Abstract
Illite-smectite clay is a new mixed mineral of illite and montmorillonite. The ability of nano illite/smectite clay to remove Pb(II) from slightly polluted aqueous solutions has been investigated. The effects of pH, contact time, initial concentration of Pb(II), nano illite/smectite clay dosage, and temperature on the adsorption process were studied. The nano illite/smectite clay was characterized by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD), Fourier transform infrared spectrometry (FTIR), and Scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The results showed that Pb(II) was adsorbed efficiently by nano illite/smectite clay in aqueous solution. The pseudo-second-order kinetic model best described the kinetic of the adsorption, and the adsorption capacity of nano illite/smectite (I-Sm) clay was found to be 256.41 μg·g−1 for Pb(II). The adsorption patterns followed the Langmuir isotherm model. Thermodynamic parameters, including the Gibbs free energy (ΔG), enthalpy (ΔH), and entropy (ΔS) changes, indicated that the present adsorption process was feasible, spontaneous, and endothermic in the temperature range of 298–333 K.
1. Introduction
Water is a source of life. In recent years, a large number of studies have indicated that the water, especially of rivers, in urban areas has been seriously contaminated by heavy metals [1,2,3]. Because heavy metals are not readily degradable in nature and accumulate in animals as well as human bodies, people who drink water or eat food containing heavy metals for a long time are susceptible to disease. Therefore, heavy metal contamination in the water environment has attracted great concern owing to its environmental toxicity and persistence.
Lead is a widely distributed and accumulative pollutant, and is the third-most common toxic element in the heavy metal toxicity list. It is also one of the 10 chemicals that the World Health Organization (WHO) has set out as a cause for significant public health concerns. Once the lead in the environment through various ways enters the human body and accumulates, the nerve, digestive, immune, and reproductive systems will be compromised and the health of human beings will be threatened, especially that of children [4,5]. The permissible limit for lead in potable water is 0.01 mg·L−1 [6]. The removal of Pb(II) has become a great concern globally due to these toxic effects of Pb(II) on living beings. In the past few years, various techniques have been used, such as chemical precipitation, membrane filtration, ion exchange, and biological treatment, for lead removal [7,8,9,10]. Among these methods, adsorption has the advantages of being easy to perform and having a low cost and high efficiency. Thus, it has been used commonly in the heavy metal pollution treatment of water [11].
Clay as an adsorbent is widely used for the removal of heavy metals and has great applicability due to its being economical and having an environment-friendly nature, a high adsorption capacity, and a wide pH range [12,13]. In recent years, many kinds of clay, i.e., bentonite, kaolin, and montmorillonite, have been reported for the removal of high-concentration heavy metals from water [13,14,15,16,17]. Illite-smectite (I-Sm) clay is a new mixed mineral of illite and montmorillonite, and a transition mineral from montmorillonite to illite, belonging to the typical 2:1-type layered silicate mineral. In 2014, nearly 30 billion tons of I-Sm mineral was discovered in Shangsi County, Guangxi. Because I-Sm mineral has the characteristics of high purity, fine particles, and a large surface area, I-Sm has been studied for use as a rubber modifier [18] and as an adsorbent to remove high concentrations of heavy metals from aqueous solution [19,20]. Only a few studies have focused on the adsorption of low concentrations of heavy metals in contaminated water using I-Sm.
In this study, the I-Sm mineral was first made nano-size, then nano I-Sm was used to adsorb Pb(II) in a solution close to that of real polluted water. The effects of various analytical conditions, such as initial pH of the solution, contact time, and initial adsorbate and adsorbent concentration, were evaluated in detail on the removal performance of nano I-Sm. Isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic modeling of the adsorption process was analyzed.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Nano I-Sm
I-Sm mineral was provided by Sino-nanotech Holdings Co., Ltd. (Shangsi, Guangxi, China). The main steps of nano I-Sm preparation included crushing, soaking, dispersing, sieving and purification, and ultrafine grinding [18,21]. In detail, the preparation was as follows. Firstly, I-Sm mineral was crushed into small pieces (d < 2 cm) and then soaked in a certain amount of water (the water-to-clay ratio was 9:11) for about 10 h. Secondly, the soaked I-Sm mud was dispersed for 30 min with a mixer beater and then passed through a 100-mesh and 325-mesh vibrating screen to obtain the primary nano I-Sm slurry (d < 45 μm). Thirdly, the slurry was ground by a high energy density medium stirring mill (FPML OML-H/V, Buhler Group Co., Uzwil, Switzerland) for 2 h. Finally, the slurry was dried by azeotropic distillation and then dispersed by high-speed mill.
2.2. Characterization of Nano I-Sm
The Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectra of nano I-Sm were recorded with the Fourier transform infrared spectrophotometer (Nicolet 380, Thermo Fisher, Waltham, MA, USA). The X-ray diffraction (XRD) analysis was determined using a MiniFlex X-ray diffractometer (Miniflex 600, Rigaku, Tokyo, Japan), and the scanning regions of the diffraction were 5–80° on the 2θ angle. The morphology of nano I-Sm was analyzed by a scanning electron microscope (SEM) (ProX, Phenom World, Shanghai, China), The Brunauer-Emmett-Teller (BET) surface area and pore properties of nano I-Sm were determined via N2 adsorption–desorption isotherms using a Micromeritics analyzer (ASAP 2460, Micromeritics, Norcross, GA, USA). The cation exchange capacity (CEC) of nano I-Sm was determined by the ammonium acetate method [22]. The slurry’s pH was determined by soaking 1 g of nano I-Sm in 50 mL distilled water, stirring the solution for 24 h, filtering it, and then measuring the final pH [23].
2.3. Batch Adsorption Experiments
Stock solutions of Pb(II) were prepared by dissolving appropriate amounts of (CH3COO)2Pb·3H2O in distilled water. Batch adsorption experiments were carried out in a series of centrifuge tubes by mixing a constant amount of nano I-Sm with 40 mL of the aqueous solution of Pb(II) at varying concentration and different temperatures. Then, the centrifuge tubes were put in a shaker incubator at 150 rpm for a certain time interval, the nano I-Sm was separated from the aqueous solutions by centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 5 min (TDZ5-WS, Cence, Changsha, China), and the supernatant was filtered through a 0.45 μm filter membrane. Pb(II) concentration in the solutions was measured by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (7700 e, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA).
The adsorption capacity of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm in the batch test was calculated using Equations (1) and (2).
where Rratio is the Pb(II) removal rate; Qe is the equilibrium capacity of lead on the nano I-Sm, mg·g−1; C0 is the initial concentration of the Pb(II) solution, mg·L−1; Ceq is the equilibrium concentration of the Pb(II) solution, mg·L−1; V is the solution volume, L; and m is the mass of nano I-Sm, g. All assays were carried out in triplicate and only mean values are presented.
The effects of process variables, including pH of the solution, initial concentration of Pb(II), contact time, adsorbent dosage, and temperature, on the adsorption were studied. The pH of the solution at the start of the experiments was adjusted with 0.1 mg·L−1 HCl or 0.1 mg·L−1 NaOH. Adsorption isotherms studies were conducted at 298, 308, 313, 323, and 333 K, whereby 0.1 g of nano I-Sm was kept in contact with 40 mL of Pb(II) solution of varying concentrations (0.25, 0.50, 1.50, 2.50, 3.50, and 5 mg·L−1) at pH 5. The kinetic experiments were performed using a Pb(II) concentration of 1 mg·L−1 with 0.1 g nano I-Sm at different time intervals (5, 10, 20, 30, and 60 min) at pH 5.
2.4. Theoretical Model
2.4.1. Adsorption Kinetics Model
The equations of the pseudo-first-order [24] and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model [25] were used to fit experiment data obtained from the batch experiments. The formulas of the pseudo-first-order and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model are expressed as Equations (3) and (4), respectively.
where Qt is the amount of Pb(II) adsorbed at time t, mg∙g−1, k1 is the pseudo-first-order rate constant adsorption rate, min−1; and k2 is the adsorption rate constant in the pseudo-second-order kinetic rate constant, g·μg−1·min−1.
2.4.2. Adsorption Equilibrium
The isotherm models of Langmuir [26] and Freundlich [27] were tested to analyze the equilibrium data. The Langmuir isotherm model and Freundlich isotherm model equations are expressed by Equations (5) and (6).
where Qmax is the monolayer capacity of nano I-Sm, mg∙g−1; KL is the Langmuir constant, L∙μg−1; Kf is the Freundlich constant, μg∙g−1; and n is the heterogeneity.
2.4.3. Adsorption Thermodynamics
The thermodynamic parameters can be determined using the equilibrium constant and temperature [28,29]. The change in the Gibbs free energy (ΔG), enthalpy (ΔH), and entropy (ΔS) in the adsorption process was calculated using Equations (7) and (8).
where R is the universal gas constant, 8.314 J∙mol−1∙K−1; T is the absolute temperature, K; and Kd is the distribution coefficient of nano I-Sm, Kd = Qe/Ceq.
3. Results
3.1. Characterization of Nano I-Sm
The chemical composition and physicochemical properties of nano I-Sm are presented in Table 1. The XRD patterns of nano I-Sm are given in Figure 1 A. Nano I-Sm is mainly composed of quartz, mixed-layer illite/smectite, illite, and kaolinite, and the characteristic diffraction peak of nano I-Sm was observed between 5 and 10° (2θ) [30]. Furthermore, an FT-IR analysis was applied to identify the functional groups on the nano I-Sm sample’s surface. The FT-IR spectra of the nano I-Sm sample are shown in Figure 1B. The absorption bands at 3698.96 and 3620.60 cm−1 represent the inner surface OH stretching vibration, while the absorption band at 3423.76 cm−1 represents the outer surface OH stretching vibration. These OH groups function as an active site for the binding of positively charged cations. The absorption band at 1629.97 cm−1 represents the OH bending of water retained in the silica matrix [23]. The absorption bands at 1031.99 and 470.19 cm−1 represent the Si–O–Si stretching vibration [31]. The absorption band at 912.4 cm−1 represents the Al–OH bending vibrations [29], while those at 798.04 and 694.4 cm−1 represent the Si–O stretching vibration [23].

Table 1.
Chemical composition and physicochemical properties of nano illite-smectite (I-Sm) clay.
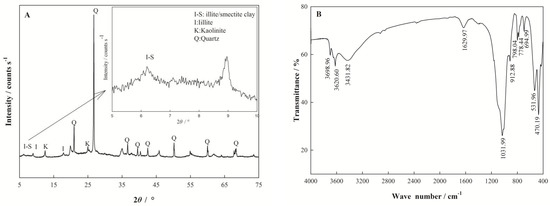
Figure 1.
XRD spectra (A) and FT-IR spectrum (B) of nano I-Sm.
SEM analysis is another important tool used in the determination of the surface morphology of an adsorbent. In this study, SEM was used to probe the change in morphological features of nano I-Sm and Pb-adsorbed nano I-Sm (Figure 2).
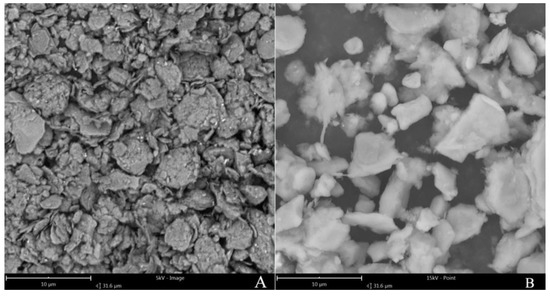
Figure 2.
(A) SEM micrograph of nano I-Sm (before adsorption); (B) after Pb(II) adsorption.
3.2. Effect of Adsorption Conditions
3.2.1. Effect of pH
The effect of pH on Pb(II) removal rate was investigated at 298 K for 60 min as shown in Figure 3A. It was observed that the levels of adsorption efficiency of Pb(II) increased significantly with increasing pH. The removal rate of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm was only 41.25 % at pH 2.0. In addition, the removal rate of Pb(II) tended to equilibrate at pH 4.0. When the solution had a pH > 6.0, the solution of Pb(II) gradually formed Pb(OH)2 precipitate, and the solution system became relatively complex.
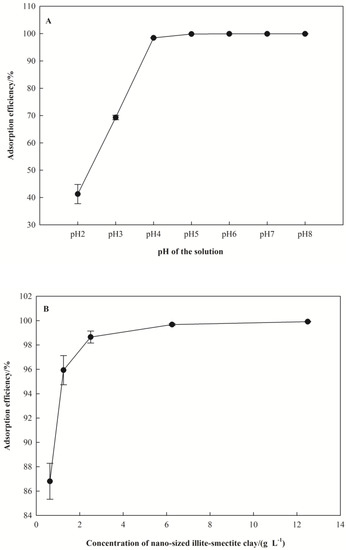
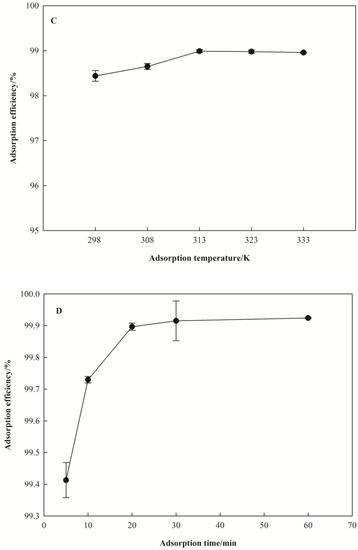
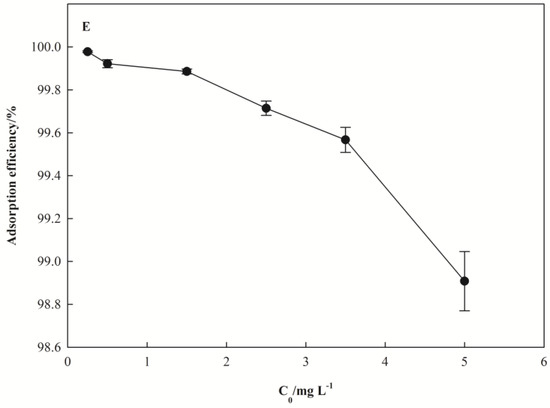
Figure 3.
Effect of adsorption conditions on the removal rate of Pb(II). (A) for pH, (B) for dosage of I-Sm, (C) for adsorption temperature, (D) for adsorption time, (E) for Pb(II) initial concentration.
3.2.2. Effect of Nano I-Sm Dosage
The effect of nano I-Sm dosage on Pb(II) removal rate is shown in Figure 3B. The nano I-Sm dosage varied from 0.625 to 12.5 g·L−1 with a constant initial Pb(II) concentration of 1 mg·L−1 for 60 min at 298 K. Figure 3B shows the effect of nano I-Sm dosage on the removal rate of Pb(II). It was observed that the removal rate of Pb(II) increased with an increase in the nano I-Sm dosage from 0.625 to 2.5 g·L−1. A further increase in the nano I-Sm dosage, however, did not result in a sufficient increase in the removal rate of Pb(II).
3.2.3. Effect of Adsorption Temperature
The effect of temperature on Pb(II) removal rate is shown in Figure 3C. It was observed that the removal rate of Pb(II) was 98.44–98.99% when the temperature was set at 298, 308, 313, 323, and 333 K. The trend of the removal rate with the increase of temperature is not obvious.
3.2.4. Effect of Adsorption Time
The effect of adsorption time on the removal rate of Pb(II) is shown in Figure 3D. In a Pb(II) solution with a low initial concentration, the removal rate of Pb(II) in solution reached 99.41% when the adsorption time was 5 min, and the removal rate of Pb(II) tended to be stable after 20 min.
3.2.5. Effect of Initial Concentration of Pb(II)
The effect of initial concentration on the removal rate of Pb(II) adsorbed by nano I-Sm is shown in Figure 3E. The removal rate of Pb(II) decreased with the increase of initial Pb(II) concentration. When the initial concentration of Pb(II) increased from 0.25 to 5 mg·L−1, the removal rate of Pb(II) decreased from 99.45% to 98.90%.
3.3. Kinetic Parameters of the Adsorption
The kinetic of adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm was fitted by pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic equations. The results are shown in Table 2 and Figure 4. The correlation coefficient of the linear plots of t/Qt against t for the pseudo-first-order model and the pseudo-second-order model was 0.985 and 1, respectively. The Qe of the pseudo-first-order kinetics model was 2.603 μg·g−1, and the Qe of pseudo-second-order dynamic model was 256.410 μg·g−1.

Table 2.
The predicted parameters by pseudo-first-order and pseudo-second-order kinetic models and experimental data.
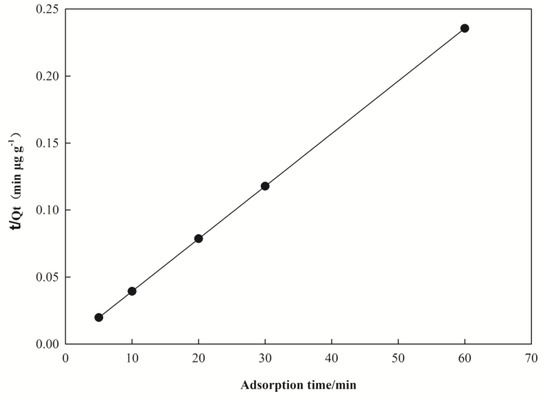
Figure 4.
Pseudo-second-order plots for the adsorption of Pb(II) at 298 K.
3.4. Equilibrium Parameters of the Adsorption
The Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models were used to analyze the adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm. All of the isotherm constants and correlation coefficients were calculated from the linear forms of the isotherm model equations and are provided in Table 3 and Figure 5.

Table 3.
Parameters calculated by the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models for the adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm.
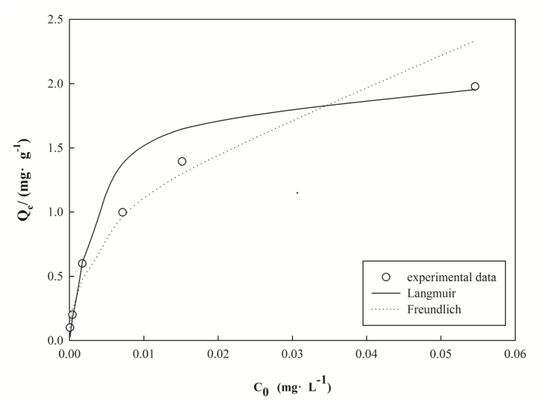
Figure 5.
Comparison of equilibrium isotherms between the experimental data and the theoretical data.
3.5. Thermodynamic Parameters of the Adsorption
The results of the analysis of the thermodynamic parameters of adsorption are shown in Table 4 and Figure 6.

Table 4.
Thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of Pb2+on nano I-Sm.
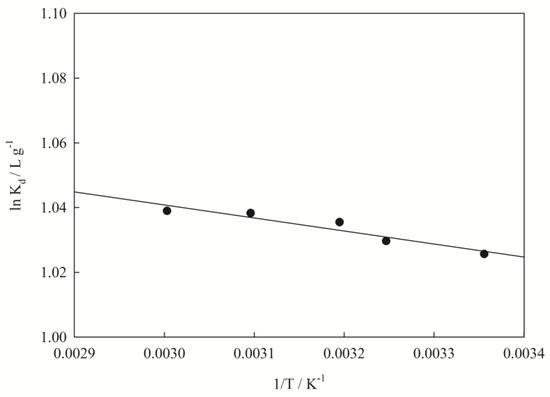
Figure 6.
Relationship between 1/T and lnKd for nano I-Sm.
4. Discussion
Among the adsorption conditions, the pH of the aqueous solution is an important variable for the adsorption of metals onto the adsorbents [32]. In this study, the adsorption efficiency was significantly inhibited when the pH of the aqueous solution was low. At a low pH, the number of H+ ions exceeds that of Pb(II) ions several times and the surface of nano I-Sm is most likely covered with H+ ions, which account for less Pb(II) adsorbed [33]. As the pH increases, more and more H+ ions leave the nano I-Sm surface, making the sites available to the Pb(II), which could increasingly bind to the nano I-Sm surface through a mechanism similar to that of exchange interactions (H(I)/Pb(II)) [28]. In the meantime, Yuan et al. [19] have found that the Zeta potential decreased from 3.29 to −69.95 mV when the pH value increased from 2 to 7 in a nano I-Sm solution, indicating that the surface charge of the nano I-Sm changed from positive to negative, and further verifying the deprotonation processes of nano- I-Sm with the increase of pH. It was observed that nano I-Sm was suitable for removing Pb(II) from waste water under an acidic condition, which was similar to the results of some clay adsorbing heavy metals [28,29]. The removal rate of Pb(II) is also related to the I-Sm dosage. At a lower nano I-Sm dosage, Pb(II) ions compete for the limited adsorption sites in the nano I-Sm. As the quantity of nano I-Sm increased, more available sites promoted a greater percentage removal of Pb(II) [33]. When the amount of nano I-Sm was 6 g·L−1, 1 mg·L−1 Pb(II) in solution would be reduced to 0.01 mg·L−1, reaching the potable water standard. In addition, nano I-Sm showed a rapid adsorption effect in the temperature range of 298–333 K. The above results revealed an important advantage of high efficiency removal of Pb(II) by the nano I-Sm.
The Qe of the pseudo-second-order dynamic model was much closer to the experimental result and the correlation coefficients were found to be relatively high. The pseudo-second-order adsorption mechanism was predominant for the adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm. The pseudo-second-order model assumes that two reactions are happening: the first one is fast and reaches equilibrium quickly, whereas the second one is a slower reaction [15]. Accordingly, the following mechanism may be proposed [33]:
in which the number of adsorption sites on the nano I-Sm surface and the number of Pb(II) ions in the liquid phase determine the kinetics. Depending on pH, different Pb-species may be held to the clay surface at appropriate ion-exchange sites [25,33].
Clay + Pb(II) = Clay⋯Pb(II)
The correlation coefficient of the Langmuir isotherm model was higher than that of the Freundlich isothermal model, from which we can conclude that the Langmuir isotherm model was more suitable for nano I-Sm removal of Pb(II) in aqueous solutions. Similar results were also reported in earlier studies in which the adsorption of heavy metal ions fitted well to the Langmuir isotherm [15,19,33]. Furthermore, the n values of the Freundlich isothermal model relate to the adsorption properties of the adsorbent, where values of n between 2 and 10 represent good adsorption [34], which is an indication of the good adsorption of Pb(II) by nano I-Sm.
The Gibbs free energy (ΔG) was −2.541, −2.637, −2.695, −2.788, and −2.876 kJ mol−1(ΔG < 0) when the temperature was set at 298, 308, 313, 323, and 333 K, respectively. These indicate that the adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm is a spontaneous process [23]. The ΔH was 4.844 kJ mol−1(0 < ΔH < 16), which indicates that the adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm is an endothermic process [19,34].
The SEM results showed that the surface morphology of Pb-adsorbed nano I-Sm is different from that of natural nano I-Sm. The natural nano I-Sm showed loose aggregates with a porous structure. After adsorption, the surface of nano I-Sm demonstrates compacted aggregates. The surface morphology of the natural nano I-Sm changed evidently during the adsorption process, indicating that significant interaction at the lead–clay interface occurred during the experiment. Similar SEM results were reported by other researchers [28,35].
5. Conclusions
As a new adsorbent, nano I-Sm can be used for depth treatment in lead-contaminated water. The pseudo-second-order adsorption mechanism was predominant for the adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm. The saturated adsorption capacity of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm in the aqueous solution was 256.41 μg∙g−1. The adsorption patterns followed the Langmuir isotherm model. The adsorption of Pb(II) on nano I-Sm is a thermodynamically feasible, spontaneous, and endothermic process.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (grant No. 2015GXNSFEA139001) from the Guangxi science and Technology Department, the project of International Scientific Exchange Program (grant No. 7–1, 2017) from the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China, and the key project of Guangxi Social Sciences. (grant No. gxsk201605)
Author Contributions
Juan Yin and Chaobing Deng designed the study; Juan Yin and Zhen Yu analyzed the data; Juan Yin wrote the article, and Xiaofei Wang and Guiping Xu provided access to the experimental site.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Dipak, P. Research on heavy metal pollution of river Ganga: A review. Ann. Agrar. Sci. 2017, 15, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IslamabMd, M.S.; Ahmed, M.K.; Raknuzzaman, M.; Mamun, M.H.-A.; Islam, M.K. Heavy metal pollution in surface water and sediment: A preliminary assessment of an urban river in a developing country. Ecol. Indic. 2015, 48, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.J.; Wang, F.Y.; Wang, G.J.; Mei, R.W.; Wang, C.Z. Study on Heavy Metal Pollution in Surface Water in China. Envron. Sci. Manag. 2017, 42, 31–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.W.; Yang, L.S.; Li, Y.H.; Li, H.R.; Wang, W.Y.; Ye, B.X. Impacts of lead /zinc mining and smelting on the environment and human health in China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2012, 184, 2261–2273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.Y.; Ma, Z.W.; Kuijp, T.J.; Yuan, Z.W.; Huang, L. A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: Pollution and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 468–469, 843–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmaruzzaman, M.; Gupta, V.K. Rice husk and its ash as low-cost adsorbents in water and wastewater treatment. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 13589–13613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.D.; Yu, Y.; Chen, P. Treatment of lead contaminated water by a PVDF membrane that is modified by zirconium, phosphate and PVA. Water Res. 2016, 101, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergili, I.; Gönder, Z.B.; Kaya, Y.; Gürdağ, G.; Çavuş, S. Sorption of Pb (II) from battery industry wastewater using a weak acid cation exchange resin. Process Saf. Environ. Prot. 2017, 107, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milind, M.N.; Santosh, K.D. Lead resistant bacteria: Lead resistance mechanisms, their applications in lead bioremediation and biomonitoring. Ecotox. Environ. Saf. 2013, 98, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreham, T.B.; Abaynesh, Y.G.; Ramato, A.T.; Dawit, N.; Efrem, C.; Lidietta, G. Removal of emerging micropollutants by activated sludge process and membrane bioreactors and the effects of micropollutants on membrane fouling: A review. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2017, 5, 2395–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.X.; Li, J.X.; Ren, X.M.; Chen, C.L.; Wang, X.K. Few-layered graphene oxide nanosheets as superior sorbents for heavy metal ion pollution management. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10454–10462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burakov, A.E.; Galunin, E.V.; Burakova, I.V.; Kucherova, A.E.; Agarwal, S.; Tkachev, A.G.; Gupta, V.K. Adsorption of heavy metals on conventional and nanostructured materials for wastewater treatment purposes: A review. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 148, 702–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, K.U. A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 438–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masindi, V.; Gitari, W.M. Simultaneous removal of metal species from acidic aqueous solutions using cryptocrystalline magnesite/bentonite clay composite: An experimental and modelling approach. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 1077–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joziane, G.M.; Murilo, P.M.; Thirugnanasambandham, K.; Sergio, H.B.F.; Marcelino, L.G.; Maria, A.S.D.B.; Sivakumar, V. Preparation and characterization of calcium treated bentonite clay and its application for the removal of lead and cadmium ions: Adsorption and thermodynamic modeling. Process Saf. Environ. 2017, 111, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, A.; Tuzen, M. Cd(II) adsorption from aqueous solution by raw and modified kaolinite. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 88–89, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atta, A.M.; Al-Lohedan, H.A.; ALOthman, Z.A.; Abdel-Khalek, A.A.; Tawfeek, A.M. Characterization of reactive amphiphilic montmorillonite nanogels and its application for removal of toxic cationic dye and heavy metals water pollutants. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2015, 31, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.Y. Preparation of Illite/Smectite Clay Nano-Powder and Its Application as Rubber Filler. Master’s Thesis, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou, China, 4 June 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, S.S.; Li, Z.Y.; Pan, Z.D.; Wang, Y.M. Removal of Copper and Cadmium Ions in Aqueous Solution via Adsorption by Nano-sized Illite-Smectite Clay. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 44, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.H.; Yuan, Y.H.; Yan, Z.G.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Zhang, C.Y.; Huang, Y.; Xu, M. Application of nano illite/smectite clay for adsorptive removal of metals in water. Res. Environ. Sci. 2016, 29, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakthivel, S.; Venkatesan, V.; Krishnan, B.; Pitchumani, B. Influence of suspension stability on wet grinding for production of mineral nanoparticles. Particuology 2008, 6, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.D. Soil Agricultural Chemistry Analysis, 3rd ed.; China Agricultural Press: Beijing, China, 2000; pp. 152–176. ISBN 9787109066441. [Google Scholar]
- Dawodu, F.A.; Akpomie, K.G. Simultaneous adsorption of Ni(II) and Mn(II) ions from aqueous solution unto a Nigerian kaolinite. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2014, 3, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagergren, S. Zur theorie der sogenannten adsorption gelöster stoffe (about the theory of so-called adsorption of soluble substances); Kungliga Svenska Vetenskapsakademiens (Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences): Stockholm, Sweden, 1898; pp. 1–39. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmuir, I. The adsorption of gases on plane surfaces of glass, mica and platinum. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1918, 40, 1361–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freundlich, H.M.F. Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z. Phys. Chem. 1906, 57, 385–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.Q.; Wang, Q.P.; Jin, X.Y.; Chen, Z.L. Removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution using modified and unmodified kaolinite clay. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 332–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olgun, A.; Atar, N. Equilibrium, thermodynamic and kinetic studies for the adsorption of lead (II) and nickel (II) onto clay mixture containing boron impurity. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2012, 18, 1751–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, M.D.; Bauluz, B.; Nieto, F.; Papa, C.D.; Hongn, F. SEM and TEM evidence of mixed-layer illite-smectite formed by dissolution- crystallization processes in continental Paleogene sequences in northwestern Argentina. Clay Miner. 2016, 51, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Zeng, L.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, T.F.; Zhang, Y.J. Preparation and Characterization of Montmorillonite Intercalation Compounds with Quaternary Ammonium Surfactant: Adsorption Effect of Zearalenone. J. Nanomater. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.L.; Yuan, P.; Liu, D.; Liu, Z.W. Effects of microstructure of clay minerals, montmorillonite, kaolinite and halloysite, on their benzene adsorption behaviors. Appl. Clay Sci. 2017, 143, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna, G.B.; Susmita, S.G. Pb(II) uptake by kaolinite and montmorillonite in aqueous medium: Influence of acid activation of the clays. Colloid Surf. A 2006, 277, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nir, S.; Undabeytia, T.; Dana, Y.; Yasser, E.; Polubesova, T.; Serban, C.; Rytwo, G.; Lagaly, G.; Rubin, B. Optimization of adsorption of hydrophobic herbicides on montmorillonite presorbed by monovalent organic cations: Interaction between phenyl rings. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 1269–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Xue, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.Z. Effect of lead (II) on the mechanical behavior and microstructure development of a Chinese clay. Appl. Clay Sci. 2015, 105–106, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).