Preliminary Numerical Analysis of the Efficiency of a Central Lake Reservoir in Enhancing the Flood and Drought Resistance of Dongting Lake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model Description
2.1. Numerical Methods
2.2. Model Validation
3. Results and Discussion
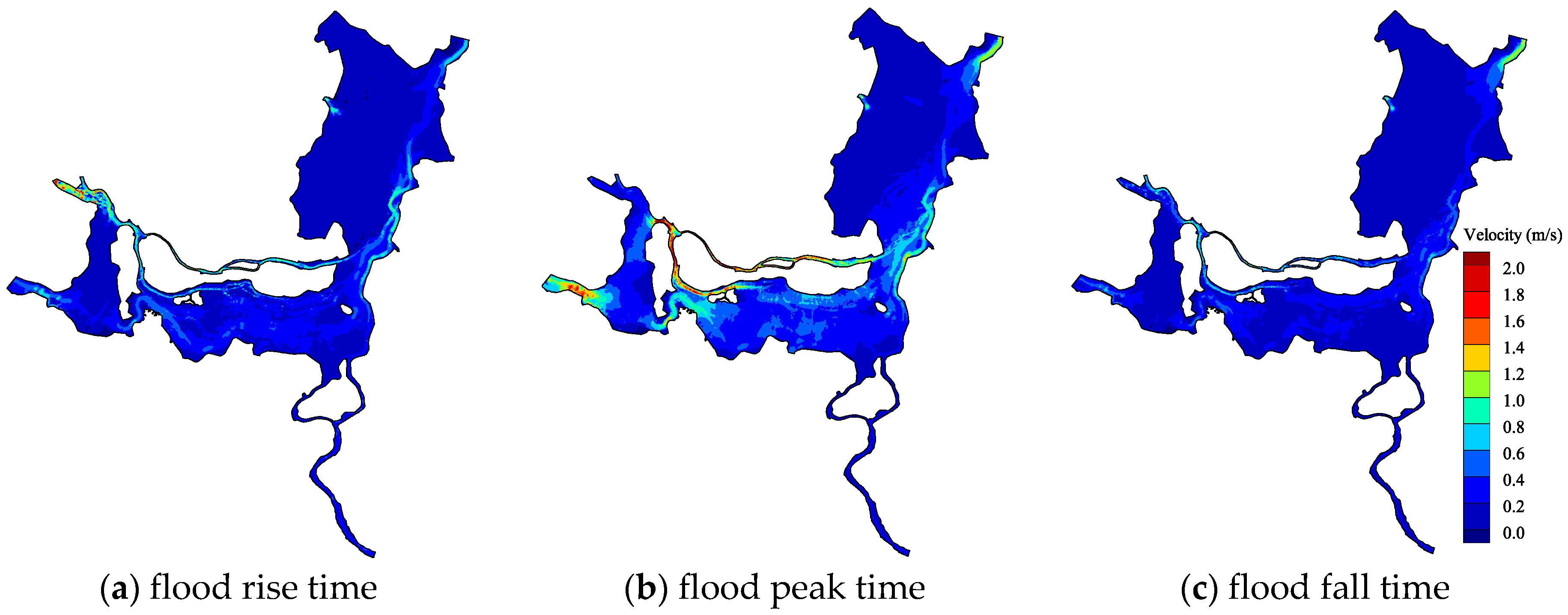
3.1. The Central Lake Reservoir Effect
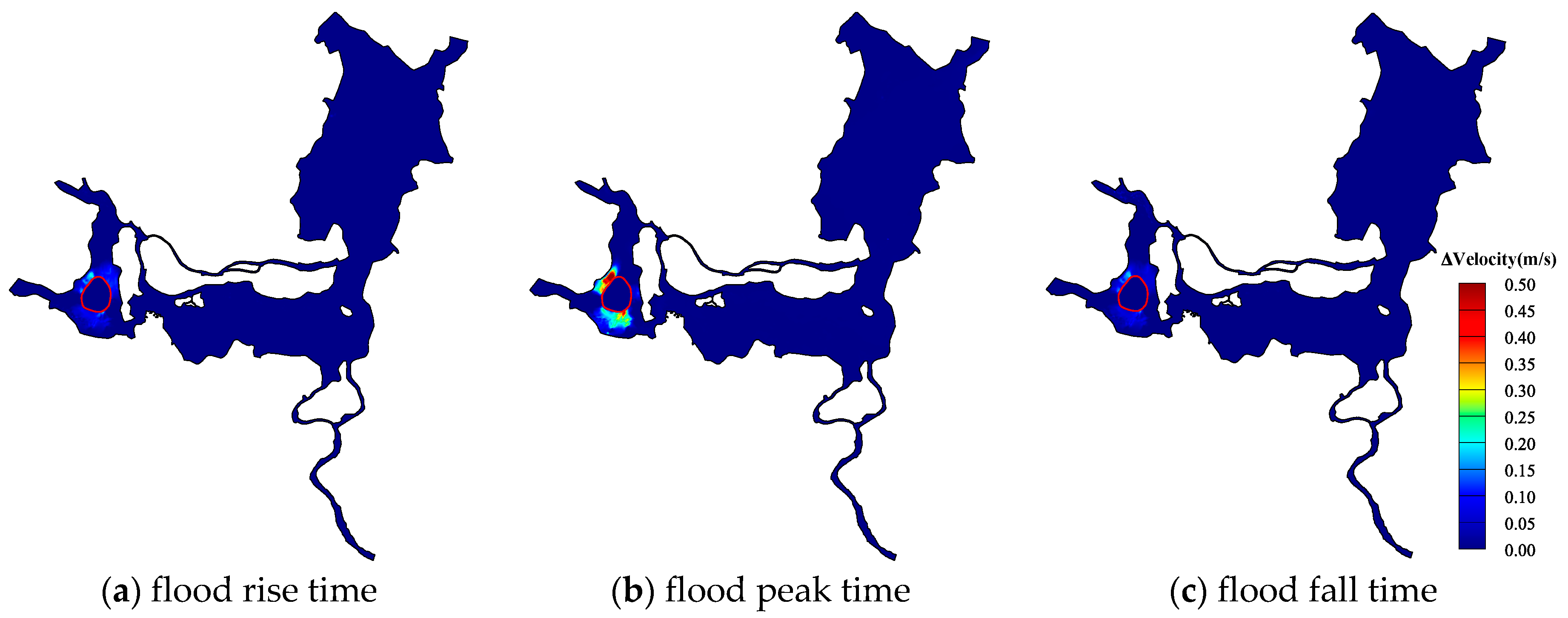
3.2. Flood Resistance Analysis
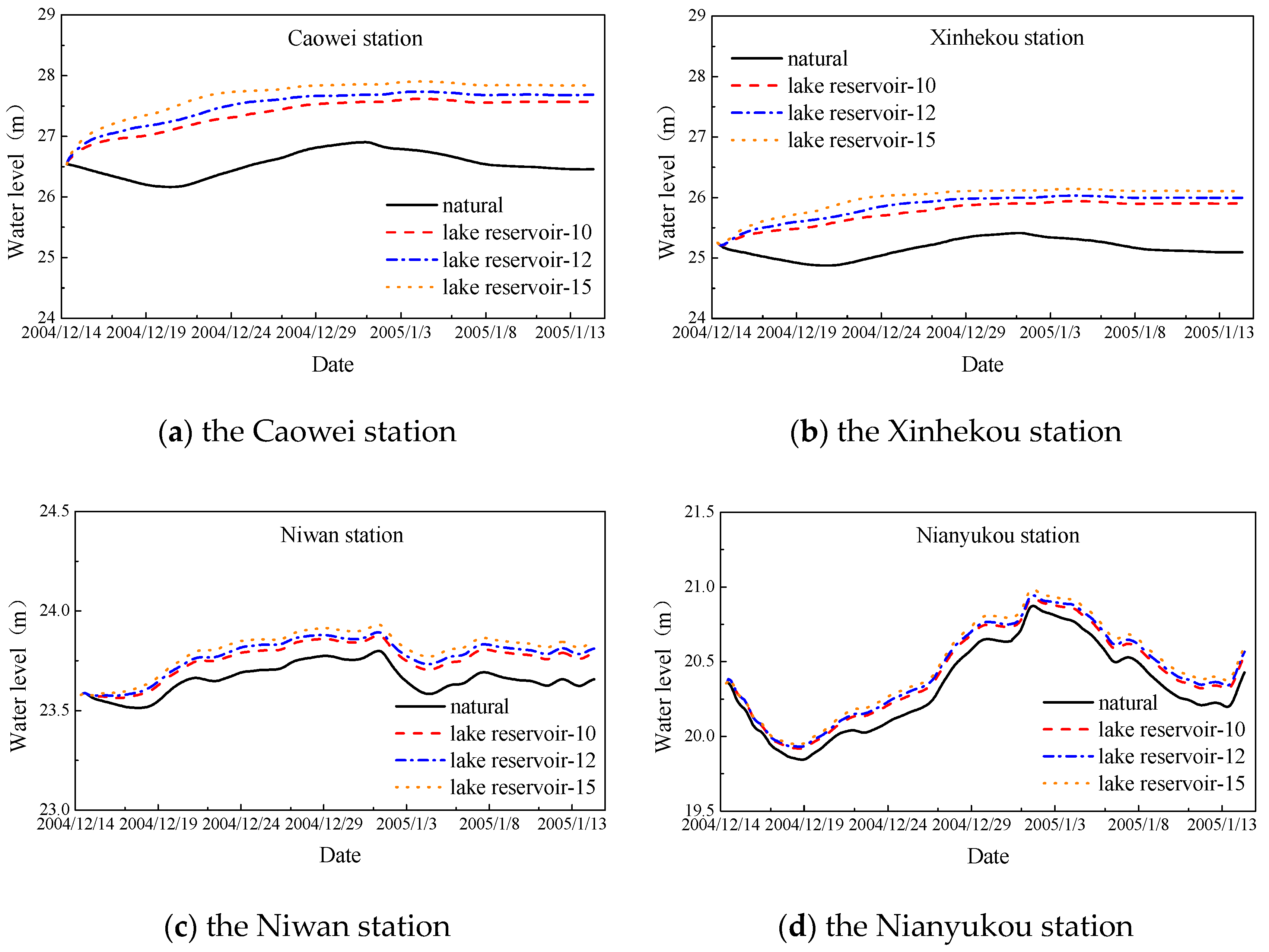
3.3. Drought Resistance Analysis
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The replenishment of the central lake reservoir can increase the water exchange rate in the Kaihu channel and the Xiangjiang River downstream channel. Therefore, it is favorable for reducing the risk of water eutrophication and improving the water environment in the channel.
- (2)
- The existence of the central lake reservoir can effectively reduce the peak flood water level in the West Dongting Lake, and finally reduce the flood pressure.
- (3)
- The capacity of water storage of the central lake reservoir during the dry season can efficiently increase the lake water level in the upstream channel and thereby, enhance the drought resistance of the lake area.
- (4)
- It is also observed that the design depth of the reservoir makes a limited contribution to the reduction of the peak flood elevation if the design depth is larger than 10 m. The uplift value of water elevation also increases when the design depth of the central lake reservoir increases.
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schneider, P.; Hook, S.J. Space observations of inland water bodies show rapid surface warming since 1985. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Reilly, C.M.; Sharma, S.; Gray, D.K.; Hampton, S.E.; Read, J.S.; Rowley, R.J.; Schneider, P.; Lenters, J.D.; McIntyre, P.B.; Kraemer, B.M.; et al. Rapid and highly variable warming of lake surface waters around the globe. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.C.; Winslow, L.A.; Read, J.S.; Hansen, G.J. Climate-induced warming of lakes can be either amplified or suppressed by trends in water clarity. Limnol. Oceanogr. Lett. 2016, 1, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woolway, R.I.; Merchant, C.J. Amplified surface temperature response of cold, deep lakes to inter-annual air temperature variability. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolway, R.I.; Dokulil, M.T.; Marszelewski, W.; Schmid, M.; Bouffard, D.; Merchant, C.J. Warming of Central European lakes and their response to the 1980s climate regime shift. Clim. Change 2017, 142, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldman, C.R.; Michio, K.; Richard, D.R. Climatic change and global warming of inland waters: impacts and mitigation for ecosystems and societies. John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Fukushima, T.; Ozaki, N.; Kaminishi, H.; Harasawa, H.; Matsushige, K. Forecasting the changes in lake water quality in response to climate changes, using past relationships between meteorological conditions and water quality. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 14, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, J. Disappearing lakes, shrinking seas. Eco-Econ. Update 2005, 3. Available online: http://www.earth-policy.org/ plan_b_updates/2005/update47 (accessed on 1 December 2017).
- Du, Y.; Xue, H.P.; Wu, S.J.; Ling, F.; Xiao, F.; Wei, X. Lake area changes in the middle Yangtze region of China over the 20th century. J. Environ. Manag. 2011, 92, 1248–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wurtsbaugh, W.A.; Miller, C.; Null, S.E.; DeRose, R.J.; Wilcock, P.; Hahnenberger, M.; Howe, F.; Moore, J. Decline of the world's saline lakes. Nature Geosci. 2017, 10, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugan, H.A.; Bartlett, S.L.; Burke, S.M.; Doubek, J.P.; Krivak-Tetley, F.E.; Skaff, N.K.; Summers, J.C.; Farrell, K.J.; McCullough, I.M.; Morales-Williams, A.M.; et al. Salting our freshwater lakes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4453–4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.L.; Pekker, T.; Wilson, C.R.; Tapley, B.D.; Kostianoy, A.G.; Cretaux, J.F.; Safarov, E.S. Long-term Caspian Sea level change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 6993–7001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Meng, W.; Jin, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, L.; Xi, H. Ecological security problems of the major key lakes in China. Environ. Earth Sci. 2015, 74, 3825–3837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, T.; Watanabe, M. Role of flood storage ability of lakes in the Changjiang River catchment. Glob. Planet. Change 2008, 63, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahaya, S.; Ahmad, N.; Abdalla, R.F. Multicriteria analysis for flood vulnerable areas in Hadejia-Jama’are River basin, Nigeria. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2010, 42, 71–83. [Google Scholar]
- Henny, C.; Meutia, A.A. Urban lakes in Megacity Jakarta: risk and management plan for future sustainability. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2014, 20, 737–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.S.; Raso, G.; Zhao, Z.Y.; He, Y.K.; Ellis, M.K.; McManus, D.P. Large water management projects and schistosomiasis control, Dongting Lake region, China. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2007, 13, 973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osti, R.; Egashira, S. Hydrodynamic characteristics of the Tam Pokhari Glacial Lake outburst flood in the Mt. Everest region, Nepal. Hydrol. Process. 2009, 23, 2943–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Liu, Q. Numerical study on the characteristics of wind-induced current in Taihu Lake. J. Hydrodyn. (Ser. A) 2009, 4, 018. [Google Scholar]
- Paerl, H.W.; Xu, H.; McCarthy, M.J.; Zhu, G.; Qin, B.; Li, Y.; Gardner, W.S. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Res. 2011, 45, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sun, Z.; Huang, Q.; Opp, C.; Hennig, T.; Marold, U. Impacts and implications of major changes caused by the Three Gorges Dam in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, China. Water Resour. Manag. 2012, 26, 3367–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Dietz, T.; Carpenter, S.R.; Alberti, M.; Folke, C.; Moran, E.; Pell, A.N.; Deadman, P.; Kratz, T.; Lubchenco, J.; et al. Complexity of coupled human and natural systems. Science 2007, 317, 1513–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, R.; Yang, G.; Wang, X. Progress of research on the relationship between the Yangtze River and its connected lakes in the middle reaches, China. J. Lake Sci. 2014, 26, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, X. Integrated management strategies for Dongting Lake, China. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2007, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, R. Impact of river bend cut-off of lower Jingjiangriver on the river and Dongtinglake, China. Yangtze River 1999, 30, 24–26. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Q.; Feng, S.; Guo, H.; Chen, G.; Jiang, T. Interactions of the Yangtze river flow and hydrologic processes of the Poyang Lake, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 347, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J. An approach on flood control strategy in middle and lower reaches of Yangtze River after the completion of the Three Gorges Dam project, China. Adv. Water Sci. 2014, 25, 745–751. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H.; Mo, D.; Su, C. Discussion on the evolutionary trend of Lake Dongting, China. Geograph. Res. 2004, 23, 78–86. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, J.; Huang, Q.; Sun, Z. Study on sediment deposition and continental beach change in dongting lake, China. Yangtze River 2009, 40, 74–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, C. The relationship between dongting lake governance and jianghu, China. Hunan Hydro & Power 2005, 50, 13–15. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Wang, K.; Qin, J. The Evolution of Annual Runoff and Sediment in the Dongting Lake and Their Driving Foeces, China. Acta Geographica Sinica 2005, 60, 503–510. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, O.; Xiong, M. Analysis on the variation and influencing factors of sediment release ratio in Dongtinglake, China. Yangtze River 2006, 37, 117–119. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Z.; Xie, Y.; Xu, D. Runoff-sediment Variation and Its Effect on the Dongting Lake, China. J. China Hydrol. 2011, 31, 010. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, Y.; Li, F.; Chen, X. Study on the Minimum Ecological Water Demand for the Dongting Lake, China. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2012, 21, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Wu, Y. Maintaining the connected river-lake relationship in the middle Yangtze River reaches after completion of the Three Gorges Projec. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2017, 32, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, M.; Yi, F.; Luan, Z. Analysis of impacts on Dongting Lake by flood control of Songzi sluice under operation of Three Gorges project. J. Hydroelectr. Eng. 2013, 32, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Xu, D.; Xiao, H. Discussion on the utilization of water resources in four water system in Dongtinglake. Express Water Resour. Hydropower Inf. 2013, 34, 13–16. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, M.H.; Zhang, B.; Bao, Z.C.; Yang, H.; Xu, X.B. Analysis of pentachlorophenol from water, sediments, and fish bile of Dongting Lake in China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicology 2000, 64, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Yao, J. Estimation of transport trajectory and residence time in large river–lake systems: application to Poyang Lake (China) using a combined model approach. Water 2015, 7, 5203–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Wu, C.; Jiang, C.; Hu, S.; Liu, Y. Simulating the Impacts of an Upstream Dam on Pollutant Transport: A Case Study on the Xiangjiang River, China. Water 2016, 8, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, C.; Liu, Y.; Long, Y.; Wu, C. Estimation of Residence Time and Transport Trajectory in Tieshangang Bay, China. Water 2017, 9, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MIKE21, D.H.I.; MIKE3 Flow Model, F.M. Hydrodynamic and Transport Module Scientific Documentation. Denmark:DHl water Environ. 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Danish Hydraulic Institute (DHI). MIKE 21 Flow Model: Hydrodynamic Module User Guide; DHIWater and Environment: Hørsholm, Denmark, 2014. [Google Scholar]

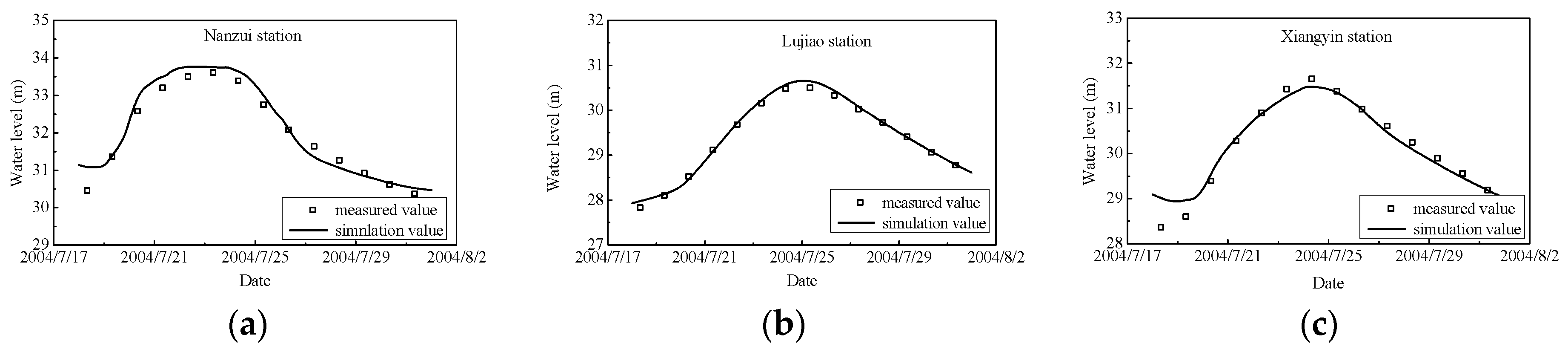
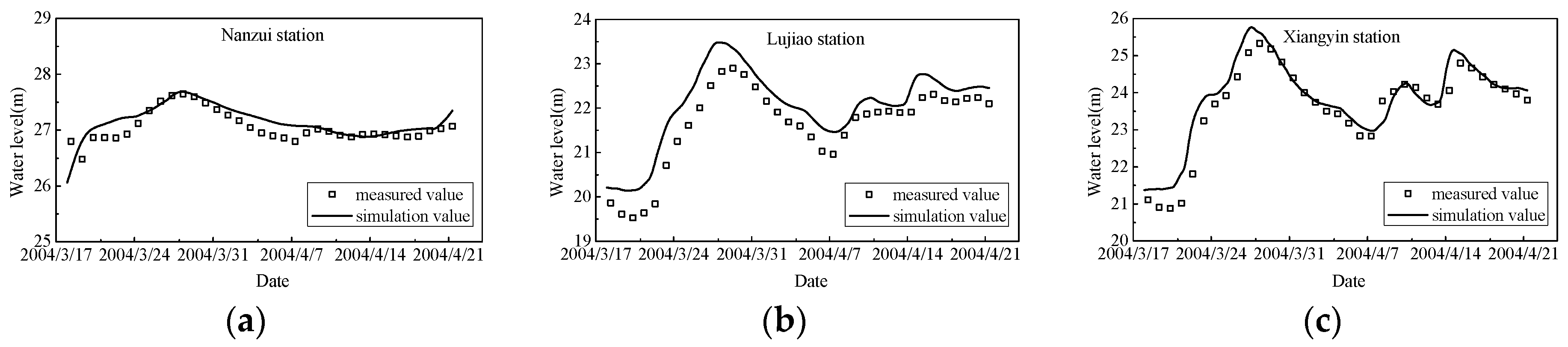
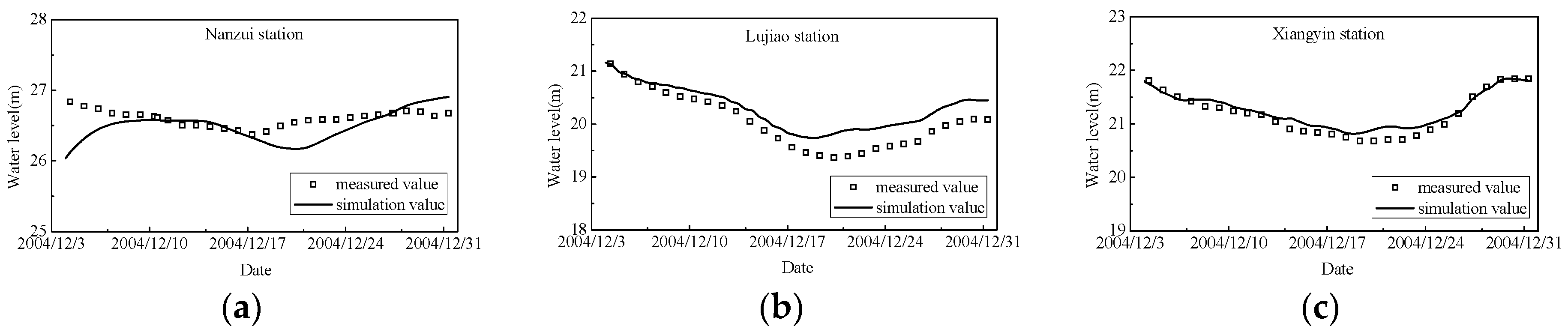



| Coefficient of variation (%) | Nanzui | Lujiao | Xiangyin |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wet season | 0.80 | 0.41 | 0.77 |
| Normal season | 0.60 | 2.15 | 1.45 |
| Dry season | 0.86 | 1.50 | 0.56 |
| Station | Measure value | The Design Depth of the Middle Lake Reservoir | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 m | 12 m | 15 m | |||||
| Water level | Water level | Difference value | Water level | Difference value | Water level | Difference value | |
| Lishui | 34.14 | 33.81 | −0.33 | 33.74 | −0.4 | 33.73 | −0.41 |
| Nanzui | 33.69 | 33.36 | −0.33 | 33.31 | −0.38 | 33.3 | −0.39 |
| Yuanshui | 35.43 | 35.4 | −0.03 | 35.36 | −-0.07 | 35.34 | −0.09 |
| 1# | 34.36 | 34.32 | −.04 | 34.24 | −0.12 | 34.22 | −0.14 |
| 2# | 34.23 | 34.12 | −0.11 | 34.05 | −0.16 | 34.02 | −0.21 |
| 3# | 34.17 | 33.89 | −0.28 | 33.82 | −0.35 | 33.81 | −0.36 |
| 4# | 34.22 | 33.92 | −0.30 | 33.85 | −0.37 | 33.84 | −0.38 |
| Xiaohezui | 33.44 | 33.22 | −0.22 | 33.2 | −0.28 | 33.16 | −0.29 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, H.; Deng, B.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wu, Z.; Long, Y. Preliminary Numerical Analysis of the Efficiency of a Central Lake Reservoir in Enhancing the Flood and Drought Resistance of Dongting Lake. Water 2018, 10, 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020225
Liu H, Deng B, Liu Y, Jiang C, Wu Z, Long Y. Preliminary Numerical Analysis of the Efficiency of a Central Lake Reservoir in Enhancing the Flood and Drought Resistance of Dongting Lake. Water. 2018; 10(2):225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020225
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Huying, Bin Deng, Yizhuang Liu, Changbo Jiang, Zhiyuan Wu, and Yuannan Long. 2018. "Preliminary Numerical Analysis of the Efficiency of a Central Lake Reservoir in Enhancing the Flood and Drought Resistance of Dongting Lake" Water 10, no. 2: 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020225
APA StyleLiu, H., Deng, B., Liu, Y., Jiang, C., Wu, Z., & Long, Y. (2018). Preliminary Numerical Analysis of the Efficiency of a Central Lake Reservoir in Enhancing the Flood and Drought Resistance of Dongting Lake. Water, 10(2), 225. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10020225






