Soil Erosion Modeling and Comparison Using Slope Units and Grid Cells in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Northern Taiwan
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Universal Soil Loss Equation
- Am = computed soil loss per unit area (t ha−1 yr−1)
- Rm = rainfall and runoff factor (MJ-mm ha−1 hr−1 yr−1)
- Km = soil erodibility factor (t-hr MJ−1 mm−1)
- L = slope-length factor
- S = slope-steepness factor
- C = cover and management factor
- P = support practice factor
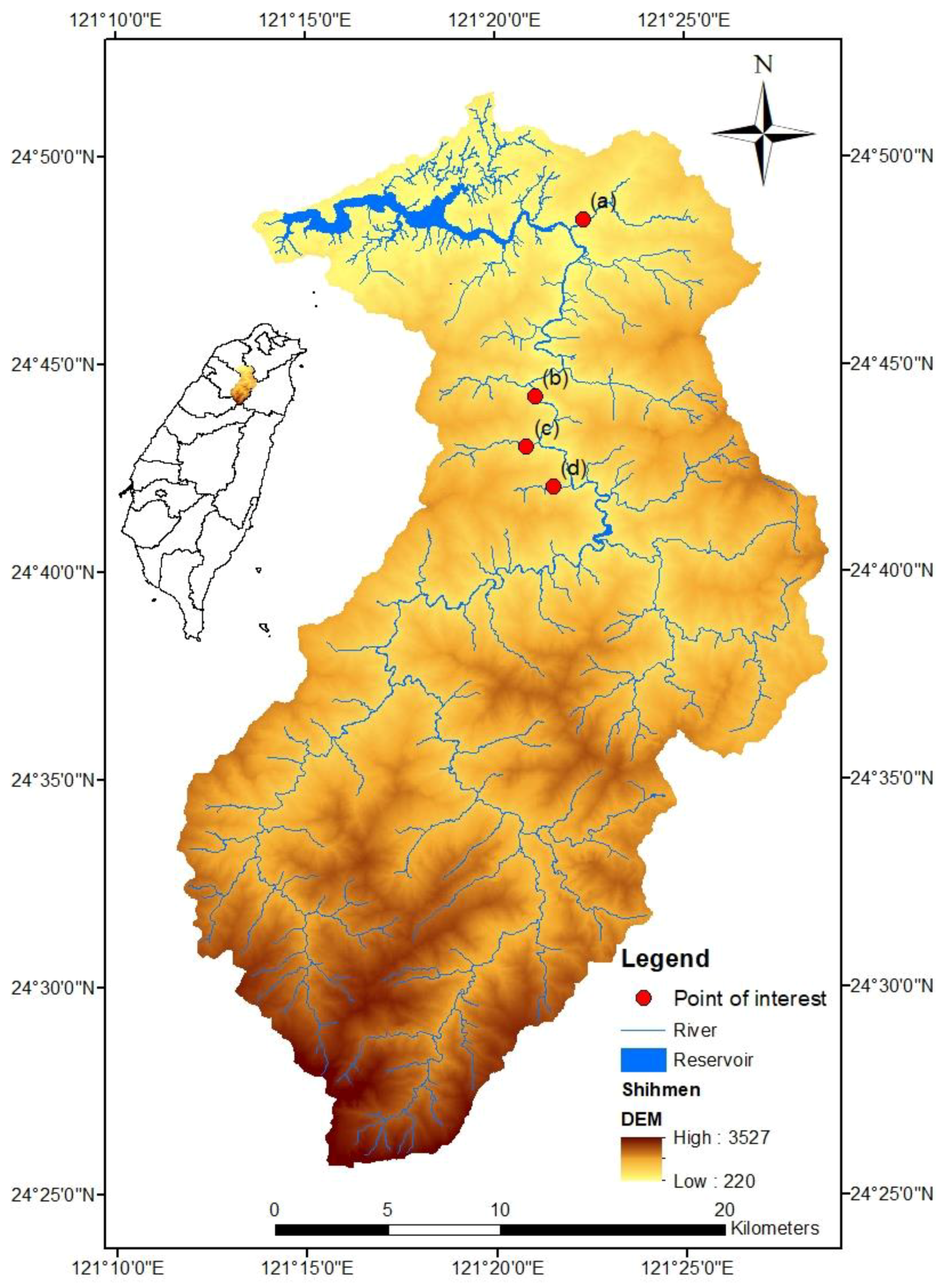
2.2. Study Area
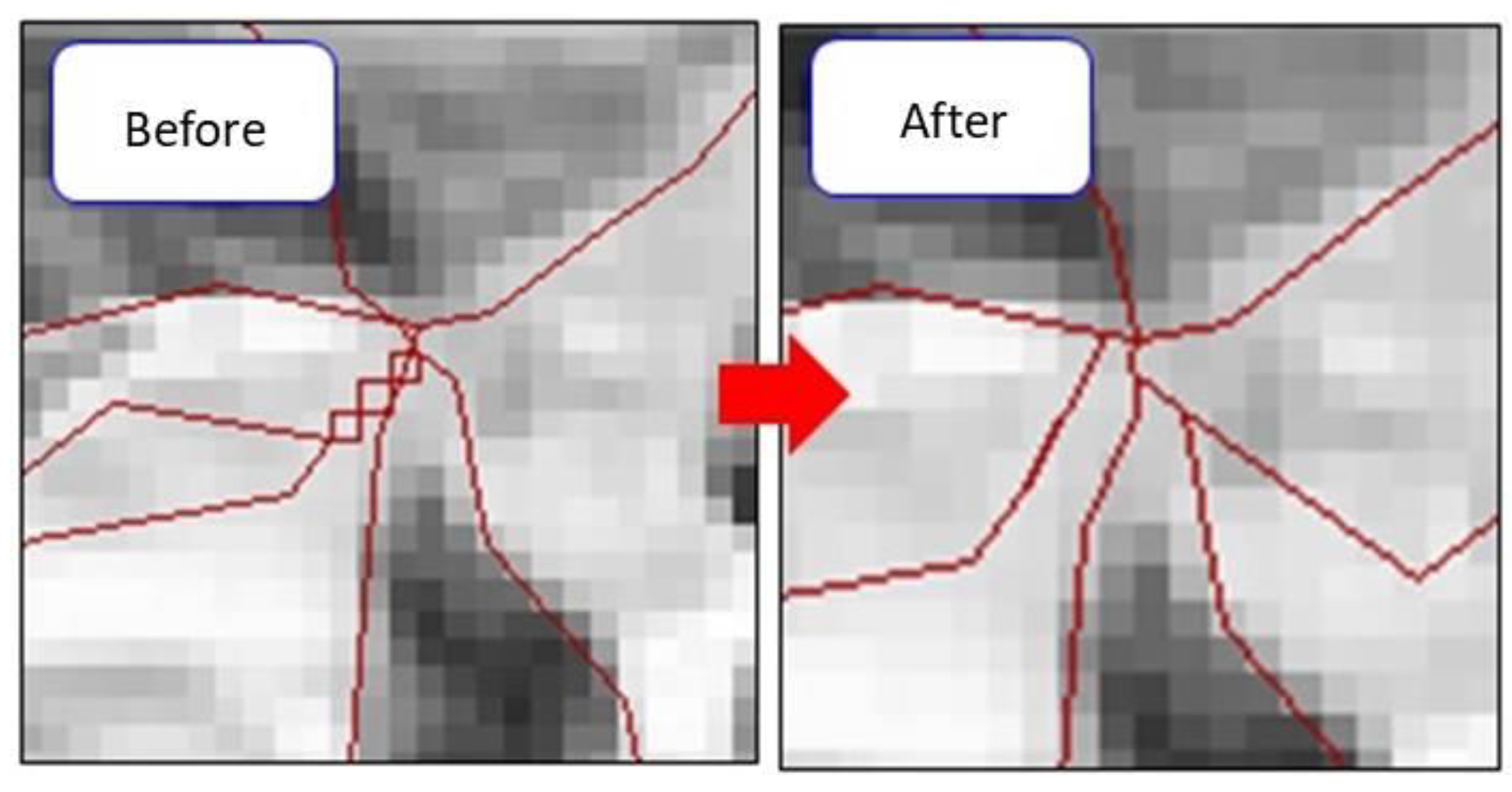
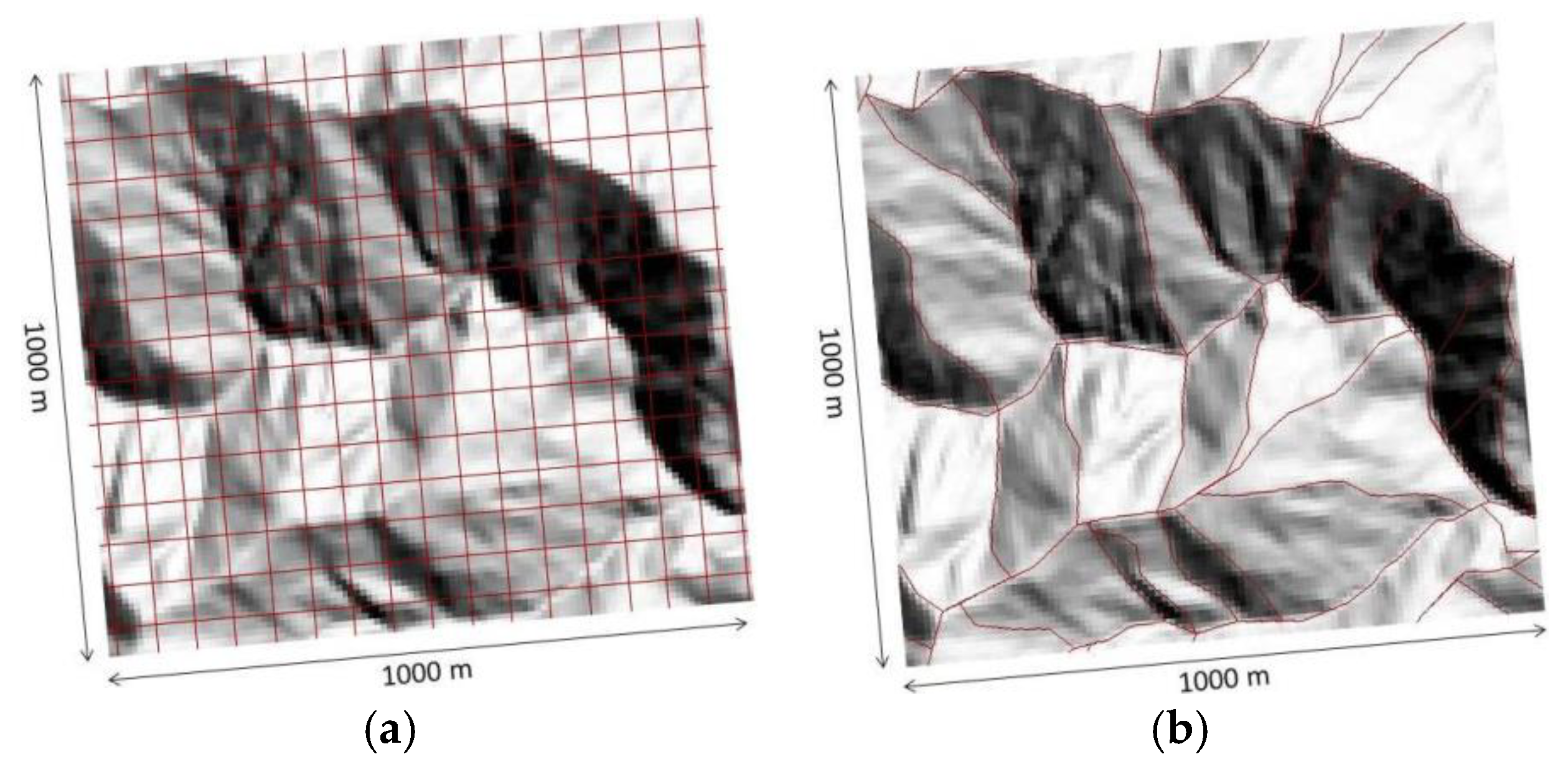
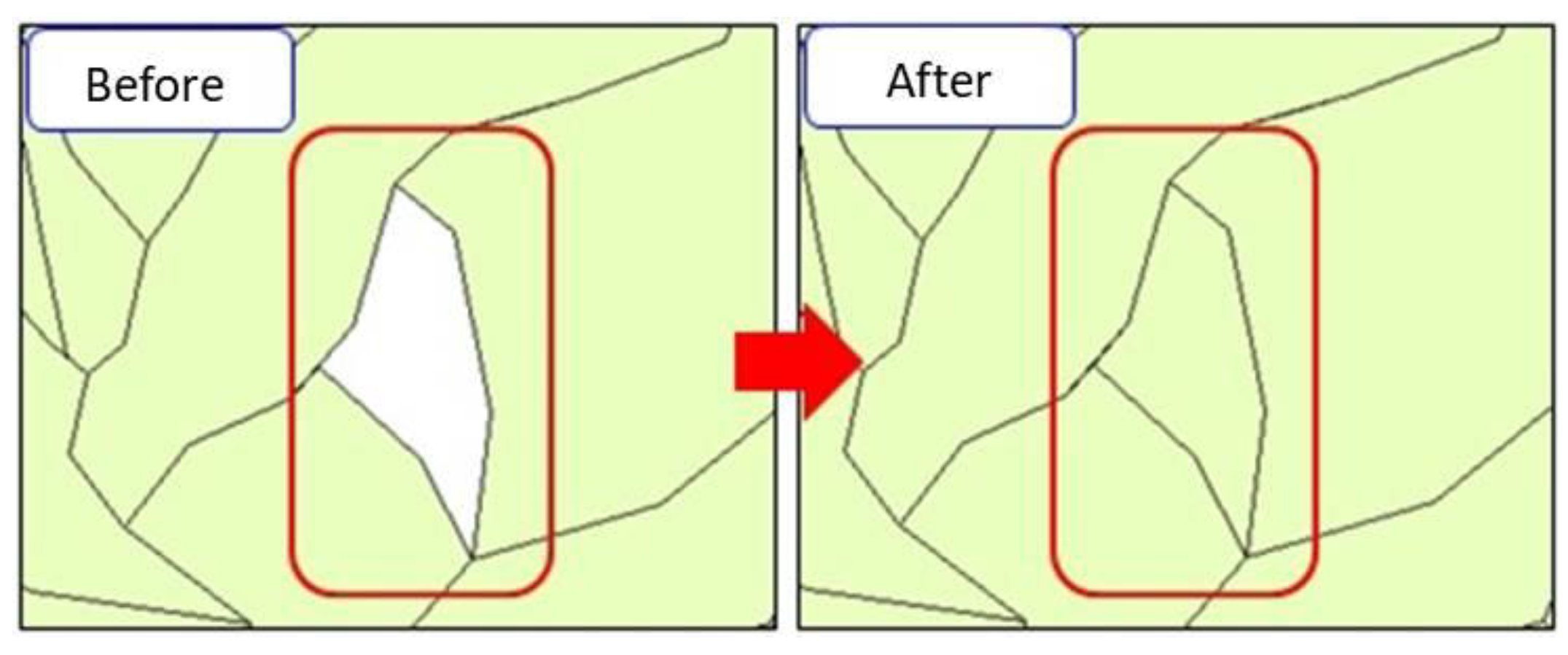
2.3. Grid Cells and Slope Units
- λ = slope length in meters
- m = 0.5 if percent slope is 5% or more
- = 0.3 on slopes of 1% to 3%
- = 0.2 on uniform gradients of less than 1%
- θ = the angle of slope
3. Results
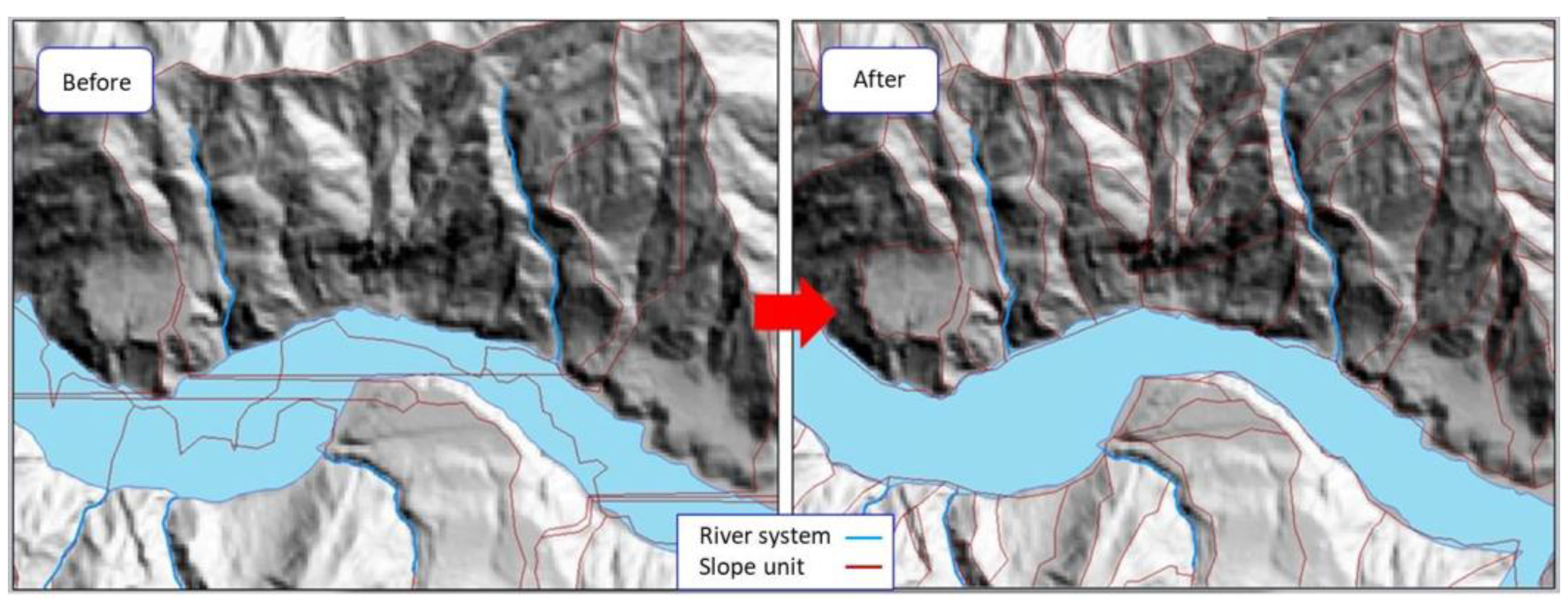
3.1. Delineation of the Study Area
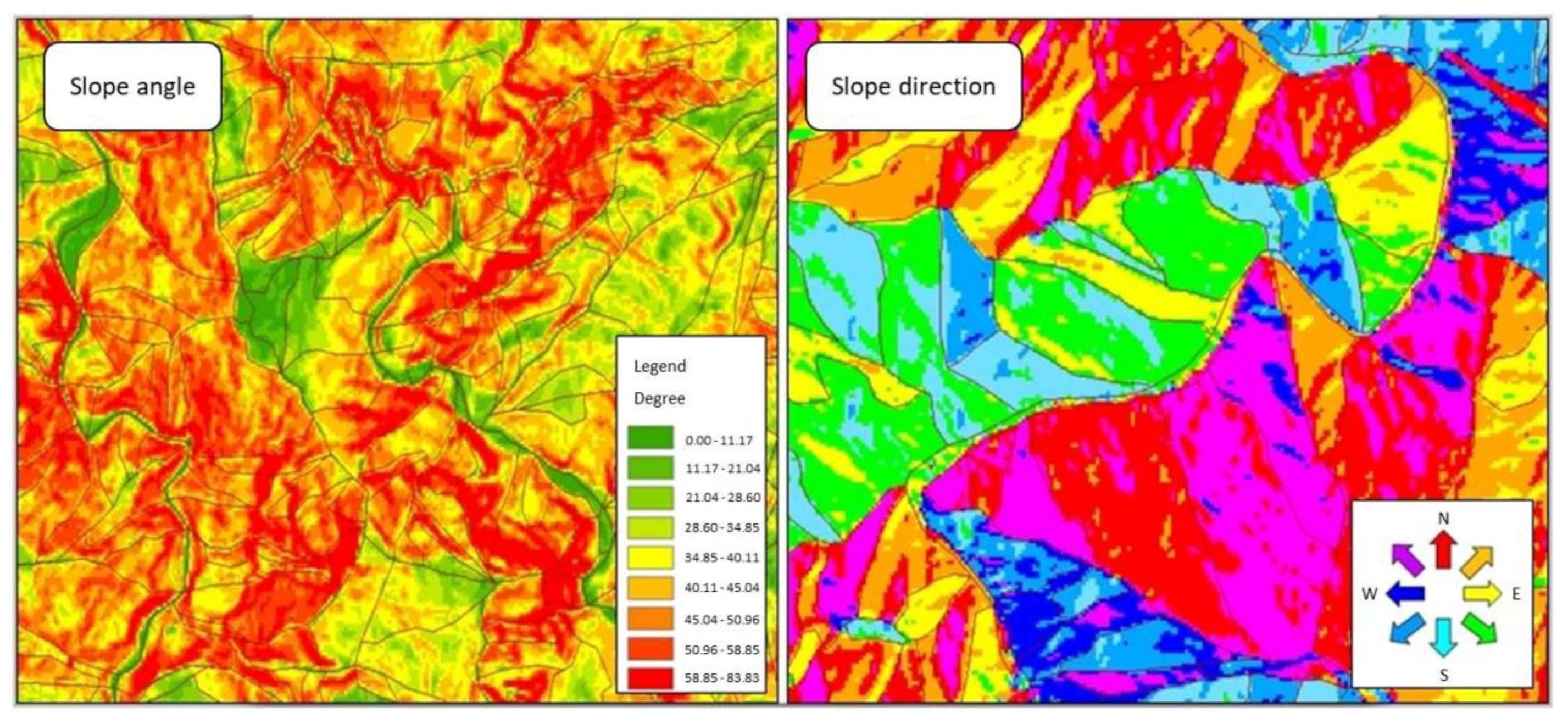
3.2. Comparison of Topographic Factors L and S
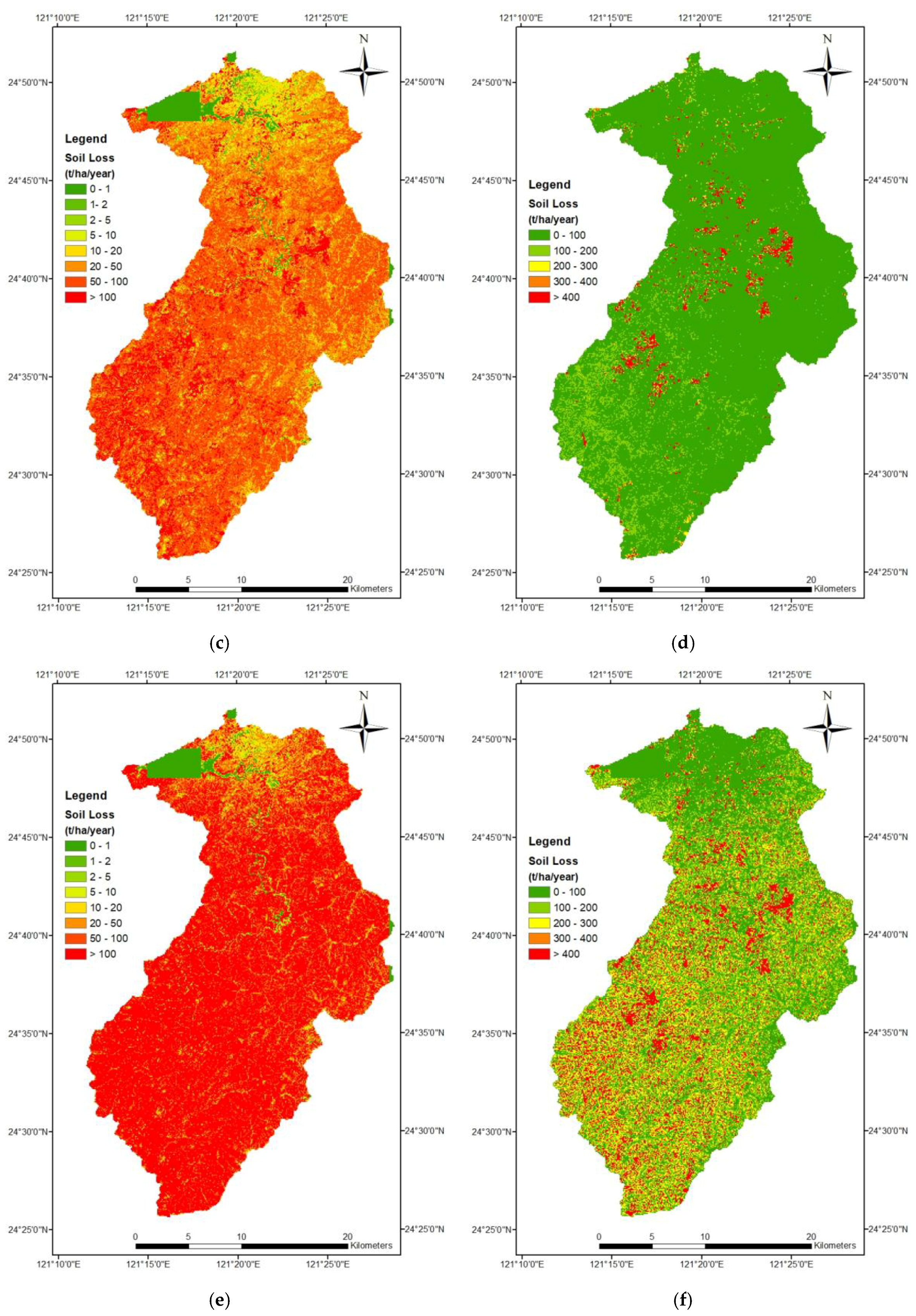
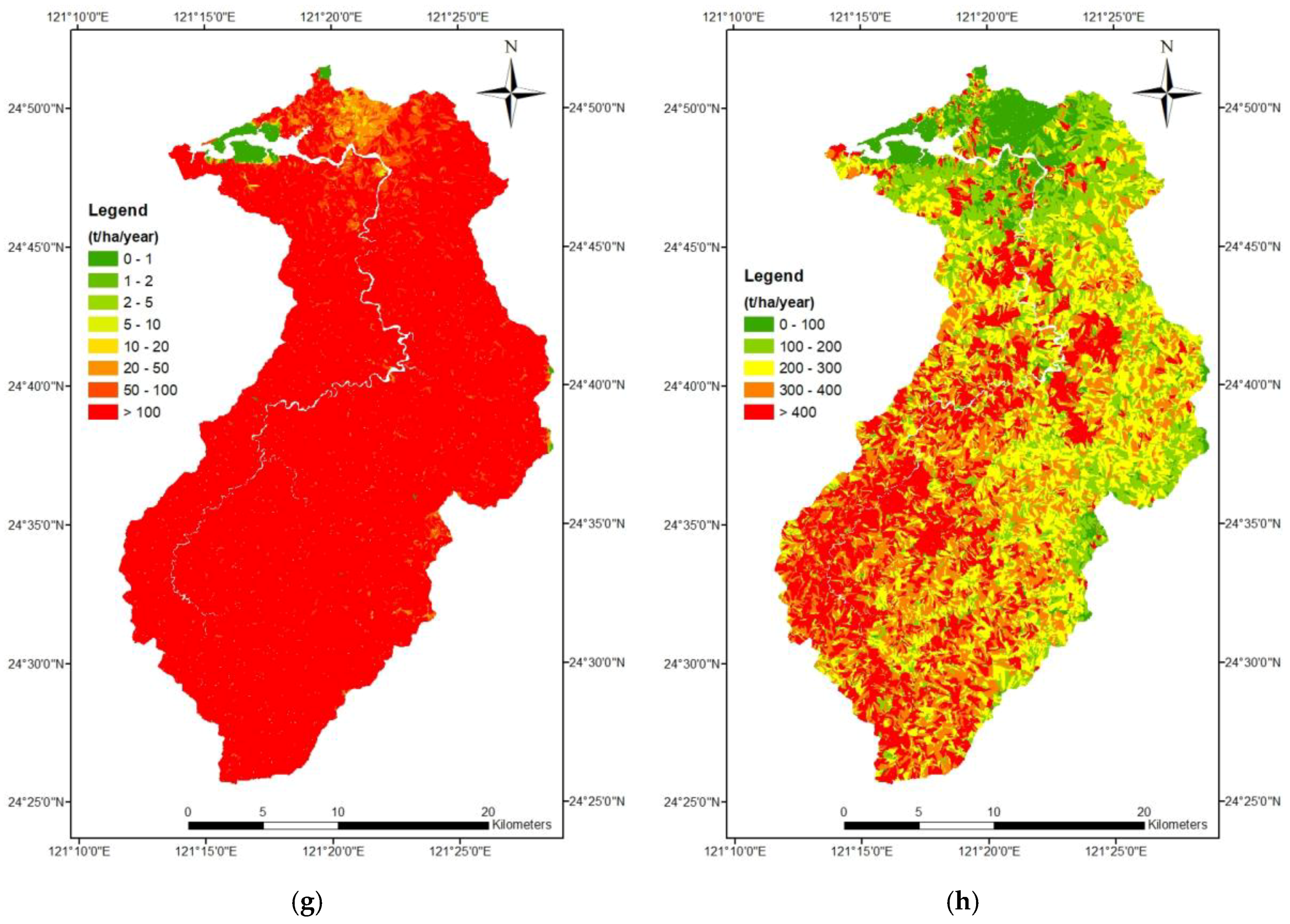
3.3. Comparison of Soil Erosion
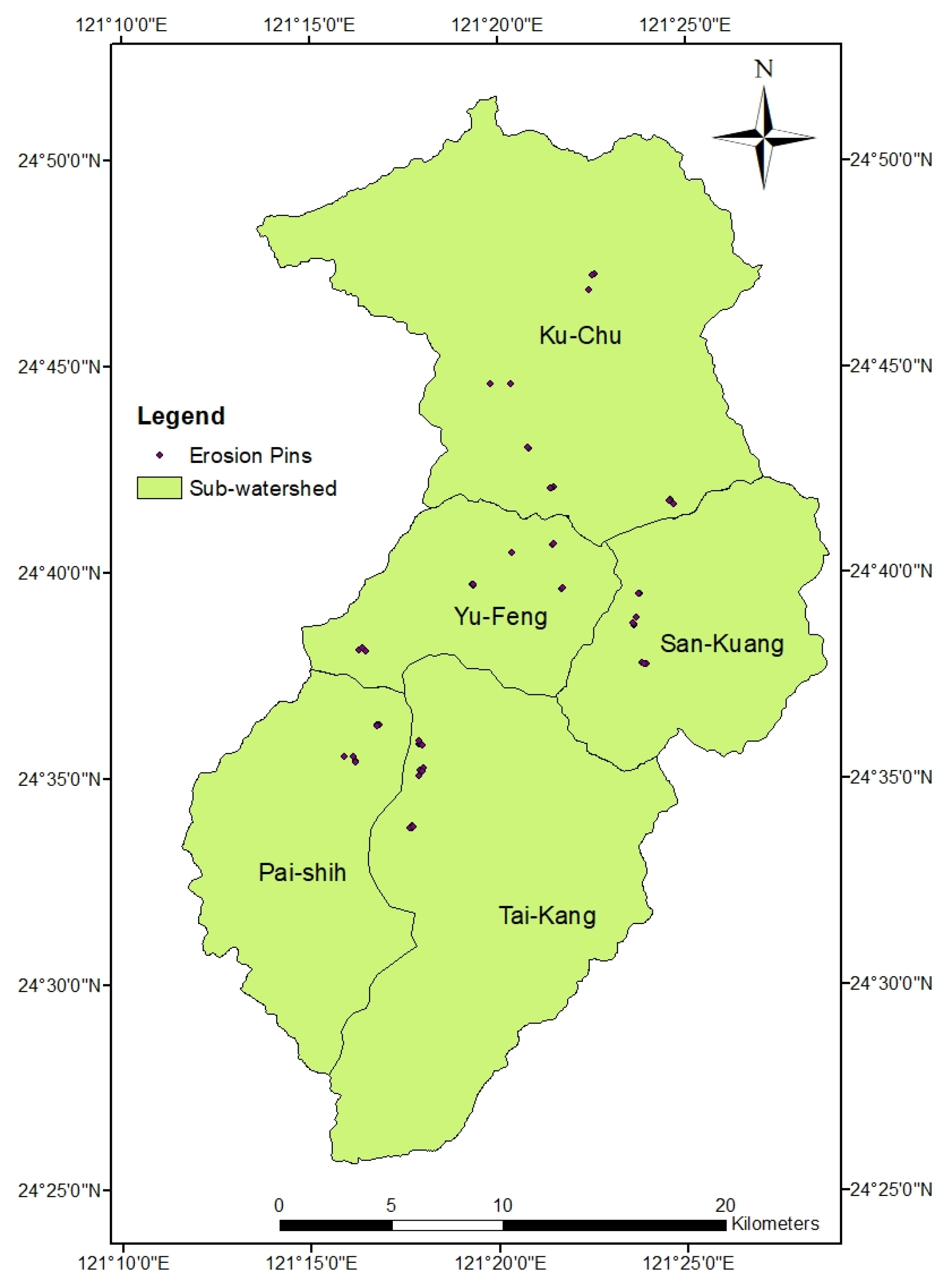
3.4. Validation with Erosion Pin Measurements
- At = total amount of soil erosion (t)
- d = erosion depth (mm)
- area = area of watershed (ha)
- γ = unit weight of soil (t m−3)
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ching, K.-E.; Hsieh, M.-L.; Johnson, K.M.; Chen, K.-H.; Rau, R.-J.; Yang, M. Modern vertical deformation rates and mountain building in Taiwan from precise leveling and continuous GPS observations, 2000–2008. J. Geophys. Res. 2011, 116, B08406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Robinson, D.A.; Fleischer, L.R.; Lugato, E.; Ballabio, C.; Alewell, C.; Meusburger, K.; Modugno, S.; Schutt, B.; Ferro, V.; et al. As assessment of the global impact of 21st century land use change on soil erosion. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, E.; Edeso, J.M.; Ormaetxea, L. Soil erosion and forests biomass as energy resource in the basin of the Oka River in Biscay, northern Spain. Forests 2017, 8, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefano, C.D.; Ferro, V.; Pampalone, V. Applying the USLE family of models at the Sparacia (south Italy) experimental site. Land Degrad. Dev. 2017, 28, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laflen, J.M.; Flanagan, D.C. The development of U.S. soil erosion prediction and modeling. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2013, 1, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Morales, S.B.; Mayer, A.; Ramirez-Marcial, N. Assessment of soil erosion vulnerability in the heavily populated and ecologically fragile communities in Motozintla de Mendoza, Chiapas, Mexico. Solid Earth 2018, 9, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Zhao, W.; Ding, J.; Fang, X.; Zhang, X. Estimation of the cover and management factor based on stratified coverage and remote sensing indices: A case study in the Loess Plateau of China. J. Soils Sediments 2018, 18, 775–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, E.; Ouyang, Z.; Yu, X.; Xiao, Y. Spatial patterns and impacts of soil conservation service in China. Geomorphology 2014, 207, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, G.; Panda, R.K. Grid-cell based assessment of soil erosion potential for identification of critical erosion prone areas using USLE, GIS and remote sensing: A case study in the Kapgari watershed, India. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Das, N.; Debnath, J.; Bhowmik, M. An assessment to prioritise the critical erosion-prone sub-watersheds for soil conservation in the Gumti basin of Tripura, North-East India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2017, 189, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subhatu, A.; Lemann, T.; Hurni, K.; Portner, B.; Kassawmar, T.; Zeleke, G.; Hurni, H. Deposition of eroded soil on terraced croplands in Minchet catchment, Ethiopian Highlands. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2017, 5, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okou, F.A.Y.; Tente, B.; Bachmann, Y.; Sinsin, B. Regional erosion risk mapping for decision support: A case study from West Africa. Land Use Policy 2016, 56, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Gray, J.; Chapman, G.; Zhu, Q.; Tulau, M.; McInnes-Clarke, S. Digital mapping of soil erodibility for water erosion in New South Wales, Australia. Soil Res. 2018, 56, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, A.; Spencer, J.; Borombovits, D.; Pietsch, T.; Olley, J. Measured hillslope erosion rates in the wet-dry tropics of Cape York, northern Australia: Part 2, RUSLE-based modeling significantly over-predicts hillslope sediment production. Catena 2014, 122, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, C.; de Rigo, D.; Dewitte, O.; Poesen, J.; Panagos, P. Modeling soil erosion at European scale: Toward harmonization and reproducibility. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2015, 15, 225–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Poesen, J.; Ballabio, C.; Lugato, E.; Meusburger, K.; Montanarella, L.; Alewell, C. The new assessment of soil loss by water erosion in Europe. Environ. Sci. Policy 2015, 54, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Ruiz, J.M.; Begueria, S.; Nadal-Romero, E.; Gonzalez-Hidalgo, J.C.; Lana-Renault, N.; Sanjuan, Y. A Meta-analysis of Soil Erosion Rates across the World. Geomorphology 2015, 239, 160–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K.; Ballabio, C.; Panagos, P.; Alewell, C. Object-oriented soil erosion modeling: A possible paradigm shift from potential to actual risk assessments in agricultural environments. Land Degrad. Dev. 2018, 29, 1270–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting Rainfall Erosion Losses—A Guide to Conservation Planning; Agriculture Handbook No. 537; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1978.
- Lin, B.S.; Thomas, K.; Chen, C.K.; Ho, H.C. Evaluation of soil erosion risk for watershed management in Shenmu watershed, central Taiwan using USLE model parameters. Paddy Water Environ. 2016, 14, 19–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-Y.; Su, C.-C.; Wu, I.-Y. Revision of the isoerodent map for the Taiwan area. J. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. 2005, 36, 159–172. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wann, S.S.; Hwang, J.I. Soil erosion on hillslopes of Taiwan. J. Chin. Soil Water Conserv. 1989, 20, 17–45. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.; Li, D.-H.; Yang, K.-J.; Tsai, F.; Seeboonruang, U. Identifying and comparing relatively high soil erosion sites with four DEMs. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 120, 449–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Nguyen, K.A.; Chen, W.; Wattanasetpong, J.; Seeboonruang, U. Comparing watershed soil erosion of Taiwan and Thailand. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Engineering, Applied Sciences and Technology (ICEAST 2018), Phuket, Thailand, 4–7 July 2018. [Google Scholar]
- National Land Surveying and Mapping Center. Report of the Second National Land Use Survey; National Land Surveying and Mapping Center: Taichung, Taiwan, 2012. (In Chinese)
- Wu, C.C.; Lo, K.-F.; Lin, L.-L. Handbook of Soil Loss Estimation; National Pingtung University of Science and Technology: Neipu, Taiwan, 1996. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Rainfall-Erosion Losses from Cropland East of the Rocky Mountains—Guide for Selection of Practices for Soil and Water Conservation; Agriculture Handbook No. 282; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1965.
- Renard, K.G.; Foster, G.R.; Weesies, G.A.; McCool, D.K.; Yoder, D.C. Predicting Soil Erosion by Water: A Guide to Conservation Planning with the Revised Universal Soil Loss Equation (RUSLE); Agricultural Handbook No. 703; U.S. Department of Agriculture: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- Oliveira, A.H.; da Silva, M.A.; Silva, M.L.N.; Curi, N.; Neto, G.K.; de Freitas, D.A.F. Development of topographic factor modeling for application in soil erosion models. In Soil Processes and Current Trends in Quality Assessment; Soriano, M.C.H., Ed.; Intech Open: London, UK, 2013; pp. 111–138. ISBN 978-953-51-1029-3. [Google Scholar]
- Begueria, S.; Vicente-Serrano, S.M.; Tomas-Burguera, M.; Maneta, M. Bias in the variance of gridded data sets leads to misleading conclusions about changes in climate variability. Int. J. Climatol. 2016, 36, 3413–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickey, R.; Smith, A.; Jankowski, P. Slope length calculations from a DEM within Arc/Info GRID. Comput. Environ. Urban Syst. 1994, 18, 365–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaya, V. SEXTANTE User’s Manual (v1.0 Rev.). Available online: https://www.eweb.unex.es/eweb/sextantegis/IntroductionToSEXTANTE.pdf (accessed on 2 October 2018).
- Desmet, P.J.J.; Govers, G. A GIS procedure for automatically calculating the USLE LS factor on topographically complex landscape units. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1996, 51, 427–433. [Google Scholar]
- Panagos, P.; Borrelli, P.; Meusburger, K. A new European slope length and steepness factor (LS-factor) for modeling soil erosion by water. Geosciences 2015, 5, 117–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wei, J.; Yang, Q.; Baartman, J.E.M.; Gai, L.; Yang, X.; Li, S.; Yu, J.; Ritsema, C.J.; Geissen, V. An improved method for calculating slope length and the LS parameters of the revised universal soil loss equation for large watersheds. Geoderma 2017, 308, 36–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, G.R.; Wischmeier, W.H. Evaluating irregular slopes for soil loss prediction. Trans. Am. Soc. Agric. Eng. 1974, 17, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Esaki, T.; Zhou, G. GIS-based probabilistic mapping of landslide hazard using a three-dimensional deterministic model. Nat. Hazards 2004, 33, 265–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.-H. Analyzing Soil Erosion of Shihmen Reservoir Watershed Using Slope Units. Master’s Thesis, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei, Taiwan, June 2017. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- Lin, W.-C. A Study on Soil Erosion and Influential Hydrologic and Geographic Factors for Shihmen Reservoir Watershed. Master’s Thesis, Tamkang University, New Taipei City, Taiwan, 2 July 2014. (In Chinese). [Google Scholar]
- McCool, D.K.; George, G.O.; Freckleton, M.; Papendick, R.I.; Douglas, C.L., Jr. Topographic effect on erosion from cropland in the northwestern wheat region. Trans. ASAE 1993, 36, 1067–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Shi, P.J.; Jia, Z.W. Slope length effects on soil loss for steep slopes. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2000, 64, 1759–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Type | L | S | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Grid cells | Max. | 2.24 | 69.26 |
| Min. | 0.67 | 0.07 | |
| Mean | 0.82 | 25.08 | |
| Slope units | Max. | 7.47 | 56.24 |
| Min. | 1.16 | 0.39 | |
| Mean | 3.05 | 25.70 |
| Erosion pins (mm) | Grid cell approach (mm) | Grid cell with a horizontal projection (mm) | Grid cell using SAGA (mm) | Slope unit approach (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ku-Chu sub-watershed | 6.0 | 5.4 | 4.7 | 15.4 | 24.0 |
| Yu-Feng sub-watershed | 4.7 | 9.2 | 7.9 | 26.4 | 44.0 |
| San-Kuang sub-watershed | 8.9 | 5.2 | 4.4 | 15.6 | 25.6 |
| Pai-Shih sub-watershed | 6.4 | 10.1 | 8.8 | 30.9 | 46.8 |
| Tai-Kang sub-watershed | 6.8 | 7.0 | 5.9 | 20.2 | 31.2 |
| Entire Shihmen reservoir watershed | 6.5 | 6.9 | 6.0 | 20.3 | 29.8 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.-H.; Li, D.-H.; Chen, W.; Lin, B.-S.; Seeboonruang, U.; Tsai, F. Soil Erosion Modeling and Comparison Using Slope Units and Grid Cells in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Northern Taiwan. Water 2018, 10, 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101387
Liu Y-H, Li D-H, Chen W, Lin B-S, Seeboonruang U, Tsai F. Soil Erosion Modeling and Comparison Using Slope Units and Grid Cells in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Northern Taiwan. Water. 2018; 10(10):1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101387
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yi-Hsin, Dong-Huang Li, Walter Chen, Bor-Shiun Lin, Uma Seeboonruang, and Fuan Tsai. 2018. "Soil Erosion Modeling and Comparison Using Slope Units and Grid Cells in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Northern Taiwan" Water 10, no. 10: 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101387
APA StyleLiu, Y.-H., Li, D.-H., Chen, W., Lin, B.-S., Seeboonruang, U., & Tsai, F. (2018). Soil Erosion Modeling and Comparison Using Slope Units and Grid Cells in Shihmen Reservoir Watershed in Northern Taiwan. Water, 10(10), 1387. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101387






