Abstract
Anthropogenic disturbances have a negative impact on lake ecosystems, such as water environmental degradation. Bacterioplankton communities are essential components in lakes and consist of a few abundant species and several rare taxa. However, little is known about the community diversity and composition of abundant and rare bacterioplankton subjected to different levels of anthropogenic disturbances. In this study, water samples were collected from twelve freshwater lakes located around the city of Nanjing, China. Both Illumina MiSeq sequencing and multivariate statistical analysis were employed to determine the bacterioplankton community composition and its relation to environmental variables. The results indicated that tourism disturbances (mostly sewage discharge and tourist activities) altered the community structure of both abundant and rare bacterioplankton by changing water physicochemical characteristics. Alpha diversity of both abundant and rare taxa did not differ among different anthropogenic disturbance lakes (p > 0.05). Rare bacterial taxa possessed higher alpha diversity than abundant taxa, though rare taxa occupied a tiny portion of abundance (4.5%). Redundancy analysis demonstrated that dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was the most significant correlation variable for constraining the variation of abundant taxa, whereas total phosphorus (TP), ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), and chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) were the most dominant environmental factors constraining the rare taxa, indicating abundant and rare taxa may have different ecological niches.
1. Introduction
Bacterioplankton, which are ubiquitous and numerous in lake ecosystems, play prominent roles in regenerating and mobilizing nutrients within freshwater food webs and have profound effects on biogeochemical cycling and water quality [1]. Bacterioplankton communities are highly sensitive to changing aquatic environmental conditions [2,3] and are strongly influenced by water chemistry [4,5,6,7]. Today, water quality for many water bodies has deteriorated due to anthropogenic disturbances, such as industrial pollution [8], agricultural nonpoint source pollution [9], domestic sewage [10], aquaculture activities [11], tourist activities [12], climate change [13], and introduction of non-native species [14]. Some studies have reported that most lakes in China are in a degraded state and water quality has become a great concern due to industrialization and urbanization [15,16]. This is particularly true for lakes situated in urban areas with high human density, such as the cities of Wuhan and Nanjing [17], as they are more exposed to pollution due to industrial effluent and domestic wastewater [18]. These remind us that microbial communities may be affected by environmental change from anthropogenic perturbations, which, in turn, alter biogeochemical processes in these water bodies [19].
A large number of previous studies have investigated the effects of anthropogenic disturbances on aquatic plants and animals [20,21,22,23], but our knowledge regarding the aquatic microbial communities of human-perturbed environments falls far behind that for macro-organisms [3]. Quite a few studies have manifested that bacterial community composition and diversity in aquatic ecosystems can be affected by anthropogenic disturbances [24,25,26]; however, whether or not all of the bacterial species showed the same variation in responses to varying degrees of anthropogenic disturbances remains largely unknown. Generally, bacterioplankton communities in lake ecosystems consist of a great number of species, but only a few of them are abundant and most of the remaining ones are low-abundant, which are known as a “rare biosphere” [27]. The taxonomic identification of the rare biosphere is made feasible using high-throughput sequencing technology [27,28,29]. Abundant and rare bacterial taxa may have different ecological roles in natural ecosystems [30,31]. Abundant bacterial taxa appear to make a significant contribution to ecosystem processes in carbon flow and nutrient cycling, whereas rare bacterial taxa can be considered as a seed bank and play a peripheral but indispensable role, but also may become more-important-function taxa when the environment changes [29,31,32]. Furthermore, recent studies have indicated that abundant and rare bacterial taxa may respond dissimilarly to changes of environmental conditions [29,33,34,35]. Accordingly, we hypothesized in this study that the diversity and composition of abundant and rare bacterioplankton responded differently to different levels of anthropogenic disturbances.
To investigate the hypothesis, we collected water samples from a series of shallow freshwater lakes around Nanjing, China, having differing degrees of anthropogenic disturbances. The patterns in alpha and beta diversity of both abundant and rare bacterioplankton were characterized by Illumina Miseq sequencing of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene. Specifically, the objectives of our study focused on the answers to the following scientific questions: (i) Do the diversity and composition differ between abundant and rare taxa? (ii) Do the diversity and composition of both abundant and rare taxa make distinct response to different levels of anthropogenic disturbances? (iii) Do the environmental variables constrain the bacterioplankton communities differently in abundant and rare taxa?
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Sites and Sample Collection
To investigate bacterioplankton community composition of lakes influenced to a variable degree by anthropogenic disturbances, we classified lakes located in the Zhongshan scenic area of Nanjing, China into 3 levels of anthropogenic disturbances (low, moderate, and high), mainly according to tourist numbers. For each level, 3–5 unstratified freshwater lakes were sampled for bacterioplankton community composition and environmental variables (Table 1). Low-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes are those lakes situated within a water-resource conservation area and kept away from urban settlements. The number of daily visitors is less than 10 people. People are not allowed to enter the water nor are boats and cruise ships allowed on the lake. Moderate-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes are those situated within a natural scenic area. Daily visitors reach around 50–300 people per day. People may access and enter the lake, although boats and cruise ships are prohibited. Small amount of sewage from scattered guesthouses has been found to drain into these lakes. High-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes are those lakes found in tourist areas and are in proximity to residential areas. The number of daily visitors can reach 500–10,000 people. Different-sized boats or cruise ships are allowed on the lake surface. Domestic sewage is often discharged directly into these lakes.

Table 1.
Sampling locations and water chemistry. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was used in combination with Duncan’s test to examine the differences in terms of environmental factors between different categorical sample sites.
Three replicate water samples were collected by boat and then mixed into 1 water sample for each lake in April 2016. The locations of sampling sites (Figure S1) were recorded using a global positioning system (GPS) (Table 1). All water samples were recovered at 0.5 m depth below the water surface using a vertical water sampler (shaped like a Van Dorn sampler) (DSC2500, Xiamen Dengxun Instruments, Xiamen, China), collected in sterilized polyethylene terephthalate plastic bottles, stored on ice, and then transported to the laboratory for further analyses.
2.2. Measurement of Environmental Factors
The pH values were measured in situ by a multiparameter water-quality monitor (YSI 6600, Yellow Springs Instruments, Yellow Springs, OH, USA). Unfiltered water samples were used for determining concentrations of total nitrogen (TN) and total phosphorus (TP) [36]. 200 mL of raw water for each sample was filtered using a vacuum pump (GM-1.0A, Tianjin Jinteng Lab Instrument Co., Ltd., Tianjin, China) through 0.45-μm pore polycarbonate membrane filters (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) for collecting phytoplankton algae. The chlorophyll-a (Chl-a) was spectrophotometrically measured with hot ethanol as the extraction solvent [37]. Dissolved organic carbon (DOC) was measured from 0.45-μm filtrates using a TOC analyzer (Multi N/C 2100, Analytic Jena, Jena, Germany). The concentrations of ammonium nitrogen (NH4+-N), nitrate nitrogen (NO3−-N), and phosphate phosphorus (PO43−-P) were measured through continuous flow analysis (Skalar SAN PLUS system, Skalar Analytical BV, Breda, The Netherlands).
2.3. DNA Extraction, Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Amplification, and Illumina MiSeq Sequencing
To collect bacterioplankton, for each sample we operated vacuum filtration and poured 200 mL of water through a 0.22-μm pore polycarbonate membrane filter (Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) and then preserved them at −80 °C for DNA extraction.
We used an E.Z.N.A.® Water DNA Kit (Omega Biotek, Doraville, GA, USA) to extract the genomic DNA of each water sample. We assessed the quality and quantity of the DNA using a NanoDrop ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies, Wilmington, DE, USA). The universal primer sets 515F (5′-GTGCCAGCMGCCGCGG-3′) and 907R (5′-CCGTCAATTCMTTTRAGTTT-3′) were used to amplify the V4–V5 variable regions of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene [38]. PCR reactions were conducted in a 20-μL mixture containing 0.4 μM of each primer, 2 μL of 2.5 mM of dNTPs, 0.4 μL of FasstPfu Polymerase (TransGen Biotech, Beijing, China), and 10 ng of DNA template. PCR amplification was carried out under the following thermocycling steps: an initial denaturation at 95 °C for 5 min, followed by 24 cycles of denaturation at 94 °C for 30 s, annealing at 55 °C for 30 s, and elongation at 72 °C for 30 s, with a final extension at 72 °C for 5 min. Following the amplification, the PCR products were checked by 2% (w/v) agarose gel electrophoresis. To minimize differences that result from PCR amplification, the PCR reactions were performed in triplicate. The PCR products for each sample were pooled together immediately and then purified using an AxyPrepDNA gel purification kit (Axygen Biotechnology Hangzhou Ltd., Hangzhou, China). The purified PCR products were sent to the Shanghai BIOZERON Co., Ltd. for sequencing on an Illumina MiSeq platform (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA) using the MiSeq Reagent Kit v3 (600-cycle) (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA).
2.4. Sequence Data Processing
The Illumina Miseq paired-end sequences were processed using the Mothur (v.1.35.0) software package (University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, USA) (https://www.mothur.org/). Only sequences that overlapped longer than 25 base pairs were assembled according to their overlap sequence. We discarded reads that could not be assembled. We first filtered the sequence reads by removing low-quality sequences (average quality < 30). Then, we excluded from further analysis sequences containing ambiguous nucleotides and homopolymers longer than 6 nucleotides. The remaining sequences were aligned based on the SILVA 16S rRNA gene template using the nearest alignment space termination (NAST) algorithm. Chimeric sequences were identified and removed using the command ‘chimera.uchime’ in Mothur. The command ‘pre.cluster’ pruned the dataset and accelerated the distance-running procedure [39]. Taxonomic classification information was obtained using the ribosomal database project (RDP) classifier at a bootstrap cutoff of 80% [40]. Operational taxonomic units (OTUs) were clustered at a 97% similarity cutoff using the farthest-neighbor method [41,42]. We selected one sequence from each OTU to be a ‘representative sequence’. The phylogenetic tree of the representative sequences was created using the FASTTREE software (v.2.1.10) [43]. Based on the OTUs table and phylogenetic tree, we calculated the richness and alpha-diversity indices including Chao1, Shannon, and Faith’s phylogenetic diversity (Faith’s PD) [44,45]. Beta-diversity was calculated on a Bray–Curtis distance matrix [46] and visualized using nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots based on an abundance-based (Bray–Curtis) distance with the statistical software R (v.3.3.1) [47]. Rarefaction curves for each sample were performed to estimate the sequence coverage.
2.5. Abundant and Rare OTUs
Consistent with recent studies [30,48,49], we followed the arbitrary definitions of abundant and rare OTUs in relation to their local relative abundance for downstream analysis. To facilitate the comparisons, we adopted thresholds following References [31,50]. According to the rank abundance curve (Figure S2), we considered OTUs to be abundant with relative abundance >0.01% in a sample, and those with relative abundance ≤0.01% were defined as rare OTUs. Subsequently, separate tables of abundant and rare OTUs were generated. To normalize sequences for comparison, we rarefied all datasets to the lowest number of sequences for community-diversity analysis [30,48]. In our study, 24,985 and 711 sequences were the lowest number of sequences recovered for abundant and rare taxa, respectively (Table S1). Finally, random subsets of 24,985 and 711 sequences from each sample were selected from abundant and rare bacterial communities, respectively. Analyses of alpha and beta diversity of abundant and rare bacterial communities were conducted as described for the total communities.
2.6. Statistical Analyses
One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) in combination with Duncan’s test, was performed in SPSS (v.17.0) software (IBM, New York, NY, USA) to examine the difference in environmental factors, alpha diversity, and bacterial phyla/family/genera of abundant and rare bacterial taxa among different lake categories. A two-tailed independent-samples t-test was also executed in SPSS to determine the difference of alpha diversity between abundant and rare taxa within the same lake category. Analysis of permutational multivariate analysis of variance (PERMANOVA) was applied to test the compositional difference between abundant and rare bacterial taxa using ‘vegan‘ package [51] in R (https://www.r-project.org). The relative contribution of environmental factors to bacterial community distribution was identified using a constrained ordination named Redundancy analysis (RDA) due to the maximum axis lengths being less than 4 (the maximum axis lengths of all, abundant, and rare taxa were 2.69, 2.71, and 3.12, respectively) [30], which was determined by detrended correspondence analysis (DCA). Both RDA and DCA were performed with the ‘vegan‘ package in R. Moreover, the function vif.cca was used to determine the multicollinearity among environmental factors in R. Then function envfit was run with 999 permutations in R to confirm the significant parameters (p < 0.05). Venn diagram analysis was conducted with the ‘VennDiagram‘ package in R to show the numbers of unique and shared OTUs between the different analyzed lakes.
2.7. Nucleotide Sequence Accession Numbers
The obtained raw-sequence data were submitted to the Sequence Read Archive (SRA) database (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sra) at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) under accession number SRP095862.
3. Results
3.1. Water Chemistry
The measured environmental factors were summarized in Table 1. TP, pH, and Chl-a were significantly higher in high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes than in other lakes (ANOVA, p < 0.05). The concentrations of PO43−-P showed significant difference between the low- and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes (p < 0.05). Additionally, the highest concentrations of both TN (1.80 ± 1.08 mg/L) and NH4+-N (0.319 ± 0.431 mg/L) were observed in high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes. The concentrations of DOC and NO3−-N indicated no significant differences between different categories (p > 0.05).
3.2. Alpha Diversity of Bacterioplankton Community
Across all 12 samples, we obtained a total of 425,591 effective sequences for the 16S rRNA gene, and the usable sequences ranged from 26,852 (ZS1 sample) to 57,195 (XW1 sample) (Table S1). The rarefaction curves of the bacterial community were observed to be approximately planar (Figure S3), suggesting that sequencing was sufficient in this study for the samples from all lakes. To minimize the bias connected with sequencing coverage [31,48], we randomly selected 26,852 sequences (the lowest number of sequences for the whole dataset) from each sample for data analysis. At a 3% dissimilarity level, a total of 2487 OTUs were detected from 322,224 (=12 × 26,852) sequences. The OTUs’ richness presented fluctuation variation among water samples and the richness ranged from 762 to 1081 OTUs (Table S1). According to the total OTUs obtained, 631 (25.4%) abundant OTUs with 307,756 (95.5%) sequences and 1856 (74.6%) rare OTUs with 14,468 (4.5%) sequences were determined (Figure S2). Venn diagram analysis indicated that abundant taxa shared more OTUs among low-, moderate-, and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes, whereas rare taxa encompassed much more unique OTUs in different classified lakes (Figure S4).
Alpha-diversity indices were calculated to comprehensively assess the species richness and evenness, and values of alpha diversity in each of the individual samples were counted (see Table S1). Both community richness (Chao1 index) and community diversity (Shannon index and phylogenetic diversity (PD)) of abundant and rare bacterial taxa showed no significant differences between the low-, moderate-, and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lake categories (ANOVA, p > 0.05) (Figure 1). However, the number of Chao1, Shannon, and PD of rare taxa was significantly higher than those of abundant taxa in terms of comparison within the same lake category (two-tailed independent-samples t-test, p < 0.05) (Figure 1). Alpha-diversity indices for all taxa are summarized in Table S1.
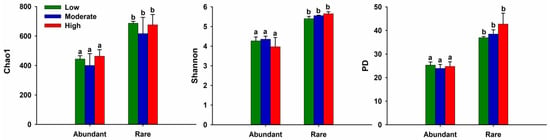
Figure 1.
Comparisons of alpha diversity of abundant and rare bacterioplankton among low-, moderate- and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes. ANOVA coupled with Duncan’s test was used to examine the differences in terms of community diversity among different lake categories. Two-tailed independent-samples t-test was conducted to determine the difference of alpha diversity between abundant and rare taxa within same lake category. Same lowercase letter above the error bars means no significant difference (p > 0.05). Abundant: abundant taxa; Rare: rare taxa; PD: Faith’s phylogenetic diversity.
3.3. Bacterioplankton Community Structure
In general, the bacterioplankton community for all analyzed lakes consisted of 44 phyla, 85 classes, 154 orders, 266 families, and 544 genera, showing typical freshwater-lake bacterial groups [1]. At the phylum level, Proteobacteria (Alpha-, Beta-, and Gammaproteobacteria), Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Cyanobacteria were the dominant phyla (their average relative abundance >10.0 %) for all bacterial taxa, and the relative abundance of total phyla exhibited variations in the lakes along the disturbance gradient (Figure S5). PERMANOVA test indicated that abundant and rare taxa were compositionally distinct (Table S2). Moreover, the taxonomic distribution of abundant and rare bacterioplankton differed (Figure 2). Concretely, Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Betaproteobacteria, and Cyanobacteria were the most predominant abundant taxa; Deltaproteobacteria, Firmicutes, Gammaproteobacteria, and Unclassified were the most predominant rare taxa. Moreover, the rare taxa had more taxonomic groups than abundant taxa (Figure 2). At the family level, Acidimicrobiaceae, Sporichthyaceae, Cryomorphaceae, Flavobacteriaceae, Chitinophagaceae, FamilyI, Planctomycetaceae, Caulobacteraceae, Rhodobacteraceae, Sphingomonadaceae, Burkholderiaceae, and Comamonadaceae were dominant in both abundant and rare taxa (Figure S6). The top 10 detected genera for all, abundant, and rare bacterial taxa are summarized in Table S3. The hgcI_clade was the most frequently identified genus in different taxa, followed by Flavobacterium and CL500-29_marine_group.
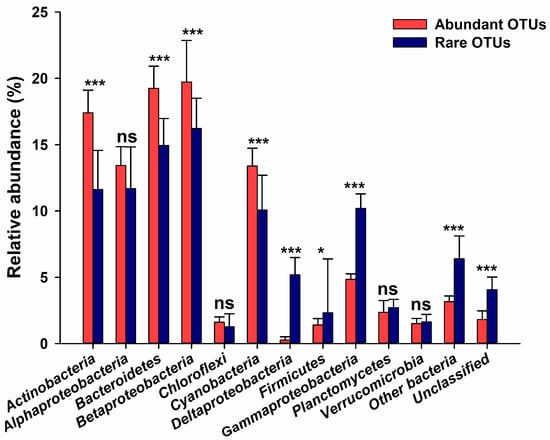
Figure 2.
Comparisons of relative abundance of dominant bacterioplankton phylum/subphylum (at least one of the two taxa has an average relative abundance >1.0 %) between abundant and rare OTUs in twelve sampled lakes. Values and error bars show averages and standard deviations, respectively. Significant differences (two-tailed paired-samples t-test, p < 0.05) are indicated in asterisks. ***: p < 0.001; *: p < 0.05. ns: not significant.
Further, the dissimilarity of bacterioplankton communities within the different categories of anthropogenic disturbance was characterized for all, abundant, and rare taxa using NMDS analysis (Figure 3). The all and abundant bacterioplankton communities at low, moderate, and high levels of anthropogenic disturbance were clustered into their respective categories. However, for NMDS plots derived from rare bacterioplankton communities, sites of low and moderate anthropogenic disturbance were clustered together. Only rare bacterioplankton from the high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes were clustered independently.
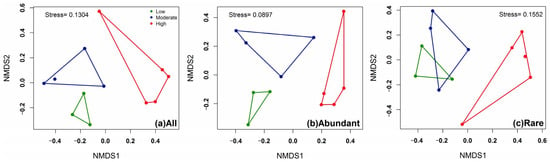
Figure 3.
Nonmetric multidimensional scaling (NMDS) plots based on Bray–Curtis distance matrix showing the differences of bacterioplankton community composition of (a) all, (b) abundant, and (c) rare taxa among low (green), moderate (blue), and high (red) anthropogenic disturbance.
In addition, the community of abundant and rare bacterioplankton varied in responses to the different anthropogenic disturbances. At the phylum level, Cyanobacteria, Chloroflexi, and Firmicutes from abundant bacterioplankton differed among low-, moderate-, and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes (ANOVA, p < 0.05) (Figure 4a), whereas all dominant phyla/subphyla of rare taxa showed no significant differences among different lake categories (ANOVA, p > 0.05) (Figure 4b). At the family level, Flavobacteriaceae (Bacteroidetes), Rhodobacteraceae (Alphaproteobacteria), and Sphingomonadaceae (Alphaproteobacteria) in abundant taxa were all observed at higher abundances in the moderate lake category (Figure S6a). As for rare bacterial taxa, Flavobacteriaceae and Chitinophagaceae assigned to Bacteroidetes exhibited significant differences among different lake categories (ANOVA, p < 0.05) (Figure S6b). At the genus level, there were, in total, nine bacterial genera having significant differences (ANOVA, p < 0.05) among different lake categories selected in abundant and rare taxa, respectively (Table 2). Among the 18 selected genera, only Hydrogenophaga assigned to Betaproteobacteria was found in both abundant and rare taxa (Table 2).
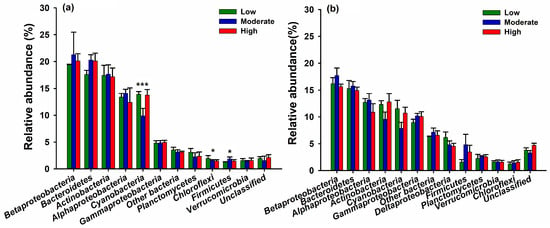
Figure 4.
Comparison of dominant bacterial phyla/subphyla (average relative abundance >1.0%) among low-, moderate-, and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes in (a) abundant and (b) rare taxa, respectively. ***: p < 0.001; *: p < 0.05 (One-way ANOVA test). No asterisk: not significant (AVOVA, p > 0.05).

Table 2.
Comparisons of all the detected bacterioplankton genera of abundant and rare taxa among low-, moderate-, and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes using one-way ANOVA analysis. Only genera having significant difference (p < 0.05) among low, moderate, and high categories are shown.
3.4. Effects of Environmental Factors on Bacterioplankton Distribution
Based on the environmental factors and the observed OTUs, the effects of environmental factors on the distribution of bacterioplankton community were examined by RDA ordination. The two RDA axes (RDA1, RDA2) explained 19.33%, 19.33%, and 17.14% of the variation in bacterial community for all, abundant, and rare taxa, respectively (Figure 5). There was no common environmental factor significantly linked to the variability of all, abundant, and rare taxa. RDA results indicated that DOC was significantly associated with the distribution of all and abundant bacterioplankton community (p < 0.05, calculated by function envfit). However, RDA for the rare bacterioplankton community showed a different constraining pattern of environmental factors. TP, NH4+-N, and Chl-a were the significant explanatory factors for the variation of the rare bacterioplankton community composition (p < 0.01).
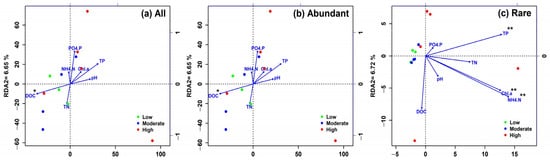
Figure 5.
Redundancy analysis (RDA) of the bacterioplankton community and environmental factors. Constrained environmental factors were determined by function vif.cca. Straight lines with an arrow represent the environmental factors and the length of the lines is associated with the strength of the correlation with the bacterioplankton community. Significance (p-value) between an environmental factor and the microbial community was determined by function envfit. *: p < 0.05; **: p < 0.01. Low: low-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes; Moderate: moderate-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes; High: high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes, (a) All taxa, (b) Abundant taxa, (c) Rare taxa.
4. Discussion
Most studies did not differentiate the microbial community when exploring the diversity and composition of the microbial community in response to anthropogenic disturbances in aquatic ecosystems [25,26,52,53]. Considering possibly discrepant ecological roles in abundant and rare bacteria [31], we chose to divide the bacterioplankton community into two main components. In this study, we examined the diversity and composition of abundant and rare taxa in freshwater lakes subjected to different levels of tourist disturbances, coupled with physicochemical analyses, high-throughput sequencing technology, bioinformatics analyses, and multivariate statistical methods. For our study sites, tourism disturbances, including sewage discharge from tourism industry and tourist activities, are the main anthropogenic perturbations [54].
4.1. Water Chemistry Characteristics under Anthropogenic Disturbance
In the present study, the measured environmental factors of the lakes reflected relatively fluctuant nutrient concentrations. In fact, those lakes having a higher anthropogenic disturbance had higher nutrient concentrations (TN, TP, PO43−-P, and NH4+-N) (Table 1). Previous studies suggested that sewage discharged into freshwater aquatic environments could generate high nutrient concentrations (e.g., TN and TP) [55,56,57]. Besides, one study recently assessed the influence of tourism on surface-water quality and reported that activities related to tourism in a river resulted in higher concentrations of TN and TP in the midstream and downstream areas than upstream [12]. Although natural processes may contribute to increased nutrient levels within aquatic systems [58], the moderate- and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes involved in our study indicated that anthropogenically derived sources were responsible for a significant proportion of total nutrient input. The high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes in our study may be suffering from considerably serious environmental degradation.
4.2. Alpha Diversity and Composition Comparisons between Abundant and Rare Bacterial Taxa
In concordance with previous research on oil-contaminated soils [49], we also observed that alpha diversity of rare bacterial taxa was significantly higher than that of abundant bacterial taxa (Figure 1), though rare bacteria occupied a tiny portion of abundance (4.5%). This result suggests that rare taxa are a significant contributor to alpha diversity [49,59]. The abundance of any given bacterial species is the results of balance between its growth rate and loss factors [29,60]. Low abundance could actually protect rare taxa from active loss by both viral lysis and predation [61]; then, rare taxa are likely to experience a low risk of extinction as equally as abundant taxa [31,60]. Relative to rare taxa, abundant ones are generally detected to a deeper degree [60,62]. However, with the aid of advanced molecular techniques and increasing sampling efforts, rare bacteria have been successfully explored in oceans [63], soils [49], wastewater treatment reactors [30], coastal lakes [33], and plateau lakes [60].
Here, our results indicate that there are marked differences in the taxonomic compositions between abundant and rare bacterioplankton communities (Figure 2 and Figure S4, Table S2). Although both abundant and rare bacterioplankton communities were dominated by Proteobacteria (mostly Alpha-, Beta-, and Gammaproteobacteria), Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria, which are common and often numerically important constituents of freshwater bodies and are important contributors to global biogeochemical processes [1], abundant taxa presented in larger proportions in Betaproteobacteria, Bacteroidetes, and Actinobacteria than rare taxa, suggesting that abundant taxa may globally act as a protagonist to mediate geochemical cycling [30,49]. However, Deltaproteobacteria were rare taxa striking higher than abundant taxa. A previous study revealed that organisms within Deltaproteobacteria play significant roles in N2O reduction in different environments [64]. This suggests that rare taxa could play non-negligible roles in the denitrification process [65]. Meanwhile, the proportion of unclassified and other bacteria is also rare taxa, significantly higher than abundant taxa, implying that rare taxa may contain astonishing explorable biological resources [59]. At a bacterial genus level, nearly all the top ten bacterial genera in abundant taxa occupied higher relative abundance than those of rare taxa (Table S3). Previous studies suggested that abundant bacterial taxa might grow on a broader-resources range compared with rare bacterial taxa, and hence being able to attain high abundance [31,66], while a few rare bacterial taxa may be adapted to use only some specific substrates [31].
4.3. Alpha Diversity and Community Composition of Abundant and Rare Bacterial Taxa under Anthropogenic Disturbance
Alpha-diversity comparisons of both abundant and rare taxa among different anthropogenic disturbance lakes showed no significant difference (ANOVA, p > 0.05), indicating that different levels of anthropogenic disturbances have less impact on alpha diversity of abundant and rare taxa in our investigated lakes. However, we observed that variable levels of anthropogenic disturbances could alter the distribution of abundant and rare bacterioplankton communities. Based on NMDS results (Figure 3), abundant bacterioplankton appeared to be more easily influenced under anthropogenic perturbations, whereas rare bacterioplankton were more likely to show resistance in moderate-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes. Previous studies reported that the rare bacterial taxa with lower abundance (<0.1%) could already reach a more stable community, whereas abundant bacterial taxa can fluctuate significantly depending on environmental conditions and were more sensitive to changed conditions than rare bacterial taxa [35,49]. However, rare bacterial taxa presented characteristic metabolic activities [63] and, therefore, can also respond rapidly to environmental changes (e.g., high anthropogenic disturbance as occurred in our current study). Moreover, in view of rare bacterial taxa that are an important contributor to alpha diversity [49,59], they may serve as a diverse source pool to improve the resistance or resilience of bacterioplankton communities and probably play fundamental roles in maintaining the lake ecosystem stability [31,49,62].
Furthermore, bacterial genera of abundant taxa having significant difference (ANOVA, p < 0.05) among different lake categories overwhelmingly exhibited higher abundance in moderate and high lake categories. However, those of rare taxa largely occupied higher abundance in the low category (Table 2). Only Hydrogenophaga, having significant difference among different lake categories, was shared in both abundant and rare taxa. Previous studies proved that Hydrogenophaga are capable of degrading a variety of environmental organic pollutants [67]. It is also known that Flavobacterium, Rhodobacter, and Sphingopyxis in abundant taxa with relatively higher abundance in moderate-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes are able to biodegrade many environmental organic compounds [68,69,70]. Filimonas in rare taxa, presenting higher relative abundance in high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes, are involved in carbohydrate degradation and can act as a carbohydrate degrader in diverse environments [71]. However, Diplorickettsia and Haliangium in rare taxa were only detected in low-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes, and were not detected in moderate and high categories, indicating that they may be not suitable to survive in unfavorable environmental conditions. Together, abundant and rare taxa may establish cooperation or complementary relationship to have synergistic effects on high-anthropogenic-disturbance ecosystems [49,50].
4.4. Linking Environmental Factors with Bacterioplankton Community Composition
An important ecological objective in environmental microbiology is to determine the possible influencing factors that are tightly associated with the bacterial community structure. Generally, water physicochemical quality was frequently identified as a significant environmental driver to bacterial community composition in many ecosystems [30,31,35,60]. Our results showed that abundant and rare bacterioplankton presented remarkably different patterns because both abundant and rare bacterioplankton were constrained by different explanatory factors (Figure 5). DOC was the most significant environmental factor for explaining the variation of abundant bacterioplankton, whereas TP, NH4+-N, and Chl-a were the most predominant factors constraining the rare bacterioplankton. This finding suggests that abundant and rare bacterioplankton may respond to distinct abiotic parameters, and those have a different ecological niche. Consistent with our present study, some recent studies revealed that abundant and rare bacterioplankton in freshwater lakes and reservoirs were also significantly correlated with different environmental factors [31,35]. Interestingly, similar observations have also been reported in activated sludge bioreactor [30], soil [50], and intertidal marine ecosystem [72]. Recent work has confirmed that abundant and rare bacterial taxa had discrepant ecological niches and different roles in oil-contaminated soils [50]. Hence, the bulk of abundant and rare bacterioplankton may play different roles in our sampled lakes, and we infer that abrupt change in those related environmental factors might lead to alteration of the abundance and structure of abundant and rare bacterioplankton. In fact, it is believed that the majority of the rare biosphere are dormant or inactive populations in an environment [35,61] but may become abundant taxa as favorable environmental conditions are met [29,63,73]. As an example, Teira et al. [74] found that the genus Cycloclasticus (a hydrocarbon-degrading Gammaproteobacteria) became an abundant species of the bacterial community when adding polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) in microcosm experiments, but once the PAHs were completely consumed, they rapidly declined their abundance.
5. Conclusions
In summary, our work reveals the diversity and composition of abundant and rare bacterial taxa derived from freshwater lakes in response to different levels of tourism disturbances. Tourism disturbances can alter water environmental factors and the community structure of both abundant and rare bacterioplankton. Alpha diversity of both abundant and rare taxa did not differ among distinct levels of anthropogenic disturbance. Abundant and rare bacterial taxa were constrained by different environmental factors. Overall, this study provides insight into the abundant and rare bacterioplankton communities subjected to varying degrees of tourism disturbances. However, further analyses of function roles of abundant and rare taxa are needed for better understanding lake-ecosystem functions under different levels of tourism disturbances.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/10/8/1075/s1. Figure S1: Map of sampling sites in Nanjing, China, Figure S2: Rank abundance curve for the obtained 2487 OTUs, Figure S3: rarefaction curves of the bacterioplankton. Figure S4: Venn diagrams showing the numbers of unique and shared OTUs between the different analyzed lakes. Figure S5: Relative abundance of dominant bacterioplankton phyla/subphyla (average relative abundance >1.0 %) for all bacterial taxa in different sampled lakes from Nanjing. Figure S6: Comparison of dominant bacterial family (average relative abundance >1.0 %) among low-, moderate- and high-anthropogenic-disturbance lakes in (a) abundant and (b) rare taxa, respectively. Table S1: Summary of diversity indices of bacterioplankton community for all, abundant, and rare taxa. Table S2: Analysis of PERMANOVA testing difference of community composition between abundant and rare bacterial taxa based on Bray–Curtis distance. Table S3: Taxonomic distribution of the average top ten bacterial genera from all, abundant, and rare bacterial taxa.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.Z. and J.Z.; methodology, X.C. and R.H.; software, X.C. and R.H.; validation, C.J., D.Z. and R.H.; formal analysis, C.J. and Y.L.; investigation, C.J. and Y.L.; writing-original draft preparation, C.J.; writing-review and editing, D.Z., W.Z., and J.Z.; supervision, D.Z.; funding acquisition, D.Z. and J.Z.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R and D Program of China (2016YFC0402710), National Natural Science Foundation of China (41571108, 41671078 and 51539003), Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province, China (BK20151614), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (2018B43414), and the Qing Lan Project of Jiangsu Province.
Acknowledgments
We thank Feng Shen, Sichen Wang, and Honghao Shi for collecting water samples and water filtration.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A guide to the natural history of freshwater lake bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.H.; Huang, S.B.; Sun, G.P.; Xu, Z.C.; Xu, M.Y. Phylogenetic diversity, composition and distribution of bacterioplankton community in the Dongjiang River, China. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2012, 80, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labbate, M.; Seymour, J.R.; Lauro, F.; Brown, M.V. Anthropogenic impacts on the microbial ecology and function of aquatic environments. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Xu, H.M.; Zeng, J.; Cao, X.Y.; Shen, F.; Yu, Z.B. Community composition and assembly processes of the free-living and particle-attached bacteria in Taihu Lake. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2017, 93, fix062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Cao, X.Y.; Huang, R.; Zeng, J.; Shen, F.; Xu, H.M.; Wang, S.C.; He, X.W.; Yu, Z.B. The heterogeneity of composition and assembly processes of the microbial community between different nutrient loading lake zones in Taihu Lake. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 5913–5923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Kojima, H.; Iwata, T.; Urabe, J.; Fukui, M. Dissolved organic carbon as major environmental factor affecting bacterioplankton communities in mountain lakes of Eastern Japan. Microb. Ecol. 2012, 63, 496–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, J.; Bian, Y.Q.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q.L. Macrophyte species drive the variation of bacterioplankton community composition in a shallow freshwater lake. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokulil, M.; Chen, W.; Cai, Q. Anthropogenic impacts to large lakes in China: The Tai Hu example. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health Manag. 2000, 3, 81–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Wu, S.X.; Ji, H.J.; Kolbe, H. Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China and the alleviating strategies I. Estimation of agricultural non-point source pollution in China in early 21 century. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2004, 37, 1008–1017. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, I.; Romshoo, S.A. Impact of anthropogenic activities on water quality of Lidder River in Kashmir Himalayas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2013, 185, 4705–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.D.; Jiang, C.L.; Zhu, L.Q.; Wang, X.W.; Hu, X.Q.; Cheng, J.Y.; Xie, M.H. Impact of pond and fence aquaculture on reservoir environment. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 92–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Zhang, X.L.; Yang, Z.P.; Xiong, H.G.; Qiu, Y. Influence of tourist disturbance on soil properties, plant communities, and surface water quality in the Tianchi scenic area of Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delpla, I.; Jung, A.V.; Baures, E.; Clement, M.; Thomas, O. Impacts of climate change on surface water quality in relation to drinking water production. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1225–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pejchar, L.; Mooney, H.A. Invasive species, ecosystem services and human well-being. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2009, 24, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Maruya, K.A.; Snyder, S.A.; Zeng, E.Y. China’s water pollution by persistent organic pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2012, 163, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, B.Q.; Gao, G.; Zhu, G.W.; Zhang, Y.L.; Song, Y.Z.; Tang, X.M.; Xu, H.; Deng, J.M. Lake eutrophication and its ecosystem response. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2013, 58, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birch, S.; Mccaskie, J. Shallow urban lakes: A challenge for lake management. Hydrobiologia 1999, 395, 365–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Tang, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.H.; Li, W.J. City clusters in China: Air and surface water pollution. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2006, 4, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, T.L.; Williams, H.N. Functional diversity of bacterioplankton in three North Florida freshwater lakes over an annual cycle. Microb. Ecol. 2014, 67, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddle, M.J.; Scorgie, H.R.A. The effects of recreation on freshwater plants and animals: A review. Biol. Conserv. 1980, 17, 183–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, C.M. Biological effects of agriculturally derived surface water pollutants on aquatic systems—A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1993, 22, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedetti-Cecchi, L.; Pannacciulli, F.; Bulleri, F.; Moschella, P.S.; Airoldi, L.; Relini, G.; Cinelli, F. Predicting the consequences of anthropogenic disturbance: Large-scale effects of loss of canopy algae on rocky shores. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2001, 214, 137–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehage, J.S.; Trexler, J.C. Assessing the net effect of anthropogenic disturbance on aquatic communities in wetlands: Community structure relative to distance from canals. Hydrobiologia 2006, 569, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nogales, B.; Lanfranconi, M.P.; Piña-Villalonga, J.M.; Bosch, R. Anthropogenic perturbations in marine microbial communities. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 275–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeffries, T.C.; Fontes, M.L.S.; Harrison, D.P.; Van-Dongen-Vogels, V.; Eyre, B.D.; Ralph, P.J.; Seymour, J.R. Bacterioplankton dynamics within a large anthropogenically impacted urban estuary. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordaan, K.; Bezuidenhout, C.C. Bacterial community composition of an urban river in the North West Province, South Africa, in relation to Physico-chemical water quality. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 5868–5880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sogin, M.L.; Morrison, H.G.; Huber, J.A.; Mark Welch, D.; Huse, S.M.; Neal, P.R.; Arrieta, J.M.; Herndl, G.J. Microbial diversity in the deep sea and the underexplored “rare biosphere”. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 12115–12120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logares, R.; Haverkamp, T.H.A.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, S.; Lanzen, A.; Nederbragt, A.J.; Quince, C.; Kauserud, H. Environmental microbiology through the lens of high-throughput DNA sequencing: Synopsis of current platforms and bioinformatics approaches. J. Microbiol. Methods 2012, 91, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. The rare bacterial biosphere. Annu. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2012, 4, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.S.; Jeong, J.Y.; Wells, G.F.; Park, H.D. General and rare bacterial taxa demonstrating different temporal dynamic patterns in an activated sludge bioreactor. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 1755–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.M.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wilkinson, D.M. The biogeography of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in the lakes and reservoirs of China. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuenschwander, S.M.; Pernthaler, J.; Posch, T.; Salcher, M.M. Seasonal growth potential of rare lake water bacteria suggest their disproportional contribution to carbon fluxes. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logares, R.; Lindström, E.S.; Langenheder, S.; Logue, J.B.; Paterson, H.; Laybourn-Parry, J.; Rengefors, K.; Tranvik, L.; Bertilsson, S. Biogeography of bacterial communities exposed to progressive long-term environmental change. ISME J. 2013, 7, 937–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baltar, F.; Palovaara, J.; Vila-Costa, M.; Salazar, G.; Calvo, E.; Pelejero, C.; Marrasé, C.; Gasol, J.M.; Pinhassi, J. Response of rare, common and abundant bacterioplankton to anthropogenic perturbations in a Mediterranean coastal site. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2015, 91, fiv058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.B.; Zeng, J.; Ren, L.J.; Wang, J.J.; Xing, P.; Wu, Q.L.L. Contrasting patterns of diversity of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in freshwater lakes along an elevation gradient. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 1570–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, E.W.B.; Eaton, R.B.; Clesceri, A.D.; Bridgewater, L.S. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; American Public Health Association: Washington, DC, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Jespersen, A.M.; Christoffersen, K. Measurements of chlorophyll-a from phytoplankton using ethanol as extraction solvent. Arch. Hydrobiol. 1987, 109, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Caporaso, J.G.; Lauber, C.L.; Walters, W.A.; Berg-Lyons, D.; Huntley, J.; Fierer, N.; Owens, S.M.; Betley, J.; Fraser, L.; Bauer, M.; et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1621–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huse, S.M.; Welch, D.M.; Morrison, H.G.; Sogin, M.L. Ironing out the wrinkles in the rare biosphere through improved OTU clustering. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1889–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Handelsman, J. Introducing DOTUR, a computer program for defining operational taxonomic units and estimating species richness. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 1501–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schloss, P.D.; Westcott, S.L.; Ryabin, T.; Hall, J.R.; Hartmann, M.; Hollister, E.B.; Lesniewski, R.A.; Oakley, B.B.; Parks, D.H.; Robinson, C.J.; et al. Introducing mothur: Open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 75, 7537–7541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree: Computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1641–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faith, D.P. Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol. Conserv. 1992, 61, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunin, V.; Engelbrektson, A.; Ochman, H.; Hugenholtz, P. Wrinkles in the rare biosphere: Pyrosequencing errors can lead to artificial inflation of diversity estimates. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 118–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, J.R.; Curtis, J.T. An ordination of the Upland forest communities of southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 1957, 27, 326–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Gong, J.; Shi, F.; Ma, B.; Dong, J.; Pachiadaki, M.; Zhang, X.L.; Edgcomb, V.P. Depth shapes α- and β-diversities of microbial eukaryotes in surficial sediments of coastal ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 3722–3737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Luo, Y.T.; Lu, M.M.; Xiao, X.; Lin, Y.B.; Chen, W.M.; Wei, G.H. Distinct succession patterns of abundant and rare bacteria in temporal microcosms with pollutants. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 225, 497–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, S.; Chen, W.M.; Wei, G.H. Biogeography and ecological diversity patterns of rare and abundant bacteria in oil-contaminated soils. Mol. Ecol. 2017, 26, 5305–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, P. VEGAN, a package of R functions for community ecology. J. Veg. Sci. 2003, 14, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, A.; Ju, F.; Hou, L.; Li, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, H.; Mulla, S.I.; Sun, Q.; Bürgmann, H.; Yu, C.P. Strong impact of anthropogenic contamination on the co-occurrence patterns of a riverine microbial community. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 4993–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mykrä, H.; Tolkkinen, M.; Heino, J. Environmental degradation results in contrasting changes in the assembly processes of stream bacterial and fungal communities. Oikos 2017, 126, 1291–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.Y.; Wang, M.; Zeng, J.; Yan, W.M.; Wang, J.Q.; Ma, T.; Huang, R. Bacterial community compositions in response to sediment properties in urban lakes of Nanjing. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 2929–2940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Zhu, J.Y.; Dai, K.W.; Gao, S.; Dou, Y.J. Impact of rapid urbanization on water quality and related mitigation options in Taihu Lake area. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2003, 23, 746–750. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.L.; Lu, Y.L.; Han, J.Y.; He, G.Z.; Wang, T.Y. Identification of anthropogenic influences on water quality of rivers in Taihu watershed. J. Environ. Sci. 2007, 19, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, C.; Zha, Y.; Li, Y.; Sun, D.; Lu, H.; Yin, B. Eutrophication of lake waters in China: Cost, causes, and control. Environ. Manag. 2010, 45, 662–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaup, E.; Burgess, J.S. Surface and subsurface flows of nutrients in natural and human impacted lake catchments on Broknes, Larsemann Hills, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 2002, 14, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.J.; Neufeld, J.D. Ecology and exploration of the rare biosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.Q.; Cao, X.F.; Wang, J.; Zhao, L.; Sun, J.H.; Jiang, D.L.; Huang, Y. Similar community assembly mechanisms underlie similar biogeography of rare and abundant bacteria in lakes on Yungui Plateau, China. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2017, 62, 723–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrós-Alió, C. Marine microbial diversity: Can it be determined? Trends Microbiol. 2006, 14, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galand, P.E.; Casamayor, E.O.; Kirchman, D.L.; Lovejoy, C. Ecology of the rare microbial biosphere of the Arctic Ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22427–22432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, B.J.; Yu, L.Y.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Kirchman, D.L. Activity of abundant and rare bacteria in a coastal ocean. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 12776–12781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, C.M.; Graf, D.R.H.; Bru, D.; Philippot, L.; Hallin, S. The unaccounted yet abundant nitrous oxide-reducing microbial community: A potential nitrous oxide sink. ISME J. 2013, 7, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawson, C.E.; Strachan, B.J.; Hanson, N.W.; Hahn, A.S.; Hall, E.R.; Rabinowitz, B.; Mavinic, D.S.; Ramey, W.D.; Hallam, S.J. Rare taxa have potential to make metabolic contributions in enhanced biological phosphorus removal ecosystems. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 4979–4993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hambright, K.D.; Beyer, J.E.; Easton, J.D.; Zamor, R.M.; Easton, A.C.; Hallidayschult, T.C. The niche of an invasive marine microbe in a subtropical freshwater impoundment. ISME J. 2015, 9, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magic-Knezev, A.; Wullings, B.; Van der Kooij, D. Polaromonas and Hydrogenophaga species are the predominant bacteria cultured from granular activated carbon filters in water treatment. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2009, 107, 1457–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kertesz, M.A.; Kawasaki, A. Hydrocarbon-degrading Sphingomonads: Sphingomonas, Sphingobium, Novosphingobium, and Sphingopyxis. In Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Timmis, K.N., Ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 1693–1705. ISBN 978-3-540-77584-3. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.Y.; Wan, R.; Wang, Q.F.; Xie, S.G. Identification of anthracene degraders in leachate-contaminated aquifer using stable isotope probing. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2011, 65, 1224–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.B.; Chen, C.; Wang, Z.; Wan, R.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, X.J.; Xie, S.G. Changes of biomass and bacterial communities in biological activated carbon filters for drinking water treatment. Process Biochem. 2013, 48, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiratori-Takano, H.; Takano, H.; Ueda, K. Whole-genome sequence of Filimonas lacunae, a bacterium of the family Chitinophagaceae characterized by marked colony growth under a high-CO2 atmosphere. Genome Announc. 2016, 4, e00667-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, H.; Holohan, B.; Vaudrey, J.; Lin, S.; McManus, G.B. The diversity and biogeography of abundant and rare intertidal marine microeukaryotes explained by environment and dispersal limitation. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 20, 462–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lennon, J.T.; Jones, S.E. Microbial seed banks: The ecological and evolutionary implications of dormancy. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teira, E.; Lekunberri, I.; Gasol, J.; Nieto-Cid, M.; Álvarez-Salgado, X.A.; Figueiras, P.G. Dynamics of the hydrocarbon-degrading Cycloclasticus bacteria during mesocosm-simulated oil spills. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2551–2562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).