Characterizing Hydrological Connectivity of Artificial Ditches in Zoige Peatlands of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Acquisition
2.3. Determination of Structural and Functional Hydrological Connectivity
3. Results and Analysis
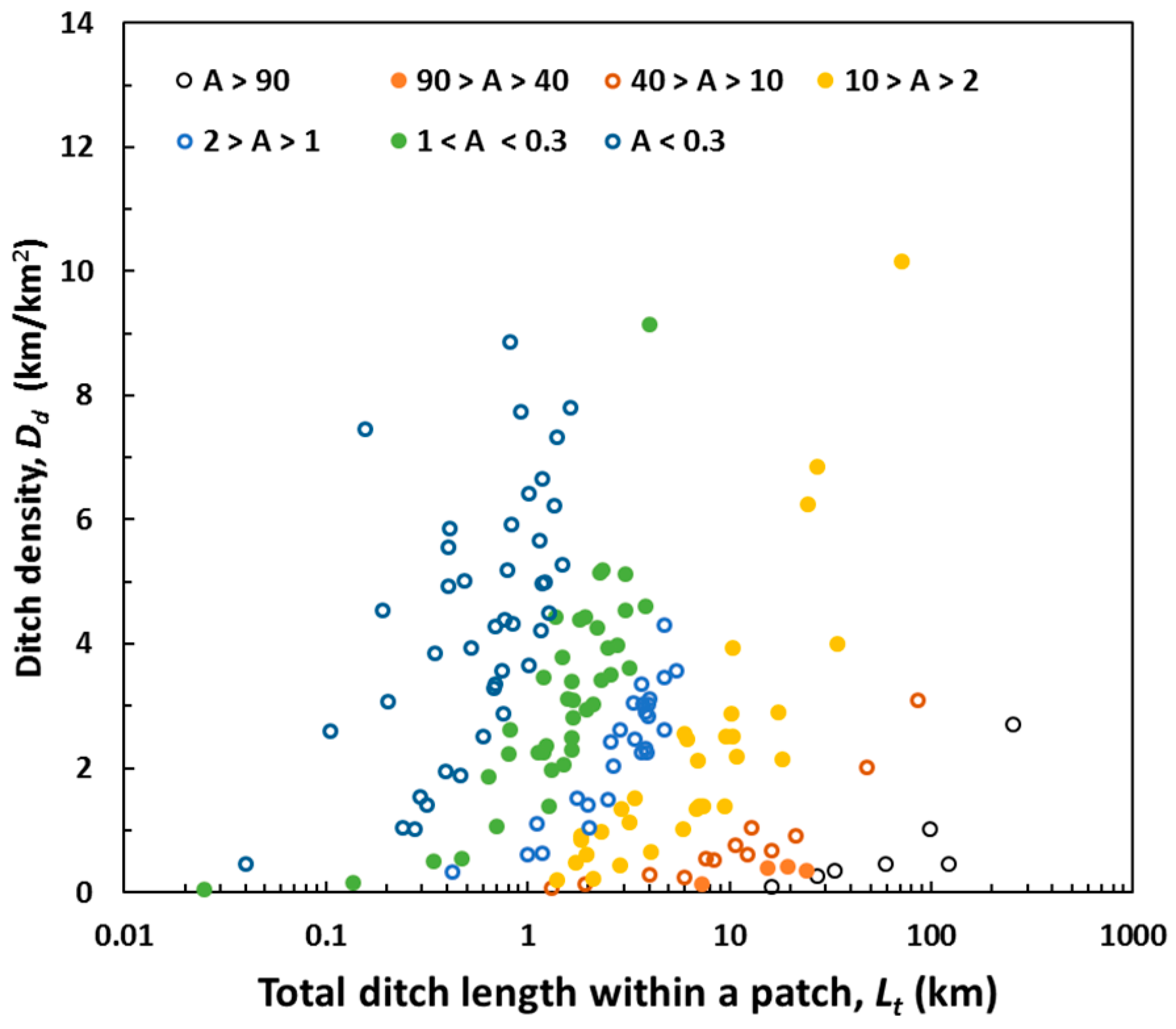
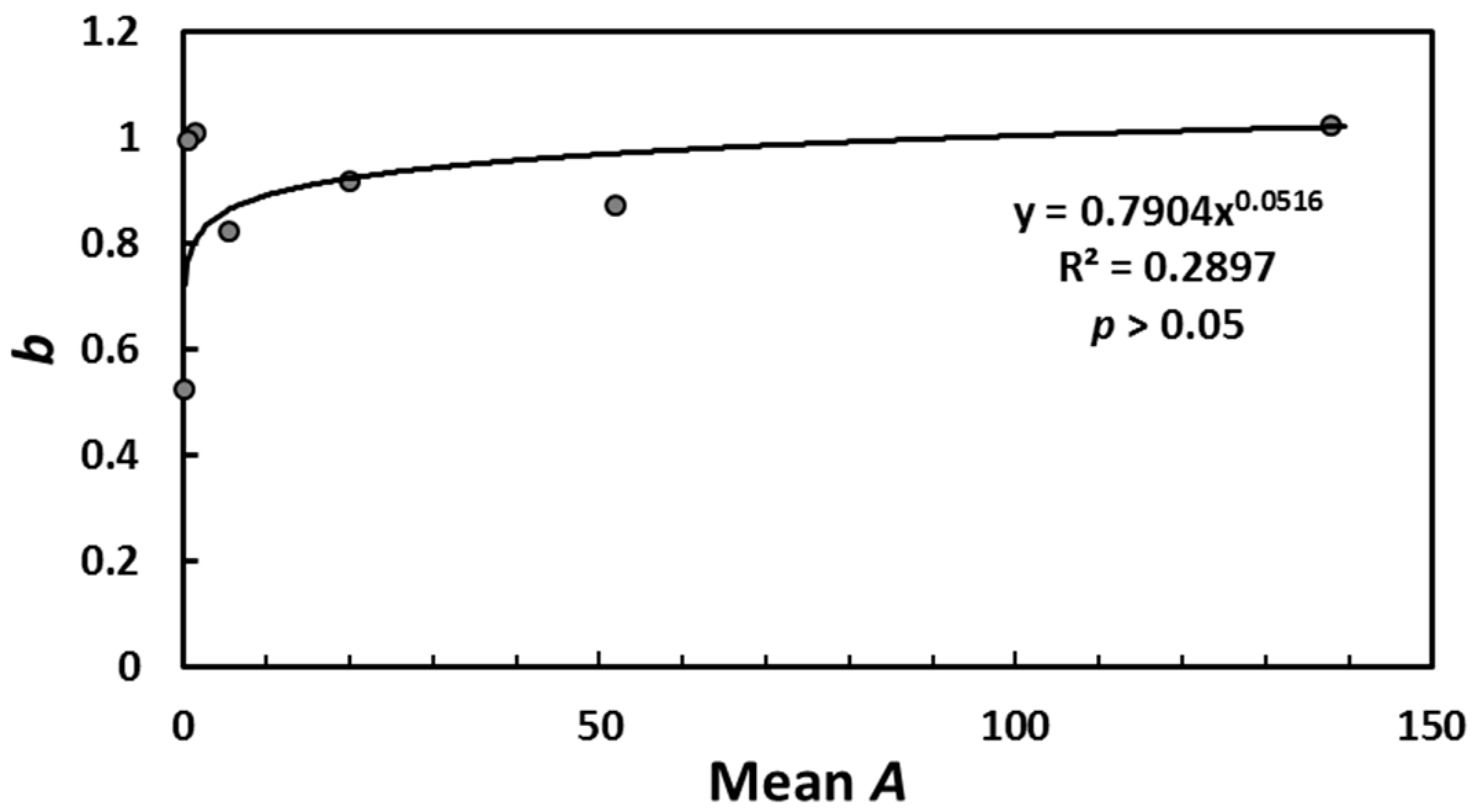
3.1. Statistical Characteristics of the Artificial Ditches
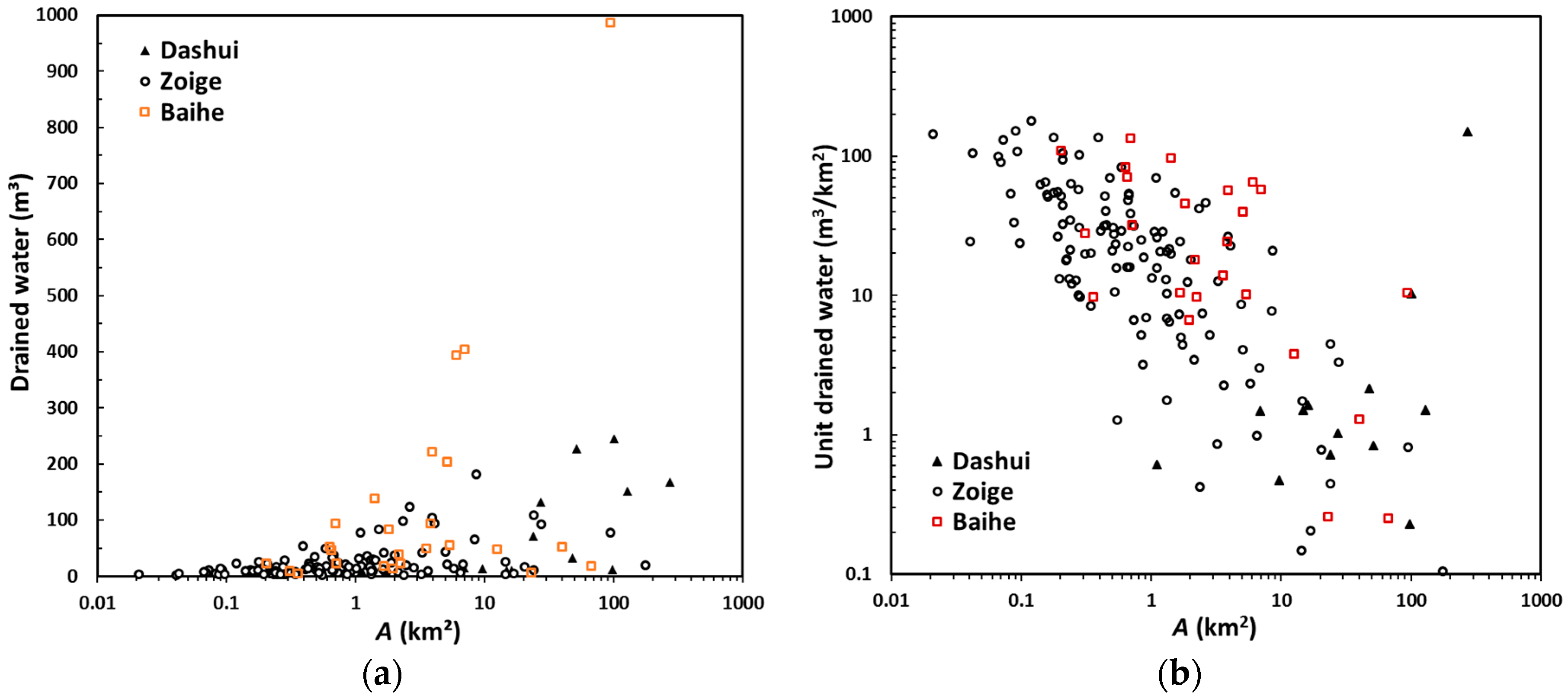
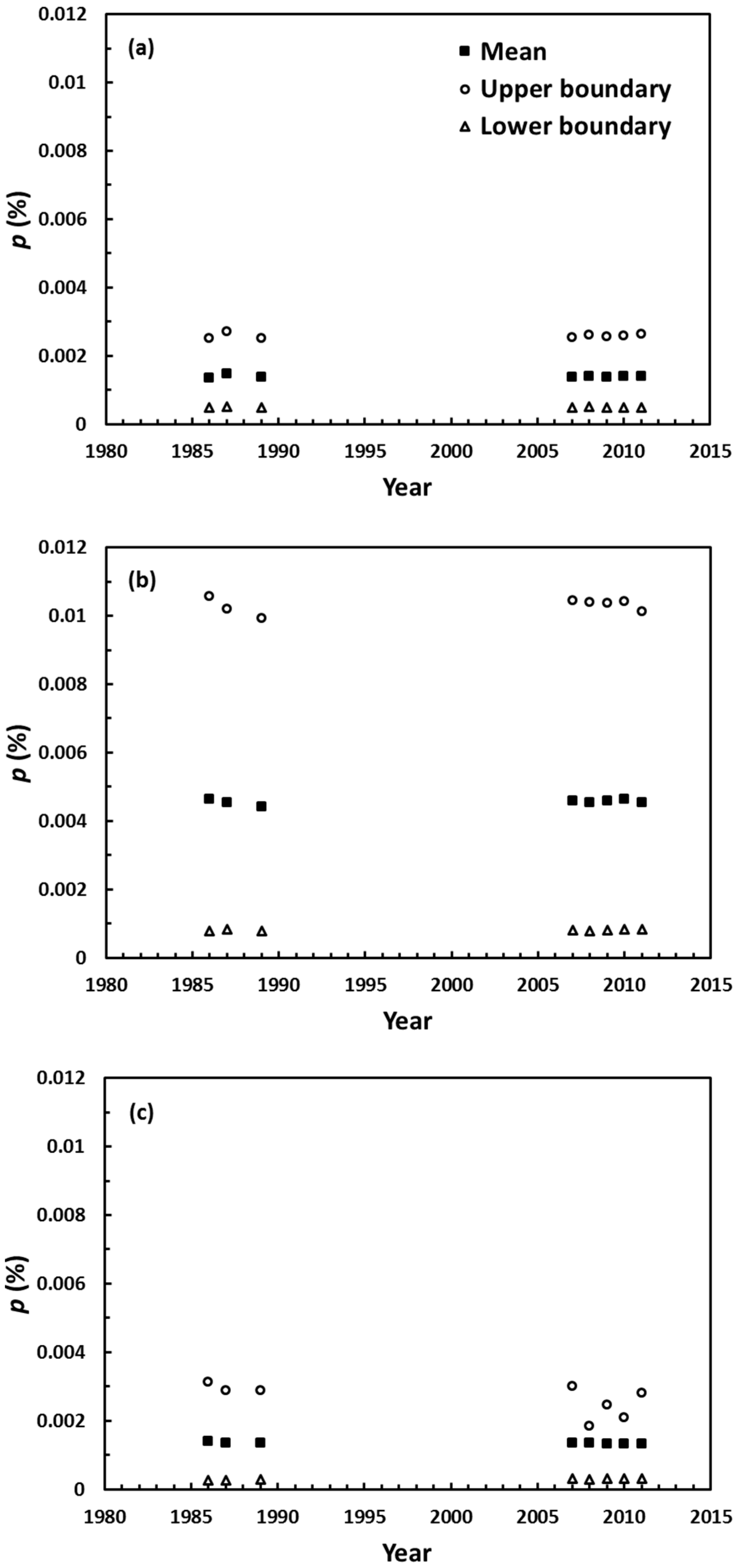
3.2. Spatial and Temporal Changes of Annual Volume of Water Drained Out of Patches
4. Discussions
4.1. Significance of Hydrological Connectivity in Peatland Management
4.2. Uncertainties in Calculations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Armstrong, A.; Holden, J.; Kay, P.; Francis, B.; Foulger, M.; Gledhill, S.; McDonald, A.T.; Walker, A. The impact of peatland drain-blocking on dissolved organic carbon loss and discolouration of water; results from a national survey. J. Hydrol. 2010, 381, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Chapman, P.J.; Labadz, J.C. Artificial drainage of peatlands: Hydrological and hydrochemical process and wetland restoration. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2004, 28, 95–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labadz, J.; Allott, T.; Evans, M.; Butcher, D.; Billett, M.; Stainer, S.; Yallop, A.; Jones, P.; Innerdale, M.; Harmon, N.; et al. Peatland Hydrology. Draft Scientific Review; IUCN UK Peatland Programme’s Commission of Inquiry on Peatlands: Edinburgh, UK, 2010; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Price, J.S.; Heathwaite, A.L.; Baird, A.J. Hydrological processes in abandoned and restored peatlands: An overview of management approaches. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2003, 11, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenberg, L.; Finer, L.; Nieminen, M.; Sarkkola, S.; Koivusalo, H. Quantification of ditch bank erosion in a drained forested catchment. Boreal Environ. Res. 2015, 20, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Holden, J.; Chapman, P.J.; Lane, S.N.; Brookes, C. Impacts of artificial drainage of peatlands on runoff production and water quality. In Peatlands: Evolution and Records of Environmental and Climate Changes; Martini, L.P., Martınez, C.A., Chesworth, W., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 501–528. [Google Scholar]
- Ramchunder, S.J.; Brown, L.E.; Holden, J. Environmental effects of drainage, drain-blocking and prescribed vegetation burning in UK upland peatlands. Progr. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniels, S.M.; Agnew, C.T.; Allott, T.E.H.; Evans, M.G. Water table variability and runoff generation in an eroded peatland, South Pennines, UK. J. Hydrol. 2008, 361, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J. Upland hydrology. In Drivers of Change in Upland Environments; Bonn, A., Allott, T.E.H., Hubacek, K., Stewart, J., Eds.; Routledge: Oxon, UK, 2009; pp. 113–134. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, P.M.; Ala-aho, P.; Ronkanen, A.K.; Klove, B. Groundwater-surface water interaction between an esker aquifer and a drained fen. J. Hydrol. 2012, 432, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.R.; Morris, P.J.; Liu, J.G.; Holden, J. PEATMAP: Refining estimates of global peatland distribution based on a meta-analysis. Catena 2018, 160, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballard, C.E.; McIntyre, N.; Wheater, H.S. Effects of peatland drainage management on peak flows. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2012, 16, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Joosten, H.; Schumann, M. Hydrogenetic aspects of peatland restoration in Tibet and Kalimantan. Glob. Environ. Res. 2007, 11, 195–204. [Google Scholar]
- Letts, M.G.; Roulet, N.T.; Comer, N.T.; Skarupa, M.R.; Verseghy, D.L. Parametrization of peatland hydraulic properties for the Canadian Land Surface Scheme. Atmos.-Ocean 2000, 38, 141–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronkanen, A.K.; Klove, B. Hydraulic soil properties of peatlands treating municipal wastewater and peat harvesting runoff. Suo 2005, 56, 43–56. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, M.; Ma, A.; Qi, H.; Zhuang, X.; Zhuang, G.; Zhao, G. Warmer temperature accelerates methane emissions from the Zoige wetland on the Tibetan Plateau without changing methanogenic community composition. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Ma, T.; De, K.; Zhou, Q.; Yao, B.; Niu, T. Retrieval of the surface evapotranspiration patterns in the alpine grassland–wetland ecosystem applying SEBAL model in the source region of the Yellow River, China. Ecol. Modell. 2013, 270, 64–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yu, Z.; Liang, Z.; Song, K.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Acharya, K. Effects of climate variations and human activities on runoff in the Zoige alpine wetland in the Eastern Edge of the Tibetan Plateau. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sprenger, M.; Tetazlaff, D.; Tunaley, C.; Dick, J.; Soulsby, C. Evaporation fractionation in a peatland drainage network affects stream water isotope composition. Water Resour. Res. 2017, 53, 851–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Wei, B.; Su, W.; Shen, W.; Wang, C.; You, D.; Liu, Z. Evapotranspiration estimation based on the SEBAL model in the Nansi Lake Wetland of China. Math. Comput. Modell. 2011, 54, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Han, M.; Xu, S. Estimating the regional evapotranspiration in Zhalong wetland with the Two-Source Energy Balance (TSEB) model and Landsat7/ETM+ images. Ecol. Inform. 2010, 5, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, Z.; Brierley, G.; Nicoll, T.; Pan, B.; Li, Y. Shrinkage of the Ruoergai Swamp and changes to landscape connectivity, Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Catena 2015, 126, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Lu, Q.; Song, K.; Qin, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, H.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Li, H. Remotely sensing the ecological influences of ditches in Zoige Peatland, Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Int. J. Remote. Sens. 2014, 35, 5186–5197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Burt, T.P. Runoff production in blanket peat covered catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2003, 39, 1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holden, J.; Evans, M.G.; Burt, T.P.; Horton, M. Impact of land drainage on peatland hydrology. J. Environ. Qual. 2006, 35, 1764–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luscombe, D.J.; Anderson, K.; Grand-Clement, E.; Gatis, N.; Ashe, J.; Benaud, P.; Smith, D.; Brazier, R.E. How does drainage alter the hydrology of shallow degraded peatlands across multiple spatial scales? J. Hydrol. 2016, 541, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allott, T.E.H.; Evans, M.G.; Lindsay, J.B.; Agnew, C.T.; Freer, J.E.; Jones, A.; Parnel, M. Water Tables in Peak District Blanket Peatlands; Moors for the Future Report No. 17; Hydrological Benefits of Moorland Restoration; Moors for the Future: Edale, UK, 2009; p. 49. [Google Scholar]
- Lane, S.N.; Brookes, C.J.; Kirkby, M.J.; Holden, J. A network-index-based version of TOPMODEL for use with high-resolution digital topographic data. Hydrol. Proc. 2004, 18, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pringle, C.M. Hydrologic connectivity and the management of biological reserves: A global perspective. Ecol. Appl. 2001, 11, 981–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, B.; Garcia, M.; Cabezas, A.; Gonzalez, E.; Gonzalez, M.; Ciancarelli, C.; Comin, F.A. Macroinvertebrate patterns along environmental gradients and hydrological connectivity within a regulated river-floodplain. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 70, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.R.; Pringle, C.M. Ecological Benefits of Reduced Hydrologic Connectivity in Intensively Developed Landscapes. BioScience 2010, 60, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Opperman, J.J.; Luster, R.; McKenney, B.A.; Roberts, M.; Meadows, A.W. Ecologically Functional Floodplains: Connectivity, Flow Regime, and Scale. J. Am.Water Resour. Assoc. 2000, 46, 211–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabezas, A.; Gonzalez, E.; Gallardo, B.; Garcia, M.; Gonzalez, M.; Comin, F.A. Effects of hydrological connectivity on the substrate and understory structure of riparian wetlands in the Middle Ebro River (NE Spain): Implications for restoration and management. Aquat. Sci. 2008, 70, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, M.; McDonough, O.; McCarty, G.; Oesterling, R.; Wilen, B. Enhanced detection of wetland-stream connectivity using Lidar. Wetlands 2012, 32, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golden, H.E.; Lane, C.R.; Amatya, D.M.; Bandilla, K.W.; Kiperwas, H.R.; Knightes, C.D.; Ssegane, H. Hydrologic connectivity between geographically isolated wetlands and surface water systems: A review of select modeling methods. Environ. Modell. Softw. 2014, 53, 190–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, L.J.; Croke, J. The concept of hydrological connectivity and its contribution to understanding runoff-dominated geomorphic systems. Hydrol. Proc. 2007, 21, 1749–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Racchetti, E.; Bartoli, M.; Soana, E.; Longhi, D.; Christian, R.R.; Pinardi, M.; Viaroli, P. Influence of hydrological connectivity of riverine wetlands on nitrogen removal via denitrification. Biogeochemistry 2011, 103, 335–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, M.C.; Pringle, C.M.; Jackson, C.R. Hydrologic connectivity and the contribution of stream headwaters to ecological integrity at regional scales. J. Am. Water Resour. Assoc. 2007, 43, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bracken, L.J.; Wainwright, J.; Ali, G.A.; Tetzlaff, D.; Smith, M.W.; Reaney, S.M.; Roy, A.G. Concepts of hydrological connectivity: Research approaches, pathways and future agendas. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2013, 119, 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tockner, K.; Pennetzdorfer, D.; Reiner, N.; Schiemer, F.; Ward, J.V. Hydrological connectivity, and the exchange of organic matter and nutrients in a dynamic river-floodplain system (Danube, Austria). Feshwater Biol. 1999, 41, 521–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lexartze-Artza, I.; Wainwright, J. Hydrological connectivity: Linking concepts with pratical implications. Catena 2009, 79, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohl, E. Connectivity in rivers. Progr. Phys. Geogr. 2017, 41, 345–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W. Manual of Hydraulic Computation, 2nd ed.; China Water & Power Press: Beijing, China, 2006; p. 676. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]


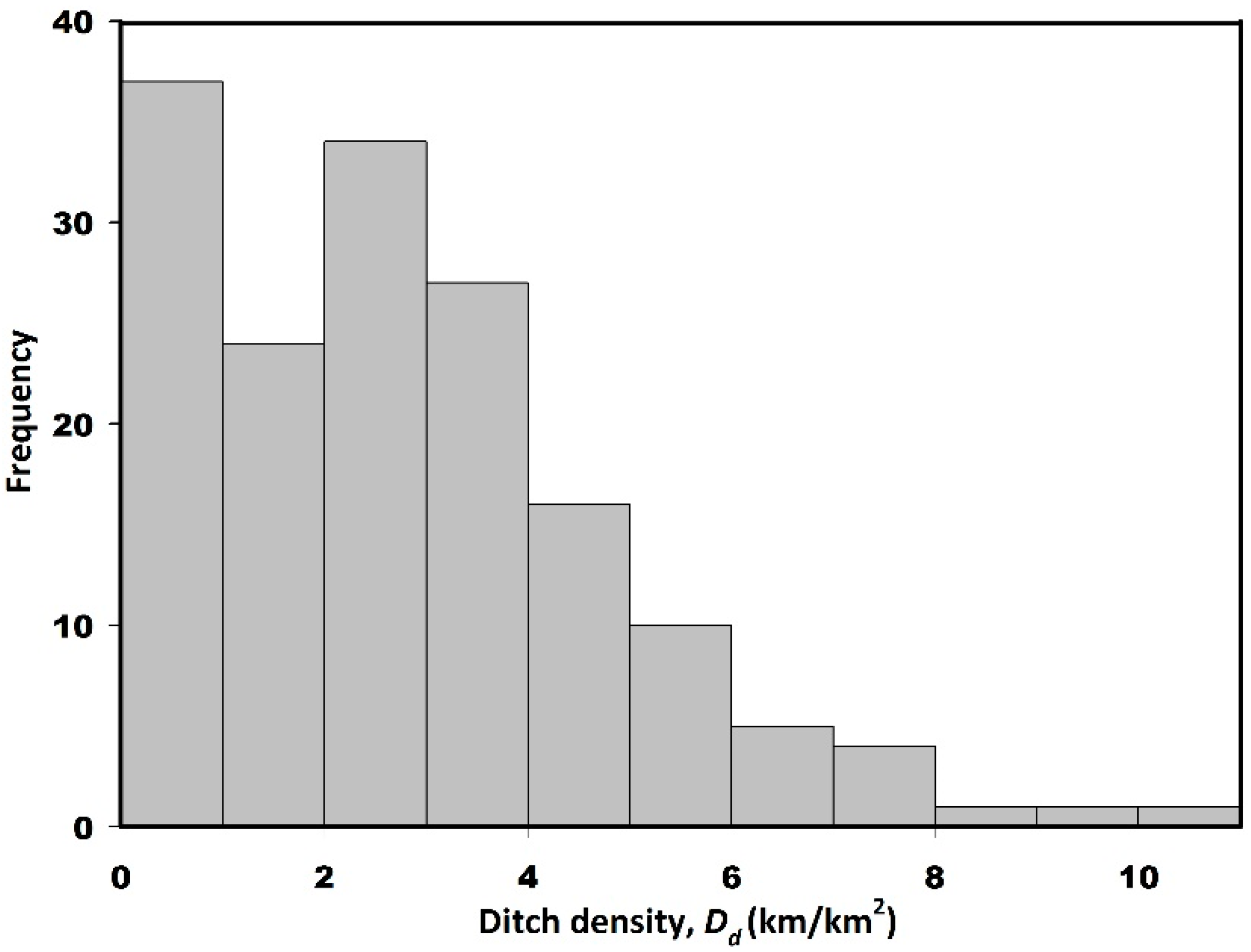
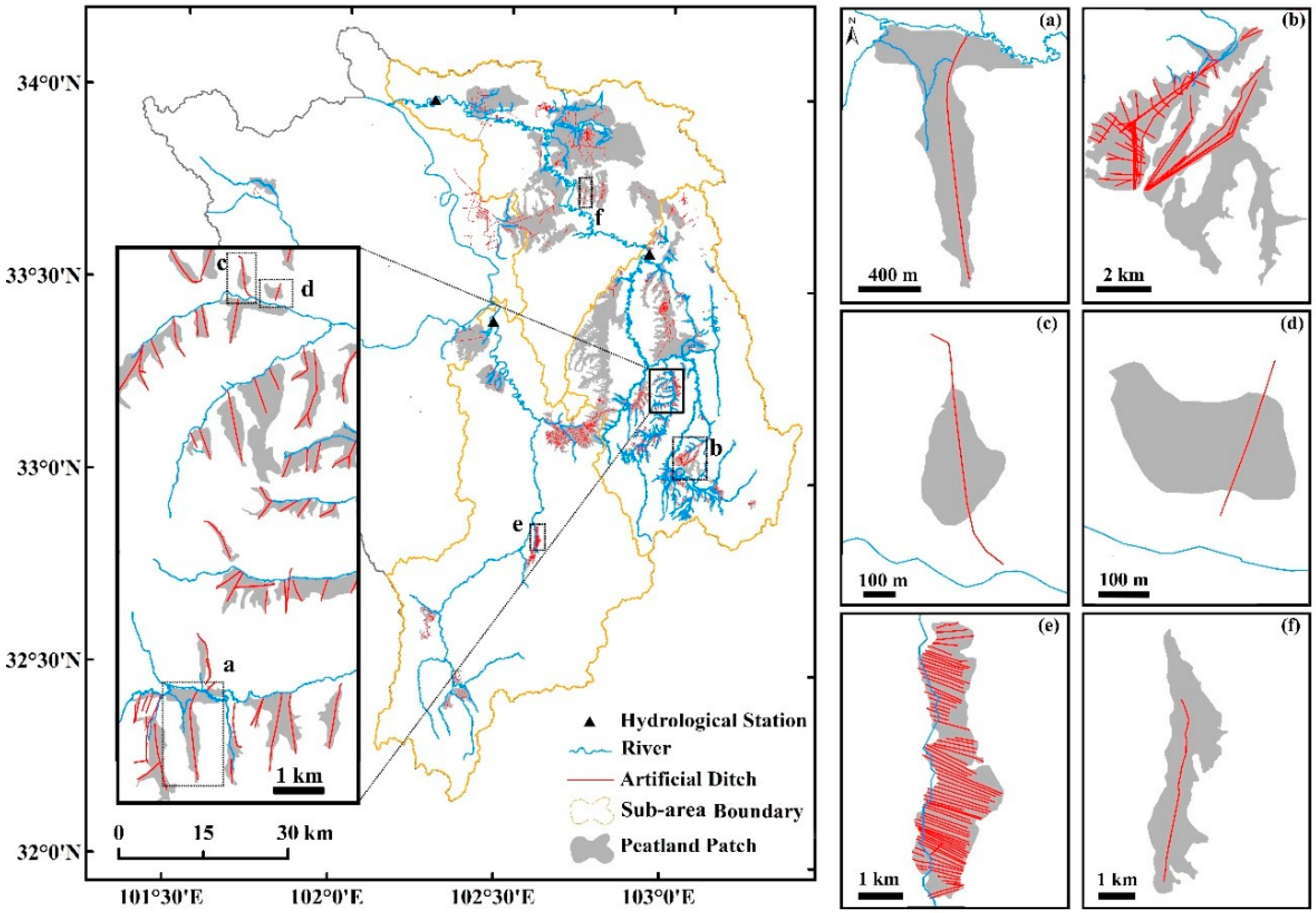
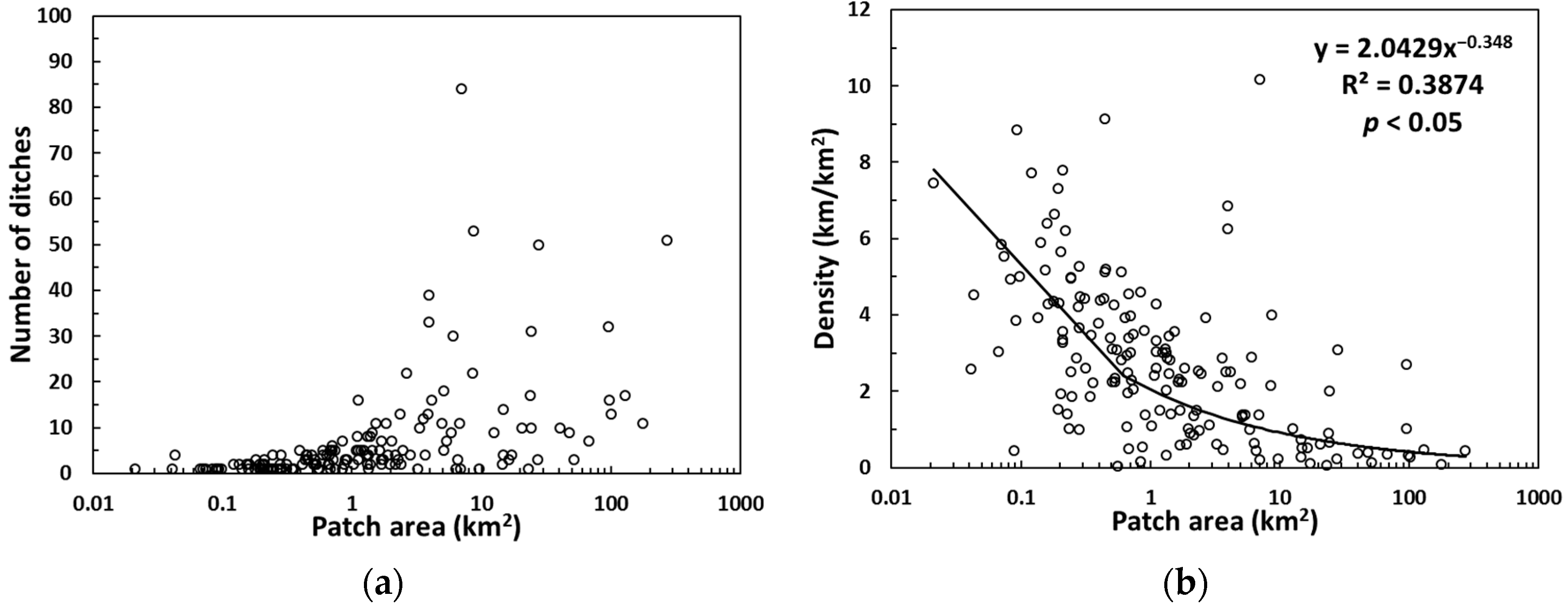
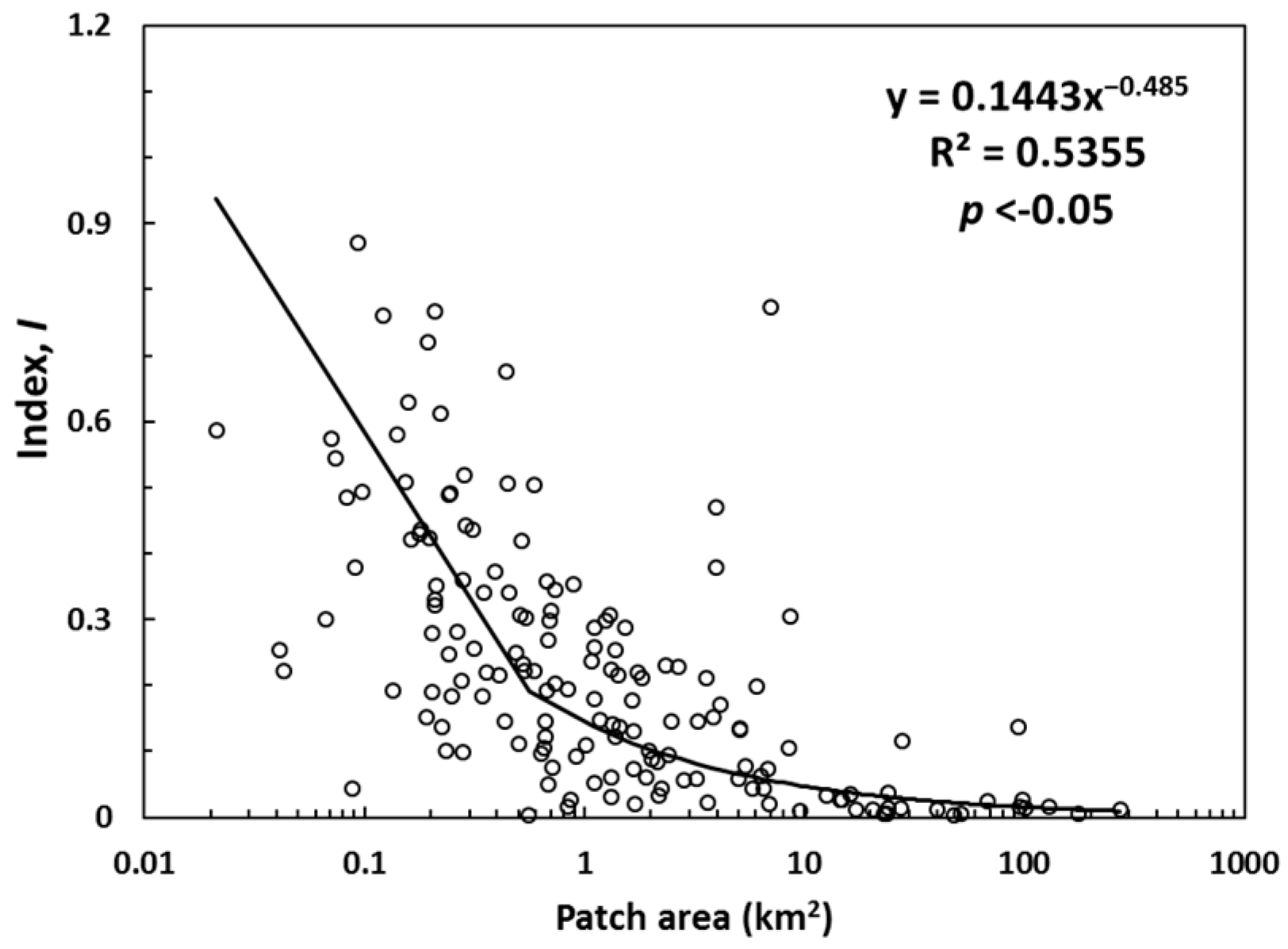
| Mean | St Dev | Maximum | Minimum | CV * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Length (m) | 1294 | 1439 | 18008 | 62.4 | 1.112 |
| Width (m) | 1.561 | 0.714 | 4.5 | 0.6 | 0.457 |
| Slope (m/m) | 0.019 | 0.028 | 0.224 | 0.0 | 1.434 |
| Class | Range of Area | a | b | R2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Class 1 | A > 90 | 0.0072 | 1.021 | 0.8577 | <0.05 |
| Class 2 | 40 < A < 90 | 0.0278 | 0.873 | 0.8314 | <0.05 |
| Class 3 | 10 < A < 40 | 0.0620 | 0.917 | 0.9449 | <0.05 |
| Class 4 | 2 < A < 10 | 0.3326 | 0.822 | 0.7791 | <0.05 |
| Class 5 | 1 < A < 2 | 0.7122 | 1.008 | 0.9088 | <0.05 |
| Class 6 | 0.3 < A < 1 | 1.7780 | 0.993 | 0.907 | <0.05 |
| Class 7 | A < 0.3 | 5.0489 | 0.523 | 0.4335 | <0.05 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Gao, P.; You, Y. Characterizing Hydrological Connectivity of Artificial Ditches in Zoige Peatlands of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water 2018, 10, 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101364
Li Z, Gao P, You Y. Characterizing Hydrological Connectivity of Artificial Ditches in Zoige Peatlands of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water. 2018; 10(10):1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101364
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhiwei, Peng Gao, and Yuchi You. 2018. "Characterizing Hydrological Connectivity of Artificial Ditches in Zoige Peatlands of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau" Water 10, no. 10: 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101364
APA StyleLi, Z., Gao, P., & You, Y. (2018). Characterizing Hydrological Connectivity of Artificial Ditches in Zoige Peatlands of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Water, 10(10), 1364. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101364






