Biofouling Formation and Bacterial Community Structure in Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-Membrane Bioreactors: Influence of Salinity Concentration
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
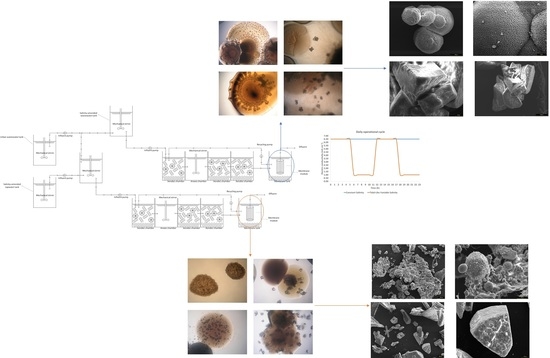
2.1. Bioreactor Configuration and Operational Conditions
2.2. Biomass Collection
2.3. Culture, Isolation, and Identification of the Bacterial Strains with Biomineralization Capacity
2.4. Environmental DNA Extraction and Massive Parallel Sequencing Procedure
2.5. Bioinformatics Pipeline
2.6. Ecological Analyses of the Massive Parallel Sequencing Samples: Analysis of Bacterial Ecological Coverage, Analyses of α-Diversity and β-Diversity of Bacterial Community Structure, Similarity Analysis of the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Bacterial Community Structure, and SIMPER Analyses Comparing Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Communities
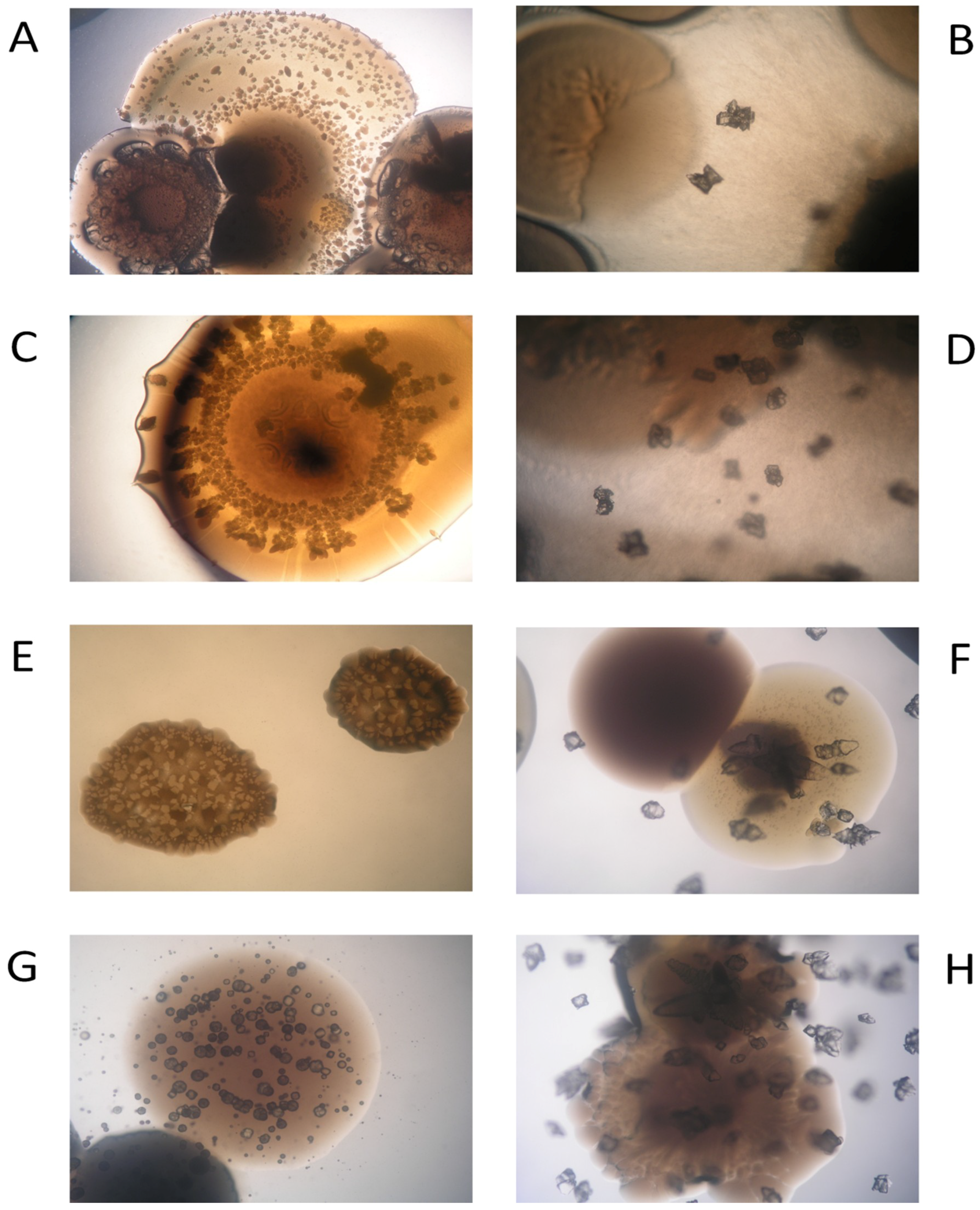
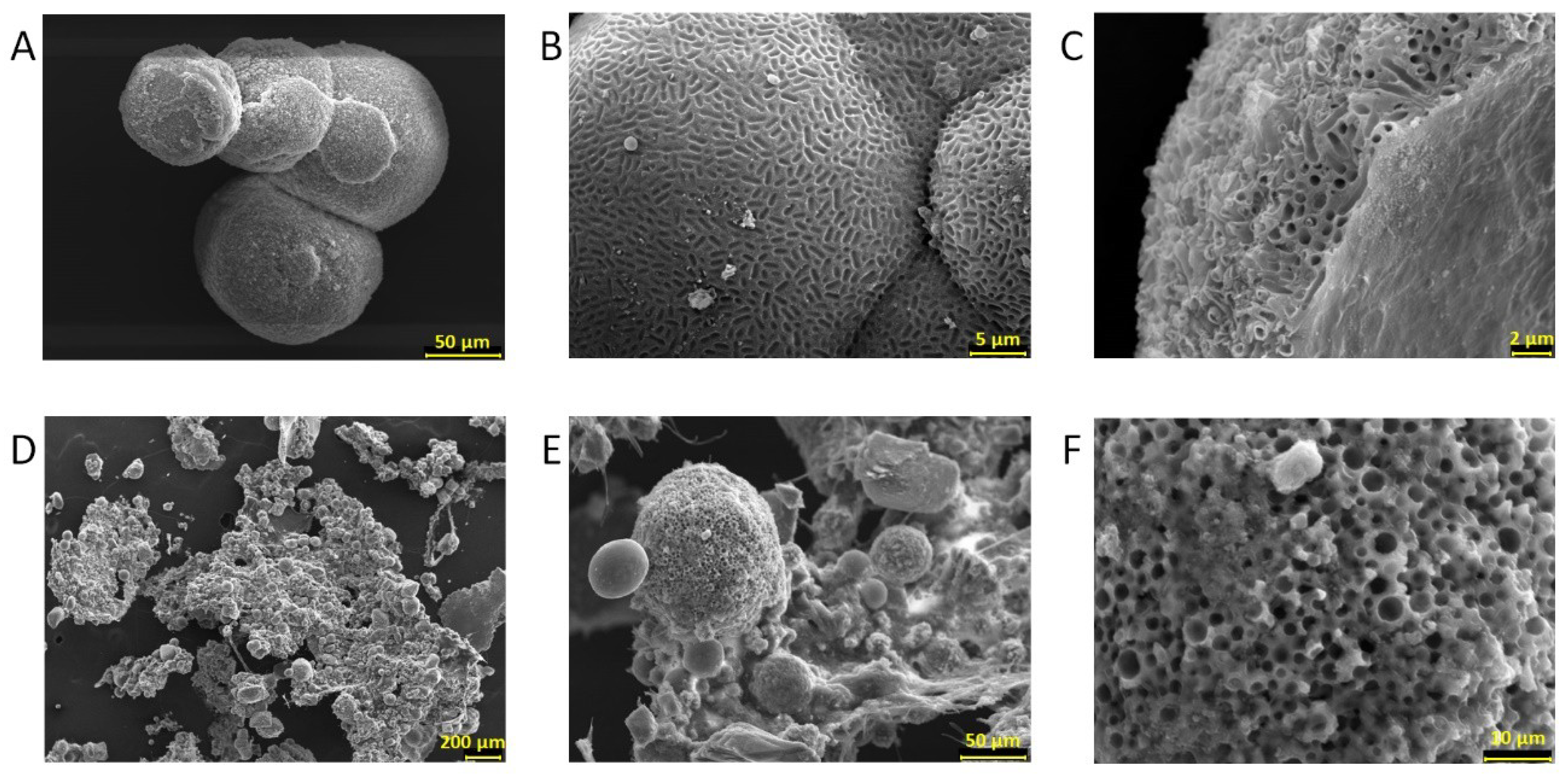
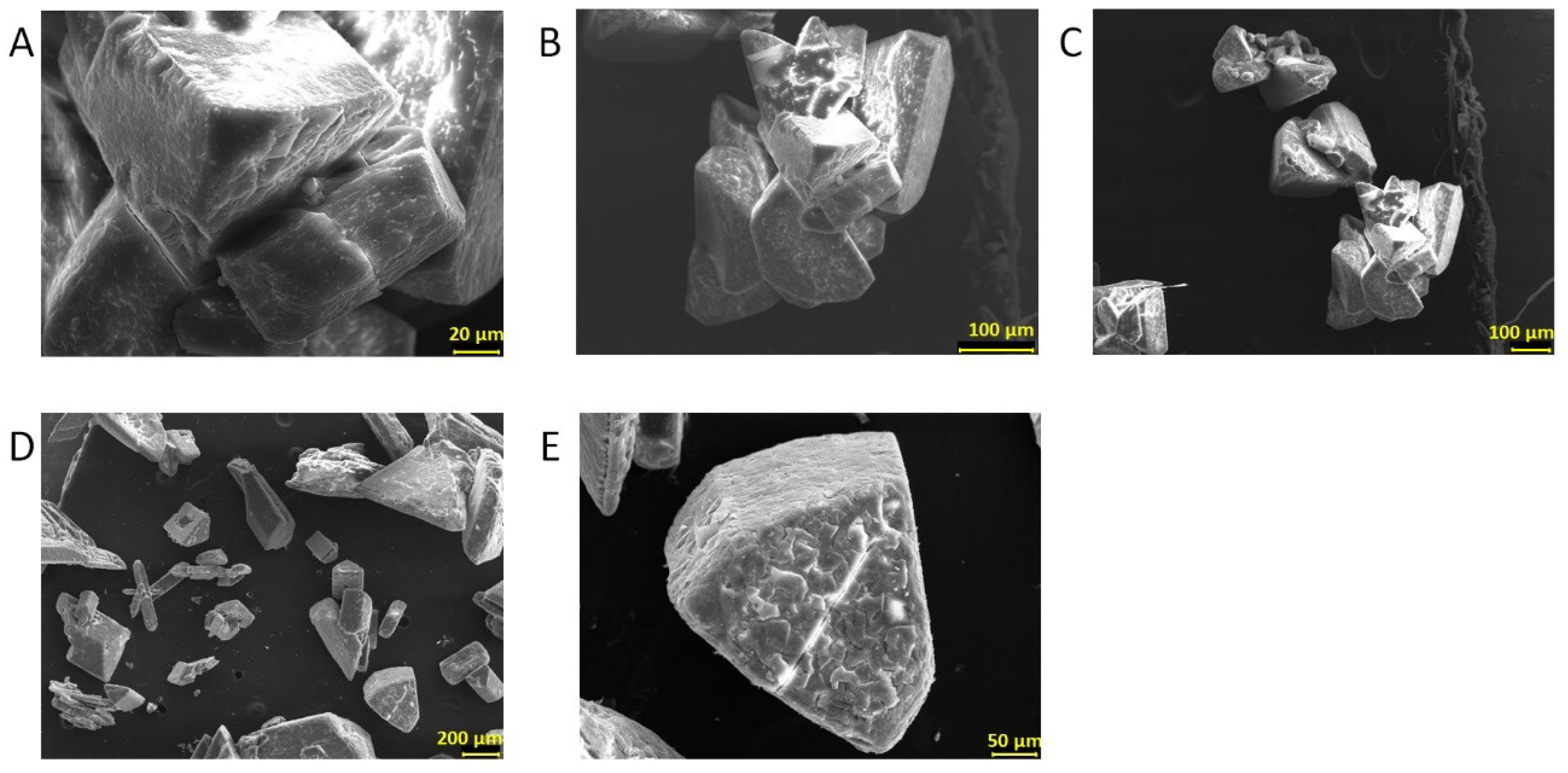
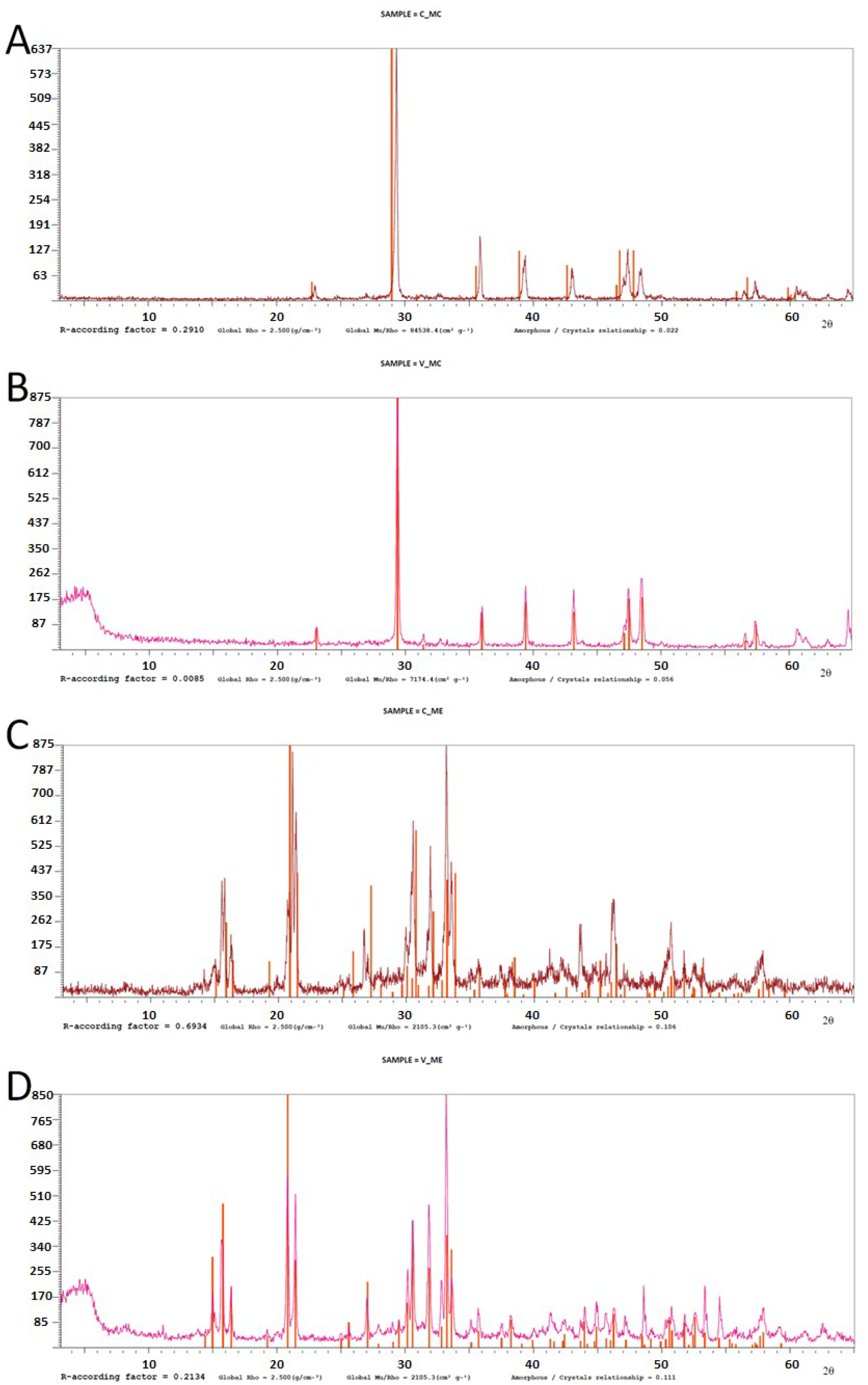
2.7. Characterization of Biominerals through X-Ray Diffractometry, Optic Microscopy, and Scanning Electron Microscopy
3. Results
3.1. Physical-Chemical Parameters and Nutrient Removal
3.2. Ecological Coverage, α-Diversity and β-Diversity Analyses of the Bacterial Community Structure in the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Samples
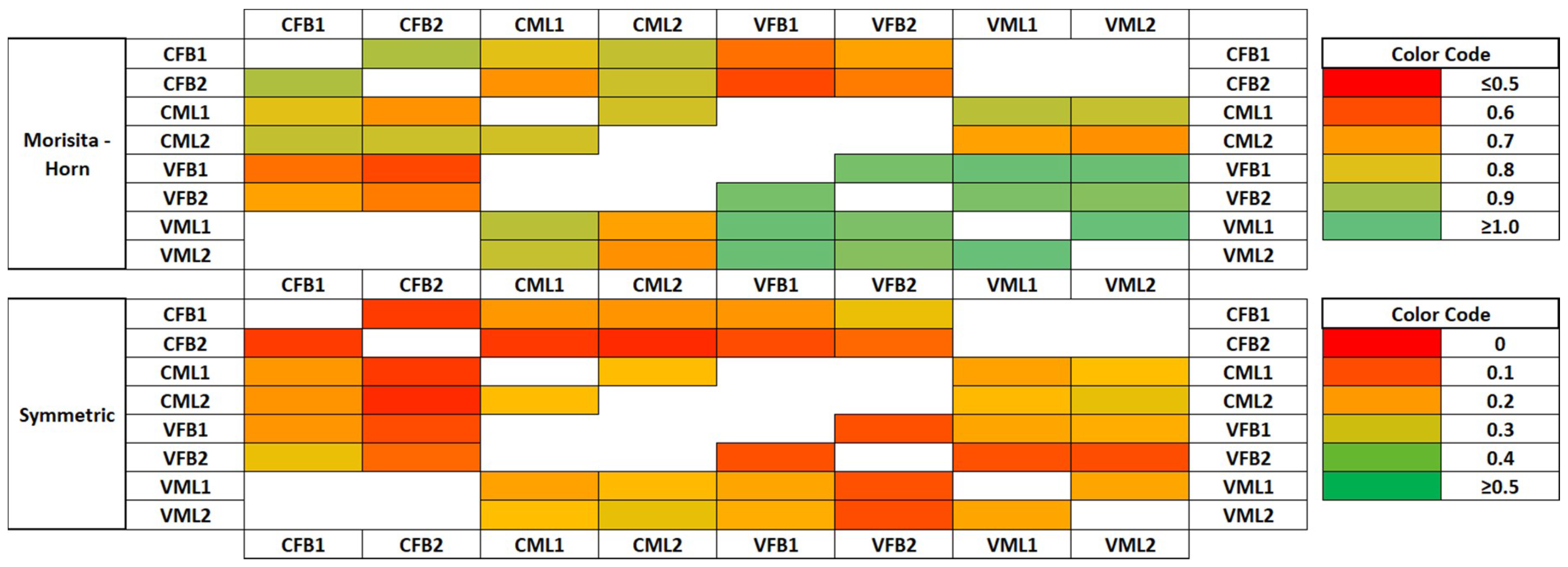
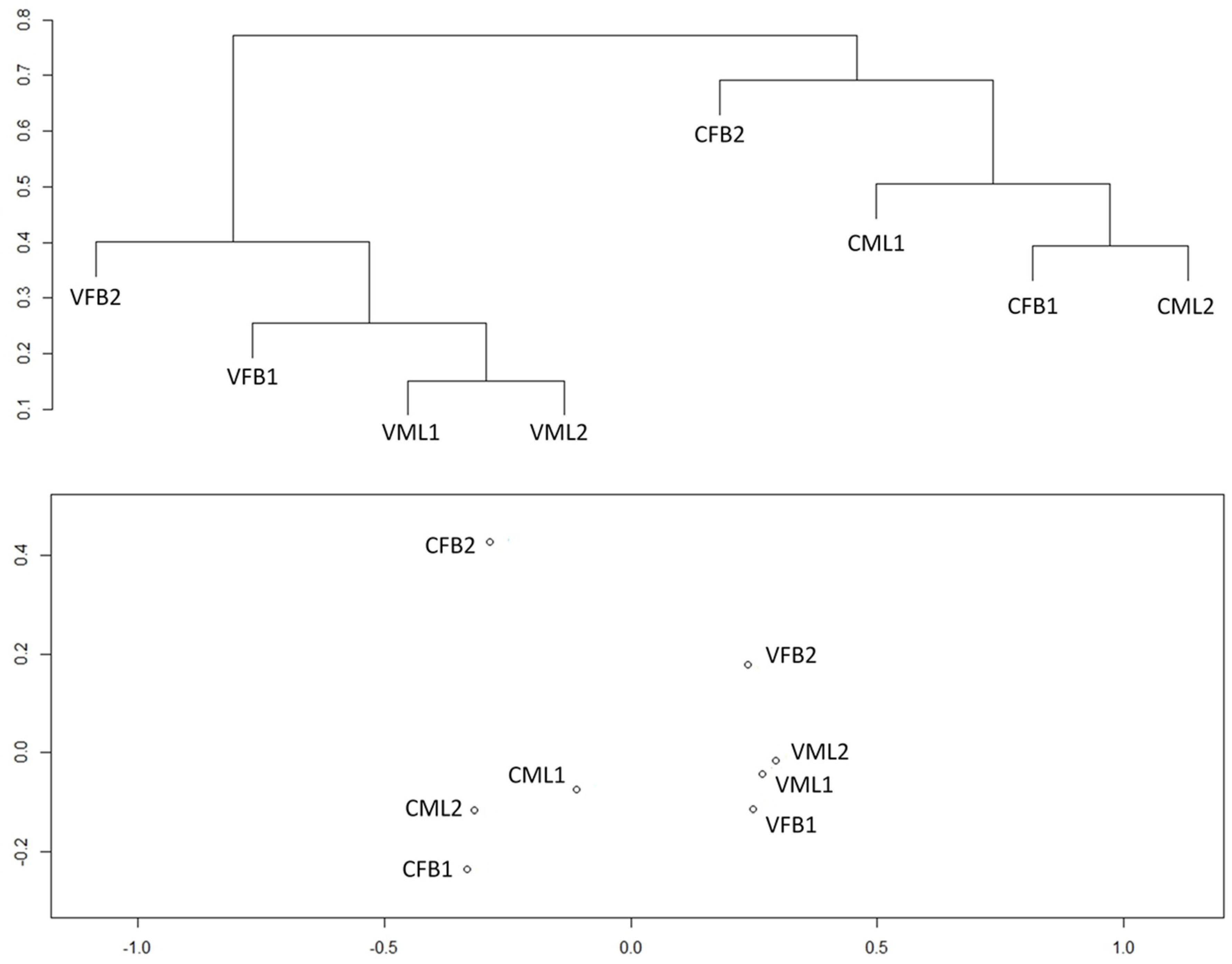
3.3. Similarity Analysis of the Bacterial Community Structure of the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Samples
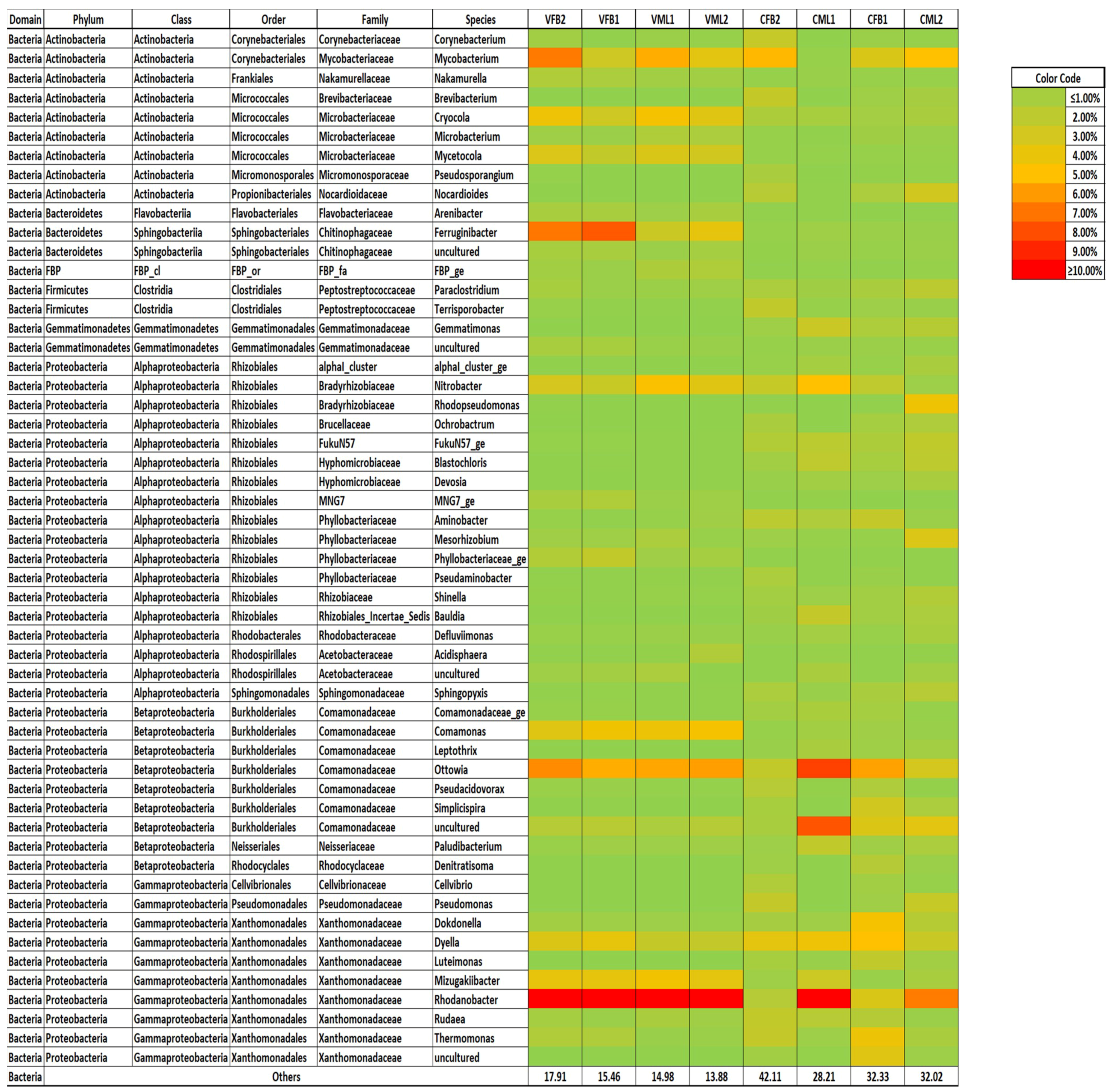
3.4. Bacterial Community Structure of the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Samples under Constant and Variable Salinity Conditions
3.5. Biomineral Precipitation by Bacteria Isolated from Fixed Biofilm under Constant and Variable Salinity Conditions
3.6. Identification of Bacterial Species Associated with Mineral Precipitation from the Biofouling Formed under Constant-Salinity and Variable-Salinity Conditions
4. Discussion
4.1. Physical-Chemical Parameters and Nutrient Removal
4.2. Ecological Coverage, α-Diversity, and β-Diversity Analyses of the Bacterial Community Structure in the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Samples
4.3. Similarity Analysis of the Bacterial Community Structure of the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Samples
4.4. Bacterial Community Structure of the Mixed Liquor and Biofouling Samples under Constant and Variable Salinity Conditions
4.5. Biomineral Precipitation by Bacteria Isolated from Fixed Biofilm under Constant and Variable Salinity Conditions
4.6. Identification of Bacterial Species Associated with Mineral Precipitation from the Biofouling Formed under Constant-Salinity and Variable-Salinity Conditions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Lotti, T.; Garcia-Ruiz, M.-J.; Osorio, F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M. Comparison of bacterial communities of conventional and A-stage activated sludge systems. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 18786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Calderon, K.; Rodriguez, F.A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Hontoria, E.; Poyatos, J.M. Comparative kinetic study between moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor and membrane bioreactor systems and their influence on organic matter and nutrients removal. Biochem. Eng. J. 2013, 77, 28–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Muñio, M.M.; Poyatos, J.M. Kinetic modeling and microbiological study of two-step nitrification in a membrane bioreactor and hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 259, 692–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Lopez-Lopez, C.; Martin-Pascual, J.; Muñio, M.M.; Poyatos, J.M. Kinetic study of the combined processes of a membrane bioreactor and a hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor with advanced oxidation processes as a post-treatment stage for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. Process. 2015, 91, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Lorenzo, C.; González-Martínez, A.; Smidt, H.; González-López, J.; Rodelas, B. Influence of salinity on fungal communities in a submerged fixed bed bioreactor for wastewater treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 285, 562–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Poyatos, J.M. Performance and kinetics of membrane and hybrid moving bed biofilm-membrane bioreactors treating salinity wastewater. AIChE J. 2017, 63, 3329–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Poyatos, J.M. Linkage of microbial kinetics and bacterial community structure of MBR and hybrid MBBR-MBR systems to treat salinity-amended urban wastewater. Biotechnol. Prog. 2017, 33, 1483–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Poyatos, J.M.; Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Martinez-Toledo, M.V. Isolation and metagenomic characterization of bacteria associated with calcium carbonate and struvite precipitation in a pure moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor. Biofouling 2015, 31, 333–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Díaz, J.C.; Martín-Pascual, J.; Muñío, M.M.; González-López, J.; Hontoria, E.; Poyatos, J.M. Comparative kinetics of hybrid and pure moving bed reactor-membrane bioreactors. Ecol. Eng. 2014, 70, 227–234. [Google Scholar]
- Di Trapani, D.; Di Bella, G.; Mannina, G.; Torregrossa, M.; Viviani, G. Comparison between moving bed-membrane bioreactor (MB-MBR) and membrane bioreactor (MBR) systems: Influence of wastewater salinity variation. Bioresour. Technol. 2014, 162, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Muñio, M.M.; Poyatos, J.M. Two-step nitrification in a pure moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor for wastewater treatment: Nitrifying and denitrifying microbial populations and kinetic modeling. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 10333–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhami, N.K.; Reddy, M.S.; Mukherjee, A. Biomineralization of calcium carbonates and their engineered applications: A review. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, A.; Cölfen, H. Mineralization and non-ideality: On nature’s foundry. Biophys. Rev. 2016, 8, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivadeneyra Torres, A.; Martinez-Toledo, M.V.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Martín-Ramos, D.; Rivadeneyra, M.A. Precipitation of carbonates by bacteria isolated from wastewater samples collected in a conventional wastewater treatment plant. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 10, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneyra, A.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Martinez-Toledo, M.V.; Rivadeneyra, M.A. Precipitation of phosphate minerals by microorganisms isolated from a fixed-biofilm reactor used for the treatment of domestic wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2014, 11, 3689–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Vahala, R.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. 16S rRNA gene-based characterization of bacteria potentially associated with phosphate and carbonate precipitation from a granular autotrophic nitrogen removal bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 817–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, A.I.; Bergwerff, L.; van Loosdrecht, M.C.M.; Picioreanu, C. Combined biofouling and scaling in membrane feed channels: A new modeling approach. Biofouling 2015, 31, 83–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Castro, G.A.; Uad, I.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Rivadeneyra, M.A. Bioprecipitation of calcium carbonate crystals by bacteria isolated from saline environments grown in culture media amended with seawater and real brine. BioMed Res. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Castro, G.A.; Uad, I.; Rivadeneyra, A.; Vilchez, J.A.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Rivadeneyra, M.A. Carbonate precipitation of bacterial strains isolated from sediments and seawater: Formation mechanisms. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Poyatos, J.M. Membrane bioreactor and hybrid moving bed biofilm reactor-membrane bioreactor for the treatment of variable salinity wastewater: Influence of biomass concentration and hydraulic retention time. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 336, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unno, T. Bioinformatic suggestions on MiSeq-based microbial community analysis. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, S.M.; Welch, D.M.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L. Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Nonpareil: A redundancy-based approach to assess the level of coverage in metagenomic datasets. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-R, L.M.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Estimating coverage in metagenomic data sets and why it matters. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2349–2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammer, Ø.; Harper, D.A.T. Palaeontological Data Analysis; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, M.J.; Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Osorio, F.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Archaeal and bacterial community dynamics and bioprocess performance of a bench-scale two-stage anaerobic digester. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 6013–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barwell, L.J.; Isaac, N.J.B.; Kunin, W.E. Measuring β-diversity with species abundance data. J. Anim. Ecol. 2015, 84, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Martin-Algarra, A.; Sanchez-Roman, M.; Sanchez-Navas, A.; Martin-Ramos, J.D. Amorphous Ca-phosphate precursors for Ca-carbonate biominerals mediated by Chromohalobacter marismortui. ISME J. 2010, 4, 922–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busquets, A.; Fornós, J.J.; Zafra, F.; Lalucat, J.; Merino, A. Microbial communities in a coastal cave: Cova des Pas de Vallgornera (Mallorca, Western Mediterranean). Int. J. Speleol. 2014, 43, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, N.; Jin, W.; Wu, S.; Sun, C. Genomic and transcriptomic insights into calcium carbonate biomineralization by marine actinobacterium Brevibacterium linens BS258. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Guo, X.; Li, Y.; Huang, T. Experimental and visual research on the microbial induced carbonate precipitation by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. AMB Express 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martín-Navarro, J.A.; Petkov-Stoyanov, V.; Gutiérrez-Sánchez, M.J.; Gordo-Flores, M.E. Struvite urolithiasis with Corynebacterium urealyticum infection: A case report. Nefrologia 2015, 35, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soares, A.; Veesam, M.; Simoes, F.; Wood, E.; Parsons, S.A.; Stephenson, T. Bio-Struvite: A new route to recover phosphorus from wastewater. Clean Soil Air Water 2014, 42, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, C.J.; ten Broek, C.M.A.; Hodson, B.; Whitehead, M.P.; Schmerer, W.M.; Sutton, R. Identification of crystals forming on porcine articular cartilage: A new method for the estimation of the postmortem interval. J. Forensic Sci. 2014, 59, 1575–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aqeel, H.; Basuvaraj, M.; Hall, M.; Neufeld, J.D.; Liss, S.N. Microbial dynamics and properties of aerobic granules developed in a laboratory-scale sequencing batch reactor with an intermediate filamentous bulking stage. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Xia, S.; Wang, R.; Zhao, J. Study on membrane fouling of submerged membrane bioreactor in treating bathing wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2008, 20, 1158–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Mao, Y.; Shi, Y.; Quan, X. Start-up and bacterial community compositions of partial nitrification in moving bed biofilm reactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.; Kim, S.; Yeon, K.; Sang, B.; Chun, J.; Lee, C. Correlation between microbial community structure and biofouling in a laboratory scale membrane bioreactor with synthetic wastewater. Desalination 2012, 287, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Poyatos, J.M.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Influent salinity conditions affect the bacterial communities of biofouling in hybrid MBBR-MBR systems. J. Water Process Eng. 2018, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, J.H.; Irshaid, F.I. Biochemical and molecular taxonomy of a mild halophilic strain of citrobacter isolated from hypersaline environment. Res. J. Microbiol. 2012, 7, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Ma, H.; Li, F.; Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Ma, F.; Wang, C. Citrobacter sp. strain GW-M mediates the coexistence of carbonate minerals with various morphologies. Geomicrobiol. J. 2013, 30, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivadeneyra, A.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Portela, G.R.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J.; Rivadeneyra, M.A. Biomineralisation of carbonate and sulphate by the halophilic bacterium Halomonas maura at different manganese concentrations. Extremophiles 2017, 21, 1049–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnapriya, S.; Venkatesh Babu, D.L.; Arulra, G.P. Isolation and identification of bacteria to improve the strength of concrete. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 174, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodriguez-Sanchez, A.; Leyva-Diaz, J.C.; Muñoz-Palazon, B.; Rivadeneyra, M.A.; Hurtado-Martinez, M.; Martin-Ramos, D.; Gonzalez-Martinez, A.; Poyatos, J.M.; Gonzalez-Lopez, J. Biofouling Formation and Bacterial Community Structure in Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-Membrane Bioreactors: Influence of Salinity Concentration. Water 2018, 10, 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091133
Rodriguez-Sanchez A, Leyva-Diaz JC, Muñoz-Palazon B, Rivadeneyra MA, Hurtado-Martinez M, Martin-Ramos D, Gonzalez-Martinez A, Poyatos JM, Gonzalez-Lopez J. Biofouling Formation and Bacterial Community Structure in Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-Membrane Bioreactors: Influence of Salinity Concentration. Water. 2018; 10(9):1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091133
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodriguez-Sanchez, Alejandro, Juan Carlos Leyva-Diaz, Barbara Muñoz-Palazon, Maria Angustias Rivadeneyra, Miguel Hurtado-Martinez, Daniel Martin-Ramos, Alejandro Gonzalez-Martinez, Jose Manuel Poyatos, and Jesus Gonzalez-Lopez. 2018. "Biofouling Formation and Bacterial Community Structure in Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-Membrane Bioreactors: Influence of Salinity Concentration" Water 10, no. 9: 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091133
APA StyleRodriguez-Sanchez, A., Leyva-Diaz, J. C., Muñoz-Palazon, B., Rivadeneyra, M. A., Hurtado-Martinez, M., Martin-Ramos, D., Gonzalez-Martinez, A., Poyatos, J. M., & Gonzalez-Lopez, J. (2018). Biofouling Formation and Bacterial Community Structure in Hybrid Moving Bed Biofilm Reactor-Membrane Bioreactors: Influence of Salinity Concentration. Water, 10(9), 1133. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10091133