Recent Trends (2012–2016) of N, Si, and P Export from the Nemunas River Watershed: Loads, Unbalanced Stoichiometry, and Threats for Downstream Aquatic Ecosystems
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
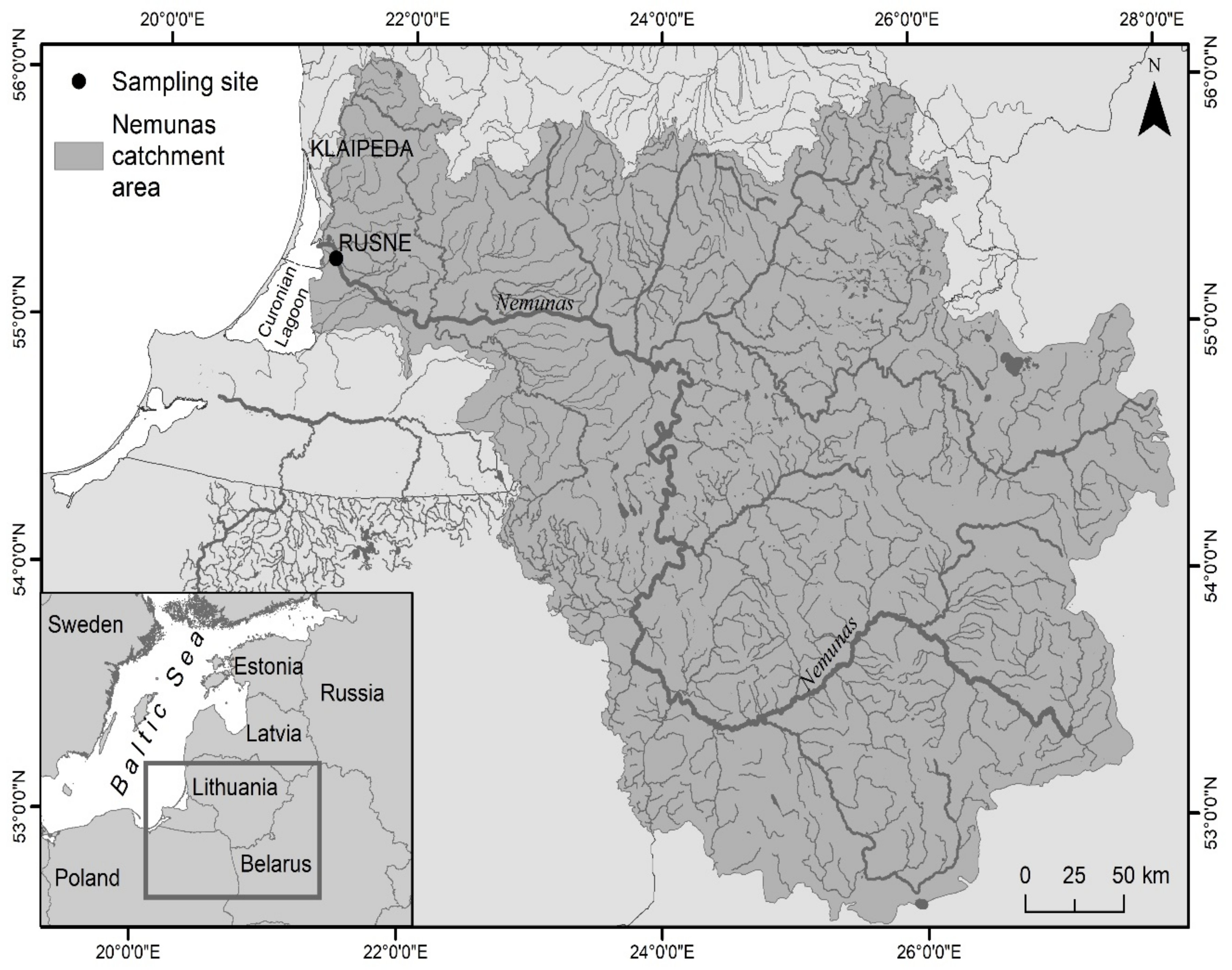
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sample Collection
2.3. Dissolved Nutrient Analyses
2.4. Particulate Nutrient Analysis
2.5. Load Calculations
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
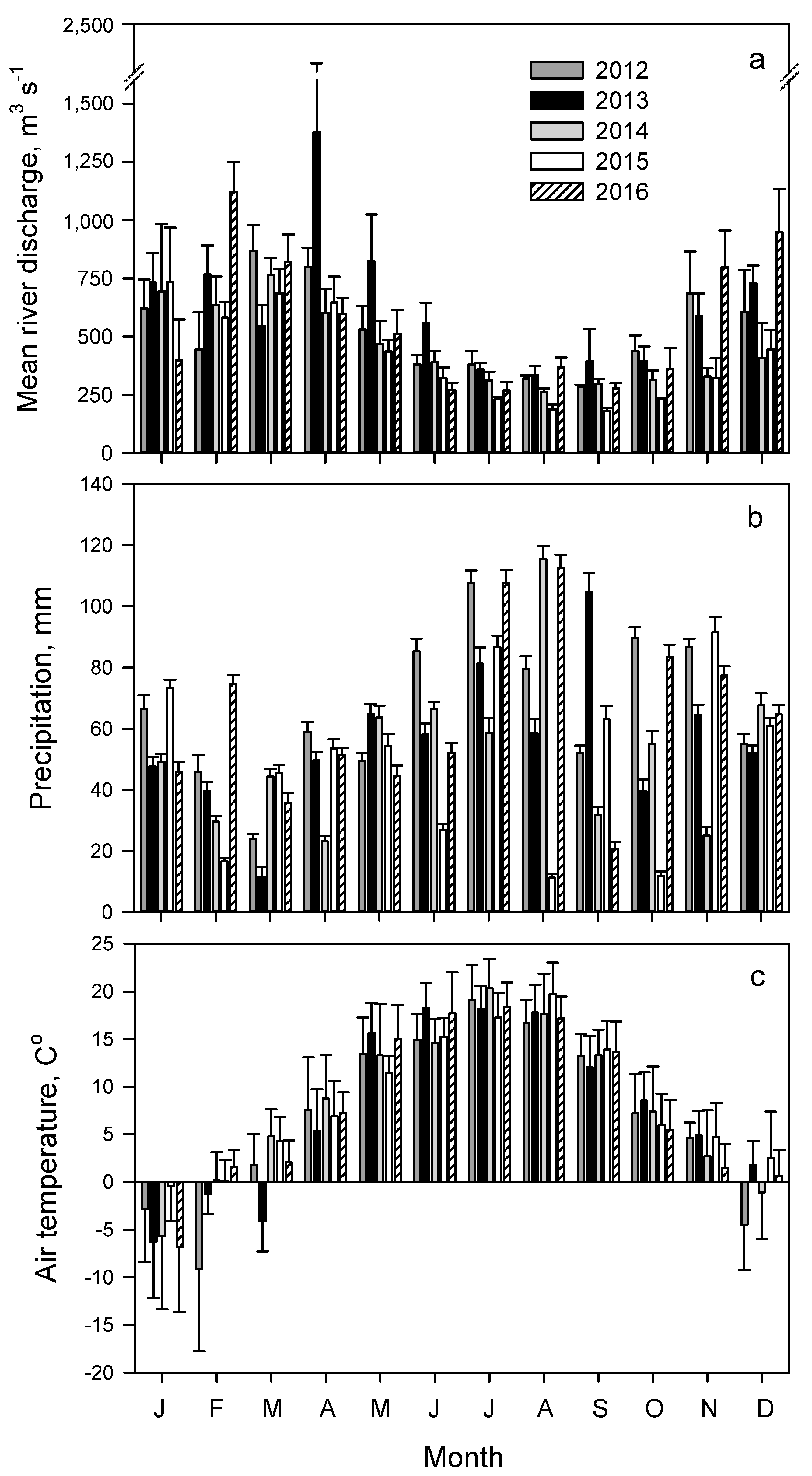
3.1. Riverine Discharge
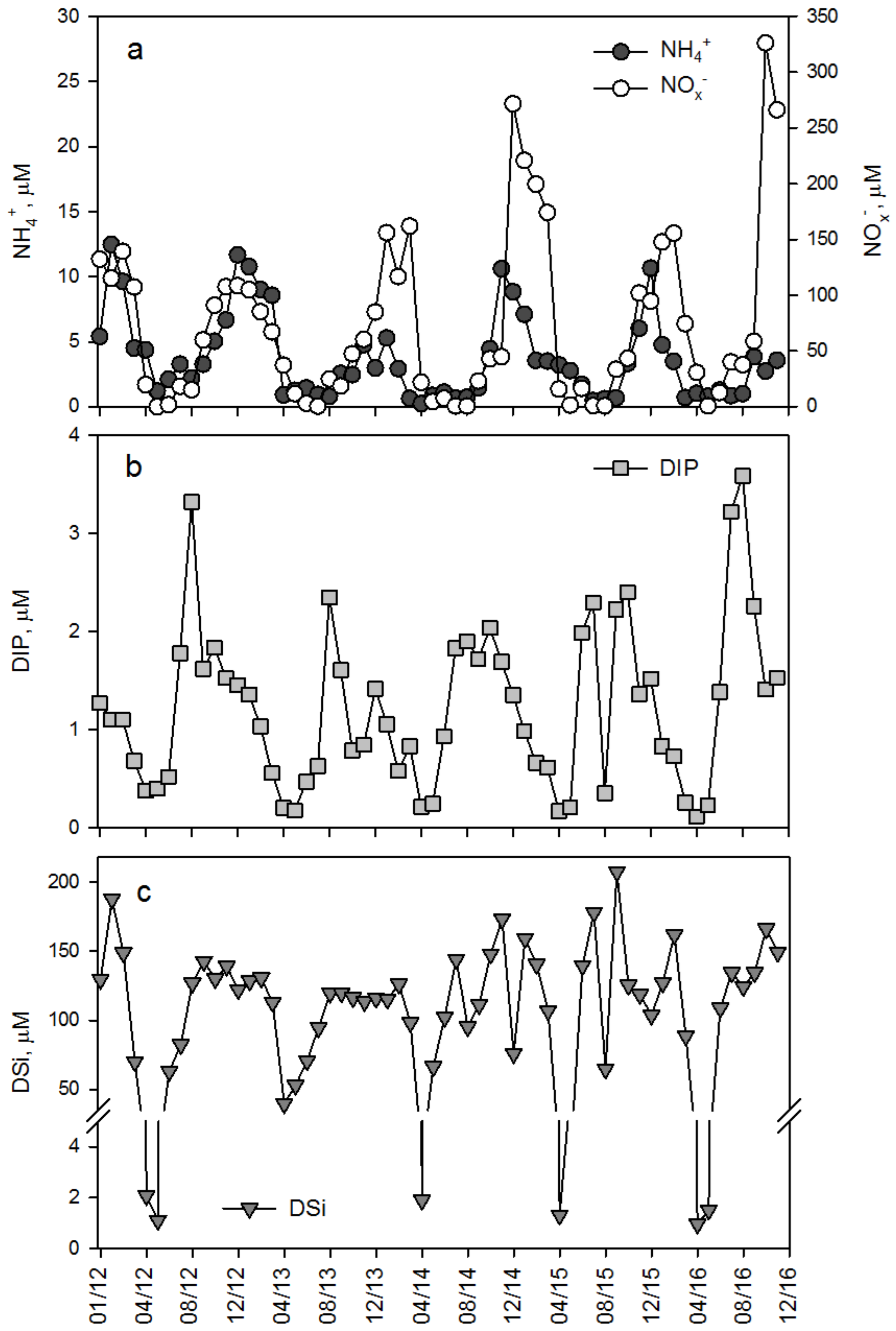
3.2. Dissolved Inorganic Nutrient Concentrations
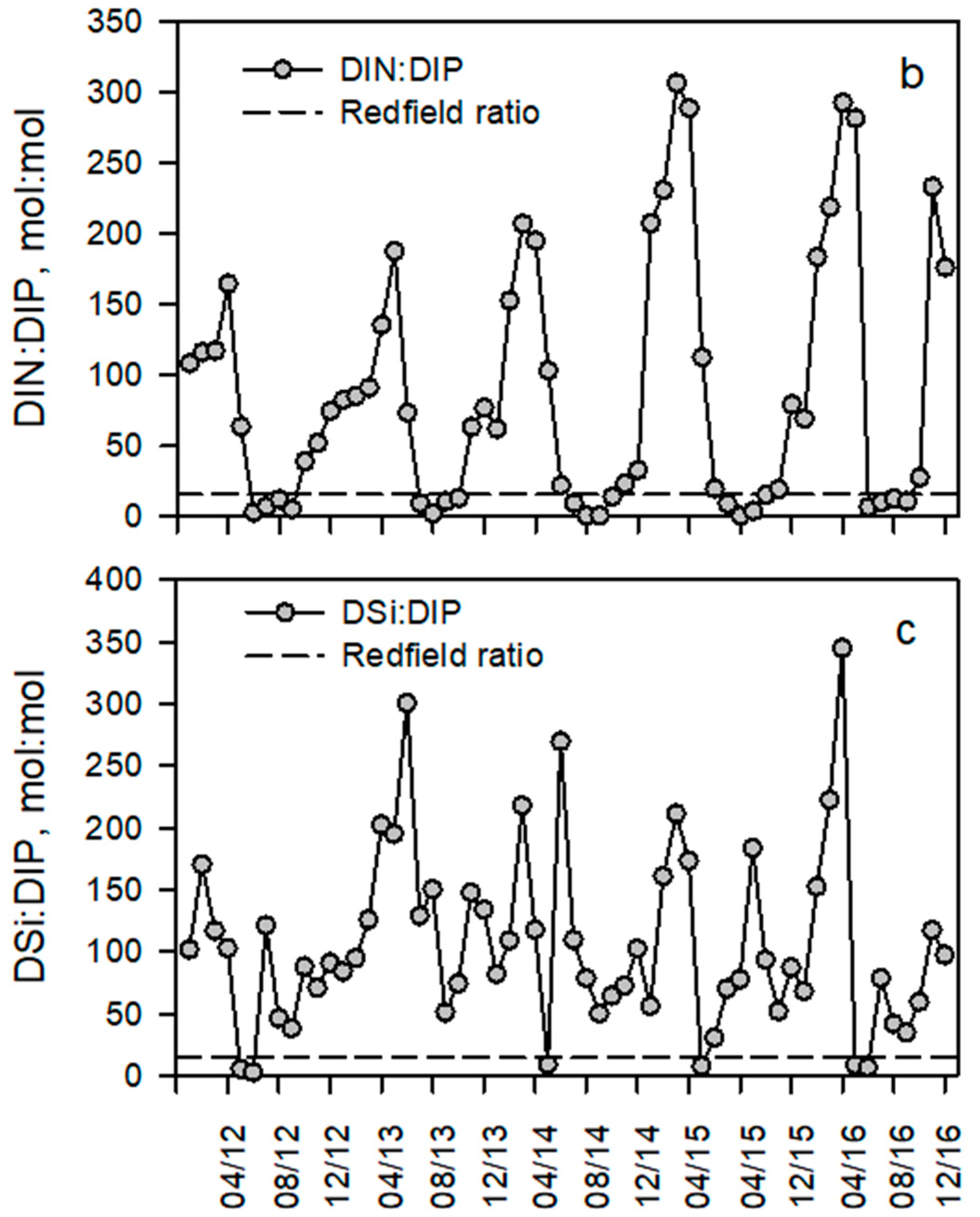
3.3. Seasonal Trends of Discharge and Dissolved Inorganic and Particulate Nutrient Concentrations
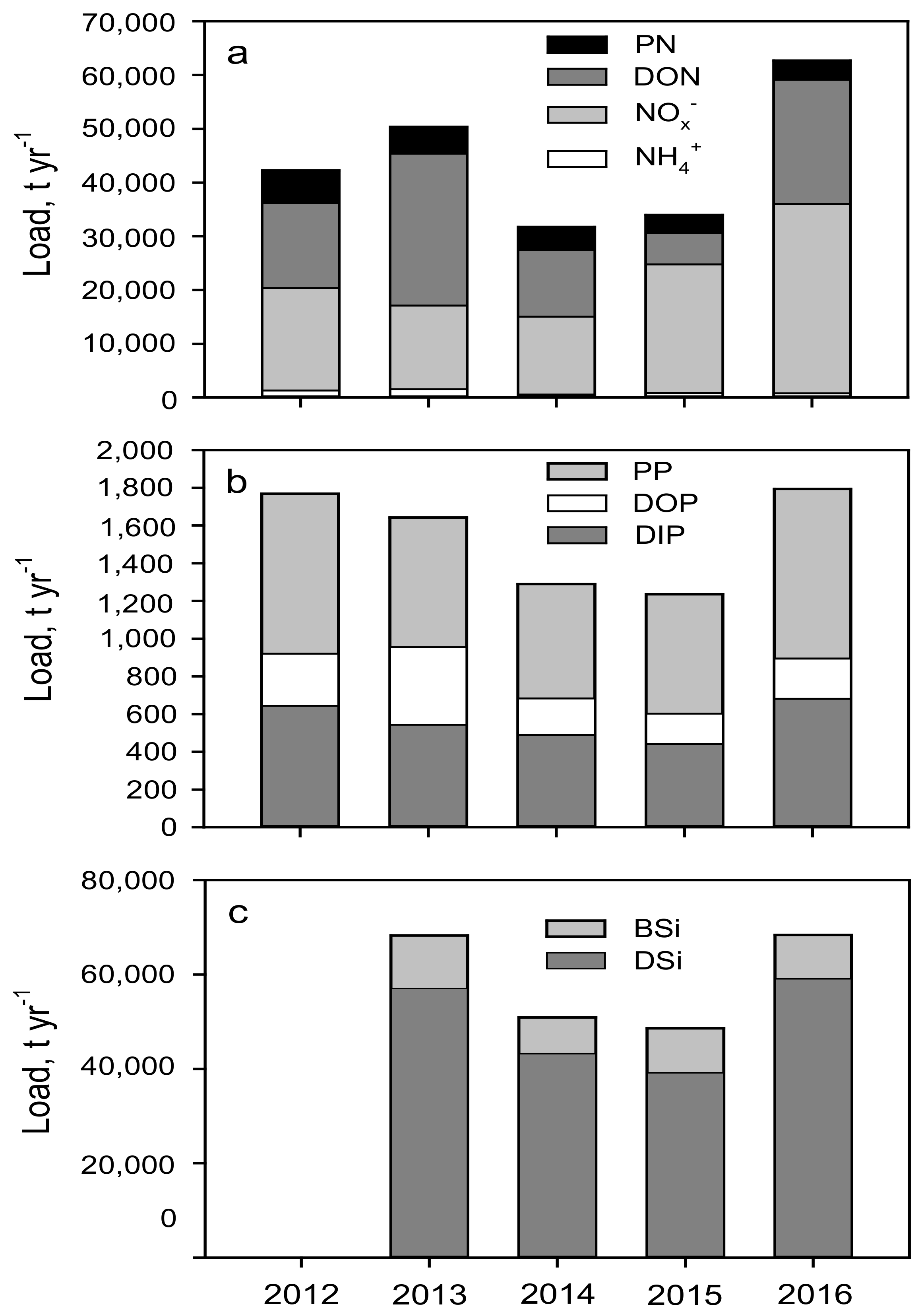
3.4. Dissolved Inorganic and Particulate Nutrient Contribution to the Total Load
4. Discussion
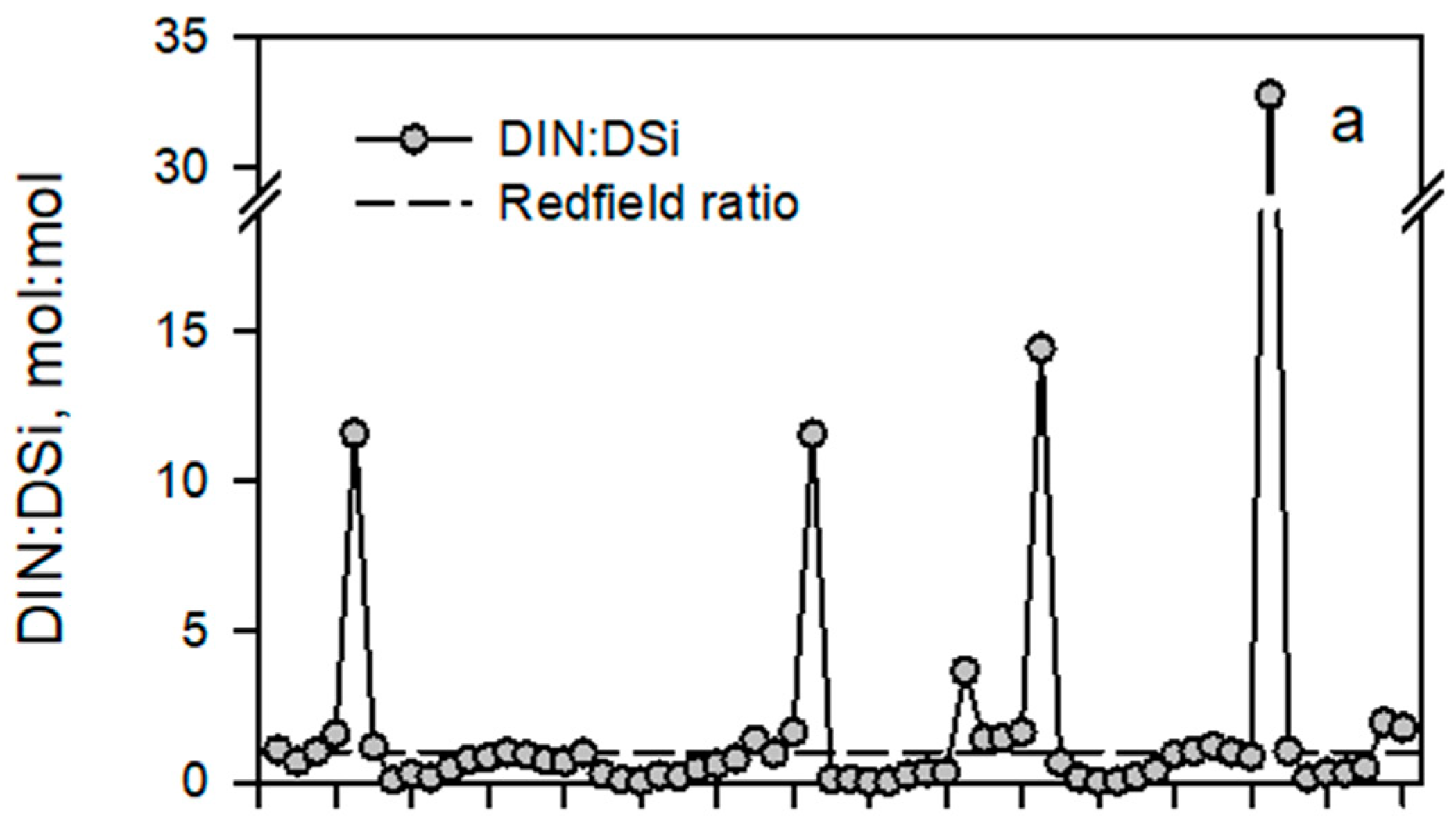
4.1. Seasonal and Interannual Variations of Discharge, Nutrient Concentrations and Stoichiometry
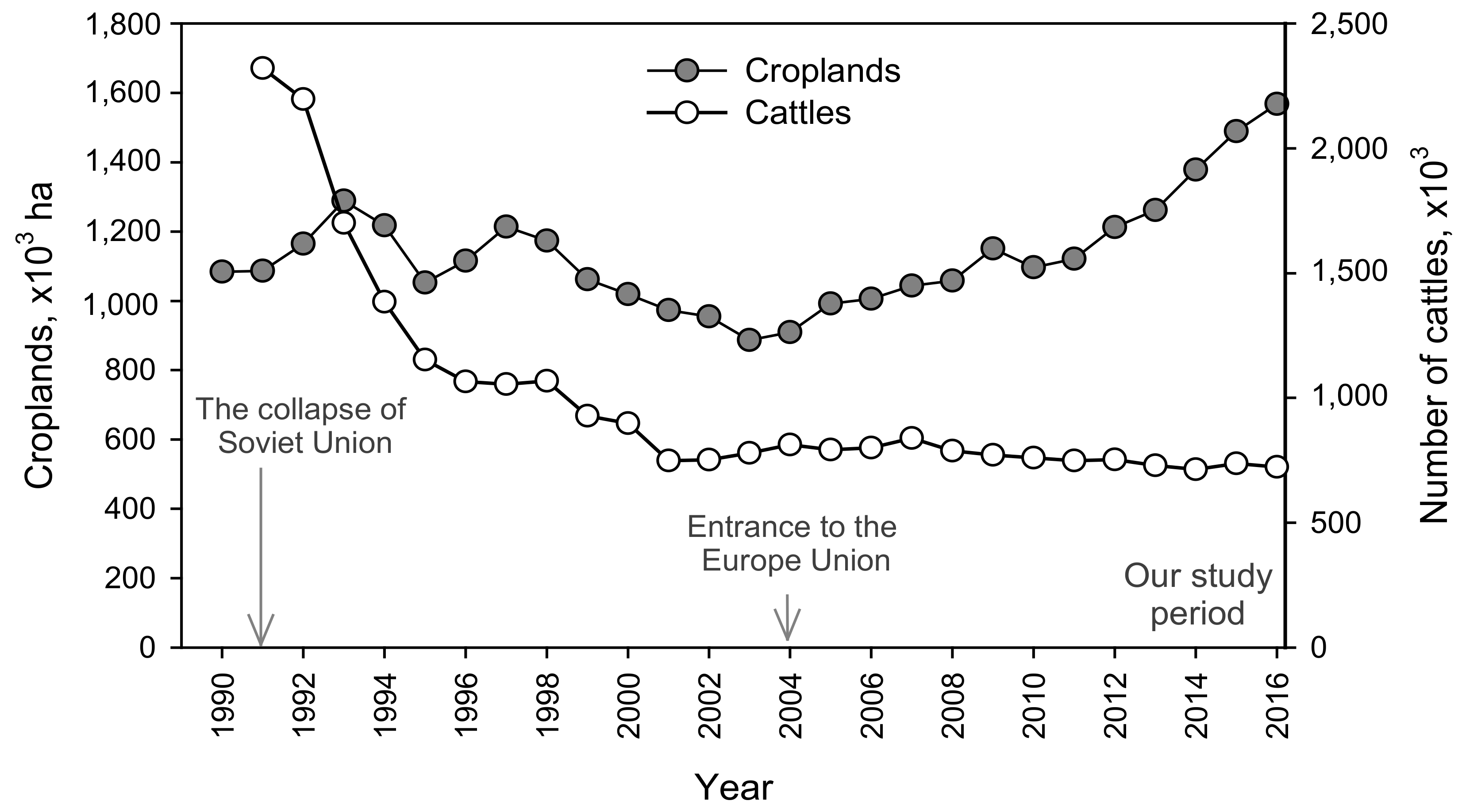
4.2. Nutrient Trends: Past, Present and Ongoing Changes
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Howarth, R.W.; Billen, G.; Swaney, D.; Townsend, A.; Jaworksi, N.; Lajtha, K.; Downing, J.A.; Elmgren, R.; Caraco, N.; Jordan, T.; et al. Regional nitrogen budgets and riverine N and P fluxes for the drainages to the North Atlantic Ocean: Natural and human influences. Biogeochemistry 1996, 35, 75–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J. Terrestrial ecosystems and the global biogeochemical silica cycle. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2002, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galloway, J.N.; Aber, J.D.; Erisman, J.W.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Howarth, R.W.; Cowling, E.B.; Cosby, B.J. The nitrogen cascade. AIBS Bull. 2003, 53, 341–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erisman, J.W.; Sutton, M.A.; Galloway, J.; Klimont, Z.; Winiwarter, W. How a century of ammonia synthesis changed the world. Nat. Geosci. 2008, 1, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schipanski, M.E.; Bennett, E.M. The influence of agricultural trade and livestock production on the global phosphorus cycle. Ecosystems 2012, 15, 256–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Paerl, H.W.; Howarth, R.W.; Boesch, D.F.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Havens, K.E.; Lancelot, C.; Likens, G.E. Controlling eutrophication: Nitrogen and phosphorus. Science 2009, 323, 1014–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoli, M.; Racchetti, E.; Delconte, C.A.; Sacchi, E.; Soana, E.; Laini, A.; Longhi, D.; Viaroli, P. Nitrogen balance and fate in a heavily impacted watershed (Oglio River, Northern Italy): In quest of the missing sources and sinks. Biogeosciences 2012, 9, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCrackin, M.L.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Hong, B.; Howarth, R.W.; Humborg, C.; Savchuk, O.P.; Svanbäck, A.; Swaney, P.D. Opportunities to reduce nutrient inputs to the Baltic Sea by improving manure use efficiency in agriculture. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struyf, E.; Smis, A.; Van Damme, S.; Garnier, J.; Govers, G.; Van Wesemael, B.; Conley, D.J.; Batelaan, O.; Frot, E.; Clymans, W.; et al. Historical land use change has lowered base-line silica mobilization from landscapes. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttunen, I.; Lehtonen, H.; Huttunen, M.; Piirainen, V.; Korppoo, M.; Veijalainen, N.; Viitasalo, M.; Vehviläinen, B. Effects of climate change and agricultural adaptation on nutrient loading from Finnish catchments to the Baltic Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 529, 168–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ockenden, M.C.; Deasy, C.E.; Benskin, C.M.H.; Beven, K.J.; Burke, S.; Collins, A.L.; Evans, R.; Falloon, P.D.; Forber, K.J.; Hiscock, K.M.; et al. Changing climate and nutrient transfers: Evidence from high temporal resolution concentration-flow dynamics in headwater catchments. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 548–549, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bricker, S.B.; Longstaff, B.; Dennison, W.; Jones, A.; Boicourt, K.; Wicks, C.; Woerner, J. Effects of nutrient enrichment in the nation′s estuaries: A decade of change. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bukaveckas, P.A.; Lesutienė, J.; Gasiūnaitė, Z.R.; Ložys, L.; Olenina, I.; Pilkaitytė, R.; Pūtys, Ž.; Tassone, S.; Wood, J. Microcystin in aquatic food webs of the Baltic and Chesapeake Bay regions. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2017, 191, 50–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hägg, H.E.; Lyon, S.W.; Wällstedt, T.; Mörth, C.M.; Claremar, B.; Humborg, C. Future nutrient load scenarios for the Baltic Sea due to climate and lifestyle changes. Ambio 2014, 43, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sileika, A.S.; Stålnacke, P.; Kutra, S.; Gaigalis, K.; Berankiene, L. Temporal and spatial variation of nutrient levels in the Nemunas River (Lithuania and Belarus). Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 122, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the nitrogen cycle: Recent trends, questions, and potential solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mallin, M.A.; McIver, M.R.; Wells, H.A.; Parsons, D.C.; Johnson, V.L. Reversal of eutrophication following sewage treatment upgrades in the New River Estuary, North Carolina. Estuar. Coast 2005, 28, 750–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaltink, R.; van der Velde, Y.; Dekkera, S.D.; Lyon, S.W.; Dahlkee, H.E. Societal, land cover and climatic controls on river nutrient flows into the Baltic Sea. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2014, 1, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humborg, C.; Pastuszak, M.; Aigars, J.; Siegmund, H.; Mörth, C.M.; Ittekkot, V. Decreased silica land–sea fluxes through damming in the Baltic Sea catchment–significance of particle trapping and hydrological alterations. Biogeochemistry 2006, 77, 265–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billen, G.; Garnier, J.; Ficht, A.; Cun, C. Modeling the response of water quality in the Seine river estuary to human activity in its watershed over the last 50 years. Estuar. Coast 2001, 24, 977–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stålnacke, P.; Grimvall, A.; Sundblad, K.; Tonderski, A. Estimation of riverine loads of nitrogen and phosphorus to the Baltic Sea, 1970–1993. Environ. Monit. Assess. 1999, 58, 173–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Scavia, D. Beyond Science into Policy: Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia and the Mississippi River: Nutrient policy development for the Mississippi River watershed reflects the accumulated scientific evidence that the increase in nitrogen loading is the primary factor in the worsening of hypoxia in the northern Gulf of Mexico. AIBS Bull. 2002, 52, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisler, J.P.; Gilbert, J.; Burkholder, J.; Anderson, D.; Cochlan, W.; Dennison, W.; Dortch, Q.; Gobler, C.J.; Heil, C.; Humphries, E.; et al. Eutrophication and harmful algal blooms: A scientific consensus. Harmful Algae 2008, 8, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Zilius, M.; Giordani, G.; Petkuviene, J.; Vaiciute, D.; Bukaveckas, P.A.; Bartoli, M. Effect of algal blooms on retention of N, Si and P in Europe's largest coastal lagoon. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2017, 194, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlson, K.; Rosenberg, R.; Bbonsdorff, E. Temporal and spatial large-scale effects of eutrophication and oxygen deficiency on benthic fauna in Scandinavian and Baltic waters: A review. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 2002, 40, 427–489. [Google Scholar]
- Vahtera, E.; Conley, D.J.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Kuosa, H.; Pitkanen, H.; Savchuk, O.P.; Tamminen, T.; Viitasalo, M.; Voss, M.; Wasmund, N.; et al. Internal ecosystem feedbacks enhance nitrogen-fixing cyanobacteria blooms and complicate management in the Baltic Sea. Ambio 2007, 36, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilius, M.; Bartoli, M.; Bresciani, M.; Katarzyte, M.; Ruginis, T.; Petkuviene, J.; Lubiene, I.; Giardino, C.; Bukaveckas, P.A.; de Wit, R.; et al. Feedback mechanisms between cyanobacterial blooms, transient hypoxia, and benthic phosphorus regeneration in shallow coastal environments. Estuar. Coast 2014, 37, 680–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming-Lehtinen, V.; Andersen, J.H.; Carstensen, J.; Łysiak-Pastuszak, E.; Murray, C.; Pyhälä, M.; Laamanen, M. Recent developments in assessment methodology reveal that the Baltic Sea eutrophication problem is expanding. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 380–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šileika, A.S.; Wallin, M.; Gaigalis, K. Assessment of nitrogen pollution reduction options in the river Nemunas (Lithuania) using FyrisNP model. J. Environ. Eng. Landsc. 2013, 21, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsinki Commission. Updated Fifth Baltic Sea pollution load compilation (PLC-5.5). In Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Hall, N.S.; Calandrino, E.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a world experiencing anthropogenic and climatic-induced change. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paerl, H.W.; Otten, T.G. Harmful cyanobacterial blooms: Causes, consequences, and controls. Microb. Ecol. 2013, 65, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, D.W. The dilemma of controlling cultural eutrophication of lakes. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012, 279, 4322–4333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouraoui, F.; Grizzetti, B. Long term change of nutrient concentrations of rivers discharging in European seas. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 4899–4916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voss, M.; Dippner, J.; Humborg, C.; Korth, F.; Neumann, T.; Hürdler, J.; Schernewski, G.; Venohr, M. History and scenarios of future development of Baltic Sea eutrophication. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2011, 92, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnier, J.; Ramarson, A.; Thieu, V.; Némery, J.; Théry, S.; Billen, G.; Coynel, A. How can water quality be improved when the urban waste water directive has been fulfilled? A case study of the Lot river (France). Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 12, 11924–11939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Povilaitis, A.; Šileika, A.; Deelstra, J.; Gaigalis, K.; Baigys, G. Nitrogen losses from small agricultural catchments in Lithuania. Agr. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 198, 54–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egge, J.K.; Aksnes, D.L. Silicate as regulating nutrient in phytoplankton competition. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 1992, 83, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gailiušis, B.; Jablonskis, J.; Kovalenkovienė, M. The Lithuanian rivers. In Hydrography and Runoff; Lithuanian Energy Institute: Kaunas, Lithuania, 2001; 792p, ISBN 9986-492-64-5. [Google Scholar]
- Vaitkuviene, D.; Dagys, M. CORINE 2006 Land Cover, Lithuania; Technical report No. CLC2006, Second Verification; Institute of Ecology of Vilnius University: Vilnius, Lithuania, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Jakimavičius, D.; Kriaučiūnienė, J. The climate change impact on the water balance of the Curonian Lagoon. Water Resour. 2013, 40, 120–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasshoff, K.; Ehrhardt, M.; Kremling, K. Methods of Seawater Analysis; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Bower, C.E.; Holm-Hansen, T. A salicylate-hypochlorite method for determining ammonia in seawater. Can. J. Fish Aquat. Sci. 1980, 37, 794–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koroleff, F. Determination of Phosphorus. In Methods of Seawater Analysis; Verlag Chemie: Weinheim, Germany, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Aspila, K.I.; Agemian, H.; Chau, A.S. A semi-automated method for the determination of inorganic, organic and total phosphate in sediments. Analyst 1976, 101, 187–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragueneau, O.; Savoye, N.; Del Amo, Y.; Cotton, J.; Tardiveau, B.; Leynaert, A. A new method for the measurement of biogenic silica in suspended matter of coastal waters: Using Si: Al ratios to correct for the mineral interference. Cont. Shelf Res. 2005, 25, 697–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsinki Commission. The Fourth Baltic Sea Pollution Load Compilation (PLC-4). In Baltic Sea Environment Proceedings; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch, R.M.; Slack, J.R.; Smith, R.A. Techniques for trend assessment for monthly water quality data. Water Resour. Res. 1982, 18, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libiseller, C.; Grimvall, A. Performance of partial Mann-Kendall tests for trends detection in the presence of covariates. Environmetrics 2002, 13, 71–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, A. Status of Nutrient Bookkeeping in the Baltic Sea Countries. Report Document Texte 95/2015. 2105. Available online: http://www.umweltbundesamt.de/publikationen/status-of-nutrient-bookkeeping-in-the-baltic-sea.pdf (accessed on 15 November 2015).
- Dupas, R.; Jomaa, S.; Musolff, A.; Borchardt, D.; Rode, M. Disentangling the influence of hydroclimatic patterns and agricultural management on river nitrate dynamics from sub-hourly to decadal time scales. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero, E.; Le Gendre, R.; Garnier, J.; Billen, G.; Fisson, C.; Silvestre, M.; Ph, R. Long-term water quality in the lower Seine: Lessons learned over 4 decades of monitoring. Environ. Sci. Policy 2016, 58, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; He, F.; Xiong, Y.J.; Qiu, G.Y. Effects of land use/land cover and climate changes on surface runoff in a semi-humid and semi-arid transition zone in northwest China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laznik, M.; Stålnacke, P.; Grimvall, A.; Wittgren, H.B. Riverine input of nutrients to the Gulf of Riga—Temporal and spatial variation. J. Mar. Syst. 1999, 23, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stankunavicius, G.; Valiuskevicius, G.; Rimkus, E.; Bukantis, A.; Gulbinas, Z. Meteorological features behind spring runoff formation in the Nemunas River. Boreal Environ. Res. 2007, 12, 643–651. [Google Scholar]
- Fulweiler, R.W.; Nixon, S.W. Terrestrial vegetation and the seasonal cycle of dissolved silica in a southern New England coastal river. Biogeochemistry 2005, 74, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korth, F.; Fry, B.; Liskow, I.; Voss, M. Nitrogen turnover during the spring outflows of the nitrate-rich Curonian and Szczecin lagoons using dual nitrate isotopes. Mar. Chem. 2013, 154, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, R.W.; Cole, N.A.; Harper, L.A.; Flesch, T.K. Flux-gradient estimates of ammonia emissions from beef cattle feed yard pens. Am. Soc. Agric. Biol. Eng. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stålnacke, P. Nutrient Loads to the Baltic Sea 1996. Ph.D. Thesis, The Linköpings University, Linköping, Swedish, September 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Ramoska, E.; Bastiene, N.; Saulys, V. Evaluation of controlled drainage efficiency in Lithuania. Irrig. Drain. 2011, 60, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilkaitytė, R.; Razinkovas, A. Factors controlling phytoplankton blooms in a temperate estuary: Nutrient limitation and physical forcing. Hydrobiologia 2006, 555, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J. Riverine contribution of biogenic silica to the oceanic silica budget. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1997, 42, 774–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justić, D.; Rabalais, N.N.; Turner, R.E.; Dortch, Q. Changes in nutrient structure of river-dominated coastal waters: Stoichiometric nutrient balance and its consequences. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 1995, 40, 339–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kronvang, B.; Jeppesen, E.; Conley, D.J.; Søndergaard, M.; Larsen, S.E.; Ovesen, N.B.; Carstensen, J. Nutrient pressures and ecological responses to nutrient loading reductions in Danish streams, lakes and coastal waters. J. Hydrol. 2005, 304, 274–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paerl, H.W. Controlling eutrophication along the freshwater–marine continuum: Dual nutrient (N and P) reductions are essential. Estuar. Coast 2009, 32, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawrocka, L.; Kobos, J. The trophic state of Vistula lagoon: An assessment based on biotic and abiotic pameters according to Water Framework Directive. Oceanologia 2011, 53, 881–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresciani, M.; Giardino, C.; Stroppiana, D.; Pilkaityt, R.; Zilius, M.; Bartoli, M.; Razinkovas, A. Retrospective analysis of spatial and temporal variability of chlorophyll-a in the Curonian Lagoon. J. Coast Conserv. 2012, 16, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilius, M.; Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Vaiciute, D.; Petkuviene, J.; Zemlys, P.; Liskow, I.; Voss, M.; Bartoli, M.; Bukaveckas, P.A. The influence of cyanobacteria blooms on the attenuation of nitrogen throughputs in a Baltic coastal lagoon. Biogeochemistry 2018, submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Humborg, C.; Smedberg, E.; Rodriguez Medina, M.; Mörth, C.M. Changes in dissolved silicate loads to the Baltic Sea—The effects of lakes and reservoirs. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 73, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conley, D.J.; Humborg, C.; Smedberg, E.; Rahm, L.; Papush, L.; Danielsson, Å.; Clarke, A.; Pastuszak, M.; Aigars, J.; Ciuffa, D.; Mörth, C.M. Past, present and future state of the biogeochemical Si cycle in the Baltic Sea. J. Mar. Syst. 2008, 73, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helsinki Commission. Baltic Sea Action Plan. Presented at HELCOM Ministerial Meeting, Krakow, Poland, 15 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Andersen, H.E.; Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Thodsen, H.; Andersen, P.M.; Larsen, S.E.; Stålnacke, P.; Humborg, C.; Mörth, C.M.; Smedberg, E. Identifying hot spots of agricultural nitrogen loss within the Baltic Sea drainage basin. Water Air Soil Poll. 2016, 227, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, B.; Swaney, D.P.; McCrackin, M.; Svanbäck, A.; Humborg, C.; Gustafsson, B.; Yershova, A.; Pakhomau, A. Advances in NANI and NAPI accounting for the Baltic drainage basin: Spatial and temporal trends and relationships to watershed TN and TP fluxes. Biogeochemistry 2017, 133, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grelowski, A.; Pastuszak, M.; Sitek, S.; Witek, Z. Budget calculations of nitrogen, phosphorus and BOD 5 passing through the Oder estuary. J. Mar. Syst. 2000, 5, 221–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petkuviene, J.; Zilius, M.; Lubiene, I.; Ruginis, T.; Giordani, G.; Razinkovas-Baziukas, A.; Bartoli, M. Phosphorus Cycling in a Freshwater Estuary Impacted by Cyanobacterial Blooms. Estuar. Coast 2016, 39, 1386–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.E.; Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Bechmann, M.; Povilaitis, A.; Iital, A.; Lagzdins, A.; Kyllmar, K. Mitigating diffuse nitrogen losses in the Nordic-Baltic countries. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2014, 195, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Year | Annual Discharge (km3·yr−1) | Slope ± SE | R2 | p | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 16.8 | 0.65 ± 0.18 | 0.57 | 0.005 | 12 |
| 2013 | 19.9 | 0.50 ± 0.19 | 0.40 | 0.027 | 12 |
| 2014 | 14.4 | 0.52 ± 0.17 | 0.46 | 0.015 | 12 |
| 2015 | 13.1 | 0.89 ± 0.09 | 0.81 | <0.001 | 23 |
| 2016 | 17.8 | 0.53 ± 0.09 | 0.74 | <0.001 | 15 |
| Pooled all year | 0.62 ± 0.06 | 0.57 | <0.001 | 74 |
| Month | Discharge | NH4+ | NOx− | DIP | DSi | PN | PP | BSi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 1.30 | 2.53 | 2.21 | 1.31 | 1.10 | 0.68 | 0.89 | 0.82 |
| February | 1.61 | 2.19 | 2.62 | 0.92 | 1.28 | 0.38 | 0.55 | 0.38 |
| March | 1.48 | 1.37 | 2.19 | 0.60 | 1.30 | 0.48 | 0.67 | 0.37 |
| April | 1.58 | 0.81 | 1.87 | 0.48 | 0.93 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 0.71 |
| May | 1.09 | 0.36 | 0.40 | 0.15 | 0.10 | 2.00 | 1.45 | 2.31 |
| June | 0.74 | 0.38 | 0.08 | 0.18 | 0.30 | 2.07 | 1.54 | 2.02 |
| July | 0.62 | 0.37 | 0.09 | 0.73 | 0.84 | 1.57 | 1.13 | 1.50 |
| August | 0.52 | 0.27 | 0.07 | 1.37 | 1.14 | 1.60 | 1.44 | 0.97 |
| September | 0.54 | 0.25 | 0.17 | 1.77 | 0.96 | 1.34 | 1.28 | 1.45 |
| October | 0.63 | 0.54 | 0.51 | 1.63 | 1.38 | 0.70 | 1.30 | 0.38 |
| November | 0.91 | 1.10 | 0.94 | 1.61 | 1.32 | 0.69 | 0.67 | 0.49 |
| December | 1.08 | 2.10 | 1.37 | 1.25 | 0.32 | 0.50 | 0.53 |
| Variable | Seasonal Mann-Kendall | Partial Mann-Kendall |
|---|---|---|
| Discharge | 0.017 (−) | |
| NH4+ | 0.005 (−) | 0.105 |
| NO3− | 0.033 (+) | 0.004 (+) |
| DSi | 0.336 | 0.090 |
| DIP | 0.389 | 0.372 |
| PN | 0.056 | 0.021 (−) |
| PP | 0.011 (+) | 0.044 (+) |
| BSi | 0.516 | 0.328 |
| Nutrient | Form | Annual Nutrient Loads (t·yr−1) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | ||
| N | NH4+ | 1290 | 1528 | 564 | 808 | 786 |
| NO2− | 190 | 310 | 208 | 186 | 268 | |
| NO3− | 18,889 | 15,254 | 14,274 | 23,792 | 34,934 | |
| DON | 15,763 | 28,267 | 12,353 | 5853 | 23,167 | |
| PN | 6128 | 5011 | 4353 | 3337 | 3525 | |
| Total N | 42,260 | 50,370 | 31,752 | 33,976 | 62,680 | |
| P | DIP | 645 | 544 | 491 | 442 | 682 |
| DOP | 276 | 411 | 193 | 161 | 214 | |
| PP | 848 | 687 | 607 | 633 | 900 | |
| Total P | 1769 | 1642 | 1291 | 1236 | 1795 | |
| Si | DSi | 49,611 | 57,044 | 43,242 | 39,194 | 59,097 |
| BSi | – | 11,244 | 7668 | 9409 | 9294 | |
| Total Si | – | 68,288 | 50,910 | 48,603 | 68,392 | |
| Period | Flow (km3 yr−1) | Nutrient Loads (t·yr−1) | DIN:DIP | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NO3− | NH4+ | TN | DIP | TP | ||||
| 1980–1993 | 20.5 | 31,650 | 58,340 | 4140 | 5410 | 8 | [21] | |
| 1986–1991 | 9702 | 8601 | 4573 | 4 | [15] | |||
| 1992–1996 | 20,604 | 5983 | 969 | 27 | [15] | |||
| 1997–2002 | 16.6 * | 25,048 | 2202 | 636 | 43 | [15] | ||
| 1997–2008 | 16.6 * | 46,335 | 2635 | [30] | ||||
| 2000–2006 | 15.9 * | 37,620 | [29] | |||||
| 2008–2010 | 18.3 * | 41,546 | 1834 | [30] | ||||
| 2012–2016 | 16.4 | 21,429 | 995 | 44,208 | 561 | 1547 | 40 | This study |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Vybernaite-Lubiene, I.; Zilius, M.; Saltyte-Vaisiauske, L.; Bartoli, M. Recent Trends (2012–2016) of N, Si, and P Export from the Nemunas River Watershed: Loads, Unbalanced Stoichiometry, and Threats for Downstream Aquatic Ecosystems. Water 2018, 10, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091178
Vybernaite-Lubiene I, Zilius M, Saltyte-Vaisiauske L, Bartoli M. Recent Trends (2012–2016) of N, Si, and P Export from the Nemunas River Watershed: Loads, Unbalanced Stoichiometry, and Threats for Downstream Aquatic Ecosystems. Water. 2018; 10(9):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091178
Chicago/Turabian StyleVybernaite-Lubiene, Irma, Mindaugas Zilius, Laura Saltyte-Vaisiauske, and Marco Bartoli. 2018. "Recent Trends (2012–2016) of N, Si, and P Export from the Nemunas River Watershed: Loads, Unbalanced Stoichiometry, and Threats for Downstream Aquatic Ecosystems" Water 10, no. 9: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091178
APA StyleVybernaite-Lubiene, I., Zilius, M., Saltyte-Vaisiauske, L., & Bartoli, M. (2018). Recent Trends (2012–2016) of N, Si, and P Export from the Nemunas River Watershed: Loads, Unbalanced Stoichiometry, and Threats for Downstream Aquatic Ecosystems. Water, 10(9), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091178






