Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a Small Mountainous Watershed Using RUSLE: A Case-Study of the Palar Sub-Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Assessment of Annual Soil Loss
2.3. Data
- (i)
- ASTER GDEM, resolution 30 m × 30 m.
- (ii)
- Satellite data, LANDSAT 8 dated 5 May 2014, of 30 m × 30 m spatial resolution (Path: 143; Row: 53).
- (iii)
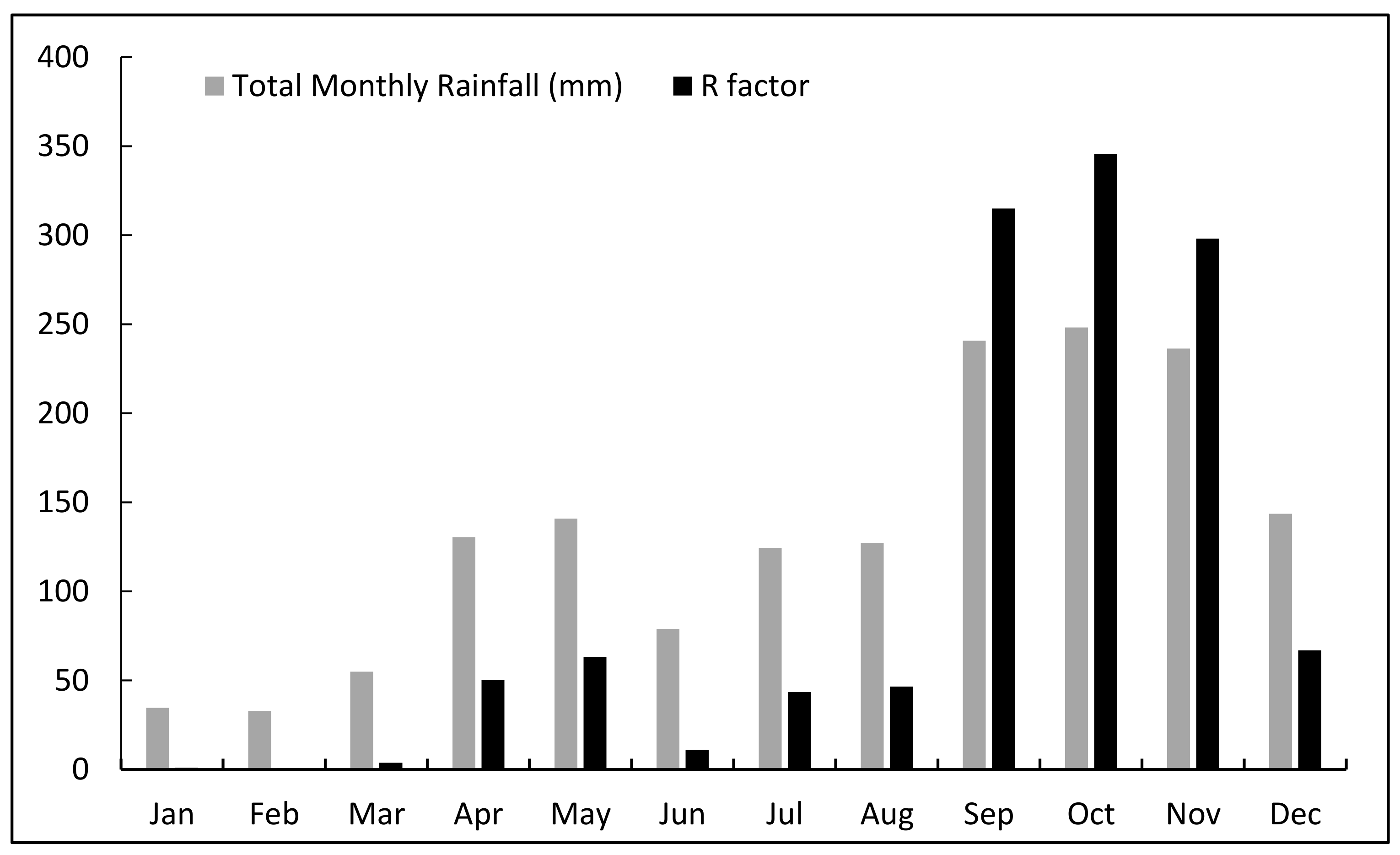
- Meteorological data, Total Monthly Rainfall Record for the years 1971–2000 from Indian Meteorological Department, Chennai.
- (iv)
- Survey of India topographical maps of 1:50,000 scale, sheet numbers 58F7, 58F8, 58F11 and 58F12.
- (v)
- Soil samples collected through field surveys for the preparation of soil erodibility map.
2.4. Digital Data Processing
2.5. Rainfall Erosivity (R)
2.6. Soil Erodibility Factor (K)
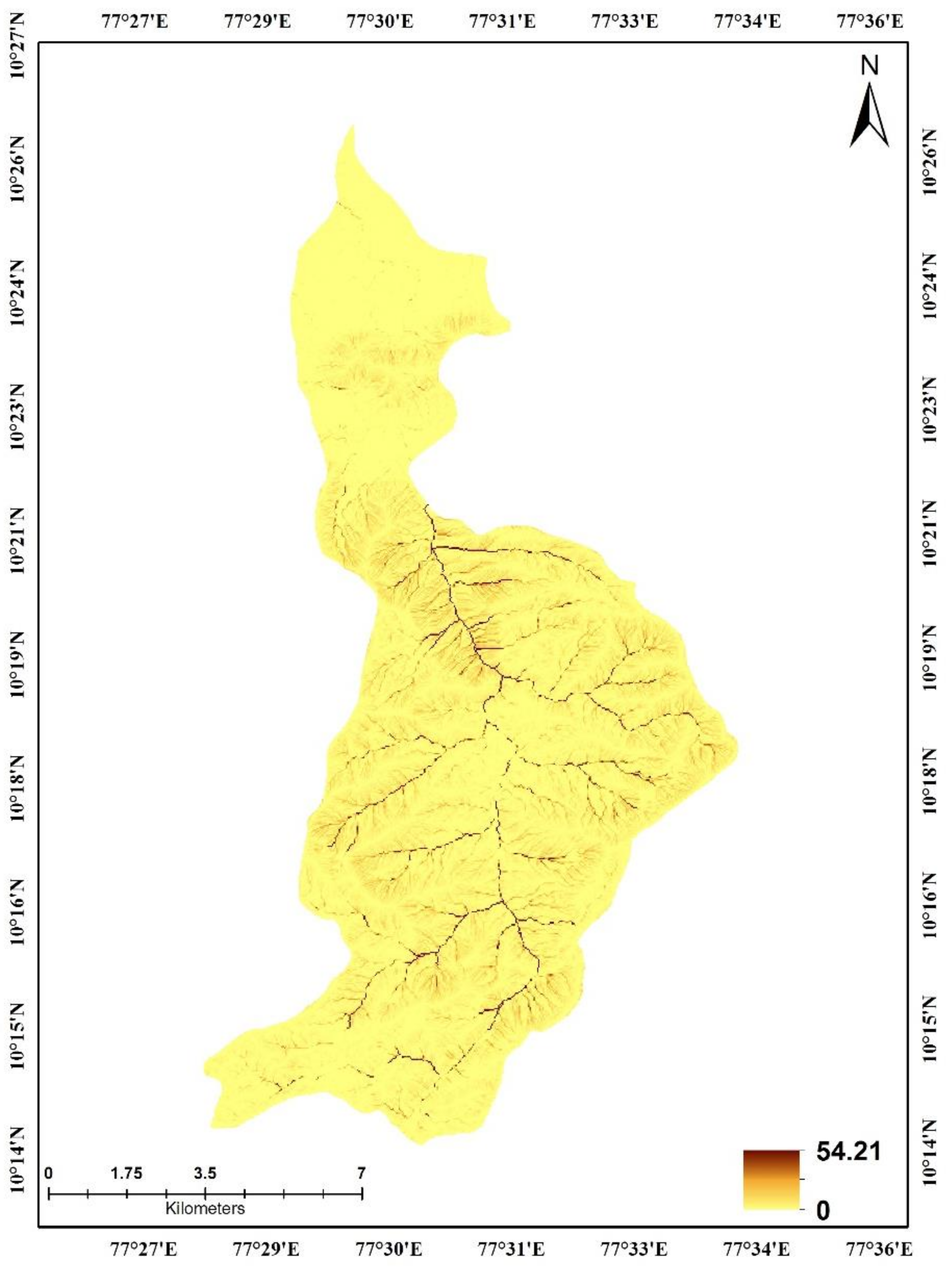
2.7. Slope Length and Steepness Factor (LS)
2.8. Crop Management Factor (C)
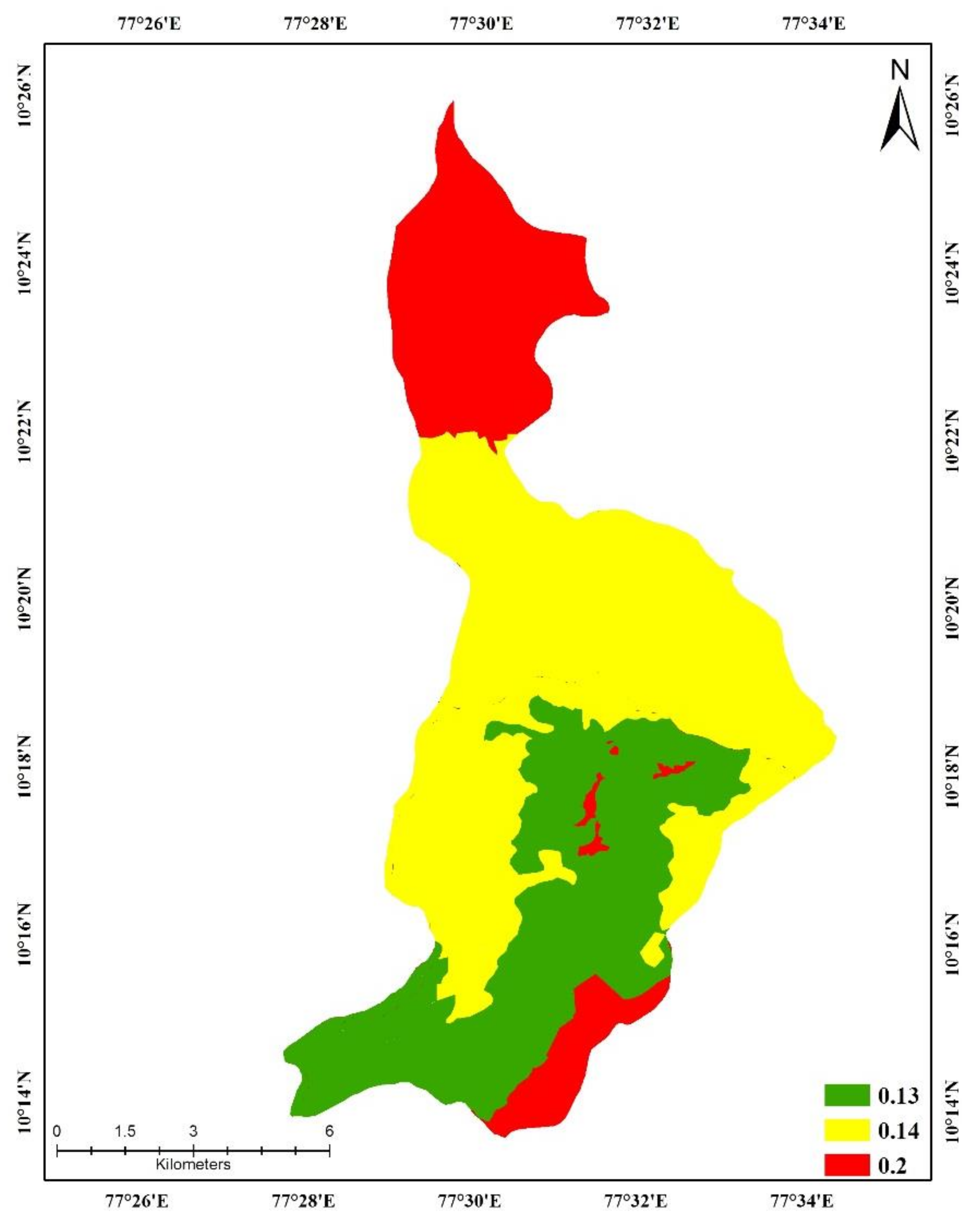
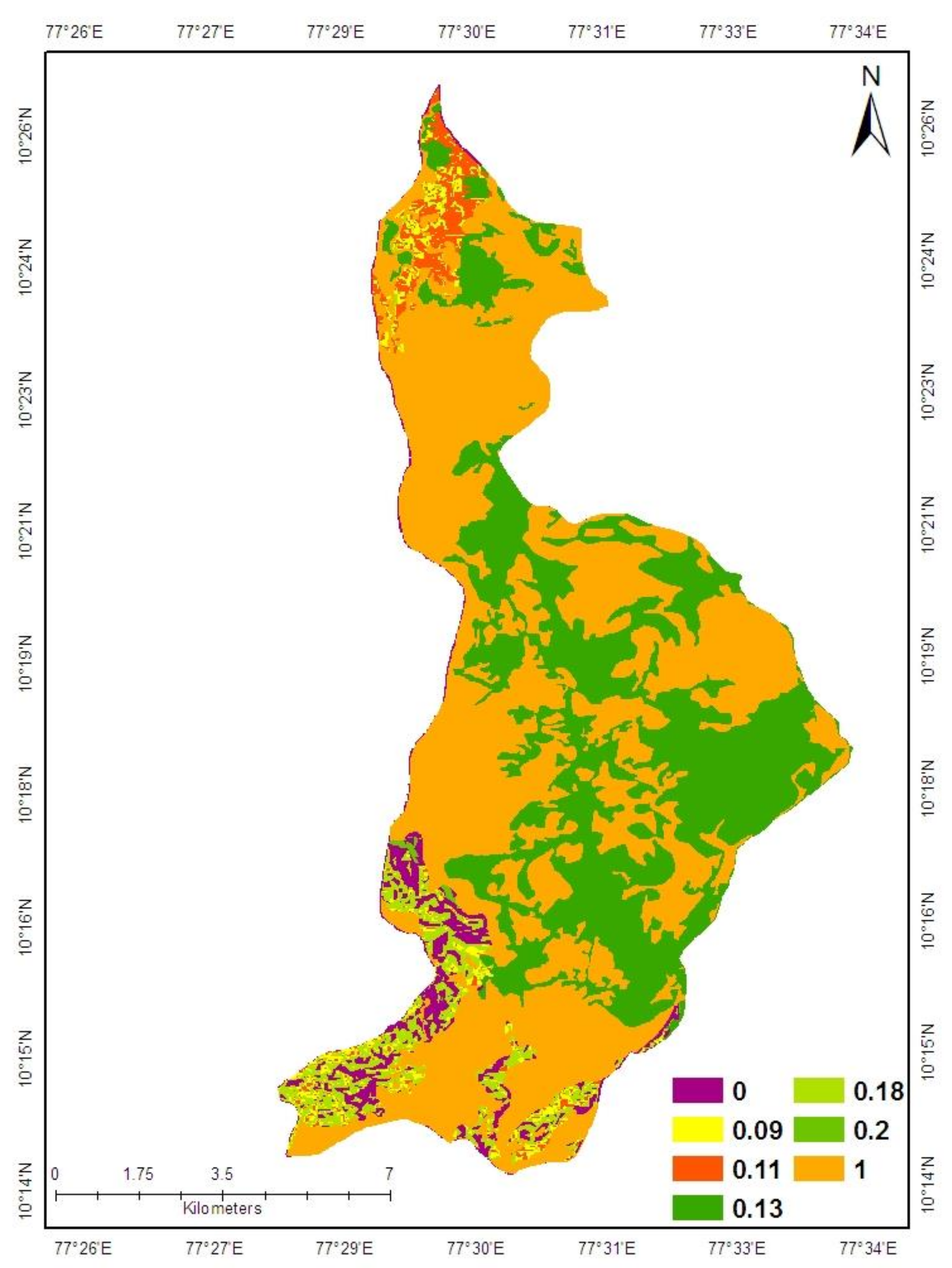
2.9. Conservation Support Practice Factor (P)
3. Spatial Distribution of Soil Loss, Validation and Sensitivity Analysis
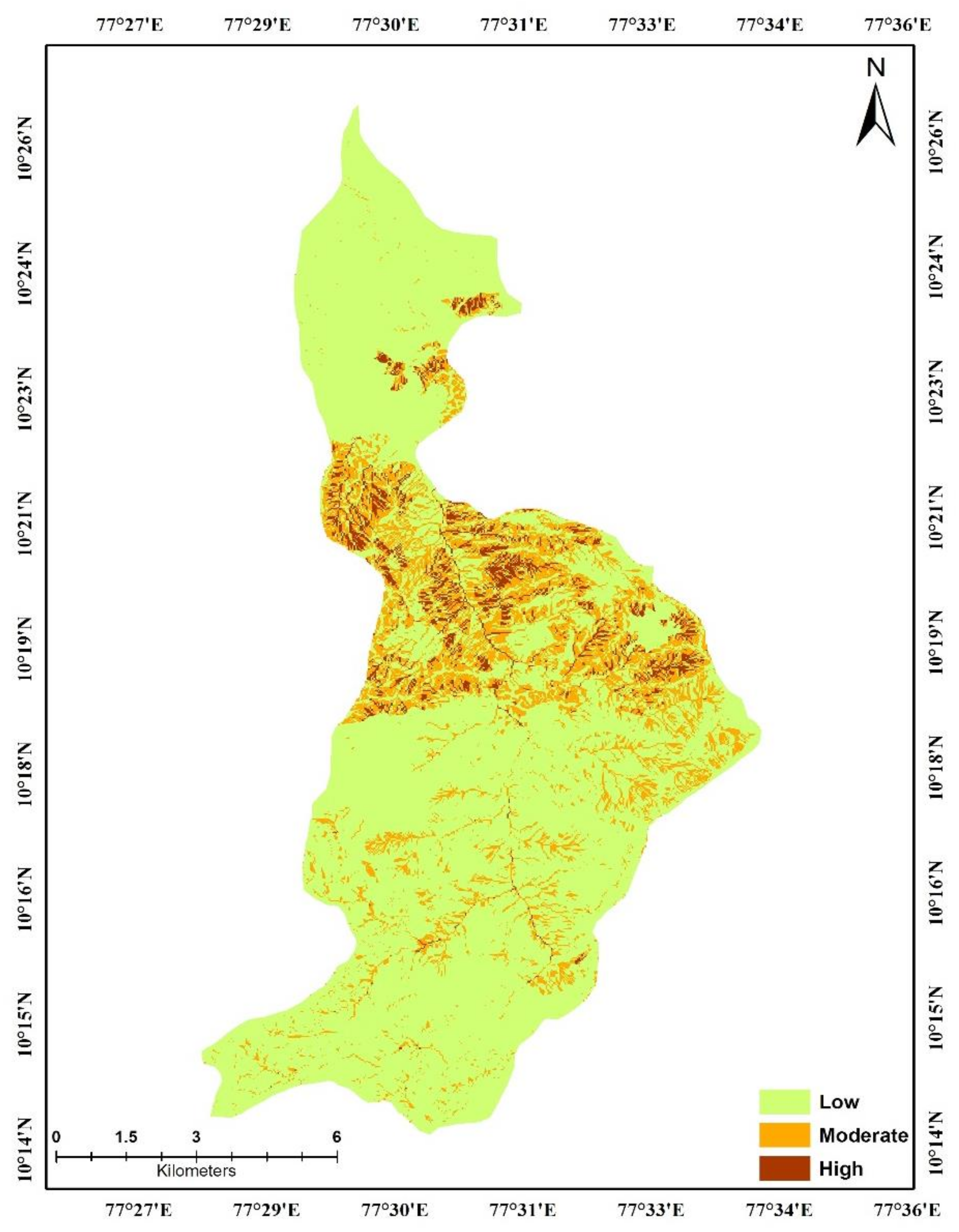
3.1. Soil Loss Map
3.2. Validation
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis
4. Results and Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agriculture Handbook; US Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997; Volume 703, pp. 1–251.
- Boyle, M. Erosion’s contribution to greenhouse gases. Eros. Control 2002, 9, 21–29. [Google Scholar]
- Narayan, V.V.D.; Babu, R. Estimation of soil erosion in India. J. Irrig. Drain. Eng. 1983, 109, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabral, P.P.; Baithuri, N.; Pandey, A. Soil erosion assessment in a hilly catchment of North Eastern India using USLE, GIS and remote sensing. Water Resour. Manag. 2008, 22, 1783–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Mathur, A.; Mishra, S.K.; Mal, B.C. Soil erosion modeling of a Himalayan watershed using RS and GIS. Environ. Earth Sci. 2009, 59, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Shiny, R.; Geetha, N.; Vijith, H. Spatial prediction of soil erosion risk by remote sensing, GIS and RUSLE approach: A case study of Siruvani river watershed in Attapady valley, Kerala, India. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 64, 965–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A. Integrating terrain and vegetation indices for identifying potential soil erosion risk area. Geol. Spat. Inf. Sci. 2010, 13, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angima, S.D.; Stott, D.E.; O’Neill, M.K.; Ong, C.K.; Weesies, G.A. Soil erosion prediction using RUSLE for central Kenyan highland conditions. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2003, 97, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Li, S. An analysis on spatial–temporal distribution of rainfall erosivity in Guizhou Province. Bull. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 4, 11–14. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.-Q.; Peng, J.; Shao, X.-M. Assessment of soil erosion using RUSLE and GIS: A case study of the Maotiao river watershed, Guizhou Province, China. Environ. Geol. 2009, 56, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Keesstra, S.D.; Temme, A.J.A.M.; Schoorl, J.M.; Visser, S.M. Evaluating the hydrological component of the new catchment-scale sediment delivery model LAPSUS-D. Geomorphology 2014, 212, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, A.; Himanshu, S.K.; Mishra, S.K.; Singh, V.P. Physically based soil erosion and sediment yield models revisited. CATENA 2016, 147, 595–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekonnen, M.; Keesstraa, S.D.; Baartmana, J.E.M.; Stroosnijdera, L.; Maroulisac, J. Reducing sediment connectivity through man-made and natural sediment sinks in the Minizr Catchment, Northwest Ethiopia. Land Degrad. Dev. 2016, 28, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, G.; Quinton, J.N.; Nearing, M.A.; Mabit, L.; Gómez, J.A. Sediment tracers in water erosion studies: Current approaches and challenges. J Soils Sediments 2013, 13, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masselink, R.J.H.; Temme, A.J.A.M.; Giménez, R.; Casalí, J.; Keesstra, S.D. Assessing hillslope-channel connectivity in an agricultural catchment using rare-earth oxide tracers and random forests models. Cuadernos de Investigación Geográfica 2017, 43, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temme, A.J.A.M.; Claessens, L.; Veldkamp, A.; Schoorl, J.M. Evaluating choices in multi-process landscape evolution models. Geomorphology 2011, 125, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses: A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; US Department of Agriculture Science and Education Administration: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Nearing, M.A.; Foster, G.R.; Lane, L.J.; Finkner, S.C. A process-based soil erosion model for USDA Water Erosion Prediction Project technology. Trans. ASABE 1989, 32, 1587–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, R.P.C.; Quinton, J.N.; Smith, R.E.; Govers, G.; Poesen, J.W.A.; Auerswald, K.; Chisci, G.; Torri, D.; Styczen, M.E. The European Soil Erosion Model (EUROSEM): A dynamic approach for predicting sediment transport from fields and small catchments. Earth Surf. Proc. Landf. 1998, 23, 527–544. [Google Scholar]
- Ganasiri, B.P.; Ramesh, H. Assessment of soil erosion by RUSLE model using remote sensing and GIS—A case study of Nethravathi Basin. Geosci. Front. 2016, 7, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhandari, K.P.; Aryal, J.; Darnsawasdi, R. A geospatial approach to assessing soil erosion in a watershed by integrating socio-economic determinants and the RUSLE model. Nat. Hazards 2015, 75, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouli, M.; Soupios, P.; Vallianatos, F. Soil erosion prediction using the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) in a GIS framework, Chania, Northwestern Crete, Greece. Environ. Geol. 2009, 57, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, D.P. Assessment of soil erosion in the Nepalese Himalaya, a case study in Likhu Khola Valley, middle mountain region. Land Husb. 1997, 2, 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Van De, N.; Douglas, I.; McMorrow, J.; Lindley, S.; Binh, D.K.N.T.; Van, T.T.; Tho, N. Erosion and nutrient loss on sloping land under intense cultivation in southern Vietnam. Geogr. Res. 2008, 46, 4–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasuhn, V. Soil erosion in the Swiss midlands: Results of a 10-year field survey. Geomorphology 2011, 126, 32–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, E.R.; Sridhar, V. Mapping Debris Flow Susceptibility using Analytical Network Process in Kodaikkanal Hills, Tamil Nadu (India). J. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 112, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujatha, E.R.; Rajamanickam, G.V. Landslide Hazard and Risk Mapping using Weighted Linear Combination Applied to Tevankarai Stream Watershed, Kodaikkanal, India. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. J. 2015, 21, 1445–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasannakumar, V.; Vijith, H.; Abinod, S.; Geetha, N. Estimation of soil erosion risk within a small mountainous subwatershed in Kerala, India, using Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE) and geo-information technology. Geosci. Front. 2012, 3, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnoldus, H.M.J. An approximation of the rainfall factor in the Universal Soil Loss Equation. In Assessment of Erosion; De Boodt, M., Gabriels, D., Eds.; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1980; pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, G.O.; Frevert, R.K.; Edminster, T.W.; Barner, K.K. Soil and Water Conservation Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1981; p. 525. [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; Brown, L.C.; Foster, G.R. Revised slope steepness factor for the universal soil loss equation. Trans. ASABE 1987, 30, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoyos, N. Spatial modeling of soil erosion potential in a tropical watershed of the Colombian Andes. CATENA 2005, 63, 85–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Physical basis of the length slope factor in the universal soil loss equation. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1986, 50, 1294–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, I.D.; Burch, G.J. Modelling erosion and deposition topographic effects. Trans. ASABE 1986, 29, 1624–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashim, G.M.; Wong, N.C. Erosion from Steep Land under Various Plant Cover and Terrains; Tay, T.H., Mokhtaruddin, A.M., Zahari, A.B., Eds.; MARDI/Malaysian Society of Soil Science: Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 1988; pp. 424–461. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Quraishi, A.M.F. Soil erosion risk prediction with RS and GIS for the northwestern part of Hebei Province, China. Pak. J. Appl. Sci. 2003, 3, 659–669. [Google Scholar]
- Schwab, G.; Frevert, R.; Dminster, T.; Barnes, K. Soil and Water Conservation Engineering, 2nd ed.; The Fergunson Foundation Agricultural Engineering Series; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1966; p. 683. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Hernández, C.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Romero-Díaz, A. Impact of lithology and soil properties on abandoned dry-land terraces during the early stages of soil erosion by water in Southeast Spain. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 3095–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuura, H. Design Guidelines for Mechanical Soil and Water Conservation Works and Water Resources Development; Technical Report for the Attapady Wasteland Comprehensive Environmental Conservation Project (AWCECOP), ID-P111; Attapady Hills Area Development Society, Government of Kerala: Kerala, India, 2000.
- Cerdà, A.; Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Novara, A.D.; Pulido, M.; Kapović-Solomun, M.; Keesstra, S.D. Policies can help to apply successful strategies to control soil and water losses. The case of chipped pruned branches (CPB) in Mediterranean citrus plantations. Land Use Policy 2018, 75, 734–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bienes, R.; Marques, M.J.; Sastre, B.; García-Díaz, A.; Ruiz-Colmenero, M. Eleven years after shrub revegetation in semiarid eroded soils. Influence in soil properties. Geoderma 2016, 273, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerdà, A.; González-Pelayo, Ó.; Giménez-Morera, A.; Jordán, A.; Pereira, P.; Novara, A.; Brevik, E.C.; Prosdocimi, M.; Mahmoodabadi, M.; Keesstra, S.; et al. Use of barley straw residues to avoid high erosion and runoff rates on persimmon plantations in eastern Spain under low frequency—High magnitude simulated rainfall events. Soil Res. 2016, 54, 154–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prosdocimi, M.; Jordán, A.; Tarolli, P.; Keesstra, S.; Novara, A.; Cerdà, A. The immediate effectiveness of barley straw mulch in reducing soil erodibility and surface runoff generation in Mediterranean vineyards. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 547, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novara, A.; Gristina, L.; Saladino, S.S.; Santoro, A.; Cerdà, A. Soil erosion assessment on tillage and alternative soil managements in a Sicilian vineyard. Soil Tillage Res. 2011, 117, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giménez-Morera, A.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Cerdà, A. The impact of cotton geotextiles on soil and water losses from Mediterranean rainfed agricultural land. Land Degrad. Dev. 2010, 21, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hueso-Gonzalez, P.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.; Martínez-Murillo, J.; Lavee, H. Overland flow generation mechanisms affected by topsoil treatment: Application to soil conservation. Geomorphology 2015, 228, 796–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brevik, E.C.; Fenton, T.E. Long-term effects of compaction on soil properties along the Mormon trail, South-Central Iowa, USA. Soil Horiz. 2012, 53, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhazo, N.; Chivenge, P.; Chaplot, V. Tillage impact on soil erosion by water: Discrepancies due to climate and soil characteristics. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigo-Comino, J.; Brings, C.; Iserloh, T.; Casper, C.M.; Seeger, M.; Senciales, M.; Brevik, E.C.; Ruiz-Sinoga, J.D.; Ries, J.B. Temporal changes in soil water erosion on sloping vineyards in the Ruwer-Mosel Valley. The impact of age and plantation works in young and old vines. J. Hydrol. Hydromech. 2017, 65, 402–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

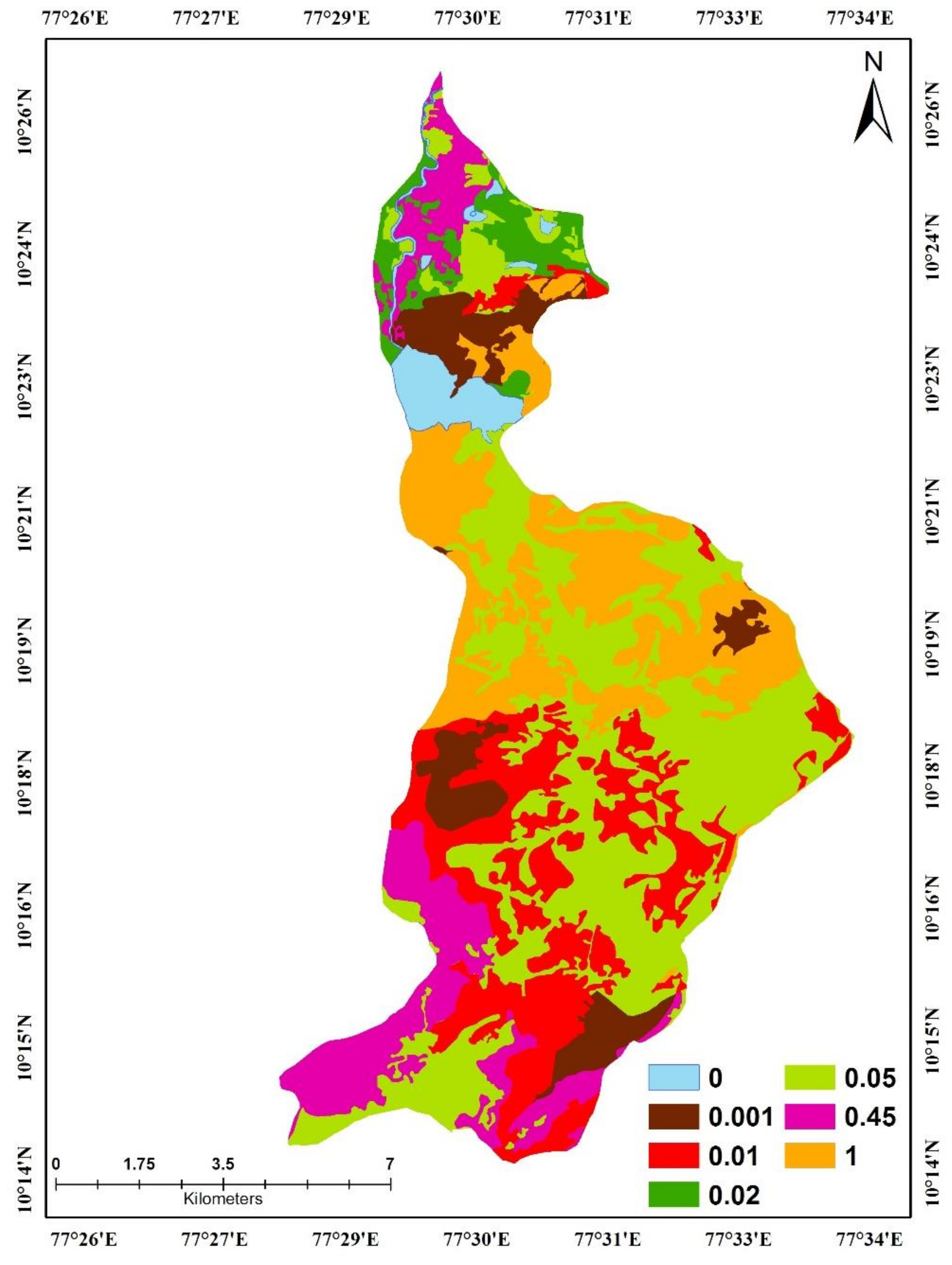
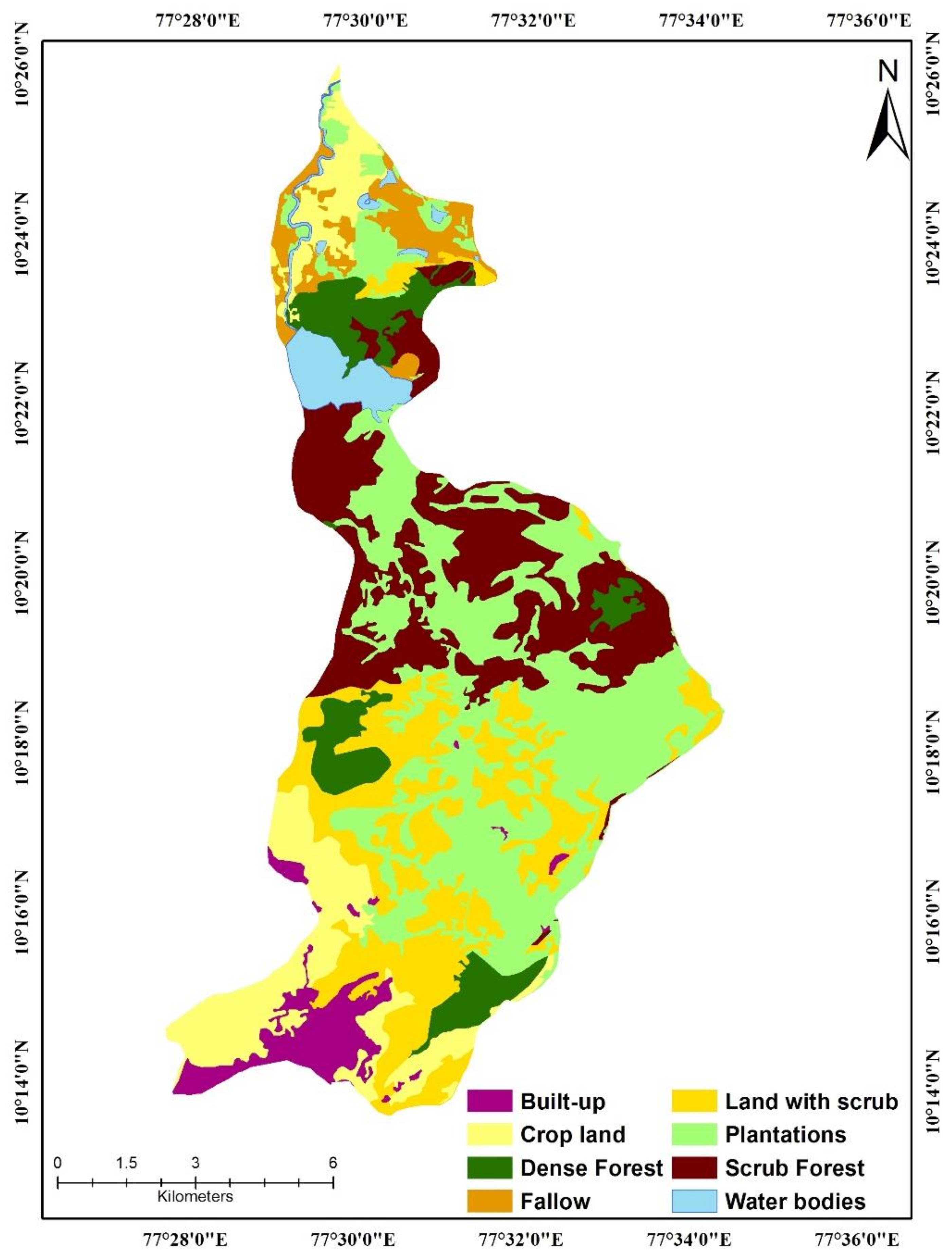
| Land Cover | Average C Value | Land Cover | Average C Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Forest | 0.05 | Scrub | 0.01 |
| Built-Up Land | 0.05 | Dense Forest | 0.001 |
| Cropland | 0.45 | Planation | 0.05 |
| Water Bodies | 0.00 | Barren Land | 1.00 |
| Land Use | Slope (°) | Conservation Support Practice Factor (P) |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | 1–4 | 0.11 |
| 5–10 | 0.09 | |
| 11–20 | 0.18 | |
| 21–40 | 0.00 | |
| >40 | 0.20 | |
| Plantation | All | 0.13 |
| All | 1.00 |
| Description | Soil Loss (Mg·ha−1·y−1) | Area (Hectares) | % Area |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low | 0–1.5 | 8798 | 81 |
| Moderate | 1.5–25 | 1624 | 15 |
| Severe | >25 | 435 | 4 |
| Description | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Standard Deviation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Removal of R | 0 | 2.68 | 0.0022 | 0.022 |
| Removal of K | 0 | 23.898 | 19.298 | 191.22 |
| Removal of LS | 0 | 249.11 | 35.39 | 69.46 |
| Removal of C | 0 | 3558.55 | 7.53 | 44.58 |
| Removal of P | 0 | 3345.85 | 3.196 | 27.62 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sujatha, E.R.; Sridhar, V. Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a Small Mountainous Watershed Using RUSLE: A Case-Study of the Palar Sub-Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India. Water 2018, 10, 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111608
Sujatha ER, Sridhar V. Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a Small Mountainous Watershed Using RUSLE: A Case-Study of the Palar Sub-Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India. Water. 2018; 10(11):1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111608
Chicago/Turabian StyleSujatha, Evangelin Ramani, and Venkataramana Sridhar. 2018. "Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a Small Mountainous Watershed Using RUSLE: A Case-Study of the Palar Sub-Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India" Water 10, no. 11: 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111608
APA StyleSujatha, E. R., & Sridhar, V. (2018). Spatial Prediction of Erosion Risk of a Small Mountainous Watershed Using RUSLE: A Case-Study of the Palar Sub-Watershed in Kodaikanal, South India. Water, 10(11), 1608. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111608






