Water Quality in Representative Tuojiang River Network in Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
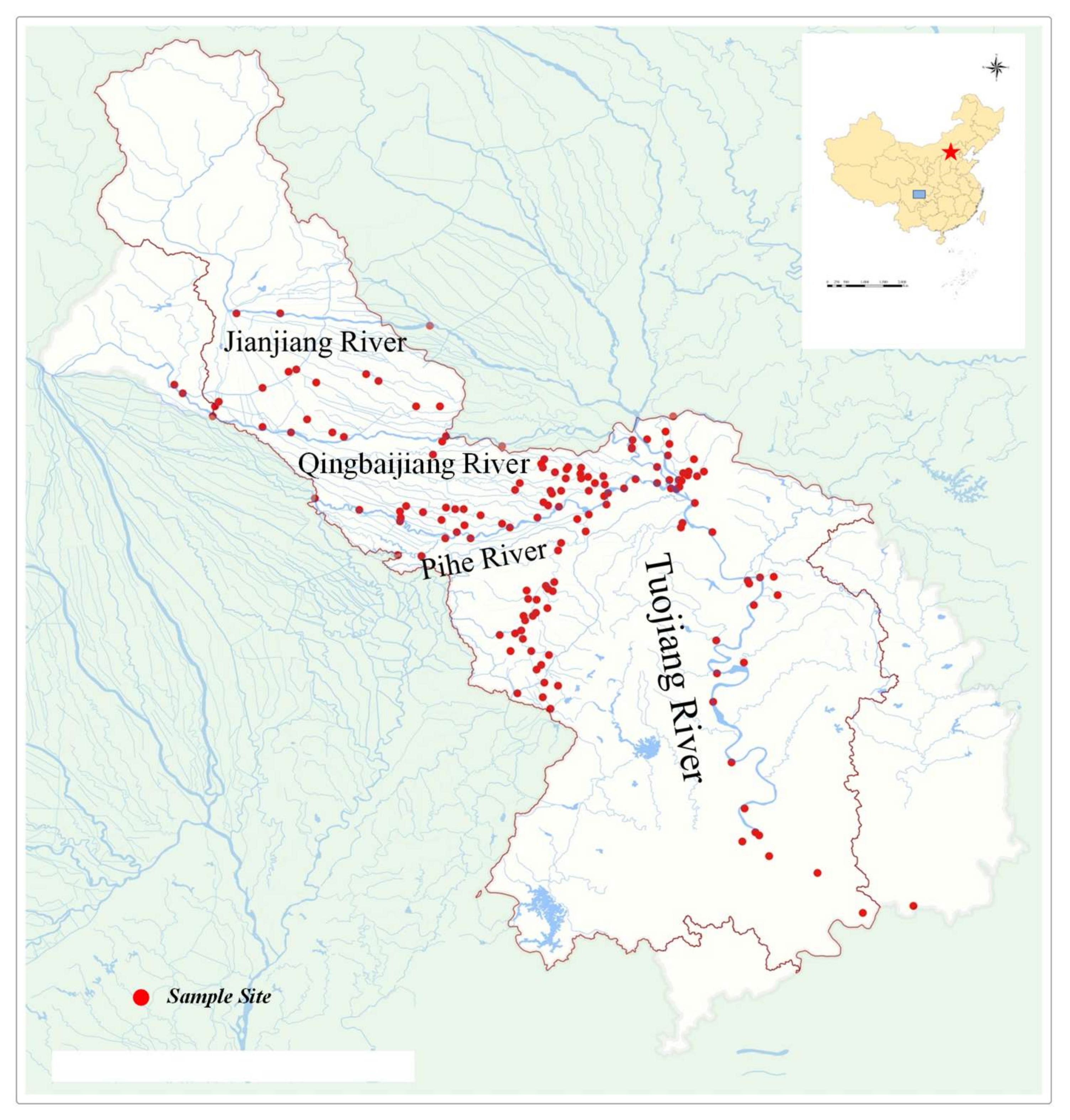
2.1. Site Description and Sample Collection
2.1.1. The River Network of the Tuojiang River in the Chengdu Area
2.1.2. Monitoring Stations and Sampling Sites
2.2. Sample Collecting and Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analysis
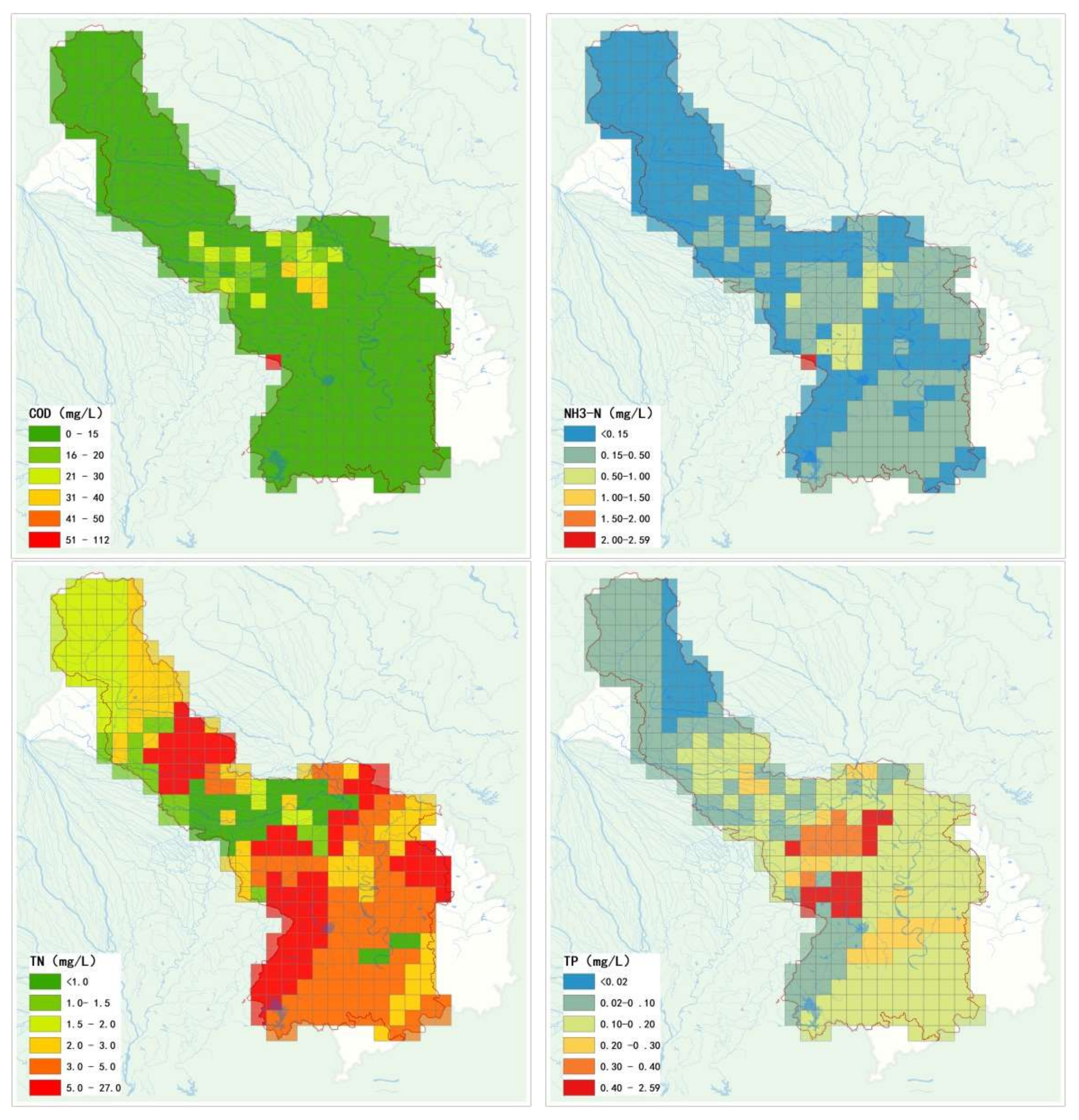
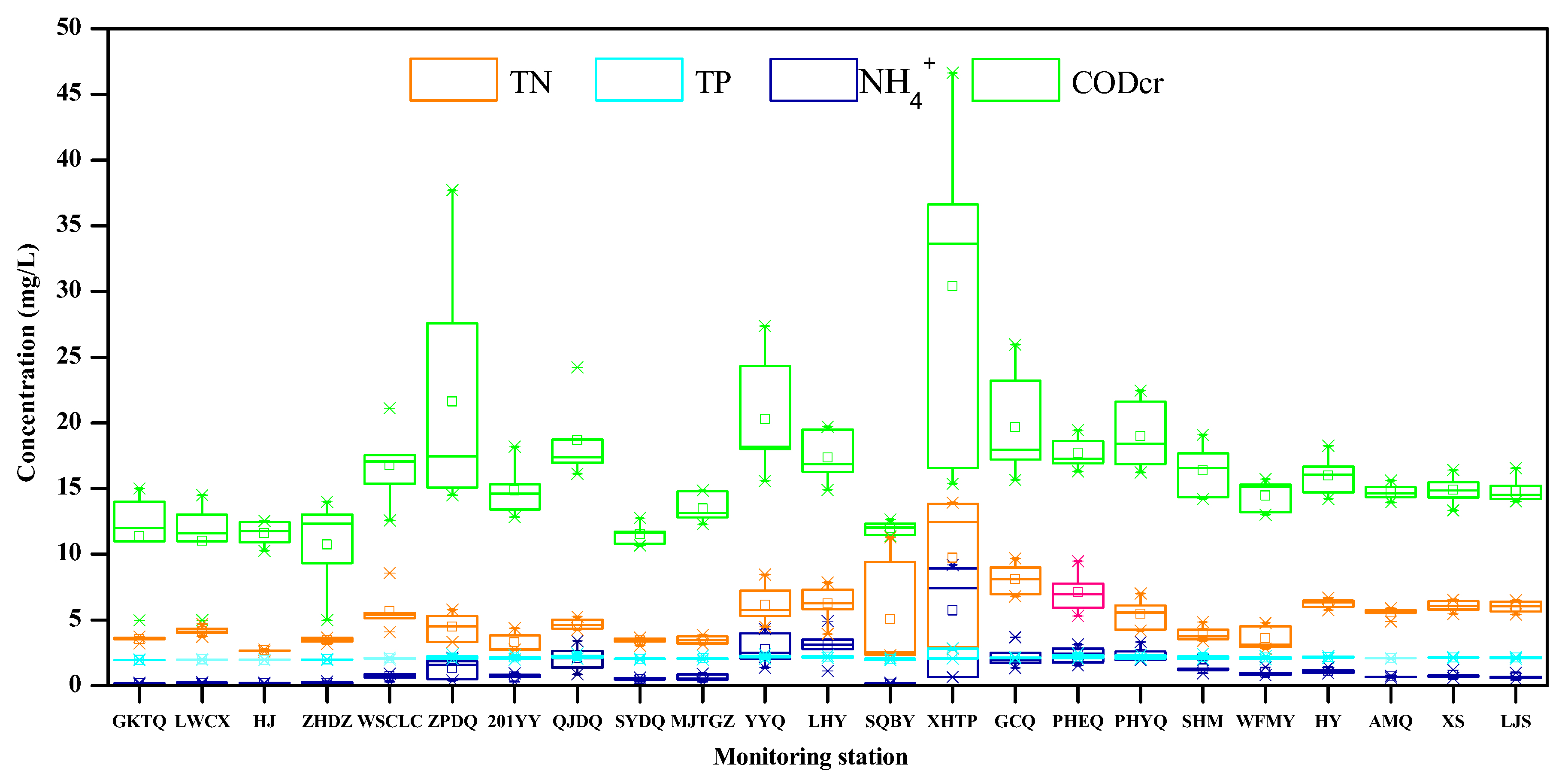
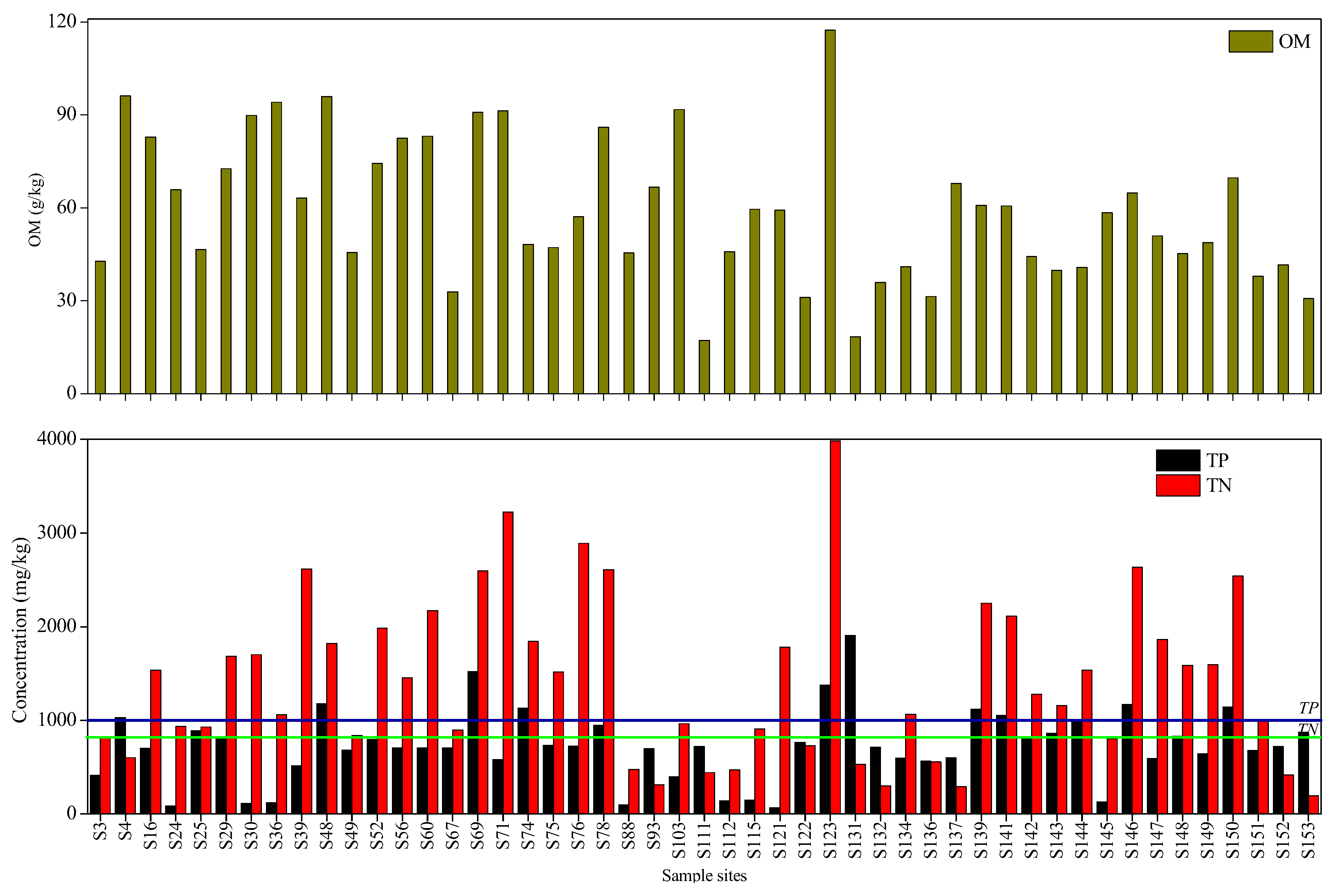
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Recent Data at Monitoring Stations
3.2. Data from the River Network System
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yu, X.G.; Jiang, J.H.; Jia, S.F. Preliminary discussion on the platform of the research on the Yangtze basin water evolution and the starting points of the research. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2001, 10, 485–490. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, R.H.; Wang, D.; Sun, H.L.; Sun, Y.H.; Zhao, Y. The basic situation of the Yangtze River water problem and the strategy of prevention and control. Environ. Prot. 2017, 19, 46–48. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Y.H.; Wang, X.L. Preliminary research on watershed division and stream order classification of the Yangtze River. J. Yangtze River Sci. Res. Inst. 2013, 30, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Evaluation Department of Chinese Academy of Sciences and Changjiang Water Resources Protection Institute. Report on Environmental Impacts of the Three Gorges Hydro-Project at the Yangtze River; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1991. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Z.J.; Du, J.Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Su, N.; Li, J.F. Variation of riverine material loads and environmental consequences on the Changjiang (Yangtze) estuary in recent decades (1955–2008). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.S.; Guo, C.B.; Ye, S.W.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.Z.; Hughes, R.M. Construction: Limit China’s sand mining. Nature 2017, 550, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, X.L.; Bai, Y.P. The spatial-temporal change pattern of wetland in the middle-lower Yangtze River: A case study of Wuhu, Anhui. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 513, 3228–3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, C.; Huang, X.; Mu, H.Q.; Yin, W. Impacts of land-use changes on the lakes across the Yangtze floodplain in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 3669–3677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.Y.; Yao, T.; Wang, C.S.; Yu, X.B. Treat and pressure for the bio-diversity conservation in the area along the middle reaches of Changjiang River with suggestions on the countermeasure. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2004, 13, 429–433. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P. Biodiversity crisis in the Yangtze River: The culprit was dams, followed by overfishing. J. Lake Sci. 2017, 29, 1279–1299. [Google Scholar]
- Stutter, M.I.; Langan, S.J.; Lumsdon, D.G. Vegetated buffer strips can lead to increased release of phosphorus to water: A biogeochemical assessment of the mechanisms. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 1858–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aear, D.A.; Mewson, M.D. Environmental changes in river channel: A neglected element. Towards geomorphological typologies, standards and monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 310, 17–23. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, K.; Xu, Q.X. Effect of urbanization on growth of Shanghai river function and stream structure. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2005, 14, 133–138. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, W.; Yang, K.; Tang, M.; Xu, Q.X. Stream structure characteristics and their impact on storage and flood control capacity in the urbanized plain river network. Geogr. Res. 2005, 24, 717–724. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, G.; Lehmer, B.; Lumsdon, A.E.; MacDonald, G.K.; Zarfl, C.; Liermann, C.R. An index-based framework for assessing patterns and trends in river fragmentation and flow regulation by global dams at multiple scales. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, M.; Christopher, T.P.; Christine, R.; Severin, S.; Hans, H.D.; Helen, R.P.; Philippe, V.C. Global phosphorus retention by river damming. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 15603–15608. [Google Scholar]
- Li, W.Z.; Li, X.Y.; Wang, H.L.; Su, J.J. Spatial distribution of the main contamination in aquatic environment in Fuyang River. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 2814–2819. [Google Scholar]
- Pernet-Coudrier, B.; Qi, W.X.; Liu, H.J.; Müller, B.; Berg, M. Sources and pathways of nutrients in the semi-arid region of Beijing-Tianjin, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 5294–5301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, B.Q.; Jian, Y.X.; Tang, W.Z.; Zhang, H. Temporal and spatial variation of nitrogen and phosphorus and eutrophication assessment in downstream river network area of North Canal River Watershed. Environ. Sci. 2012, 3, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Hobbies, S.E.; Finlay, J.C.; Janke, B.D.; Nidzgorski, D.A.; Millet, D.B.; Baker, L.A. Contrasting nitrogen and phosphorus budgets in urban watersheds and implications for managing urban water pollution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4177–4182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, V.H.; Schindler, D.W. Eutrophication science: Where do we go from here? Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008, 24, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyenje, P.M.; Foppen, J.W.; Uhlenbrook, S.; Kulabako, R.; Muwanga, A. Eutrophication and nutrient release in urban areas of sub-Saharan Africa-A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 447–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vörösmarty, C.J.; McIntyre, P.B.; Gessner, M.O.; Dudgeon, D.; Prusevich, A.; Green, P.; Glidden, S.; Bunn, S.E.; Sullivan, C.A.; Liermann, C.R.; et al. Global threats to human water security and river biodiversity. Nature 2010, 467, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, K.Y. On the relationship between Dujiangyan irrigation system and the “Land of Abundance”—Special study 2 about the ancient “Land of Abundance”. J. Chengdu Univ. Soc. Sci. 2011, 6, 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Jensen, H.S.; Kristensen, P.; Jeppesen, E.; Skytthe, A. Iron/Phosphorus ratio in surface sediment as an indicator of phosphate release from aerobic sediments in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 1992, 235, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correll, D.L. The role of phosphorus in the eutrophication of receiving waters: A review. J. Environ. Qual. 1998, 27, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.D.; Li, T.X.; Zheng, Z.C.; Pu, Y. Characteristics analysis of agricultural nonpoint source pollution on Tuojiang River Basin. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2015, 48, 3654–3665. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, H.; Wu, J.; Tian, X.G.; Yang, G.; Tang, L.J. Non-point pollution status and control measures in Ziyang section of Tuojiang watershed. J. Anhui Agric. Sci. 2011, 39, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. Guidelines for Remediation of Black and Odorous Water Bodies in Cities; Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2015.
- Huo, S.L.; Zhang, J.T.; Yeager, K.M.; Xi, B.D.; Wang, J.; He, Z.S.; Wu, F.C. High-resolution profiles of dissolved reactive phosphorus in overlying water and porewater of Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2014, 21, 12989–12999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Zhu, X.L.; Jin, X.; Meng, X.; Tang, W.Z.; Shan, B.Q. Evidence for organic phosphorus activation and transformation at the sediment-water interface during plant debris decomposition. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 583, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.T.; Zan, F.Y.; Xi, B.D.; Huo, S.L. Study on sediment TN and TP criteria in Eastern Shallow Lakes, China. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2014, 23, 992–999. [Google Scholar]
- Meng, F.D.; Jiang, X.; Jin, X.C. Physcial-Chemical characteristics of the sediments in lakes from the middle and lower reaches of the Yangtze River. Res. Environ. Sci. 2004, 17, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, W.J.; Wu, J.S.; Xiao, H.A.; Dong, C.L. Profile distribution characteristics and accumulation of organic carbon in typical wetlands in SANJIANG plain. Adv. Earth Sci. 2004, 19, 558–562. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, W.L.; Wang, S.R.; Jin, X.C.; Wang, G.D. Distribution of total organic matter and the forms on the sediments from shallow lakes in the Middle and Lower Reaches of the Yangtze River. J. Northwest A F Univ. 2008, 36, 141–147. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.H.; Wang, S.R. Release mechanism and kinetic exchange for phosphorus (P) in lake sediment characterized by diffusive gradients in thin film (DGT). J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 331, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayor, M.; Ronny, L.; Pierre, R.; Philippe, V.C. Global perturbation of organic carbon cycling by river damming. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedl, G.; Wüest, A. Disrupting biogeochemical cycles—Consequences of damming. Aquat. Sci. 2002, 64, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teodoru, C.; Wehrli, B. Retention of sediments and nutrients in the Iron Gate I Reservoir on the Danube River. Biogeochemistry 2005, 76, 539–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, J.A.; Bouwman, A.F.; Mayorga, E.; Seitzinger, S. Magnitudes and sources of dissolved inorganic phosphorus inputs to surface fresh waters and the coastal zone: A new global model. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 2010, 24, 355–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| MS | WQT | NH4+ | TN | TP | CODcr | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | TUS * | C | TUS | C | TUS | C | TUS | ||
| GKTQ | III | 0.17 | 1.64 | 0.64 | 0.04 | 12.79 | |||
| LWCZ | III | 0.19 | 2.35 | 1.35 | 0.06 | 9.08 | |||
| HJ | III | 0.19 | 0.76 | 0.05 | 11.43 | ||||
| ZHDZ | III | 0.24 | 1.63 | 0.63 | 0.05 | 10.02 | |||
| WSCLC | III | 0.69 | 3.54 | 2.54 | 0.15 | 16.54 | |||
| XPDQ | III | 1.35 | 0.35 | 2.65 | 1.65 | 0.23 | 0.16 | 21.60 | 0.08 |
| 201YY | III | 0.68 | 1.43 | 0.43 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 14.80 | ||
| QJDQ | III | 2.09 | 1.09 | 2.89 | 1.89 | 0.33 | 0.67 | 18.60 | |
| SYDQ | III | 0.51 | 1.56 | 0.56 | 0.12 | 11.50 | |||
| MJTGZ | III | 0.60 | 1.63 | 0.63 | 0.17 | 13.50 | |||
| YYQ | III | 2.79 | 1.79 | 4.41 | 3.41 | 0.30 | 0.50 | 20.20 | 0.01 |
| LHY | III | 3.09 | 2.09 | 4.50 | 3.50 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 17.30 | |
| SQBY | III | 0.15 | 3.31 | 2.31 | 0.10 | 12.13 | |||
| XHTP | III | 5.55 | 4.55 | 8.27 | 7.27 | 0.41 | 1.07 | 32.01 | 0.60 |
| GCQ | III | 2.19 | 1.19 | 6.44 | 5.44 | 0.21 | 0.03 | 19.60 | |
| PHEQ | III | 2.36 | 1.36 | 5.37 | 4.37 | 0.30 | 0.49 | 17.70 | |
| PHYQ | III | 2.39 | 1.39 | 3.67 | 2.67 | 0.29 | 0.47 | 18.90 | |
| SHM | III | 1.31 | 0.31 | 2.12 | 1.12 | 0.26 | 0.30 | 16.30 | |
| WFMY | III | 0.97 | 1.77 | 0.77 | 0.20 | 0.02 | 14.40 | ||
| HY | III | 1.02 | 0.02 | 4.29 | 3.29 | 0.28 | 0.40 | 15.35 | |
| AMQ | III | 0.71 | 4.04 | 3.04 | 0.17 | 14.64 | |||
| XS | IV | 0.70 | 4.20 | 3.20 | 0.21 | 0.05 | 14.49 | ||
| LJS | III | 0.78 | 4.29 | 3.29 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 14.22 | ||
| WQI # | I | II | III | IV | V |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NH4+ | 0.15 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| TN | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.0 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| TP | 0.02 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| CODcr | 15 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 40 |
| TN | NH4+ | TP | CODcr | OM | TPs | TNs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TN | 1 | 0.168 * | 0.574 ** | 0.192 * | 0.056 | −0.019 | 0.062 |
| NH4+ | 1 | 0.503 ** | 0.654 ** | 0.333 ** | 0.442 ** | 0.472 ** | |
| TP | 1 | 0.573 ** | 0.243 ** | 0.183 * | 0.244 ** | ||
| CODcr | 1 | 0.175 * | 0.275 ** | 0.270 ** | |||
| OM | 1 | 0.768 ** | 0.872 ** | ||||
| TPs | 1 | 0.784 ** | |||||
| TNs | 1 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, W.; Jin, X.; Cao, H.; Zhao, Y.; Shan, B. Water Quality in Representative Tuojiang River Network in Southwest China. Water 2018, 10, 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070864
Zhang W, Jin X, Cao H, Zhao Y, Shan B. Water Quality in Representative Tuojiang River Network in Southwest China. Water. 2018; 10(7):864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070864
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Wenqiang, Xin Jin, Huiming Cao, Yu Zhao, and Baoqing Shan. 2018. "Water Quality in Representative Tuojiang River Network in Southwest China" Water 10, no. 7: 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070864
APA StyleZhang, W., Jin, X., Cao, H., Zhao, Y., & Shan, B. (2018). Water Quality in Representative Tuojiang River Network in Southwest China. Water, 10(7), 864. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10070864





