Does Mussel Farming Promote Cost Savings and Equity in Reaching Nutrient Targets for the Baltic Sea?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Conceptual Approach
2.1. Cost-Effectiveness
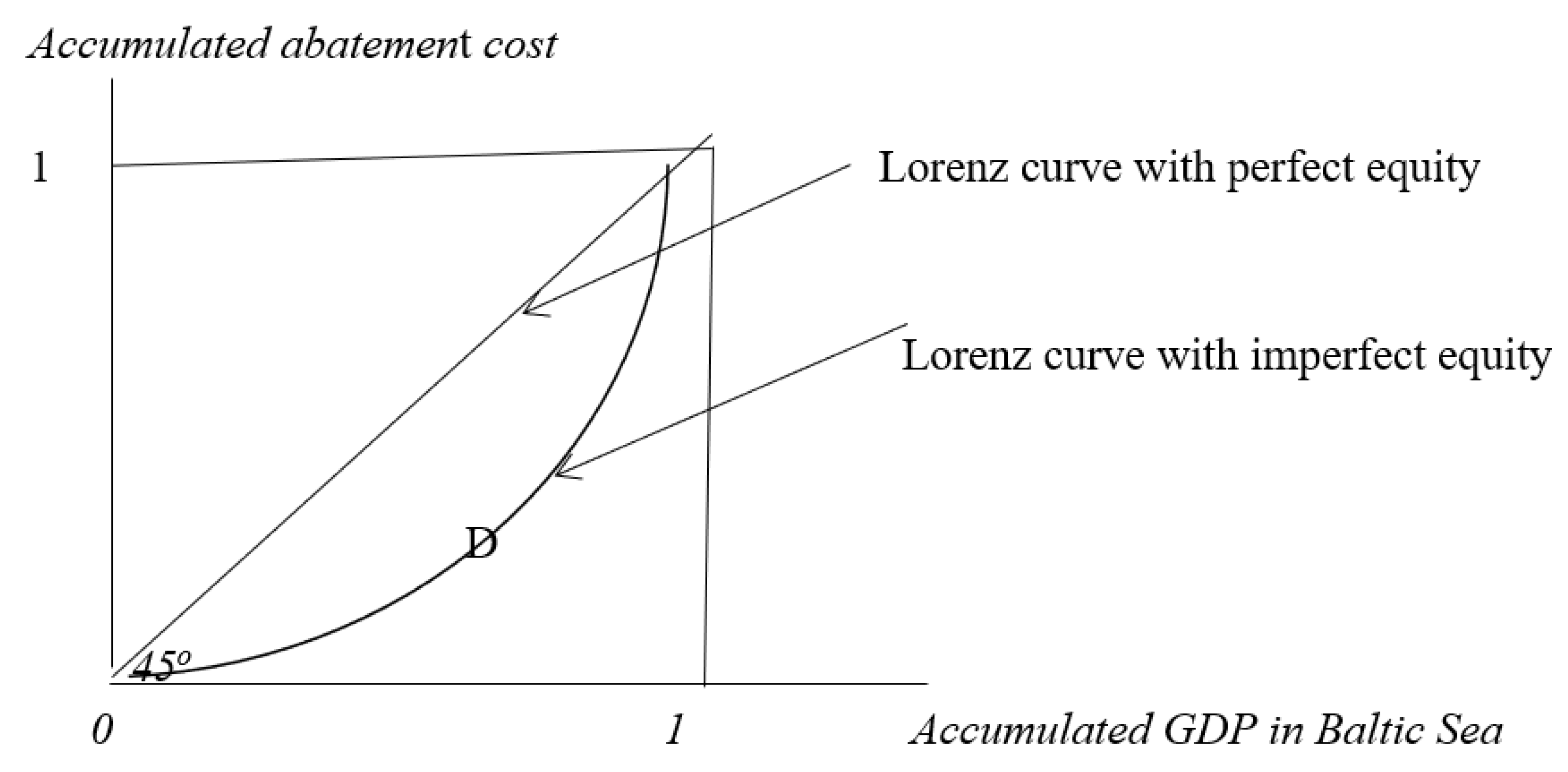
2.2. Equity
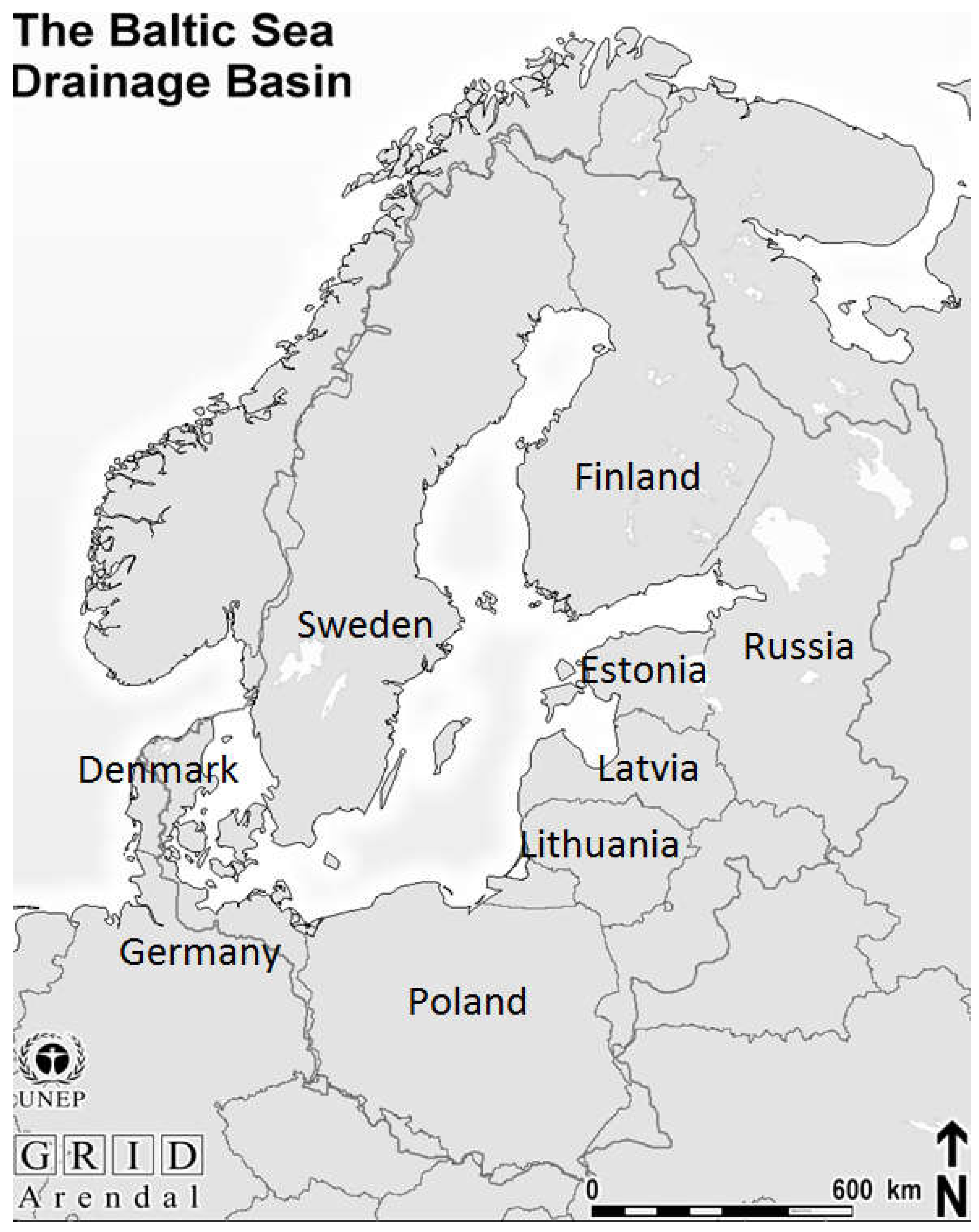
3. Description of Data in the Optimization Model
4. Results—Cost Savings and Equity Outcomes
4.1. Total and National Cost
4.2. Equity
5. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A. First-Order Conditions for Optimal Solutions
Appendix B. Tables A1 and A2, Figure A1
| Countries | Share of Total GDP a | GDP/Cap., Thousand SEK b,d | Nitrogen, Kton c; Load Reduction | Phosphorus, Kton c; Load Reduction | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEN | 0.078 | 447 | 71 | 2.89 | 1.928 | 0.038 |
| EST | 0.254 | 145 | 28 | 1.8 | 0.804 | 0.32 |
| FIN | 0.142 | 358 | 83 | 3.43 | 3.56 | 0.356 |
| GER | 0.127 | 349 | 63 | 7.67 | 0.526 | 0.17 |
| LAT | 0.267 | 115 | 78 | 1.67 | 2.227 | 0.22 |
| LIT | 0.016 | 121 | 46 | 8.97 | 2.635 | 1.47 |
| POL | 0.018 | 107 | 221 | 43.6 | 12.31 | 7.48 |
| RUS | 0.028 | 79 | 94 | 10.38 | 7.178 | 3.79 |
| SWE | 0.070 | 429 | 130 | 9.24 | 3.639 | 0.53 |
| Total | 1 (15,022 billion SEK d) | 173 | 814 | 89.65 | 34.807 | 14.374 |
| Countries | Cost of Mussel Farm, Mill SEK/Farm a | Live Mussel Production, ton/Farm a | Cost in SEK/kg Live Mussel | Maximum Total Production, kton Biomass b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEN | 0.30 | 225 c, 110 d | 1.31 c, 2.68 d | 1168 |
| EST | 0.13 | 70 | 1.32 | 172 |
| GER | 0.24 | 110 d, 90 e | 2.16 d, 3.00 e | 1074 |
| LAT | 0.11 | 90 | 1.23 | 158 |
| LIT | 0.11 | 90 | 1.23 | 28 |
| POL | 0.12 | 90 | 1.26 | 202 |
| RUS (Kaliningrad) | 0.09 | 90 | 0.97 | 46 |
| SWE | 0.27 | 225 c, 110 d,70 f | 1.01 c, 2.60 d, 3.81 f | 1046 |
References
- Galloway, J.N.; Townsend, A.R.; Erisman, J.W.; Bekunda, M.; Cai, Z.; Freney, J.R.; Martinelli, L.A.; Seitzinger, S.P.; Sutton, M.A. Transformation of the Nitrogen Cycle: Recent Trends, Questions, and Potential Solutions. Science 2008, 320, 889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conley, D.J.; Björck, S.; Bonsdorff, E.; Carstensen, J.; Destouni, G.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Hietanen, S.; Kortekaas, M.; Kuosa, H.; Meier, M.H.E.; et al. Hypoxia-related processes in the Baltic Sea. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3412–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz, R.J.; Rosenberg, R. Spreading dead zones and consequences for marine ecosystems. Science 2008, 321, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmgren, R.; Larsson, U. Europhication in the Baltic Sea area. Integrated coastal management issues. In Science and Integrated Coastal Management; Bodugen, B.V., Turner, R.K., Eds.; Dahlem University Press: Berlin, Germany, 2001; pp. 15–35. [Google Scholar]
- Conley, D.J.; Bonsdorff, E.; Carstensen, J.; Destouni, G.; Gustafsson, B.G.; Hansson, L.A.; Rabalais, N.N.; Voss, M.; Zillén, L. Tackling hypoxia in the Baltic Sea: Is engineering a solution? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 3407–3411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindahl, O.; Herroth, B.; Kollberg, S.; Loo, L.-O.; Olrog, L.; Rehnstam-Holm, A.-S.; Svensson, J.; Svensson, S.; Syversen, U. Improving marine water quality by mussel farming: A profitable solution for Swedish society. Ambio 2005, 34, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gren, I.-M.; Lindahl, O.; Lindqvist, M. The value of mussel cultivation for combating eutrophication in the Baltic Sea. Ecol. Eng. 2009, 35, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernewski, G.; Stybel, N.; Neumann, T. Zebra mussel farming in the Szczecin (Oder) lagoon: Water-quality objectives and cost-effectiveness. Ecol. Soc. 2012, 17, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.K.; Hasler, B.; Timmermann, K.; Nielsen, P.; Törring, D.; Larsen, M.M.; Holmer, M. Mussels as a tool for mitigation of nutrient in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 82, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, T.; van Deurs, M.; Ravn-Jonsen, L.; Roth, E. Assessment of Financial Feasibility of Farming Blue Mussel in the Great Belt by the Smart Farm System. Department of Environmental and Business Economics, University of Southern Denmark. Available online: http://www.marbio.sdu.dk/uploads/MarBioShell/Thong%20et%20al%202013%20Final%20-%20SDU%20%20Thongrapport.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2018).
- HELCOM (Helsinki Commission). The Baltic Sea Joint Comprehensive Environmental Action Programme; Baltic Sea Environmental Proceedings No. 48; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM (Helsinki Commission). An Approach to Set Country-Wise Nutrient Reduction Allocations to Reach Good Marine Environment of the Baltic Sea; Helcom BSAP Eutro Expo, Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- HELCOM (Helsinki Commission). Helcom Copenhagen Ministerial Declaration; Helsinki Commission: Helsinki, Finland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Gren, I.M. Evaluation of cost-effectiveness and equity of the Helcom Baltic Sea Action Plan. Vatten 2008, 4, 271–281. [Google Scholar]
- Carraro, C. (Ed.) Efficiency and Equity in Climate Change Policy; Kluwer Academic Publisher: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Carraro, C.; Buchner, B. Equity, development and climate change policy. In Climate Change Policy Regimes, International Trade and Growth; Carraro, C., Kemfert, C., Buchner, B., Eds.; CEPS-ESRI Collaboration studies: Buxelles, Belgium, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, A.; Vogt, C.; Ziegler, A. On the importance of equity in international climate policy: An empirical analysis. Energy Econ. 2007, 29, 545–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bérubé, G.; Cusson, C. The environmental legal and regulatory frameworks. Assessing equity and efficiency. Energy Policy 2002, 30, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UNEP. 2001. Available online: https://wedocs.unep.org/bitstream/handle/20.500.11822/17018/UNEP-guidelines-compliance-MEA.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y (accessed on 25 September 2018).
- Dietz, S.; Atkinson, G. The equity-efficiency trade-off in environmental policy: Evidence from stated preferences. Land Econ. 2010, 86, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gren, I.-M.; Destouni, G. Do nutrient measurements matter for eutrophication management? Ambio 2012, 41, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gini, C. Measurement of inequality of incomes. Econ. J. 1921, 31, 124–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munnich-Vass, M.; Elofsson, K.; Gren, I.-M. An equity assessment of introducing carbon sequestration in EU climate policy. Energy Policy 2013, 61, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadam, I.; Kaluarachchi, J. Trade off between cost minimization and equity in water quality management for agricultural watersheds. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42, W10404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutcliffe, B. World inequality and globalization. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2005, 20, 15–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Secondi, G. (Ed.) The Development Economics Reader; Routledge: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). Incorporating Green Growth and Sustainable Development Policies into Structural Reform Agendas; OECD: Paris, France, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Gren, I.-M.; Wulff, F. Cost-effective management of polluted coupled heterogeneous marine basins in the Baltic Sea. Reg. Environ. Chang. 2004, 4, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumol, W.; Oates, W. The Theory of Environmental Policy, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- NEFCO. Framework for a Nutrient Quota and Credits Trading System for the Contracting Parties of the HELCOM in Order to Reduce Eutrophication in the Baltic; Nordic Environment and Finance Cooperation: Helsinki, Finland, 2008; Available online: https://www.nefco.org/news-media/publications-reports/studyassesment/framework-nutrient-quota-and-credits-trading-systemefco (accessed on 20 March 2018).
- Gren, I.-M.; Elofsson, K. Credit stacking in nutrient trading markets for the Baltic Sea. Mar. Policy 2017, 79, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A. Development as Freedom; Anchor: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Gren, I.M.; Säll, S. Cost-effective eutrophication and climate change management in the Baltic Sea. Environ. Econ. 2015, 6, 80–90. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal, R. GAMS—A User’s Guide; GAMS Development Corporation: Washington, DC, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Elofsson, K. Cost uncertainty and unilateral abatement. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2010, 36, 143–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulff, F.; Humborg, C.; Andersen, H.; Blicher-Mathiesen, G.; Czajkowski, M.; Elofsson, K.; Fonnesbech-Wulff, A.; Hasler, B.; Hong, B.; Jansons, V.; et al. Reduction of Baltic Sea nutrient inputs and allocation of abatement costs within the Baltic Sea catchment. Ambio 2014, 43, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The World Bank. GDP per Capita. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/ny.gdp.pcap.cd (accessed on 26 September 2018).

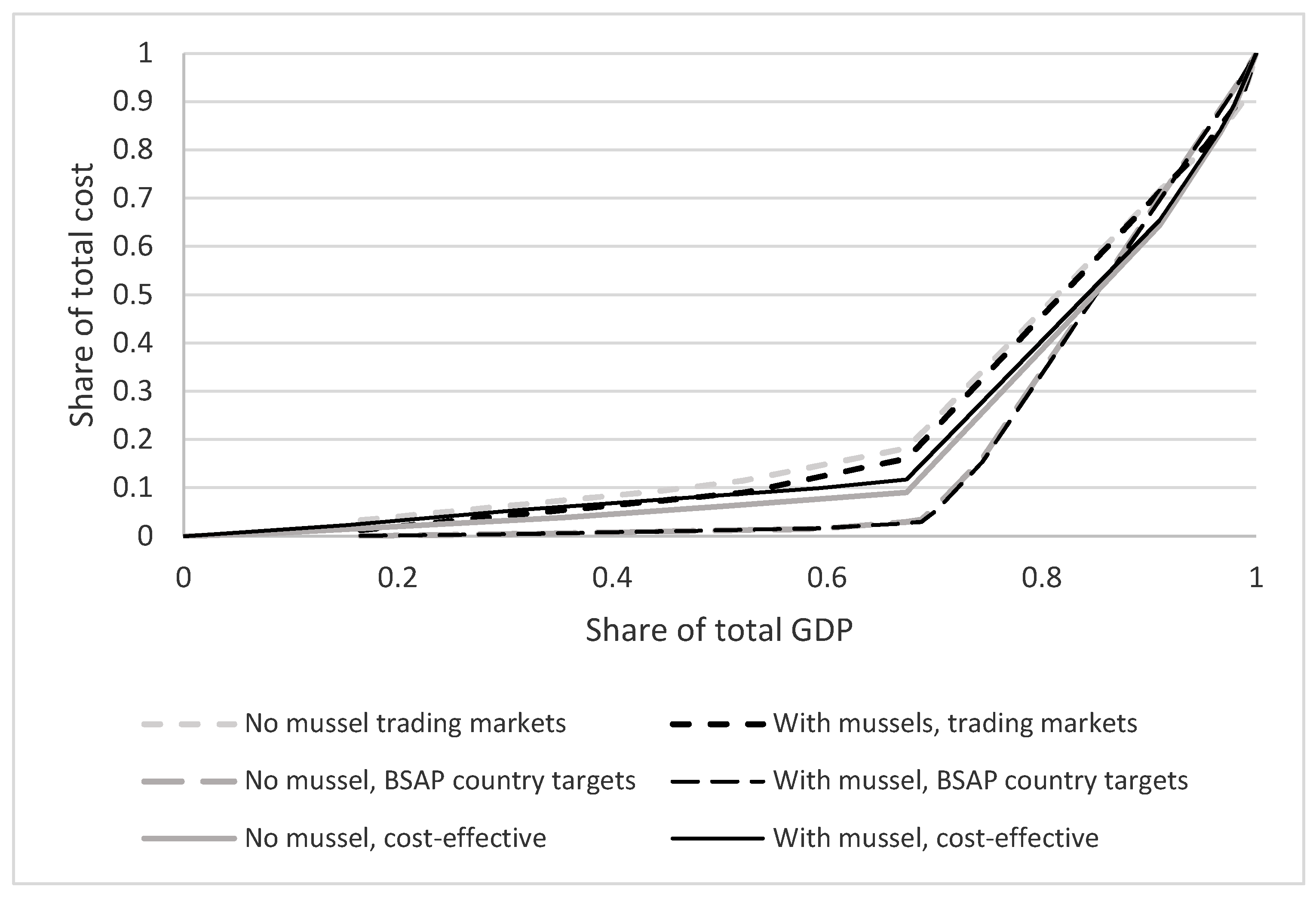
| Countries | Cost-Effectiveness; No Mussel with Mussel | BSAP Country Targets; No Mussel with Mussel | Trading Markets after Trade a; No Mussel with Mussel | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DEN | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 1.14 | 0.71 |
| EST | 1.38 | 1.21 | 1.26 | 1.00 | 1.33 | 1.08 |
| FIN | 0.73 | 0.62 | 0.18 | 0.18 | 2.28 | 1.93 |
| GER | 0.19 | 0.50 | 0.94 | 0.47 | 0.91 | 0.48 |
| LAT | 2.23 | 1.98 | 0.19 | 0.11 | 2.20 | 1.93 |
| LIT | 3.42 | 2.90 | 3.31 | 3.25 | 1.54 | 1.61 |
| POL | 16.80 | 14.50 | 34.99 | 33.19 | 16.20 | 14.78 |
| RUS | 4.46 | 3.84 | 4.46 | 4.30 | 3.13 | 3.11 |
| SWE | 1.00 | 1.21 | 0.49 | 0.48 | 2.32 | 1.99 |
| Total | 31.04 | 27.62 | 45.86 | 43.01 | 31.04 | 27.62 |
| Mussel Farming Option | Cost-Effective | BSAP Country Targets | Nutrient-Trading Markets |
|---|---|---|---|
| No mussel farming | 0.63 | 0.68 | 0.54 |
| With mussel farming | 0.60 | 0.69 | 0.57 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gren, I.-M.; Säll, S.; Aklilu, A.Z.; Tirkaso, W. Does Mussel Farming Promote Cost Savings and Equity in Reaching Nutrient Targets for the Baltic Sea? Water 2018, 10, 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111682
Gren I-M, Säll S, Aklilu AZ, Tirkaso W. Does Mussel Farming Promote Cost Savings and Equity in Reaching Nutrient Targets for the Baltic Sea? Water. 2018; 10(11):1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111682
Chicago/Turabian StyleGren, Ing-Marie, Sarah Säll, Abenezer Zeleke Aklilu, and Wondmagegn Tirkaso. 2018. "Does Mussel Farming Promote Cost Savings and Equity in Reaching Nutrient Targets for the Baltic Sea?" Water 10, no. 11: 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111682
APA StyleGren, I.-M., Säll, S., Aklilu, A. Z., & Tirkaso, W. (2018). Does Mussel Farming Promote Cost Savings and Equity in Reaching Nutrient Targets for the Baltic Sea? Water, 10(11), 1682. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111682





