Abstract
Soil erosion is a major environmental and economic concern affecting all continents around the world. Soil loss facilitates land degradation, threatening both agricultural and natural environments in continental Europe. The overall objective of the present study is to reveal temporal changes of erosion risk in the Maritsa Basin, and also assess the temporal effects of land use and land cover changes (LULCC) on the gross erosion rate. The Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) was utilized to monitor the distribution of the erosion risk zones and soil loss in the basin. The variables were either directly derived from the satellite imagery or computed using established equations or previous studies. The dynamic parameters were categorized into two-time frames as 1990 and 2015. The results indicate that the annual average erosion rate decreased from 0.895 to 0.828 t ha−1 year−1. This reduction is within the range of modeling error, potentially originated from input data uncertainties. The most extensive changes in the gross soil loss were found in both agricultural and artificial areas, which emphasize the significance of these two classes in soil erosion models. The research summarized here enhances understanding the impacts of land use and land cover (LULC) classes on erosion intensities.
1. Introduction
In the 21st century, the erosion rate is expected to increase due to global warming and anthropogenic activities, such as land use and land cover changes (LULCC), which are associated with a more powerful hydrological cycle characterized by a higher magnitude of rainfall and more frequent occurrences of heavy precipitation [1,2]. Therefore, the dynamics of the phenomenon of erosion are identified, and important information is provided in the planning, development, and management of natural resources. The Earth surface has weathered because of its intensive usage by various civilizations since ancient times of human history has been considerably altered in the past few decades. Climate change due to anthropogenic activities such as LULCC [3] and global warming [4] might cause direct and indirect effects on soil erosion at various scales. Such natural and human-induced changes have altered the dynamics of soil erosion, thereby resulting in erosion intensity through years.
Soil erosion by water is influenced by various natural and human forces and, accordingly, has direct/indirect impacts on natural ecosystems [5,6]. In addition to the natural processes, soil erosion rates have increased above normal levels because of human alterations. Boardman, Parson, Holland and Holmes [7] emphasized the history of human disturbance (e.g., urbanization, deforestation, and tillage) has played a key role due to its impacts on soil surface conditions. Therefore, the most significant land degradation factor is human activities [8]. Both human alterations (e.g., contour farming, strip cropping, terracing, and subsurface drainage) and climate (e.g., precipitation, temperature) have been reported as significant factors controlling soil erosion [9,10,11,12].
Hydrological models enhance the understanding of soil erosion dynamics and allow for reasonable predictions and forecasting. The two most common methods (empirical and physically based) have been applied, and both existed with varying degrees of complexity in the literature. The Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE), developed by Wischmeier and Smith [13], is one of the oldest empirical methods for computing the sheet and rill erosion at basin scale. Its revised (RUSLE) and modified (MUSLE) versions have been increasingly used to evaluate soil loss in a large number of studies [14,15,16]. In the RUSLE method, the amount of erosion rate is mainly controlled by the following input parameters: rainfall erosivity (R-factor), soil erodibility (K-factor), slope length and slope steepness (LS-factor), cover management (C-factor), and conservation practices (P-factor). The factors play a key role in better understanding of the dynamics of erosion phenomena, and they are crucial for soil and water conservation practices [17,18]. Indeed, land degradation processes that affect soil fertility and cause land use restriction [19,20], which may result from dramatic changes in climate, soil characteristics, LULC, and conservation practices [21,22]. A combination of extreme natural events, such as climate issues (e.g., global warming, heavy rainfall more frequently following long dry periods) or inappropriate LULC patterns can accelerate soil erosion. An effective modeling method is required to determine the trends and current rate of erosion.
Soil erosion is one of the major environmental and economic phenomena in the Mediterranean Basin due to its climate, relief, soils, lithology, and LULC characteristics [23,24,25]. Numerous studies have examined the effects of climate change and LULCC on soil erosion [26,27,28,29]. These studies utilized various methods, generally in the ArcGIS framework. In addition, the RUSLE method has been widely used in Europe (e.g., [30]) and Turkey (e.g., [22]). The Maritsa Basin, one of the largest transboundary river basins of Eastern Europe and the Balkan Peninsula in the Mediterranean Basin, is also exposed to heavy soil erosion due to its favorable climatic and geographical characteristics. Examining the relative importance of climate, LULC and conservation practices contributes to better understanding the changing nature of soil erosion threatening both agricultural fertility and the natural environment resulting from land degradation over time. Numerous studies have used RUSLE to cover various sections of the Maritsa Basin (e.g., [31,32,33,34]); however, none directly addressed the entire basin.
The aim of this research is to enhance understanding of the relative importance of dynamic parameters, especially LULCC, on soil erosion and to monitor erosion risk zones using the RUSLE equation in the Maritsa Basin. Dynamic parameters in the simulation (e.g., rainfall erosivity, R-factor; cover management, C-factor; and conservation practices, P-factor) were divided into two time frames as in 1990 and in 2015 [12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35]. The research also aimed to determine the impacts of dynamic parameter changes on the risk of erosion at catchment scale. This study also allows for determining the intensity of gross soil loss not only in Europe, but also in its surroundings in Turkey.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
The Maritsa Basin, with an area of 53,000 km2 [36], is located within the borders of three countries (Bulgaria, Turkey, Greece) in the Mediterranean Basin. The study area (42°52′40″–40°37′20″ N; 23°35′31″–28°14′36″ E) is one of the largest transboundary river basins of the Eastern Europe and Balkan Peninsula (Figure 1).
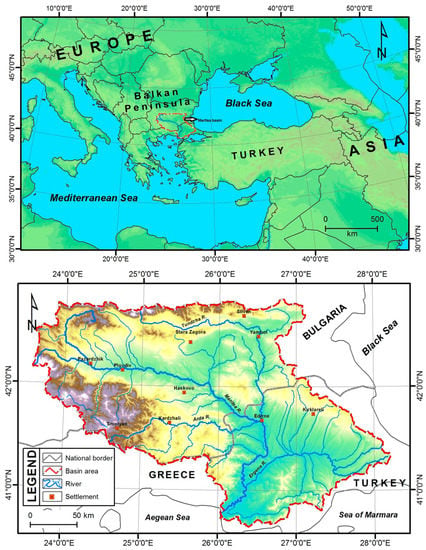
Figure 1.
Location of the Maritsa Basin and its network.
The mean annual precipitation is approximately 600 mm, and mostly occurs during winter. The Maritsa River is generally characterized by a flashy water discharge regime, meaning the stream flow rises sharply after an extreme rainfall event and then falls more gradually. Seasonally the discharge varies, with lower flows during summer and early autumn and higher flows in the winter and spring. The basin morphologically consists of alluvial plains, plateaus, and low-relief areas ranging from 0 to 2883 m in altitude. In the studied basin, the widespread soil types are Alfisol, Entisol, Inceptisol, Mollisol and Vertisol according to soil taxonomy by Soil Atlas of Europe. The climatic and geographical features of the Maritsa Basin cause frequent floods and heavy soil erosion [37]. Soil erosion by water threatens both agriculture and the natural environment by causing land degradation over time [38,39]. Erosion is a natural phenomenon causing environmental and economic consequences in the Eastern Europe and Balkan Peninsula, as well. Hence, the European Commission’s Soil Thematic Strategy has defined soil erosion as a significant problem and monitored soil erosion in Europe [30]. It is very significant to determine the changing nature of soil erosion, and predict the trends of soil erosion in the future, and take precautions, accordingly.
2.2. Methodology
Due to limited funding, most developing countries cannot finance many complex field measurements and spatial data requirements for spatial analysis. Therefore, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and RUSLE have become widely accepted conservation-planning tools throughout the world because the approach is user-friendly and applicable for a basin with limited data. This method has been reported by various researchers [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40], who applied the following equation:
where E is the annual average soil loss (t ha−1 year−1), R the rainfall erosivity factor (MJ mm ha−1 h−1 year−1), K the soil erodibility factor (t ha h ha−1 MJ−1 mm−1), LS the slope length and slope steepness factor (dimensionless), C the cover management factor (dimensionless), and P the conservation practices factor (dimensionless).
During the simulation, the RUSLE method was used in two time steps in the years 1990 and 2015, which were relatively assigned in the dynamic parameters (Figure 2). In fact, the LS-factor and K-factor controlling erosion in the RUSLE method are more constant factors through years, while the R-factor, C-factor, and P-factor are more dynamic parameters [15].
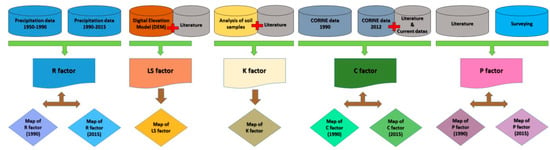
Figure 2.
Demonstration of the RUSLE input data.
2.2.1. Rainfall Erosivity Factor (R-Factor)
The R-factor represents a meteorological factor determining potential erosive forces of rainfall, making it a critical input parameter in the RUSLE method. The R values were usually obtained from the long-term average meteorological data as a product of total storm energy [15]. In the present study, R-factor values were separately calculated using the long-term monthly rainfall values for 1950–1990 and 1991–2015 from the meteorological stations in the basin (Figure 3), and the results were compared with the studies by Panagos et al. [41] and Ballabio [42]. The following equation, proposed by Wischmeier and Smith [43] and revised by Arnoldus [44], was assigned to compute the R-factor:
where R is rainfall erosivity measured in MJ mm ha−1 h−1 year−1, and Pi and P are monthly and annual rainfall in millimeters. The interpolation technique of Inverse Distance Weighted (IDW) was utilized for the values obtained from the above equations [45], and the maps of R-factors were also generated based on average meteorological data mentioned above.
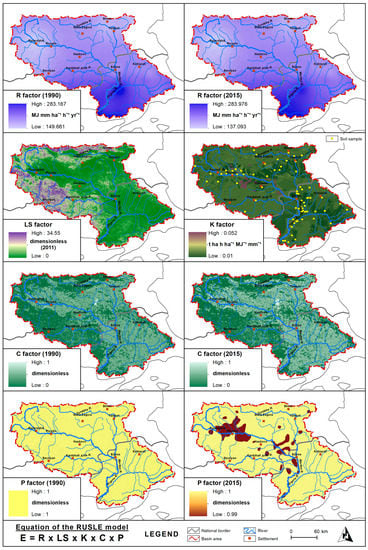
Figure 3.
Spatiotemporal distribution of input parameters in RUSLE.
2.2.2. Soil Erodibility Factor (K-Factor)
The K-factor represents the relationship among annual average soil loss, hydraulic processes, and sediment transportability under ordinary soil conditions. The relationship between annual average soil loss and hydraulic processes is associated with the infiltration rate during storm events. In this study, the K-factor was estimated by combining the results of previous studies, utilizing the following equation developed by Wischmeier and Smith [43] and Renard et al. [15] based on the statistics of soil samples from various parts of the basin [46,47,48]. We have randomly taken General Directorate of State Hydraulic in the entire basin shown in Figure 3. These samples were initially compared with the maps of Soil Geographical Database of Eurasia and Turkey, and then the K-factor map was generated by using ArcGIS. Due to the widespread usage in soil studies [49], IDW method was utilized to avoid incompatibility of R-factor and K-factor maps.
where m is (silt (%)) + (very fine sand (%)) (100 − clay (%)); a is organic matter (%); b is structure code; and c is the profile permeability code.
2.2.3. Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS-Factor)
The LS-factor in RUSLE reflects the ratio of gross soil loss under given conditions with respect to slope length (L-factor) and slope steepness (S-factor). Although the most accurate values of the LS-factor can be observed from field work, the traditional method is not cost-effective. Therefore, LS-factor values were computed from SRTM DEM data (2011) at 90 m resolution in the present study [50]. The computational process was done based on the following equation proposed by Moore, Burch [51] and Moore, Grayson, Ladson [52]:
where LS is the topographic factor; A is the product of flow accumulation and cell size; Q is the slope in degrees.
2.2.4. Cover Management Factor (C-factor)
In RUSLE, the relative impacts of human applications are mainly considered through the C-factor, representing the effects of LULC and roughness to gross soil loss. A protective vegetation layer assists in stabilizing topsoil, thereby preventing soil degradation. The places where vegetation is scarce tend to have higher C values, so the places without a mature vegetation layer are potentially more susceptible to soil erosion. In the present study, the C-factor was derived from the LULC datasets of the CORINE Land Cover (CLC) system, and then the values were determined based on both previous studies and observations/field studies for the years of 1990 and 2012 (Figure 3). However, the LULC data for 2012 were revised according to the database presented by Panagos et al. [53], and then the C-factor values were obtained for the year 2015.
2.2.5. Land Support Practice Factor (P-factor)
The support practice (P-factor) represents the effects of conservation practices corresponding to the average annual erosion rate. P-factor values for the year 1990 were assigned 1 due to the lack of conservation practices, as reported in various studies [54]; the p value of 2015 was estimated based on the previous study [55] and field works (Figure 3). All input data of the model were fixed at a resolution of 100 m by using the framework of the grid-based method in the ArcGIS software. Thus, a standard data scale for input factors was established, and a map in the same scale with the European Union [30] was obtained. Then erosion risk maps were generated for the years 1990 and 2015, separately. These maps have been categorized based on a study by Panagos et al. [30] using a similar method of erosion risk classification at the European continental scale. The results thus obtained were compared to the rest of Europe.
3. Results and Discussion
The dynamic parameters (rainfall erosivity, cover-management and conservation practices) have been mapped on the basis of similar time frame in 1990 and 2015 since the changes in these input parameters are also capable of altering the rate of soil water erosion. However, the LS-factor and K-factor are represented as a single map because of not being dynamic through years. As shown in Figure 3, a higher magnitude of LS-factor was obtained at the north-western boundary of the catchment. Higher differentiations in soil classes and widespread conservation practices have been observed along the mainstream channel. The periods of 1950–1990 and 1991–2015 were merely used for R-factor values, and the results represented an increase between 1990 and 2015 with the values of 186.8 and 194.5 MJ mm ha−1 h−1 year−1, respectively. The raised R-factor values potentially increased the risk of soil erosion, rather than a decrease in the catchment. Therefore, the areas with the higher magnitude of R-factors enlarged from 1990 to 2015. In the most recent time frame, more vulnerable R-factor values to soil erosion risk spatially dominated at the middle and lower portions of the catchment. The C-factor values spatiotemporally varied due to LULCC in the entire basin, such as the higher magnitude of the values were widespread along the valley plains in 1990, and then inclined to spread around the plains, mainly used for settlement and agricultural purposes, in the year 2015. Nevertheless, the values, relatively higher in the plateau and mountainous areas, tended to decrease, resulting from the spatial expansion in forests and semi-natural areas. In terms of wetlands and water, a reduction in the soil erosion risk was expected since the cover management factor values for these LULC classes have typically shown an increasing trend over the years.
The resulting maps illustrate positive growth on artificial surfaces, water bodies, forests; negative growth in agricultural areas and wetlands (Table 1; Figure 4). An explosive population growth and industrialization, construction of new dams, and afforestation practices led to an increase in these three types of LULC classes. The construction of new dams in a different portion of the basin and the establishment of new forest areas due to afforestation practices have brought to the forefront spatial growth on forests and water bodies. The highest rate of change was seen due to downsizing agricultural areas, while artificial surfaces were trended toward growth, which indicated that approximately 353.62 km2 of the basin area has been changed from cultivated areas to non-cultivated areas. Agricultural land settlements and fragmentation through inheritance also triggered spatial downsizing in agricultural areas. Moreover, draining wetlands for the purposes of urbanization and cultivation have contributed to reducing wetlands.

Table 1.
The list of LULC classes according to CORINE Land Cover (CLC).
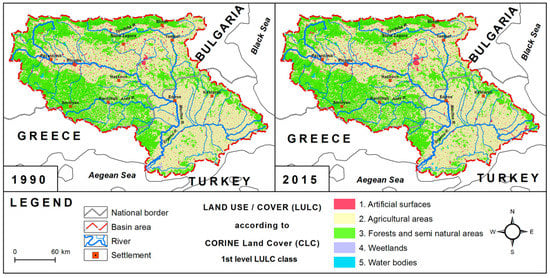
Figure 4.
The map of LULC classes according to CORINE Land Cover (CLC).
In order to obtain a higher accuracy for the C values, CORINE: 3rd level was taken into consideration; however, CORINE: 1st level LULC classes were utilized while drawing resulting maps in the purpose of more visual and understandable demonstration. Thus, the spatial changes of C-factors were computed in more detail as a result of CORINE: 3rd level LULC classes; the erosion risk maps more explicitly illustrated, as well. Hence, some negligible values were assigned to the non-erosion-prone land surfaces consisting of artificial area, wetlands and water bodies. The other reason assigning minimal C-factor values for non-erosion-prone areas was to optimize intercorrelation for each LULC classes. The C-factors, especially in artificial surfaces, wetlands and water bodies, found ineffective, but artificial surfaces had relatively low impacts on annual average soil loss.
The areas with extensive erosion are mainly located on steep slopes with a lack of protective vegetation cover or an existing vegetation layer is not capable of preserving the topsoil from scouring. Figure 5 represents severe soil erosion prone areas with varying land cover characteristics. A meaningful variation in native vegetation, especially on steeper slope, contributes receiving the higher variation of the soil loss in the studied region. As shown in the figure higher gradient slopes with sparse vegetation potentially increase soil loss as runoff can flow down more sediment at the higher energy level. The other regions with slightly higher vegetation density are supposedly less prone to soil erosion because an existing vegetation layer is capable of preserving topsoil from scouring. Furthermore, the pictures were taken from the various portion of the basin present variability in climate and native vegetation, which can also be associated with the spatial distribution of R-factor values.
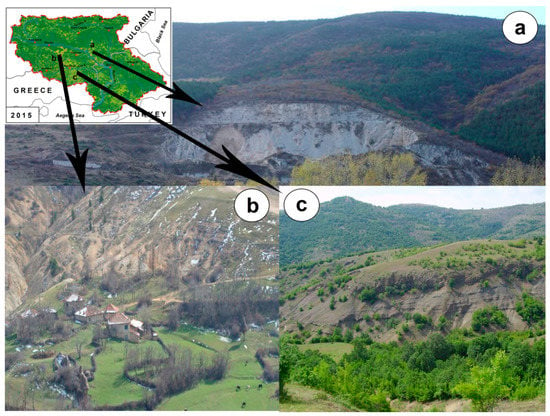
Figure 5.
Severe soil erosion-prone areas in the Maritsa Basin, illustrating the region with (a) higher vegetation density is supposedly less prone; (b) sparse vegetation density is supposed more prone; (c) moderate vegetation density is proposed as moderately susceptible to soil erosion.
In recent years, climate, especially precipitation, has shown a slight upward trend similar to the world’s river basins [62]. Numerous studies have already addressed the probable impacts of climate change to soil erosion [63,64,65]. The statistics demonstrate that the changes in precipitation are limited, but a notable rise in the annual minimum/maximum, and total annual precipitation was found during the period of 1991–2015 compared to 1950–1990 period. Furthermore, the statistics for the period of 1991–2015 represents alike symmetrical distribution, while the annual precipitation values in the period of 1950–1990 is more negatively skewed (Figure 6). As seen in the figure, the tail of 1950-1990 is longer on the left, which is related to deviations in the precipitation regime since rainfall has more recently become characteristic of the form of heavy storm events [66,67,68]. The deviation in the precipitation regime also reflects that the intensity of the erosion through recent catastrophic rainfall has been increasing even more.
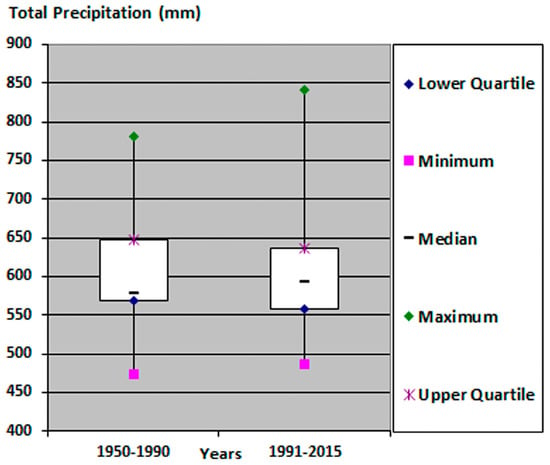
Figure 6.
Boxplots showing the variation of relative change in annual precipitation, compared with historical the 1950–1990 and 1991–2015 periods in the Maritsa Basin.
The last dynamic erosion factor observed in the Maritsa Basin is conservation practices (P-factor). It should be noted here that no conservation practices were applied prior to 1990; however, various effective assessments of soil conservation measures had been performed by 2015 [50]. These measures include identifying and implementing procedures to ensure public participation in solving the problem of overgrazing, the proper usage of land, and practices aimed to reduce the erosion rate by establishing an approach to existing plant cover, strip cropping, terracing, cultivating, and erosion-related practices [69]. However, conservation practices have already been shown not adequate enough using regularly and systematic ally throughout the basin [22].
As result of the RUSLE simulation, the annual gross soil loss rates were 0.585 and 0.589 t ha−1 year−1 in the year 1990 and 2015, respectively, for the entire basin (Table 2). The table also exhibits the mean suspended sediment load values, obtained from the General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works (DSI) at the downstream portion of the Maritsa Basin, Turkey, were 0.04 t ha−1 year−1 in 1990 and 0.03 t ha−1 year−1 in 2015 [70]. The main goal of suspended sediment load demonstration in the figure is to make a comparison between the statistics obtained from RUSLE and observed sediment load. The magnitude and percentage uncertainty of RUSLE can lead to a decrease in soil erosion on account of being likely within the range of uncertainty. These uncertainties might have resulted from data uncertainties (e.g., missing values, measurement errors, and coarse resolution imageries), model uncertainties (e.g., algorithmic/numerical, parameter, structural uncertainty), and stochastic nature of soil erosion processes [71]. The main source of uncertainty in this study was possibly associated with data uncertainties depending on coarse resolution imageries.

Table 2.
The mean annual soil loss and suspended sediment load in 1990 and 2015.
During 1990 and 2015, the most extensive erosion rates were observed in agricultural, with the soil loss rate of 1.35 and 1.23 t ha−1 year−1, respectively. Besides, a variation in the temporal distribution of soil erosion was limited among each LULC classes. However, a notable change in the rate of soil loss was observed not only in agricultural areas but also in artificial surfaces, which can be interpreted as these two classes have more critical impacts on monitoring gross soil loss by RUSLE method. Contrarily, the soil loss rate in wetlands and water bodies remain constant with the values of 0.001 and 0.003 t ha−1 year−1, respectively (Table 3). The wetlands and water bodies are the categories, less responsive to gross soil loss comparing to artificial surface, as the soil loss rate in these two categories remain constant between 1990 and 2015, even if the rate of LULCC varied −0.04 and +0.18, respectively (Table 1, Table 3). As mentioned earlier no significant change of rainfall regime was observed over time; however, increase of artificial areas (e.g., roads, contractions) potentially generate a higher amount of runoff mainly in densely populated areas. In addition, the amount of suspended sediment load decreased during the second time period. The reason receiving a lower amount of suspended sediment load might be new dam constructions since river’s total sediment load have been captured along the reservoir bottom. Despite a decrease in the area of agricultural lands, lower soil erosion rate received because of being a widespread usage of intensive agricultural techniques. Hereby, the weighted average annual soil loss of 0.895 in 1990 and 0.828 in 2015 was computed from each LULC classes shown in Table 3.

Table 3.
The average annual soil loss for each LULC classes and weighted averages in 1990 and 2015.
The minimum and maximum of the annual average erosion rate was 0–912 and 0–960 t ha−1 year−1 in 1990 and in 2015, respectively. The criteria, followed to establish the soil loss limit for each class, were also determined based on the study conducted by Panagos et al. [55]. Thus, the results of this study can be compared to the rest of Europe. A slight decreasing trend was observed in the low, moderate, very high, and extremely high erosion risk classes, ranging from −0.01% to −0.11%. In contrast, the change rates of negligible, very low, and high erosion risk classes increased by +0.14%, +0.02%, and +0.03%, respectively (Table 4; Figure 7). A downward trend in the erosion risk classes, considered as the very high and extreme category, potentially reduced the rate of extensive erosion in recent times.

Table 4.
Spatial distribution of soil loss, erosion risk classes and the erosion rates in 1990 and 2015.
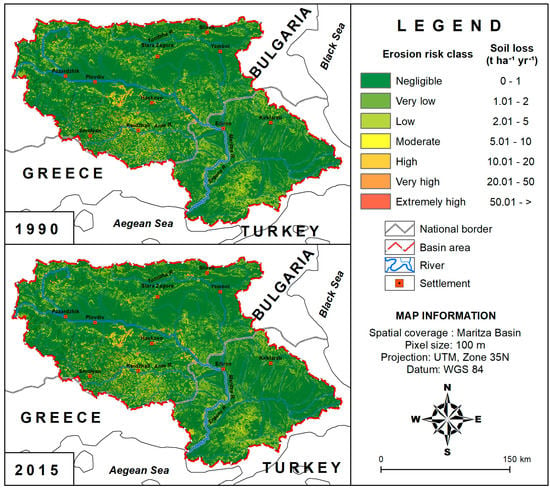
Figure 7.
Map of soil loss rates in the Maritsa Basin based on RUSLE.
In previous decades, the main factors controlling the natural environment have been anthropogenic activities in the Maritsa Basin [72]. As a result, similar effects have also been seen on erosion dynamics in the basin, and some controlling factors have been changed under the control of anthropogenic activities. The variation of soil erosion may also have had a positive effect on the sustainable conservation and utilization balance of topsoil. In addition, the mean annual rate of soil loss was found substantially lower than the average values of Europe (2.46 t ha−1 year−1), including Bulgaria (2.05 t ha−1 year−1), Greece (4.13 t ha−1 year−1) [55], and Turkey (6.14 t ha−1 year−1) [73]. This should be due to the fact that the factors affecting erosion (natural factors, use of land and planning factors, and socio-economic factors) and dynamic factors are taken into account during the implementation phase of the method vary within the basin, as well. Similar results have been found in previous studies [74,75].
4. Conclusions
This study assesses the impact of LULC on soil erosion by applying the RUSLE in the Maritsa Basin. The map of LULC illustrates positive growth on artificial surfaces, water bodies, and forests, which has resulted in an explosive population growth and industrialization, the construction of new dams, and afforestation practices. A negative growth has also been observed in agricultural areas and wetlands due to agricultural land settlements, fragmentation through inheritance and draining wetlands for the purposes of urbanization and cultivation. In addition, a change in rainfall regime is was limited depending on more frequent cyclic variations in precipitation during the second time period. In all regions, conservation practices have been used more extensively in 2015 even in some humid regions. The results indicate that the annual average erosion rate reduced from 0.895 to 0.828 t ha−1 year−1 in 1990 and in 2015, respectively. The most extensive erosion rates were observed in both agricultural and artificial areas, with the soil loss rate of 1.23 and 0.88 t ha−1 year−1, respectively. During 1990 and 2015, notable changes in the rate of soil loss were observed in agricultural areas, which could be interpreted as the cultivated lands have more critical impacts on the results of the RUSLE method. Monitoring erosion risk zones for an extensive heterogeneous area during different time frames enhances understand to the dynamics of soil erosion and allows for an acceptable prediction and forecasting. In future studies, the erosion models can also be practiced in accordance with the climate change scenarios, especially for an efficient erosion management practice.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Peter Nojarov, Svetla Rousseva, and Vijith Hamza for their essential role in the process of data collection and determining an appropriate methodology. We would also thank to Mehdi Ahmadi for sharing his valuable thoughts on R factor computational process. The anonymous reviewers and the editor will be also thanked for providing insightful and detailed reviews to greatly improve the manuscript.
Author Contributions
Emre Ozsahin carried out data collection, field investigations, model simulations; Emre Ozsahin and Umit Duru developed the methodology, organized the model results into figures and tables. Ilker Eroglu not only performed climate analyses, but also provide precious discussions in the model outputs; Umit Duru translated the manuscript in English and carried out manuscript revision.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Panagos, P.; Karydas, C.G.; Gitas, I.Z.; Montanarella, L. Monthly soil erosion monitoring based on remotely sensed biophysical parameters: A case study in Strymonas river basin towards a functional pan-European service. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2012, 5, 461–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Yu, B.; Klik, A.; Lim, K.J.; Yang, J.E.; Ni, J.; Miao, C.; Chattopadhyay, N.; et al. Global rainfall erosivity assessment based on high-temporal resolution rainfall records. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konukçu, F.; Albut, S.; Altürk, B. Land use/land cover change modelling of Ergene River Basin in western Turkey using CORINE land use/land cover data. Agron. Res. 2017, 15, 435–443. [Google Scholar]
- Nojarov, P. Circulation factors affecting precipitation over Bulgaria. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2017, 127, 87–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leh, M.; Bajwa, S.; Chaubey, I. Impact of land use change on erosion risk: An integrated remote sensing, geopraphic information system and modeling methodology. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erol, A.; Koşkan, Ö.; Başaran, M.A. Socioeconomic modifications of the universal soil loss equation. Solid Earth 2015, 6, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.; Parson, A.J.; Holland, R.; Holmes, P.J.; Washington, R. Development of badlands and gullies in the Sneeuberg, Great Karoo, South Africa. Catena 2003, 50, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, G.L.; Fan, J. Reservoir Sedimentation Handbook; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, X.C.; Liu, W.Z.; Zheng, F.L. Simulating site-specific impacts of climate change on soil erosion and surface hydrology in southern Loess Plateau of China. Catena 2009, 79, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Tiwari, K.; Bhadoria, P.B.S. Effect of land use land cover change on soil erosion potential in an agricultural watershed. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2011, 173, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quan, B.; Romkens, M.; Li, R.; Wang, F.; Chen, J. Effect of land use and land cover change on soil erosion and the spatio-temporal variation in Liupan Mountain Region, southern Ningxia, China. Front. Environ. Sci. Eng. 2011, 5, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare, M.; Mohammady, M.; Pradha, N.B. Modeling the effect of land use and climate change scenarios on future soil loss rate in Kasilian watershed of northern Iran. Environ. Earth Sci. 2017, 76, 305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains; Agriculture Handbook No. 282; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Williams, J.R. Sediment Yield Prediction with Universal Equation Using Runoff Energy Factor; Present & Prospective Technology for Predicting Sediment Yield and Sources ARS-S-40; United States Department of Agriculture (USDA): Washington, DC, USA, 1975.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook No. 703; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Lee, G.S.; Lee, K.H. Scaling effect for estimating soil loss in the RUSLE model using remotely sensed geospatial data in Korea. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2006, 3, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmati, O.; Tahmasebipour, N.; Haghizadeh, A.; Pourghasemi, H.R.; Feizizadeh, B. Evaluating the influence of geo-environmental factors on gully erosion in a semi-arid region of Iran: An integrated framework. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 913–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayas, A.; Vanwalleghem, T.; Laguna, A.; Peña, A.; Giráldez, J.V. Reconstructing long-term gully dynamics in Mediterranean agricultural areas. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gessesse, B.; Bewket, W.; Bràuning, A. Model-based characterization and monitoring of runoff and soil erosion in response to land use/land cover changes in the Modjo watershed, Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2015, 26, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selkimäki, M.; González-Olabarria, J.R. Assessing gully erosion occurrence in forest lands in Catalonia (Spain). Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.P.; Damsawasdi, R. Sensitivity analysis of soil erosion on impacts of land use landcover change in Phewa watershed. Int. J. Curr. Eng. Technol. 2014, 4, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Özşahin, E. Ergene Havzasında (Trakya) arazi kullanımı ve arazi örtüsü değişikliklerinin erozyon üzerine etkileri. Anadolu Tarım Bilim. Derg. 2016, 31, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Casasnovas, J.A.; Anto’n-Ferna’ndez, C.; Ramos, M.C. Sediment production in large gullies of the Mediterranean area (NE Spain) from high-resolution digital elevation models and geographical information systems analysis. Earth Surf. Process. Landf. 2003, 28, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.C.; Nearing, M.A. Impact of climate change on soil erosion, runoff, and wheat productivity in central Oklohoma. Catena 2005, 61, 185–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boardman, J.B. Damage to property by runoff from agricultural land, South Downs, southern England 1976–1993. Geogr. J. 1995, 161, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.; Nearing, M.A.; Nicks, A.; Skidmore, E.; Valentine, C.; King, K.; Savabi, R. Using soil erosion models for global change studies. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 381–385. [Google Scholar]
- Van-Oost, K.; Grovers, G.; Desmet, P.J.J. Evaluating the effects of changes in landscape structure on soil erosion by water and tillage. Landsc. Ecol. 2000, 15, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nearing, M.A. Potential changes in rainfall erosivity in the U.S. with climate change during the 21st century. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2001, 56, 229–232. [Google Scholar]
- Poesem, J.; Nachtergaele, J.; Verstraeten, G.; Valentin, C. Gully erosion and environmental change: Impartoance and research needs. Catena 2003, 50, 91–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseva, S. Factors and rates of soil erosion in the Balkan Peninsula. In Proceedings of the International Conference “Ecology—Interdisciplinary Science and Practice”, Sofia, Bulgaria, 25–26 October 2012; pp. 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Milevski, I.; Ivanova, E. Erosion potential modeling of the territory of municipalities Pehchevo and Simitli using Remote Sensing data. In Proceedings of the Safety SES-2013 from the Conference Space, Ecology, Sofia, Bulgaria, 20–22 November 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blinkov, I. The Balkans: The most erosive part of Europe? Glas. Sumar. Fak. 2015, 111, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseva, S.; Malinov, I.; Stefanova, V. Soil erosion risk assessments using GIS technologies—Bulgarian experience. Bulg. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 22, 205–208. [Google Scholar]
- Ziyan, Y.; Lijuan, Z.; Shihao, T.; Xiaxiang, L.; Tiantian, H. The basic characteristics and spatial pattern of global cultivated land change since the 1980s. J. Geogr. Sci. 2017, 27, 771–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibaroglu, A. Meriç nehir havzası sınıraşan su politikalari. In Proceedings of the 5. Dünya Su Forumu Türkiye Bölgesel Su Toplantıları, Taşkın Konferansı Bildiri Kitabı, Edirne, Türkiye, 7–8 August 2008; pp. 1–11. (In Turkish). [Google Scholar]
- Artinyan, E.; Habets, F.; Noilhan, J.; Ledoux, E.; Dimitrov, D.; Martin, E.; Le Moigne, P. Modelling the water budget and the riverflows of the Maritsa basin in Bulgaria. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 21–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldız, D.; Özbay, Ö.; Yıldırım, E.; Çakmak, C.; Soylu, N. Meriç Havzasında Uluslararası su Yönetimi; Rapor No: 2; Hydropolitics Academy: Ankara, Turkey, 2014. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Özdemir, N.; Öztürk, E.; Kop, Ö.T.; Ekberli, İ. Effects of organic and inorganic amendments on soil erodibility. Eurasian J. Soil Sci. 2015, 4, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H. Use and misuse of the universal soil loss equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1978, 31, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Klik, A.; Rousseva, S.; Tadić, P.M.; Michaelides, S.; Hrabalíková, M.; Olsen, P.; et al. Rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 801–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ballabio, C. Mapping monthly rainfall erosivity in Europe. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 579, 1298–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No: 537; USDA: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Arnoldus, H.M.J. An approximation of the rainfall factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In Assessment of Erosion; De Boodt, M., Gabriels, D., Eds.; Chichester: New York, NY, USA, 1980; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Vijith, H.; Seling, L.W.; Dodge-Wan, D. Estimation of soil loss and identification of erosion risk zones in a forested region in Sarawak, Malaysia, northern Borneo. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2017, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doğan, O.; Küçükçakar, N.; Cebel, H.; Akgül, S. Türkiye Büyük Toprakları “K” Faktörleri; Köy Hizmetleri Genel Müdürlüğü Araştırma Enstitüsü Müdürlüğü Yayınları: Ankara, Turkey, 2000. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Rousseva, S.; Stefanova, V. Assessment and mapping of soil erodibility and rainfall erosivity in Bulgaria. In Proceedings of the BALWOIS 2006 Conference on Water Observation and Information System for Decision Support, Ohrid, Republic of Macedonia, 23–26 May 2006; pp. 28–29. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Borrelli, P.; Alewell, C. Soil erodibility in Europe: A high-resolution dataset based on LUCAS. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 479–480, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tunçay, T.; Bayramin, I.; Atalay, F.; Unver, I. Assessment of inverse distance weighting (IDW) interpolation on spatial variability of selected soil properties in the Cukurova Plain. J. Agric. Sci. 2016, 22, 377–384. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-Factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Physical basis of the length slope factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 1986, 50, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Grayson, R.B.; Ladson, A.R. Digital Terrain modelling: A review of hydrological, geomorphological, and biological applications. Hydrol. Process. 1991, 5, 3–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, C.; Alewell, C.; Lugato, E.; Montanarella, L. Estimating the soil erosion cover-management factor at European scale. Land Use Policy 2015, 48C, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; Porter, J.P. RUSLE: Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1991, 46, 30–33. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; van der Zanden, E.H.; Poesen, J.; Alewell, C. Modelling the effect of support practices (P-factor) on the reduction of soil erosion by water at European Scale. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 51, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, M.M.; Govers, G.; Doorn, A.; Quetier, F.; Chouvardas, D.; Rounsevell, M. The response of soil erosion and sediment export to land-use change in four areas of Europe: The importance of landscape pattern. Geomorphology 2008, 98, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigalos, G.; Loukaidi, V.; Dasaklis, S.; Alexouli, L.A. Assessment of the quantity of the material transported downstream of Sperchios River, Central Greece. In Proceedings of the 12th International Congress, Bulletin of the Geological Society of Greece, Patras, Greece, 19–22 May 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, V.; Samora-Arvela, A.; Panagopoulos, T. Soil erosion vulnerability under scenarios of climate land-use changes after the development of a large reservoir in a semi-arid area. J. Environ. Plan. Manag. 2016, 59, 1238–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, C.; Rigo, D.; Dewitte, O.; Poesen, J.; Panagos, P. Modelling soil erosion at European scale: Towards harmonization and reproducibility. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rulli, M.C.; Offeddu, L.; Santini, M. Modeling post-fire water erosion mitigation strategies. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 2323–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijith, H.; Seling, L.W.; Dodge-Wan, D. Effect of cover management factor in quantification of soil loss: Case study of Sungai Akah subwatershed, Baram River basin Sarawak, Malaysia. Geocarto Int. 2017, 33, 505–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.A.; Kumar, P.; Kakosimos, K.E. Flux estimation of fugitive particulate matter emissions from loose Calcisols at construction sites. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 141, 96–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, M.; Nearing, M.A.; Vining, R.; Southworth, J.; Pfeifer, A. Climate change impacts on soil erosion in Midwest United States with changes in crop management. Catena 2005, 61, 165–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litschert, S.E.; Theobald, D.M.; Brown, T.C. Effects of climate change and wildfire on soil loss in the southern Rockies Ecoregion. Catena 2014, 118, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; He, C.; Burnham, M.; Zhang, L. Evaluating the coupling effects of climate aridity and vegetation restoration on soil erosion over the Loess Plateau in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 539, 439–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavalle, C.; Micale, F.; Houston, T.D.; Camia, A.; Hiederer, R.; Lazar, C.; Conte, C.; Amatulli, G.; Genovese, G. Climate change in Europe. 3. Impact on agriculture and forestry. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2009, 29, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radeva, S.; Alexandrov, V. Climate variability and change over the Balkan Peninsula and related impacts on sunflower. In Climate Variability, Modeling Tools and Agricultural Decision-Making; Utset, A., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Nikulin, G.; Kjellström, E.; Hansson, U.; Strandberg, G.; Ullerstig, A. Evaluation and future projections of temperature, precipitation and wind extremes over Europe in an ensemble of regional climate simulations. Tellus 2011, 63, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoinova, V.; Rousseva, S.; Malinov, I. Geographic information system for land capability evaluation and mapping supporting erosion preventive land use. In Proceedings of the Second European SCGIS Conference, “Conservation of Natural and Cultural Heritage for Sustainable Development: GIS-Based Approach”, Sofia, Bulgaria, 24 September 2003. [Google Scholar]
- The General Directorate of State Hydraulic Works. Suspended Sediment Data for Surface Water in Turkey; DSI: Ankara, Turkey, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Swarnkar, S.; Malini, A.; Tripathi, S.; Sinha, R. Assessment of uncertainties in soil erosion and sediment yield estiamtes at ungauged basins: An application to the Garra River basin, India. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokatli, C. Assessment of the water quality in the Meriç river: As an element of ecosystem in the Thrace region of Turkey. Polish J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 24, 2205–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- İrvem, A.; Topaloglu, F.; Uygur, V. Estimating spatial distribution of soil loss over Seyhan river basin in Turkey. J. Hydrol. 2007, 336, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkal, T.; Yıldırım, Ü. Soil erosion risk assessment in the Sincanlı Sub-Watershed of the Akarçay Basin (Afyonkarahisar, Turkey) using the Universal Soil Loss Equation (USLE). Ekoloji 2012, 21, 18–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özşahin, E.; Atasoy, A. Soil erosion estimation in Lower Asi River catchment using GIS. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2013, 120, 730–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).