Influence of Flushing Velocity and Flushing Frequency on the Service Life of Labyrinth-Channel Emitters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
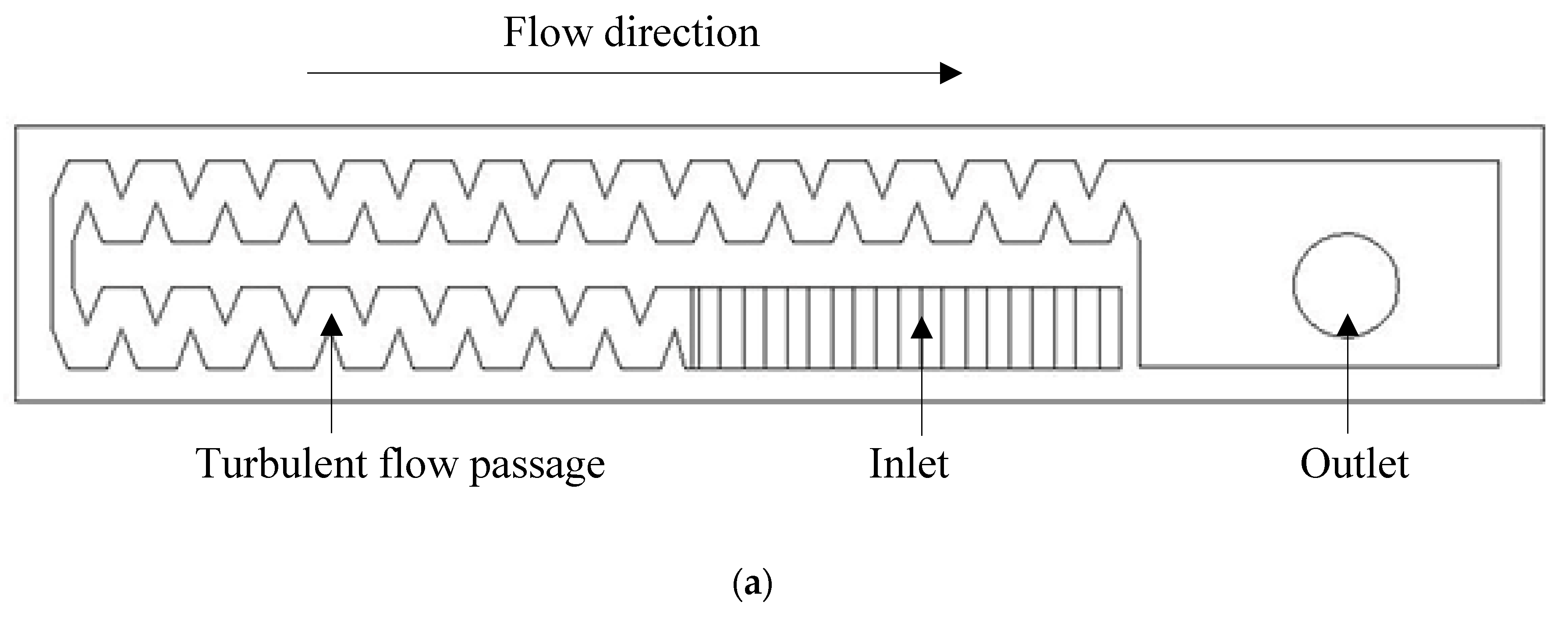
2.1. Emitter Characteristics
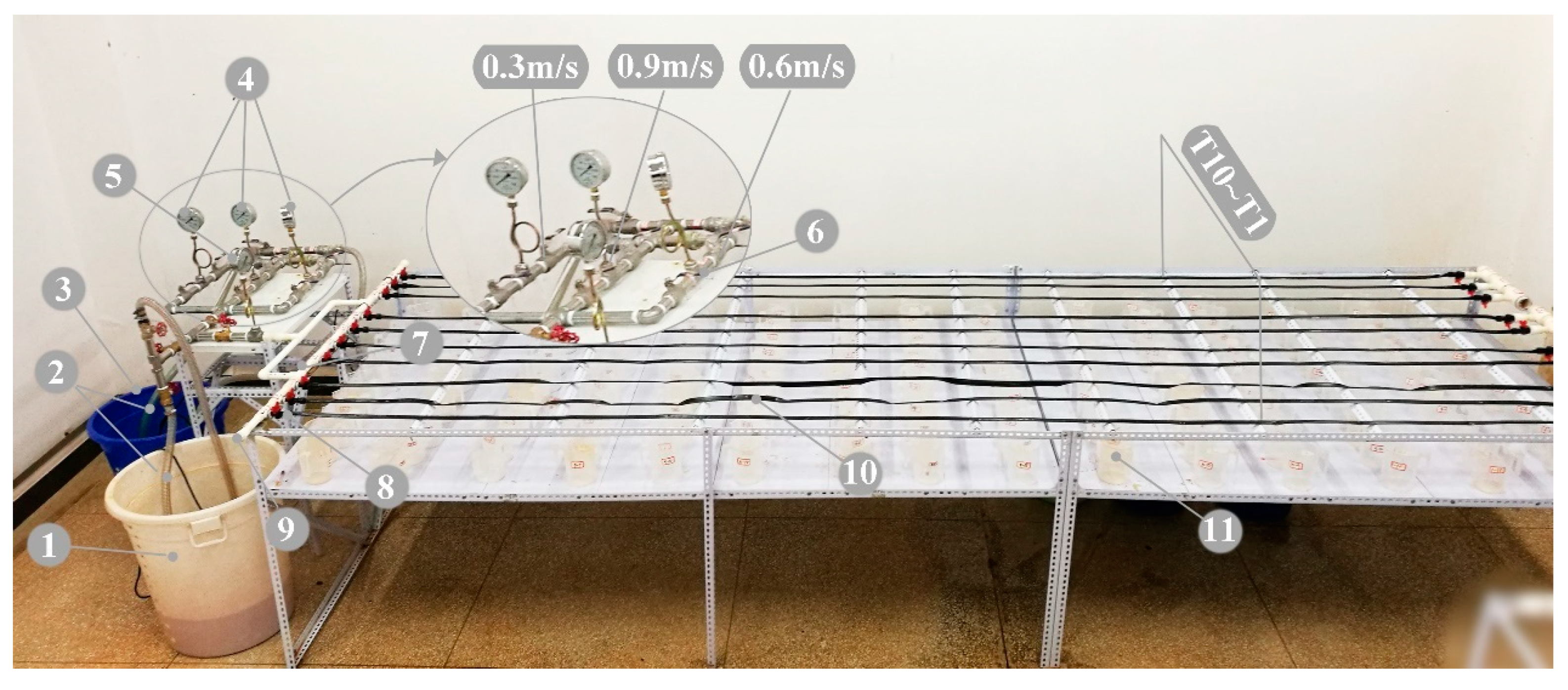
2.2. Experimental Setup
2.3. Measurement of Particle Size Distribution and Water Source
2.4. Test Procedures
2.4.1. Muddy Water Irrigation
2.4.2. Sampling and Testing
2.4.3. Clean Water Flushing
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Variations in Emitter Discharge
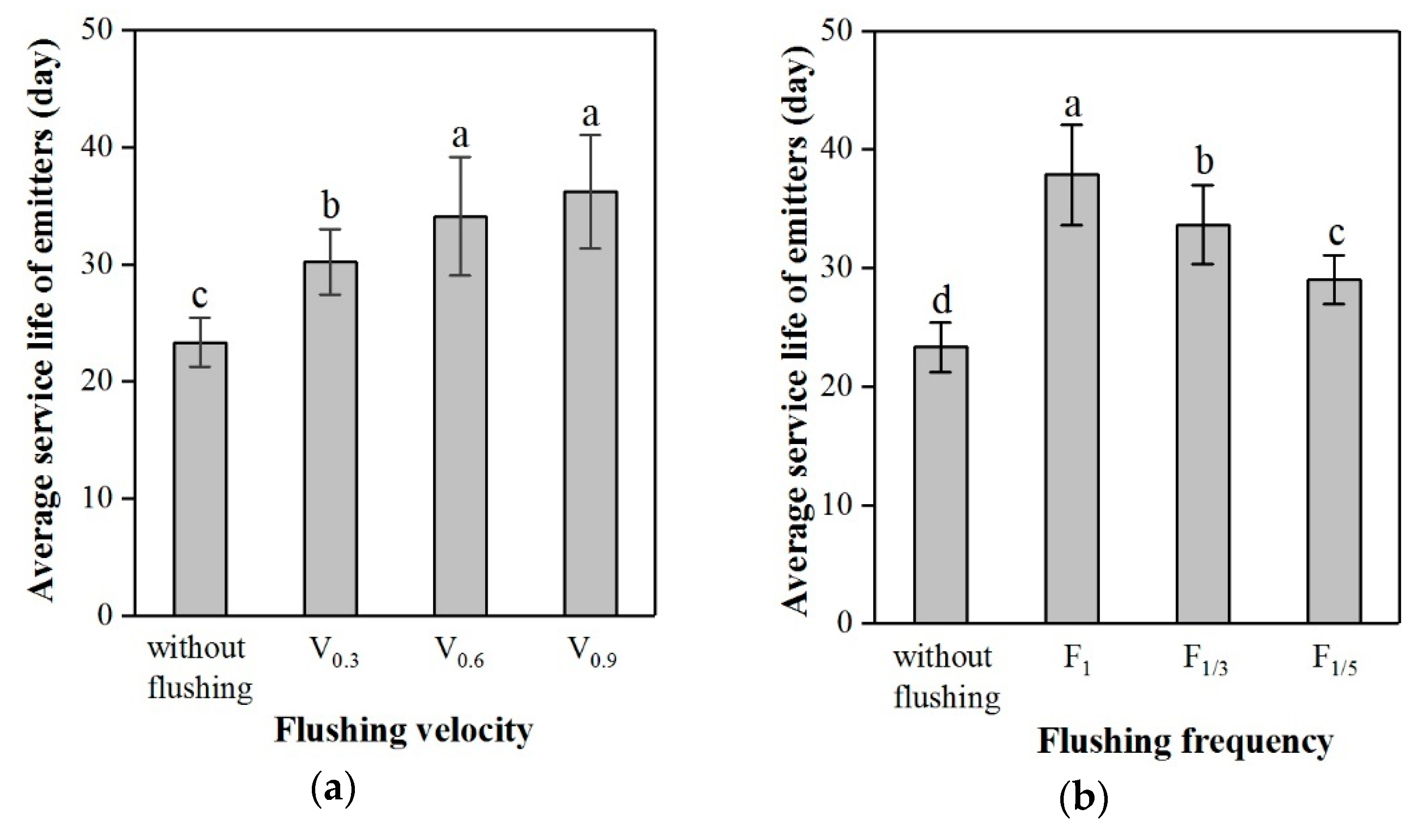
3.2. Variance Analysis of the Two Flushing Factors on the Service Life of Emitters
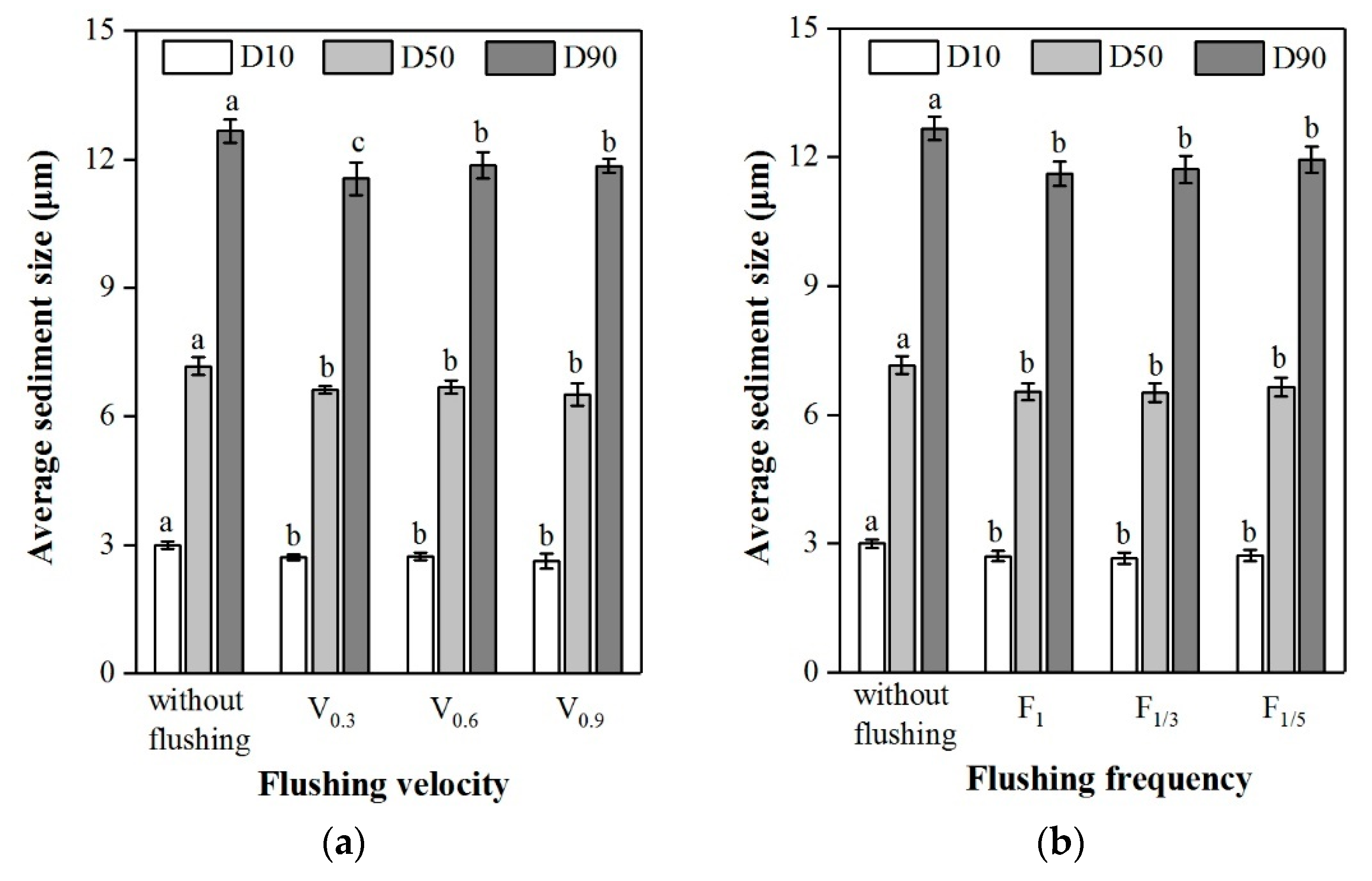
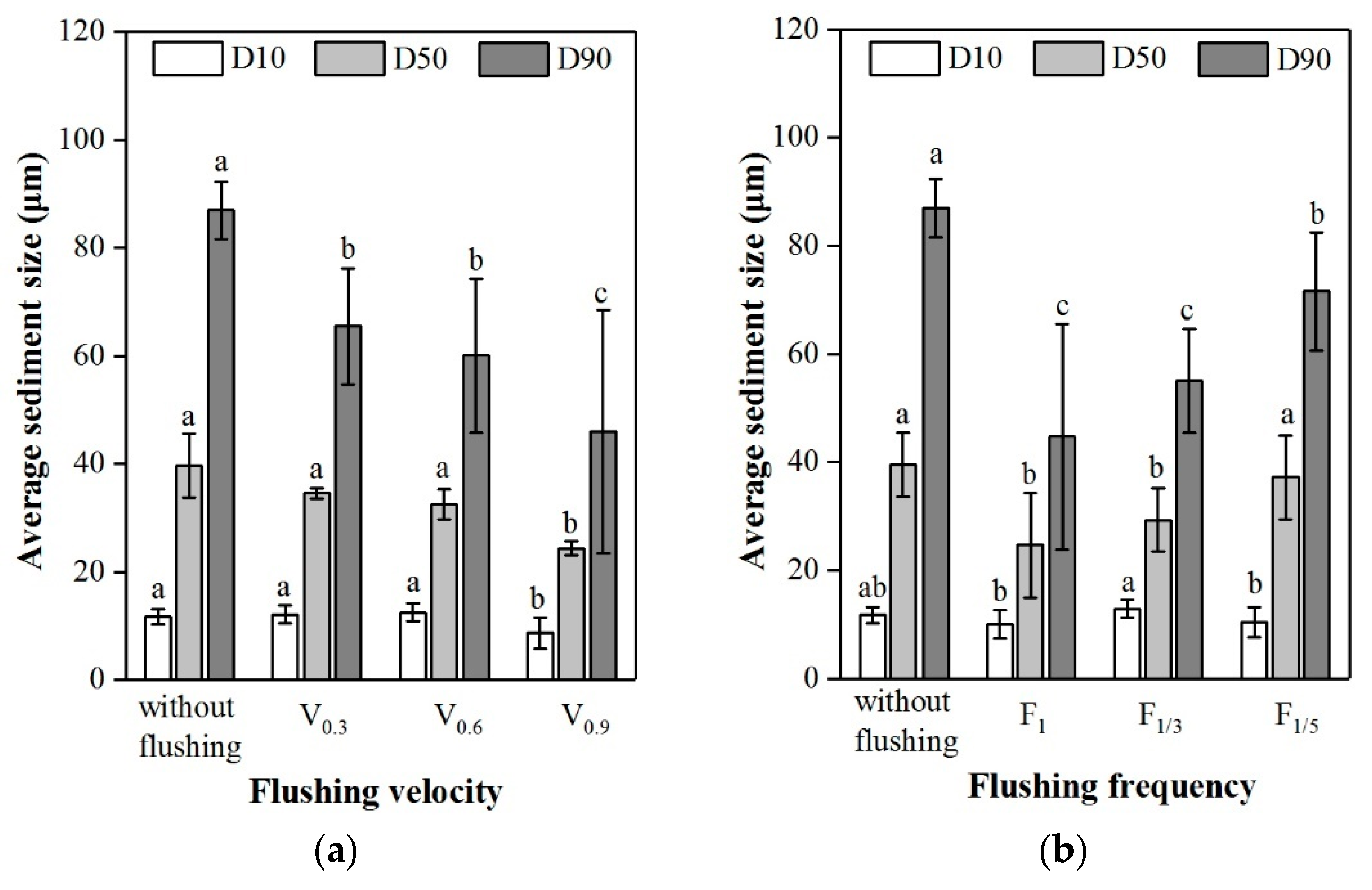
3.3. Particle Size of Discharged Sediments
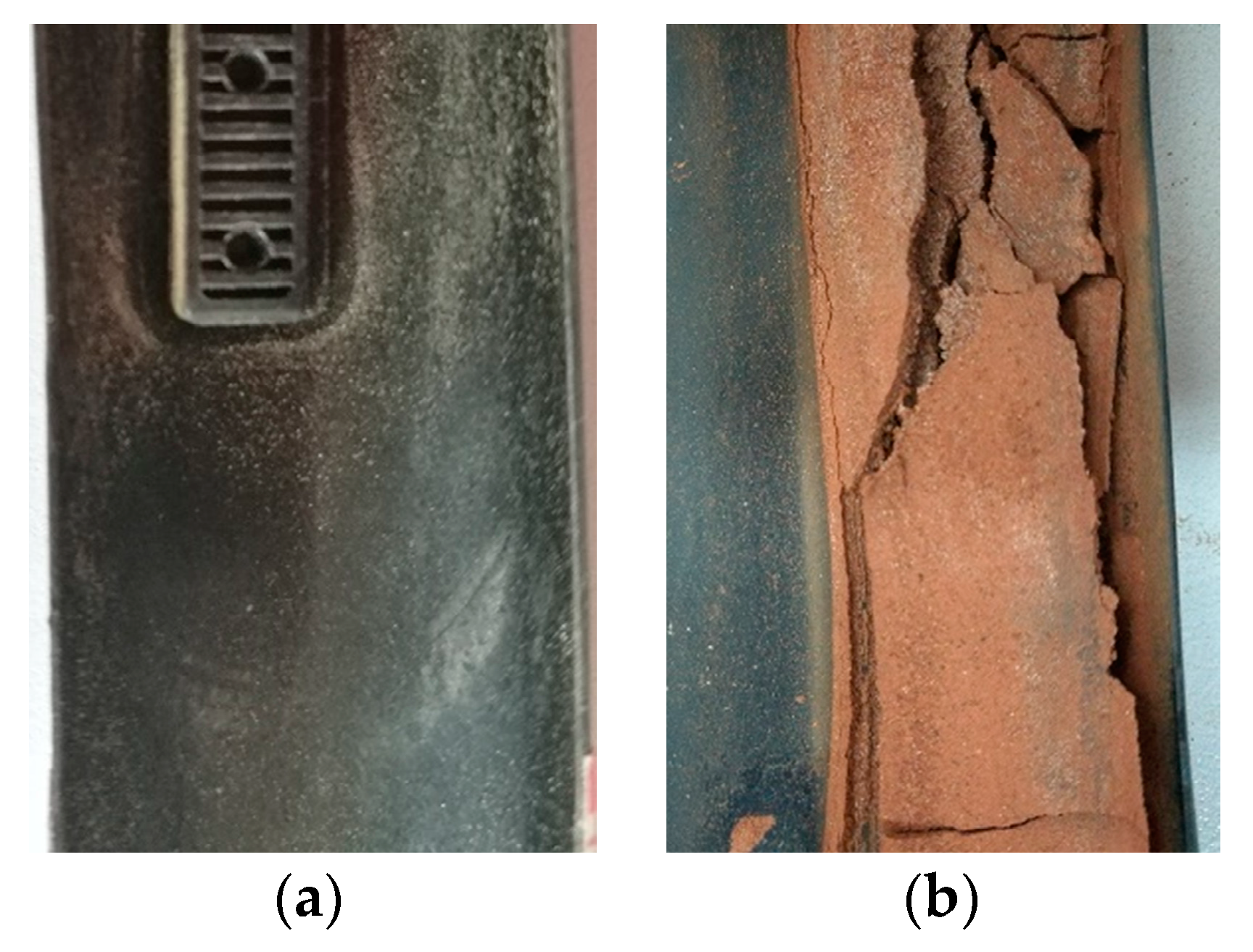
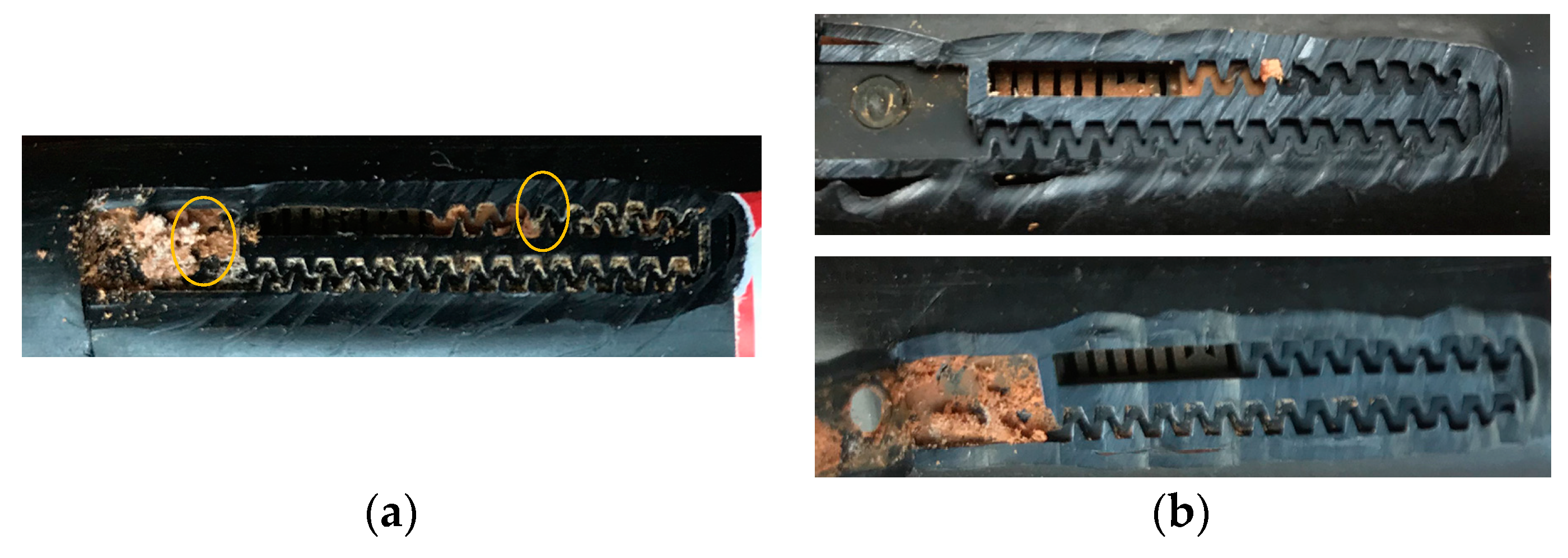
3.4. Residual Sediments in Drip Tape and Emitters
4. Discussion
4.1. Influence of Flushing Treatment on Emitter Clogging
4.2. Influence of Flushing Treatment on Particle Size Distributions
4.3. Influence of Particle Size on Emitter Clogging
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adin, A.; Sacks, M. Dripper-clogging factors in wastewater irrigation. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1991, 117, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina, I.; Paz, E.; Sofer, Z.; Marcu, A.; Shisha, A.; Sagi, G. Control of emitter clogging in drip irrigation with reclaimed wastewater. Irrig. Sci. 1992, 13, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, F.S.; Bucks, D.A. Water quality in drip/trickle irrigation: A review. Irrig. Sci. 1991, 12, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitts, D.J.; Haman, D.Z.; Smajstrla, A.G. Causes and prevention of emitter plugging in micro-irrigation systems. Bull. Fla. Cooperative Ext. Serv. 2011, 40, 201–218. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, D.Z.; Bai, Z.H.; Mike, R.; Gu, L.K.; Ren, S.M.; Yang, P.L. Biofilm structure and its influence on clogging in drip irrigation emitters distributing reclaimed wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. 2009, 21, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.K.; Liu, Y.Z.; Li, G.B.; Xu, T.W.; Liu, H.S.; Ren, S.M.; Yan, D.Z.; Yang, P.L. Surface topographic characteristics of suspended particulates in reclaimed wastewater and effects on clogging in labyrinth drip irrigation emitters. Irrig. Sci. 2012, 30, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamm, F.R.; Camp, C.R. Chapter 13: Subsurface drip irrigation. In Micro-Irrigation for Crop Production: Design, Operation, and Management, 1st ed.; Lamm, F.R., Ayars, J.E., Nakayama, F.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 473–551. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Burrows, R. Modelling the free surface flow in rectangular shallow basins by lattice Boltzmann method. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2011, 137, 1680–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Burrows, R. Modelling solute transport in shallow water with the lattice Boltzmann method. Comput. Fluids 2011, 50, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Zhou, J.G. Lattice Boltzmann model using two-relaxation-time for shallow water equations. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2016, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhang, J.M.; Meng, J.P. Second order force scheme for lattice Boltzmann model of shallow water flows. J. Hydraul. Res. 2017, 55, 592–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Zhang, J.M.; Burrows, R. Modeling moving boundary in shallow water by LBM. Int. J. Mod. Phys. C 2013, 24, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Zhang, J.M.; Liu, H.F. Lattice Boltzmann modelling of shallow water flows over discontinuous beds. Int. J. Numer. Meth. Fluids 2014, 75, 608–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, J.G.; Zhang, J.M. Mixed numerical method for bed evolution. Proc. Inst. Civ. Eng. Water Manag. 2015, 168, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, F.S.; Boman, B.J.; Pitts, D.J. Chapter 11: Maintenance. In Micro-Irrigation for Crop Production: Design, Operation, and Management, 1st ed.; Lamm, F.R., Ayars, J.E., Nakayama, F.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 389–430. [Google Scholar]
- ASAE Standards. EP405.1: Design and Installation of Micro-Irrigation Systems; ASAE: St. Joseph, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Brenes, M.J.; Hills, D.J. Micro-irrigation of wastewater effluent using drip tape. Appl. Eng. Agric. 2001, 17, 303–308. [Google Scholar]
- Puig-Bargués, J.; Lamm, F.R.; Trooien, T.P.; Clark, G.A. Effect of dripline flushing on subsurface drip irrigation systems. Trans. ASABE 2010, 53, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravina, I.; Paz, E.; Sofer, Z.; Marm, A.; Schischa, A.; Sagi, G.; Yechialy, Z.; Leve, Y. Control of clogging in drip irrigation with stored treated municipal sewage effluent. Agric. Water Manag. 1997, 33, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hills, D.J.; Tajrishy, M.A.; Tchobanoglous, G. The influence of filtration on ultraviolet disinfection of secondary effluent for micro-irrigation. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 1499–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Song, P.; Pei, Y.; Feng, J. Effects of lateral flushing on emitter clogging and biofilm components in drip irrigation systems with reclaimed water. Irrig. Sci. 2015, 33, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig-Bargués, J.; Arbat, G.; Elbana, M.; Duran-Ros, M.; Barragán, J.; Ramírezde Cartagena, F.; Lamm, F.R. Effect of flushing frequency on emitter clogging in micro-irrigation with effluents. Agric. Water Manag. 2010, 97, 883–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elberry, A.M.; Abuarab, M.E.; Elebaby, F.G. Effect of flushing frequency with sulfuric and phosphoric acids on emitter clogging. In Proceedings of the ASABE Annual International Meeting, Louisville, KY, USA, 7–10 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.F.; Li, J.S.; Zhao, W.X.; Wang, Z. Review on irrigation technology applying sewage effluent-advances and prospects. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Mach. 2015, 46, 102–110. [Google Scholar]
- Puig-Bargués, J.; Lamm, F.R. Effect of flushing velocity and flushing duration on sediment transport in micro-irrigation driplines. Trans. ASABE 2013, 56, 1821–1828. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, L.; Wu, P.T.; Zhu, D.L. Effect of pulsating pressure on labyrinth emitter clogging. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, N.; Liu, X.; Yang, Q.; Long, J. Influence of flushing pressure, flushing frequency and flushing time on the service life of a labyrinth-channel emitter. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 172, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Li, N.; Yang, Q.; Liu, X. Influence of flushing pressure before irrigation on the anti-clogging performance of labyrinth channel emitters. Irrig. Drain. 2017, 67, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, D.; Kang, Y.; Wan, S.; Liu, S. Lateral flushing regime for managing emitter clogging under drip irrigation with saline groundwater. Irrig. Sci. 2017, 35, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, P.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Pei, Y. Chlorination with lateral flushing controlling drip irrigation emitter clogging using reclaimed water. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2017, 33, 80–86. [Google Scholar]
- Kou, B.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Xia, C.; Li, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, A.; Zhang, J.; Kob, W.; Wang, Y. Granular materials flow like complex fluids. Nature 2017, 551, 360–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.; Tang, Y.; Wen, J.; Lu, B. Two-phase flow analysis and experimental investigation of micro-PIV and anti-clogging for micro-channels of emitter. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2008, 24, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, Q.; Lu, G.; Liu, J.; Shi, Y.; Dong, W.; Huang, S. Evaluation of emitter clogging in drip irrigation by two-phase flow simulation and laboratory experiments. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2008, 63, 294–303. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Chen, L.; Li, Y. Field evaluation of emitter clogging in subsurface drip irrigation system. J. Hydraul. Eng. 2008, 39, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, W.Q.; Liu, L.; Chen, X. Influence of fine particle size and concentration on the clogging of labyrinth emitters. Irrig. Sci. 2013, 31, 545–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhao, W.; Wei, Z.; Tang, Y.; Lu, B. Numerical and experimental study on hydraulic performance of emitters with arc labyrinth channels. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2007, 56, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wang, F.; Niu, W.; Hu, X. Numerical analysis of influence of emitter channel structure on suspended granule distribution. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2009, 25, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.; Niu, W.; Bob, Z. Influence of sediment particle size on clogging performance of labyrinth path emitters. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2012, 28, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, K.; Luo, C.; Niu, W.; Yu, L. Influence of particle size and concentration of sediment on clogging of labyrinth channels emitters. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2014, 30, 99–108. [Google Scholar]
- Qian, N.; Wan, Z. Kinetics of Sediments; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1983. [Google Scholar]



| D10 | D20 | D30 | D40 | D50 | D60 | D70 | D80 | D90 | D100 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Particle size | 6.92 | 10.54 | 13.72 | 16.79 | 19.93 | 23.35 | 27.29 | 32.18 | 39.51 | 97.45 |
| Standard deviation | 0.34 | 0.45 | 0.55 | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 1.00 | 1.27 | 1.65 | 1.33 |
| Treatment No. | Flushing Velocity (V) | Flushing Frequency (F) | Average Irrigation Events Before Emitter Clogging (d) |
|---|---|---|---|
| T1 | V0.3 | F1 | 32.67 |
| T2 | V0.3 | F1/3 | 30.67 |
| T3 | V0.3 | F1/5 | 27.33 |
| T4 | V0.6 | F1 | 39.67 |
| T5 | V0.6 | F1/3 | 33.67 |
| T6 | V0.6 | F1/5 | 29.00 |
| T7 | V0.9 | F1 | 41.33 |
| T8 | V0.9 | F1/3 | 36.67 |
| T9 | V0.9 | F1/5 | 30.67 |
| T10 | No flushing | 23.33 | |
| Factors | F Value |
|---|---|
| Flushing velocity | 21.94 ** |
| Flushing frequency | 46.82 ** |
| Flushing velocity × Flushing frequency | 2.03 |
| Factors | F Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| D10 | D50 | D90 | |
| Flushing velocity | 2.15 | 3.38 | 4.18 * |
| Flushing frequency | 0.66 | 1.20 | 3.41 |
| Flushing velocity × Flushing frequency | 0.14 | 0.39 | 0.91 |
| Factors | F Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| D10 | D50 | D90 | |
| Flushing velocity | 18.07 ** | 7.48 ** | 10.85 ** |
| Flushing frequency | 10.06 ** | 10.36 ** | 19.58 ** |
| Flushing velocity × Flushing frequency | 2.81 | 2.47 | 2.67 |
| D10 | D50 | D90 | D100 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discharged sediments | With flushing | 2.68 ± 0.07 | 6.56 ± 0.14 | 11.73 ± 0.25 | 25.30 ± 0.50 |
| Without flushing | 2.98 ± 0.29 | 7.17 ± 0.42 | 12.70 ± 0.74 | 27.18 ± 3.05 | |
| Residual sediments in emitters | With flushing | 11.14 ± 2.30 | 30.49 ± 8.14 | 57.12 ± 14.68 | 69.63 ± 9.67 |
| Without flushing | 11.74 ± 1.41 | 39.67 ± 5.92 | 86.88 ± 5.32 | 89.68 ± 6.71 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Yu, L.; Li, N.; Chang, L.; Cui, N. Influence of Flushing Velocity and Flushing Frequency on the Service Life of Labyrinth-Channel Emitters. Water 2018, 10, 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111630
Li Z, Yu L, Li N, Chang L, Cui N. Influence of Flushing Velocity and Flushing Frequency on the Service Life of Labyrinth-Channel Emitters. Water. 2018; 10(11):1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111630
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhangyan, Liming Yu, Na Li, Liuhong Chang, and Ningbo Cui. 2018. "Influence of Flushing Velocity and Flushing Frequency on the Service Life of Labyrinth-Channel Emitters" Water 10, no. 11: 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111630
APA StyleLi, Z., Yu, L., Li, N., Chang, L., & Cui, N. (2018). Influence of Flushing Velocity and Flushing Frequency on the Service Life of Labyrinth-Channel Emitters. Water, 10(11), 1630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111630





