, under such conditions we should expect complete saturation/use of the surface of prtc by adsorbed substances; i.e., L and P-PO4 in sww flocs, and SS, sorg and P in nww flocs. In this case, individual units of flocs being formed should be characterized by higher porosity than units formed under “stoichiometric” conditions, especially in excessive amounts of a coagulant [37,39]. Porosity of floc-cluster units may influence the growth of Sps. At the same time, the larger filling of the centers on the adsorbent surface (prtc) should favor the aaf processes, as the forces of mutual repulsion decrease between the “saturated” surfaces of the units. As a result, the final porosity of these units only exerts a slight effect on the size, and on the final Sps value, for closed floc structures formed under sub-stoichiometric conditions.
It has been explained [43] that flocs of the analyzed sludge are formed from the units presented in Figure 9. Filling the space with the mass of a sludge floc can be defined with the fractal dimension, Df, previously defined in Equation (2). There are more data available [19,29,46,47,48] on the fractal dimension values of various types of flocs, including the values of Df in sludge of municipal wastewater. Depending on the measurement method applied, the type of a coagulant and other parameters of the process, the values of Df can be equal with the following values: 1.72 [19]; 1.68–1.74 [3]; 1.50–1.87 [4]; 1.69–1.96 [20]; 1.7–1.8 [46], 1.67–1.90 [47] and 1.8 [48]. Both fundamentally and practically, it may be interesting to compare the number of units, schematically illustrated in Figure 3 and Figure 4, in a single floc of sww and nww sludge. Based on the aforementioned Df values, the following assumptions were made for simple calculations of the number of units in such “statistical” floc: Df = 1.75 and R = Dv50. For comparative purposes, it seems sufficient to choose R = Dv50, as it is implied by the definition of Dv, according to which this value can be the closest to the R diameter of a “statistical” floc. The values of the number of n units in a statistical municipal wastewater sludge floc, as comprised in Table 2, were calculated from the following equation:
where: R = Dv50 in μm, while r = 0.17 μm and is an approximate sum of diameters of individual components in a sww unit:
r(H2PO4−) + r{Al(OH)3} + r(H2PO4−) + r(D)
= 0.0012 + 0.165 + 0.0012 + 0.010 = 0.1685 (μm)
= 0.0012 + 0.165 + 0.0012 + 0.010 = 0.1685 (μm)
Earlier, an assumption was made that r(sorg) is slightly larger than r(D). Simultaneously, considering the fact that the r of a unit of nww sludge:
does not contain r(H2PO4−) and in view of the lack of other data for calculations, the value of r for nww was also adopted as being equal to 0.17 μm, because the dominant component of r of a nww floc always has to be r{Al(OH)3}.
r{Al(OH)3} + r(sorg)
The data contained in Table 2 are not absolute values and can be used only for comparative purposes. They indicate a much denser filling of the space by units-clusters in a bigger floc (Dv50) of nnw sludge than that of a smaller floc (Dv50) in sww sludge. Within a certain range, these data confirm the general hypothesis of higher homogeneity of nww sludge, than of sww sludge (Figure 9).
The data allowed a comparison of the structures of two types of municipal wastewater sludge. In all presented case studies, the obtained sludge after chemical treatment of wastewater contained 3–5% dry solids, of which an average of 45% of the dry solids content was organic.
The results of such studies, when advanced and developed, can aid the improvement of practical wastewater treatment technologies. Simple procedures of simultaneous online measurements of Dv10, Dv50, Dv90 and Sps could be easily implemented at wastewater treatment plants. If a wastewater treatment plant is equipped with such an online measuring system, it will allow:
- (1)
- additional monitoring of the coagulation-flocculation process,
- (2)
- broader assessment of the “health”/quality of activated sludge,
- (3)
- better control and regulation of the process of municipal wastewater sludge dewatering.
4. Conclusions
Molecules of dye are adsorbed to prtc by bridging, with the help of H2PO4− ions previously adsorbed to these surfaces. Unlike in sww, negatively charged sorg in nww are directly adsorbed on the surface of prtc.
As the dose of a coagulant increased, the CSTsww increased, while the CSTnww decreased. The sww sludge with PAX binds water more effectively at higher Al doses. Aggregates composed of spherical {Al(OH)3} units leave more internal space for water than aggregates built from rod-shaped {Fe(OH)3} units and, in consequence, a higher dose of PAX (Al) means that it is more difficult to remove water from Al-sww sludge (longer CST) than from Fe-sww (shorter CST).
Particles that are smaller in size dominate in sww sludge, while larger particles prevail in nww sludge. Except for PIX in nww, the analyzed particles of the types of sludge tested were characterized by similar Sps, irrespective of the type of wastewater or the applied coagulant. Values of Dv90 for sww are slightly higher than Dv90 nww, which means that the differentiation of structures of sww sludge particles is greater than in nww sludge. Slightly larger, negatively charged sorg bridges, directly anchored on the surface of positive prtc, more effectively close structures of nww sludge than smaller L bridges, anchored on the surface of prtc via HPO4− ions. The porosity of units has only a slight influence on the size and final value of Sps of closed structures of flocs formed under sub-stoichiometric conditions. The larger statistical floc of nww sludge is more densely packed with units-clusters than the space of a smaller sww floc.
Author Contributions
This article was written by L.S. and H.R. based on the investigations carried out in the frame of Polish-Norwegian Research Program operated by the National Centre for Research and Development under the Norwegian Financial Mechanism 2009–2014. These authors designed the research project and conducted the laboratory tests and analyses developed by Ph.D students M.K. and M.T. S.K. designed the equipment and provided technical knowledge to support the experimental work. M.S. carried out optical investigations and visualization and I.C. participated in reviewing and final writing of this manuscript.
Funding
This research was mainly funded by Polish-Norwegian Research Program, grant number, POL-NOR/196364/7/2013.; 561755-1-2015-1-NO-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP, (2015-3386/001-001); and statutory grant 20610.001-300.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Polish-Norwegian Research Program operated by the National Centre for Research and Development under the Norwegian Financial Mechanism 2009–2014 in the framework of Project Contract No. POL-NOR/196364/7/2013; “Harmonizing water related graduate education” under grant 561755-1-2015-1-NO-EPPKA2-CBHE-JP (2015-3386/001-001); and under statutory grant 20610.001-300.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Nomenclature
| sww | synthetic wastewater |
| nww | real municipal wastewater (natural origin) |
| CST | capillary suction time (s) |
| aaf | aggregation-agglomeration-flocculation |
| SD | standard deviation of the sample (% or mg/L) |
| fes | number of mg Fe3+ (PIX) which remove 50% P from 1 L of sww |
| als | umber of mg Al3+ (PAX) which remove 50% P from 1 L of sww |
| fen | number of mg Fe3+ (PIX) which remove 50% P from 1 L of nww |
| aln | number of mg Fe3+ (PIX) which remove 50% P from 1 L of nww |
| Dv | volumetric dimension (μm) |
| Sps | specific surface area (m2/g) |
| L | disperse dye (Synthene Scarlet P3GL) |
| SS | Suspended Solids (mg/L) |
| prtc | colloidal particle {Fe(OH)3} or {Al(OH)3} |
| sorg | organic substances (responsible for COD in nww) |
References
- Duan, J.; Gregory, J. Coagulation by hydrolyzing metal salts. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2003, 100–102, 475–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The, C.Y.; Budiman, P.M.; Shak, K.P.; Wu, T.Y. Recent advancement of coagulation-flocculation and its application in wastewater treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 4363–4389. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, H.; Shu, G.; Jiang, S.; Tshukudu, T.; Xiang, X.; Zhang, P.; He, Q. Investigations of coagulation-flocculation process by performance optimization, model prediction and fractal structure of flocs. Desalination 2011, 269, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.P.; Lee, D.J. Effect of pre-hydrolysis on floc structure. J. Environ. Manag. 2004, 71, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.X.; Shon, H.K.; Wang, Y.; Kim, J.H.; Yue, Q.Y. The effect of second coagulant dose on the regrowth of flocs formed by charge neutralization and sweep coagulation using titanium tetrachloride (TiCl4). J. Hazard Mater. 2011, 198, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fytili, D.; Zabaniotou, A. Utilization of sewage sludge in EU application of old and new methods—A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2008, 12, 116–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verna, S.; Prased, B.; Mishra, I.M. Pretreatment of petrochemical wastewater by coagulation and the sludge characteristics. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 178, 1055–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohrsetzer, S.; Paszli, I.; Csempesz, F.; Ban, S. Colloidal stability of electrostatically stabilized sol particles. Part I: The role of hydration in coagulation and repeptization of ferric hydroxide sol. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1992, 270, 1243–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczyński, L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Kosobucka, M.; Kvaal, K.; Smoczyński, M. Image Analysis of Sludge Aggregates Obtained at Preliminary Treatment of Sewage. Water Sci. Technol. 2014, 70, 1048–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirtharajah, A.; Mills, M.K. Rapid-mix design for mechanism of alum coagulation. JAWWA 1982, 74, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, E.; Hung, Y.T.; Yu, L.R.; Al Ahmad, M. Electrocoagulation in wastewater treatment. Water 2011, 3, 395–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaleschi, L.; Teodosiu, C.; Cretescu, I.; Rodrigo, M.A. A Comparative Study of Electrocoagulation and Chemical Coagulation Processes Applied for Wastewater Treatment. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2012, 11, 1517–1525. [Google Scholar]
- Smoczynski, L.; Munska, K.; Pierozynski, B. Electrocoagulation of synthetic dairy wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 2013, 67, 404–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groterud, O.; Smoczyński, L. Removal of phosphorus and residual aluminium by a recirculating electrolysis of wastewater. Vatten 1986, 42, 293–296. [Google Scholar]
- Mikkelsen, L.H.; Keiding, K. Physico-chemical characteristics of full scale sewage sludge with implications to dewatering. Water Res. 2002, 36, 2451–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, B.; Wilen, B.M.; Lant, P. Impact of morphological, physical and chemical properties of sludge flocs on dewaterability of activated sludge. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 98, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turchiuli, C.; Fargues, C. Influence of structural properties of alum and ferric flocs on sludge dewaterability. Chem. Eng. J. 2004, 103, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, M.; Zhang, W.; Wang, D.; Chen, Y.; Chen, R. Correlation of physiochemical properties and sludge dewaterability under chemical conditioning using inorganic coagulants. Bioresour. Technol. 2013, 144, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q. Correlations between floc physical properties and optimum polymer dosage in alum sludge conditioning and dewatering. Chem. Eng. J. 2003, 92, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Ge, S.; Chen, Z.; Li, X. Study on pore characteristics of flocs and sludge dewaterability based on fractal methods (pore characteristics of flocs and sludge dewatering). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2013, 58, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, O.; Scholz, M. Assessment of capillary suction time (CST) test methodology. Environ. Technol. 2007, 28, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawalha, O.; Scholz, M. Innovative enhancement of the design and precision of the capillary suction time testing device. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 2344–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholtz, M.; Tapp, J. Development of the revised Capillary Suction Time (CST) test. Water Cond. Purif. 2006, 48, 46–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tuan, P.-A.; Sillanpaa, M. Migration of ions and organic matter during electro-dewatering of anaerobic sludge. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 173, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Liu, J.C. Sludge dewaterability and floc structure in dual polymer conditioning. Adv. Environ. Res. 2001, 5, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meakin, P. The effects of reorganization processes on two dimensional cluster—Cluster aggregation. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1986, 112, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Liu, T.; Gregory, J.; Li, G.; Liu, H.; Qua, J. Aggregation of nano-sized alum–humic primary particles. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 99, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pastor-Satorras, R.; Rubí, J.M. Particle-cluster aggregation with dipolar interactions. Phys. Rev. E 1995, 51, 5994–6003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczyński, L.; Bukowski, Z.; Wardzyńska, R.; Załęska-Chróst, K. Dłużyńska, B. Simulation of coagulation, flocculation and sedimentation. Water Environ. Res. 2009, 81, 348–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jullien, R.; Meakin, P. Simple models for the restructuring of 3-dimensional ballistic aggregates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1989, 127, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarvis, P.; Jefferson, B.; Parsons, S.A. Measuring floc structural characteristics. Rev. Environ. Sci. Bio-Technol. 2005, 4, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.P.; Lee, D.J. Structural analysis of sludge flocs. Adv. Powder Technol. 2004, 15, 515–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Q. Settling behaviour of polymer flocculated water treatment sludge II: Effects of floc structure and floc packing. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2004, 35, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandelbrot, B.B. The Fractal Geometry of Nature; Freeman: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Leman, J.; Smoczynski, M.; Dolgan, T.; Dziuba, Z. Fractal analysis of structure of cow and goat β-lactoglobulin preparation. J. Food Technol. 2005, 42, 428–430. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, X.; Li, H.; Li, A.; Cheng, R. A new method for calculation of flocculation kinetics combining Smoluchowski model with fractal theory. Colloids Surf. A 2013, 423, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.G.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, Y.S.; Zhang, X.W.; Yang, F.L.; Xiao, J.N. Cake layer morphology in microfiltration of activated sludge wastewater based on fractal analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2005, 44, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczynski, L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Kosobucka, M.; Smoczynski, M.; Pieczulis-Smoczynska, K.; Cretescu, I. The size of aggregates formed during coagulation and electrocoagulation of synthetic wastewater. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2016, 17, 1160–1170. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, B.Y.; Xu, X.M.; Xu, G.Y. Characterization of floc size, strength and structure in various aluminum coagulants treatment. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 332, 354–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczynski, L.; Kosobucka, M.; Smoczynski, M.; Ratnaweera, H.; Pieczulis-Smoczynska, K. Sizes of particles formed during municipal wastewater treatment. Water Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 971–977. [Google Scholar]
- Smoczyński, L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Kosobucka, M.; Smoczyński, M.; Kalinowski, S.; Kvaal, K. Modelling the structure of sludge aggregates. Environ. Technol. 2016, 37, 1122–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczyński, L.; Ratnaweera, H.; Kosobucka, M.; Smoczyński, M. Image analysis of sludge aggregates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 122, 412–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malvern Instruments Limited. A Basic Guide to Particle Characterization; Malvern Instruments Limited: Worcestershire, UK, 2012; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Macedo, M.L.F.; Osawa, C.C.; Bertran, C.A. Sol-gel synthesis of transparent alumina gel and pure gamma alumina by urea hydrolysis of aluminum nitrate. J. Sol.-Gel. Sci. Technol. 2004, 30, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, W.; Zrinyi, M.; Kilian, H.G.; Heise, B. Structural analysis of anisometric colloidal iron(III)-hydroxide particles and particle-aggregates incorporated in poly(vinyl-acetate) networks. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1993, 271, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, T.D. Measurement and implications of flock structure in water and wastewater treatment. Colloids Surf. A 1999, 151, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smoczynski, L.; Wardzynska, R. Study on macroscopic aggregation of silica suspensions and sewage. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 183, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, J. The role of floc density in solid-liquid separation. Filtr. Sep. 1998, 35, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).