Flood Forecasting Based on an Improved Extreme Learning Machine Model Combined with the Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methodologies
2.1. Flood Forecasting Based on the Data-Diven Model
2.2. Extreme Learning Machine
2.3. Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm
2.4. The Proposed ELM-BSA Model for Flood Forecasting
2.5. Performance Indexes
3. Case Study
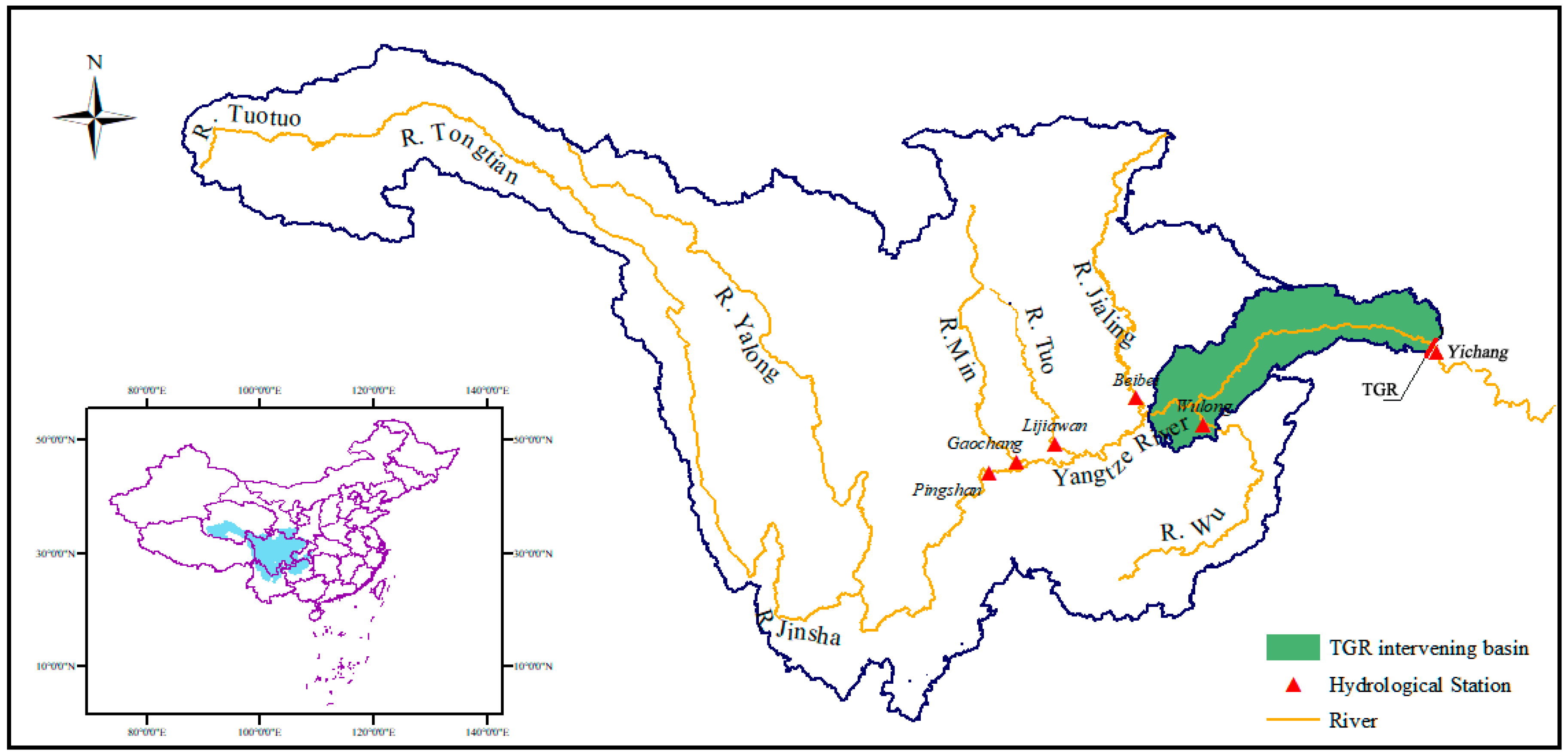
3.1. Study Area and Data
3.2. Establishment of the Flood Forecasting Models
3.3. Sensitivity Analysis of Different Input Sets
3.4. Sensitivity Analysis of Different Training Sample Sizes
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yaseen, Z.M.; El-Shafie, A.; Jaafar, O.; Afan, H.A.; Sayl, K.N. Artificial intelligence based models for stream-flow forecasting: 2000–2015. J. Hydrol. 2015, 530, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S. Measure of correlation between river flows using the copula-entropy method. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2013, 18, 1591–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Lu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Guo, S. Streamflow forecast uncertainty evolution and its effect on real-time reservoir operation. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 712–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Ye, L.; Chen, L.; Wang, Q.; Dai, L.; Zhou, J.; Singh, V.P.; Huang, M.; Zhang, J. Risk analysis of flood control reservoir operation considering multiple uncertainties. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 672–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costabile, P.; Costanzo, C.; Macchione, F. A storm event watershed model for surface runoff based on 2D fully dynamic wave equations. Hydrol. Process. 2013, 27, 554–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, M.; Cerdan, O.; Delestre, O.; Dupros, F.; James, F.; Cordier, S. Overland flow modeling with the shallow water equations using a well-balanced numerical scheme: Better predictions or just more complexity. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2015, 20, 04015012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bout, B.; Jetten, V.G. The validity of flow approximations when simulating catchment-integrated flash floods. J. Hydrol. 2018, 556, 674–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellos, V.; Tsakiris, G. A hybrid method for flood simulation in small catchments combining hydrodynamic and hydrological techniques. J. Hydrol. 2016, 540, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, T.; Zhang, C.; Sun, N. Data pre-analysis and ensemble of various artificial neural networks for monthly streamflow forecasting. Water 2018, 10, 628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ye, L.; Singh, V.; Asce, F.; Zhou, J.; Guo, S. Determination of input for artificial neural networks for flood forecasting using the copula entropy method. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2014, 19, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, G.J.; Dandy, G.C.; Maier, H.R. Input determination for neural network models in water resources applications. Part 1—Background and methodology. J. Hydrol. 2005, 301, 75–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.-J.; Tsai, M.-J. A nonlinear spatio-temporal lumping of radar rainfall for modeling multi-step-ahead inflow forecasts by data-driven techniques. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Lai, H.C. Adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system for the prediction of monthly shoreline changes in northeastern taiwan. Ocean Eng. 2014, 84, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Chang, F.J.; Guo, S.; Ba, H.; He, S. A robust recurrent anfis for modeling multi-step-ahead flood forecast of three gorges reservoir in the yangtze river. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. Discuss. 2017, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, B.; Gan, R.; Liu, G.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y. Monthly mean streamflow prediction based on bat algorithm-support vector machine. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2016, 21, 04015057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tayyab, M.; Zhou, J.; Dong, X.; Ahmad, I.; Sun, N. Rainfall-runoff modeling at jinsha river basin by integrated neural network with discrete wavelet transform. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2017, 129, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Fu, W. Streamflow forecasting using empirical wavelet transform and artificial neural networks. Water 2017, 9, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Niu, W.; Feng, Z.; Shen, J.; Chau, K. Daily reservoir runoff forecasting method using artificial neural network based on quantum-behaved particle swarm optimization. Water 2015, 7, 4232–4246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, F.J.; Chen, P.A.; Lu, Y.R.; Huang, E.; Chang, K.Y. Real-time multi-step-ahead water level forecasting by recurrent neural networks for urban flood control. J. Hydrol. 2014, 517, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deo, R.C.; Şahin, M. An extreme learning machine model for the simulation of monthly mean streamflow water level in eastern queensland. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2016, 188, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Sun, N.; Jia, B.; Tian, P. A novel decomposition-optimization model for short-term wind speed forecasting. Energies 2018, 11, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Xiao, Z.; Xia, X.; Zou, W.; Zhang, C. A hybrid model based on synchronous optimisation for multi-step short-term wind speed forecasting. Appl. Energy 2018, 215, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Zhu, Q.; Siew, C. Extreme learning machine: Theory and applications. Neurocomputing 2006, 70, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yaseen, Z.M.; Jaafar, O.; Deo, R.C.; Kisi, O.; Adamowski, J.; Quilty, J.; El-Shafie, A. Stream-flow forecasting using extreme learning machines: A case study in a semi-arid region in iraq. J. Hydrol. 2016, 542, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yao, H.F.; Ling, Q.H. An improved evolutionary extreme learning machine based on particle swarm optimization. Neurocomputing 2013, 116, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Civicioglu, P. Backtracking search optimization algorithm for numerical optimization problems. Appl. Math. Comput. 2013, 219, 8121–8144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.; Zhou, J.; Ye, L. Copula entropy coupled with artificial neural network for rainfall–runoff simulation. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2014, 28, 1755–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini, S.M.; Mahjouri, N. Integrating support vector regression and a geomorphologic artificial neural network for daily rainfall-runoff modeling. Appl. Soft Comput. 2016, 38, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.; Zhang, J. Real-time error correction method combined with combination flood forecasting technique for improving the accuracy of flood forecasting. J. Hydrol. 2014, 521, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Guo, S.; Liu, P.; Chen, G. Dynamic control of flood limited water level for reservoir operation by considering inflow uncertainty. J. Hydrol. 2010, 391, 126–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Water Resources (MWR). Regulation for Calculating Design Flood of Water Resources and Hydropower Projects; Chinese Shuili Shuidian Press: Beijing, China, 2008. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Huang, K.D.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J.; Singh, V.P. Flood hydrograph coincidence analysis for mainstream and its tributaries. J. Hydrol. 2018, 565, 341–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Sun, N.; Chen, L.; Ding, Y.; Zhou, J.; Zha, G.; Luo, G.; Dai, L.; Yang, X. Optimal operation of cascade reservoirs for flood control of multiple areas downstream: A case study in the upper Yangtze river basin. Water 2018, 10, 1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.L.; Hao, Z.C.; Li, T.Y. Flood coincidence risk analysis using multivariate copula functions. J. Hydrol. Eng. 2012, 17, 742–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P.; Guo, S.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, J. Copula-based method for multisite monthly and daily streamflow simulation. J. Hydrol. 2015, 528, 369–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.; Huang, K. Bayesian technique for the selection of probability distributions for frequency analyses of hydrometeorological extremes. Entropy 2018, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Singh, V.P. Entropy-based derivation of generalized distributions for hydrometeorological frequency analysis. J. Hydrol. 2018, 557, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
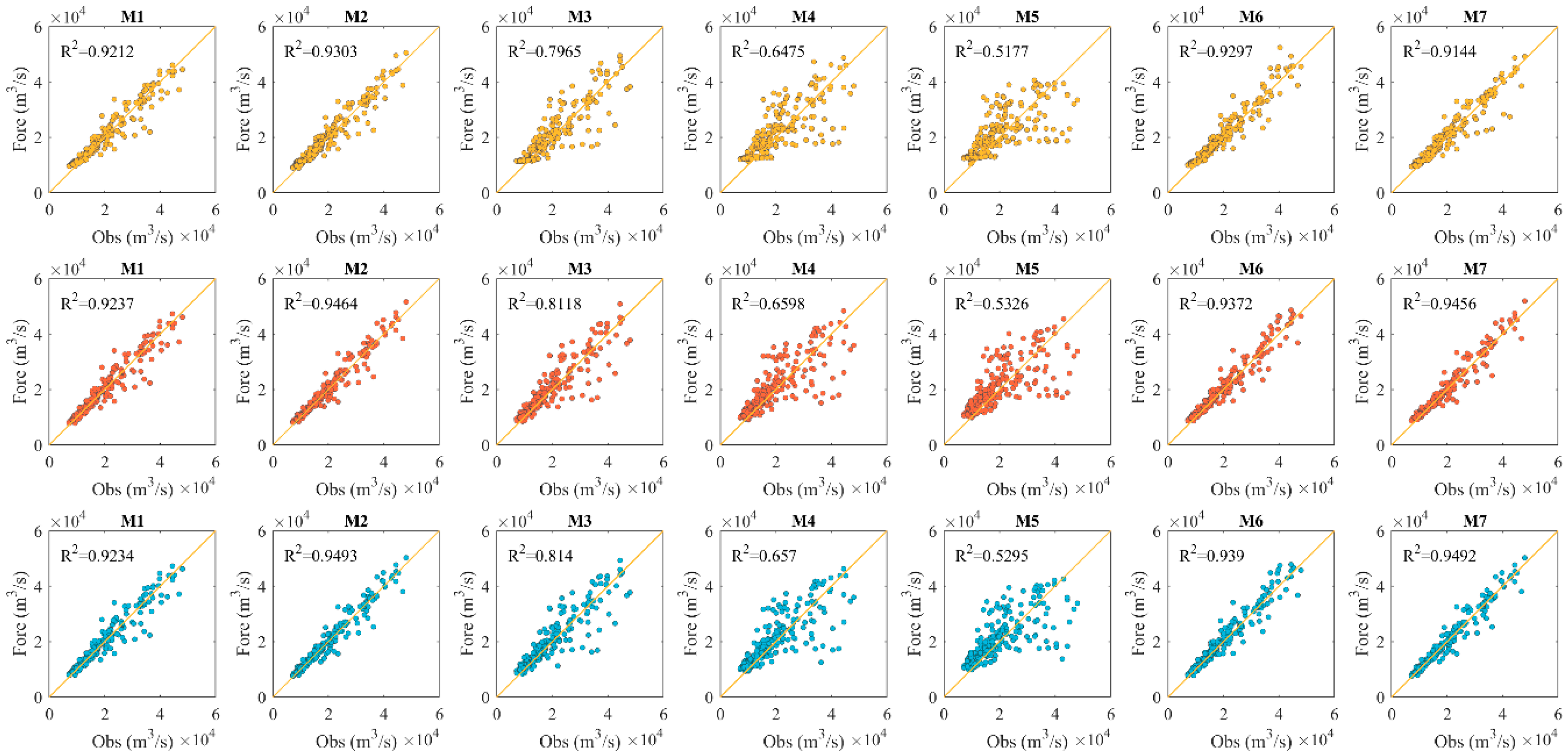


| Schemes | Number of Input Variables | Established Models |
|---|---|---|
| M1 | 1 | |
| M2 | 2 | |
| M3 | 3 | |
| M4 | 4 | |
| M5 | 5 | |
| M6 | 6 | |
| M7 | 7 |
| Schemes | Training Period | Testing Period | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| r | NSE | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | QR | r | NSE | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | QR | |
| GRNN | ||||||||||
| M1 | 0.9684 | 0.9377 | 2734 | 1939 | 0.9632 | 0.9598 | 0.9183 | 2735 | 1865 | 0.8319 |
| M2 | 0.9791 | 0.9584 | 2234 | 1573 | 0.9800 | 0.9645 | 0.9271 | 2583 | 1792 | 0.8571 |
| M3 | 0.9264 | 0.8579 | 4128 | 3012 | 0.8319 | 0.8925 | 0.7759 | 4530 | 3159 | 0.6597 |
| M4 | 0.8605 | 0.7399 | 5585 | 4152 | 0.6828 | 0.8047 | 0.6062 | 6006 | 4374 | 0.5084 |
| M5 | 0.7950 | 0.6314 | 6649 | 4972 | 0.6166 | 0.7195 | 0.4844 | 6872 | 5098 | 0.3992 |
| M6 | 0.9793 | 0.9589 | 2220 | 1592 | 0.9664 | 0.9642 | 0.9191 | 2722 | 1907 | 0.8319 |
| M7 | 0.9781 | 0.9565 | 2283 | 1617 | 0.9737 | 0.9562 | 0.9111 | 2853 | 1879 | 0.8487 |
| ELM | ||||||||||
| M1 | 0.9681 | 0.9371 | 2746 | 1956 | 0.9674 | 0.9611 | 0.9226 | 2663 | 1715 | 0.9286 |
| M2 | 0.9778 | 0.9561 | 2294 | 1562 | 0.9706 | 0.9729 | 0.9440 | 2265 | 1457 | 0.9580 |
| M3 | 0.9187 | 0.8439 | 4327 | 3088 | 0.8508 | 0.9010 | 0.8019 | 4260 | 2823 | 0.7311 |
| M4 | 0.8471 | 0.7175 | 5821 | 4271 | 0.6859 | 0.8123 | 0.6347 | 5785 | 4036 | 0.5420 |
| M5 | 0.7807 | 0.6094 | 6845 | 5139 | 0.5809 | 0.7298 | 0.4916 | 6824 | 4983 | 0.4370 |
| M6 | 0.9742 | 0.9490 | 2473 | 1788 | 0.9674 | 0.9681 | 0.9320 | 2495 | 1747 | 0.9076 |
| M7 | 0.9771 | 0.9547 | 2331 | 1608 | 0.9664 | 0.9724 | 0.9415 | 2315 | 1538 | 0.9160 |
| ELM-BSA | ||||||||||
| M1 | 0.9681 | 0.9372 | 2745 | 1957 | 0.9622 | 0.9609 | 0.9222 | 2669 | 1729 | 0.9286 |
| M2 | 0.9787 | 0.9578 | 2251 | 1519 | 0.9685 | 0.9743 | 0.9477 | 2188 | 1390 | 0.9454 |
| M3 | 0.9199 | 0.8461 | 4296 | 3062 | 0.8424 | 0.9022 | 0.8046 | 4231 | 2804 | 0.7311 |
| M4 | 0.8497 | 0.7220 | 5775 | 4227 | 0.6933 | 0.8106 | 0.6328 | 5800 | 3978 | 0.5798 |
| M5 | 0.7853 | 0.6167 | 6780 | 5093 | 0.5945 | 0.7276 | 0.4907 | 6830 | 4900 | 0.4580 |
| M6 | 0.9747 | 0.9501 | 2447 | 1762 | 0.9643 | 0.9690 | 0.9340 | 2458 | 1627 | 0.9328 |
| M7 | 0.9787 | 0.9578 | 2250 | 1516 | 0.9706 | 0.9743 | 0.9477 | 2188 | 1388 | 0.9454 |
| Model | R | NSE | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | QR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRNN (M6) | 0.9642 | 0.9191 | 2722 | 1906.7 | 0.8319 |
| ELM (M2) | 0.9729 | 0.9440 | 2265 | 1456.5 | 0.9580 |
| ELM-BSA (M7) | 0.9743 | 0.9477 | 2188 | 1387.7 | 0.9454 |
| Improvement (ELM-BSA vs. GRNN, %) | 1.05 | 3.12 | 19.63 | 27.22 | 13.64 |
| Improvement (ELM-BSA vs. ELM, %) | 0.15 | 0.40 | 3.42 | 4.72 | 1.32 |
| Model | GRNN | ELM | ELM-BSA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Proportion | Number | Proportion | Number | Proportion | |
| Beyond ±15% | 59 | 24.79 | 54 | 22.69 | 26 | 10.92 |
| Beyond ±20% | 34 | 14.29 | 22 | 9.24 | 13 | 5.46 |
| Beyond ±25% | 20 | 8.40 | 8 | 3.36 | 8 | 3.36 |
| Case | Year | Period | r | NSE | RMSE (m3/s) | MAE (m3/s) | QR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRNN | |||||||
| Case 1 | 1994–2005 | training | 0.9723 | 0.9451 | 2200 | 1507 | 0.9664 |
| testing | 0.9611 | 0.9201 | 2705 | 1924 | 0.8151 | ||
| Case 2 | 1995–2005 | training | 0.9731 | 0.9469 | 2082 | 1474 | 0.9681 |
| testing | 0.9561 | 0.9082 | 2900 | 1970 | 0.8193 | ||
| Case 3 | 1996–2005 | training | 0.9650 | 0.9255 | 2477 | 1742 | 0.9636 |
| testing | 0.9658 | 0.9255 | 2613 | 1911 | 0.8109 | ||
| Case 4 | 1997–2005 | training | 0.9740 | 0.9485 | 2130 | 1499 | 0.9856 |
| testing | 0.9652 | 0.9282 | 2565 | 1806 | 0.8277 | ||
| Case 5 | 1998–2005 | training | 0.9791 | 0.9584 | 2234 | 1573 | 0.9800 |
| testing | 0.9645 | 0.9271 | 2583 | 1792 | 0.8571 | ||
| ELM | |||||||
| Case 1 | 1994–2005 | training | 0.9711 | 0.9431 | 2241 | 1479 | 0.9517 |
| testing | 0.9741 | 0.9483 | 2175 | 1367 | 0.9538 | ||
| Case 2 | 1995–2005 | training | 0.9724 | 0.9455 | 2108 | 1414 | 0.9580 |
| testing | 0.9741 | 0.9482 | 2178 | 1385 | 0.9538 | ||
| Case 3 | 1996–2005 | training | 0.9726 | 0.9459 | 2110 | 1402 | 0.9608 |
| testing | 0.9740 | 0.9481 | 2181 | 1379 | 0.9538 | ||
| Case 4 | 1997–2005 | training | 0.9747 | 0.9500 | 2097 | 1409 | 0.9664 |
| testing | 0.9739 | 0.9477 | 2189 | 1380 | 0.9580 | ||
| Case 5 | 1998–2005 | training | 0.9778 | 0.9561 | 2294 | 1562 | 0.9706 |
| testing | 0.9729 | 0.9440 | 2265 | 1457 | 0.9580 | ||
| ELM-BSA | |||||||
| Case 1 | 1994–2005 | training | 0.9714 | 0.9436 | 2231 | 1465 | 0.9517 |
| testing | 0.9747 | 0.9496 | 2148 | 1352 | 0.9454 | ||
| Case 2 | 1995–2005 | training | 0.9727 | 0.9461 | 2097 | 1391 | 0.9597 |
| testing | 0.9748 | 0.9498 | 2143 | 1351 | 0.9454 | ||
| Case 3 | 1996–2005 | training | 0.9728 | 0.9463 | 2103 | 1392 | 0.9594 |
| testing | 0.9745 | 0.9491 | 2159 | 1368 | 0.9454 | ||
| Case 4 | 1997–2005 | training | 0.9748 | 0.9503 | 2091 | 1405 | 0.9652 |
| testing | 0.9745 | 0.9486 | 2169 | 1380 | 0.9454 | ||
| Case 5 | 1998–2005 | training | 0.9787 | 0.9578 | 2250 | 1516 | 0.9706 |
| testing | 0.9743 | 0.9477 | 2188 | 1388 | 0.9454 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Sun, N.; Zhou, C.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, Q. Flood Forecasting Based on an Improved Extreme Learning Machine Model Combined with the Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm. Water 2018, 10, 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101362
Chen L, Sun N, Zhou C, Zhou J, Zhou Y, Zhang J, Zhou Q. Flood Forecasting Based on an Improved Extreme Learning Machine Model Combined with the Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm. Water. 2018; 10(10):1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101362
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lu, Na Sun, Chao Zhou, Jianzhong Zhou, Yanlai Zhou, Junhong Zhang, and Qing Zhou. 2018. "Flood Forecasting Based on an Improved Extreme Learning Machine Model Combined with the Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm" Water 10, no. 10: 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101362
APA StyleChen, L., Sun, N., Zhou, C., Zhou, J., Zhou, Y., Zhang, J., & Zhou, Q. (2018). Flood Forecasting Based on an Improved Extreme Learning Machine Model Combined with the Backtracking Search Optimization Algorithm. Water, 10(10), 1362. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101362






