Abstract
Oil sands process-affected water (OSPW), generated from bitumen extraction in the Canadian oil sands, may require treatment to enable safe discharge to receiving watersheds, as dissolved naphthenic acids (NAs) and other acid extractable organics (AEO), identified as the primary toxic components of OSPW, are environmentally persistent and poorly biodegradable. However, conventional advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) are impractically expensive to treat the volumes of OSPW stockpiled in the Athabasca region. Here we prepared floating photocatalysts (FPCs) by immobilizing TiO2 on glass microbubbles, such that the composite particles float at the air-water interface for passive solar photocatalysis. The FPCs were demonstrated to outperform P25 TiO2 nanoparticles in degrading AEO in raw OSPW under natural sunlight and gentle mixing conditions. The FPCs were also found to be recyclable for multiple uses through simple flotation and skimming. This paper thus demonstrates the concept of a fully passive AOP that may be scalable to oil sands water treatment challenges, achieving efficient NA reduction solely through the energy provided by sunlight and natural mixing processes (wind and waves).
1. Introduction
Bitumen extraction in Canada’s oil sands uses large volumes of water, which is contaminated in the process by compounds leached from the oil sands ore, and referred to as oil sands process-affected water (OSPW). Release of OSPW to the environment is hindered by the toxicity of the water, due primarily to dissolved naphthenic acids (NAs) and other acid extractable organics (AEO) [1,2], and thus an estimated 1 billion m3 of OSPW to date has been retained in tailings ponds on site. NAs are not fully biodegradable [3,4], and their toxicity persists over decades [5], therefore a water treatment solution may be required to enable OSPW discharge.
Recently the oil sands industry has sought passive, or low energy, water treatment technologies capable of addressing large volumes of OSPW [6]. Considering the large sunlight-exposed surface area of oil sands tailings ponds, solar photocatalysis is a promising advanced oxidation process (AOP) with demonstrated capability to fully degrade OSPW AEO through hydroxyl and superoxide radical-mediated oxidative mineralization [7,8,9]. In contrast to other advanced oxidation processes (AOPs) that have been tested for OSPW treatment [10,11], solar photocatalysis enables complete degradation of even recalcitrant NAs, without the need for chemical amendment of the water or electrical power consumption. Nevertheless, there remain a number of key technical challenges towards application of photocatalysis for OSPW treatment. Previous research has studied photocatalytic nanoparticles dispersed into OSPW as a slurry, and while slurries enable high treatment rates through efficient mass transfer, they require continuous mixing to remain suspended, as without mixing the photocatalyst near the water surface, the turbidity of OSPW is likely to occlude sunlight from reaching the catalyst. Indeed, our previous measurements indicated the UV light penetrates <1 cm into OSPW [7]. Since the photocatalytic reaction thus only occurs at the water surface, the bulk majority of slurried catalyst dispersed in the dark zone below the surface is not effectively utilized, resulting in unnecessary material oversupply. Furthermore, slurries present challenges for cost effective nanocatalyst recovery and reuse at a large scale.
It was hypothesized that immobilizing a photocatalyst onto a buoyant support could address the above challenges, while adapting this promising treatment technology into a passive platform enabling large-scale deployment. On floating cores, the photocatalyst is naturally concentrated without any mixing at the water surface, where sunlight intensity is greatest, and the catalyst can be easily collected by simple skimming. Thus, in this work we sought to demonstrate treatment of AEO in raw OSPW by use of floating photocatalysts under natural sunlight. While buoyant photocatalysts have been synthesized previously [12,13,14], this report represents the first demonstration of such materials as a passive treatment for OSPW remediation.
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
OSPW collected on 17 March 2014 was provided by Shell Canada (Calgary, AB, Canada), and stored in sealed polyethylene containers in the dark at 4 °C. The OSPW was homogenized by stirring before each use, herein referred to as raw OSPW. The OSPW was characterized previously to have a conductivity of 1.695 mS/cm, 1450 mg/L total dissolved solids (TDS), 49.5 mg/L total suspended solids (TSS), and a turbidity >200 NTU [7]. The AEO concentration was measured by the FTIR method (Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, USA) below to be 26.3 mg/L.
A commercial mixture of naphthenic acids (technical grade, carbon numbers 6–20, z-classes 0 to −4, as characterized by Damasceno et al. [15]), dichloromethane (DCM, ≥99.9%, HPLC grade) NaOH (≥98%, ACS grade) and nitric acid (70%, ACS grade) were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA) and used as received. Sulfuric acid (95–98%, ACS grade, Fisher, Hampton, NH, USA) and titanium dioxide nanoparticles (Aeroxide P25, ~10–50 nm particle diameter, 55 m2 g−1 surface area, Acros, Geel, Belgium) were used as received. Glass microbubbles (3M iM30k, Maplewood, MN, USA, soda-lime-borosilicate glass, ~10–30 µm diameter, 0.6 g/cm3 density) were washed by 1 mol/L HNO3 and 0.1 mol/L NaOH before use (at 125 g/L microbubbles), rinsing thrice with deionized (DI) water after each wash, then drying at 120 °C in air.
2.2. Floating Photocatalyst Synthesis and Characterization
TiO2 nanoparticle powder was dispersed at 60 g/L into DI water by probe sonication, after which 0.1 mol/L HNO3 was added to a concentration of 1 mmol/L, thereby adjusting the suspension to a nominal pH of ~3. This TiO2 suspension was then added to microbubble powder (17.75 mL per g microbubbles), and the mixture was stirred at 500 rpm for 2 h, before transferring to a separatory funnel. The floating layer was collected after 1 h, vacuum filtered to form a cake, dried and crushed to a powder, which was then calcined for 4 h at 500 °C in air (5 °C/min ramp rate) to form the floating photocatalysts (FPCs).
Particle morphology was analysed by SEM (Zeiss Merlin FESEM, Oberkochen, Germany), and elemental composition was measured by EDX (EDAX, Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany). Crystal phase was assessed by powder XRD (Bruker D8-Advance, Våntec-1 detector, 1.5405 Å Cu-Kα radiation, Billerica, MA, USA).
2.3. Photocatalysis Experiments
Outdoor solar photocatalytic experiments were performed between 22 and 28 August 2015 at the University of Waterloo (Waterloo, ON, Canada). 1 g of FPC powder (or 0.5 g of P25 TiO2) was stirred into 500 mL of raw OSPW in a borosilicate glass beaker (90 mm O.D.). Beakers were sealed from above with polyethylene film (Glad, measured to be UV transparent by spectrophotometry) to prevent evaporation during the experiments, and wrapped around the sides with Al foil. The beakers were then placed on a rooftop outdoors (43°28′17.9″ N 80°32′32.2″ W) and exposed to sunlight while stirring at 130 rpm, where a control included OSPW exposed to sunlight in the absence of TiO2. The stirring Reynolds number was calculated according to the formula , where is the rotational frequency (130 rpm), is the radius of the stir bar (1.905 cm) and is the kinematic viscosity of water [16]. Following solar treatment, the photocatalyst was separated from the OSPW by flotation or centrifugation, retaining the water for analysis (stored at 4 °C in the dark).
Weather data was obtained from the University of Waterloo Weather Station archives [17]. Cumulative insolation was calculated by integrating the incoming shortwave radiation (measured by the weather station using a Kipp & Zonen CM11 pyranometer (Delft, Netherlands), spectral range 285 to 2800 nm) over the duration of the experiment (Figure S1). Cumulative UV exposure was estimated on the basis of the ASTM G173-03 global tilt solar spectrum as 4.72% of the cumulative insolation.
Photocatalyst recyclability experiments were performed under in a custom photoreactor enclosure, consisting of an array of UVA fluorescent bulbs (Philips F20T12/BL, Amsterdam, Netherlands, peak emission ~350 nm) suspended above the samples [9]. The UV intensity was measured to be ~40 W/m2 with a UVA/B light meter (Sper Scientific, Scottsdale, AZ, USA, NIST certified calibration), which is similar to the UV content of the solar spectrum (ASTM G173-03 global tilt). Following UV exposure, the photocatalyst was separated from the OSPW by flotation, and then directly redispersed into a fresh sample of OSPW for another round of photocatalytic testing.
2.4. Analysis
The concentration of AEO was measured by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR, PerkinElmer, Waltham, MA, United States) according to the standard method [18,19] with minor modifications (viz., the acidified samples were extracted thrice with DCM in a 1:12.5 solvent to sample volumetric ratio, with 80 ± 4% total recovery), using the commercial NA mixture to prepare the calibration curve. AEO is a composite measure of classical NAs, oxy-NAs (CnH2n+zOx, where x > 2), and other organic acids [20]. Samples were filtered prior to the analysis (Whatman 934-AH glass fiber filter, Little Chalfont, Buckinghamshire, UK). Pseudo-first order rate constants were calculated on the basis of cumulative incoming solar shortwave insolation (285–2800 nm).
3. Results and Discussion
Photocatalysts were immobilized on the outer surface of buoyant microspheres, such that the composite particles would passively float at the air-water interface and degrade aqueous organic contaminants under sunlight illumination (Figure 1a). A heterocoagulation and sintering process was used to adhere photocatalytic TiO2 nanoparticles to a high strength glass microbubble (GMB) core, wherein the TiO2 and GMBs were mixed together at a pH between their respective isoelectric points to induce electrostatic attraction, followed by high temperature calcination to fix the nanoparticles in place. Thermal sintering has been previously demonstrated to promote strong adhesion of immobilized TiO2 to glass supports [21,22,23], although reducing specific surface area of the TiO2 in the process [24]. Floating photocatalysts synthesized previously have used plastic supports susceptible to photocatalytic degradation [25,26,27,28,29,30], or fragile materials such as perlite [31,32,33], which sink upon breaking. The floating photocatalyst (FPC) composites prepared herein are entirely inorganic and resistant to photodissolution, and thus more suitable towards long term emplacement in a passive treatment system. The synthesized particles were observed to readily float at the water surface as intended (Figure 1b).
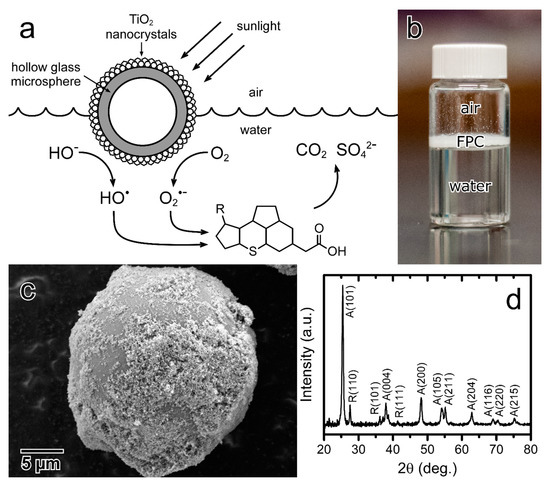
Figure 1.
(a) Schematic of the floating photocatalyst (FPC) structure and mechanism of solar water treatment for napthenic acid mineralization (not to scale), (b) photograph of the FPCs added to water, (c) SEM image of a single FPC particle, and (d) XRD pattern of the FPC powder.
SEM was used to confirm the presence of immobilized TiO2 on the surface of the GMBs, observed as a rough particulate coating (Figure 1c), with a particle diameter of ~25 nm, similar to the diameter of the TiO2 nanocrystals used (Figure S2). SEM images of the uncoated GMBs are presented in Figure S3. EDX analysis further confirmed the presence of Ti, and the TiO2 content of the composite particles was estimated to be 36.6 ± 4.1 wt % (Figure S4, Table S1). TiO2 nanocrystals are known to partially sinter at the temperatures applied during the synthesis [24], which is proposed to be the mechanism of TiO2 adhesion [34,35]. XRD revealed the presence of anatase and rutile phases in the FPCs, characteristic of the mixed-phase TiO2 nanocrystals used [36], confirming that the calcination step did not significantly affect the crystal phase of the particles. In fact, mild calcination at the temperatures applied herein has been reported to enhance the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles [24].
The photocatalytic activity of the FPC particles was assessed under natural sunlight for the degradation of AEO in raw OSPW under gentle mixing conditions (Figure 2). The FPC particles degraded >80% of the AEO within 22 h of sunlight exposure (~33.4 kJ L−1 cumulative solar UV), from a starting concentration of ~30 mg L−1 down to 4 mg L−1. The oxidized intermediate compounds produced during photocatalytic AEO degradation have been thoroughly characterized in our previous work, where photocatalysis was demonstrated to result in nearly complete mineralization of organic carbon [7,9]. The kinetics were apparently first order, as observed previously [7], and the pseudo-first order rate constant for the FPCs was 3.46 ± 0.20 × 10−8 m2 J−1. The FPCs compared favourably to P25 TiO2 as a benchmark photocatalyst, which had a pseudo-first order rate constant of 4.15 ± 0.34 × 10−8 m2 J−1, where the measured rate constants were indistinguishable from each other (p > 0.1). However, normalized on a TiO2 mass basis, the FPCs outperformed the P25 TiO2, with a rate constant of 9.45 × 10−8 m2 J−1 g−1 compared to 8.30 × 10−8 m2 J−1 g−1, respectively. Conventionally, nanoparticle slurries would be expected to outperform immobilized photocatalysts, such as the FPCs, due to enhanced contaminant mass transfer and higher accessible catalyst surface area [37,38]. However, in the low mixing regimes studied herein, the advantages provided by the FPCs of concentrating the photocatalyst at the water surface where sunlight intensity is highest apparently outweighed the typical disadvantages of immobilized systems. Thus the FPCs exceeded the activity of a known excellent photocatalyst formulation while enabling a convenient means of recycling through their buoyant properties.
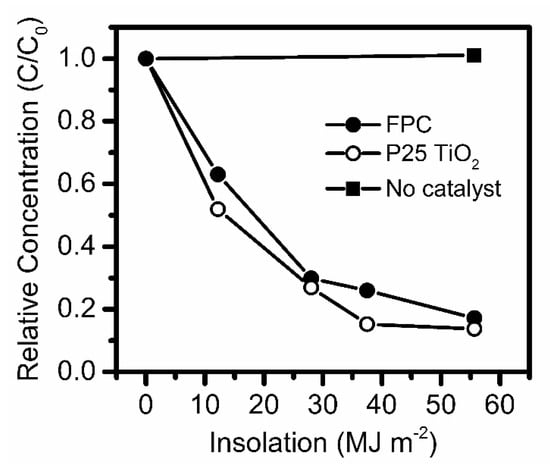
Figure 2.
Photocatalytic degradation of AEO in raw OSPW under natural sunlight, where C and C0 are the concentration and initial concentration of AEO, respectively.
The Reynolds number of mixing during the test was calculated to be 786, characteristic of a gentle laminar flow regime. The OSPW cap layer in oil sands tailings ponds is known to be well mixed by wind and waves [39,40,41], and NAs are furthermore constantly replenished to the interface by methanogenic bubbling in a similar process to dissolved gas flotation (estimated flux of 12 g CH4 m−2 day−1) [42]. Thus, as the above photocatalytic results were observed under gentle mixing conditions, it is anticipated that the natural mixing processes provided in the tailings ponds could be sufficient for OSPW treatment, although this question will be the topic of future studies. These results suggest the possibility for photocatalysis to serve as a truly passive AOP process with no electrical power input, where energy is provided solely by sunlight and wind.
Finally, the recyclability of the FPC particles for treating multiple batches of raw OSPW was tested under controlled illumination conditions (Figure 3), simply separating the catalyst by flotation. The catalyst was found to be reusable with equivalent activity for at least 3 cycles. Some deterioration in treatment performance was observed after the third cycle, possibly due to experimental difficulties in transferring 100% of the FPC material between cycles with small sample volumes, or alternatively due to progressive surface fouling of the catalyst. Effects of long term FPC exposure to raw OSPW is the topic of ongoing investigations in our laboratory.
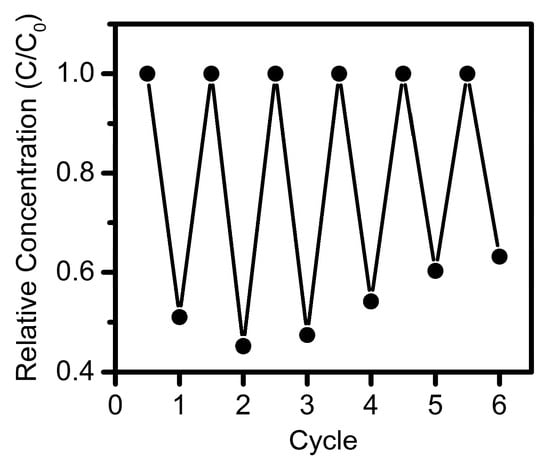
Figure 3.
Recyclability of a single batch of FPC particles to degrade AEO in raw OSPW, where C and C0 are the concentration and initial concentration of AEO, respectively.
4. Conclusions
A floating photocatalyst composite was demonstrated to match the photocatalytic activity of P25 TiO2 in raw OSPW under natural sunlight. This is a significant finding, since photocatalytic activity was not sacrificed through this immobilization strategy, while the following advantages were gained:
- Due to their buoyancy, FPCs naturally concentrate at the air-water interface where sunlight intensity and dissolved oxygen concentrations are highest (i.e., the optimal treatment zone);
- Substantially less photocatalyst material is needed to achieve the same treatment rate as slurry deployment, since TiO2 comprises only a minority of the buoyant composite mass, while in photocatalytic slurries, the vast majority of particles suspended below the illuminated air-water interface do not participate in the treatment process;
- NAs are naturally enriched at the air-water interface due to their surfactant properties, and are replenished to the surface from deeper OSPW in tailings ponds by methane bubbling, and through natural mixing provided by wind and waves;
- FPCs can be easily contained and collected by skimming from the surface, compared with the significant technical challenges of collecting colloidal nanoparticles from a slurry.
The use of sunlight and low energy mixing suggests the possibility that photocatalysis could serve as a truly passive water treatment process amenable to large scale deployment in the oil sands.
Supplementary Materials
The following are available online at http://www.mdpi.com/2073-4441/10/2/202/s1, Figure S1: Solar irradiance measured throughout the duration of the photocatalytic experiment of Figure 2. Figure S2: SEM image of TiO2 nanostructures on the surface of a FPC particle. Figure S3: SEM images of uncoated glass microbubbles (GMBs) at (a) 500× and (b) 3000× magnification. GMBs were sputtered with Au prior to imaging. Figure S4: (a–c) SEM regions used for EDX elemental analysis and (d) typical EDX spectrum, as obtained from region (b). Table S1: Results of EDX analysis, referring to SEM regions in Figure S4.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Shell Canada for supplying OSPW samples for our experiments, and for continued support. We would also like to thank Tong Leung and Nafiseh Moghimi, Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, for assistance with the SEM and EDX analysis, as well as David Wulff, Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Waterloo, for assistance with the SEM analysis. We also thank Linda Nazar and Guerman Popov, Department of Chemistry, University of Waterloo, for assistance with the XRD analysis. This work was financially supported by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC) and NSERC’s Toward Environmentally Responsible Resource Extraction Network (TERRE-NET), and Tim Leshuk gratefully acknowledges support of the NSERC Vanier Canada Graduate Scholarship and Ontario Graduate Scholarship.
Author Contributions
T.L. conceived and designed the experiments; T.L. and H.K. synthesized the floating photocatalysts; H.K. and D.d.O.L. performed the experiments; T.L. analyzed the data and wrote the paper; F.G. supervised the project, contributed reagents, materials, analysis tools, and critically reviewed the paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The following authors, T.L. and F.G., declare involvement as co-founders (with stock ownership) in H2nanO Inc., an organization with a financial interest in the subject matter and materials discussed in this manuscript. The following authors, H.K. and D.d.O.L., declare no competing financial interest. The funding sponsors had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Morandi, G.D.; Wiseman, S.B.; Pereira, A.; Mankidy, R.; Gault, I.G.M.; Martin, J.W.; Giesy, J.P. Effects-Directed Analysis of Dissolved Organic Compounds in Oil Sands Process-Affected Water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12395–12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, S.; Ramsay, B.A.; Wang, J.; Ramsay, J. Toxicity and composition profiles of solid phase extracts of oil sands process-affected water. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 538, 573–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Scott, A.C.; Fedorak, P.M.; Bataineh, M.; Martin, J.W. Influence of Molecular Structure on the Biodegradability of Naphthenic Acids. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 1290–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; MacKinnon, M.D.; Martin, J.W. Estimating the in situ biodegradation of naphthenic acids in oil sands process waters by HPLC/HRMS. Chemosphere 2009, 76, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marentette, J.R.; Frank, R.A.; Bartlett, A.J.; Gillis, P.L.; Hewitt, L.M.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Brunswick, P.; Shang, D.; Parrott, J.L. Toxicity of naphthenic acid fraction components extracted from fresh and aged oil sands process-affected waters, and commercial naphthenic acid mixtures, to fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas) embryos. Aquat. Toxicol. 2015, 164, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- COSIA Challenge #0014: Passive Organics Treatment Technology. Available online: http://www.cosia.ca/initiatives/water/water-challenge-statements (accessed on 29 October 2016).
- Leshuk, T.; Wong, T.; Linley, S.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Gu, F. Solar photocatalytic degradation of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected water. Chemosphere 2016, 144, 1854–1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Headley, J.V.; Du, J.-L.; Peru, K.M.; McMartin, D.W. Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry of the photodegradation of naphthenic acids mixtures irradiated with titanium dioxide. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part A 2009, 44, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leshuk, T.; de Oliveira Livera, D.; Peru, K.M.; Headley, J.V.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Wong, T.; Gu, F. Photocatalytic degradation kinetics of naphthenic acids in oil sands process-affected water: Multifactorial determination of significant factors. Chemosphere 2016, 165, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, A.C.; Zubot, W.; MacKinnon, M.D.; Smith, D.W.; Fedorak, P.M. Ozonation of oil sands process water removes naphthenic acids and toxicity. Chemosphere 2008, 71, 156–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Z.; Li, C.; Belosevic, M.; Bolton, J.R.; El-Din, M.G. Application of a Solar UV/Chlorine Advanced Oxidation Process to Oil Sands Process-Affected Water Remediation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9692–9701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valencia, S.; Marín, J.; Restrepo, G. Photocatalytic Degradation of Humic Acids with Titanium Dioxide Embedded into Polyethylene Pellets to Enhance the Postrecovery of Catalyst. Environ. Eng. Sci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.; Lin, Y.-P.; Bai, R. Removal of phenol in aqueous solutions by novel buoyant Composite photocatalysts and the kinetics. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2013, 115, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhou, W.; Huo, P.; Luo, Y.; He, M.; Pan, J.; Li, C.; Yan, Y. Performance of a novel TiO2 photocatalyst based on the magnetic floating fly-ash cenospheres for the purpose of treating waste by waste. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 225, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damasceno, F.C.; Gruber, L.D.A.; Geller, A.M.; de Campos, M.C.V.; Gomes, A.O.; Guimarães, R.C.L.; Péres, V.F.; Jacques, R.A.; Caramão, E.B. Characterization of naphthenic acids using mass spectroscopy and chromatographic techniques: Study of technical mixtures. Anal. Methods 2014, 6, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halász, G.; Gyüre, B.; Jánosi, I.M.; Szabó, K.G.; Tél, T. Vortex flow generated by a magnetic stirrer. Am. J. Phys. 2007, 75, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Current Readings for UW Weather Station. Available online: http://weather.uwaterloo.ca/ (accessed on 16 December 2014).
- Jivraj, M.N.; MacKinnon, M.; Fung, B. Naphthenic Acid Extraction and Quantitative Analysis with FT-IR Spectroscopy; Syncrude Canada Ltd.: Edmonton, Alberta, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Holowenko, F.M.; MacKinnon, M.D.; Fedorak, P.M. Naphthenic acids and surrogate naphthenic acids in methanogenic microcosms. Water Res. 2001, 35, 2595–2606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewer, D.M.; Young, R.F.; Whittal, R.M.; Fedorak, P.M. Naphthenic acids and other acid-extractables in water samples from Alberta: What is being measured? Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5997–6010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, N.B.; Wang, C.M.; Luo, Z.; Schwitzgebel, J.; Ekerdt, J.G.; Brock, J.R.; Heller, A. Attachment of TiO2 Powders to Hollow Glass Microbeads: Activity of the TiO2—Coated Beads in the Photoassisted Oxidation of Ethanol to Acetaldehyde. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1991, 138, 3660–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espino-Estévez, M.R.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.; González-Díaz, O.M.; Navío, J.A.; Fernández-Hevia, D.; Doña-Rodríguez, J.M. Enhancement of stability and photoactivity of TiO2 coatings on annular glass reactors to remove emerging pollutants from waters. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 279, 488–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, L.L.P.; Lynch, R.J.; In, S.-I. Comparison of simple and economical photocatalyst immobilisation procedures. Appl. Catal. A 2009, 365, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yin, T.; Han, D. Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of TiO2 Powders (P25) via Calcination Treatment. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, J.; Valencia, S.; Rios, L.; Restrepo, G.; Marín, J. Characterization and photocatalytic evaluation of polypropylene and polyethylene pellets coated with P25 TiO2 using the controlled-temperature embedding method. Chem. Eng. J. 2012, 203, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiyi, M.E.; Skelton, R.L. Photocatalytic mineralisation of methylene blue using buoyant TiO2-coated polystyrene beads. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 2000, 132, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalhães, F.; Moura, F.C.C.; Lago, R.M. TiO2/LDPE composites: A new floating photocatalyst for solar degradation of organic contaminants. Desalination 2011, 276, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Shi, L.; Zhu, Y. Solid-phase photocatalytic degradation of polyethylene plastic under UV and solar light irradiation. J. Mol. Catal. A 2007, 268, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, J.; Chai, M.; Zhu, Y. Photocatalytic degradation of polystyrene plastic under fluorescent light. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2003, 37, 4494–4499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tennakone, K.; Kottegoda, I.R.M. Photocatalytic mineralization of paraquat dissolved in water by TiO2 supported on polythene and polypropylene films. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A 1996, 93, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faramarzpour, M.; Vossoughi, M.; Borghei, M. Photocatalytic degradation of furfural by titania nanoparticles in a floating-bed photoreactor. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 146, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Zhai, J. Preparation and characterization of Fe3+-doped TiO2 on fly ash cenospheres for photocatalytic application. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 3473–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.N.; Borghei, S.M.; Vossoughi, M.; Taghavinia, N. Immobilization of TiO2 on perlite granules for photocatalytic degradation of phenol. Appl. Catal. B 2007, 74, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthews, R.W. Photooxidative degradation of coloured organics in water using supported catalysts. TiO2 on sand. Water Res. 1991, 25, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzo, R.L.; Giombi, J.L.; Baltanás, M.A.; Cassano, A.E. The performance in a fluidized bed reactor of photocatalysts immobilized onto inert supports. Catal. Today 2000, 62, 175–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurum, D.C.; Agrios, A.G.; Gray, K.A.; Rajh, T.; Thurnauer, M.C. Explaining the Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity of Degussa P25 Mixed-Phase TiO2 Using EPR. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 4545–4549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malato, S.; Fernandez-Ibanez, P.; Maldonado, M.; Blanco, J.; Gernjak, W. Decontamination and disinfection of water by solar photocatalysis: Recent overview and trends. Catal. Today 2009, 147, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spasiano, D.; Marotta, R.; Malato, S.; Fernandez-Ibañez, P.; Di Somma, I. Solar photocatalysis: Materials, reactors, some commercial, and pre-industrialized applications. A comprehensive approach. Appl. Catal. B 2015, 170–171, 90–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, G.A.; Ward, P.R.B.; MacKinnon, M.D. Wind-wave-induced suspension of mine tailings in disposal ponds—A case study. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 1991, 18, 1047–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, G.A.; Tedford, E.W.; Pieters, R. Suspended solids in an end pit lake: Potential mixing mechanisms. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2015, 43, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dompierre, K.A.; Barbour, S.L. Characterization of physical mass transport through oil sands fluid fine tailings in an end pit lake: A multi-tracer study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2016, 189, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holowenko, F.M. Methanogenesis and Fine Tailings Waste from Oil Sands Extraction: A Microcosm-Based Laboratory Examination. Master’s Thesis, University of Alberta, Edmonton, Alberta, 2000. [Google Scholar]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).