Abstract
Coagulation and precipitation appear to be the most efficient and economical methods for the removal of antimony from aqueous solution. In this study, antimony removal from synthetic water and Fe solubility with ferric chloride (FC) coagulation has been investigated. The effects of pH, FC dosage, initial antimony loading and mixed Sb(III), Sb(V) proportions on Fe solubility and antimony removal were studied. The results showed that the Sb(III) removal efficiency increased with the increase of solution pH particularly due to an increase in Fe precipitation. The Sb(V) removal was influenced by the solution pH due to a change in Fe solubility. However, the Fe solubility was only impaired by the Sb(III) species at optimum pH 7. The removal efficiencies of both Sb species were enhanced with an increase in FC dose. The quantitative analysis of the isotherm study revealed the strong adsorption potential of Sb(III) on Fe precipitates as compared to Sb(V). Furthermore, the removal behavior of antimony was inhibited in mixed proportion with high Sb(V) fraction. In conclusion, this study contributes to better understanding the fate of Sb species, their mobilities, and comparative removal behavior, with implications for Fe solubility using ferric chloride in different aqueous environments.
1. Introduction
Antimony, a metalloid, is the fourth element of group VA of the periodic table, and usually found in soils and water due to natural and anthropogenic sources. Worldwide reserves of antimony are 4–5 million metric tons [1,2]. It is produced globally in very large quantities i.e., 165,000 tons per year [3,4] with 80% of its total production taking place in China [1]. In addition, about 100,000 tons of antimony is consumed annually in the production of a variety of industrial goods, including 72% flame retardants, 10% transport and batteries, 10% chemicals, 4% glass and ceramics, and 4% in other uses [5,6,7,8]. Antimony contamination in soils and water have been detected around power plants, smelting, and mining, shooting-range soils and roadsides containing dust from tires and brake pads [7,9,10,11,12,13]. For instance, groundwater near abandoned Sb mines in Slovakia presented Sb levels up to 1000 µg/L [14]; while water bodies near anthropogenic sources contain higher concentrations of antimony pollution. In Stampede and Slate Creek watersheds, Kantishna Hills mining district (Alaska, USA), Sb concentrations of 239 μg/L were found [15]; and around the world at the largest antimony mine at Xikuangshan in Hunan Province (China), high levels of Sb (2–6384 μg/L) were also found in rivers [16]. The level of Sb detected in wastewater from a metal industry facility in Korea was 40,000 µg/L to 60,000 µg/L.
Antimony is usually found as Sb(III) and Sb(V) in environmental, biological and geochemical contexts [2,17]. In anoxic water solutions, Sb(III) is the stable and predominant species, and occurs as Sb(OH)3 [18,19], while under aerobic conditions, Sb(V) occurs as Sb(OH)6− [19]. Its exposure to soil and water bodies poses a great threat to human health, due to its toxicity and carcinogenicity [20]. In particular, antimonite (Sb(III)) is reported to be 10 times more toxic than antimonate (Sb(V)) [13,21]. Having generated increased concern, antimony was declared a high-priority pollutant of interest by the United States Environment Protection Agency (USEPA) and European Union (EU). Therefore, the maximum allowable antimony concentration in drinking water has been regulated by USEPA and the EU as 6 µg/L and 10 µg/L, respectively, while the World Health Organization (WHO) and China set the water standard for antimony as 5 µg/L [3]. Korea set the standard for antimony in tap water as 20 µg/L, while in bottled water the standard is 15 µg/L [22].
In general, aluminum and iron-based coagulants are commonly used in heavy-metal removal from water due to their relatively low cost compared with other commercially available treatment technologies [3,23]. The relatively poor performances of aluminum-based coagulants for antimony removal from water had already been evidenced by several studies [3,13,23,24]. Iron-based coagulants revealed better performance in antimony removal from water [13,24,25,26,27,28]. The viability of ferric chloride (FC) had been found to be promising for antimony elimination from water [3,24], while, the removal efficiency was reduced in chlorinated or oxidized water [24]. Under suboptimal conditions with a FC coagulant, Sb(V) was found to be more sensitive than Sb(III) in the presence of interfering ions [13]. Treatment of arsenic-rich water, which was similar in chemical properties and toxicity as that of antimony, had been addressed with number of studies using FC coagulant [29,30,31,32]. Previously, investigations on arsenic removal had already been carried out by FC coagulation under the influence of solution chemistry, along with implications of Fe precipitation, its size and zeta potential [33]. However, antimony removal using FC, with particular emphasis on Fe solubility under different solution chemistry environments, has been rarely touched by environmental scholars.
The main objective of this study was to analyze Fe solubility in the absence and presence of Sb(III, V)species and, subsequently, to compare the removal behavior of corresponding Sb species using a FC coagulant (1) under different pH conditions, (2) with different FC doses, (3) from respective isotherms, and (4) under coexisting antimonite and antimonate species ratios.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
All chemicals were reagent-grade, including antimony (III) oxide (Sb2O3) and potassium hexahydro-antimonate (V) (KSb(OH)6) purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA); while iron (III) chloride hexahydrate (FeCl3·6H2O), hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) were purchased from local suppliers. Deionized water was used to prepare stock solutions and synthetic water. All glassware and polyethylene bottles were washed with 15% HNO3 solution and then rinsed with deionized water before use, while sampling vessels were used for storing supernatant.
2.2. Experimental Methodology
2.2.1. Preparation of Solutions
The 1 g/L of Sb(III)-stock solution was prepared by dissolving Sb2O3 in 2M HCl solution. The 100 mg/L of Sb(V)-stock solution was prepared by dissolving KSb(OH)6 in deionized water. Coagulant stock solution, i.e., 0.1M FC solution was prepared by dissolving FeCl3·6H2O into deionized water. While synthetic test water with elevated antimony was prepared according to the purpose of the study by spiking Sb-stock solution into deionized water.
2.2.2. Batch Experiments
The controlled coagulation experiments were performed to compare Fe solubility in deionized water and spiked water containing 1 mg/L Sb(III, V), respectively, at various pH values in the range from 4–10 and at a 0.1 mM FC dose. Subsequently, Fe solubility was evaluated at neutral pH with various FC doses (0.05–0.2) mM. Furthermore, Sb removal was also analyzed under the same experimental conditions. For follow-up experiments, the experimental conditions were chosen as 0.1 mM FC and neutral pH. The isotherm study was conducted with initial Sb concentrations i.e., 0.1–10 mg/L. In addition, the effect on Sb removal was analyzed by using different Sb(III), Sb(V) mixing ratios from 0.9/0.1 to 0.1/0.9 mg/L with total initial Sb loading of 1 mg/L. The pH of synthetic test water was adjusted to the predetermined pH by drop-wise addition of 0.1 M HCl or 0.1 M NaOH. All experiments were conducted at a temperature of 25 ± 1 °C.
2.2.3. Jar Test
Jar tests were performed using a jar tester with six beakers (Model: SJ-10, Young Hana Tech Co., Ltd., Gyeongsangbuk-Do, Korea). Synthetic test water (100 mL) was transferred to a 250 mL beaker. FC coagulant was dosed at a predetermined amount, and the solution was rapidly mixed with a stirring speed of 140 rpm to initiate coagulation; while the pHs of synthetic waters were adjusted to predetermined levels. After 3 min. of rapid stirring, the stirring speed was changed to 40 rpm for a duration of 20 min to enhance the flocculation process [3]. Then, after 30 min of quiescent settling, 50 mL of the supernatant was collected in a sampling vessel by filtering through 0.45 µm glass fiber filter. The residual antimony in the supernatant was then analyzed to evaluate removal efficiency.
2.2.4. Analytical Procedures
The antimony solution and residual Fe was analyzed by inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP-OES: Model Varian, Agilent technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The solution pH was measured with a pH meter (HACH: HQ40d Portable pH, Conductivity, oxidation reduction potential (ORP) and ion selective electrode (ISE) Multi-Parameter Meter (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), which was initially calibrated with pH buffer solutions of 4.01, 7.00 and 10.01 at 25 °C before use. Fe precipitates were also measured in terms of total suspended solids using the APHA procedure [34]. Fe(III), Sb(III) and Sb(V) speciation diagrams were drawn from data obtained from Visual MINTEQ 3.1. (KTH, Stockholm, Sweden) In addition, the popular graphical software OriginPro 9.0 (OriginLab, Massachusetts, MA, USA) was used to plot the experimental data. Furthermore, JASCO FT–IR-4700 (Fourier transform infrared spectrometer) in the range of 400–4000 cm−1 was used for functional groups as well as bond analysis.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Solution pH on Fe Solubility and Antimony Removal
The Fe precipitation and dissolution behavior as a function of pH using ferric chloride coagulation is presented in Figure 1A. The dotted line of “FC only” indicates the precipitated Fe in the absence of Sb species while the two solid lines indicate the corresponding Fe precipitate concentration in the presence of Sb(III) and Sb(V) species, respectively. In case of FC only, precipitated Fe gradually increase from pH 4–5 and showed complete Fe precipitation at pH range 6–10. In the presence of Sb(III) species, Fe precipitation behavior was almost the same for the pH range 4–10 as with FC only. The presence of Sb(V) species under pH 6–8 did not cause any effect on Fe precipitation. However, under an acidic condition, i.e., pH 4–5, a relatively small amount of Fe precipitates dissociates in solution when compared with FC only. In addition, the presence of Sb(V) species caused a significant effect upon Fe precipitation at high pH conditions 9,10 where complete Fe dissolution occurs. The same results were observed in previous studies which suggested such a dissolution effect is caused by ligands [35,36]. Specifically, ligands binding as inner-sphere complexes to the surface groups of iron increased the speed of the dissolution process (also called the dissolution rate), [36,37,38,39]. Moreover, at pH 9 and 10, the dominant form of Fe(III) was Fe(OH)4−, while Sb(V) existed as Sb(OH)6−, as shown in Figure S1A,C. The increase in dissolution rate was proportional to the surface concentration of ligand and its binding strength [40] (in our case Sb(OH)6− was ligand binding to Fe(OH)4−). Strong electron donation by the ligand to a surficial Fe atom will remove electron density in the bonds between Fe and oxygen atoms of the mineral lattice, thus weakening the bond and lowering the energy barrier for the dissolution of Fe atoms [35]. Furthermore, ligands which formed inner-sphere, bidentate mononuclear complexes contained two or more functional groups for chelation and, hence, were effective in promoting the dissolution rate [40]. As reported, Sb(V) form inner-sphere bidentate mononuclear complexes with Fe(III) [26], hence are capable of promoting Fe dissolution being reported in our study.
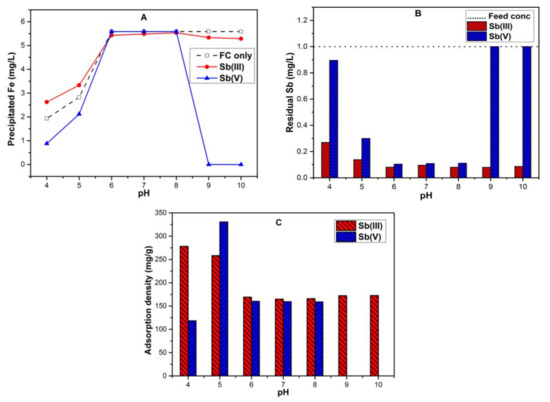
Figure 1.
Across various pH in the range 4–10, 0.1 mM ferric chloride coagulation (FC) dose, 1 mg/L initial Sb concentration and temperature T 25 ± 1 °C showing (A) Fe precipitation (mg/L); (B) residual Sb (mg/L); (C) adsorption densities (mg/g).
The results indicated that Fe precipitation had a direct influence on antimony removal under various pH conditions as presented in Figure 1B. The removal efficiency of antimonite by FC coagulation increased in the entire pH range 4–10 due to more Fe precipitation (Figure 1A,B). A similar trend of Sb(III) removal during Sb(III)-FC coagulation was reported in previous studies [3,24]. Moreover, with the first dissociation constant pKa of H3SbO3 being at 10.4, Sb(III) exists predominantly in the neutral molecular form in the pH range of 2 to 10.4 (also presented in Figure S1B) [41]. Hence, this might have resulted in the diffusion of H3SbO3 into the Fe precipitate surface regardless of the surface charge required to engage in an adsorption process. Furthermore, the adsorption density of Sb(III) was calculated by normalizing the adsorbed Sb(III) with respect to precipitated Fe as a function of pH, as presented in Figure 1C. The adsorption density gives the potential of Fe precipitates to adsorb Sb(III) at various pH. Interestingly, Fe precipitate contains strong adsorption potential for Sb(III) at pH 4–5 having adsorption densities (278.2, 258.4) mg/g respectively. Moreover, the Fe precipitate formation at this pH was almost half of the Fe dose supplied (Figure 1A). From pH 6–10, almost complete Fe precipitation was observed with relatively less adsorption densities (164.9–172.8) mg/g (Figure 1A,C).
Compared with antimonite, the best removal of antimonate occurred in the pH range of 6–8 where complete Fe precipitation occurs (Figure 1A), and Fe precipitate contains positive surface charge and Fe(OH)2+ as the dominant form (Figure S1A). At low pH 4 and 5, due to less available Fe precipitates (around 0.88 mg/L and 2.11 mg/L), Sb(V) removal efficiencies of 10% and 70% were observed (Figure 1B). Our findings contradicted previous reported results, which presented high Sb(V) removal efficiency under acidic conditions and might be due to the fact that they considered 20 times less Sb(V) concentration (50 µg/L) as compared to 1 mg/L Sb(V) and the same FC dose being used as in our study [3]. At pH 9 and 10, all antimonate retained in the solution (Figure 1B) due to the complete dissociation of Fe precipitates (Figure 1A). Moreover, antimonate exists as anionic form Sb(OH)6− from pH > 2.7 [17,41]. The result further illustrates that in addition to Fe precipitation, the electrostatic attractions between the negatively charged antimonate species and positively charged Fe(III) hydrolyzed species might have resulted in efficient Sb(V) removal (around 90%) at pH of 6–8. In addition, such attraction had favored the Sb(V) diffusion and adsorption on the hydrolyzed Fe precipitate surface. While at high pH 9 and 10, interestingly, complete dissociation of precipitates had resulted in the mobility of antimonate. Furthermore, normalizing the adsorbed Sb(V) with respect to precipitated Fe as a function of pH illustrates the Sb(V) adsorption density (Figure 1C). Sb(V) showed high adsorption density (330.6 mg/g) at pH 5 which was twice more when compared with other pH 6, 7 and 8 (160.3, 159.5 and 159.1) mg/g, respectively, while having low adsorption potential (118.5 mg/g) at pH 4. Such results confirmed the strong potential of precipitated Fe for Sb(V) under acidic conditions that were in agreement with results reported in previous studies [3,24,25].
The results suggested that the pH not only affects the speciation of antimony ions in water (Figure S1B,C) but also affects the surface charge of precipitated Fe (Figure S1A). In addition, the pH value also determines the Fe solubility behavior in the absence and presence of antimony species (Figure 1A). Furthermore, it affects the removal behavior of antimonite and antimonate species under various pH levels in water (Figure 1B).
3.2. Effect of Different Ferric Chloride Coagulation (FC) Dose on Fe Solubility and Antimony Removal
At neutral pH, it was assumed that antimony species might influence Fe precipitation under different FC doses. Therefore, different FC doses were supplied with antimony-spiked water. The result confirmed that the Fe precipitation was not affected in the absence and presence of Sb(V) species but showed slight dissociation in the presence of Sb(III) (Figure 2A). The corresponding residual Sb and adsorption densities for FC doses 0.05 mM to 0.2 mM was presented in Figure 2B,C. The residual Sb(III) and Sb(V) after reaction with 0.05 mM FC was found to be 0.189 mg/L and 0.18 mg/L, respectively. As the FC dose was increased from 0.05 mM to 0.2 mM, Sb removal efficiency was enhanced and only 0.025 mg/L Sb(III) and 0.02 mg/L Sb(V) were retained in the solution. Similar results were presented in the previous study, where better Sb removal efficiency was obtained at higher FC doses [3].
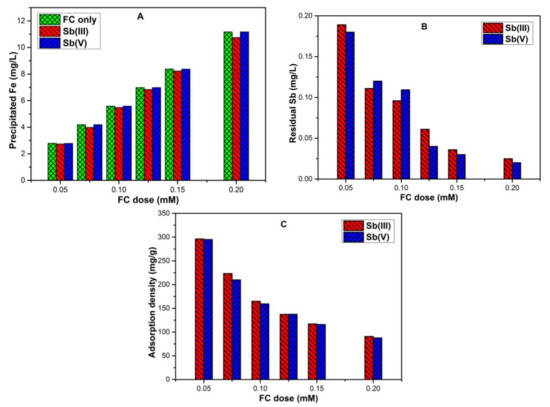
Figure 2.
Across various FC doses of 0.05 mM to 0.2 mM (i.e., 13.51 mg/L to 54.06 mg/L), at pH 7, 1 mg/L initial Sb concentration and temperature T 25 ± 1 °C showing (A) Fe precipitation (mg/L); (B) residual Sb (mg/L); (C) adsorption densities (mg/g).
Conversely, the adsorption density was continuously reduced when the FC dose was increased from 0.05 mM to 0.2 mM (Figure 2C). The maximum adsorption density for corresponding Sb(III) and Sb(V) species using 0.05 mM FC were (296.1 and 294.9) mg/g, respectively. When the dose was increased to 0.2 mM FC, it eventually decreased to (90.7 and 87.7) mg/g, respectively. The decrease in adsorption density suggested that the mass of Sb sequestered per unit mass of Fe decreases probably due to the availability of more Fe precipitates.
3.3. Modelling Coagulation Data by Isotherm Studies
The Langmuir and Freundlich isotherms are the two most commonly used isotherms [28]. The Langmuir model assumes the homogeneous surface of the sorbent [42]. The non-linear equation of the Langmuir isotherm is given by:
where Qe is equilibrium adsorption capacity (mg/g); Ce is equilibrium concentration (mg/L); KL is an adsorption constant related to binding energy (L/mg); and Qm is maximum adsorption capacity (mg/g), respectively. The Freundlich model, on the other hand, is empirical and assumes heterogeneous adsorption on the surface sites with different energies of adsorption [28]. Its equation is as follows:
where Kf is roughly an indicator of adsorption capacity (L/mg), and n is heterogeneity factor with lower value for more heterogeneous surfaces.
Qe = KfCe 1/n,
Figure 3 shows the adsorption experimental results and non-linear adsorption isotherm fittings for the analyzed data. As expected, Sb(III) showed strong adsorption ability independent of initial concentrations. The regression value (R2) for Sb(III) species for Langmuir fitting was 0.9823 while for Freundlich fitting it was 0.9896. Similarly, Sb(III) showed high adsorption affinity without any saturation point when ferrihydrite was used as a sorbent [43]. This contrasted with Sb(V), which almost reached an adsorption maximum (Qm: 586.5 mg/g). The R2 value for Sb(V) for Langmuir fitting was 0.9929 while for Freundlich fitting it was 0.8289 suggesting Sb(V) adsorption on the FC surface followed Langmuir, thus indicating a homogeneous surface of FC adsorption sites with the same energy of adsorption for Sb(V) and monolayer formation between precipitated Fe and Sb(V) [44].
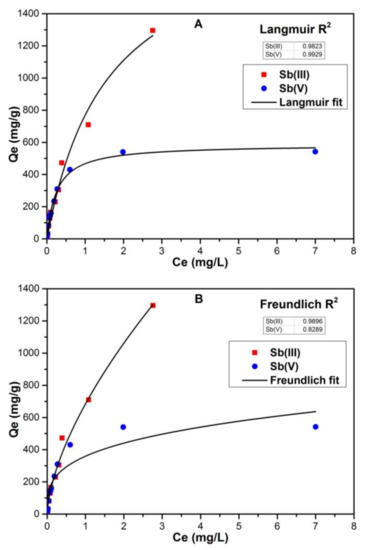
Figure 3.
Adsorption isotherms for adsorption of Sb(III) and Sb(V) onto Fe precipitates (5.585 mg/L) at pH 7 and initial Sb concentrations: 0.1 to 10 mg/L. The symbols indicate the experimental results and the solid lines represent the non-linear fitting for (A) Langmuir adsorption; (B) Freundlich adsorption models.
3.4. Effect of Coexisting Sb(III)-Sb(V) Species Ratio on Fe Solubility and Total Sb Removal
3.4.1. Antimony Adsorption Performance
The antimony adsorption performance of FC was evaluated in synthetic water containing different proportions of Sb(III) and Sb(V) species at pH 7. The total antimony concentration (Sb(III) + Sb(V)) in all test solutions were fixed at 1 mg/L. The antimony solutions with different proportions i.e., Sb(III)/Sb(V) were denoted as 0.9/0.1 (mg/L), 0.8/0.2 (mg/L), 0.5/0.5 (mg/L), 0.2/0.8 (mg/L) and 0.1/0.9 (mg/L). The removal efficiencies of antimony as a function of different coexisting Sb species proportion was presented in Figure 4A. At the initial 0.1/0.9 (mg/L) antimony solution, the antimony removal by FC was 74.2%. Upon increasing the Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportion to 0.2/0.8 (mg/L), the antimony removal increases to 77.3%. Further increasing the Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportion to 0.5/0.5 (mg/L) and 0.2/0.8 (mg/L) considerably increase the antimony removal efficiency to 79.1% and 88.7%, respectively. The highest antimony removal, i.e., 92.7% by FC was obtained when the Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportion was set to 0.9/0.1 (mg/L). The result indicates that the presence of coexisting Sb species in solution significantly affects the antimony removal by FC, and the higher the fraction of Sb(III) species, the higher the antimony removal.
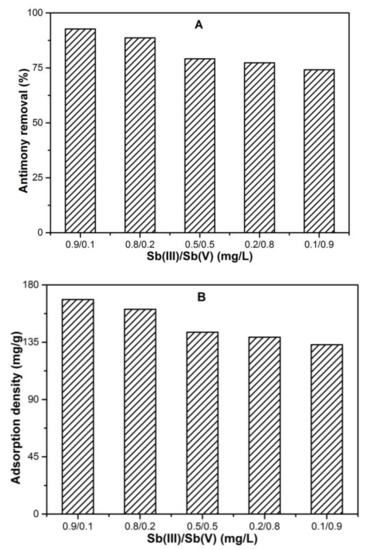
Figure 4.
Overview of removal response for coexisting Sb(III) and Sb(V) species under neutral pH, 0.1 mM FC dose, 1 mg/L initial Sb concentration and temperature T 25 °C; (A) antimony removal (%); (B) adsorption densities (mg/g).
Furthermore, the adsorption densities of Sb under different mixed proportions were calculated by normalizing the adsorbed Sb with respect to precipitated Fe, as presented in Figure 4B. The dissociated Fe under different Sb(III)/Sb(V) ratios for corresponding 0.9/0.1 (mg/L), 0.8/0.2 (mg/L), 0.5/0.5 (mg/L), 0.2/0.8 (mg/L) and 0.1/0.9 (mg/L) were analyzed to be 85 (µg/L), 72 (µg/L), 45 (µg/L), 18 (µg/L) and 9 (µg/L), respectively. This indicate dissolution of Fe precipitates into solution with order of Sb(III)/Sb(V) to be 0.9/0.1 (mg/L) > 0.8/0.2 (mg/L) > 0.5/0.5 (mg/L) > 0.2/0.8 (mg/L) > 0.1/0.9 (mg/L). While the corresponding adsorption densities were calculated to be 168.5 (mg/g), 160.9 (mg/g), 142.8 (mg/g), 138.9 (mg/g) and 133.03 (mg/g). So, these results suggest that increasing Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportion might dissociate a greater portion of the precipitated Fe into solution. In addition, such an effect will create more Fe vacancy defects leading to considerable change in Fe precipitate surface, that facilitate the more active sites for antimony immobilization. Similar results were reported previously while treating arsenic wastewater containing the coexisting arsenite (As(III)) and arsenate (As(V)) species using manganese oxide [45].
3.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT–IR) Spectra Analysis
The FT–IR spectra of the ferric chloride hexahydrate (FC) before and after reaction with 0.1/0.9 (mg/L), 0.5/0.5 (mg/L) and 0.9/0.1 (mg/L) antimony solutions were investigated (Figure 5). The bands that appeared at approximately ~3249 cm−1 were assigned to the strong O-H stretching vibrations [46]. The small peaks that appeared at ~2346 cm−1 were attributed to some impurities, since FC used in this study was 99% pure. The band near to ~1633 and ~1739 cm−1 was ascribed to the deformation of water molecules, indicating the presence of physiosorbed water on the FC surface [45]. The peaks appeared in range 1215–1366 cm−1 were assigned to the bending vibration of the hydroxyl group, being associated with Sb and Fe [47]. The peak that appeared at ~739 cm−1 was subjected to the bending of the Fe–O bond whereas, interestingly, no peak at ~549 cm−1 was observed, which means no stretching of the Fe–O bond occurred in all samples [48]. After reacting with different antimony solutions, a new peak at approximately ~490 cm−1 was observed in all samples, which was near to the ~488 cm−1 peak and, hence, assigned to the Sb(V)-O stretching vibration [28]. Interestingly, the peak at approximately ~466 cm−1, which was assigned to the Sb(III)-O vibrations, did not appear in all selected samples. This result indicates that antimony species adsorbed on the FC surface only in the form of Sb(V) species; such adsorption behavior was different than that in the case of FeOOH [28].
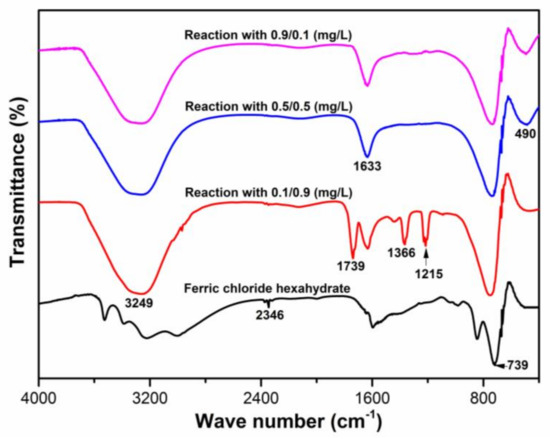
Figure 5.
The Fourier transform infrared (FT–IR) spectra of ferric chloride hexahydrate before and after reaction with Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportions of 0.1/0.9 (mg/L), 0.5/0.5 (mg/L), and 0.9/0.1 (mg/L) solutions at pH 7 (the solution pH was adjusted using 0.1M HCl and 0.1M NaOH solutions).
3.4.3. The Origin of the Significant Effect of the Sb(III)/Sb(V) Mixed Fractions on Antimony Removal
Based on current findings and previous studies, the origin of a significant effect of coexisting antimonite and antimonate species proportions on antimony removal was identified. FT–IR analysis and dissolved Fe content in solutions of various Sb proportions after reactions confirm the Sb(III) oxidation to Sb(V) on the FC surface and support the conjecture of reductive dissolution of a fraction of Fe precipitates into solution. Similar Sb(III) oxidative behavior onto goethite had already been evidenced in a previous study [8]. Such oxidative behavior of Sb(III) with the release of Fe2+ was enhanced in the presence of sunlight [49]. Moreover, the Fe(II) dissolution rate from goethite was markedly enhanced by oxalate (ligand) where electron transfer from oxalate to the surface Fe(III) center precedes the detachment step [36]. In addition, the oxidation of Sb(III) to Sb(V) in the presence of ferrihydrite was also reported in previous studies [43,50]. In our study, Sb(III) adsorption onto Fe hydroxides provides the major pathway for Sb(III) oxidation to Sb(V), thus dissociating Fe content into solution. It is probable that the coordination of Sb(III) to precipitated Fe increased the electron density of the incorporated Sb atom, which facilitated the oxidation process [8]. In addition, Fe(III) has higher redox potential than Sb(III) only below pH 7.5, so it has a tendency to readily oxidize Sb(III) species to Sb(V) below pH 7.5 [8]. This suggests direct reduction, subsequent to adsorption of Sb(III), or, indirectly, by electron transfer from dissolved Fe(II) ions which were generated by the Sb(III) in solution [36].
The spectroscopic techniques such as extended X-ray adsorption fine structure (EXAFS) and X-ray photon spectroscopy (XPS) in previous studies further confirm the Sb(III) oxidation onto the iron oxide and FC surfaces [13,26,28]. Similarly, X-ray adsorption near-edge structure (XANES) analysis further revealed that the aqueous solution contains Sb(V) as a dominant form [26]. Furthermore, FT-IR and XPS analysis of Fe–Mn binary oxide (FMBO) after reaction with Sb(III) reported the oxidation of Sb(III) to Sb(V) followed by the sorption mechanism on the FMBO surface [28]. In addition, investigations on coexisting As(III) and As(V) molar ratios using manganese oxide (MnO2) sorbent also showed the oxidation of As(III) followed by sorption on MnO2 surface [45]. Therefore, the FT–IR analysis in our study also suggests the Sb(III) oxidation followed by adsorption on the FC surface under different coexisting Sb(III), Sb(V) ratios which was found to be in close correlation with the aforementioned studies.
The behavior of Sb(III) and Sb(V) species under neutral pH conditions showed insignificant variation in removal efficiency and adsorption density (Figure S2A,B). Even then, under coexisting Sb proportions, the Sb species with more Sb(V) fraction showed less removal than that with a greater Sb(III) fraction. This correlated to the fact that the Sb(III) coordination with oxygen (Sb(III)/O: 0.54) has a larger spatial structure than that of Sb(V) species (Sb(V)/O: 0.51) [50]. Additionally, Sb(III) has a stronger Lewis base [8] while Sb(V) was described as antimonic acid [51]. Therefore, Sb(III) is capable of forming a coordinate bond with precipitated Fe because it has more affinity to adsorb on the FC surface. Sb(III) and precipitated Fe have equal valence, thus according to the coprecipitation law, both can anomalously incorporate with each other. Therefore, under coexisting Sb proportions, Sb(III) (even in a small fraction) can cause crystal distortion of precipitated Fe, that might cause a decrease in available active sites for Sb(V) [13]. Thus, a significant impact on removal efficiency might be observed, while removing Sb from the wastewater with high Sb(V) fraction. To better understand the reason behind the adsorption affinity of mixed Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportion, insight shedding into molecularly fine structure of Sb(III)/Sb(V) proportion with Fe(III) composite is required. In the recent study, similar behavior was reported where Sb(III) species significantly reduced the removal efficiency of Sb(V) under binary conditions [43]. Therefore, our study revealed that the antimony removal efficiency in mixed proportions decreases significantly, following the order of Sb(III)/Sb(V) as (0.9/0.1 > 0.8/0.2 > 0.5/0.5 > 0.2/0.8 > 0.1/0.9) mg/L.
4. Conclusions
Coagulation was a generally effective technique for Sb removal. Our study demonstrated the Fe solubility behavior and Sb removal under different aqueous matrices. The Fe precipitation depends upon pH and Sb species. However, Fe solubility was adversely affected by the presence of Sb(V) species at various pH ranges. The removal efficiency of Sb(III) gradually increases with pH, but Sb(V) removal was affected by highly acidic and basic conditions; while at neutral pH, Sb removal was enhanced with an increase in FC dose. Isotherm study showed that Sb(III) species have a strong adsorption potential on Fe precipitates as compared to Sb(V). Furthermore, the mixed Sb(III) and Sb(V) proportion containing a high Sb(V) fraction showed the antagonistic effect on total antimony removal. To understand this effect, FT–IR analysis was performed, which confirmed Sb(III) oxidation on the surface of Fe precipitates, which might cause adsorption sites to be less active for Sb(V), thus significantly decreasing the adsorption performance for Sb removal. The present work provides novel insights into the role of Sb (III, V) removal from aqueous solution by Fe precipitates.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/10/4/418/s1, Figure S1: Speciation of (A) Fe(III); (B) Sb(III); (C) Sb(V) in water at 25 °C. Diagrams derived by Visual MINTEQ 3.1 (http://vminteq.lwr.kth.se), Figure S2: Across various initial Sb concentrations 0.1 to 1 mg/L, neutral pH, 0.1 mM FC dose and temperature T 25 °C, (A) antimony removal (%); (B) adsorption densities (mg/g).
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Korea Environmental Industry and Technology Institute (KEITI, No. 2016000200005).
Author Contributions
Muhammad Ali Inam, Yong-Woo Lee and Ick Tae Yeom designed the study; Muhammad Ali Inam, Rizwan Khan and Du Ri Park performed the experiment and analyzed the data, and Muhammad Ali Inam wrote the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Miao, Y.; Han, F.; Pan, B.; Niu, Y.; Nie, G.; Lv, L. Antimony (V) removal from water by hydrated ferric oxides supported by calcite sand and polymeric anion exchanger. J. Environ. Sci. 2014, 26, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M.; Belzile, N.; Chen, Y.W. Antimony in the environment: A review focused on natural waters II. Relevant solution chemistry. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2002, 59, 265–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M. Removal of antimony (V) and antimony(III) from drinking water by coagulation-flocculation-sedimentation (CFS). Water Res. 2009, 43, 4327–4335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Wang, X.; Wu, F.; Fu, Z. Antimony pollution in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2012, 421–422, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mubarak, H.; Chai, L.-Y.; Mirza, N.; Yang, Z.-H.; Pervez, A.; Tariq, M.; Shaheen, S.; Mahmood, Q. Antimony (Sb)—Pollution and removal techniques—Critical assessment of technologies. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2015, 97, 1296–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, D.-J.; Liu, X.; Chen, X.; Tay, J.-H. Mechanism of enhanced Sb(V) removal from aqueous solution using chemically modified aerobic granules. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 284, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; He, M.; Lin, C.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, L. Antimony(III) oxidation and antimony(V) adsorption reactions on synthetic manganite. Chem. Erde Geochem. 2012, 72, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuz, A.-K.; Mönch, H.; Johnson, C.A. Sorption of Sb (III) and Sb (V) to goethite: Influence on Sb (III) oxidation and mobilization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 7277–7282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, H.C.; Meharg, A.A.; Bowyer, P.K.; Paton, G.I. Antimony bioavailability in mine soils. Environ. Pollut. 2003, 124, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M. Distribution and phytoavailability of antimony at an antimony mining and smelting area, Hunan, China. Environ. Geochem. Health 2007, 29, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheinost, A.C.; Rossberg, A.; Vantelon, D.; Xifra, I.; Kretzschmar, R.; Leuz, A.K.; Funke, H.; Johnson, C.A. Quantitative antimony speciation in shooting-range soils by EXAFS spectroscopy. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 2006, 70, 3299–3312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westerhoff, P.; Prapaipong, P.; Shock, E.; Hillaireau, A. Antimony leaching from polyethylene terephthalate (PET) plastic used for bottled drinking water. Water Res. 2008, 42, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.; He, M.; Guo, X.; Zhou, R. Removal of antimony (III) and antimony (V) from drinking water by ferric chloride coagulation: Competing ion effect and the mechanism analysis. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2010, 76, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiller, E.; Lalinská, B.; Chovan, M.; Jurkovič, Ľ.; Klimko, T.; Jankulár, M.; Hovorič, R.; Šottník, P.; Fľaková, R.; Ženišová, Z.; et al. Arsenic and antimony contamination of waters, stream sediments and soils in the vicinity of abandoned antimony mines in the Western Carpathians, Slovakia. Appl. Geochem. 2012, 27, 598–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritchie, V.J.; Ilgen, A.G.; Mueller, S.H.; Trainor, T.P.; Goldfarb, R.J. Mobility and chemical fate of antimony and arsenic in historic mining environments of the Kantishna Hills district, Denali National Park and Preserve, Alaska. Chem. Geol. 2013, 335, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; He, M.; Xi, J.; Lu, X. Antimony distribution and mobility in rivers around the world’s largest antimony mine of Xikuangshan, Hunan Province, China. Microchem. J. 2011, 97, 4–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungureanu, G.; Santos, S.; Boaventura, R.; Botelho, C. Arsenic and antimony in water and wastewater: Overview of removal techniques with special reference to latest advances in adsorption. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 151, 326–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Salmon, K.; DuBow, M.S. A chromosomal ars operon homologue of Pseudomonas aeruginosa confers increased resistance to arsenic and antimony in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 1998, 144, 2705–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, W.J.; Zika, R.J.; Petasne, R.G.; Fischer, A.M. Sunlight-Induced Photochemistry of Humic Substances in Natural Waters: Major Reactive Species. Adv. Chem. 1989, 219, 333–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rapant, S.; Dietzová, Z.; Cicmanová, S. Environmental and health risk assessment in abandoned mining area, Zlata Idka, Slovakia. Environ. Geol. 2006, 51, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebel, T. Aresnic and antimony: Comparative approach on mechanistic toxicology. Chem. Biol. Interact. 1997, 107, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, M.; Kim, T.; Choi, S.; Jung, J.; Song, H.; Lee, H.; Park, G.; Lim, S.; Sung, Y.; Oh, J. Investigation of Antimony in Natural Water and Leaching from Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Bottled Water. In Proceedings of the 3rd World Congress on New Technologies (NewTech’17), Rome, Italy, 6–8 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Zheng, H.; Teng, H.; Sun, Y.; Guo, J.; Xie, W.; Yang, Q.; Chen, W. Chemical coagulation process for the removal of heavy metals from water: A review. Desalination Water Treat. 2014, 57, 1733–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kamei, T.; Magara, Y. Comparing polyaluminum chloride and ferric chloride for antimony removal. Water Res. 2003, 37, 4171–4179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.-J.; Jin, C.-S.; Ren, B.-Z.; Hou, B.-L.; Hursthouse, A.S. The potential for the treatment of antimony-containing wastewater by iron-based adsorbents. Water 2017, 9, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wu, Z.; He, M.; Meng, X.; Jin, X.; Qiu, N.; Zhang, J. Adsorption of antimony onto iron oxyhydroxides: Adsorption behavior and surface structure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 276, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dou, X.; Li, J. Antimony(V) removal from water by iron-zirconium bimetal oxide: Performance and mechanism. J. Environ. Sci. 2012, 24, 1197–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wang, H.; Liu, R.; Zhao, X.; Qu, J. The mechanism of antimony(III) removal and its reactions on the surfaces of Fe-Mn Binary Oxide. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 363, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, Y.; Kang, J.; Shen, J.; Chen, Z.; Fan, L. Influence of humic acid on the removal of arsenate and arsenic by ferric chloride: Effects of pH, As/Fe ratio, initial As concentration, and co-existing solutes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2017, 24, 2381–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, J.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, B.; Sun, Y.; Wang, Q.; Guan, X. Arsenate and arsenite removal by FeCl 3: Effects of pH, As/Fe ratio, initial As concentration and co-existing solutes. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2012, 92, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, J.G.; Chen, P.Y.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M.; Liang, S. Arsenic removal by ferric chloride. J. Am. Water Work. Assoc. 1996, 88, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hering, B.J.G.; Member, A.; Chen, P.; Wilkie, J.A.; Elimelech, M. Arsenic removal from drinking water during coagulation. J. Environ. Eng. 1997, 123, 800–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Duan, J.; Liu, S.; Li, W.; Van Leeuwen, J.; Mulcahy, D. Removal of As(III) and As(V) by ferric salts coagulation - Implications of particle size and zeta potential of precipitates. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2014, 135, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; Clesceri, L.S., Greenberg, A.E., Eaton, A.D., Eds.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; ISBN 0875530478. [Google Scholar]
- Stumm, W. The Inner-Sphere Surface Complex. Aquat. Chem. 1995, 244, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinder, B.; Furrer, G.; Stumm, W. The coordination chemistry of weathering: II. Dissolution of Fe(III) oxides. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1986, 50, 1861–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, A.T.; Torrents, A.; Smolen, J.; Vasudevan, D.; Hadley, J. Adsorption of Organic Compounds Possessing Ligand Donor Groups at the Oxide/Water Interface. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1993, 27, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stumm, W. Reactivity at the mineral-water interface: Dissolution and inhibition. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 1997, 120, 143–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, T.A. Reaction of extracellular organic ligands with dissolved mental ions and mineral surfaces. Geomicrobiol. Interact. Microbes Miner. 1997, 309–344. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, S. Precipitation and Dissolution of Iron and Manganese Oxides. Environ. Catal. 2005, 61–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Kawasaki, M.; Tamada, S.; Kamei, T.; Magara, Y. Effect of pH on the removal of arsenic and antimony using reverse osmosis membranes. Desalination 2000, 131, 293–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, S.; Gupta, A.K. Arsenic adsorption onto iron oxide-coated cement (IOCC): Regression analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherm models and their optimization. Chem. Eng. J. 2006, 122, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, P.; Pichler, T. Competitive adsorption of As(III), As(V), Sb(III) and Sb(V) onto ferrihydrite in multi-component systems: Implications for mobility and distribution. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 330, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, H.; Liu, R.; Qu, J. Removal of phosphate from water by a Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 335, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, J.; Luo, J.; Song, S.; Li, Y.; Li, Q. The remarkable effect of the coexisting arsenite and arsenate species ratios on arsenic removal by manganese oxide. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 315, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.F.M.; Macedo, L.J.A.; Chaves, M.H.; Espinoza-Castañeda, M.; Merkoçi, A.; Limac, F.D.C.A.; Cantanhêde, W. Hybrid self-assembled materials constituted by ferromagnetic nanoparticles and tannic acid: A theoretical and experimental investigation. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2016, 27, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.S.; Qu, J.H.; Liu, H.J.; Liu, R.P.; Li, G.T. Removal mechanism of As(III) by a novel Fe-Mn binary oxide adsorbent: Oxidation and sorption. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 4613–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rengasamy, M.; Anbalagan, K.; Kodhaiyolii, S.; Pugalenthi, V. Castor leaf mediated synthesis of iron nanoparticles for evaluating catalytic effects in transesterification of castor oil. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 9261–9269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.X.; Wang, Y.J.; Fan, T.T.; Cui, X.D.; Zhou, D.M. Photo-induced oxidation of Sb(III) on goethite. Chemosphere 2014, 95, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauling, L. The Formulas of Antimonic Acid and the Antimonates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1933, 55, 1895–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.C.; Lockwood, P.V.; Ashley, P.M.; Tighe, M. The chemistry and behaviour of antimony in the soil environment with comparisons to arsenic: A critical review. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1169–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).