A Comparative Analysis of the Wind and Wave Climate in the Black Sea Along the Shipping Routes
Abstract
1. Introduction
- a better understanding of the wind and wave conditions in the vicinity of the major ports and shipping routes of the Black Sea, by considering multiple datasets;
- to highlight the spatial and temporal variability of the wind and wave climate as resulting from the analysis of various datasets; and,
- to perform a comparative analysis of the datasets along the main shipping routes.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. The Target Area
2.2. Dataset
3. Results
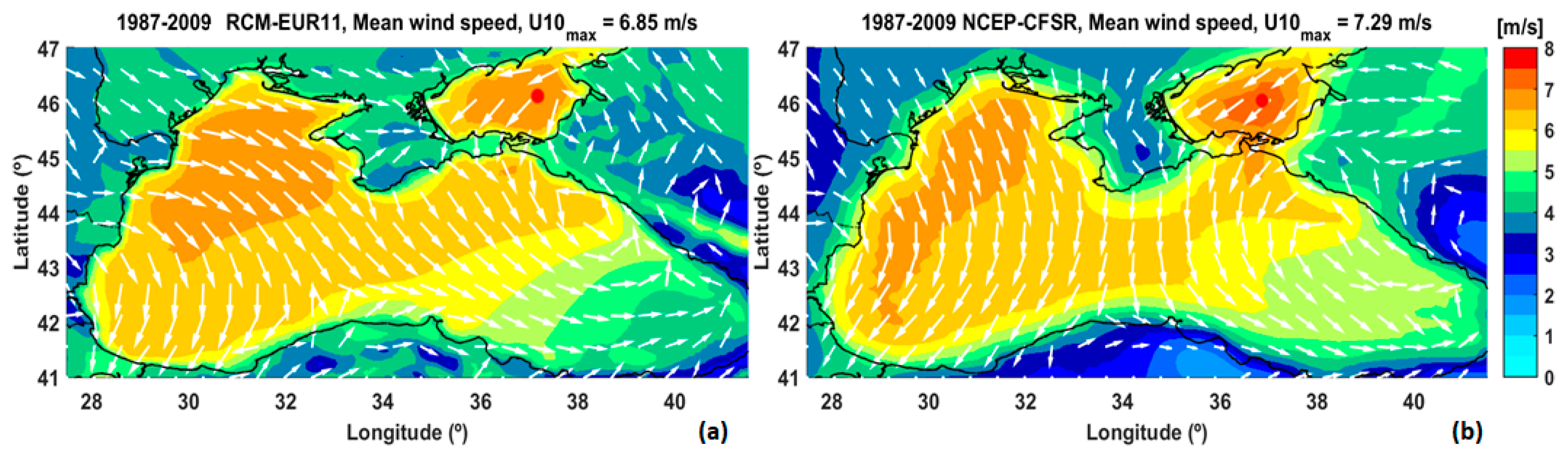
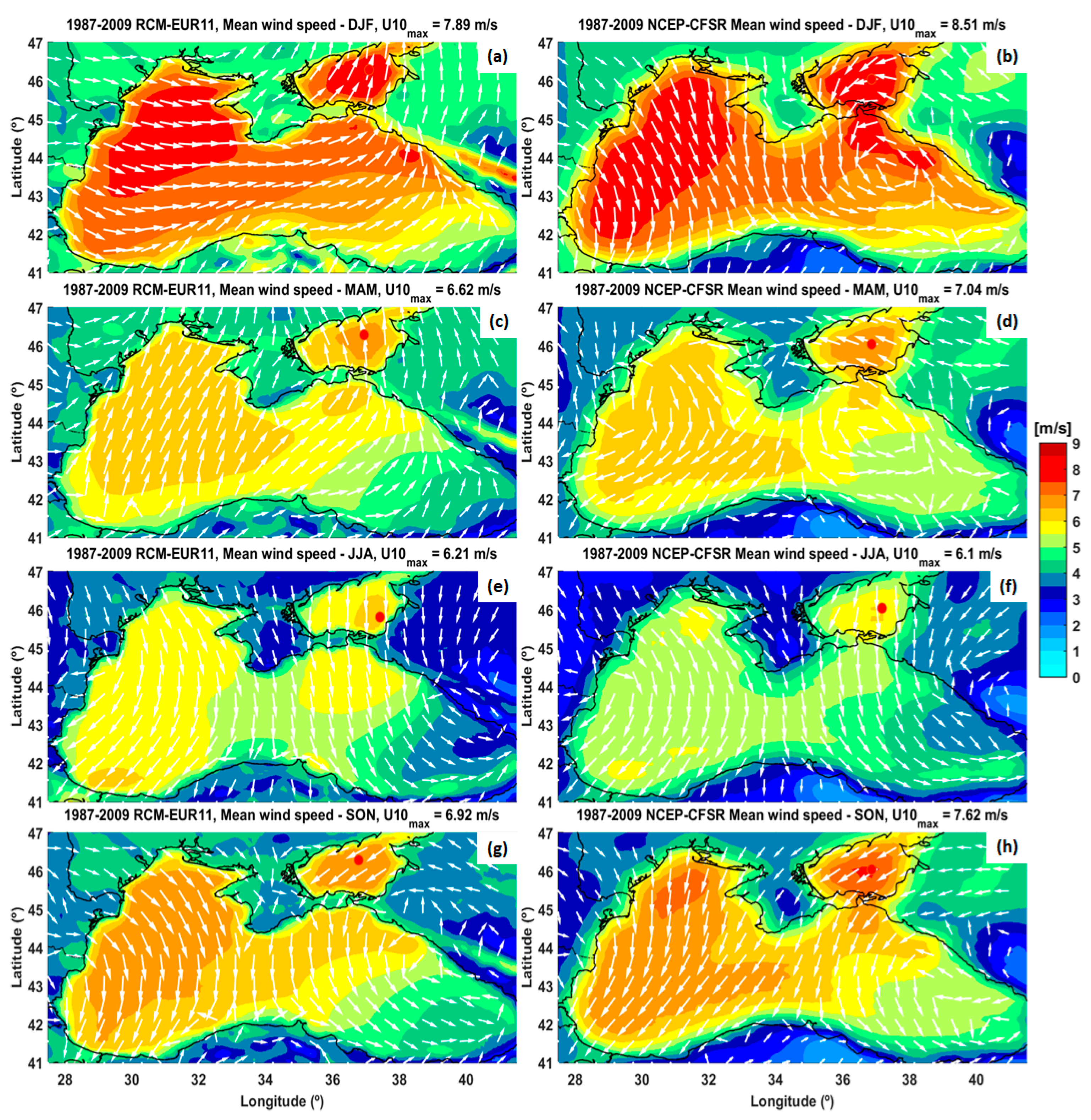
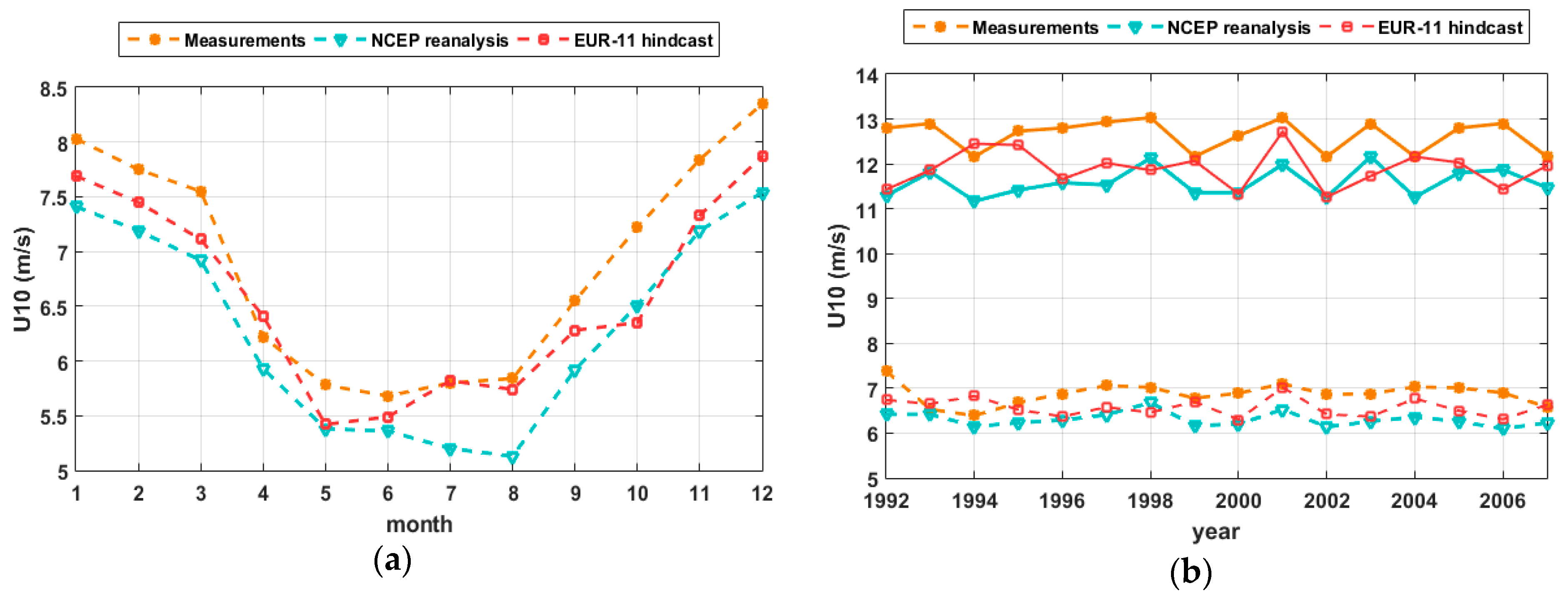
3.1. Analysis of the Wind Conditions
3.2. Analysis of the Wave Conditions
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lyratzopouoou, D.; Zarotiadis, G. Black Sea: Old Trade Routes and Current Perspectives of Socioeconomic Co-operation. Procedia Econ. Financ. 2014, 9, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onea, F.; Rusu, L. A Long-Term Assessment of the Black Sea Wave Climate. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onea, F.; Raileanu, A.; Rusu, E. Evaluation of the Wind Energy Potential in the Coastal Environment of Two Enclosed Seas. Adv. Meteorol. 2015, 808617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davy, R.; Gnatiuk, N.; Pettersson, L.; Bobylev, L. Climate change impacts on wind energy potential in the European domain with a focus on the Black Sea. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 81, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allenbach, K.; Garonna, I.; Herold, C.; Monioudi, I.; Giuliani, G.; Lehmann, A.; Velegrakis, A.F. Black Sea beaches vulnerability to sea level rise. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 46, 95–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Limber, P.W.; Barnard, P.L. Coastal knickpoints and the competition between fluvial and wave-driven erosion on rocky coastlines. Geomorphology 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nastase, G.; Serban, A.; Nastase, A.F.; Dragomir, G.; Brezeanu, A.I.; Iordan, N.F. Hydropower development in Romania. A review from its beginnings to the present. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 80, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosyan, R.D.; Velikova, V.N. Coastal zone—Terra (and aqua) incognita—Integrated Coastal Zone Management in the Black Sea. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2016, 169, A1–A16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Mather, P.; Fitzgerald, G.; McRae, D.; Verrall, K.; Walker, D. Assessing the Vulnerability of Eco-Environmental Health to Climate Change. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2010, 7, 546–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhore, S.J. Paris Agreement on Climate Change: A Booster to Enable Sustainable Global Development and Beyond. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2016, 13, 1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodla, V.B.; Desamsetti, S.; Yerramilli, A. A Comparison of HWRF, ARW and NMM Models in Hurricane Katrina (2005) Simulation. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2011, 8, 2447–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, M.Z. Fundamentals of Atmospheric Modeling, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; ISBN 978-0-521-54865-6. [Google Scholar]
- Rogers, W.E.; Dykes, J.D.; Wittmann, P.A. US Navy global and regional wave modeling. Oceanography 2014, 27, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holthuijsen, L.H. Waves in Oceanic and Coastal Waters; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, L.; Soares, C.G. Evaluation of a high-resolution wave forecasting system for the approaches to ports. Ocean Eng. 2013, 58, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherneva, Z.; Andreeva, N.; Pilar, P.; Valchev, N.; Petrova, P.; Guedes Soares, C. Validation of the WAMC4 wave model for the Black Sea. Coast. Eng. 2008, 55, 881–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koletsis, I.; Kotroni, V.; Lagouvardos, K.; Soukissian, T. Assessment of offshore wind speed and power potential over the Mediterranean and the Black Seas under future climate changes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 234–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislov, A.V.; Surkova, G.V.; Arkhipkin, V.S. Occurence Frequency of Storm Wind Waves in the Baltic, Black, and Caspian Seas under Changing Climate Conditions. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2016, 41, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velea, L.; Bojariu, R.; Cica, R. Occurrence of Extreme Winds over the Black Sea during January Under Present and Near Future Climate. Turk. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2014, 14, 973–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onea, F.; Rusu, E. An Evaluation of the Wind Energy in the North-West of the Black Sea. Int. J. Green Energy 2014, 11, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argin, M.; Yerci, V. Offshore wind power potential of the Black Sea region in Turkey. Int. J. Green Energy 2017, 14, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucukali, S.; Dinckal, C. Wind energy resource assessment of Izmit in the West Black Sea Coastal Region of Turkey. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 30, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L.; Butunoiu, D. Evaluation of the Wind Influence in Modeling the Black Sea Wave Conditions. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2014, 13, 305–314. [Google Scholar]
- Van Vledder, G.P.; Akpınar, A. Wave model predictions in the Black Sea: Sensitivity to wind fields. Appl. Ocean Res. 2015, 53, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin-Ye, J.; García-León, M.; Gràcia, V.; Ortego, M.I.; Stanica, A.; Sánchez-Arcilla, A. Multivariate hybrid modelling of future wave-storms at the northwestern Black Sea. Water 2018, 10, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booij, N.; Ris, R.C.; Holthuijsen, L.H. A third-generation wave model for coastal regions: 1. Model description and validation. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 7649–7666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divinsky, B.V.; Kosyan, R.D. Spatiotemporal variability of the Black Sea wave climate in the last 37 years. Cont. Shelf Res. 2017, 136, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L. Assessment of the Wave Energy in the Black Sea Based on a 15-Year Hindcast with Data Assimilation. Energies 2015, 8, 10370–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, E. Wave energy assessments in the Black Sea. J. Mar. Sci. Technol. 2009, 14, 359–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L.; Bernardino, M.; Guedes Soares, C. Wind and wave modelling in the Black Sea. J. Oper. Oceanogr. 2014, 7, 5–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rusu, L.; Butunoiu, D.; Rusu, E. Analysis of the Extreme Storm Events in the Black Sea Considering the Results of a Ten-Year Wave Hindcast. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2014, 15, 445–454. [Google Scholar]
- Erselcan, İ.Ö.; Kükner, A. A numerical analysis of several wave energy converter arrays deployed in the Black Sea. Ocean Eng. 2017, 131, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpınar, A.; Kömürcü, M.İ. Wave energy potential along the south-east coasts of the Black Sea. Energy 2012, 42, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min’kovskaya, R.Y. Contamination of the Black Sea surface water layer with oil hydrocarbons. Russ. Meteorol. Hydrol. 2014, 39, 705–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrova, O.Y.; Mityagina, M.I. Satellite monitoring of oil slicks on the Black Sea surface. Izv. Atmos. Ocean. Phys. 2013, 49, 897–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparotti, C.; Rusu, E. Methods for the risk assessment in maritime transportation in the Black Sea basin. J. Environ. Prot. Ecol. 2012, 13, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar]
- Raţă, V.; Gasparotti, C.; Rusu, L. The importance of the reduction of air pollution in the black sea basin. Mech. Test. Diagn. 2017, 7, 5–15. [Google Scholar]
- Griffies, S.M.; Harrison, M.J.; Pacanowski, R.C.; Rosati, A. A Technical Guide to MOM4; GFDL Ocean Group Technical Report No. 5; NOAA/Geophysical Fluid Dynamics Laboratory: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2004; p. 371. [Google Scholar]
- Hodges, K.I.; Lee, R.W.; Bengtsson, L. A comparison of extratropical cyclones in recent reanalyses ERA-Interim, NASA MERRA, NCEP CFSR, and JRA-25. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 4888–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Pan, H.-L.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Kistler, R.; Woollen, J.; Behringer, D.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Reanalysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1015–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutowski, W.J., Jr.; Giorgi, F.; Timbal, B.; Frigon, A.; Jacob, D.; Kang, H.-S.; Raghavan, K.; Lee, B.; Lennard, C.; Nikulin, G.; et al. WCRP COordinated Regional Downscaling EXperiment (CORDEX): A diagnostic MIP for CMIP6. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 4087–4095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.; Gutowski, W.J. Regional Dynamical Downscaling and the CORDEX Initiative. In Annual Review of Environment and Resources; Gadgil, A., Tomich, T.P., Eds.; Annual Reviews: Palo Alto, CA, USA, 2015; Volume 40, pp. 467–490. ISBN 978-0-8243-2340-0. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.; Dieterich, C.; Döscher, R.; Höglund, A.; Hordoir, R.; Meier, H.M.; Samuelsson, P.; Schimanke, S. Development and evaluation of a new regional coupled atmosphere–ocean model in the North Sea and Baltic Sea. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2015, 67, 24284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, D.; Petersen, J.; Eggert, B.; Alias, A.; Christensen, O.B.; Bouwer, L.M.; Braun, A.; Colette, A.; Déqué, M.; Georgievski, G.; et al. EURO-CORDEX: New high-resolution climate change projections for European impact research. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2014, 14, 563–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, P.M.; Lima, D.C.; Cardoso, R.M.; Nascimento, M.L.; Semedo, A. Western Iberian offshore wind resources: More or less in a global warming climate? Appl. Energy 2017, 203, 72–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemer, M.A.; Trenham, C.E. Evaluation of a CMIP5 derived dynamical global wind wave climate model ensemble. Ocean Model. 2016, 103, 190–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilks, D.S. Statistical Methods in the Atmospheric Sciences, 3rd ed.; International Geophysics Series; Academic Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2011; 704p, ISBN 978-0-12-385022-5. [Google Scholar]
- Tukey, J.W. Exploratory Data Analysis; Addison-Wesley Publishing Company: Reading, MA, USA, 1977; 688p, ISBN 978-0-20-107616-5. [Google Scholar]
- Cornett, A.M. A Global Wave Energy Resource Assessment. In Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Offshore and Polar Engineering Conference, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 6–11 July 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Rusu, L.; Ganea, D.; Mereuta, E. A joint evaluation of wave and wind energy resources in the Black Sea based on 20-year hindcast information. Energy Explor. Exploit. 2018, 36, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butunoiu, D.; Rusu, E. A data assimilation scheme to improve the Wave Predictions in the Black Sea. In Proceedings of the IEEE OCEANS 2015-Genova, Genova, Italy, 18–21 May 2015; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Akpıar, A.; Bingölbali, B.; Van Vledder, G.P. Wind and wave characteristics in the Black Sea based on the SWAN wave model forced with the CFSR winds. Ocean Eng. 2016, 126, 276–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akpinar, A.; de León, S.P. An assessment of the wind re-analyses in the modelling of an extreme sea state in the Black Sea. Dyn. Atmos. Oceans 2016, 73, 61–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamlington, P.E.; Collins, S.G.; Alexander, S.R.; Kim, K.Y. Effects of climate oscillations on wind resource variability in the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
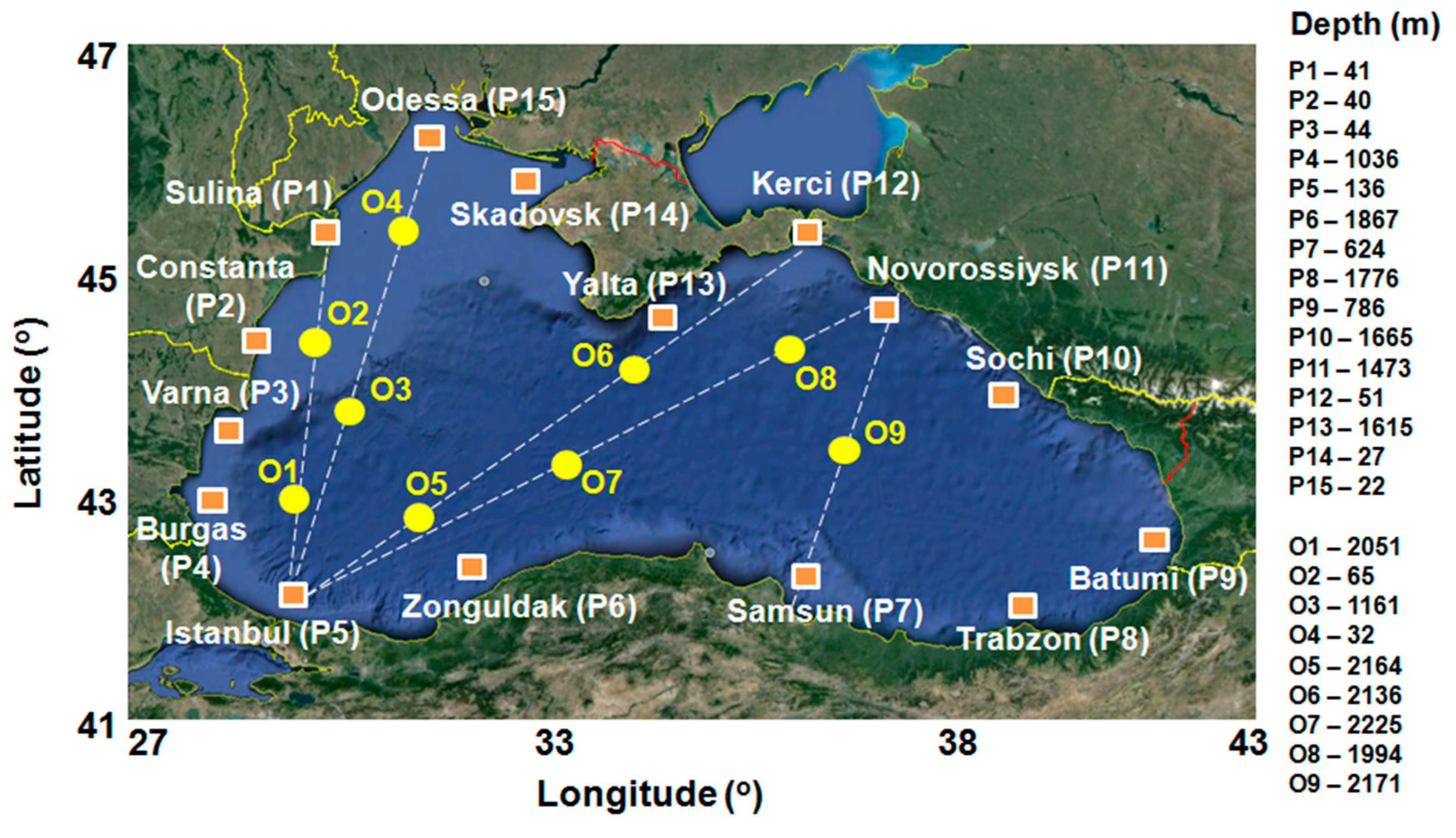

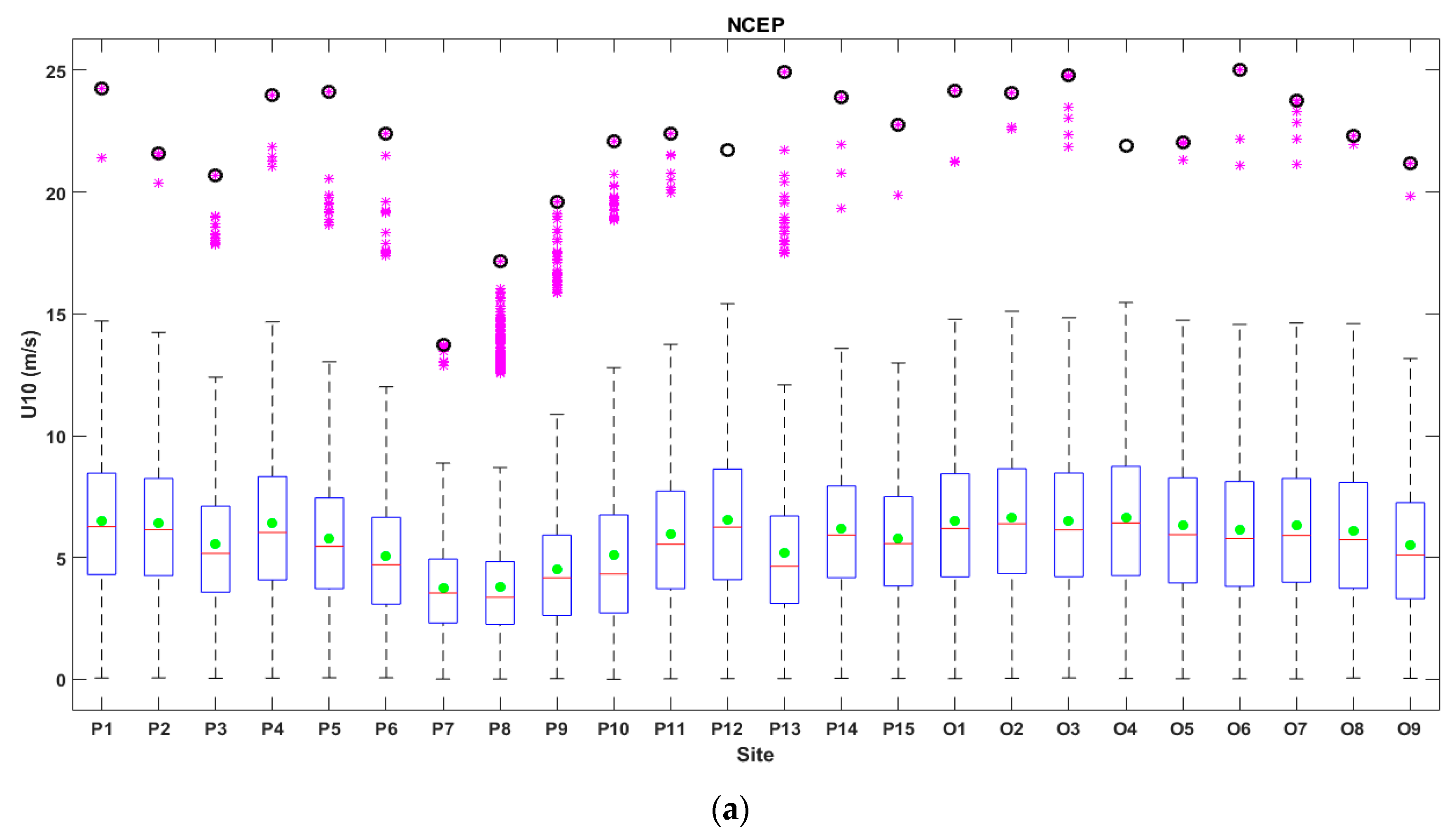

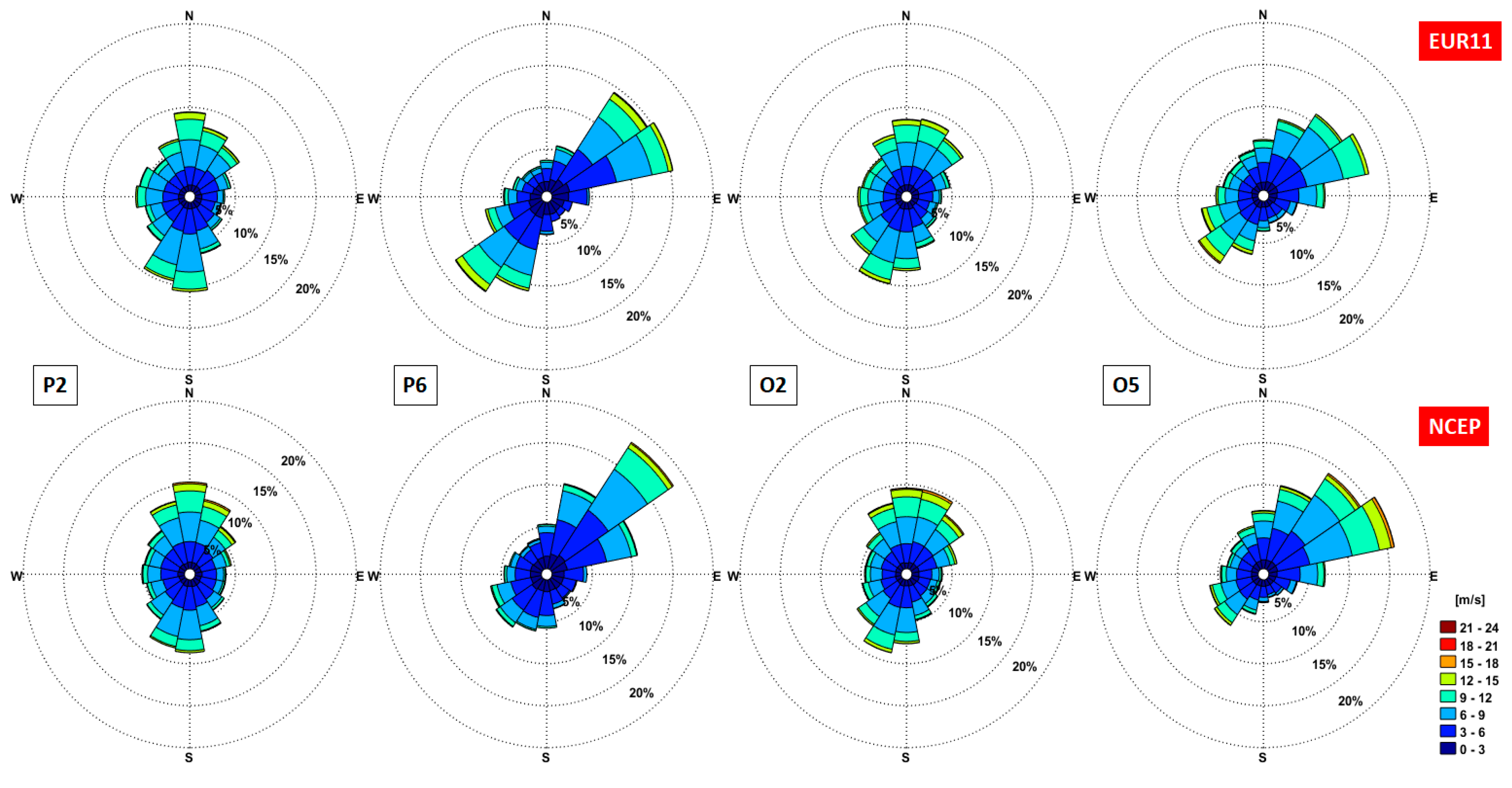

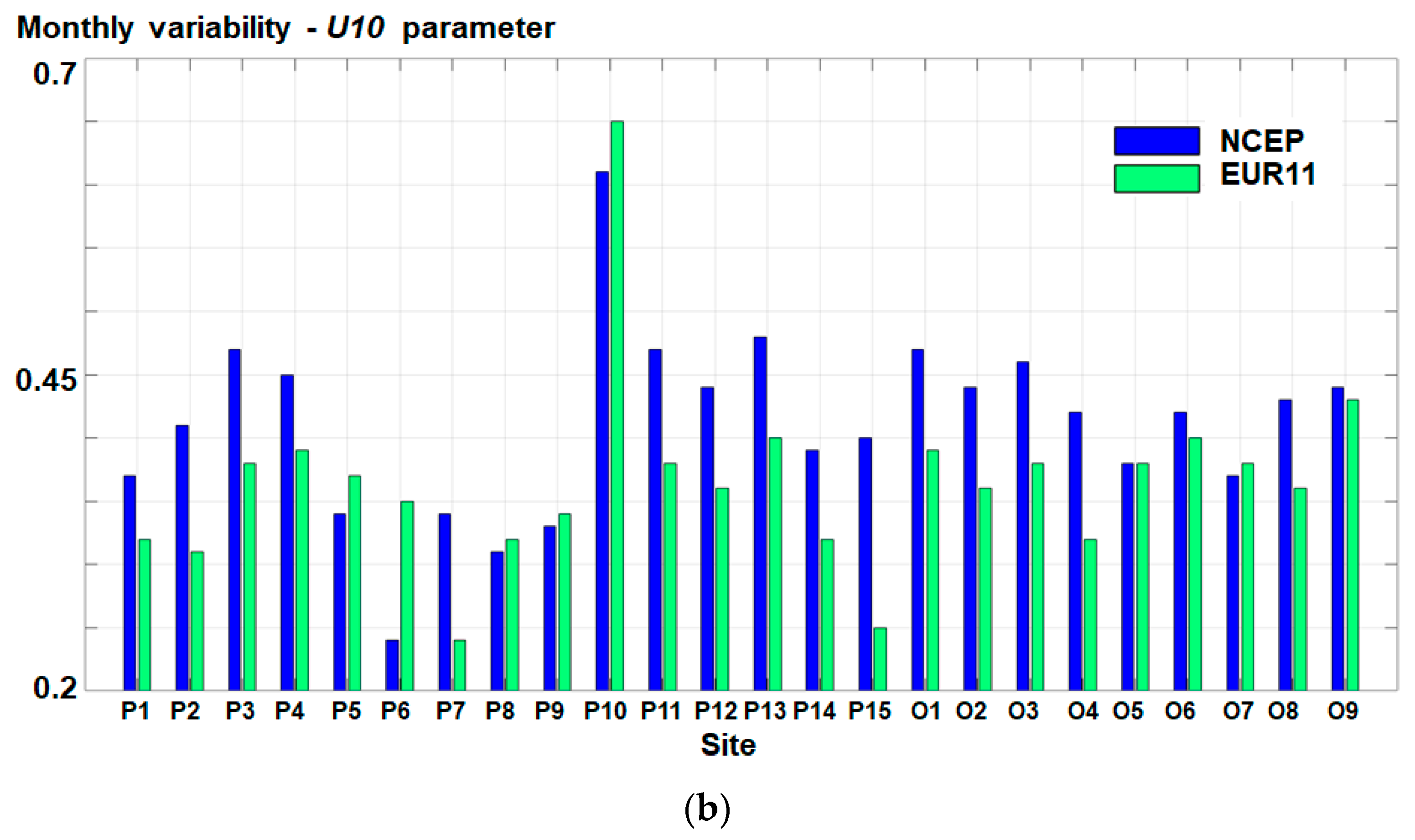
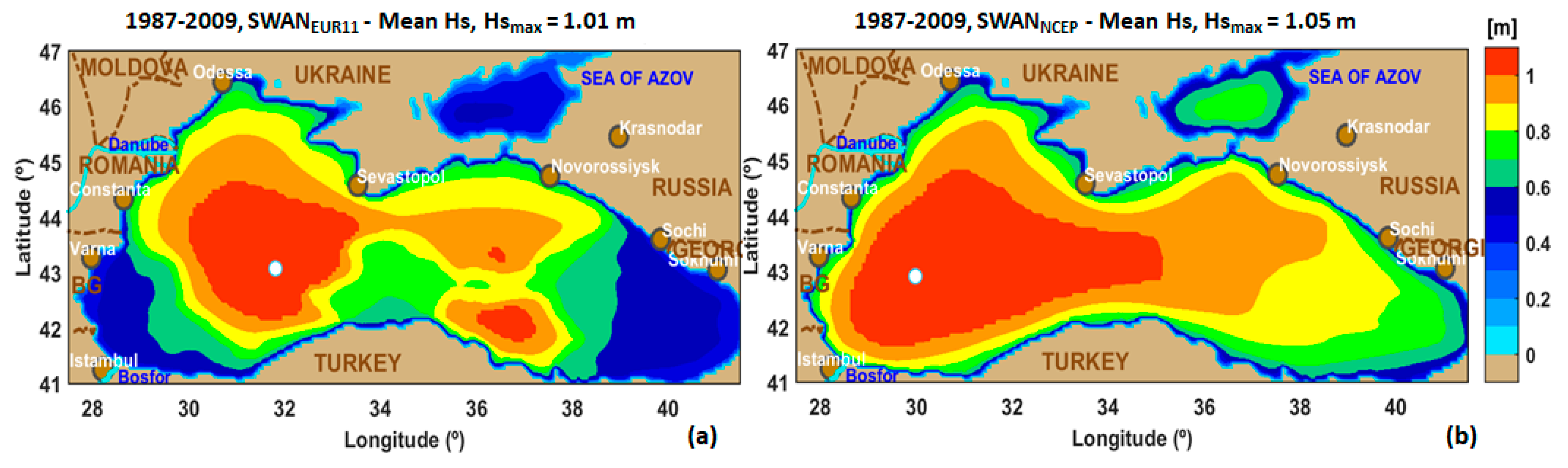
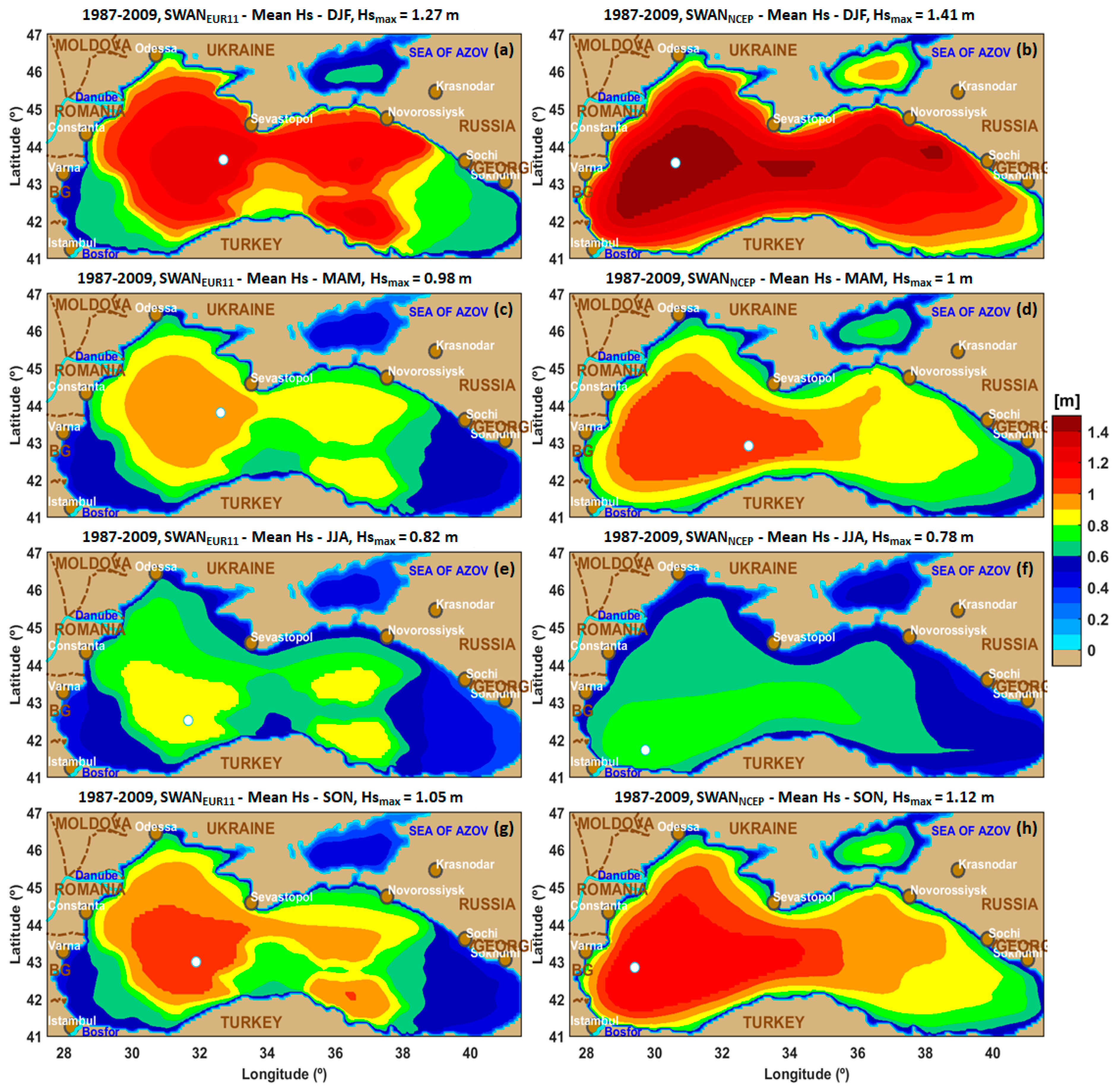
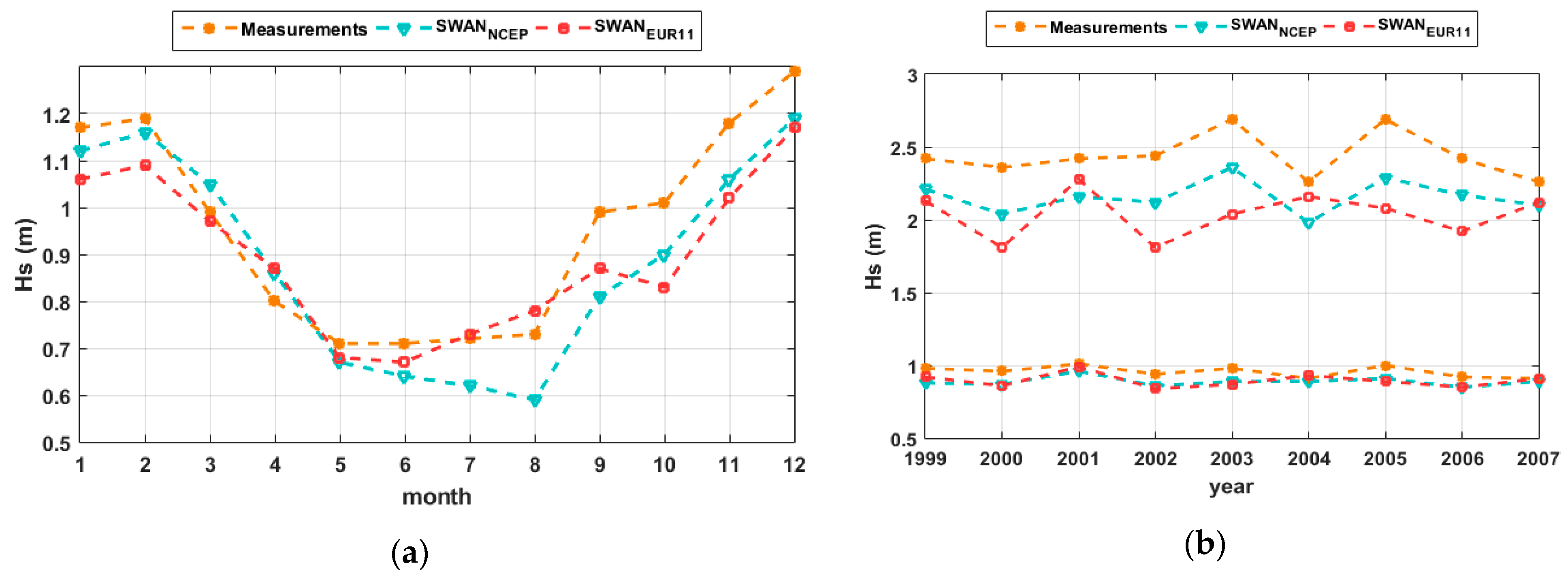

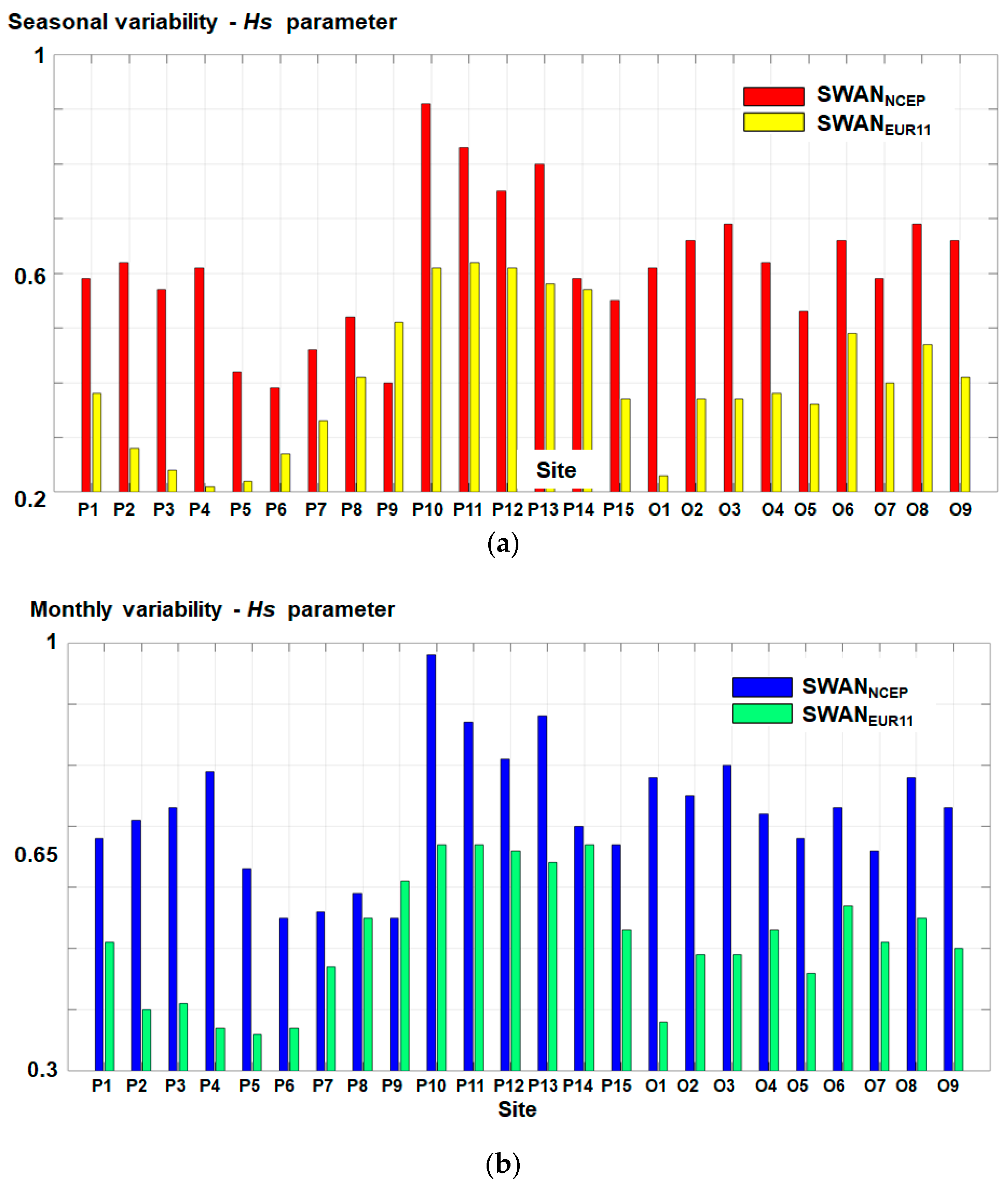
| No. | Site | Long (o) | Lat (o) | No. | Site | Long (o) | Lat (o) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Sulina (P1) | 30.2 | 45.08 | 13 | Yalta (P13) | 34.48 | 44.35 |
| 2 | Constanta (P2) | 29.08 | 44.15 | 14 | Skadovsk (P14) | 32.37 | 45.82 |
| 3 | Varna (P3) | 28.28 | 43.15 | 15 | Odessa (P15) | 31.08 | 46.28 |
| 4 | Burgas (P4) | 28.67 | 42.45 | 16 | O1 | 29.35 | 42.42 |
| 5 | Istanbul (P5) | 29.2 | 41.5 | 17 | O2 | 29.62 | 44.13 |
| 6 | Zonguldak (P6) | 31.62 | 41.68 | 18 | O3 | 30.02 | 43.42 |
| 7 | Samsun (P7) | 36.48 | 41.52 | 19 | O4 | 30.87 | 45.62 |
| 8 | Trabzon (P8) | 39.72 | 41.27 | 20 | O5 | 31.22 | 42.38 |
| 9 | Batumi (P9) | 41.3 | 41.78 | 21 | O6 | 33.72 | 43.72 |
| 10 | Sochi (P10) | 39.35 | 43.52 | 22 | O7 | 33.3 | 42.98 |
| 11 | Novorossiysk (P1) | 37.57 | 44.4 | 23 | O8 | 36.15 | 44.03 |
| 12 | Kerci (P12) | 36.5 | 44.8 | 24 | O9 | 37.08 | 43.03 |
| WIND | ||
|---|---|---|
| Database | NCEP | EUR11 |
| Start date | 1 January 1987 | 1 January 1987 |
| End date | 31 December 2009 | 31 December 2009 |
| Time step | 3 h (8 per day) | 6 h (4 per day) |
| Spatial resolution (o) | 0.312° × 0.312° | 0.11° × 0.11° |
| WAVES | ||
| Database | SWANNCEP | SWANEUR11 |
| Start date | 1 January 1987 | 1 January 1987 |
| End date | 31 December 2009 | 31 December 2009 |
| Time step | 3 h (8 per day) | 3 h (8 per day) |
| Spatial resolution (o) | 0.08° × 0.08° | 0.08° × 0.08° |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rusu, L.; Raileanu, A.B.; Onea, F. A Comparative Analysis of the Wind and Wave Climate in the Black Sea Along the Shipping Routes. Water 2018, 10, 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070924
Rusu L, Raileanu AB, Onea F. A Comparative Analysis of the Wind and Wave Climate in the Black Sea Along the Shipping Routes. Water. 2018; 10(7):924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070924
Chicago/Turabian StyleRusu, Liliana, Alina Beatrice Raileanu, and Florin Onea. 2018. "A Comparative Analysis of the Wind and Wave Climate in the Black Sea Along the Shipping Routes" Water 10, no. 7: 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070924
APA StyleRusu, L., Raileanu, A. B., & Onea, F. (2018). A Comparative Analysis of the Wind and Wave Climate in the Black Sea Along the Shipping Routes. Water, 10(7), 924. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070924







