Abstract
A first-order analytical solution is proposed for the actual depth-averaged concentration of tracers in shallow river flows in the presence of large Peclet numbers (defined as the ratio of section-averaged velocity times channel width to turbulent diffusion coefficient). The solution shows how complete transverse mixing is never achieved due to the typical shape of the velocity and diffusion coefficient profile, which alternatively tend—depending on the downstream location of the cross-section—to concentrate the mass at the centre or at the boundaries of the cross-section itself. The first-order analytical solution proves to be consistent with the results of Lagrangian numerical simulations based on real-field input data, which show how the solute mass breakthrough curves always exhibit anomalous behaviour and a considerable and persistent delay when compared with those that are analytically obtained by assuming a truly one-dimensional process.
1. Introduction
Scalar mixing and spreading processes are fundamental in many geophysical systems and engineering applications [1,2]. The increasing need for scientific tools aimed at predicting, monitoring and controlling chemical contamination and sediment transport in natural channels has recently inspired extensive studies about different aspects of dispersion in stream flows, from the analysis of the effects of heterogeneous channel morphology and asymmetry to that of release conditions and backwater flows, and even to suspended load dynamics. Transient analytical solutions of the advection-dispersion equation (ADE) for dissolved chemicals and fine sediments in open channels were given by the authors: (1) in the case of deterministic depth-averaged velocity distributions and different initial conditions based on Aris’ method of moments [3]; (2) in the case of randomly uniform flows in the presence of morphologic heterogeneity represented by short-range correlations based on a stochastic Lagrangian approach [4,5,6]; (3) and in terms of second-order concentration statistics based on a stochastic Eulerian approach [7]. An analytical-numerical model was elaborated to solve ADE in a stochastic Lagrangian framework in the case of backwater flows in large rivers, highlighting the occurrence of a global re-densification of the cloud and a persistent transverse non-uniformity [8]. A stochastic Lagrangian numerical model was developed to handle ADE in the case of depth-dependent turbulent diffusion coefficient, highlighting the occurrence of concentration boundary side-pockets [9]. In the last few years, several studies (e.g., [10]) have described solute mixing in terms of Shannon’s information entropy [11,12,13,14]. A steady-state uniform-flow solution was recently given by the authors for the concentration of small-size suspended sediments [15] by modeling the cross-sectional velocity distribution based on the principle of maximum information entropy and by investigating the effects of velocity-dip position (e.g., [16,17]). The great interest in the investigation of pollutant/sediment dispersion and the correct quantification of mixing in river flows is justified by its crucial role in implementing effective natural or engineered remediation strategies and in performing risk assessment analysis (e.g., [18]).
As a matter of fact, the classic one-dimensional advection-dispersion equation with constant coefficients and its instantaneous point source solution were always found to be inadequate for the interpretation of field measurements of chemical dispersion. The typical explanation given to justify this discrepancy is that the tracer’s travel time was not long enough, implicitly meaning that section-averaged concentration would have been well-described by Taylor’s [19] model once the theoretical asymptotic regime of dispersion had finally been achieved.
Nevertheless, all the data available in the literature highlight a persistent skewness of the distribution and an increasing peripheral drift of the solute clouds that seem to be incompatible with a pre-asymptotic phase of the process [20,21,22,23,24], the reason for the failure of Taylor’s asymptotic theory is likely related to the permanent cross-sectional non-uniformity of solute mass. Several attempts were made to relate the persistent concentration skewness to the presence of dead zones induced by morphological singularities as edges and corners or subsurface retention phenomena (e.g., [25,26,27]). Ahmad analysed the effect of variable transverse mixing on stream-wise dispersion in terms of longitudinal mixing length for different initial conditions [28] and a classic large-time Fickian behaviour. Later, based on 2-D Lagrangian numerical simulations and the investigation of the time behaviour of cloud moments, Pannone found that tracer dispersion in large rivers is singularly affected by (depth-dependent) transverse diffusion [9]. Specifically, the interplay between zero-bank velocity and the zero-bank transverse mixing coefficient leads to the occurrence of persistent solute side pockets and an anomalous transient behaviour of the spatial moments.
In the present paper, the peculiarities of longitudinal dispersion in large rivers in the presence of suitably variable transverse mixing is discussed through the numerical analysis of the breakthrough curves. Additionally, the permanent peripheral drift of solute mass and the persistence of cross-sectional incomplete mixing, even in the absence of morphological singularities and adsorption phenomena, are justified by a first order analytical solution of the depth-averaged advection-diffusion equation, which is pursued for large channel aspect ratios and large Peclet numbers. The scope of the study is: (a) showing that the incomplete transverse mixing is a ubiquitous feature of open channel flows; (b) providing a closed-form analytical solution that could serve as a fast predicting tool for the deviatory depth-averaged concentrations of chemicals subject to advection and dispersion along almost uniform reaches of steady wide river flows.
2. Formulation and First Order Analytical Solution
Let us consider the time-mean advection-diffusion equation that governs steady uniform turbulent flows in straight open channels, Equation (1):
where x, y, and z are the orthogonal axes of a reference frame originating on the free surface at the right bank, c = c(x, y, z, t) is the time-mean concentration of tracer, u = u(y, z) is the time-mean longitudinal velocity, and εx(y, z), εy(y, z), and εz(y, z) indicate longitudinal, transverse, and vertical turbulent diffusion coefficient, respectively.
The longitudinal macro-dispersion coefficient, widely investigated in the literature to analyse the asymptotic macroscopic characteristics of the process (e.g., [3,4,5,6,9,29,30,31]), appears in the one-dimensional transport equation derived from Equation (1) after section averaging, which is here performed according to Equation (2) [9]:
where h(y) is the local depth, A the flow area, B the free-surface width, and Heq indicates the depth of the equivalent rectangular cross-section. When the variation of the flow depth along the transverse coordinate is very slow and the width is much larger than the equivalent depth, the depth-averaged diffusive deviatory fluxes are negligible if compared to those that are associated with the joint variability of u and c. Considering the no-flux condition at the banks, Equation (3) is obtained:
where U is the section-averaged velocity, represents the longitudinal macro-dispersion coefficient expressed by Equation (4) combined with Equations (5) and (6):
the overbar indicates depth-average and the prime the corresponding deviation. Equation (3) holds in the reasonable and well-documented hypothesis that the dispersive effect induced by the transverse heterogeneity of and dominates the corresponding effect induced by vertical heterogeneity and turbulent diffusion (e.g., [20,30,32]).
Dispersion and dilution phenomena in large rivers can be analysed either by solving advection-diffusion equations like Equation (1) or Equation (3) (e.g., [7]), or by estimating the spatial moments of the equivalent discrete distributions of mass in terms of solute particle trajectories after [33]. The solution of Equation (3) for instantaneous point solute source at x = 0 reads:
where t0 indicates the initial longitudinal relaxation time, M total mass and H the cross-sectional average flow depth.
In the present study, in the hypothesis of shallow waters, and assuming that vertical mixing is much faster than its transverse and longitudinal counterparts [30], the problem is solved based on a 2-D numerical Lagrangian approach (e.g., [9]) in terms of downstream breakthrough curves, and based on a 2-D analytical Eulerian approach in terms of actual depth-averaged concentration. To our knowledge, this is the first attempt at finding an explicit analytical solution for the deviatory concentration (whose contribution is routinely analysed in an average sense by the corresponding variance).
The depth-averaged advection-diffusion equation is formulated as, Equation (8):
where only the transverse diffusive term, whose order of magnitude is comparable with that of the stream-wise component [32], is maintained because of its crucial role in triggering longitudinal dispersion by the cross-sectional displacement of solute particles that enables the sampling of the whole velocity distribution.
Subtracting Equation (3) from Equation (8) gives the governing equation for the deviatory concentration, Equation (9):
An approximate solution of Equation (9) can be pursued in the case of straight reaches of large regular rivers in steady uniform-flow conditions. At the first order in the velocity/concentration deviations, Equation (10):
where, Equation (11) [30]:
indicates shear velocity, g is the acceleration due to gravity and if channel slope. According to the above-mentioned hypotheses, Equation (10) will be solved here for large cross-sections and large related Peclet numbers, Equation (12):
where, Equation (13):
The adoption of suitable scales for length, velocity, time and concentration, respectively, Equation (14):
leads to the following (Equation (15)) dimensionless version of Equation (10):
where, Equation (16):
and function Ψ has to be defined according to the assumed flow-section shape. When Pe is very large, its inverse δ can be adopted as the small parameter of a perturbation expansion of the solution, Equation (17):
Substituting Equation (17) into Equation (15), one finds that, at order δ0, the equation to be solved is, Equation (18):
while at order δ1 one has, Equation (19):
with initial condition (uniform cross-sectional strip injection at x = 0 and t = 0), Equation (20):
Let us consider a parabolic flow-section shape, Equation (21):
and a velocity profile expressed by the generalized Manning’s formula [34] transformed into the equivalent depth-averaged velocity, Equation (22) [9]:
where θ = θ(B/H) is a calibration coefficient accounting for the difference between average flow depth and hydraulic radius. In the case of large cross-sections and large aspect ratios (B>>H), θ ~ 1 and Heq ~ H. Thus, Equation (23):
and, Equation (24):
In a longitudinal reference frame moving with the section-averaged velocity, Equation (25):
Equations (23) and (24) respectively become, Equation (26):
and, Equation (27):
whose general solutions are, Equation (28):
and, Equation (29):
In dimensionless terms, the gradient of the section-averaged concentration (7) is given by Equation (30):
In Equation (30) and in what follows, PeM represents the macro-Peclet number PeM = UB/Dx. Equation (28) has the following closed-form solution, Equation (31):
with, Equation (32):
and, Equation (33):
where “Erf” indicates Error Function (e.g., [35]).
Equation (29) then yields Equation (34):
with, Equation (35):
and, Equation (36):
where “Ei” indicates Exponential-Integral Function (e.g., [35]). See Figure 1, Figure 2, Figure 3, Figure 4, Figure 5 and Figure 6 for a graphical illustration of the solution with reference to two different macro-Peclet numbers (1 and 0.01, respectively) assuming . Specifically, Figure 1a,b display and , respectively; Figure 2a,b display and , respectively, as a function of ; finally, Figure 3a,b display and , respectively, as a function of . Note that Equations (31) and (34) consistently give zero at the section-averaged concentration maximum and at the section-averaged concentration tails (). Additionally, they would reproduce the typical two-peaked longitudinal structure detected in previous studies on concentration variance in heterogeneous velocity fields (e.g., [7,36,37,38]). Indeed, since concentration spatial variance in constant-width stream flows by definition is, Equation (37):
for example, at order zero, we have, Equation (38):
or, Equation (39):
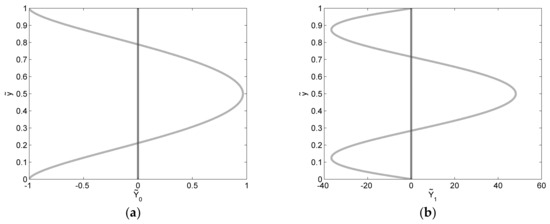
Figure 1.
(a) Function ; (b) Function .
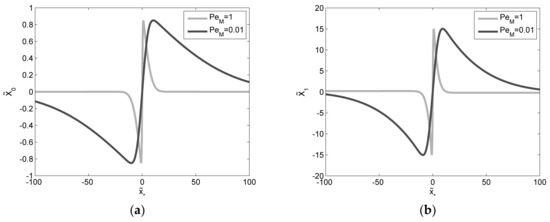
Figure 2.
(a) Function for two different macro-Peclet numbers at (b) Function for two different macro-Peclet numbers at .
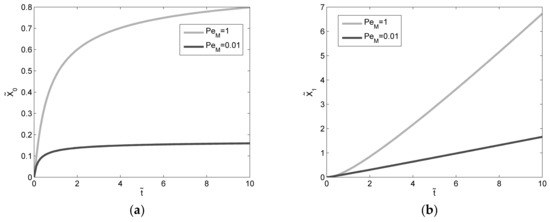
Figure 3.
(a) Function for two different macro-Peclet numbers at (b) Function for two different macro-Peclet numbers at .
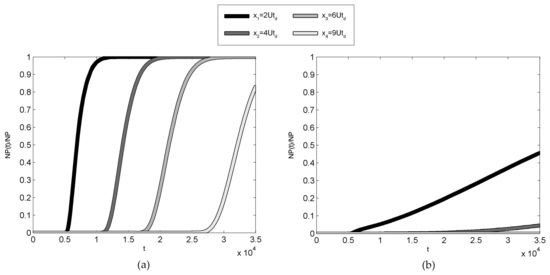
Figure 4.
Breakthrough curves for R1. (a) Uniform mixing; (b) Non-uniform mixing.
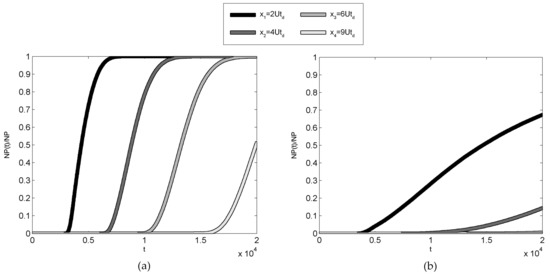
Figure 5.
Breakthrough curves for R2. (a) Uniform mixing; (b) Non-uniform mixing.
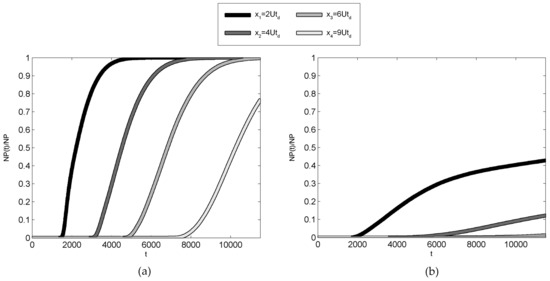
Figure 6.
Breakthrough curves for R3. (a) Uniform mixing; (b) Non-uniform mixing.
Therefore, the longitudinal variability of the leading-order variance coincides with the longitudinal variability of function . As one can see from Figure 2a,b, function (like function ) is characterized by a maximum (positive) and a minimum (negative), with the same absolute value and the same distance from the origin. Its square is therefore characterized by two equal and symmetrical positive peaks. Their distance is, Equation (40):
Both and are obtained as the product of a function of and ( or ) and a function of ( or ). Where or is positive, the sign of or as a function of coincides with the sign of or . Where or is negative, the sign of or as a function of is opposite of or ’s. Thus, for example, where is negative (and that happens for , that is, in the raising branch of the section-average Gaussian bell), we have < 0 in the central part of the cross-section and > 0 near the side boundaries. That means that, at order δ0, while in the central part of the cross section total concentration is lower than the average, at the side boundaries it is higher. Vice versa for positive . That means that, while at the back of the section-average Gaussian wave (7) solute mass is concentrated at the boundaries (the slower part of flow field), at the front of the section-average Gaussian wave (7) solute mass is concentrated at the center (the faster part of flow field). Specifically, along the transverse direction, exhibits two (positive) maxima at the banks and a (negative) minimum at the channel axis for , where ; it is > 0 for and < 0 for . Conversely, exhibits two (negative) minima at the banks and a (positive) maximum at the channel axis for , where ; it is > 0 for and < 0 for and (see Figure 1a combined with Figure 2a). Unlike the leading order component, the first-order diffusive contribution is characterized by four zeros (). Thus, depending on the local sign of function (> 0 for and < 0 for ), it has its maximum at the centre of the cross-section or within more peripheral layers, for and (see Figure 1b combined with Figure 2b). This asymmetry would justify an anomalous delay in the breakthrough curves between first particle arrivals and last particle arrivals. It should also be noted that, whereas , viewed as a function of time, tends to a constant proportional to PeM, tends to increase linearly. In term of the deviatory first order concentration solution (according to Equation (17)), this continuous increase is partially balanced by the small value of (see Figure 3).
3. Numerical Lagrangian Simulations
A numerical investigation of dispersion within straight reaches of open channel flows was already discussed in previous authors’ work [9]. The study focused on the analysis of solute cloud spatial moments reconstructed by 2-D particle tracking based on input experimental data collected along six rivers of southern Italy [39]. The six study cases were equally distributed among compact rectangular (CR), bi-rectangular (BR), and triangular cross-sections (T), characterized by width-to-depth ratio B/H ranging between ~15 and ~56. At the time of the field survey, the six channels were characterized by relatively large bed grain size, with no suspended load and no relevant bed-forms. In order to work on a more dense and regular grid, a larger number of depth values was derived from field data by 3 to 5 level linear interpolation. Each river was discretized into a variable number of transverse elements (from 80 to 320). Each element was characterized by the suitable value of and according to Equations (22) and (11), respectively. A high number of particles (NP = 200,000) was instantaneously released at x = 0 and y = B/2 and then tracked based on Equations (41) and (42):
with (depth-dependent transverse mixing) or, for the sake of comparison, (uniform mixing). In Equations (41) and (42), Gζ(0, 1) represents the generic element of a normal distribution (i.e., a zero-mean and unit-variance Gaussian), and the length of the time step Δt was selected in such a way as to minimize the number of diffusive multiple-element jumps while keeping the computational time within reasonable limits. Indeed, to avoid tracking the particle with wrong velocity values, must not exceed the transverse dimension of the computational grid , Equation (43):
Thus, Equation (44):
Since, Equation (45):
we had, Equation (46):
With , . The total number of tracked particles was NP = 200,000. Setting, Equation (47):
we were certain that only 0.2 of 200,000 displacements had the probability to be performed with the wrong velocity at each time step.
In the present study, we resorted to the same methodology for the numerical reconstruction of the breakthrough curves referred to in three of the six study cases (Table 1) in the presence of uniform and non-uniform turbulent mixing at four different downstream cross-sections (x1 = 2Utd, x2 = 4Utd, x3 = 6Utd, x4 = 9Utd, with indicating the average diffusive time).

Table 1.
Summary of the main geometric and hydrodynamic parameters for the cases under investigation.
It is well known that the breakthrough curves are a measure of the percentage solute mass that has crossed a given section at a given time and allow us to establish whether, and to what extent, concentration distribution is affected by tails and decelerations. As a matter of fact, their use by-passes the evaluation of the actual , which is analytically accessible only in approximate forms (an example was shown above) and is numerically affected by unavoidable errors due to discretization issues and virtual diffusion. Following the mentioned Lagrangian approach, we evaluated the cumulate of concentration by counting the percentage number of particles that, at the generic time t, were characterized by Figure 4a, Figure 5a and Figure 6a show the breakthrough curves for the three cases under investigation in conditions of uniform turbulent mixing; Figure 4b, Figure 5b and Figure 6b do the same in the presence of non-uniform mixing (for R1, R2 and R3, respectively). The time on the abscissa corresponds in every case to 2 average diffusive times. Finally, for the sake of comparison, Figure 7a–c display the theoretical cumulative distributions corresponding to the one-dimensional Gaussian in the presence of uniform mixing, Equation (48):
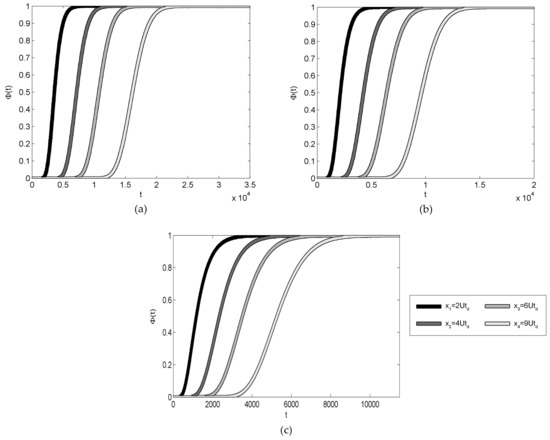
Figure 7.
Theoretical Taylor-like breakthrough curves for uniform mixing. (a) R1, (b) R2, and (c) R3.
The longitudinal macro-dispersion coefficients Dx used in Equation (48) (110, 220, and 105 m2/s, respectively, for the three cases under investigation), were consistently obtained as one-half of the time-derivative of the cloud central inertia moment Sx, Equation (49) [9]:
where, Equation (50):
indicates longitudinal average trajectory. Note that the reconstruction of the theoretical breakthrough curves based on Equation (48) implicitly assumes a transversally uniform distribution, with .
The comparison between the curves numerically obtained for uniform and non-uniform mixing reveals that the uniform approximation (which is in qualitative agreement with the cumulate of the section-averaged concentration (48)) yields totally misleading results. Indeed, in the case of non-uniform mixing, and regardless of the morphological typology of the cross-section, even the shape of the curves is anomalous and is characterized by a considerable delay with respect to the theoretical one. This considerable and persistent delay can find a very reasonable explanation on the basis of the first-order analytical solution presented in the previous section. As a matter of fact, as above mentioned, both the leading order component and first order diffusion-related component are characterized by (positive) maxima near the banks and (negative) minima at the centre of the cross-section for , that is, at the back of the C-wave. Conversely, they are characterized by a (positive) maximum at the centre of the cross section and (negative) minima in the more peripheral layers for , that is, at the front of the C-wave. That means that solute mass is concentrated in the faster areas of the cross-section at the front and in the slower areas of the cross-section at the back, thus producing the detected delay in the breakthrough curves. Additionally, and unlike the leading-order component of the solution , which tends to a constant different from zero for any the first-order diffusion-related component linearly increases in time for any , meaning that its effect gets stronger and stronger as time elapses. Thus, the first-order analytical model proposed by the present study and based on the analysis of depth-averaged concentration behaviour in the presence of a symmetric parabolic cross-section characterized by a large aspect ratio and large Peclet number, seems to be able to grasp the basic features of tracer dispersion also under the more general conditions simulated by the numerical analysis. Additionally, since in the presence of shallow waters (for which the problem of monitoring and predicting the fate of pollutant substances is even more serious) a parabolic shape of the cross-section can be an acceptable approximation of reality, the solution may be easily utilized to assess the maximum cross-sectional value of concentration and its location.
4. Conclusions
The assessment of the value and position of chemical concentration peaks in river flows is a fundamental requirement for the monitoring and the control of contamination events, which can be very frequent along river reaches that cross urban or industrial areas. We have shown that, for large aspect ratios, at the first order in the deviatory velocity and at least for large Peclet numbers, complete transverse mixing is never achieved. Therefore, the commonly used one-dimensional Gaussian is not a suitable predictor. The proposed analytical model allows evaluating the time-dependent deviatory depth-averaged concentration at any location along the channel axis and within the cross section. Assuming a large parabolic shape of the flow area, we found that, at the front of the section-averaged wave, the mass is concentrated at the centre. Conversely, at the back of the section-averaged wave, it is relegated near the banks. Additionally, while the large-time leading component of the solution tends to a constant, the first-order diffusion-related component linearly increases in time. This peculiar behaviour fully justifies what emerges from Lagrangian numerical simulations applied to three real-field cases represented by more or less asymmetric cross-sections and finite Peclet numbers. Indeed, all the reconstructed downstream breakthrough curves exhibited a considerable and highly persistent delay as compared to those obtained from the one-dimensional Gaussian, thus validating the theoretical conclusion even in more general and less restrictive cases.
Author Contributions
M.P. conceived and designed the work, provided the analytical closed-form solution and performed the numerical simulations; D.M. graphically elaborated the output and analysed the state-of-art (numerical and experimental studies); A.D.V. performed the analysis of field data and transformed them in computational format; B.M. analysed the state-of-art (theoretical studies) and critically revised the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Notation
| A | flow area |
| B | free-surface width |
| c | (time-mean) concentration |
| depth-averaged concentration | |
| deviation of depth-averaged concentration | |
| C | section-averaged concentration |
| C0 | initial section-averaged concentration |
| dimensionless c | |
| dimensionless C | |
| zeroth order solution of perturbation expansion | |
| first order solution of perturbation expansion | |
| dimensionless distance between the two peaks of concentration variance | |
| Dx | longitudinal macro-dispersion coefficient |
| Δt | numerical time step |
| εx | longitudinal mixing coefficient |
| εy | transverse mixing coefficient |
| εz | vertical mixing coefficient |
| depth-averaged transverse mixing coefficient | |
| section-averaged transverse mixing coefficient | |
| Ei | Exponential-Integral Function |
| Erf | Error Function |
| Φxi | Cumulate of concentration at xi |
| g | acceleration due to gravity |
| generic element of a normal distribution | |
| h | local flow depth |
| H | average flow depth |
| Heq | depth of the equivalent rectangular cross-section |
| if | channel bed slope |
| M | total mass |
| NP | total number of particles |
| Pe | Peclet number |
| PeM | macro-Peclet number |
| Ψ | flow section-shape function |
| Sx | cloud longitudinal inertia moment |
| concentration variance | |
| t | time |
| dimensionless t | |
| t0 | longitudinal relaxation time |
| dimensionless longitudinal relaxation time | |
| td | average diffusive time |
| θ | aspect ratio calibration coefficient |
| u | (time-mean) longitudinal velocity |
| depth-averaged longitudinal velocity | |
| deviation of depth-averaged longitudinal velocity | |
| shear velocity | |
| depth-averaged shear velocity | |
| U | section-averaged longitudinal velocity |
| x | longitudinal spatial coordinate |
| y | transverse spatial coordinate |
| z | vertical spatial coordinate |
| dimensionless x | |
| dimensionless y | |
| dimensionless x in a reference frame moving with the section-averaged velocity | |
| X(t) | longitudinal particle position at time t |
| <X(t)> | longitudinal average trajectory |
| Y(t) | transverse particle position at time t |
References
- Weiss, J.B.; Provenzale, A. Transport and Mixing in Geophysical Flows; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vincenzo, A.; Molino, B.; Viparelli, R.; Caramuscio, P. A methodological approach for estimating turbidity in a river. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2011, 26, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. On the exact analytical solution for the spatial moments of the cross-sectional average concentration in open channel flows. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W08511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Transient Hydrodynamic Dispersion in Rough Open Channels: Theoretical Analysis of Bed-Form Effects. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2010, 136, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Longitudinal Dispersion in River Flows Characterized by Random Large-Scale Bed Irregularities: First-Order Analytical Solution. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2012, 138, 400–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M.; De Vincenzo, A.; Brancati, F. A Mathematical Model for the Flow Resistance and the Related Hydrodynamic Dispersion Induced by River Dunes. J. Appl. Math. 2013, 2013, 432610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Predictability of tracer dilution in large open channel flows: Analytical solution for the coefficient of variation of the depth-averaged concentration. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 2617–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M.; De Vincenzo, A. Stochastic numerical analysis of anomalous longitudinal dispersion and dilution in shallow decelerating stream flows. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2015, 29, 2087–2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M. Effect of nonlocal transverse mixing on river flows dispersion: A numerical study. Water Resour. Res. 2010, 46, W08534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Barros, F.; Dentz, M.; Koch, J.; Nowak, W. Flow topology and scalar mixing in spatially heterogeneous flow fields. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, L08404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, C.E. A Mathematical Theory of Communications. Bell Syst. Tech. J. 1948, 27, 379–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Mirauda, D.; Plantamura Volpe, A. Manning’s roughness through the entropy parameter for steady open channel flows in low submergence. Procedia Eng. 2014, 70, 773–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, M.; Mirauda, D. An Entropy Based Velocity Profile for Steady Flows with Large-Scale Roughness. In Engineering Geology for Society and Territory, River Basins, Reservoir Sedimentation and Water Resources; Lollino, G., Arattano, M., Rinaldi, M., Giustolisi, O., Marechal, J.C., Grant, G.E., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; Volume 3, pp. 641–645. ISBN 978-3-319-09054-2. [Google Scholar]
- Greco, M.; Mirauda, D. Entropy parameter estimation in large-scale roughness open channel. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 04014047-1–04014047-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; De Vincenzo, A.; Pannone, M. Simplified entropic model for the evaluation of suspended load concentration. Water 2018, 10, 378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; De Vincenzo, A.; Pannone, M. Statistical characterization of flow field structure in evolving braided gravel beds. Spat. Stat. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; Pannone, M.; De Vincenzo, A. An entropic model for the assessment of stream-wise velocity dip in wide open channels. Entropy 2018, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirauda, D.; Ostoich, M. Surface water vulnerability assessment applying the integrity model as a decision support system for quality improvement. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2011, 31, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I. The dispersion of matter in turbulent flow through a pipe. Proc. R. Soc. A 1954, 223, 446–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.B. The mechanics of dispersion in natural streams. J. Sanit. Eng. Div. Proc. Am. Soc. Civ. Eng. 1967, 93, 187–216. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, H.B. Methods for predicting dispersion coefficient in natural streams, with applications to lower reaches of the Green and Duwamish Rivers. U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1968, 582. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0582a/report.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2018).
- Rutheford, J.C.; Taylor, M.E.U.; Davies, J.D. Waikato River pollutant flushing rates. J. Environ. Eng. 1980, 106, 1131–1150. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, P.M.; Atkinson, T.C. Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels: 1, Experimental results from the River Severn. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 345–353. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, P.M.; Atkinson, T.C. Longitudinal dispersion in natural channels: 2, The roles of shear flow dispersion and dead zones in the River Severn. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2000, 4, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.R.; Wallis, S.G.; Hope, D. A conservative semi-Lagrangian transport model for rivers with transient storage zones. Water Resour. Res. 2001, 37, 3321–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambertz, P.; Palancar, M.C.; Aragon, L.M.; Gil, R. Determining the dispersion characteristics of rivers from the frequency response of the system. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W09414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marion, A.; Zaramella, M.; Bottacin-Busolin, A. Solute transport in rivers with multiple storage zones: The STIR model. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 44, W10406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, Z. Mixing length for establishment of longitudinal dispersion in streams. Int. J. Modell. Simul. Acta Press 2004, 29, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, R.B. A mixing cell model for longitudinal dispersion in open channels. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 357–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, H.B.; List, E.J.; Koh, R.C.Y.; Imberger, J.; Brooks, N.H. Mixing in Inland and Coastal Waters; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1979; p. 483. [Google Scholar]
- Seo, I.W.; Cheong, T.S. Predicting longitudinal dispersion coefficient in natural streams. J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 1998, 124, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayre, W.W.; Chang, F.M. A laboratory investigation of open-channel dispersion processes for dissolved, suspendend, and floating dispersants. U.S. Geol. Surv. Prof. Pap. 1968, 433. Available online: https://pubs.usgs.gov/pp/0433e/report.pdf (accessed on 7 April 2018).
- Batchelor, G.K. Diffusion in a field of homogeneous turbulence, 2: The relative motion of particles. Proc. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1952, 48, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Singh, V.P.; Bengtsson, L. Longitudinal dispersion coefficient in straight rivers. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2001, 127, 919–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradshteyn, I.S.; Ryzhik, I.M. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products, 5th ed.; Academic Press Inc.: San Diego, CA, USA, 1994; p. 1204. ISBN 0-12-294755-X. [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor, V.; Gelhar, L.W. Transport in three-dimensionally heterogeneous aquifers: 1. Dynamics of concentration fluctuations. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1775–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapoor, V.; Gelhar, L.W. Transport in three-dimensionally heterogeneous aquifers: 2. Predictions and observations of concentration fluctuations. Water Resour. Res. 1994, 30, 1789–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, M.; Kitanidis, P.K. Large-time behavior of concentration variance and dilution in heterogeneous formations. Water Resour. Res. 1999, 35, 623–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosimo, C.; Copertino, V.A.; Veltri, M. La Resistenza Al Moto Nei Corsi D’acqua Naturali a Letto Fisso. Primi Risultati Di Una Ricerca Sperimentale; Atti del XXXIII “Convegno di Idraulica e Costruzioni Idrauliche”; University of Bologna: Bologna, Italy, 1982; pp. 101–115. (In Italian) [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).