Introduction of an Experimental Terrestrial Forecasting/Monitoring System at Regional to Continental Scales Based on the Terrestrial Systems Modeling Platform (v1.1.0)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods: Terrestrial Monitoring Systems’ Components and Domains
2.1. Software and Hardware Components of the Terrestrial Monitoring System, TMS
2.2. Monitoring Domain Setup
2.2.1. The North Rhine-Westphalia domain
2.2.2. The Pan-European Domain
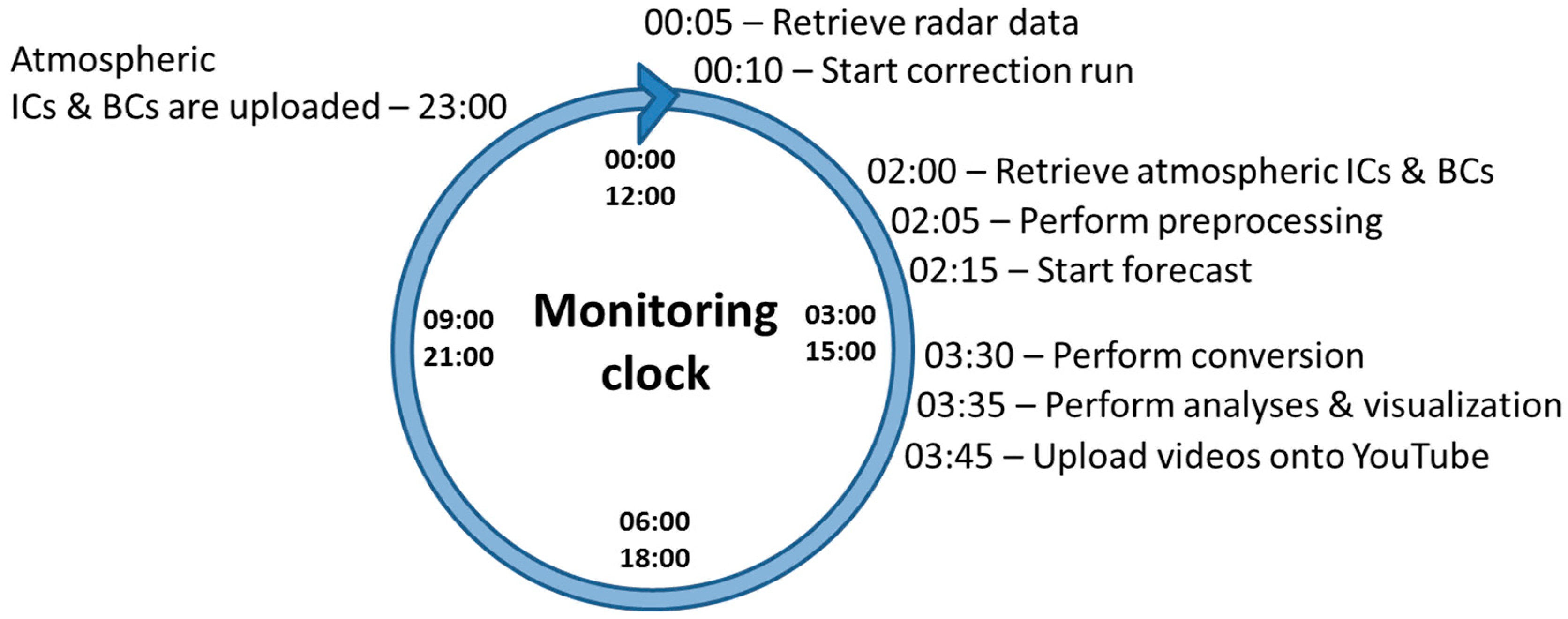
2.3. Monitoring Clock
3. Workflows and Automation
3.1. Monitoring EU and NRW
3.1.1. Retrieval of Boundary and Initial Conditions
3.1.2. Preprocessing
3.1.3. Forward Simulation
3.1.4. Postprocessing and Visualization
3.1.5. YouTube Upload and Archiving
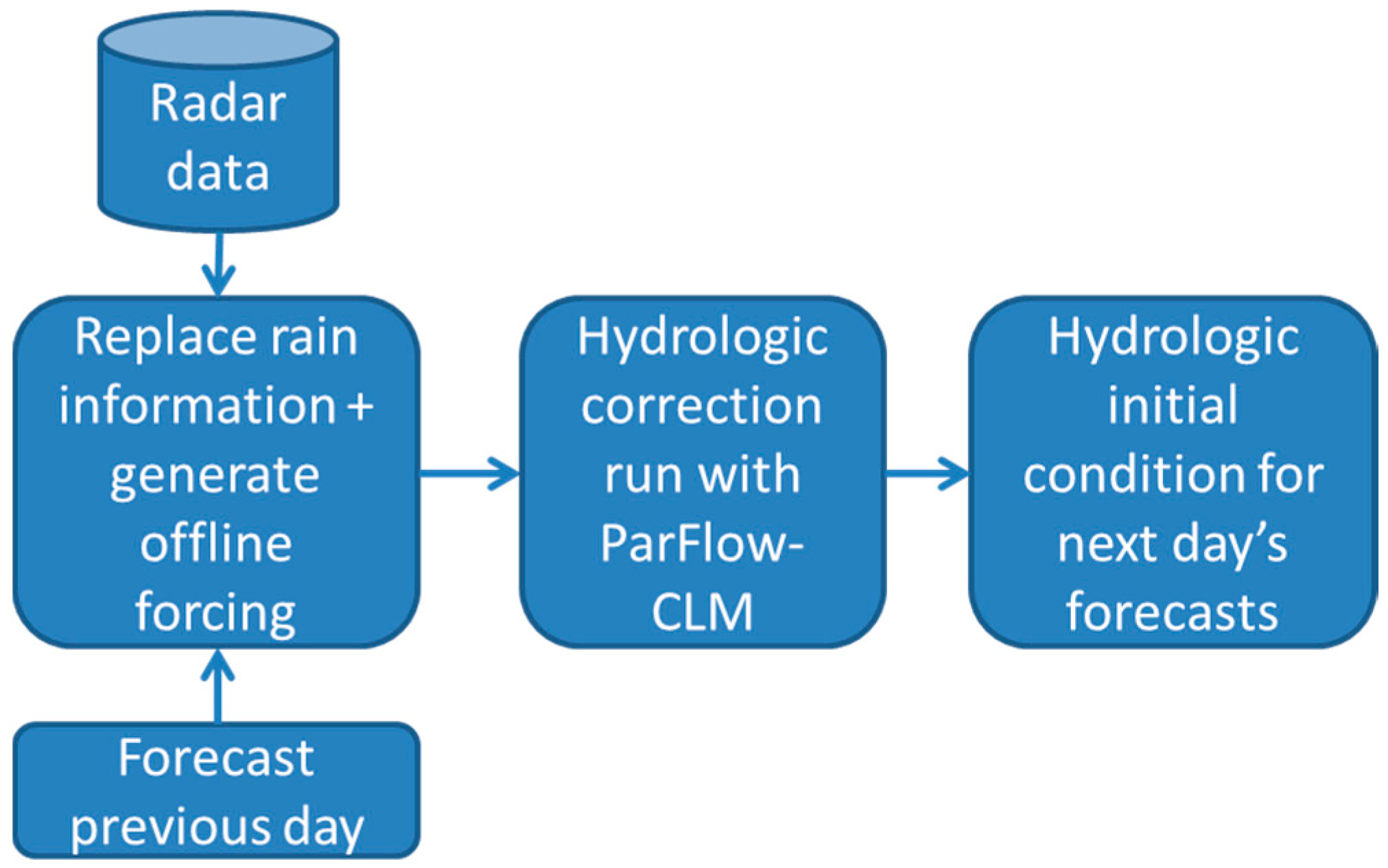
3.2. Precipitation Radar Integration for NRW
3.2.1. Radar Data Retrieval and Preprocessing
3.2.2. TSMP Correction Run and Upload/Archiving
3.3. Publication of Monitoring Products
4. Results and Discussion
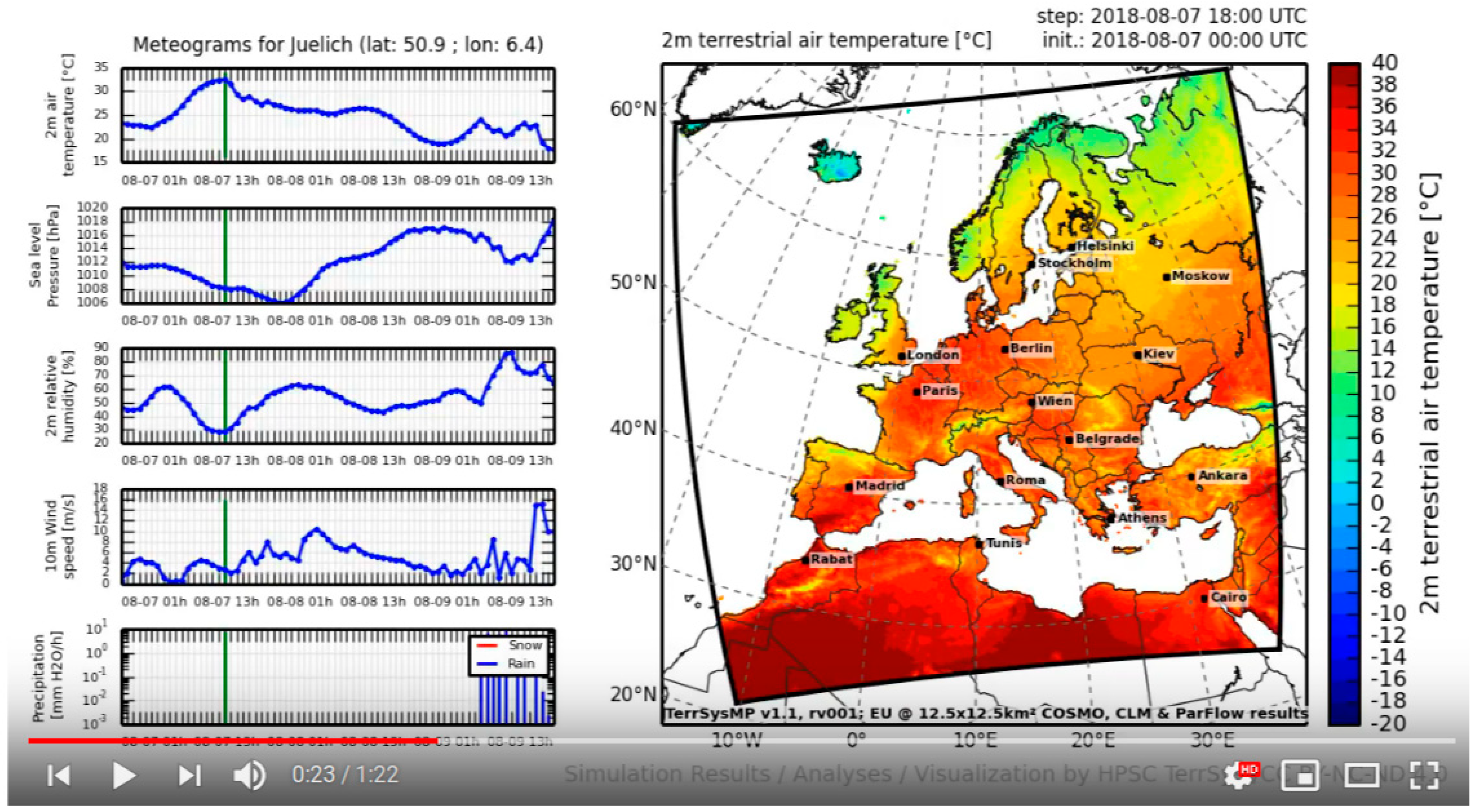
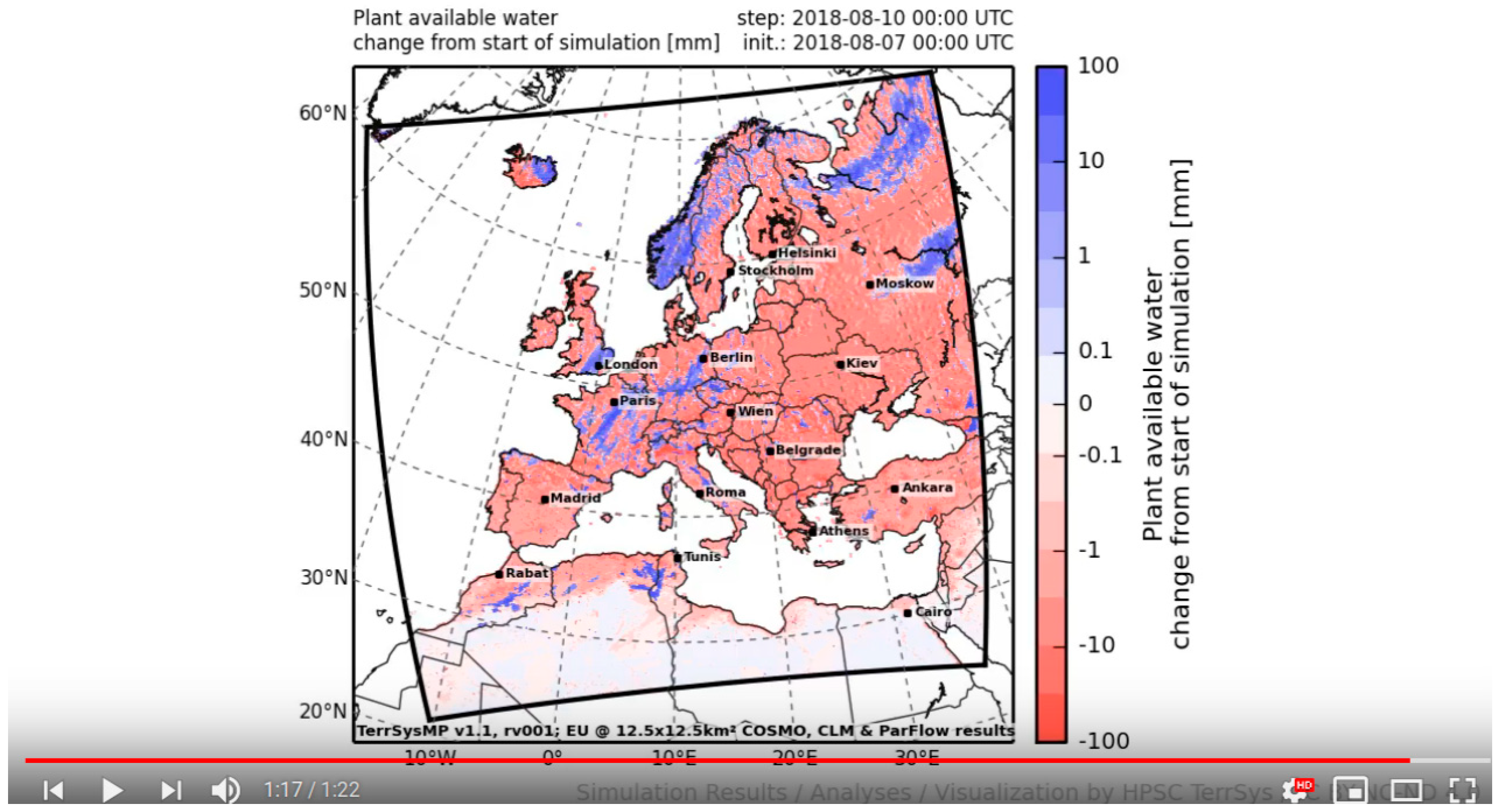
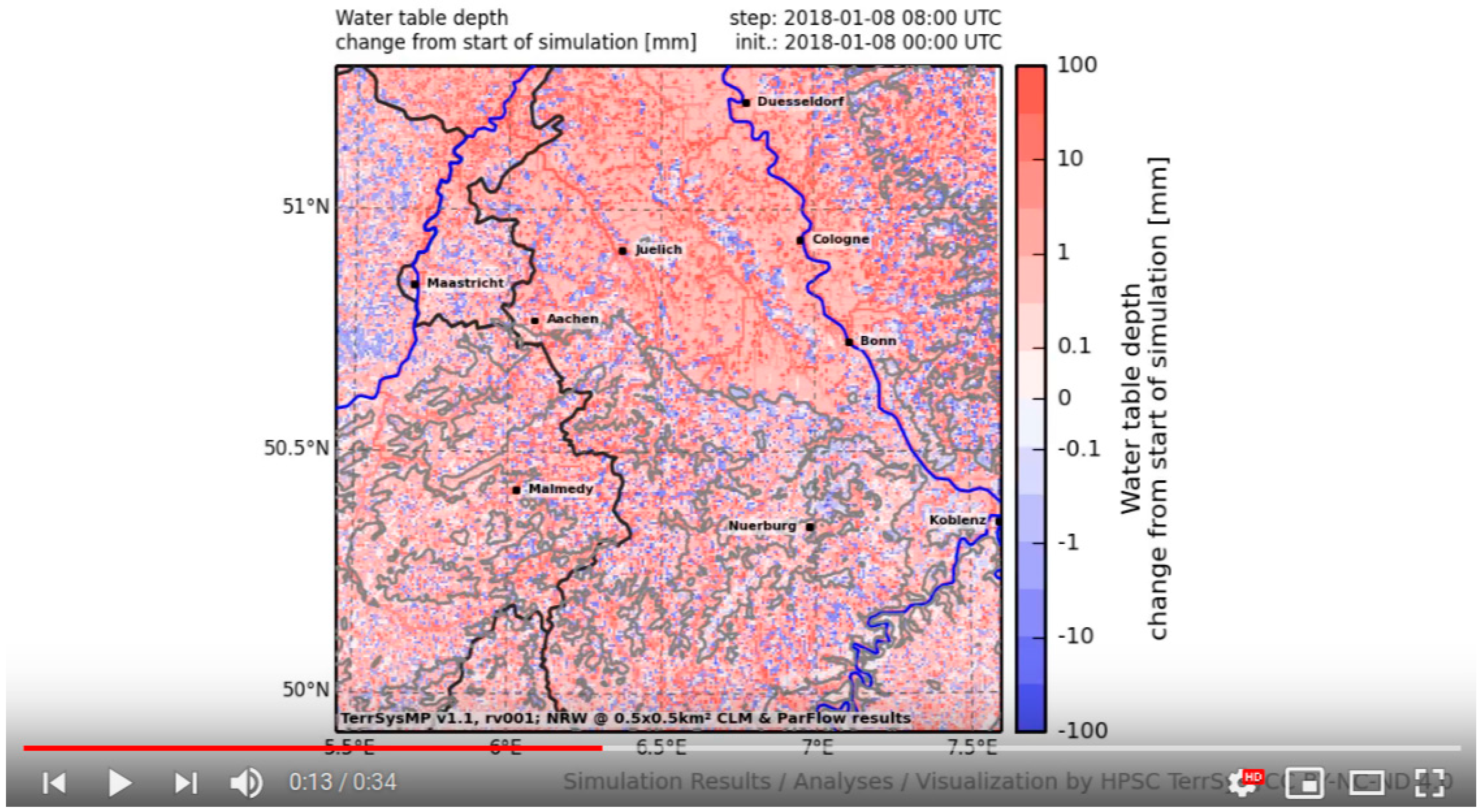
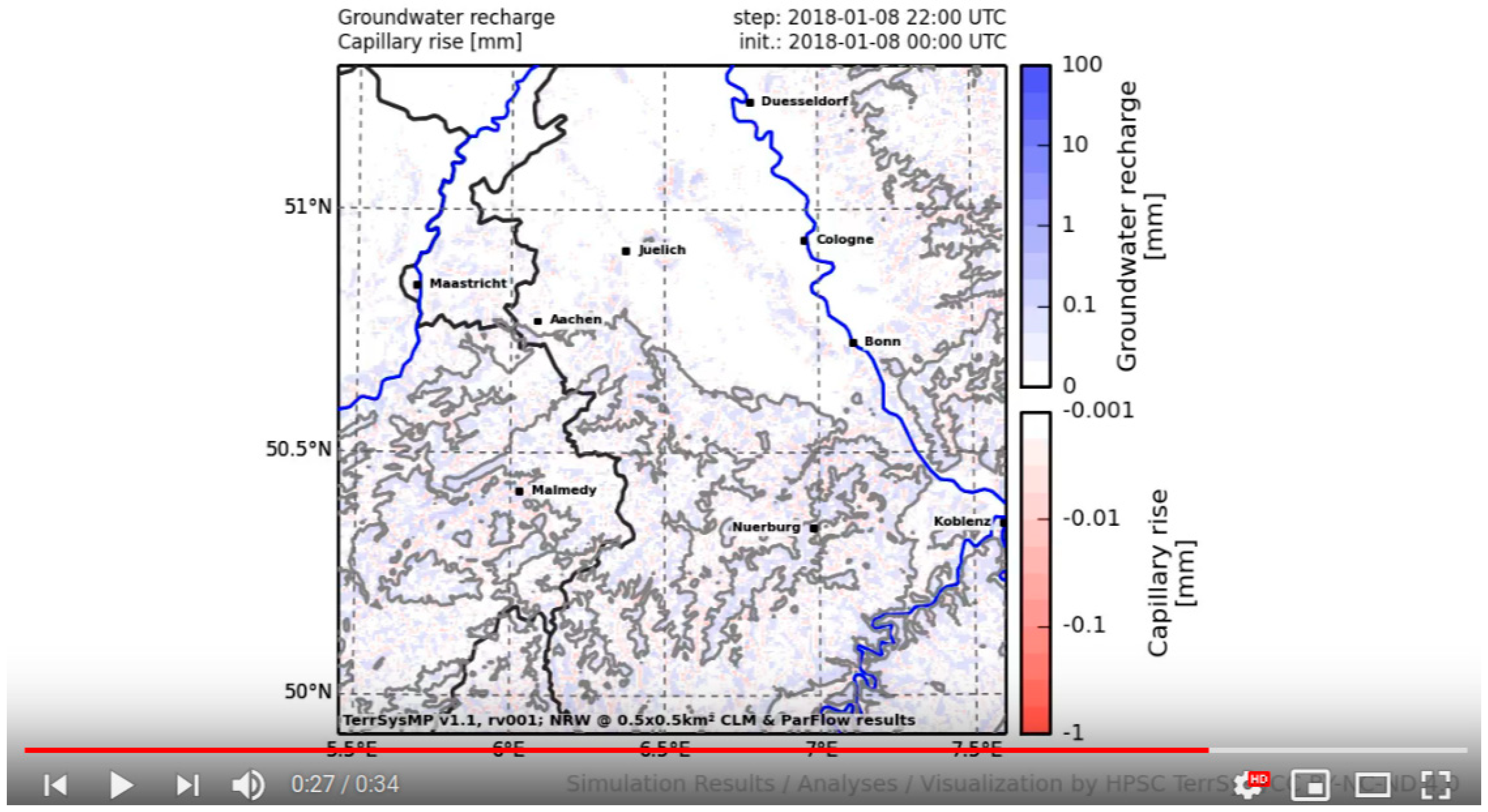
4.1. Monitoring EUR-11 and NRW Domains
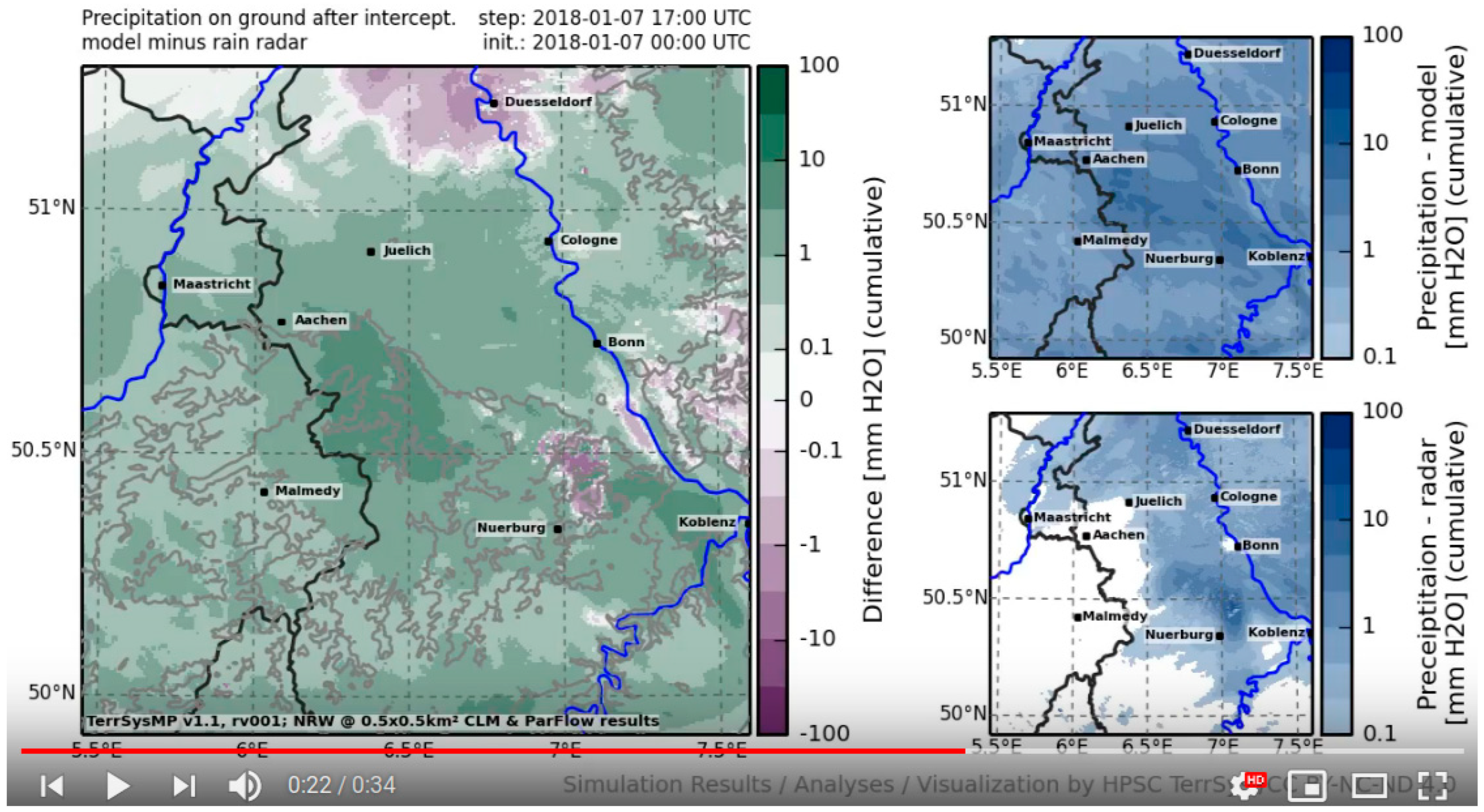
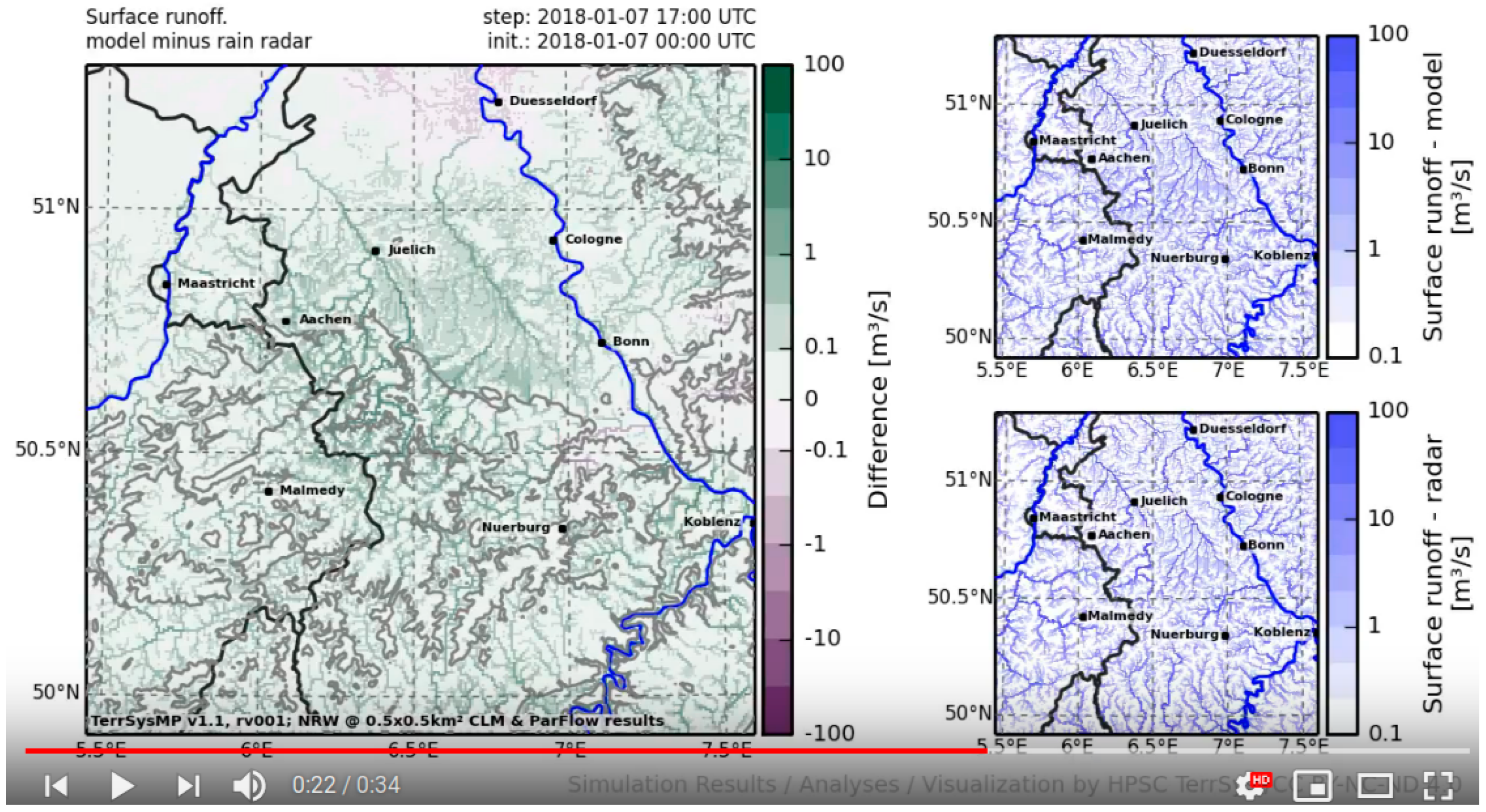
4.2. Radar Correction for NRW
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Swinbank, R.; Kyouda, M.; Buchanan, P.; Froude, L.; Hamill, T.M.; Hewson, T.D.; Keller, J.H.; Matsueda, M.; Methven, J.; Pappenberger, F.; et al. The TIGGE Project and Its Achievements. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2015, 97, 49–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damrath, U.; Doms, G.; Frühwald, D.; Heise, E.; Richter, B.; Steppeler, J. Operational quantitative precipitation forecasting at the German Weather Service. J. Hydrol. 2000, 239, 260–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmer, T. The ECMWF ensemble prediction system: Looking back (more than) 25 years and projecting forward 25 years. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, P. The origins of computer weather prediction and climate modeling. J. Comp. Phys. 2008, 227, 3431–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bauer, P.; Thorpe, A.; Brunet, G. The quiet revolution of numerical weather prediction. Nature 2015, 525, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Moorthi, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, J.; Nadiga, S.; Tripp, P.; Behringer, D.; Hou, Y.-T.; Chuang, H.; Iredell, M.; et al. The NCEP Climate Forecast System Version 2. J. Clim. 2013, 27, 2185–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roebber, P.J.; Schultz, D.M.; Colle, B.A.; Stensrud, D.J. Toward improved prediction: High-resolution and ensemble modeling systems in operations. Weather Forecast. 2004, 19, 936–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Roo, A.P.J.; Gouweleeuw, B.; Thielen, J.; Bartholmes, J.; Bongioannini-Cerlini, P.; Todini, E.; Bates, P.D.; Horritt, M.; Hunter, N.; Beven, K.; et al. Development of a European flood forecasting system. Int. J. River Basin Manag. 2003, 1, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thielen, J.; Bartholmes, J.; Ramos, M.-H.; de Roo, A. The European flood alert system—part 1: Concept and development. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2009, 13, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refsgaard, J.C. Validation and intercomparison of different updating procedures for real-time forecasting. Hydrol. Res. 1997, 28, 65–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emerton, R.; Zsoter, E.; Arnal, L.; Cloke, H.L.; Muraro, D.; Prudhomme, C.; Stephens, E.M.; Salamon, P.; Pappenberger, F. Developing a global operational seasonal hydro-meteorological forecasting system: GloFAS-Seasonal v1.0. Geosci. Model Dev. 2018, 11, 3327–3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.; McNally, A.; Husak, G.; Funk, C. A seasonal agricultural drought forecast system for food-insecure regions of East Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2014, 18, 3907–3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, W.J.; Prinsen, G.F.; Hoogewoud, J.C.; Veldhuizen, A.A.; Verkaik, J.; Oude Essink, G.H.P.; van Walsum, P.E.V.; Delsman, J.R.; Hunink, J.C.; Massop, H.T.L.; et al. An operational, multi-scale, multi-model system for consensus-based, integrated water management and policy analysis: The Netherlands hydrological instrument. Environ. Model. Softw. 2014, 59, 98–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, P.; Sulis, M.; Masbou, M.; Kollet, S.; Simmer, C. A scale-consistent terrestrial systems modeling platform based on COSMO, CLM, and parflow. Mon. Weather Rev. 2014, 142, 3466–3483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasper, F.; Goergen, K.; Shrestha, P.; Sulis, M.; Rihani, J.; Geimer, M.; Kollet, S. Implementation and scaling of the fully coupled terrestrial systems modeling platform (TerrSysMP v1.0) in a massively parallel supercomputing environment—A case study on JUQUEEN (IBM Blue Gene/Q). Geosci. Model Dev. 2014, 7, 2531–2543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmer, C.I.; Thiele-Eich, M.; Masbou, W.; Amelung, S.; Crewell, B.; Diekkrueger, F.; Ewert, H.-J.; Hendricks-Franssen, A.J.; Huisman, A.; Kemna, N.; et al. Monitoring and modeling the terrestrial system from pores to catchments—The transregional collaborative research center on patterns in the soil-vegetation-atmosphere system. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2014, 96, 1765–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Sulis, M.; Kollet, S.J. The concept of dual-boundary forcing in land surface-subsurface interactions of the terrestrial hydrologic and energy cycles. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8531–8548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Sulis, M.; Kollet, S.J. The subsurface-land surface-atmosphere connection under convective conditions. Adv. Water Resour. 2015, 83, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keune, J.; Gasper, F.; Goergen, K.; Hense, A.; Shrestha, P.; Sulis, M.; Kollet, S. Studying the influence of groundwater representations on land surface-atmosphere feedbacks during the European heat wave in 2003. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 13301–13325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, M.; Williams, J.L.; Shrestha, P.; Diederich, M.; Simmer, C.; Kollet, S.J.; Maxwell, R.M. Coupling groundwater, vegetation, and atmospheric processes: A comparison of two integrated models. J. Hydrometeor. 2017, 18, 1489–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sulis, M.; Keune, J.; Shrestha, P.; Simmer, C.; Kollet, S.J. Quantifying the impact of subsurface-land surface physical processes on the predictive skill of subseasonal mesoscale atmospheric simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 123, 9131–9151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keune, J.; Sulis, M.; Kollet, S.; Siebert, S.; Wada, Y. Human water use impacts on the strength of the continental sink for atmospheric water. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2018, 45, 4068–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keune, J.; Sulis, M.; Kollet, S. Potential added value of incorporating human water use in the simulation of evapotranspiration and precipitation in a continental-scale bedrock-to-atmosphere modeling system. J. Adv. Model. Earth Sys. 2018. under review. [Google Scholar]
- Baldauf, M.; Seifert, A.; Förstner, J.; Majewski, D.; Raschendorfer, M.; Reinhardt, T. Operational convective-scale numerical weather prediction with the COSMO model: Description and sensitivities. Mon. Weather Rev. 2011, 139, 3887–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oleson, K.W.; Niu, G.-Y.; Yang, Z.-L.; Lawrence, D.M.; Thornton, P.E.; Lawrence, P.J.; Stöckli, R.; Dickinson, R.E.; Bonan, G.B.; Levis, S.; et al. Improvements to the community land model and their impact on the hydrological cycle. J. Geophys. Res Biogeosci. 2008, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.; Woodward, C.S. Newton-Krylov-multigrid solvers for large-scale, highly heterogeneous, variably saturated flow problems. Adv. Water Resour. 2001, 24, 763–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kollet, S.J.; Maxwell, R.M. Integrated surface-groundwater flow modeling: A free-surface overland flow boundary condition in a parallel groundwater flow model. Adv. Water Resour. 2006, 29, 945–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.M. A terrain-following grid transform and preconditioner for parallel, large-scale, integrated hydrologic modeling. Adv. Water Resour. 2013, 53, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valcke, S. The OASIS3 coupler: A European climate modelling community software. Geosci. Model Dev. 2013, 6, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodwell, M.J.; Magnusson, L.; Bauer, P.; Bechtold, P.; Bonavita, M.; Cardinali, C.; Diamantakis, M.; Earnshaw, P.; Garcia-Mendez, A.; Isaksen, L.; et al. Characteristics of occasional poor medium-range weather forecasts for Europe. Bull. Am. Meteor. Soc. 2013, 94, 1393–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, W.; He, G.; Kollet, S.J.; Maxwell, R.M.; Vereecken, H.; Hendricks-Franssen, H.-J. TerrSysMP–PDAF (version 1.0): A modular high-performance data assimilation framework for an integrated land surface-subsurface model. Geosci. Model Dev. 2016, 9, 1341–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Kurtz, W.; Kollet, S.; Vereecken, H.; Hendricks-Franssen, H.J. Comparison of different assimilation methodologies of groundwater levels to improve predictions of root zone soil moisture with an integrated terrestrial systems model. Adv. Water Resour. 2018, 111, 224–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, M.; Ryzhkov, A.; Simmer, C.; Zhang, P.; Troemel, S. Use of specific attenuation for rainfall measurement at X-band radar wavelengths—Part 1: Radar calibration and partial beam blockage estimation. J. Hydrometeor. 2015, 16, 487–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diederich, M.; Ryzhkov, A.; Simmer, C.; Zhang, P.; Trömel, S. Use of specific attenuation for rainfall measurement at X-band radar wavelengths—Part II: Rainfall estimates and comparison with rain gauges. J. Hydrometeor. 2015, 16, 503–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schättler, U.; Blahak, U. A Description of the Nonhydrostatic Regional COSMO-Model. Part V: Preprocessing: Initial and Boundary Data for the COSMO-Model. 2018. Available online: http://www.cosmo-model.org/content/model/documentation/core/int2lm_2.03.pdf (accessed on 23 October 2018).




| Variable Name | Units |
|---|---|
| Subsurface hydraulic pressure | (m) |
| Subsurface relative saturation | (-) |
| Subsurface Darcy flow | (m·h−1) |
| Overland flow, surface runoff | (m·s−1) |
| Evapotranspiration | (mm·s−1) or W·m−2) |
| Sensible heat flux | (W·m−2) |
| Ground heat flux | (W·m−2) |
| Long/short wave radiation (incoming and outgoing) | (W·m−2) |
| Precipitation (liquid and frozen) | (mm·s−1) |
| Snow water equivalent | (m) |
| Barometric pressure | (Pa) |
| Air temperature | (K) |
| Air humidity | (kg·kg−1) |
| Air wind speeds | (m·s−1) |
| Cloud cover | (-) |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kollet, S.; Gasper, F.; Brdar, S.; Goergen, K.; Hendricks-Franssen, H.-J.; Keune, J.; Kurtz, W.; Küll, V.; Pappenberger, F.; Poll, S.; et al. Introduction of an Experimental Terrestrial Forecasting/Monitoring System at Regional to Continental Scales Based on the Terrestrial Systems Modeling Platform (v1.1.0). Water 2018, 10, 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111697
Kollet S, Gasper F, Brdar S, Goergen K, Hendricks-Franssen H-J, Keune J, Kurtz W, Küll V, Pappenberger F, Poll S, et al. Introduction of an Experimental Terrestrial Forecasting/Monitoring System at Regional to Continental Scales Based on the Terrestrial Systems Modeling Platform (v1.1.0). Water. 2018; 10(11):1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111697
Chicago/Turabian StyleKollet, Stefan, Fabian Gasper, Slavko Brdar, Klaus Goergen, Harrie-Jan Hendricks-Franssen, Jessica Keune, Wolfgang Kurtz, Volker Küll, Florian Pappenberger, Stefan Poll, and et al. 2018. "Introduction of an Experimental Terrestrial Forecasting/Monitoring System at Regional to Continental Scales Based on the Terrestrial Systems Modeling Platform (v1.1.0)" Water 10, no. 11: 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111697
APA StyleKollet, S., Gasper, F., Brdar, S., Goergen, K., Hendricks-Franssen, H.-J., Keune, J., Kurtz, W., Küll, V., Pappenberger, F., Poll, S., Trömel, S., Shrestha, P., Simmer, C., & Sulis, M. (2018). Introduction of an Experimental Terrestrial Forecasting/Monitoring System at Regional to Continental Scales Based on the Terrestrial Systems Modeling Platform (v1.1.0). Water, 10(11), 1697. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111697







