Abstract
Groundwater is the main supply of fresh water in many parts of the world. The intrusion of saline water into the fresh water is a serious threat to groundwater resources. Delineation of fresh-saline aquifer zones is essential to exploit the potable fresh water. The conventional method to differentiate fresh-saline water interface is to collect and test groundwater samples from boreholes using a number of laboratory tests. However, such techniques are expensive and time consuming. A non-invasive geoelectrical method, in combination with borehole data and physicochemical analysis, is proposed to assess the fresh-saline aquifers. This investigation was conducted in Jahanian area of Pakistan with forty-five vertical electrical soundings (VES) using Schlumberger array, nine bore wells and fifty physicochemical samples. The fresh-saline aquifers are delineated by aquifer resistivity and Dar-Zarrouk parameters namely transverse unit resistance and longitudinal unit conductance. The aquifer potential of fresh-saline water zones is estimated by the aquifer parameters namely transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity. Integration of subsurface resistivity with hydrogeological information reveals the subsurface formation of five layered succession, that is, topsoil having dry strata with resistivity greater than 30 Ωm, clay containing saline water with resistivity less than 15 Ωm, clay-sand with brackish water having resistivity between 15 and 25 Ωm, sand containing fresh water with resistivity ranging from 25 to 45 Ωm and gravel-sand having fresh water with resistivity greater than 45 Ωm. The geoelectrical columns and geological cross-sections constructed by the aquifer resistivity provide effectiveness of the interpretations for the evaluation of fresh-saline aquifers. The results of physicochemical analysis using WHO guideline validate the fresh-saline aquifer zones delineated by the geophysical method. This investigation contributes towards predicting the fresh-saline water interface using inexpensive geoelectrical method.
1. Introduction
Saline water intrusion is becoming a serious threat to fresh water supply for half of the world’s population that largely depends on groundwater resources [1]. The saline water intrusion arises when the salinity level exceeds the standard of drinking water. The saline intrusion is caused by a disturbance in the hydrostatic balance between the saline and fresh aquifers mainly due to the human action [2]. The main causes of saline water intrusion include intensive farming, industrial waste materials, overexploitation of groundwater resources, natural events and climate change and so forth [3]. The saline water intrusion is the displacement of fresh aquifer by saline aquifer caused by the excess withdrawal of groundwater including other human actions that can decline the groundwater table and result in saline water intrusion [4,5]. For several decades, the characterization of fresh-saline water interface has been the main subject of several field investigations [6,7,8,9,10]. The saline water contains high salt concentration such as NaCl.
Groundwater is the major source of fresh water supply in most of the countries. The intrusion of saline water into the fresh water is the sternest challenge in many areas of the world [11,12]. In case of Pakistan where more than 200 million people are dependent on groundwater assets especially for drinking, agricultural, domestic and industrial uses, saline water intrusion is a serious threat. At present, Pakistan is facing dilemma of water deficiency and this problem will become even worse in future due to the continuous dry of hydrologic cycle. The availability of surface water is not enough to meet the required demands of water supply for different uses especially for drinking and agricultural purposes. The groundwater resources have been exploited more particularly in last two decades. Recently, the surface water supply has reduced to 51% during winter [13]. The country needs more dams to store water during monsoon season. Tarbela and Mangla dams constructed forty years ago are not enough to store the surface water to meet the demands of the growing population. As a result, the installation of tube wells is increasing rapidly to extract the groundwater resources without considering the water quality consequences [14]. Consequently, the groundwater table is declining and the saline water intrusion is increasing in many areas of Pakistan. The deficiency of groundwater resources and the saline-water intrusion are the major problems which Pakistan is facing recently. Jahanian is one of the areas in Pakistan where saline water intrusion is the major problem. Therefore, understanding the delineation of fresh-saline aquifers is crucial for effective management of groundwater resources [10,15].
The boreholes method is one of the reliable approaches to get subsurface information about the fresh-saline aquifers. However, this traditional technique is expensive and time taking; it needs heavy machinery and enough labor to conduct and it is limited only to a small scale. In contrast, the surface electrical resistivity methods are fast, user friendly, noninvasive, robust and low-cost, and can just take one fifth to one tenth of the time taken by the borehole technique for investigating the area. The electrical method has no geophysical limitation to work in the urban sites [16]. It can significantly reduce the number of boreholes to assess the subsurface formation regarding the fresh-saline water interface.
Geophysical methods, especially the geoelectrical resistivity methods, have been adopted by many researchers to map the salinity and delineate the fresh-saline aquifer interface [10,16,17,18,19,20,21]. Such techniques are commonly applied to characterize the groundwater zones mostly because of the close relation between subsurface resistivity, saturated subsurface materials and water salinity [22,23,24]. These methods have been very successful to distinguish between the fresh and saline aquifers due to their sensitivity to detect the variations in resistivity values of such aquifers [25]. One of the advantages of the use of geoelectrical methods over other geophysical techniques is that resistivity is measured in Ωm units which have larger range than other geophysical units [26]. The bulk resistivity (aquifer resistivity) shows a clear contrast between the saturated fresh and saline formations which is important to delineate the fresh-saline water interface [10,16]. Resistivity decreases with increasing the salinity; hence, the resistivity methods are very useful to isolate the fresh-saline water zones [27]. Such surveys are conducted on the ground surface using a specific configuration to get the apparent-resistivity data, apparent-resistivity sounding curves and apparent-resistivity pseudo-sections which provide vertical or horizontal variations in the subsurface resistivity. The geoelectrical methods offer the complementary data to obtain geological association even for those stations where no borehole data exist. Such methods generate constant data throughout the entire area or along a given profile to understand spatial relations between fresh, saline and brackish aquifers. Transverse resistance and longitudinal conductance collectively named as the Dar-Zarrouk parameters computed from resistivity measurements depend on thickness and resistivity with different combinations for each medium and are successfully used to estimate the fresh-saline aquifers [10,22]. The hydraulic parameters namely transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity are derived from surface resistivity data using different empirical relations to estimate the aquifer reserves [16,26,28]. Physicochemical analysis can be used to assess the groundwater quality [29,30].
The investigated area has saline intruded aquifers and declined water table due to the growing population, exhaustive agriculture and increasing industrialization. Consequently, the demarcation of fresh-saline aquifers is essential to exploit and manage the fresh groundwater resources properly. Hence, in this proposed investigation, an attempt has been made for delineating the fresh-saline water zones using the inexpensive resistivity survey.
2. Study Area and Hydrogeological Setting
This investigation was conducted in Jahanian area, Lower Bari Doab, Pakistan. The studied area is situated in the Upper Indus Basin with the latitude from 29.87° to 30.22°N and the longitude from 71.58° to 71.97°E as shown in Figure 1. Its summer lasts for six months from April to October with temperature range of 20–45 °C and the rainy season of monsoon comes during July and August. The temperature remains between 1 and 25 °C during winter from November to February. March and October are the spring and autumn seasons respectively in the studied area. The average annual precipitation is 430 mm with maximum rain during the monsoon season. It has vast canal system including main canals, branch canals and number of small tributaries originated from Ravi and Chenab River. Its hydrogeological settings have different classification depending on different textural characteristics [10,16]. The surface soil textures have good permeability properties ranging from fine to moderately medium. It lies in an alluvium plain with the lithologies such as gravel-sand, sand, clay-sand and clay. It has almost flat topographic relief gently sloping in NE-SW direction. Its aquifer system was created by the sediment deposition over Precambrian and Tertiary igneous/metamorphic rocks [31]. These sediments were deposited by the Indus River and the tributaries originating from the Great Himalayan Mountains in north. It has an unconfined aquifer system like most of the aquifers in Punjab province [32]. The transmissibility coefficients remain between 0.2 and 1.0 cusecs per foot in most of the aquifers in Bari Doab [31]. The lower storage coefficients obtained in the pumping tests mark the conditions based on the presence of comparatively less permeable clay layers within the aquifer system. The permeability was found between 0.00033 and 0.01573 ft/s in most of the areas in Bari Doab [32]. Water table lies between 6 and 18 m in the investigated area. Groundwater is the major water supply for different purposes due to the scarce precipitation and insufficient surface water. Due the rapid installation of tube wells, the groundwater table is decreasing rapidly. The canal system is the major cause of groundwater recharge in the investigated area [31].
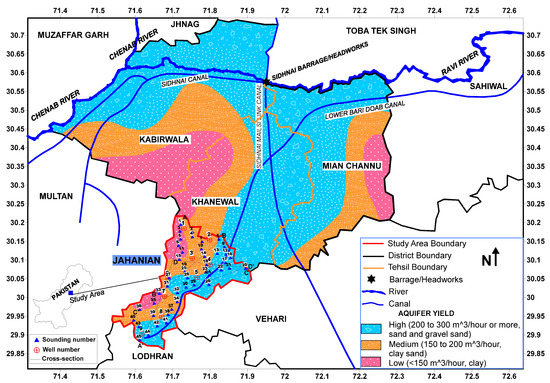
Figure 1.
map showing simplified hydrogeological settings [33] and measurements of the investigated area.
The hydrogeological settings divide the studied area into three main aquifer zones, that is, the low potential aquifer containing saline water with clay, the medium potential aquifer with brackish water having clay-sand, and the high potential aquifer with fresh water containing gravel-sand and sand [33] (Figure 1). The aquifer yields the low, medium and high potential zones are less than 150 m3/h, 150 to 200 m3/h and 200 to 300 m3/h respectively as shown in Figure 1 [33].
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Electrical Resistivity Method
The geoelectrical resistivity method computes the distributed subsurface resistivity which is a physical property depending on the characteristics of the materials [34]. Resistivity of a subsurface geological formation is related with the electric current flowing through the formation. It depends on nature of mineralization, rock texture and electrolytic conductivity of the rock [35]. The subsurface resistivity not only varies from one formation to another but it also changes within the formation [36]. It increases with grain size and shows maximum values for the coarse grains and also when the rock is compacted with fine grains. It significantly decreases with increasing the clay content. In saturated formation, it shows low values due to increase in salinity or clay content. Consequently, the resistivity surveys are conducted to effectively delineate the salinity or clay formation [37]. In this investigation, a Syscal (V11.4) IRIS instrument was used to conduct the apparent resistivity measurements.
George Simon Ohm proposed an equation in 1827 involving voltage, current and resistance:
where, V is measured as voltage with volts units, the resistance R is calculated in ohms units, and I shows the current in Amp. Resistivity measured in field is the apparent resistivity (ρa) calculated by using the relation:
where, I measures the current in Amp, the potential difference ΔV is measured in volts, and K is known as the geometric factor; K values show the subsurface stratification and depend on electrode position. The apparent resistivity is dependent on the measured potential V, the injected current I, and K the geometric factor [10,38].
Voltage = Current × Resistance
V = IR
Vertical electrical sounding (VES) determines the variations in subsurface resistivity with respect to the depth. It was carried out on the ground surface assumed to be with very little lateral variation or almost horizontal layered. It was carried out using Schlumberger array, in which the potential electrodes with small spacing are located in a fixed position and the current electrodes are positioned symmetrically out sides the potential electrodes. In order to obtain the deeper penetration, the current electrodes are moved further away from the center of the array with each resistivity measurement. The spacing of the potential electrodes is increased between a pair of current electrodes for large distance to enhance the signal to noise ratio for the measured voltage and to increase the efficiency of the instrument [39]. The inversion process of the VES curves was performed using IPI2WIN software [40]. The root mean squares (RMS) values varied between 1.1% and 4.8%. In this investigation, a total number of 45 VES and 9 boreholes were conducted to cover the entire area (Figure 1). The Schlumberger configuration was used to obtain the VES measurements with 200 m depth (maximum half-electrode spacing). The aquifer resistivity was estimated from the VES models after the inversion program.
3.2. Dar-Zarrouk Parameters
Dar-Zarrouk parameters namely longitudinal unit conductance (Sc) and transverse unit resistance (Tr) first introduced by Mailet [41] provide adequate solutions to the subsurface resistivity for the evaluation of saturated formations [16]. These parameters can delineate the fresh-saline aquifer zones efficiently [10]. Dar-Zarrouk parameters consist of various combinations of resistivity and thickness for subsurface geologic VES layers and hence, provide better understanding about the subsurface geoelectrical models [16,42,43]. Thickness h and resistivity ρ are two fundamental parameters that define the geoelectrical layer [44]. Longitudinal unit conductance (Sc) and transverse unit resistance (Tr) are computed from the above two basic parameters (h and ρ) from the VES models [10]. Transverse unit resistance and longitudinal unit conductance were estimated using the relations [10]:
where Tr is transverse unit resistance measured in Ωm2, Sc is longitudinal conductance is computed in Siemens or mho, ρ shows resistivity of the layers in Ωm, h is the layer thickness in meters and i indicates the number of subsurface layers. Specific ranges of Tr and Sc for the saline, brackish and fresh aquifers are obtained depending on the local hydrogeological information and the boreholes data of the investigated area.
3.3. Estimation of Aquifer Parameters
The hydraulic parameters namely transmissivity (T) and hydraulic conductivity (K) are efficiently used to estimate the groundwater reserves [16,22]. In this investigation, these parameters were determined to estimate the groundwater potential contained in the fresh-saline aquifer zones. The Kozeny–Carman–Bear formula was applied for estimating hydraulic conductivity [45]. This equation is commonly used to calculate hydraulic conductivity especially for the homogeneous aquifer. Since the studied area has homogeneous aquifer system, so, hydraulic conductivity was estimated using the following equation:
where, hydraulic conductivity K is measured in m/day, Φ indicates the porosity, d represents the grain size, g is the acceleration caused by the gravity (9.81 m/s2), μ is measured as dynamic viscosity of the water (0.0014 kg/ms), and δw is known as the fluid density (1000 kg/m3) [46]. The above Equation (5) was used to calculate K for the selected 9 VES locations nearby the bore-wells.
K = (δwg/μ) (d2/180) [Φ3/(1 − Φ)2]
Archie’s equation was applied to obtain the porosity (Φ) needed in the Kozeny–Carman–Bear relation [47]:
ρa= αρwΦ−m
From Equation (1):
where
and
where, ρa is known as the aquifer resistivity or bulk resistivity for the saturated layers computed from the VES models, Φ represents the porosity of the aquifer medium, Fi is the intrinsic formation factor valid for a clay-free medium, α indicates the coefficient of saturation, m shows the cementation factor, and ρw is the groundwater resistivity. EC is electrical conductivity with the units of μS/cm.
Φ = e(1/m) ln(α)+(1/m)ln(1/Fi)
Fi = ρo/ρw
ρw = 10,000/EC
The values of m and α required in Equation (7) are essential to calculate the porosity. Generally, α ≈ 1 and m varying between 1 and 2.5 are used for the aquifer of unconsolidated materials [48,49]. These values are related only with homogeneous sediments and are mostly determined in the laboratory tests. For this study, a = 1 and m ranging from 1.18 to 1.93 were used in Equation (7) to calculate porosity (Table 1). The pumping tests were conducted at a constant pumping rate of 24 h and the static water level was noted. Just after the pumping test, a recovery test was conducted and the water level was again noted.

Table 1.
Estimated values of aquifer resistivity, water resistivity, aquifer thickness, longitudinal conductance, transverse resistance, electrical conductivity, formation factor, the coefficients, porosity, transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity for the selected 9 sounding stations near the boreholes of the study area.
The drawdown curves were interpreted to obtain the information for the calculation of hydraulic parameters such as hydraulic conductivity (Kw) and transmissivity (Tw) at nine borehole sites by applying Eden-Hazel approach with the StepMaster (version 2.0) software [50]. The pumped aquifer parameters were determined to compare with the estimated hydraulic parameters to check the reliability of the geophysical method.
However, Equation (7) is applicable only for clay-free medium. For aquifer containing clay content, an alteration in the Archie’s equation is mandatory. The studied area contains significant clay content. For the clay medium, we use the following Waxman–Smits model [51,52]:
where, BQv depends on effects of surface conduction. If the effects of surface conduction are non-existent, in such cases Fa becomes equal to Fi. A linear relationship was obtained between 1/Fa and ρw by rearranging Equation (10):
Fa = Fi(1 + BQvρw)−1
1/Fa = (1/Fi) + (BQv/Fi)ρw
1/Fa in above Equation (11) is equal to ρw/ρo. Equation (11) shows a linear relation between 1/Fa (Fa = ρo/ρw) and ρw. Here, BQv/Fi shows the gradient, and 1/Fi indicates the intercept of the straight line [52]. Consequently, the intrinsic formation factor (1/Fi = 0.2 or Fi = 5) was obtained by the plot between 1/Fa and ρw (Figure A1a given in Appendix A) to calculate porosity using Equation (7).
The following equation was used to determine transmissivity (T) for the selected sounding stations close to the bore-wells [53]:
where, the aquifer thickness h is measured in meters (m) and transmissivity T in m2/day.
T = Kh
From Equation (3):
Tr = hρ
Combining Equations (12) and (13):
T = TrK/ρ
K = ρT/Tr
From (14):
and from Equation (15):
T ∞ Tr
K ∞ ρa
The above Equations (16) and (17) show a direct relation between T and Tr [26,28], and K and ρa [54] respectively. In order to estimate transmissivity (T’) and hydraulic conductivity (K’) for all sounding stations to cover the entire area, the following relations were obtained from the plots of T versus Tr and K versus ρa for the selected sounding stations near 9 bore-wells as shown in Figure A1b,c (given in Appendix A):
and
T = 1.294Tr + 275.9
K = 1.501ρa− 2.279
3.4. Hydrochemical Method
Total 50 groundwater samples were obtained from different locations during October 2016 for the assessment of the groundwater quality in the studied area. The physicochemical analysis was carried out for major and minor ions including potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), calcium (Ca2+), sodium (Na+); sulphates (SO42−), chloride (Cl−) and bicarbonates (HCO−3) and the physical parameters including total dissolved solids (TDS), electrical conductivity (EC) and pH [29,55] in the laboratory of Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resource (PCRWR). The Concentrations of sodium, potassium, calcium, magnesium, chloride, sulphate and bicarbonate were obtained using the standard procedures [23,56]. The atomic absorption spectrometry was used to analyze sodium, potassium, calcium and magnesium. The volumetric method was applied to estimate the ions such as chlorides and bicarbonates. The UV–visible spectrophotometer was used to analyze sulphates. The concentration of all ions was estimated in milligrams per liter (mg/L), except EC and pH. The concentration of EC was measured in microsiemens per centimeter (μS/cm) at 25 °C. The ionic balance of water was used to check the reliability of results. The acceptable reliability was observed in the percentage range from −5% to +5%. The groundwater samples were collected with the depth ranging from 30 m to 110 m.
4. Results
4.1. Resistivity Model Curves and Lithological Calibration
Geoelectrical method measures the subsurface resistivity in the geophysical field survey which is known as the apparent resistivity or iso-resistivity. It is the weighted average resistivity of all subsurface geological materials. Moreover, it shows more effects for the subsurface materials at shallow depth (less than 100 m) than the materials at higher depth (greater than 100 m depth) [22]. Hence, the apparent resistivity cannot provide the actual resistivity effects of the geological materials at the depth of some hundred meters. In order to assess the subsurface formation at greater depth, the field data of the apparent resistivity were processed using IpI2Winv software [57] to get best fit vertical electrical soundings (VES) curves. The modeled VES curves were generated on the logarithmic graph sheets by the plot of half electrode spacing and the apparent resistivity. The field data were obtained for 45 geoelectrical soundings using Schlumberger configuration for the maximum depth of 200 m. 1D inversion program of the software generates models of different subsurface layers that provide information about the true resistivity and thickness of each layer. The changes in the physical parameters of the subsurface geologic layers make up the model of true resistivity [58]. True resistivity of rock mass depends on many factors such as porosity, clay content and water content, fault and fault zone, groundwater resistivity, and temperature [24]. Resistivity range for groundwater is from 10 ohm-m to 115 Ωm. Under any damp conditions, clay formation has less resistivity value than sandy formation and sandy formation has less resistivity than gravel formation [22].
Calibration between the true resistivity and the litho logs was performed at nine wells to establish a unified layered-model appropriate to all resistivity modeled curves. This correlation depends on the local basis, that is, the hydrogeological information of the studied area [22,24]. The correlation between resistivity and borehole data constrained the subsurface formation into different layers, that is, dry strata with resistivity greater than 30 Ωm (above water table), clay containing saline water with resistivity less than 15 Ωm (below water table), clay-sand having brackish water with resistivity ranging from 15 to 25 Ωm (below water table), sand with fresh water containing resistivity range between 25 and 45 Ωm (below water table) and gravel-sand having fresh water with resistivity greater than 45 Ωm (below water table) as shown in Table 2. This calibration (shown in Table 2) is applicable to the studied area only. However, the proposed geophysical method can be successfully applied to establish such calibration for any area based on the hydrogeological information of that area. The calibration in Table 2 was carried out using only the dominant/common lithologies of the boreholes in order to interpret the fresh-saline aquifer zones clearer. However, other lithologies (not common or dominant in the investigated area) such as clay-sand with saline water (well 1), sand with brackish water (well 2 and well 3), clay with brackish water (well 7) and clay-sand with fresh water (well 8) were also revealed by the bore-well data as shown in Figure 2. Every specific area has its own different combinations of lithologies with each range of resistivity. For any type of lithology with specific range of resistivity in any area, the proposed method can be integrated with only few numbers of boreholes to delineate the subsurface geologic formation (fresh-saline water interface) over the entire area and therefore can be suggested as cost-effective by reducing large number of expensive boreholes.

Table 2.
Resistivity and lithology calibration in the study area.
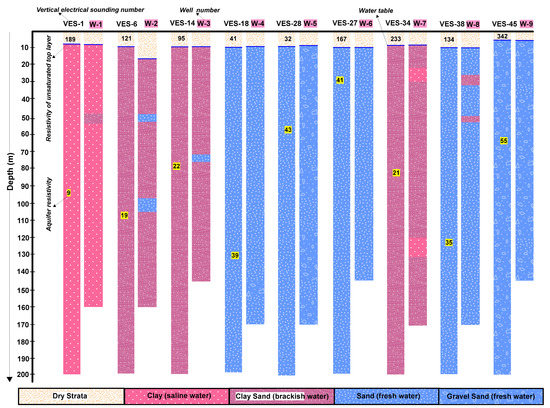
Figure 2.
Comparison between geoelectric columns constructed from aquifer resistivity and lithologic logs of the boreholes for the selected stations of the studied area.
4.2. Geoelectrical Columns and Aquifer Resistivity
Aquifer resistivity (ρa) also known as bulk resistivity was calculated as the average resistivity of all saturated subsurface geologic layers acquired from 1D inversion procedure of VES field data (VES modeled curves). Geoelectrical columns were constructed based on the aquifer resistivity for the selected nine sounding locations near the bore-well sites as shown in Figure 2. Geoelectrical columns were interpreted for saline, brackish and fresh aquifers depending on specific range of resistivity values and the lithologies. These interpreted resistivity columns were then compared with the litho logs of the boreholes. This comparison shows good correlation between the litho logs and the geoelectrical columns. The results suggest that resistivity column 1 and well 1 reveal saline water containing clay content; resistivity columns 6, 14, 34 with wells 2, 3, 7 delineate brackish water having clay-sand; resistivity columns 18, 27, 38 and wells 4, 6, 8 evaluate fresh water with sand as dominant lithology; and column 45 and well 9 show fresh water with gravel-sand. However, resistivity column 28 shows fresh water with sand but well 5 reveals freshwater with gravel-sand as the dominant lithology.
The aquifer resistivity estimated for all sounding stations was plotted as a contour map to delineate the saline, brackish and fresh aquifer zones over the entire area. The saline aquifer was evaluated by clay content with the aquifer resistivity less than 15 Ωm in NW. The fresh aquifer was revealed in SE by sand with resistivity ranged from 25 to 45 Ωm and gravel-sand with resistivity greater than 45 Ωm. The brackish water lying between fresh and saline water was revealed by clay-sand with resistivity between 15 and 25 Ωm.
4.3. Transverse Resistance and Longitudinal Conductance
Dar-Zarrouk parameters known as longitudinal conductance (Sc) and transverse resistance (Tr) were estimated using various combinations of resistivity and thickness of the layers obtained from VES modeled curves. Specific values range of Tr and Sc for saline, brackish and fresh aquifers were obtained depending on the hydrogeological information of the investigated area. The estimated values of Tr and Sc are given in Table 1. The values of Tr increase with the gain size and the fresh water, whereas Sc values decrease with grain size and the fresh water [10]. The fresh aquifer zone was delineated by Tr > 1500 Ωm2 and Sc < 2 mho containing sand and gravel-sand content. The brackish aquifer with clay-sand lithology was revealed by Tr between 500 and 1500 Ωm2 and Sc from 2 to 2.5 mho. The saline water having clay content was evaluated by Tr < 500 Ωm2 and Sc > 2.5 mho. The maps of Tr and Sc show the distribution of saline, brackish and fresh aquifer zones over the entire area. The aquifer zones of saline, brackish and fresh aquifers differentiated by Tr and Sc show strong correlation with each other. These results show good matching with the groundwater zones assessed by hydrogeological map and the aquifer resistivity. Fresh water was observed in SE, whereas saline water was revealed in NW of the studied area.
4.4. Hydraulic Conductivity and Transmissivity
The hydraulic parameters namely hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity were calculated for estimating the groundwater reserves contained within fresh, brackish and saline aquifers. Firstly, transmissivity (T) and hydraulic conductivity (K) were measured for the selected sounding stations close to the bore-well sites given in Table 1. Afterwards, a relation between calculated hydraulic conductivity (K) and aquifer resistivity (ρa), and another empirical relation between measured transmissivity (T) and transverse resistance (Tr) were established for estimating hydraulic conductivity (K’) and transmissivity (T’) for all sounding stations over the entire area (Table 3). The pumped hydraulic parameters such as transmissivity (Tw) and hydraulic conductivity (Kw) were also calculated from the pumping test at nine boreholes (Table 3). The pumped aquifer parameters (Kw and Tw) and the calculated aquifer parameters (K and T) show very good matching (81–98%) for all selected stations (Table 3). The comparison between estimated parameters (K’ and T’) and pumped parameters (Kw and Tw) also show good correlation for most of the stations as shown in Table 3. However, the low %matching (i.e., 72%) between T’ and Tw at VES-1 is caused by different factors such as the difference in aquifer thickness (change in thickness of the subsurface geologic layers) at VES station and the borehole site, change in the lithology (well 1 lies at or near the interface of saline-brackish aquifers whereas VES-1 lies in saline aquifer as interpreted by the geophysical maps), the lowest value in the empirical equation (the station with the lowest values in the empirical plot increases the %error between the estimated and the calculated values as compared to the other stations with higher values) and the inevitable non-uniqueness of the geophysical measurements (geophysical measurements are non-unique and cannot provide 100% matching with the boreholes for all stations, however, they can provide satisfactory results with 70–90% matching even where the boreholes do not exist) [22,16]. The estimated hydraulic conductivity (K’) and transmissivity (T’) clearly delineated the aquifer potential of the entire area into three aquifer zones (i.e., fresh, brackish and saline aquifer zone). The fresh aquifer was estimated by K’ > 35 m/day and T’ > 2000 m2/day. The saline aquifer was delineated by K’ < 20 m/day and T’ < 1000 m2/day. The brackish aquifer lying between the fresh and saline aquifer zones was revealed with K’ ranging from 20 to 35 m/day and T’ from 1000 to 2000 m2/day. The estimated fresh, brackish and saline aquifers as a function of aquifer resistivity, transverse resistance and hydraulic conductivity are shown in Figure 3. Figure A2 given in Appendix A shows the saline, brackish and fresh water zones delineated by longitudinal conductance and estimated transmissivity. The saline, brackish and fresh aquifers estimated by K’ and T’ show good correlation with that of the aquifer zones delineated by ρa, Tr, Sc and hydrogeological map. A statistical analysis was performed to see the correlation between these parameters as shown in Table 4a. This Table shows very strong correlation between Tr and T’ (i.e., correlation coefficient = R = 1) and between ρa and K’ (i.e., R = 0.99). Next good correlation between electrical parameters (ρa, Tr and Sc) and hydraulic parameters (T’ and K’) was found to be R = −0.93 (between Sc and K’) and R = 0.92 (between ρa and T’ and Tr and K’). Thus, the statistical analysis suggests the best correlation between Tr and T’ and between ρa and K.’ That is why we established empirical equations by the graphical plots between these parameters to estimate K’ and T’ over the entire area. The specific values range of ρa, Tr, Sc, K’ and T’ for the delineation of saline, brackish and fresh aquifers is shown in Table 4b.

Table 3.
Comparison between estimated and pumped aquifer parameters for the secreted stations.
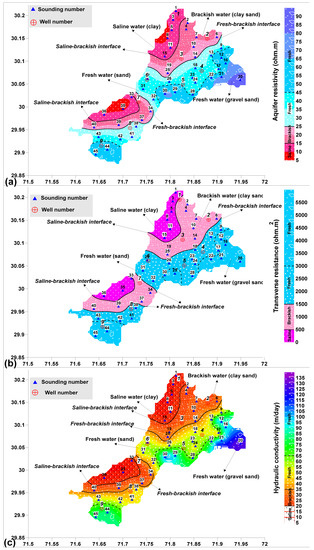
Figure 3.
Estimation of fresh, brackish and saline aquifers as a function of (a) aquifer resistivity; (b) transverse resistance and (c) hydraulic conductivity.

Table 4.
(a) Statistical analysis for the correlation between aquifer resistivity, transverse resistance, longitudinal conductance, hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity; (b) Delineation of fresh, brackish and saline water zones as a function of aquifer resistivity, transverse resistance, longitudinal conductance, hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity.
4.5. Geological Cross-Sections
The geoelectrical method can also provide 2D mapping of the subsurface geologic layers using specific number of VES stations along different profiles. The geological cross-sections can effectively evaluate the distribution of the subsurface resistivity and lithology both vertically and horizontally [59]. Such profiles provide a detail view of the subsurface geologic structures along different cross-sections. In this investigation, four cross-sections (AA,’ BB,’ CC’ and DD’) were constructed on the basis of aquifer resistivity of the specific VES stations along different profiles. These sections evaluated the subsurface geologic layers up to the depth of 200 m. The VES stations were chosen to construct the cross-sections along four different profiles in such a way that the entire area can be covered. These cross-sections included the information such as subsurface lithologies (dry strata, clay, clay-sand, sand and gravel-sand), fresh, brackish and saline aquifers, water table, topography, boreholes data and mean sea level as shown in Figure 4. These cross-sections were interpreted for fresh water with aquifer resistivity of 25–45 Ωm for sand and >45 Ωm for gravel-sand, brackish water with aquifer resistivity range of 15–25 Ωm containing clay-sand and saline water with aquifer resistivity <15 Ωm having clay content. The interpreted aquifer zones of fresh, brackish and saline water along these cross-sections match very well with the aquifer zones delineated by Dar-Zarrouk parameters, hydraulic parameters and hydrogeological map.
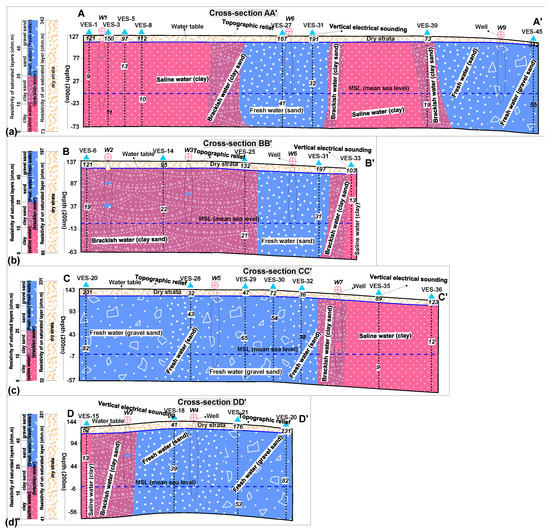
Figure 4.
Delineation of fresh, brackish and saline aquifers based on aquifer resistivity along cross-section (a) AA’; (b) BB’; (c) CC’ and (d) DD’ over the entire area.
The cross-section AA’ was constructed using 8 VES stations (i.e., VES 1, 3, 5, 8, 27, 31, 39 and 45) in NE-SW direction as shown in Figure 4a. Clay containing saline water and sand/gravel-sand having fresh water are the dominant lithologies along this cross-section. The lithologies of three boreholes (i.e., well 1, 6 and 9) match good with the lithologies interpreted by the aquifer resistivity along AA.’ The places near W-6 (VES-27, 31) and W-9 (VES-45) are most appropriate to extract the fresh water resources along this profile.
Five VES stations (6, 14, 25, 31 and 33) were used to construct cross-section BB’ in NE-SW direction as shown in Figure 4b. Clay-sand containing brackish water is the dominant lithology along this profile. The interpreted subsurface lithologies show good correlation with the data of three boreholes (W-2, W-3 and W-6). The most suitable location for the exploration of fresh aquifer is along well 6 (VES-31).
The cross-section CC’ includes seven VES stations (20, 28, 29, 30, 32, 35 and 36) and two boreholes (W-5 and W-7) in E-W orientation as shown in Figure 4c. This profile has sand/gravel-sand with fresh water as a dominant lithology in east. Clay with saline water in west is the second dominant lithology along CC’. The suitable locations for the exploitation of fresh water are found along VES-20, 28, 29, 30, 32 and W-5.
This short profile along cross-section DD’ was constructed by four VES stations (15, 18, 21 and 20) in W-E direction as shown in Figure 4d. Sand/gravel-sand with fresh aquifer is the dominant lithology in the east, whereas clay-sand with brackish water is the dominant in the western side. The eastern part including VES-18, 21, 20 and W-4 has the most appropriate locations to extract the fresh water resources along DD.’
4.6. Physicochemical Analysis
The groundwater quality was also assessed using physicochemical analysis to supplement the results obtained from geophysical method to delineate the fresh-saline aquifers. The analytical results of physicochemical parameters were obtained into statistical parameters like minimum, maximum, mean, median and standard deviation as given in Table 5. The guideline provided by the World Health Organization (WHO) [60] for drinking water quality and the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations [61] for irrigation water quality was used to perform this physicochemical analysis as shown in Table 5. The results of the physicochemical analysis suggest that the groundwater samples which do not exceed the suggested limits of WHO for drinking water and FAO for irrigation water, have good water quality (fresh water). The groundwater samples which exceed the suggested limit for most of the physicochemical parameters such as EC, TDS, Na+, Mg2+, Cl−, SO42− and HCO3− reveal poor water quality (saline water) [62]. The groundwater samples that exceed the suggested limit for some of the physicochemical parameters like EC, TDS or Na+ show medium water quality (brackish water) [62]. The results of physicochemical analysis for drinking water quality show good correlation with the saline, brackish and fresh aquifers revealed by the geoelectrical method. Figure 5 shows the zones of good, medium and poor water quality for drinking and irrigation purposes based on physicochemical analysis of groundwater samples. Statistical distribution and analysis of physicochemical parameters for drinking and irrigation water quality is shown in Table 5.

Table 5.
Statistical distribution and analysis of physicochemical parameters in the investigated area using 50 groundwater samples for (a) drinking water quality and (b) irrigation water quality.
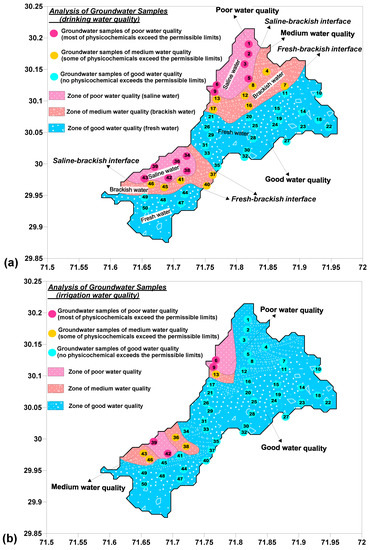
Figure 5.
Mapping of aquifers based on physicochemical analysis of groundwater samples for (a) drinking water quality; and (b) irrigation water quality.
5. Discussion
In this investigation, an economical approach of geoelectrical method was used for delineating the saline, brackish and fresh aquifers. The evaluation of saline water intrusion into the fresh water is essential to exploit the fresh groundwater resources. Generally, the traditional boreholes methods are applied to get the groundwater samples for laboratory tests for the delineation of saline water intrusion. However, such methods are expensive and time consuming and are hardly conducted to cover the entire area. Geophysical approach especially the geoelectrical method is cheap and user friendly and can assess the entire area with minimum number of boreholes for the delineation of fresh-saline water interface. This approach can significantly reduce the number of boreholes and can provide the subsurface geologic information of the aquifer properties with about 70–90% accuracy where the borehole data is not available. However, the geoelectrical method alone cannot evaluate the subsurface layers for aquifer characteristics; it needs to be integrated with some boreholes to conduct. In this study, the aquifer resistivity in combination with Dar-Zarrouk parameters namely longitudinal conductance and transverse resistance were estimated to reveal the fresh, brackish and saline aquifers. In addition, the aquifer potential contained within fresh, brackish and saline zones was estimated by the aquifer parameters such as transmissivity and hydraulic conductivity. The construction of geological cross-sections (AA,’ BB,’ CC’ and DD’) along different profiles using the aquifer resistivity values provides useful information about the delineation of fresh/saline aquifer with 2D view of the subsurface geologic layers up to the depth of 200 m. The delineation of fresh, brackish and saline aquifers along four different profiles show good matching with the aquifer zones interpreted by geological map and other geophysical parameters as shown in Figure 6. In order to check the reliability of the resistivity method to delineate the fresh-saline water interface, physicochemical analysis was performed using the suggested limit of WHO. The saline, brackish and fresh aquifers revealed by the geoelectrical method (aquifer resistivity, transverse resistance, longitudinal conductance, hydraulic conductivity and transmissivity, geological cross-sections) show strong correlation with the geochemical analysis and the hydrogeological information of the studied area. The results suggest that the proposed geophysical method is cost-effective and can be applied in any area with confidence to obtain the aquifer characteristics including the delineation of fresh-saline aquifers where the borehole data are scarce or of uncertain quality. However, this approach was used for homogenous aquifer system in the investigated area. This approach is applicable in any aquifer system with similar hydrogeological characteristics. It can also be applied in the heterogeneous aquifer with further studies.
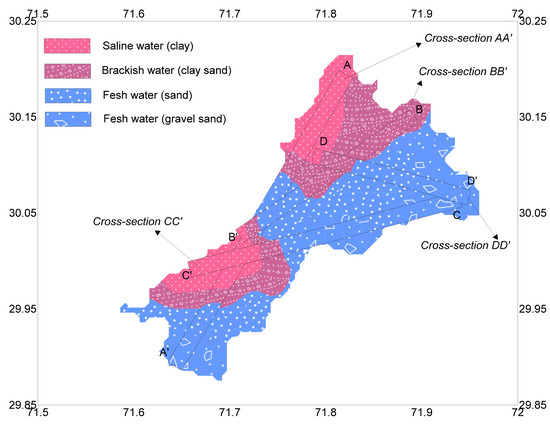
Figure 6.
Map showing cross-sections AA,’ BB,’ CC’ and DD’ along four profiles for the delineation of fresh, brackish and saline water aquifers in the investigated area.
6. Conclusions
This investigation was conducted to delineate the fresh-saline aquifers using an integrated approach of the electrical resistivity method, geochemical method and boreholes data including the pumping tests. The geoelectrical method was performed for 45 sounding stations using Schlumberger array with maximum depth of 200 m. VES modeled curves were obtained using 1D inversion program of IpI2Winv software from the field data of the apparent resistivity. The true resistivity and aquifer thickness of the subsurface geological layers were obtained from the modeled curves. The subsurface resistivity was correlated with the borehole data to constrain the subsurface layers with specific resistivity values range, that is, dry strata with resistivity values greater than 30 Ωm, clay containing the saline water with resistivity less than 15 Ωm, clay-sand having the brackish water with resistivity ranged from 15 to 25 Ωm, sand with the fresh water and resistivity between 25 and 45 Ωm and gravel-sand with the fresh water having resistivity greater than 45 Ωm. The aquifer resistivity was interpreted as the average resistivity of the saturated subsurface geologic layers acquired from the inversion program of the modeled VES curves. The geoelectrical columns constructed based on the aquifer resistivity for the selected sounding numbers show good correlation with litho logs of the nearby boreholes for the delineation of saline, brackish and fresh aquifers. Dar-Zarrouk parameters delineated the saline aquifer with Tr<500 Ωm2 and Sc>2.5 mho, the brackish water with Tr from 500 to 1500 Ωm2 and Sc from 2 to 2.5 mho and the fresh water with Tr>1500 Ωm2 and Sc<2 mho. The aquifer parameters estimated the saline water with K’<20 m/day and T’<1000 m2/day, the brackish aquifer with K’ ranging from 20 to 35 m/day and T’ from 1000 to 2000 m2/day and the fresh water with K’>35 m/day and T’>2000 m2/day. The aquifer zones delineated for the fresh, brackish and saline water along cross-sections of different profiles show good matching with the zones delineated by ρa, Tr, SC, K’ and T’ and hydrogeological map. Physicochemical results interpreted by WHO compliment the saline, brackish and fresh aquifers zones evaluated by the geoelectrical method. This approach is useful to assess the saline water intrusion in any homogeneous aquifer system and thus, can reduce significantly the number of expensive boreholes. However, it can also be effectively used in a heterogeneous aquifer system with further studies.
Author Contributions
M.H., Y.S., G.A. and W.J. did the preliminary studies, designed and performed the experiments, conducted field studies, analyzed the data and wrote the paper.
Funding
This research was sponsored by CAS-TWAS President’s Fellowship for International PhD Students; and financially supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of the University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No. XDB 10030100), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41772320).
Acknowledgments
Authors wish to acknowledge support received from Key Laboratory of Shale Gas and Geoengineering, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing China, and Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources (PCRWR), Islamabad Pakistan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix A
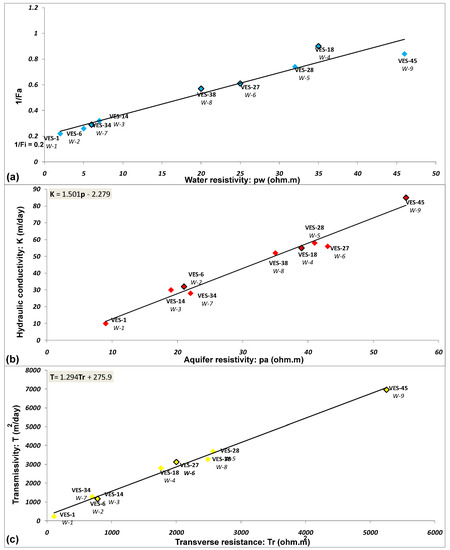
Figure A1.
(a) The estimation of intrinsic formation factor (Fi) from the graphical plot of 1/Fa vs. groundwater resistivity (ρw); (b) graphical plot between aquifer resistivity (ρa) and hydraulic conductivity (K) of the selected stations to obtain a relation for the estimation of hydraulic conductivity (K’) over the entire area; and (c) graphical plot of transverse resistance (Tr) vs. transmissivity (T) for the selected stations to estimate the transmissivity (T’) for all stations.
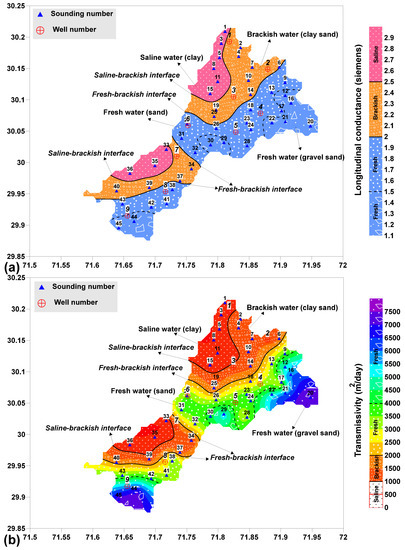
Figure A2.
(a) The delineation of fresh, brackish and saline water zones as a function of (a) longitudinal conductance and (b) transmissivity.
References
- Zawawi, M.H.; Syafalni; Abustan, I. Detection of Groundwater Aquifer Using Resistivity Imaging Profiling at Beriah Landfill Site, Perak, Malaysia. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 250, 1852–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaouti, F.E.; Mandour, A.E.; Khattach, D.; Benavente, J.; Kaufmann, O. Salinization processes in the unconfined aquifer of Bou-Areg (NE Morocco): A geostatistical, geochemical, and tomographic study. Appl. Geochem. 2009, 24, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, C.; Calvache, M.L.; Pedrera, A.; Martín-Rosales, W.; López-Chicano, M. Combined time domain electromagnetic soundings and gravimetry to determine marine intrusion in a detrital coastal aquifer Southern Spain. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 536–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balasubramanian, M.; Srinivasamoorthy, K.; Gopinath, S.; Saravanan, K.; Prakash, R.; Ravindran, A.; Sarma, V.S. Efficacy of diverse electrode configurations in 2D electrical resistivity imaging for effective delineation of saline water intrusion: Pondicherry coastal aquifers, India: A case study. J. Coast. Sci. 2018, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Baba, A.; Gündüz, O. Effect of Geogenic Factors on Water Quality and Its Relation to Human Health around Mount Ida, Turkey. Water 2017, 9, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, H.H. A hypothesis concerning the dynamic balance of fresh water and salt water in a coastal aquifer. J. Geophys. Res. 1959, 64, 461–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Cheng, R.T. On seawater encroachment in coastal aquifers. Water Resour. Res. 1974, 10, 1039–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicks, C.M.; Herman, J.S. The Effect of Zones of High Porosity and Permeability on the Configuration of the Saline–Freshwater Mixing Zone. Ground Water. 1995, 33, 733–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barlow, P.M.; Reichard, E.G. Saltwater intrusion in coastal regions of North America. Hydrogeol. J. 2010, 18, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Khan, M. Geophysical Investigation of Fresh-Saline Water Interface: A Case Study from South Punjab, Pakistan. Groundwater 2017, 55, 841–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todd, D.K.; Mays, L.W. Groundwater Hydrology, 3rd ed.; Wiley: Hoboken, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Z.; Morton, L.W.U.S. Midwestern Residents Perceptions of Water Quality. Water 2011, 3, 217–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haq, A.U. Drought Mitigation interventions by improved water management: A case study from Punjab –Pakistan. In Proceedings of the 18th International Congress on Irrigation and Drainage, Montreal, Canada, 21–28 July 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Latif, M.; Naghmi, E.H. Development of private tube wells for draught mitigation and their impact on aquifers. In Proceedings of the 3rd National Seminar on Drainage, Peshawar, Pakistan, 7–8 June 2004; Volume I, pp. 46–54. [Google Scholar]
- Post, V.E.A. Fresh and saline groundwater interaction in coastal aquifers: Is our technology ready for the problems ahead. Hydrol. J. 2005, 13, 120–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Jin, W. Geophysical Assessment of Groundwater Potential: A Case Study from MianChannu Area, Pakistan. Groundwater 2017, 56, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Ko, I.; Lee, S.; Hwang, H. Geochemical and geophysical monitoring of saline water intrusion in Korean paddy fields. Environ. Geochem. Health 2002, 24, 277–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bataynch, A.T. Use of electrical resistivity methods for detecting subsurface fresh and saline water and delineating their interfacial configuration: A case study of the eastern Dead Sea coastal aquifers, Jordan. Hydrogeol. J. 2006, 14, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; Ingham, M.; McConchie, J.A. The applicability of earth resistivity methods for saline interface definition. J. Hydrol. 2006, 316, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrow, F.J.; Ingham, M.R.; McConchie, J.A. Monitoring of tidal influences on the saline interface using resistivity traversing and cross-borehole resistivity tomography. J. Hydrol. 2010, 389, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mario, Z.; Joan, B.; Rogelio, L.; Xavier, M.P. Electrical methods (VES and ERT) for identifying, mapping and monitoring different saline domains in a coastal plain region (Alt Emporda, Northern Spain). J. Hydrol. 2011, 409, 407–422. [Google Scholar]
- Akhter, G.; Hasan, M. Determination of aquifer parameters using geoelectrical sounding and pumping test data in Khanewal District, Pakistan. Open Geosci. 2016, 8, 630–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Shang, Y.; Hasan, M.; Jin, W.; Yang, P. Evaluation of a Weathered Rock Aquifer Using ERT Method in South Guangdong, China. Water 2018, 10, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Jin, W. Delineation of weathered/fracture zones for aquifer potential using an integrated geophysical approach: A case study from South China. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 157, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M. Tutorial: 2D and 3D Electrical Imaging Surveys; Universiti Sains Malaysia: Penang, Malaysia, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Soupios, P.M.; Kouli, M.; Vallianatos, F.; Vafidis, A.; Stavroulakis, G. Estimation of aquifer hydraulic parameters from surficial geophysical methods: A case study of Keritis Basin in Chania (Crete–Greece). J. Hydrol. 2007, 338, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamdan, H.A.; Vafidis, A. Joint inversion of 2D resistivity and seismic travel time data to image saltwater intrusion over karstic areas. Environ. Earth Sci. 2013, 68, 1877–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akaolisa, C. Aquifer transmissivity and basement structure determination using resistivity sounding at Jos Plateau state Nigeria. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 114, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Jin, W. Evaluation of Groundwater Suitability for Drinking and Irrigation Purposes in Toba Tek Singh District, Pakistan. Irrig. Drain. Syst. Eng. 2017, 6, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Florescu, D.; Ionete, R.E.; Sandru, C.; Iordache, A.; Culea, M. The influence of pollution monitoring parameters in characterizing the surface water quality from Romania southern area. Roman. J. Phys. 2010, 56, 1001–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA). Hydro Geological Data of Lower Bari Doab; WAPDA: Lahore, Pakistan, 1980; V 01.1. [Google Scholar]
- Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA). Hydro Geological Data of Lower Bari Doab; WAPDA: Lahore, Pakistan, 1978; V 01. [Google Scholar]
- Water and Power Development Authority (WAPDA). Annual Reports 1988–1989; WAPDA: Lahore, Pakistan, 1989; pp. 21–98. [Google Scholar]
- Store, H.; Storz, W.; Jacobs, F. Electrical resistivity tomography to investigate geological structures of earth’s upper crust. Geophys. Prospect. 2000, 48, 455–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouzana, L.; Benassi, R.; Ben Mammou, A.; Felfoul, M.S. Geophysical and hydrochemical study of the seawater intrusion in Mediterranean semi arid zones. Case of the Korba coastal aquifer (Cap-Bon, Tunisia). J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2010, 58, 242–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.V. Environmental and Engineering Geophysics; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1997; p. 475. [Google Scholar]
- Kirsch, R. Groundwater Geophysics, a Tool for Hydrogeology, 2nd ed.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2009; p. 493. [Google Scholar]
- Kearey, P.; Brooks, M.; Hill, I. An Introduction to Geophysical Exploration, 3rd ed.; Blackwell Publishing: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003; Chapter 8; pp. 185–189. [Google Scholar]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, L.P.; Sheriff, R. Applied Geophysics, 2nd ed.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1990; p. 790. [Google Scholar]
- Bobachev, A.; Modin, I.; Shevnin, V. Resistivity Sounding Interpretation, Version 3.1.2c; Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 2 December 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Maillet, R. The fundamental equations of electrical prospecting. Geophysics 1947, 12, 529–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batayneh, A.T. The estimation and significance of Dar-Zarrouk parameters in the exploration of quality affecting the Gulf of Aqaba coastal aquifer systems. J. Coast. Conserv. 2013, 17, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.P. Nonlinear estimation of aquifer parameters from surficial resistivity measurements. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2005, 2, 917–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehirim, C.N.; Nwankwo, C.N. Evaluation of aquifer characteristics and groundwater quality using geoelectric method in Choba, Port Harcourt. Arch. Appl. Sci. Res. 2010, 2, 396–403. [Google Scholar]
- Domenico, P.A.; Schwartz, F.W. Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology; Wiley Press: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990; p. 324. [Google Scholar]
- Fetter, C.W. Applied Hydrogeology, 3rd ed.; Prentice-Hall, Inc.: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 1994; p. 600. [Google Scholar]
- Archie, G.E. The Electrical Resistivity Log as an Aid in Determining Some Reservoir Characteristics; Technical Publication 1422, Petroleum Technology; American Institute of Mineral and Metal Engineering: Englewood, CO, USA, 1942; Volume 146, pp. 54–62. [Google Scholar]
- Schön, J.H. Physical Properties of Rocks; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Riedel, M.; Long, P.; Liu, C.S.; Schultheiss, P.; Collett, T. Physical properties of near surface sediments at southern hydrate ridge: Results from ODP leg 204. In Proceedings of the Ocean Drilling Program, Scientific Results; Trehu, A.A., Bohrmann, G., Torres, M.E., Colwell, F.S., Eds.; Texas A & M University: College Station, TX, USA, 2005; Volume 204. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, R.N.; Hazel, C.P. Computer and Graphical Analysis of Variable Discharge Pumping Tests of Wells; Institution of Engineers Australia: Sydney, Australia, 1973; pp. 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Vinegar, H.J.; Waxman, M.H. Induced polarisation of shaly sands. Geophysics 1984, 49, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthington, P.F. The uses and abuses of the Archie equations: 1. The formation factor–porosity relationship. J. Appl. Geophys. 1993, 30, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetter, C.W. Applied Hydrogeology; Merrill Publishing: Columbus, OH, USA, 1988; p. 592. [Google Scholar]
- Dasargues, A. Modeling base flow from an alluvial aquifer using hydraulic-conductivity data obtained from a derived relation with apparent electrical resistivity. Hydrogeol. J. 1997, 5, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- APHA (American Public Health Association). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 21st ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- IpI2Winv.2.1 Users guide. In Computer Software User Guide Catalog; Department of Geophysics, Geological Faculty, Moscow State University: Moscow, Russia, 2001; p. 25.
- Sjödahl, P. Resistivity Investigation and Monitoring for Detection of Internal Erosion and Anomalous Seepage in Embankment Dams; Engineering Geology, Lund University: Lund, Sweden, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Constantinescu, T.; Constantin, S. Genesis and the Evolution of the Big Sinkholes (Obans) of the Karst Zone of Mangalia (Southern Dobruja, Romania). Theoretical and Applied Karstology; Editura Academiei Romane: Bucharest, Romania, 2001; pp. 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization (WHO). Guidelines for Drinking-Water Quality, 3rd ed.; Recommendations Incorporating1ST and 2nd Addenda; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2008; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Ayers, R.S.; Westcot, D.W. Water Quality for Agriculture FAO Irrigation and Drain; Paper No. 29; Food and Agriculture Organization: Rome, Italy, 1985; p. 97. [Google Scholar]
- Hasan, M.; Shang, Y.; Akhter, G.; Jin, W. Evaluation of groundwater potential in Kabirwala area, Pakistan: A case study by using geophysical, geochemical and pump data. Geophys. Prospect. 2018, 66, 1737–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).