Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials
2.1. Test Sites
2.2. Landsat 8 OLI Data
2.3. Reference Data
3. Methods
3.1. Image Preprocessing
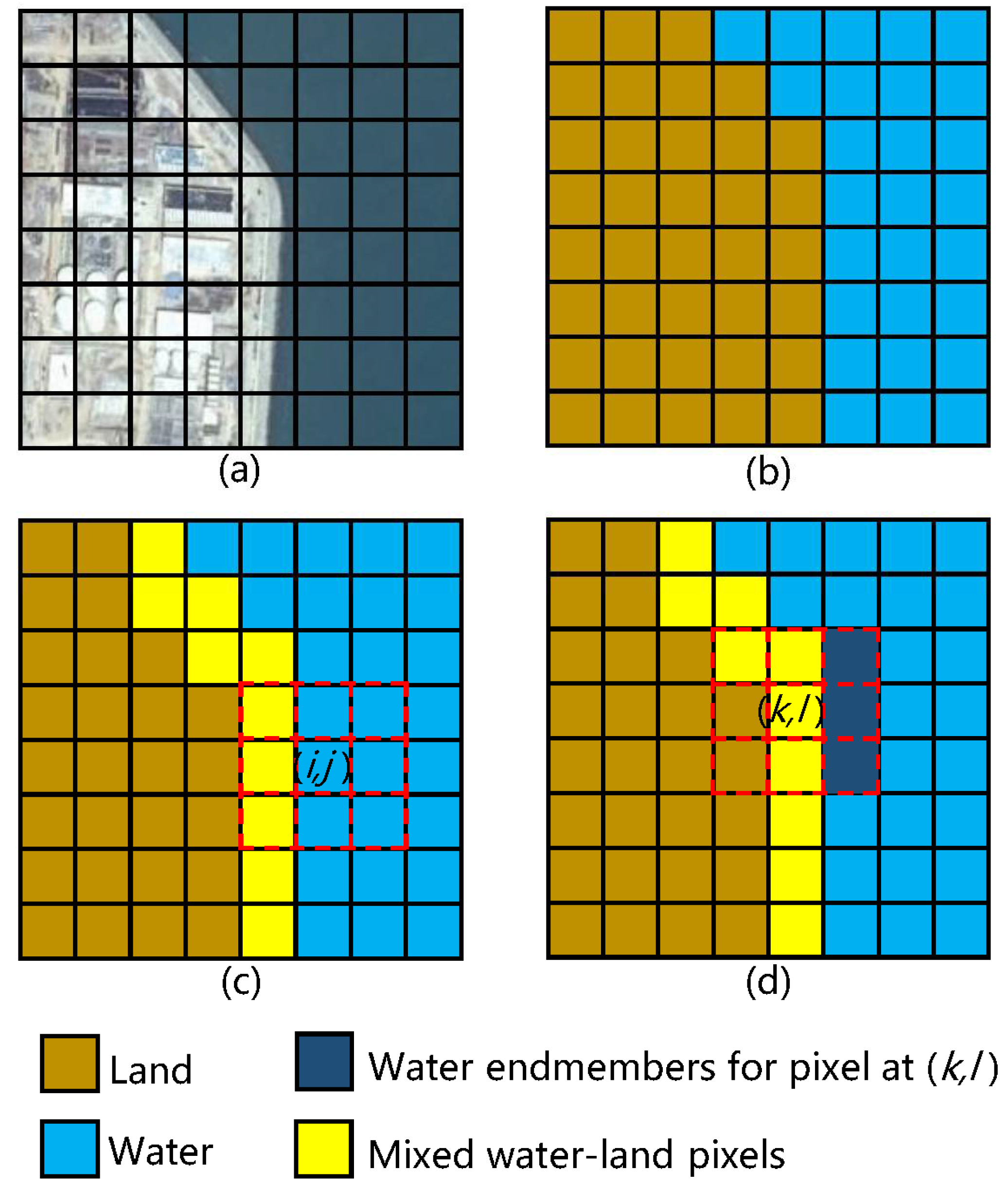
3.2. Subpixel Surface Water Extraction
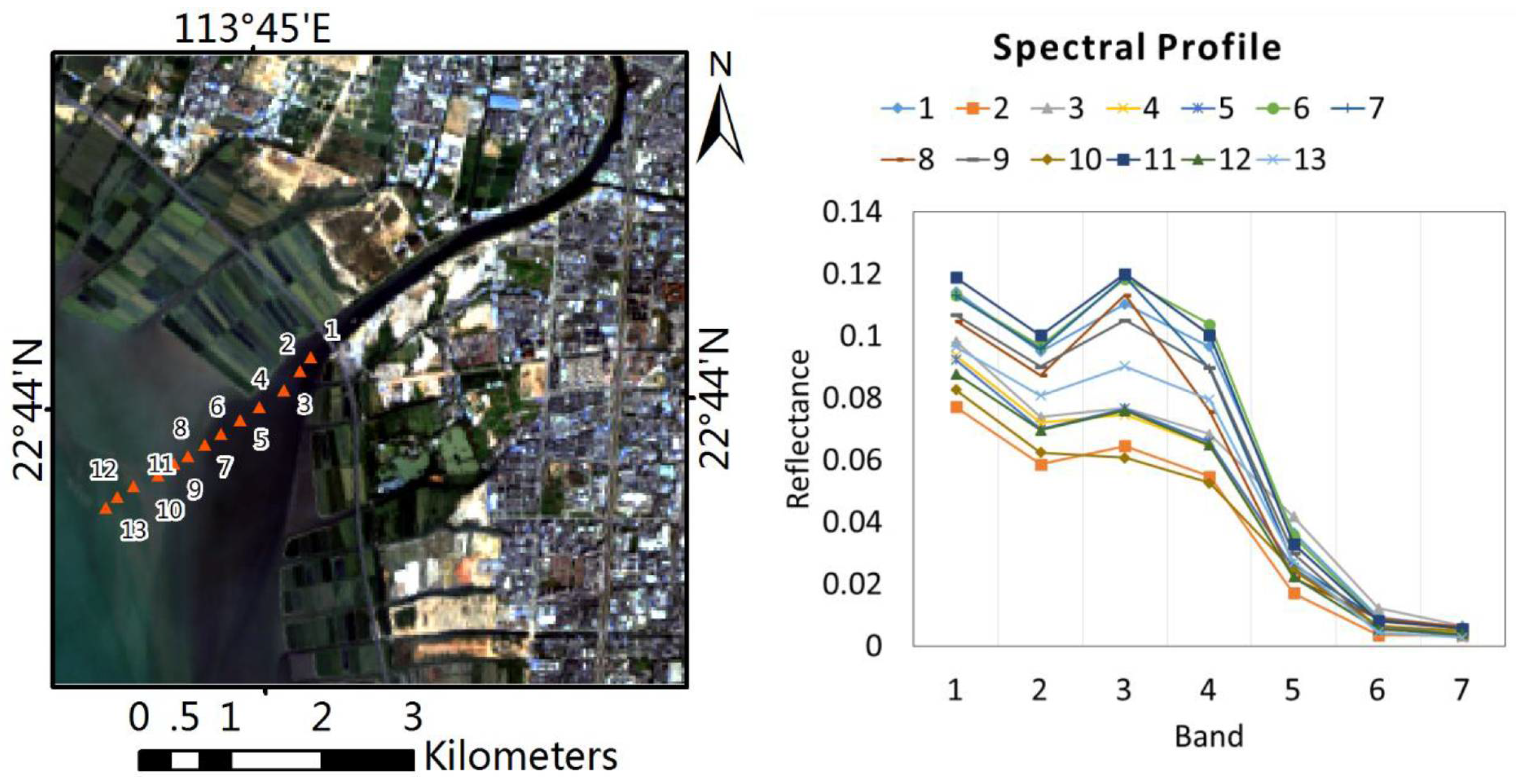
3.2.1. Extraction of Pure Water Pixels
3.2.2. Mixed Water–Land Pixels Extraction
3.2.3. Local Multiple Endmember Spectral Mixture Analysis
3.3. Accuracy Assessment
4. Results
4.1. Extraction of Pure Water Pixels
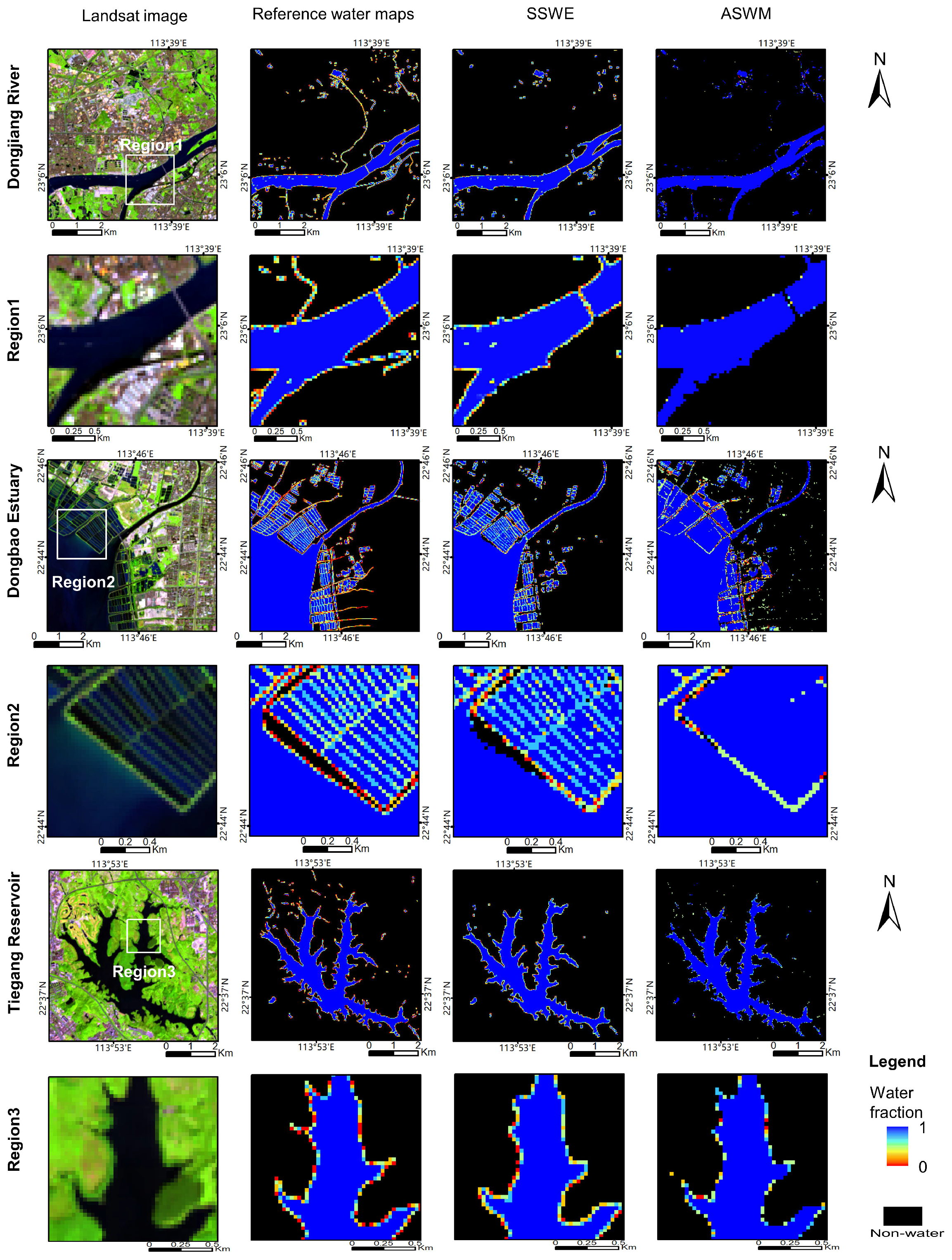
4.2. Subpixel Surface Water Extraction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Postel, S.L. Entering an era of water scarcity: The challenges ahead. Ecol. Appl. 2000, 10, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duker, L.; Borre, L. Biodiversity Conservation of the World’s Lakes: A Preliminary Framework for Identifying Priorities; LakeNet Report Series, Number 2; Monitor International: Annapolis, MD, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- McGwire, K.; Minor, T.; Fenstermaker, L. Hyperspectral mixture modeling for quantifying sparse vegetation cover in arid environments. Remote Sens. Environ. 2000, 72, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Willems, P.; Liu, T. Integrated modeling system for water resources management of Tarim River basin. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2010, 27, 255–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacava, T.; Filizzola, C.; Pergola, N.; Sannazzaro, F.; Tramutoli, V. Improving flood monitoring by the Robust AVHRR Technique (RAT) approach: The case of the April 2000 Hungary flood. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2010, 31, 2043–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, B.D.; Mathews, R.; Wigington, R. Ecologically sustainable water management: Managing river flows for ecological integrity. Ecol. Appl. 2003, 13, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viala, E. Water for food, water for life a comprehensive assessment of water management in agriculture. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2008, 22, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, S.C.J.; Kutser, T.; Hunter, P.D. Remote sensing of inland waters: Challenges, progress and future directions. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 157, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pekel, J.F.; Vancutsem, C.; Bastin, L.; Clerici, M.; Vanbogaert, E.; Bartholomé, E.; Defourny, P. A near real-time water surface detection method based on HSV transformation of MODIS multi-spectral time series data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 704–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Tateishi, R.; Hara, K.; Nguyen, L. Developing superfine water index (SWI) for global water cover mapping using MODIS data. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13807–13841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jawak, S.D.; Luis, A.J. A semiautomatic extraction of Antarctic lake features using Worldview-2 imagery. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2014, 80, 939–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.; Danaher, T. A water index for SPOT5 HRG satellite imagery, New South Wales, Australia, determined by linear discriminant analysis. Remote Sens. 2013, 5, 5907–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Doko, T.; Fukui, H.; Yan, W. Changes in Imja Lake and Karda Lake in the Everest Region of Himalaya. Nat. Resour. 2013, 4, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryant, R.G.; Rainey, M.P. Investigation of flood inundation on playas within the Zone of Chotts, using a time-series of AVHRR. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 82, 360–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, P.S.; Page, K.J. Water body detection and delineation with Landsat TM data. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2000, 66, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, S.; Zhan, W.; Sun, C.; Duan, Y. Landsat 8 OLI image based terrestrial water extraction from heterogeneous backgrounds using a reflectance homogenization approach. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 171, 14–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Wu, B.; Yan, N.; Wang, H. Water body mapping method with HJ-1A/B satellite imagery. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2011, 13, 428–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Wang, C.; Dong, D.; Luo, J.; Shen, Z.; Yang, K. High-resolution mapping of urban surface water using ZY-3 multi-spectral imagery. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 12336–12355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahlevan, N.; Lee, Z.; Wei, J.; Schaaf, C.B.; Schott, J.R.; Berk, A. On-orbit radiometric characterization of OLI (Landsat-8) for applications in aquatic remote sensing. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 154, 272–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.K.; Singh, R.D.; Jain, M.K.; Lohani, A.K. Delineation of flood-prone areas using remote sensing techniques. Water Resour. Manag. 2005, 19, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, J.; Won, J.; Min, K.D. Waterline extraction from Landsat TM data in a tidal flat: A case study in Gomso Bay, Korea. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 83, 442–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feyisa, G.L.; Meilby, H.; Fensholt, R.; Proud, S.R. Automated Water Extraction Index: A new technique for surface water mapping using Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 140, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFeeters, S.K. The use of the Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) in the delineation of open water features. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 1425–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H. Modification of normalised difference water index (NDWI) to enhance open water features in remotely sensed imagery. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 3025–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daya Sagar, B.S.; Gandhi, G.; Prakasa Rao, B.S. Applications of mathematical morphology in surface water body studies. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaschke, T. Object based image analysis for remote sensing. ISPRS J. Photogramm. Remote Sens. 2010, 65, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Sun, G.; Liu, B. Mapping of water body in Poyang Lake from partial spectral unmixing of MODIS data. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE International Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’05), Seoul, Korea, 25–29 July 2005; pp. 4539–4540. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, L.; Gong, P.; Geng, X.; Zhao, Y. Improving the accuracy of the water surface cover type in the 30 m FROM-GLC product. Remote Sens. 2015, 7, 13507–13527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, C.; Zhang, S. Automated extraction and mapping for desert wadis from Landsat imagery in arid West Asia. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 246:1–246:23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Feng, M.; Zhu, Y.; Lu, N.; Huang, J.; Xiao, T. An automated method for extracting rivers and lakes from Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 5067–5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sethre, P.R.; Rundquist, B.C.; Todhunter, P.E. Remote detection of prairie pothole ponds in the Devils Lake Basin, North Dakota. Gisci. Remote Sens. 2005, 42, 277–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpoorter, C.; Kutser, T.; Tranvik, L. Automated mapping of water bodies using Landsat multispectral data. Limnol. Oceanogr. Methods 2012, 10, 1037–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Li, M.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, L.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, M. River Delineation from Remotely Sensed Imagery Using a Multi-Scale Classification Approach. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2014, 7, 4726–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Zhang, L.; Wylie, B. Analysis of dynamic thresholds for the normalized difference water index. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 2009, 75, 1307–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, K.; Jiang, W.; Li, J.; Tang, Z. Spectral matching based on discrete particle swarm optimization: A new method for terrestrial water body extraction using multi-temporal Landsat 8 images. Remote Sens. Environ. 2018, 209, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Peng, Y.; Lang, M.; Yeo, I.; McCarty, G. Wetland inundation mapping and change monitoring using Landsat and airborne LiDAR data. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 141, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Huang, C.; Lang, M.W.; Yeo, I.; Stehman, S.V. Monitoring of wetland inundation dynamics in the Delmarva Peninsula using Landsat time-series imagery from 1985 to 2011. Remote Sens. Environ. 2017, 190, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reschke, J.; Hüttich, C. Continuous field mapping of Mediterranean wetlands using sub-pixel spectral signatures and multi-temporal Landsat data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. 2014, 28, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabisky, M.; Moskal, L.M.; Gillespie, A.; Hannam, M. Reconstructing semi-arid wetland surface water dynamics through spectral mixture analysis of a time series of Landsat satellite images (1984–2011). Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 177, 171–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Du, B.; Xiong, S. Quantifying sub-pixel surface water coverage in urban environments using low-albedo fraction from Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 428:1–428:15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoeye, J.; Wulf, R.D. Land cover mapping at sub-pixel scales using linear optimization techniques. Remote Sens. Environ. 2002, 79, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.; Luo, X.; Xu, X.; Pan, H.; Tong, X. Automated subpixel surface water mapping from heterogeneous urban environments using Landsat 8 OLI imagery. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 584:1–584:16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, D.A.; Gardner, M.; Church, R.; Ustin, S.; Scheer, G.; Green, R.O. Mapping chaparral in the Santa Monica Mountains using multiple endmember spectral mixture models. Remote Sens. Environ. 1998, 65, 267–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, K.L.; Dennison, P.E.; Roth, K.L.; Roberts, D.A.; Coates, A.R. A multi-temporal spectral library approach for mapping vegetation species across spatial and temporal phenological gradients. Remote Sens. Environ. 2015, 167, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Manso, A.; Quintano, C.; Roberts, D.A. Burn severity influence on post-fire vegetation cover resilience from Landsat MESMA fraction images time series in Mediterranean forest ecosystems. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 184, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Painter, T.H.; Rittger, K.; McKenzie, C.; Slaughter, P.; Davis, R.E.; Dozier, J. Retrieval of subpixel snow covered area, grain size, and albedo from MODIS. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 868–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, R.; Roberts, D.; Dennison, P.; Hess, L. Sub-pixel mapping of urban land cover using multiple endmember spectral mixture analysis: Manaus, Brazil. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EarthExplorer. Available online: http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov (accessed on 5 May 2016).
- Roy, D.P.; Wulder, M.A.; Loveland, T.R.; Woodcock, C.E.; Allen, R.G.; Anderson, M.C.; Helder, D.; Irons, J.R.; Johnson, D.M.; Kennedy, R.; et al. Landsat-8: Science and product vision for terrestrial global change research. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 145, 154–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris Geospatial Solutions. Available online: http://www.harrisgeospatial.com (accessed on 11 May 2017).
- Help Articles. Available online: http://www.harrisgeospatial.com/Support/SelfHelpTools/HelpArticles.aspx (accessed on 19 May 2017).
- NASA Goddard Space Flight Center for Aerosol Optical Depth. Available online: http://aeronet.gsfc.nasa.gov/new_web/aerosols.html (accessed on 16 May 2016).
- Fisher, A.; Flood, N.; Danaher, T. Comparing Landsat water index methods for automated water classification in eastern Australia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2016, 175, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O.; Gillespie, A.R.; Adams, J.B.; Smith, M.O. Imaging spectroscopy: Interpretation based on spectral mixture analysis. In Remote Geochemical Analysis: Elemental and Mineralogical Composition. Topics in Remote Sensing 4; Pieters, C.M., Englert, P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 145–166. [Google Scholar]
- Somers, B.; Zortea, M.; Plaza, A.; Asner, G.P. Automated extraction of image-based endmember bundles for improved spectral unmixing. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Appl. Earth Obs. Remote Sens. 2012, 5, 396–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Test Sites | Path/Row | Acquisition Date | Landsat Scene ID | Cloud Cover |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| East River | 122/44 | 2 October 2015 | LC81220442015275 | 19.61% |
| Dongbao Estuary | 122/44 | 16 November 2014 | LC81220442014320 | 8.90% |
| Tiegang Reservoir | 122/44 | 18 October 2015 | LC81220442015291 | 1.15% |
| Test Sites | Water | Vegetation | Impervious Surface | Soil |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dongjiang River | 1533 | 6 | 8 | 5 |
| Dongbao Estuary | 4568 | 5 | 7 | 7 |
| Tiegang Reservoir | 2097 | 8 | 5 | 4 |
| Test Sites | KC | TE (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABWI | NDWI | ABWI | NDWI | |
| Dongjiang River | 0.952 | 0.931 | 9.83 | 12.41 |
| Dongbao Estuary | 0.945 | 0.912 | 8.16 | 11.67 |
| Tiegang Reservoir | 0.973 | 0.960 | 4.68 | 6.72 |
| Average | 0.957 | 0.934 | 7.56 | 10.26 |
| Test Sites | SE | RMSE | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SSWE | ASWM | SSWE | ASWM | |
| Dongjiang River | −0.005 | −0.013 | 0.110 | 0.129 |
| Dongbao Estuary | −0.007 | 0.047 | 0.163 | 0.214 |
| Tiegang Reservoir | −0.005 | −0.010 | 0.085 | 0.087 |
| Average | −0.005 | 0.008 | 0.117 | 0.143 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiong, L.; Deng, R.; Li, J.; Liu, X.; Qin, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liu, Y. Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data. Water 2018, 10, 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050653
Xiong L, Deng R, Li J, Liu X, Qin Y, Liang Y, Liu Y. Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data. Water. 2018; 10(5):653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050653
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiong, Longhai, Ruru Deng, Jun Li, Xulong Liu, Yan Qin, Yeheng Liang, and Yingfei Liu. 2018. "Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data" Water 10, no. 5: 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050653
APA StyleXiong, L., Deng, R., Li, J., Liu, X., Qin, Y., Liang, Y., & Liu, Y. (2018). Subpixel Surface Water Extraction (SSWE) Using Landsat 8 OLI Data. Water, 10(5), 653. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10050653






