Effects of Dredging Season on Sediment Properties and Nutrient Fluxes across the Sediment–Water Interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description and Sampling
2.2. Laboratory Microcosm Experiment
2.3. In Situ Porewater Sampling
2.4. Analyses of Sediment and Water Characteristics
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Sediment Characterization
3.2. Temporal and Spatial Variations of Porewater Chemistry
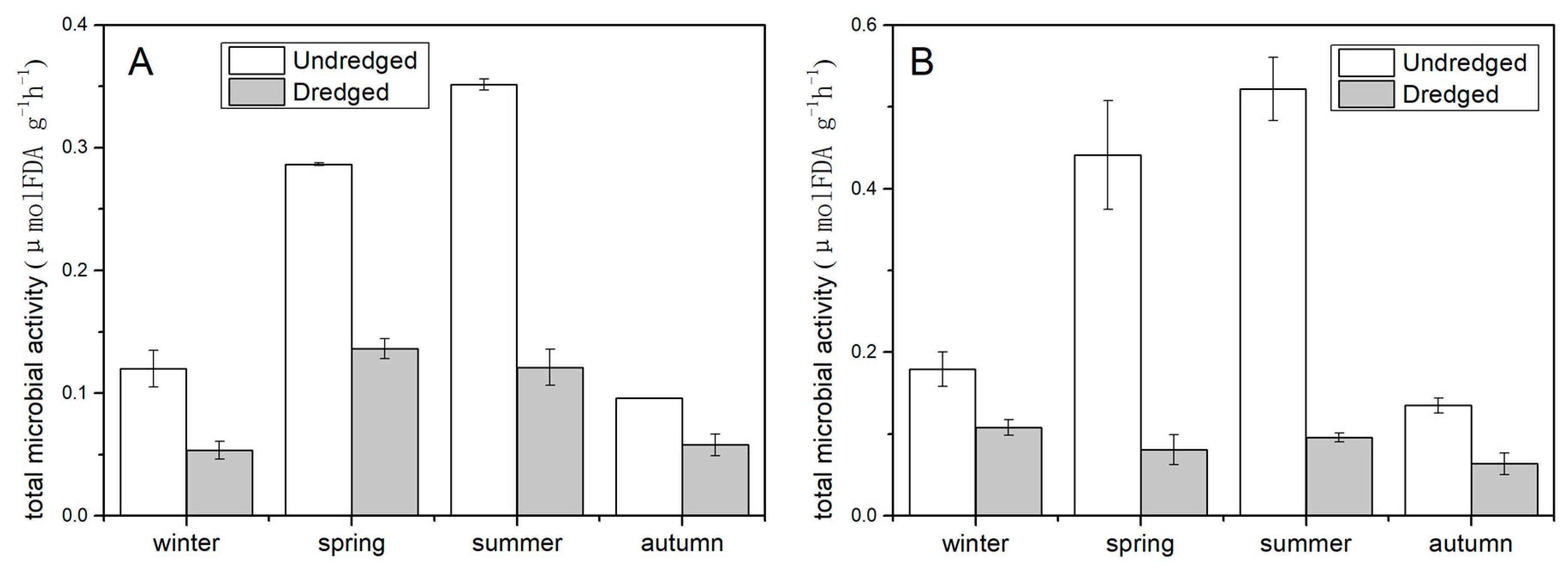
3.3. Effects of Dredging on Total Microbial Activity and Sediment Oxygen Demand
3.4. Effects of Dredging on Phosphorous Flux
3.5. Effects of Dredging on Inorganic Nitrogen Flux
3.6. Optimum Dredging Season for Minimal Environmental Risk
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| OC | Organic carbon |
| LOI | Loss on ignition |
| Fe | Iron |
| SRP | Soluble reactive phosphorus |
| SOD | Sediment oxygen demand |
References
- Zhang, Y.L.; Qin, B.Q.; Liu, M.L. Tempral-spatial variations of chlorophyll a and primary production in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu, China from 1995–2003. J. Plankton Res. 2007, 39, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.R.; Chen, W.; Peng, L. Distribution and bioaccumulation of microcystins in water columns: A systematic investigation into the environmental fate and the risks associated with microcystins in Meiliang Bay, Lake Taihu. Water Res. 2007, 41, 2853–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Yu, J.W.; Li, Z.L.; Guo, Z.H.; Burch, M.; Lin, T.F. Taihu Lake not to blame for Wuxi’s woes. Science 2008, 319, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, G.H.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.H. Analysis of black water aggregation in Taihu Lake. Water Sci. Eng. 2011, 4, 374–385. [Google Scholar]
- Schindler, D. Evolution of phosphorus limitation in lakes. Science 1977, 195, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penn, M.R.; Auer, M.T.; Doerr, S.M.; Driscoll, C.T.; Brooks, C.M.; Effer, S.W. Seasonality in phosphorus release rates from sediments of a hypereutrophic lake under a matrix of pH and redox conditions. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2000, 57, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, T.P.; Lawson, A.; Kumagai, M.; Babin, J. Review of emerging issues in sediment treatment. Aquat. Ecosyst. Health 1999, 2, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, U.; Neumann, T.; Donnert, D.; Nüesch, R.; Stüben, D. Sediment capping in eutrophic lakes-efficiency of undisturbed calcite barriers to immobilized phosphorus. Appl. Geochem. 2004, 19, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.R.; Zhang, H.Q.; Zhu, X. Innovation and Practice of Cyanobacteria Control in Taihu Lake; China Water Resources and Hydropower Publishing Press: Beijing, China, 2012. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, V.; Masciandaro, G.; Ceccanti, B.; Doni, S.; Lannelli, R. Phytoremediation and bio-physical conditioning of dredged marine sediments for their re-use in the environment. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2010, 210, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustavson, K.E.; Burton, G.A.; Francingues, N.R.; Reible, D.D.; Vorhees, D.J.; Wolfe, J.R. Evaluating the effectiveness of contaminated-sediment dredging. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5042–5047. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryding, S.O. Lake Trehörningen restoration project, Changes in water quality after sediment dredging. Hydrobiologia 1982, 9, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Does, V.D.; Verstraelen, P.; Boers, P.; Roestel, J.V.; Roijackers, R.; Moser, G. Lake restoration with and without dredging of phosphorus-enriched upper sediment layers. Hydrobiologia 1992, 233, 197–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, J.J.; Zheng, C.H.; Gao, G.; Wang, S.M. Processes and mechanism of effects of sludge dredging on internal source release in lakes. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2004, 49, 1853–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.Y.; Song, C.L.; Li, Q.M.; Zhou, Y.Y. Dredging effects on P status and phytoplankton density and composition during winter and spring in Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Research Council. Sediment Dredging at Superfund Megasites: Assessing the Effectiveness; The National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Kleeberg, A.; Kohl, J.G. Assessment of the long-term effectiveness of sediment dredging to reduce benthic phosphorus release in shallow Lake Müggelsee (Germany). Hydrobiologia 1999, 394, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, K.R.; Fisher, M.M.; Wang, Y.; White, J.R.; James, R.T. Potential effects of sediment dredging on internal phosphorus loading in a shallow, subtropical lake. Lake Reserv. Manag. 2007, 23, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.H.; Fan, C.X.; Zhong, J.C.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, C.H.; Yao, X.L. Effects of sediment dredging on nitrogen cycling in Lake Taihu, China: Insight from mass balance based on a 2-year field study. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3871–3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.H.; Ding, S.M.; Zhong, J.C.; Fan, C.X.; Chen, Q.W.; Yin, H.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.L. Evaluation of simulated dredging to control internal phosphorus release from sediments: Focused on phosphorus transfer and resupply across the sediment-water interface. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 592, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annadotter, H.; Cronberg, G.; Aagren, R.; Lundstedt, B.; Nilsson, P.Ǻ.; Ströbeck, S. Multiple techniques for lake restoration. Hydrobiologia 1999, 395, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhong, J.C.; Fan, C.X.; Kong, M.; Yu, J.H. Simulation research on the release of internal nutrients affected by different dredging methods in lake. Environm. Sci. 2013, 34, 3872–3978. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.; Shao, S.G.; Shen, Q.S.; Fan, C.X.; Zhou, Q.L.; Yin, H.B.; Xu, F.L. Use of multi-objective dredging for remediation of contaminated sediments: A case study of a typical heavily polluted confluence area in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 17839–17849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Zhong, J.C.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Fan, C.X. Fifteen-year study of environmental dredging effect on variation of nitrogen and phosphorus exchange across the sediment-water interface of an urban lake. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 219, 639–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.; Zhong, J.C.; Yu, J.H.; Shen, Q.S.; Fan, C.X.; Kong, F.X. Optimum dredging time for inhibition and prevention of algae-induced black blooms in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 14636–14645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graca, B.; Burska, D.; Matuszewska, K. The impact of dredging deep pits on organic matter decomposition in sediments. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2004, 158, 237–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luijn, F.V.; Boers, P.C.M.; Lijklema, L.; Sweerts, J.P.R.A. Nitrogen fluxes and processes in Sandy and Muddy sediments from a shallow eutrophic lake. Water Res. 1999, 33, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michel, P.; Boutier, B.; Chiffolear, J.F. Net fluxes of Dissolved Arsenic, Cadmium, Copper, Zine, Nitrogen and phosphorus from the Gironde Estuary (France): Seasonal variations and trends. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 2000, 51, 451–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brossard, D.M.; Lhoumear, C.; Jankowska, H.P. Seasonal variability of benthic ammonium release in the surface sediments of the Gulf of Gdańsk (southern Blatic Sea). Oceanologia 2001, 43, 113–136. [Google Scholar]
- Malecki, L.M.; White, J.R.; Reddy, K.R. Nitrogen and Phosphorus Flux Rates from Sediment in the Lower St. Johns River Estuary. J. Environ. Qual. 2004, 33, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Jin, X.C.; Yao, Y.; Li, L.H.; Wu, F.C. Effects of biological activity, light, temperature and oxygen on phosphorus release processes at the sediment and water interface of Taihu Lake, China. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2251–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madura, K.K.; Goldyn, R.; Dera, M. Spatial and seasonal changes of phosphorus internal loading in two lakes with different trophy. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 74, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Némery, J.; Gratiot, N.; Doan, P.T.K.; Duvert, C.; Vlvarado-Villanueva, R.; Duwig, C. Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and sediment sources and retention in a small eutrophic tropical reservoir. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 78, 171–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.W.; Fan, C.X.; Teubner, X.K.; Dokulil, M. Changes of nutrients and phytoplankton chlorophyll-a in a large shallow lake, Taihu, China: An 8-year investigation. Hydrobiologia 2003, 506, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.J.; Liu, R.M. Spatial analysis and eutrophication assessment for chlorophyll a in Taihu Lake. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2005, 101, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, W.P.; Zhai, S.J.; Zhu, Z.C.; Han, H.J. Impacts of the Yangtze River water transfer on the restoration of Lake Taihu. Ecol. Eng. 2008, 34, 30–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.C.; Fan, C.X.; Liu, G.F.; Zhang, L.; Shang, J.G.; Gu, X.Z. Seasonal variation of potential denitrificaiton rates of surface sediment from Meiliang Bay, Taihu, China. J. Environ. Sci. 2010, 22, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, L.Y.; Huang, W.Y.; Xu, P.Z. Simulation of internal loading of nitrogen and phosphorus in a lake. Oceanol. Limnol. Sin. 2002, 33, 370–378. [Google Scholar]
- Hesslein, R.H. An in-situ sampler for close interval porewater studies. Limnol. Oceanogr. 1976, 21, 912–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, P.H. A new rechargeable dialysis pore water sampler for monitoring sub-aqueous in-situ sediment caps. Water Res. 2002, 36, 3121–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urban, N.R.; Dinkel, C.; Wehrli, B. Solute transfer across the sediment surface of a eutrophic lake: I. Porewater profiles from dialysis samplers. Aquat. Sci. 1997, 59, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruban, V.; López-Sánchez, J.F.; Pardo, P.; Rauret, G.; Muntau, H.; Quevauviller, P. Selection and evaluation of sequential extraction procedures for the determination of phosphorus forms in lake sediment. J. Environ. Monitor. 1999, 1, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, G.; Duncan, H. Development of a sensitive and rapid method for the measurement of total microbial activity using fluorescein diacetate (FDA) in a range of soils. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2001, 33, 943–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, M.M.; Reddy, K.R. Phosphorus flux from wetland soils affected by long-term nutrient loading. J. Environ. Qual. 2001, 30, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinese EPA. Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 4th ed.; China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2002. (In Chinese)
- Rasheed, M.; Badran, M.I.; Huettel, M. Particulate matter filtration and seasonal nutrient dynamics in permeable carbonate and silicate sands of the Gulf of Aqaba, Red Sea. Coral Reefs 2003, 22, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCarthy, M.J.; Lavrentyev, P.J.; Yang, L.Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Gardner, W.S. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.G.; Lu, J.W.; Wang, W.D.; Huang, P.S.; Yin, C.Q. Spatio-temporal distribution of nitrogen in the undulating littoral zone of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 2007, 581, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Paerl, H.W.; Qin, B.Q.; Zhu, G.W.; Gao, G. Nitrogen and phosphorus inputs control phytoplankton growth in eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Limmol. Oceanogr. 2010, 55, 420–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mermillod-Blondin, F.; Nogaro, G.; Datry, T.; Malard, F.; Gibert, J. Do tubificid worms influence the fate of organic matter and pollutants in stormwater sediments? Environ. Pollut. 2005, 134, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jing, L.D.; Liu, X.L.; Bai, S.; Wu, C.X.; Ao, H.Y.; Liu, J.T. Effects of sediment dredging on internal phosphorus: A comparative field study focused on iron and phosphorus forms in sediments. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 82, 267–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, J.C.; You, B.S.; Fan, C.X.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.M. Influence of sediment dredging on chemical forms and release of phosphorus. Pedoshpere 2008, 18, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, L.D.; Wu, C.X.; Liu, J.T.; Wang, H.G.; Ao, H.Y. The effects of dredging on nitrogen balance in sediment–water microcosms and implications to dredging projects. Ecol. Eng. 2013, 52, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shao, S.G.; Shen, Q.S.; Fan, C.X.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q.L. Effects of riverine suspended particulate matter on the post-dredging increase in internal phosphorus loading across the sediment-water interface. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, J.C.; Liu, G.F.; Fan, C.X.; Li, B.; Zhang, L.; Ding, S.M. Environmental effect of sediment dredging in lake: II. The role of sediment dredging in reducing internal nitrogen release. J. Lake Sci. 2009, 21, 335–344. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.H.; Fan, C.X.; Zhong, J.C.; Zhang, Y.L.; Wang, C.H.; Zhang, L. Evaluation of in situ simulated dredging to reduce internal nitrogen flux across the sediment-water interface in Lake Taihu, China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 214, 866–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Shen, Q.S.; Zhou, Q.; Fan, C.X.; Shao, S.G. Precontrol of algae-induced black blooms through sediment dredging at appropriate depth in a typical eutrophic shallow lake. Ecol. Eng. 2015, 77, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhong, J.-C.; Yu, J.-H.; Zheng, X.-L.; Wen, S.-L.; Liu, D.-H.; Fan, C.-X. Effects of Dredging Season on Sediment Properties and Nutrient Fluxes across the Sediment–Water Interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Water 2018, 10, 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111606
Zhong J-C, Yu J-H, Zheng X-L, Wen S-L, Liu D-H, Fan C-X. Effects of Dredging Season on Sediment Properties and Nutrient Fluxes across the Sediment–Water Interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Water. 2018; 10(11):1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111606
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhong, Ji-Cheng, Ju-Hua Yu, Xiao-Lan Zheng, Shuai-Long Wen, De-Hong Liu, and Cheng-Xin Fan. 2018. "Effects of Dredging Season on Sediment Properties and Nutrient Fluxes across the Sediment–Water Interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China" Water 10, no. 11: 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111606
APA StyleZhong, J.-C., Yu, J.-H., Zheng, X.-L., Wen, S.-L., Liu, D.-H., & Fan, C.-X. (2018). Effects of Dredging Season on Sediment Properties and Nutrient Fluxes across the Sediment–Water Interface in Meiliang Bay of Lake Taihu, China. Water, 10(11), 1606. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10111606




