Spatiotemporal Variation of Snowfall to Precipitation Ratio and Its Implication on Water Resources by a Regional Climate Model over Xinjiang, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
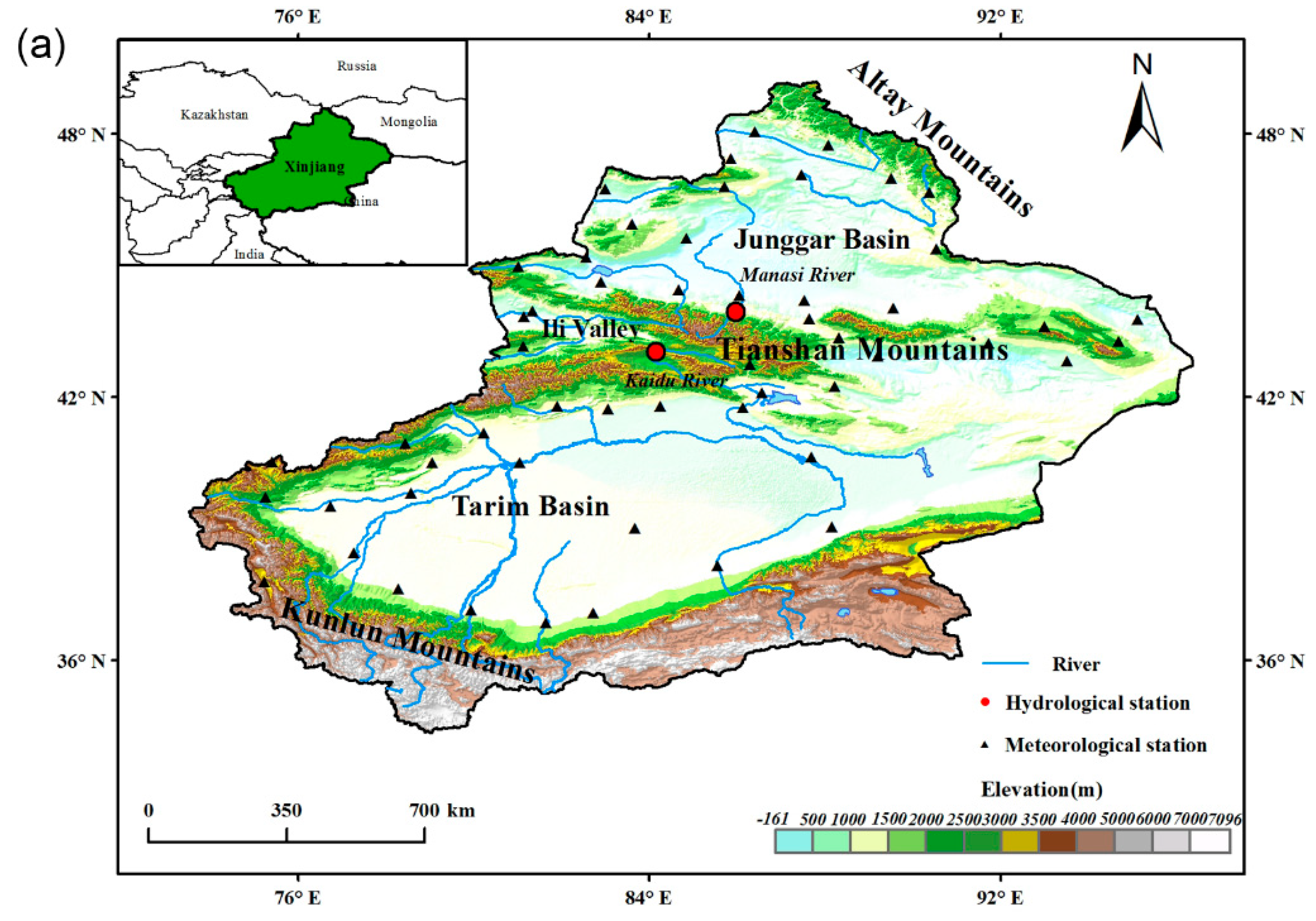
2.1. Study Area
2.2. WRF Model Set Up
2.3. Meteorological and Streamflow Datasets
2.4. Snowfall Calculation
2.5. Assessment of Performance of the WRF Model
2.6. Trend Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Performance of the WRF Model
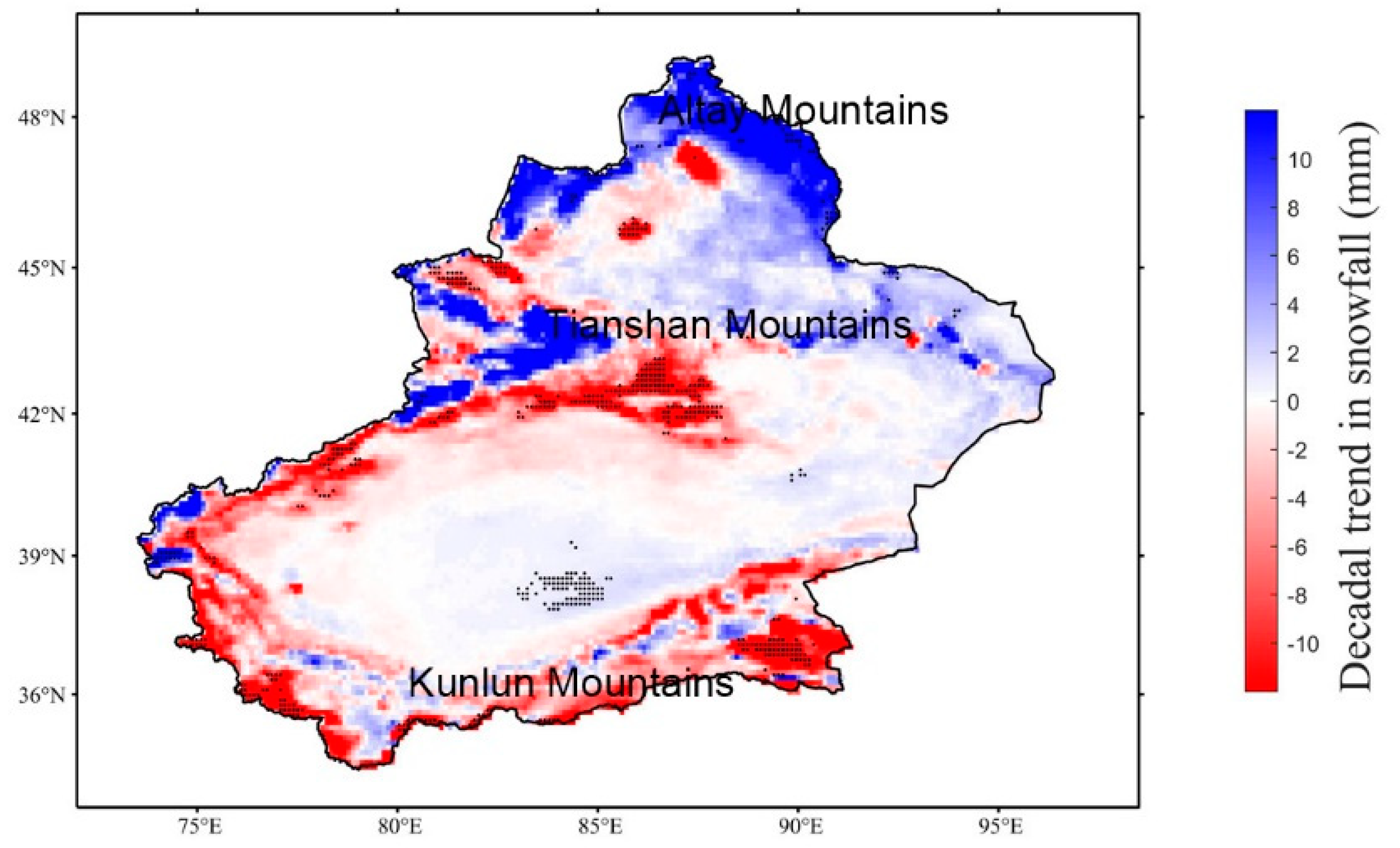
3.2. Climatology and Changes of Snowfall over Xinjiang
3.3. Climatology and Changes of S/P Ratio over Xinjiang
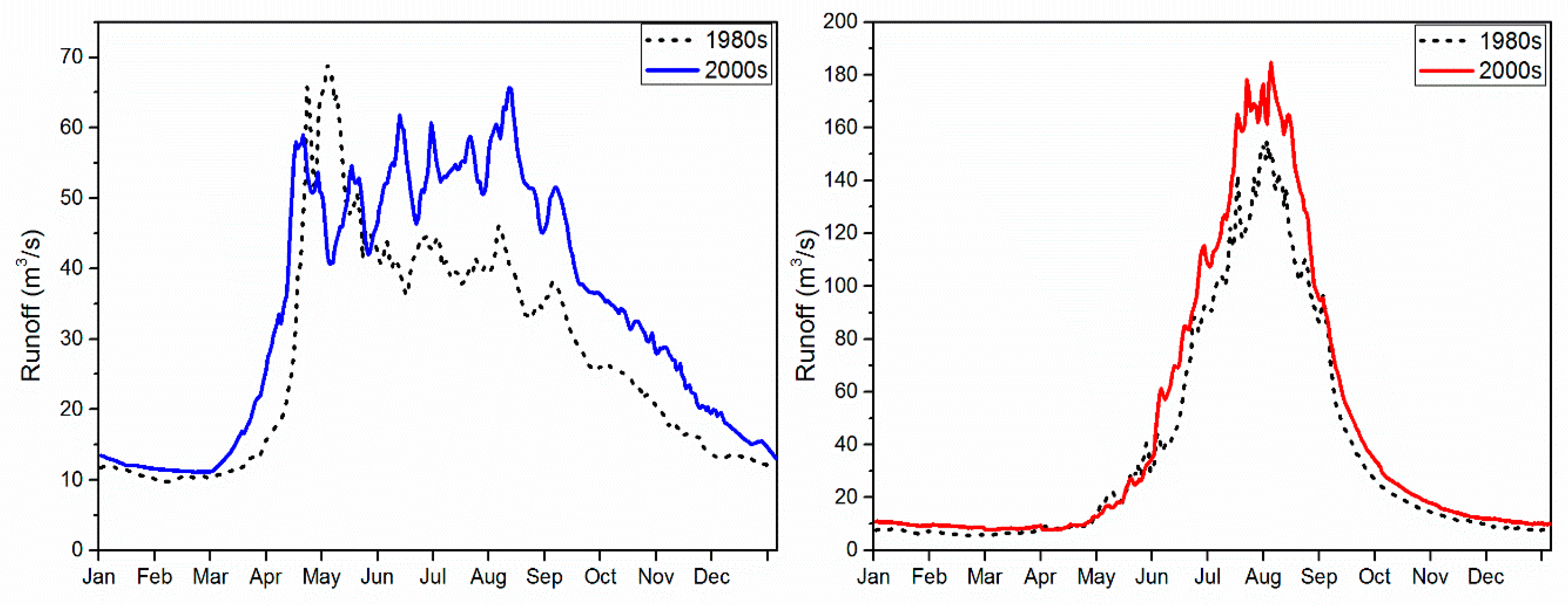
3.4. Changes in Hydrological Processes in the Tianshan Mountains
4. Discussion
4.1. Performance of WRF
4.2. Spatiotemporal Variations of Snowfall and S/P Ratio
4.3. Water Resources Management in Different Regions Based on Current Findings
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Groisman, P.Y.; Karl, T.R.; Knight, R.W.; Stenchikov, G.L. Changes of snow cover, temperature, and radiative heat balance over the Northern Hemisphere. J. Clim. 1994, 7, 1633–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonovic, S.P.; Li, L.H. Sensitivity of the Red River basin flood protection system to climate variability and change. Water Resour. Manag. 2004, 18, 89–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.D.; Mote, P.W. The response of Northern Hemisphere snow cover to a changing climate. J. Clim. 2009, 22, 2124–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, R.D. Northern Hemisphere Snow Cover Variability and Change, 1915–1997. J. Clim. 2000, 13, 2339–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, C.; Brown, R. Spring snow cover extent reductions in the 2008–2012 period exceeding climate model projections. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2012, 39, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mudryk, L.R.; Kushner, P.J.; Derksen, C. Interpreting observed northern hemisphere snow trends with large ensembles of climate simulations. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 43, 345–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCabe, G.J.; Wolock, D.M. Long-term variability in Northern Hemisphere snow cover and associations with warmer winters. Clim. Chang. 2010, 99, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghuijs, W.R.; Woods, R.A.; Hrachowitz, M. A precipitation shift from snow towards rain leads to a decrease in streamflow-supplement. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2014, 4, 583–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatchett, B.J.; Daudert, B.; Garner, C.B.; Oakley, N.S.; Putnam, A.E.; White, A.B. Winter snow level rise in the Northern Sierra Nevada from 2008 to 2017. Water (Switzerland) 2017, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beniston, M.; Stoffel, M. Rain-on-snow events, floods and climate change in the Alps: Events may increase with warming up to 4 °C and decrease thereafter. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 571, 228–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, G.J.; Clark, M.P.; Hay, L.E. Rain-on-Snow Events in The Western United States. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2007, 88, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harpold, A.A.; Kaplan, M.L.; Zion Klos, P.; Link, T.; McNamara, J.P.; Rajagopal, S.; Schumer, R.; Steele, C.M. Rain or snow: Hydrologic processes, observations, prediction, and research needs. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Li, L. Variation of the proportion of precipitation occurring as snow in the Tian Shan Mountains, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 1379–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huntington, T.G.; Hodgkins, G.A.; Keim, B.D.; Dudley, R.W. Changes in the proportion of precipitation occurring as snow in New England (1949–2000). J. Clim. 2004, 17, 2626–2636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knowles, N.; Dettinger, M.D.; Cayan, D.R. Trends in snowfall versus rainfall in the western United States. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 4545–4559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Przybylak, R. Variability of total and solid precipitation in the Canadian Arctic from 1950 to 1995. Int. J. Climatol. 2002, 22, 395–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serquet, G.; Marty, C.; Dulex, J.-P.; Rebetez, M. Seasonal trends and temperature dependence of the snowfall/precipitation-day ratio in Switzerland. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011, 38, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Fang, G.; Chen, Y.; De-Maeyer, P. Climate change in the Tianshan and northern Kunlun Mountains based on GCM simulation ensemble with Bayesian model averaging. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 622–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littell, J.S.; McAfee, S.A.; Hayward, G.D. Alaska snowpack response to climate change: Statewide snowfall equivalent and snowpack water scenarios. Water (Switzerland) 2018, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G. Potential impacts of climate change on vegetation dynamics in Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Jiang, F.; Li, L.; Wang, G. Spatial and temporal variability of precipitation concentration index, concentration degree and concentration period Xinjiang, China. Int. J. Climatol. 2011, 31, 1679–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Bai, L.; Li, L.; Wang, Q. Sensitivity of runoff to climatic variability in the northern and southern slopes of the Middle Tianshan Mountains, China. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fan, Y.; Wang, H.; Deng, H. Progress and prospects of climate change impacts on hydrology in the arid region of northwest China. Environ. Res. 2015, 139, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, M.; Kang, S.; Wu, H.; Yuan, X. Detection of spatio-temporal variability of air temperature and precipitation based on long-term meteorological station observations over Tianshan Mountains, Central Asia. Atmos. Res. 2018, 203, 141–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Li, W.; Deng, H.; Fang, G.; Li, Z. Changes in Central Asia’s Water Tower: Past, Present and Future. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Li, Z.; Fang, G.; Li, W. Large Hydrological Processes Changes in the Transboundary Rivers of Central Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2018, 5059–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groisman, P.Y.; Koknaeva, V.V.; Belokrylova, T.A.; Karl, T.R. Overcoming Biases of Precipitation Measurement: A History of the USSR Experience. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1991, 72, 1725–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.C. Adjustment of global gridded precipitation for systematic bias. J. Geophys. Res. 2003, 108, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, J.C.; Clark, E.A.; Lettenmaier, D.P.; Wood, E.F. Correction of global precipitation products for orographic effects. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 15–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maussion, F.; Scherer, D.; Finkelnburg, R.; Richters, J.; Yang, W.; Yao, T. Sciences WRF simulation of a precipitation event over the Tibetan Plateau, China—An assessment using remote sensing and ground observations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1795–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, D. Evaluation of WRF mesoscale climate simulations over the Tibetan Plateau during 1979–2011. J. Clim. 2015, 28, 2823–2841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Niu, X.; Wang, S.; Gao, H.; Wang, X.; Wu, J. Statistical downscaling and dynamical downscaling of regional climate in China: Present climate evaluations and future climate projections. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2016, 121, 2110–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, J.; Carvalho, L.M.V.; Jones, C.; Cannon, F.; Bookhagen, B.; Palazzi, E.; Tahir, A.A. The spatiotemporal variability of precipitation over the Himalaya: Evaluation of one-year WRF model simulation. Clim. Dyn. 2016, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Choi, J.; Lee, O.; Yoon, J.; Kim, S. Estimation of probable maximum precipitation in Korea using a regional climate model. Water (Switzerland) 2017, 9, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.; Liu, C.; Ikeda, K.; Gochis, D.; Yates, D.; Chen, F.; Tewari, M.; Barlage, M.; Dudhia, J.; Yu, W.; et al. High-resolution coupled climate runoff simulations of seasonal snowfall over Colorado: A process study of current and warmer climate. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 3015–3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Ahmad, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, X.; Feng, X.; Li, L. Simulating low and high streamflow driven by snowmelt in an insufficiently gauged alpine basin. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2016, 30, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Chen, X.; Li, L.; Bao, A.; De, M.J. Incorporating accumulated temperature and algorithm of snow cover calculation into the snowmelt runoff model. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 3595, 3589–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, L.; Guo, L.; Zhang, F.; Adsavakulchai, S.; Shang, M. Impact of climate factors on runoff in the Kaidu River watershed: Path analysis of 50-year data. J. Arid Land 2011, 3, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The Kain–Fritsch Convective Parameterization: An Update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 16663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical Study of Convection Observed during the Winter Monsoon Experiment Using a Mesoscale Two-Dimensional Model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an Advanced Land Surface–Hydrology Model with the Penn State–NCAR MM5 Modeling System. Part I: Model Implementation and Sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Lim, J. The WRF single-moment 6-class microphysics scheme (WSM6). J. Korean Meteorol. Soc. 2006, 42, 129–151. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, P.; Chen, M.; Fukushima, Y.; Yang, S.; Liu, C.; Yatagai, A.; Hayasaka, T. A Gauge-Based Analysis of Daily Precipitation over East Asia. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 607–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Gao, J.; Shen, Y.; Xu, C.; Shi, Y.; Giorgi, F. A Daily Temperature Dataset over China and Its Application in Validating a RCM Simulation. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2009, 26, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Temperature and pressure dependence of the rain-snow phase transition over land and ocean. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennings, K.S.; Winchell, T.S.; Livneh, B.; Molotch, N.P. Spatial variation of the rain-snow temperature threshold across the Northern Hemisphere. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, H.V. Status of automatic calibration for hydrologic models: Comparison with multilevel expert calibration. J. Hydrol. Eng. 1999, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, S.; Pilon, P.; Cavadias, G. Power of the Mann-Kendall and Spearman’s rho tests for detecting monotonic trends in hydrological series. J. Hydrol. 2002, 259, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.H. Trend detection in hydrologic data: The Mann-Kendall trend test under the scaling hypothesis. J. Hydrol. 2008, 349, 350–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, R.; Baker, B.; Kochendorfer, J.; Meyers, T.; Landolt, S.; Fischer, A.P.; Black, J.; Thériault, J.M.; Kucera, P.; Gochis, D.; et al. How well are we measuring snow: The NOAA/FAA/NCAR winter precipitation test bed. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2012, 93, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossi, G.; Lendvai, A.; Peretti, G.; Ranzi, R. Snow precipitation measured by gauges: Systematic error estimation and data series correction in the central Italian Alps. Water (Switzerland) 2017, 9, 461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, E.; Sun, J.; Chen, H.; Xiang, W. Evaluation of a high-resolution historical simulation over China: Climatology and extremes. Clim. Dyn. 2015, 45, 2013–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, H.; Fan, K. Dynamic downscaling of summer precipitation prediction over China in 1998 using WRF and CCSM4. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2015, 32, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marteau, R.; Richard, Y.; Pohl, B.; Smith, C.C.; Castel, T. High-resolution rainfall variability simulated by the WRF RCM: Application to eastern France. Clim. Dyn. 2014, 44, 1093–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnett, T.P.; Adam, J.C.; Lettenmaier, D.P. Potential impacts of a warming climate on water availability in snow-dominated regions. Nature 2005, 438, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duethmann, D.; Bolch, T.; Farinotti, D.; Kriegel, D.; Vorogushyn, S.; Merz, B.; Pieczonka, T.; Jiang, T.; Su, B.; Güntner, A. Attribution of streamflow trends in snow-and glacier melt dominated catchments of the Tarim River, Central Asia. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 4727–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, W. Characteristics in streamflow and extremes in the Tarim River, China: Trends, distribution and climate linkage. Int. J. Climatol. 2015, 35, 761–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duethmann, D.; Menz, C.; Jiang, T.; Vorogushyn, S. Projections for headwater catchments of the Tarim River reveal glacier retreat and decreasing surface water availability but uncertainties are large. Environ. Res. Lett. 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Temperature Bias (°C month−1) | RMSE (°C month−1) | Precipitation Bias (mm month−1) | RMSE (mm month−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 0.33 | 2.44 | 7.54 | 15.56 |
| MAM | −2.02 | 3.51 | 11.12 | 16.85 |
| SON | 0.81 | 2.51 | 5.65 | 13.01 |
| DJF | 1.16 | 4.00 | 11.45 | 17.22 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Qi, Z.; Li, L. Spatiotemporal Variation of Snowfall to Precipitation Ratio and Its Implication on Water Resources by a Regional Climate Model over Xinjiang, China. Water 2018, 10, 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101463
Li Q, Yang T, Qi Z, Li L. Spatiotemporal Variation of Snowfall to Precipitation Ratio and Its Implication on Water Resources by a Regional Climate Model over Xinjiang, China. Water. 2018; 10(10):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101463
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Qian, Tao Yang, Zhiming Qi, and Lanhai Li. 2018. "Spatiotemporal Variation of Snowfall to Precipitation Ratio and Its Implication on Water Resources by a Regional Climate Model over Xinjiang, China" Water 10, no. 10: 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101463
APA StyleLi, Q., Yang, T., Qi, Z., & Li, L. (2018). Spatiotemporal Variation of Snowfall to Precipitation Ratio and Its Implication on Water Resources by a Regional Climate Model over Xinjiang, China. Water, 10(10), 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101463






