Woody Plant Encroachment Impacts on Groundwater Recharge: A Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Groundwater Recharge and Estimation Methods
2.1. Water Balance Method
2.2. Water Table Method
2.3. Isotopes
2.4. Chloride Mass Balance
2.5. Modeling Approach
2.5.1. Soil and Water Assessment Tool (SWAT)
2.5.2. HYDRUS
2.5.3. The Regional Hydro-Ecological Simulation System (RHESSys)
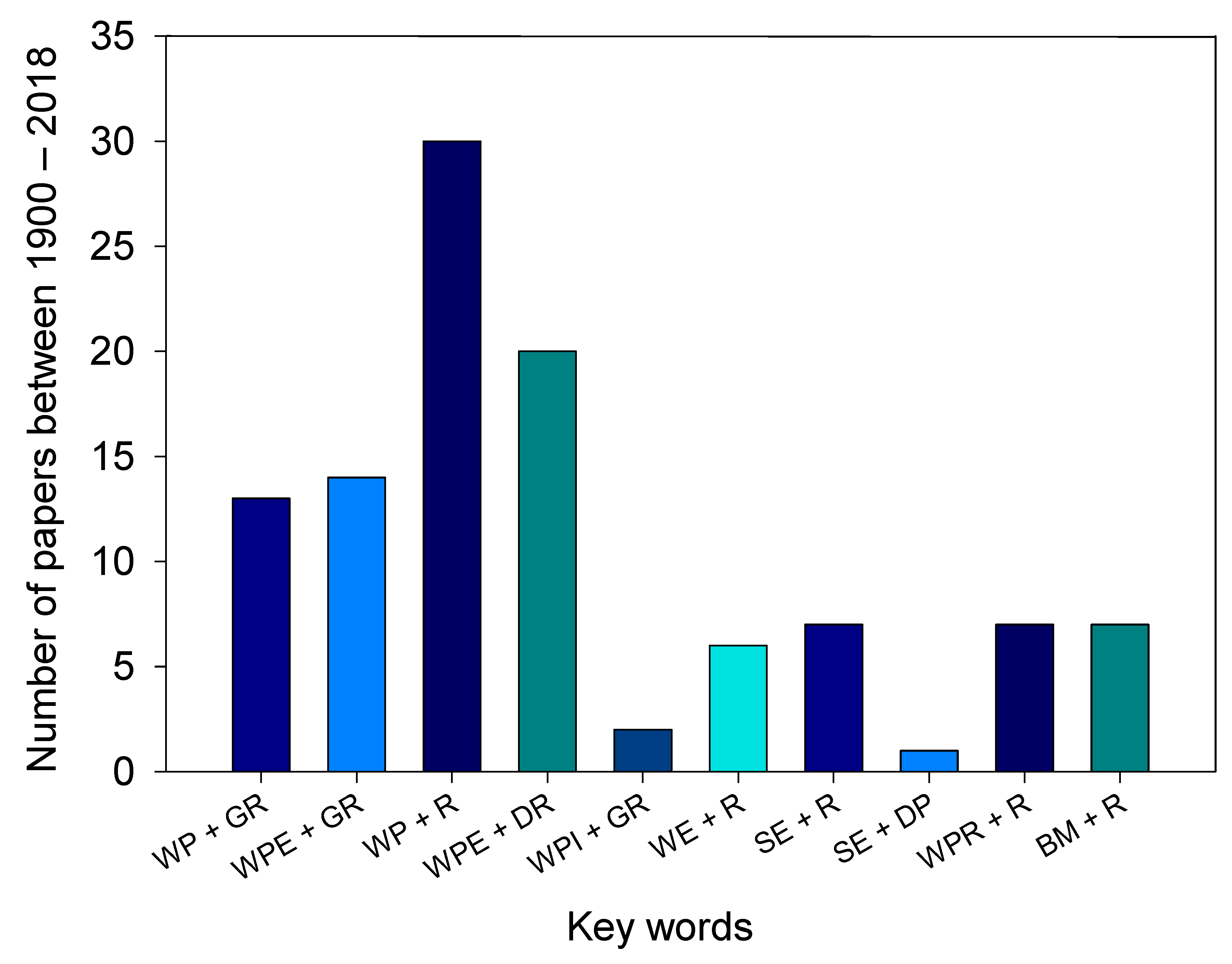
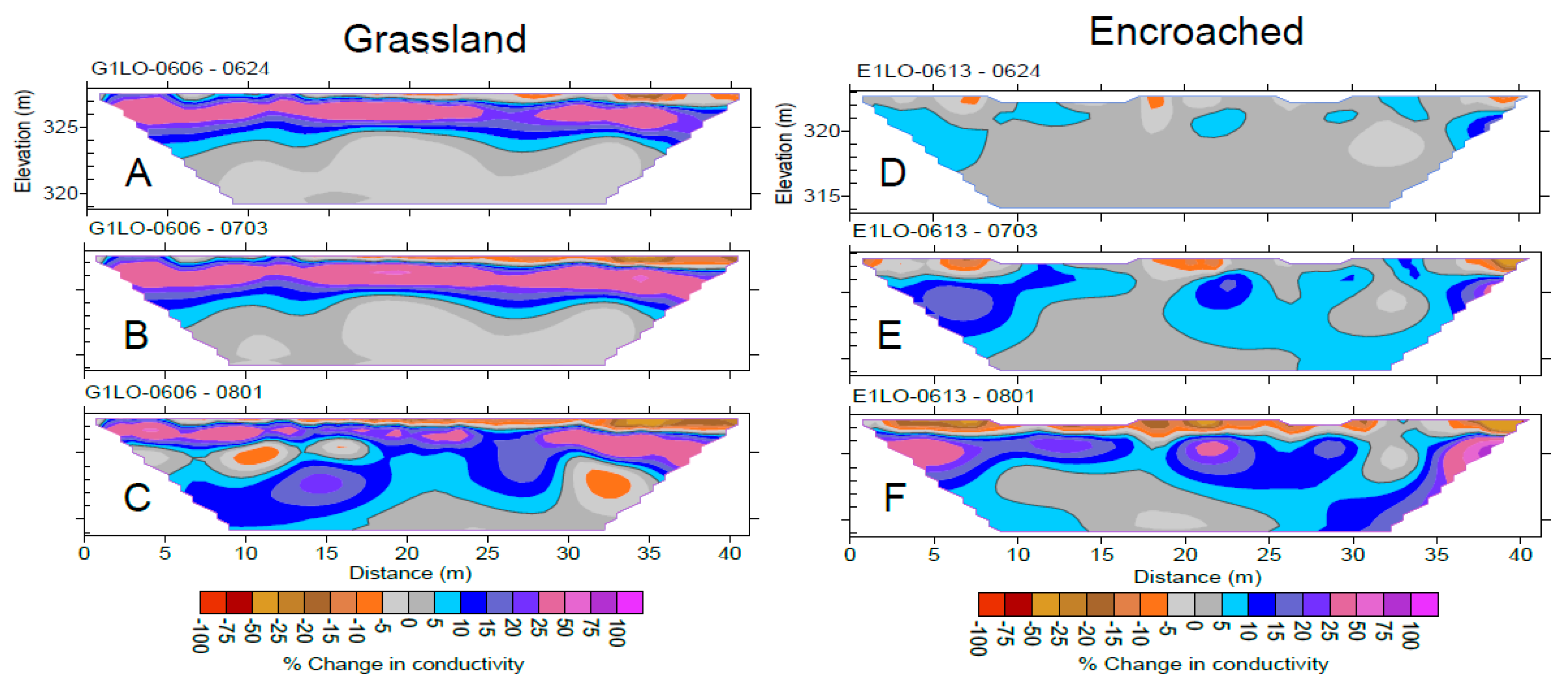
2.6. Geophysical Imaging
3. Mechanisms by Which Woody Plant Encroachment Affects Deep Drainage and Recharge
3.1. Water Use and Evapotranspiration
3.2. Infiltration
3.3. Plant Traits
3.3.1. Canopy and Litter Interception
3.3.2. Soil Water Repellency
4. Recharge as Affected by Geology and Substrate
4.1. Sandstone Bedrock
4.2. Karst Ecosystems
5. Recharge as Affected by Soil Texture and Depth
6. Does Woody Plant Removal Increase Groundwater Recharge?
7. Climate Change, Woody Encroachment, and Groundwater Recharge
8. Summary and the Way Forward in Woody Plant Encroachment Impact on Groundwater Recharge
- It is important to quantify recharge under different woody plant species and environment at spatial and temporal scales.
- Litter interception of rainfall under woody plant encroachment is poorly studied. While litter interception affects deep drainage and groundwater recharge, only a few studies have quantified the interception storage capacity and interception loss.
- Root depth, size, shape, spread, and water uptake have not been extensively researched within the context of woody encroachment. Information on woody root systems is important to predict ecosystem functions (e.g., hydraulic lift, drainage, and water balance) and biosphere-atmosphere interactions [149]. Use of stable isotopes can provide valuable information on rooting depths, plant water uptake, and the hydrologic linkage of transpiration and groundwater and/or surface and groundwater, among others.
- Very few studies have tested the effect of woody plant removal on groundwater recharge. Effects of brush control/woody plant removal vary with site and plant characteristics, and therefore removal should be focused in areas where positive effects are likely. Recently, the “alternative stable state theory” and “pyric herbivory” theories have been discussed to understand the mechanisms of such woody plant encroachment and to inform management solutions [22]. An alternative stable state theory largely predicts ecosystem state transitions in savannas based on resilience and adaptability, whereas pyric herbivore theory emphasizes fire and grazing interactions to manage and restore grassland biomes. The effects of woody plant control on bypass flow, regional scale water quality and quantity, and regional climate also needs to be studied [135].
- Vegetation mapping is envisioned as a proxy for groundwater recharge [10]; yet broader understanding and development of interrelationships between vegetation, hydraulic factors, and recharge continues to be an enigma.
- We reviewed major techniques to estimate recharge based on unsaturated and saturated zone data. While different methods can be used to complement recharge estimates, it is highly important to identify a cost-effective approach.
- Global climate change is likely to alter rainfall and temperature regimes, increase frequency and intensity of extreme events, and shift plant functional types, which could modify interception, infiltration, evapotranspiration, subsurface flow, groundwater recharge, and climatic feedbacks. The effects of climate change are largely uncertain and further research is warranted.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Van Auken, O. Causes and consequences of woody plant encroachment into western north American grasslands. J. Environ. Manag. 2009, 90, 2931–2942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Auken, O.W. Shrub invasions of north American semiarid grasslands. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2000, 31, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayers, D.; Melville, G.; Bean, J.; Beckers, D.; Ellis, M.; Mazzer, T.; Freudenberger, D. Woody Weeds, Biodiversity and Landscape Function in Western New South Wales; WEST 2000: Dubbo, Australia, 2001; ISBN 0731363620. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, J.C. The Delicate and Noxious Scrub: Csiro Studies on Native Tree and Shrubproliferation in the Semi-Arid Woodlands of Eastern Australia; Csiro Publishing: Clayton, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Maestre, F.T.; Bowker, M.A.; Puche, M.D.; Belén Hinojosa, M.; Martínez, I.; García-Palacios, P.; Castillo, A.P.; Soliveres, S.; Luzuriaga, A.L.; Sánchez, A.M.; et al. Shrub encroachment can reverse desertification in semi-arid Mediterranean grasslands. Ecol. Lett. 2009, 12, 930–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Archer, S.; Boutton, T.W.; Hibbard, K.A. Trees in grasslands: Biogeochemical consequences of woody plant expansion. In Global Biogeochemical Cycles in the Climate System; Schulze, M., Heimann, S., Harrison, E., Holland, J., Lloyd, I., Prentice, C., Schimel, D., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; pp. 115–137. [Google Scholar]
- Moleele, N.; Ringrose, S.; Vanderpost, C.; Matheson, W. More woody plants? The status of bush encroachment in botswana’s grazing areas. J. Environ. Manag. 2002, 64, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engle, D.M.; Coppedge, B.R.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. From the dust bowl to the green glacier: Human activity and environmental change in great plains grasslands. In Western North American Juniperus Communities; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008; pp. 253–271. [Google Scholar]
- Huxman, T.E.; Wilcox, B.P.; Breshears, D.D.; Scott, R.L.; Snyder, K.A.; Small, E.E.; Hultine, K.; Pockman, W.T.; Jackson, R.B. Ecohydrological implications of woody plant encroachment. Ecology 2005, 86, 308–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, B.D.; Wilcox, B.P.; Archer, S.R.; Breshears, D.D.; Dahm, C.N.; Duffy, C.J.; McDowell, N.G.; Phillips, F.M.; Scanlon, B.R.; Vivoni, E.R. Ecohydrology of water-limited environments: A scientific vision. Water Resour. Res. 2006, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wainwright, J.; Parsons, A.J.; Abrahams, A.D. Plot-scale studies of vegetation, overland flow and erosion interactions: Case studies from Arizona and New Mexico. Hydrol. Process. 2000, 14, 2921–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guido, A.; Salengue, E.; Dresseno, A. Effect of shrub encroachment on vegetation communities in Brazilian forest-grassland mosaics. Perspect. Ecol. Conserv. 2017, 15, 52–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolo, V.; Moreno, G. Shrub species affect distinctively the functioning of scattered quercus ilex trees in Mediterranean open woodlands. For. Ecol. Manag. 2011, 261, 1750–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lunt, I.D.; Winsemius, L.M.; McDonald, S.P.; Morgan, J.W.; Dehaan, R.L. How widespread is woody plant encroachment in temperate Australia? Changes in woody vegetation cover in lowland woodland and coastal ecosystems in Victoria from 1989 to 2005. J. Biogeogr. 2010, 37, 722–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Li, Z.-C.; Li, X.-Y.; Liu, Y. Influence of shrub encroachment on ct-measured soil macropore characteristics in the inner Mongolia grassland of northern China. Soil Tillage Res. 2015, 150, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venter, Z.; Cramer, M.; Hawkins, H.-J. Drivers of woody plant encroachment over Africa. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wine, M.L.; Zou, C.B. Long-term streamflow relations with riparian gallery forest expansion into tallgrass prairie in the southern great plains, USA. For. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 266, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barger, N.N.; Archer, S.R.; Campbell, J.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Morton, J.A.; Knapp, A.K. Woody plant proliferation in north American drylands: A synthesis of impacts on ecosystem carbon balance. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2011, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, N.; Lehmann, C.E.; Murphy, B.P.; Durigan, G. Savanna woody encroachment is widespread across three continents. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2017, 23, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knapp, A.K.; Briggs, J.M.; Collins, S.L.; Archer, S.R.; Bret-Harte, M.S.; Ewers, B.E.; Peters, D.P.; Young, D.R.; Shaver, G.R.; Pendall, E. Shrub encroachment in north American grasslands: Shifts in growth form dominance rapidly alters control of ecosystem carbon inputs. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2008, 14, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacala, S.W.; Hurtt, G.C.; Baker, D.; Peylin, P.; Houghton, R.A.; Birdsey, R.A.; Heath, L.; Sundquist, E.T.; Stallard, R.; Ciais, P. Consistent land-and atmosphere-based us carbon sink estimates. Science 2001, 292, 2316–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Birt, A.; Fuhlendorf, S.D.; Archer, S.R. Emerging frameworks for understanding and mitigating woody plant encroachment in grassy biomes. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2018, 32, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.B.; Archer, S.R. Scale-dependent influence of topography-based hydrologic features on patterns of woody plant encroachment in savanna landscapes. Lands. Ecol. 2005, 20, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S.; Schimel, D.S.; Holland, E.A. Mechanisms of shrubland expansion: Land use, climate or CO2? Clim. Chang. 1995, 29, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.M.; Hoch, G.A.; Johnson, L.C. Assessing the rate, mechanisms, and consequences of the conversion of tallgrass prairie to Juniperus virginiana forest. Ecosystems 2002, 5, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Briggs, J.M.; Knapp, A.K.; Brock, B.L. Expansion of woody plants in tallgrass prairie: A fifteen-year study of fire and fire-grazing interactions. Am. Midl. Nat. 2002, 147, 287–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archer, S.R.; Andersen, E.M.; Predick, K.I.; Schwinning, S.; Steidl, R.J.; Woods, S.R. Woody plant encroachment: Causes and consequences. In Rangeland Systems; Briske, D.D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 25–84. [Google Scholar]
- Ramírez, J.A.; Díaz, M. The role of temporal shrub encroachment for the maintenance of Spanish holm oak quercus ilex dehesas. For. Ecol. Manag. 2008, 255, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, J.N.; Morgan, J.W. Multi-decadal increases in shrub abundance in non-riverine red gum (eucalyptus camaldulensis) woodlands occur during a period of complex land-use history. Aust. J. Bot. 2009, 57, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Halihan, T.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.E. Vegetation controls on the spatio-temporal heterogeneity of deep moisture in the unsaturated zone: A hydrogeophysical evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, B.S.; Hao, Y.; Ochsner, T.E.; Zou, C.B. Woody plant encroachment alters soil hydrological properties and reduces downward flux of water in tallgrass prairie. Plant Soil 2017, 414, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, B.S.; Stebler, E.; Zou, C.B. Monitoring litter interception of rainfall using leaf wetness sensor under controlled and field conditions. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, N.G. Facts about Global Groundwater Usage; National Groundwater Association: Westerville, OH, USA, 2016; p. 2. [Google Scholar]
- Siebert, S.; Burke, J.; Faures, J.-M.; Frenken, K.; Hoogeveen, J.; Döll, P.; Portmann, F.T. Groundwater use for irrigation–a global inventory. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2010, 14, 1863–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gleeson, T.; Befus, K.M.; Jasechko, S.; Luijendijk, E.; Cardenas, M.B. The global volume and distribution of modern groundwater. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, J.A.; Ramankutty, N.; Brauman, K.A.; Cassidy, E.S.; Gerber, J.S.; Johnston, M.; Mueller, N.D.; O’Connell, C.; Ray, D.K.; West, P.C.; et al. Solutions for a cultivated planet. Nature 2011, 478, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wada, Y.; van Beek, L.P.; van Kempen, C.M.; Reckman, J.W.; Vasak, S.; Bierkens, M.F. Global depletion of groundwater resources. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konikow, L.F.; Kendy, E. Groundwater depletion: A global problem. Hydrogeol. J. 2005, 13, 317–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Healy, R.W.; Cook, P.G. Choosing appropriate techniques for quantifying groundwater recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sophocleous, M. Groundwater recharge. In Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS); Silveira, L.S.W., Ed.; Unesco Eolss: Oxford, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Villegas, J.C.; Dominguez, F.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Adams, H.D.; Guardiola-Claramonte, M.; Sommer, E.D.; Selvey, A.W.; Espeleta, J.F.; Zou, C.B.; Breshears, D.D.; et al. Sensitivity of regional evapotranspiration partitioning to variation in woody plant cover: Insights from experimental dryland tree mosaics. Glob. Ecol. Biogeogr. 2015, 24, 1040–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zou, C. Impacts of woody plant encroachment on regional climate in the southern great plains of the United States. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 9093–9104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jasechko, S.; Birks, S.J.; Gleeson, T.; Wada, Y.; Fawcett, P.J.; Sharp, Z.D.; McDonnell, J.J.; Welker, J.M. The pronounced seasonality of global groundwater recharge. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 8845–8867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Keese, K.E.; Flint, A.L.; Flint, L.E.; Gaye, C.B.; Edmunds, W.M.; Simmers, I. Global synthesis of groundwater recharge in semiarid and arid regions. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3335–3370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weltz, M.A.; Blackburn, W.H. Water budget for south Texas rangelands. J. Range Manag. 1995, 48, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Dowhower, S.L.; Teague, W.R.; Thurow, T.L. Long-term water balance in a semiarid shrubland. Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2006, 59, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Healy, R.W.; Cook, P.G. Using groundwater levels to estimate recharge. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-K.; Schilling, K. Effects of land cover on water table, soil moisture, evapotranspiration, and groundwater recharge: A field observation and analysis. J. Hydrol. 2006, 319, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.; Wendland, E.; Nearing, M.; Scott, R.; Rosolem, R.; Da Rocha, H. The water balance components of undisturbed tropical woodlands in the Brazilian Cerrado. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 19, 2899–2910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, P.T.S.; Leite, M.B.; Mattos, T.; Nearing, M.A.; Scott, R.L.; de Oliveira Xavier, R.; da Silva Matos, D.M.; Wendland, E. Groundwater recharge decrease with increased vegetation density in the Brazilian Cerrado. Ecohydrology 2017, 10, e1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Groundwater use and salinization with grassland afforestation. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2004, 10, 1299–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Le Maitre, D.; Jobbagy, E.; Wang, L.; Breshears, D.D. Ecohydrology: Processes and implications for rangelands. In Rangeland Systems; Briske, D.D., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 85–129. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, G.R.; Zhang, L.; Ellis, T.W.; Hatton, T.J.; Petheram, C. Estimating impacts of changed land use on recharge: Review of modelling and other approaches appropriate for management of dryland salinity. Hydrogeol. J. 2002, 10, 68–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scanlon, B.R.; Reedy, R.C.; Stonestrom, D.A.; Prudic, D.E.; Dennehy, K.F. Impact of land use and land cover change on groundwater recharge and quality in the southwestern US. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2005, 11, 1577–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudley, B.D.; Marttila, H.; Graham, S.L.; Evison, R.; Srinivasan, M. Water sources for woody shrubs on hillslopes: An investigation using isotopic and Sapflow methods. Ecohydrology 2018, 11, e1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossatto, D.; Silva, L.; Sternberg, L.; Franco, A. Do woody and herbaceous species compete for soil water across topographic gradients? Evidence for niche partitioning in a Neotropical Savanna. South Afr. J. Bot. 2014, 91, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeta, A.; Peñuelas, J. Relative contribution of groundwater to plant transpiration estimated with stable isotopes. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 10580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evaristo, J.; McDonnell, J.J. Prevalence and magnitude of groundwater use by vegetation: A global stable isotope meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonnell, J.J. The two water worlds hypothesis: Ecohydrological separation of water between streams and trees? Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Water 2014, 1, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glover, E.; Akiti, T.; Osae, S. Environmental stable isotope studies of groundwater in the Accra plains. Elixir Pollut. 2013, 55, 12813–12819. [Google Scholar]
- Midwood, A.; Boutton, T.; Archer, S.R.; Watts, S.E. Water use by woody plants on contrasting soils in a savanna parkland: Assessment with δ2h and δ18o. Plant Soil 1998, 205, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allison, G.; Gee, G.; Tyler, S. Vadose-zone techniques for estimating groundwater recharge in arid and semiarid regions. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1994, 58, 6–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaye, C.; Edmunds, W. Groundwater recharge estimation using chloride, stable isotopes and tritium profiles in the sands of northwestern Senegal. Environ. Geol. 1996, 27, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibanda, T.; Nonner, J.C.; Uhlenbrook, S. Comparison of groundwater recharge estimation methods for the semi-arid Nyamandhlovu area, Zimbabwe. Hydrogeol. J. 2009, 17, 1427–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gee, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tyler, S.; Albright, W.; Singleton, M. Chloride-Mass-Balance for Predicting Increased Recharge after Land-Use Change; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.H.; Jackson, R.B. A global analysis of groundwater recharge for vegetation, climate, and soils. Vadose Zone J. 2012, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wine, M.L.; Hendrickx, J.M.; Cadol, D.; Zou, C.B.; Ochsner, T.E. Deep drainage sensitivity to climate, edaphic factors, and woody encroachment, Oklahoma, USA. Hydrol. Process. 2015, 29, 3779–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Barre, D.A.; Owens, M.K. Does shrub removal increase groundwater recharge in southwestern Texas semiarid rangelands? Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2012, 65, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyner, J.; Brown, G.; Vogel, J.; Garbrecht, J. Chloride mass balance to determine water fluxes beneath kcl-fertilized crops. Trans. ASAE 2000, 43, 1553–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E. Calibration of swat model for woody plant encroachment using paired experimental watershed data. J. Hydrol. 2015, 523, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Qiao, L.; Wilcox, B.P. Woodland expansion in central Oklahoma will significantly reduce streamflows—A modelling analysis. Ecohydrology 2016, 9, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, J.G.; Srinivasan, R.; Muttiah, R.S.; Williams, J.R. Large area hydrologic modeling and assessment part i: Model development 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 1998, 34, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.W.; Reyes, M.R.; Green, C.H.; Arnold, J.G. The soil and water assessment tool: Historical development, applications, and future research directions. Trans. ASAE 2007, 50, 1211–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shope, C.; Maharjan, G.; Tenhunen, J.; Seo, B.; Kim, K.; Riley, J.; Arnhold, S.; Koellner, T.; Ok, Y.; Peiffer, S. An interdisciplinary swat ecohydrological model to define catchment-scale hydrologic partitioning. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 10, 7235–7290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L.; Shuttleworth, W.J.; Keefer, T.O.; Warrick, A.W. Modeling multiyear observations of soil moisture recharge in the semiarid American southwest. Water Resour. Res. 2000, 36, 2233–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simunek, J.; Van Genuchten, M.T.; Sejna, M. The Hydrus-1d Software Package for Simulating the One-Dimensional Movement of Water, Heat, and Multiple Solutes in Variably-Saturated Media; Agricultural Research Service, United States Department of Agriculture: Riverside, CA, USA, 2005; pp. 1–240.
- Feddes, R.; Kowalik, P.; Zaradny, H. Simulation of Field Water Use and Crop Yield; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1978; p. 188. [Google Scholar]
- Van Genuchten, M.T. A Numerical Model for Water and Solute Movement in and Below the Root Zone; United States Department of Agriculture Agricultural Research Service U.S. Salinity Laboratory: Riverside, CA, USA, 1987.
- Christensen, L.; Tague, C.L.; Baron, J.S. Spatial patterns of simulated transpiration response to climate variability in a snow dominated mountain ecosystem. Hydrol. Process. 2008, 22, 3576–3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittman, T.; Band, L.E.; Hwang, T.; Smith, M.L. Distributed hydrologic modeling in the suburban landscape: Assessing parameter transferability from gauged reference catchments 1. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2012, 48, 546–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tague, C.; McMichael, C.; Hope, A.; Choate, J.; Clark, R. Application of the rhessys model to a California semiarid shrubland watershed 1. JAWRA J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2004, 40, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tague, C.; Peng, H. The sensitivity of forest water use to the timing of precipitation and snowmelt recharge in the California sierra: Implications for a warming climate. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosci. 2013, 118, 875–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tague, C.; Band, L. Rhessys: Regional hydro-ecologic simulation system—An object-oriented approach to spatially distributed modeling of carbon, water, and nutrient cycling. Earth Interact. 2004, 8, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierl, B.; Bugmann, H.; Tague, C.L. Water and carbon fluxes of European ecosystems: An evaluation of the ecohydrological model rhessys. Hydrol. Process. 2007, 21, 3328–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tague, C.; Seaby, L.; Hope, A. Modeling the eco-hydrologic response of a Mediterranean type ecosystem to the combined impacts of projected climate change and altered fire frequencies. Clim. Chang. 2009, 93, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawickreme, D.H.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Geophysical subsurface imaging for ecological applications. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1170–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayawickreme, D.H.; Santoni, C.S.; Kim, J.H.; Jobbágy, E.G.; Jackson, R.B. Changes in hydrology and salinity accompanying a century of agricultural conversion in Argentina. Ecol. Appl. 2011, 21, 2367–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niemeyer, R.J.; Heinse, R.; Link, T.E.; Seyfried, M.S.; Klos, P.Z.; Williams, C.J.; Nielson, T. Spatiotemporal soil and saprolite moisture dynamics across a semi-arid woody plant gradient. J. Hydrol. 2017, 544, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halihan, T.; Fenstemaker, T. Proprietary Electrical Resistivity Imaging Method; Oklahoma State University Office of Intellectual Property: Stillwater, OK, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Halihan, T.; Paxton, S.; Graham, I.; Fenstemaker, T.; Riley, M. Post-remediation evaluation of a Lnapl site using electrical resistivity imaging. J. Environ. Monit. 2005, 7, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Van Dam, R.L.; Jayawickreme, D.H. Soil moisture variability in a temperate deciduous forest: Insights from electrical resistivity and throughfall data. Environ. Earth Sci. 2014, 72, 1367–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samouëlian, A.; Cousin, I.; Tabbagh, A.; Bruand, A.; Richard, G. Electrical resistivity survey in soil science: A review. Soil Tillage Res. 2005, 83, 173–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayawickreme, D.H.; Van Dam, R.L.; Hyndman, D.W. Hydrological consequences of land-cover change: Quantifying the influence of plants on soil moisture with time-lapse electrical resistivity. Geophysics 2010, 75, WA43–WA50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.; Chambers, J.; Rucker, D.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mares, R.; Barnard, H.R.; Mao, D.; Revil, A.; Singha, K. Examining diel patterns of soil and xylem moisture using electrical resistivity imaging. J. Hydrol. 2016, 536, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa, C.G.; Caruso, P.; Ray, G.; Deboodt, T.; Jarvis, W.T.; Guldan, S.J. Ecohydrologic connections in semiarid watershed systems of central oregon USA. Water 2018, 10, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikiti, S.; Schachtschneider, K.; Naiken, V.; Gush, M.; Moses, G.; Le Maitre, D.C. Water relations and the effects of clearing invasive prosopis trees on groundwater in an arid environment in the northern cape, south africa. J. Arid Environ. 2013, 90, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikiti, S.; Ntshidi, Z.; Le Maitre, D.C.; Bugan, R.D.; Mazvimavi, D.; Schachtschneider, K.; Jovanovic, N.Z.; Pienaar, H.H. Assessing water use by prosopis invasions and vachellia karroo trees: Implications for groundwater recovery following alien plant removal in an arid catchment in south africa. For. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 398, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardella Dammeyer, H.; Schwinning, S.; Schwartz, B.F.; Moore, G.W. Effects of juniper removal and rainfall variation on tree transpiration in a semi-arid karst: Evidence of complex water storage dynamics. Hydrol. Process. 2016, 30, 4568–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazan, R.A.; Wilcox, B.P.; Munster, C.; Gary, M. Removing woody vegetation has little effect on conduit flow recharge. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 435–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilstedt, U.; Tobella, A.B.; Bazié, H.; Bayala, J.; Verbeeten, E.; Nyberg, G.; Sanou, J.; Benegas, L.; Murdiyarso, D.; Laudon, H.; et al. Intermediate tree cover can maximize groundwater recharge in the seasonally dry tropics. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; He, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Yun, J.; Wei, S.; Yue, X. The response of soil water and deep percolation under caragana microphylla to rainfall in the horqin sand land, northern china. Catena 2016, 139, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P. Shrub control and streamflow on rangelands: A process based viewpoint. J. Range Manag. 2002, 55, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, C.B.; Turton, D.J.; Will, R.E.; Engle, D.M.; Fuhlendorf, S.D. Alteration of hydrological processes and streamflow with juniper (juniperus virginiana) encroachment in a mesic grassland catchment. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 6173–6182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, G.W.; Heilman, J.L. Proposed principles governing how vegetation changes affect transpiration. Ecohydrology 2011, 4, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Zou, C.B.; Wilcox, B.; Stebler, E. Effect of vegetation on the energy balance and evapotranspiration in tallgrass prairie: A paired study using the eddy-covariance method. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2018, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Hao, Y.; Stebler, E.; Tanaka, N.; Zou, C.B. Impact of plant functional types on coherence between precipitation and soil moisture: A wavelet analysis. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2017, 44, 12197–12207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.L.; Huxman, T.E.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Darrel Jenerette, G.; Young, J.M.; Hamerlynck, E.P. When vegetation change alters ecosystem water availability. Glob. Chang. Biol. 2014, 20, 2198–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, C.B.; Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Stebler, E.; Turton, D. Canopy interception for a tallgrass prairie under juniper encroachment. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, D.; Wiegand, K.; Getzin, S.J.O. Walter’s two-layer hypothesis revisited: Back to the roots! Oecologia 2013, 172, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, L.; Zou, C.B.; Stebler, E.; Will, R.E. Woody plant encroachment reduces annual runoff and shifts runoff mechanisms in the tallgrass prairie, u sa. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 4838–4849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldridge, D.J.; Wang, L.; Ruiz-Colmenero, M. Shrub encroachment alters the spatial patterns of infiltration. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wine, M.L.; Ochsner, T.E.; Sutradhar, A.; Pepin, R. Effects of eastern redcedar encroachment on soil hydraulic properties along oklahoma's grassland-forest ecotone. Hydrol. Process. 2012, 26, 1720–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magliano, P.N.; Fernández, R.J.; Florio, E.L.; Murray, F.; Jobbágy, E.G. Soil physical changes after conversion of woodlands to pastures in dry chaco rangelands (argentina). Rangel. Ecol. Manag. 2017, 70, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Niu, G.Y.; Yang, Z.L. Impacts of vegetation and groundwater dynamics on warm season precipitation over the central united states. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2009, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, T.; El-Hage, R.; Geha, M.; Wedin, D.A.; Huddle, J.A.; Zhou, X.; Msanne, J.; Sudmeyer, R.A.; Martin, D.L.; Brandle, J.R. Intra-annual variability and environmental controls over transpiration in a 58-year-old even-aged stand of invasive woody juniperus virginiana l. In the nebraska sandhills, USA. Ecohydrology 2013, 6, 731–740. [Google Scholar]
- Alaoui, A.; Caduff, U.; Gerke, H.H.; Weingartner, R. Apreferential flow effects on infiltration and runoff in grassland and forest soils. Vadose Zone J. 2011, 10, 367–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caterina, G.L.; Will, R.E.; Turton, D.J.; Wilson, D.S.; Zou, C.B. Water use of juniperus virginiana trees encroached into mesic prairies in oklahoma, USA. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 1124–1134. [Google Scholar]
- Owens, M.K.; Lyons, R.K.; Alejandro, C.L. Rainfall partitioning within semiarid juniper communities: Effects of event size and canopy cover. Hydrol. Process. Int. J. 2006, 20, 3179–3189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starks, P.J.; Venuto, B.C.; Dugas, W.A.; Kiniry, J. Measurements of canopy interception and transpiration of eastern redcedar grown in open environments. Environ. Nat. Resour. Res. 2014, 4, 103. [Google Scholar]
- Thurow, T.; Blackburn, W.; Warren, S.; Taylor, C., Jr. Rainfall interception by midgrass, shortgrass, and live oak mottes. J. Range Manag. 1987, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villegas, J.C.; Breshears, D.D.; Zou, C.B.; Law, D.J. Ecohydrological controls of soil evaporation in deciduous drylands: How the hierarchical effects of litter, patch and vegetation mosaic cover interact with phenology and season. J. Arid Environ. 2010, 74, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doerr, S.; Shakesby, R.; Walsh, R. Soil water repellency, its characteristics, causes and hydro-geomorphical consequences. Earth Syst. Sci. Rev. 2000, 51, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, D.A.; Lebron, I.; Ryel, R.J.; Jones, S.B. Soil water repellency: A method of soil moisture sequestration in pinyon–juniper woodland. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2010, 74, 624–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madsen, M.; Zvirzdin, D.; Petersen, S.; Hopkins, B.; Roundy, B.; Chandler, D. Soil water repellency within a burned piñon–juniper woodland: Spatial distribution, severity, and ecohydrologic implications. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2011, 75, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggemeyer, K.D.; Awada, T.; Harvey, F.E.; Wedin, D.A.; Zhou, X.; Zanner, C.W. Seasonal changes in depth of water uptake for encroaching trees juniperus virginiana and pinus ponderosa and two dominant c4 grasses in a semiarid grassland. Tree Physiol. 2009, 29, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Owens, M.K.; Knight, R.W.; Lyons, R.K. Do woody plants affect streamflow on semiarid karst rangelands? Ecol. Appl. 2005, 15, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwinning, S. The water relations of two evergreen tree species in a karst savanna. Oecologia 2008, 158, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilman, J.L.; Litvak, M.E.; McInnes, K.J.; Kjelgaard, J.F.; Kamps, R.H.; Schwinning, S. Water-storage capacity controls energy partitioning and water use in karst ecosystems on the edwards plateau, texas. Ecohydrology 2014, 7, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, B.P.; Huang, Y. Woody plant encroachment paradox: Rivers rebound as degraded grasslands convert to woodlands. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennett-Smith, A.; Cook, P.; Walker, G. Factors affecting groundwater recharge following clearing in the south western murray basin. J. Hydrol. 1994, 154, 85–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, C.; Burnett, E.; Bovey, R. Hydrologic effects of brush control on texas rangelands. Trans. ASAE 1979, 22, 315–0319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, M.; Schwinning, S.; Walvoord, M.; Pockman, W.; Newman, B.; Jackson, R.; Phillips, F. Ecohydrological control of deep drainage in arid and semiarid regions. Ecology 2005, 86, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Wilcox, B.P.; Stern, L.; Perotto-Baldivieso, H. Springs on rangelands: Runoff dynamics and influence of woody plant cover. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3277–3288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchesini, V.A.; Fernández, R.J.; Reynolds, J.F.; Sobrino, J.A.; Di Bella, C.M. Changes in evapotranspiration and phenology as consequences of shrub removal in dry forests of central argentina. Ecohydrology 2015, 8, 1304–1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzikiti, S.; Gush, M.B.; Le Maitre, D.C.; Maherry, A.; Jovanovic, N.; Ramoelo, A.; Cho, M.A. Quantifying potential water savings from clearing invasive alien eucalyptus camaldulensis using in situ and high resolution remote sensing data in the berg river catchment, western cape, south africa. For. Ecol. Manag. 2016, 361, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, B. From the Mountain to the Tap: How Land Use and Water Management Can Work for THE Rural Poor; DFID Forestry Research Program: Kent, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Saleh, A.; Wu, H.; Brown, C.; Teagarden, F.; McWilliams, S.; Hauck, L.; Millican, J. Effect of brush control on evapotranspiration in the north concho river watershed using the eddy covariance technique. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2009, 64, 336–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfried, M.S.; Wilcox, B.P. Soil water storage and rooting depth: Key factors controlling recharge on rangelands. Hydrol. Process. 2006, 20, 3261–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wyatt, C.J.; O’Donnell, F.C.; Springer, A.E. Semi-arid aquifer responses to forest restoration treatments and climate change. Groundwater 2015, 53, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Global Warming of 1.5 °C. Summary for Policymakers; IPCC: Incheon, Korea, 2018; p. 34. Available online: http://report.ipcc.ch/sr15/pdf/sr15_spm_final.pdf (accessed on 12 October 2018).
- Wang, L.; d’Odorico, P.; Evans, J.; Eldridge, D.; McCabe, M.; Caylor, K.; King, E. Dryland ecohydrology and climate change: Critical issues and technical advances. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2585–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breshears, D.D.; Myers, O.B.; Meyer, C.W.; Barnes, F.J.; Zou, C.B.; Allen, C.D.; McDowell, N.G.; Pockman, W.T. Tree die-off in response to global change-type drought: Mortality insights from a decade of plant water potential measurements. Front. Ecol. Environ. 2009, 7, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savi, T.; Bertuzzi, S.; Branca, S.; Tretiach, M.; Nardini, A. Drought-induced xylem cavitation and hydraulic deterioration: Risk factors for urban trees under climate change? New Phytol. 2015, 205, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.D.; Guardiola-Claramonte, M.; Barron-Gafford, G.A.; Villegas, J.C.; Breshears, D.D.; Zou, C.B.; Troch, P.A.; Huxman, T.E. Temperature sensitivity of drought-induced tree mortality portends increased regional die-off under global-change-type drought. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 7063–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bond, W.J. What limits trees in c4 grasslands and savannas? Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 2008, 39, 641–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tietjen, B.; Jeltsch, F.; Zehe, E.; Classen, N.; Groengroeft, A.; Schiffers, K.; Oldeland, J. Effects of climate change on the coupled dynamics of water and vegetation in drylands. Ecohydrology 2010, 3, 226–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, J.; Zou, C.B.; Andrews, W.J.; Long, J.M.; Liang, Y.; Qiao, L. Climate, water use, and land surface transformation in an irrigation intensive watershed—streamflow responses from 1950 through 2010. Agric. Water Manag. 2015, 160, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, R.B.; Sperry, J.S.; Dawson, T.E. Root water uptake and transport: Using physiological processes in global predictions. Trends Plant Sci. 2000, 5, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Country | Population 2010 | Groundwater Use 2010 | GW—Irrigation | GW— Domestic Use | GW—Industry |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (thousands) | (km3 year−1) | (%) | (%) | (%) | |
| India | 1,224,614 | 251.0 | 89 | 9 | 2 |
| China | 1,341,335 | 112.0 | 54 | 20 | 26 |
| U.S. | 310,384 | 111.7 | 71 | 23 | 6 |
| Pakistan | 173,593 | 64.8 | 94 | 6 | 0 |
| Iran | 73,974 | 63.4 | 87 | 11 | 2 |
| Bangladesh | 148,692 | 30.2 | 86 | 13 | 1 |
| Mexico | 113,423 | 29.5 | 72 | 22 | 6 |
| Saudi Arabia | 27,448 | 24.2 | 92 | 5 | 3 |
| Indonesia | 239,871 | 14.9 | 2 | 93 | 5 |
| Turkey | 72,752 | 13.2 | 60 | 32 | 8 |
| Study Type | Methods | References |
|---|---|---|
| Experimental/ field | Water balance | Weltz and Blackburn [45]; Wilcox et al. [46]; Huxman et al. [9]; Oliveira et al. [49] |
| Water table | Acharya et al. [30]; Oliveira et al. [49]; Zhang et al. [48]; Oliveira et al. [50]; Ochoa et al. [96]; Dzikiti et al. [97]; Dzikiti et al. [98] | |
| CMB | Acharya et al. [31]; Wine et al. [67]; Moore et al. [68] | |
| Electrical Imaging | Acharya et al. [30]; Niemeyer et al. [88]; Jayawickreme et al. [93] | |
| Isotopes | Dudley et al. [55]; Rossatto et al. [56]; Cardella Dammeyer et al. [99]; Dzikiti et al. [98] | |
| Chambers/collectors/ Lysimeters | Bazan et al. [100]; Ilstedt et al. [101]; Liu et al. [102] | |
| Modeling | SWAT | Qiao et al. [70]; Zou et al. [71] |
| HYDRUS | Acharya et al. [31]; Wine et al. [67] | |
| RHESSys | Christensen et al. [79]; Mittman et al. [80]; Tague et al. [81] |
| Continent | Region | Climate | Precipitation (mm/Year) | Soil | Woody Type | Key Findings | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| North America | Oklahoma, USA | Continental | 948 | Stephenville–Darnell complex, Grainola–Lucien complex and Coyle soil series | Eastern redcedar | -Vegetation caused differences in bulk electrical resistivity -Encroachment decreased the water level in the perched groundwater aquifer | Acharya et al. [30] |
| Oklahoma, USA | Continental | 932 | Stephenville–Darnell complex, Grainola–Lucien complex and Coyle soil series | Eastern redcedar | -Annual drainage rate of 9.0 mm in the tallgrass prairie vs. 0.3 mm in the encroached woodland -Cumulative bottom flux of 27.5 cm under tallgrass prairie vs. 17.1 cm under eastern redcedar for 275 cm deep soil during 2011–2014 -Lower soil moisture under juniper compared to tallgrass at 0.8 m depth | Acharya et al. [31] | |
| Oklahoma, USA | Continental | 875 | Stephenville–Darnell complex, Grainola–Lucien complex and Coyle soil series | Eastern redcedar | -Woody plants attenuate the precipitation pulse in the rooting zone-High frequency periodicities in soil moisture reduce after encroachment -Coherence between precipitation and soil moisture for deeper soil occur at low frequency | Liu et al. [107] | |
| Oklahoma, USA | Temperate subhumid | Site1: 894 Site 2: 601 | Site1: Zaneis–Huska complex and Renfrow loam Site 2: Quinlan loam and Woodward loam | Eastern redcedar | -Deep drainage largely affected by climate and rooting depth -Deep drainage decreased by 12 mm/year as rooting depth increased from 90 to 200 cm | Wine et al. [67] | |
| Oklahoma, USA | Temperate subhumid | 900 | Stephenville–Darnell complex, Grainola–Lucien complex and Coyle soil series | Eastern redcedar | -Reduced soil water content, soil water storage, and runoff were observed from encroached watershed | Zou et al. [104] | |
| Arizona, USA | 313–386 | Gravelly sandy loam | Mesquite | -Higher average annual groundwater use by woodland compared to grassland (641 vs. 398 mm/year) | Scott et al. [108] | ||
| Idaho, USA | Semi-arid | 554 | Fine-textured soil with the average clay content of 35% for the top 10 cm | Western juniper | -Juniper can extract water from up to 12 m deep below the surface in the saprolite; suggesting higher potential to transpire subsurface moisture from deep layers -Hydrophobicity below juniper canopies | Niemeyer et al. [88] | |
| Texas, USA | Semi-arid to subhumid | 836 | Shallow rocky soil | Ashe juniper | -Tree transpiration during May 2009 to December 2011 was 5 to 10 times higher in the woodland compared with woodland removal -Understory growth was increasingly compensating for the loss of juniper transpiration -Shallow-rooted trees when removed and replaced by herbaceous vegetation and low shrubs has little effect on deep recharge | Cardella Dammeyer et al. [99] | |
| Oregon, USA | Semi-arid | 358 | Westbutte very stony loam, Madeline Loam, and Simas gravelly silt loam | Western juniper | -Juniper woodlands intercepted up to 46% of total precipitation -Canopy interception effects were higher on deep soil moisture in the downstream -Juniper removal increased spring flows by 5 times -Strong hydrologic connectivity between uplands and downstream valleys during winter precipitation and snowmelt runoff seasons | Ochoa et al. [96] | |
| Texas, US | Semiarid-subhumid | 400–850 | Rocky soil with highly organic A horizon | Ashe juniper | -Woody plant removal had little effect on groundwater recharge | Bazan et al. [100] | |
| Texas, US | Semi-arid | 526 | Antosa (Arenic Paleustalfs) and Bobillo (Grossarenic Paleustalfs) series | Honey mesquite | -Removal of woody plant could increase recharge | Moore et al. [68] | |
| South America | São Paulo, Brazil | Humid sub-tropical | 1506 | Ortic Quartzarenic Neosol with sandy texture | Cerrado | -No evidence of net groundwater table changes | Oliveira et al. [49] |
| São Paulo, Brazil | Humid sub-tropical | 1500 | Ortic Quartzarenic Neosol with sandy texture | Cerrado | -Increased density of woody plants tends to reduce groundwater recharge -Average annual recharge were 363 mm, 354 mm, 324 mm, and 315 mm for Cerrado grassland, shrub Cerrado, open wooded Cerrado, and wooded Cerrado, respectively | Oliveira et al. [50] | |
| San Luis, Argentina | 400 | Alluvial and calcareous soils | Mesquite and Quebracho | -Woody plant removal over large area of dry forests could shorten growing season by up to 3 months and reduce ET by as much as 30% | Marchesini et al. [135] | ||
| Africa | South Africa | Arid | 75–200 | Apedal with a coarse sandy texture | Mesquite | -Water table was consistently lower under mesquite invasion compared with grassland site -Groundwater savings of up to 70 m3/month in spring for each hectare of woody plant removal | Dzikiti et al. [97] |
| South Africa | Mediterranean | 450–500 | Shallow sandy soils | Red River Gum | -Eucalyptus invaded site had consistently higher rates of water use compared to cleared site during December 2013 to November 2014 with large differences during summer -Water savings of up to 2 ML per year with each ha of woody plant removal | Dzikiti et al. [136] | |
| South Africa | Arid | 150 | Dark red clayey loam dolerite vertisols | Mesquite | -Clearing woody plants slowed the rate of water table decline from a pre-clearing peak of −8.9 to 5.0 mm d−1 -Mesquite used approx. 64% groundwater in spring and 80% in mid-summer -Mesquite negatively affected groundwater | Dzikiti et al. [98] | |
| Asia | Inner Mongolia, China | Semi-arid | 351 | Sand dunes | Littleleaf peashrub | -Shrub cover and canopy size were negatively related to coefficient of deep percolation -Deep percolation declined with increasing age of Caragana microphylla | Liu et al. [102] |
| Inner Mongolia, China | Semi-arid | 407 | Calcic–orthic Aridisol | Littleleaf peashrub | -1.4 to 3.4 times higher macroporosity under shrub than interspace grass -Macroporosity decreased with increase in shrub encroachment | Hu et al. [15] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Acharya, B.S.; Kharel, G.; Zou, C.B.; Wilcox, B.P.; Halihan, T. Woody Plant Encroachment Impacts on Groundwater Recharge: A Review. Water 2018, 10, 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101466
Acharya BS, Kharel G, Zou CB, Wilcox BP, Halihan T. Woody Plant Encroachment Impacts on Groundwater Recharge: A Review. Water. 2018; 10(10):1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101466
Chicago/Turabian StyleAcharya, Bharat Sharma, Gehendra Kharel, Chris B. Zou, Bradford P. Wilcox, and Todd Halihan. 2018. "Woody Plant Encroachment Impacts on Groundwater Recharge: A Review" Water 10, no. 10: 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101466
APA StyleAcharya, B. S., Kharel, G., Zou, C. B., Wilcox, B. P., & Halihan, T. (2018). Woody Plant Encroachment Impacts on Groundwater Recharge: A Review. Water, 10(10), 1466. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101466








