Conditioning Fixed-Bed Filters with Fine Fractions of Granulated Iron Hydroxide (µGFH)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Characterization of µGFH
2.2. Fixed Bed Conditioning
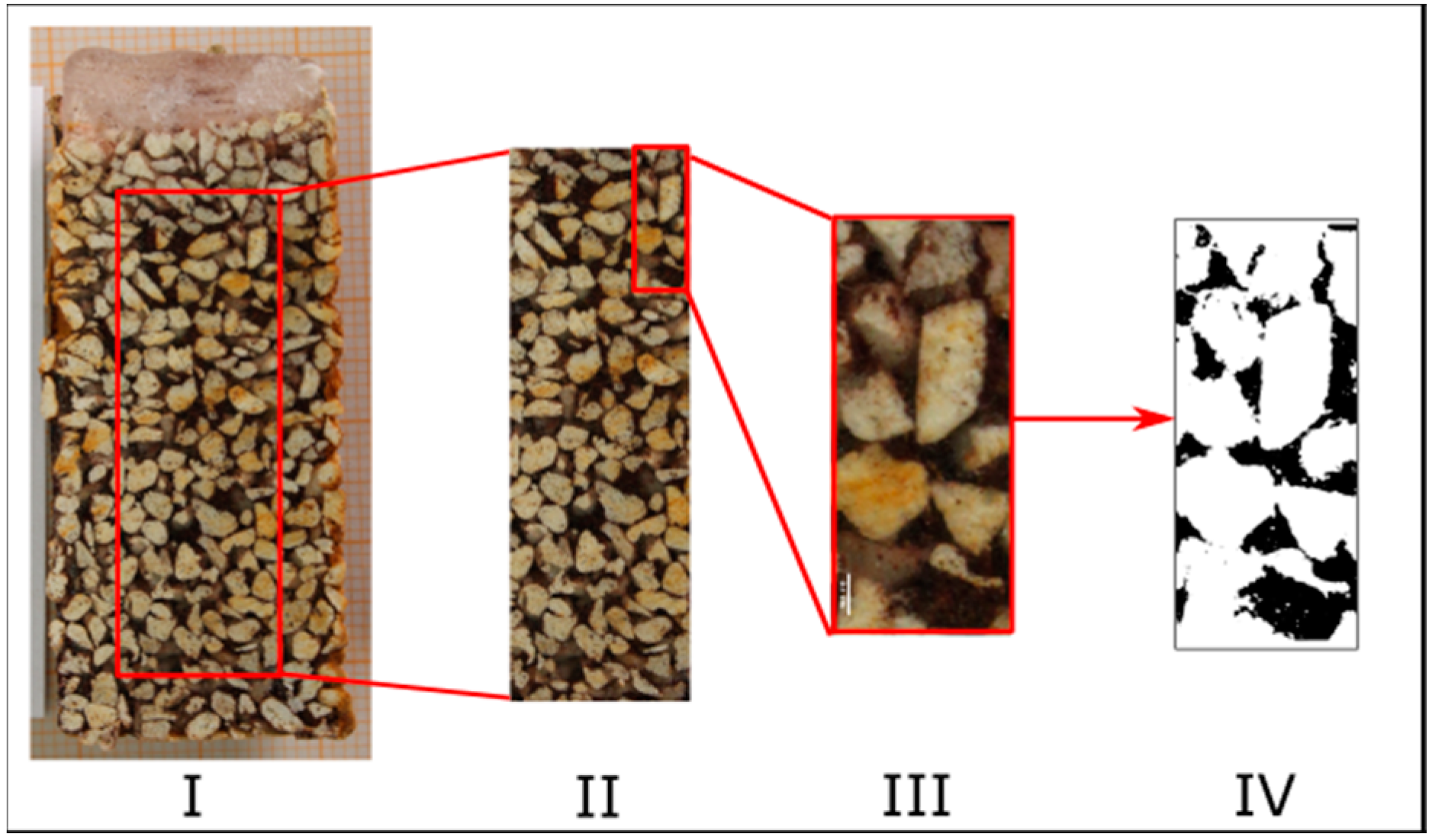
2.3. Image Analysis
2.4. Fixed Bed Adsorption Tests
3. Results
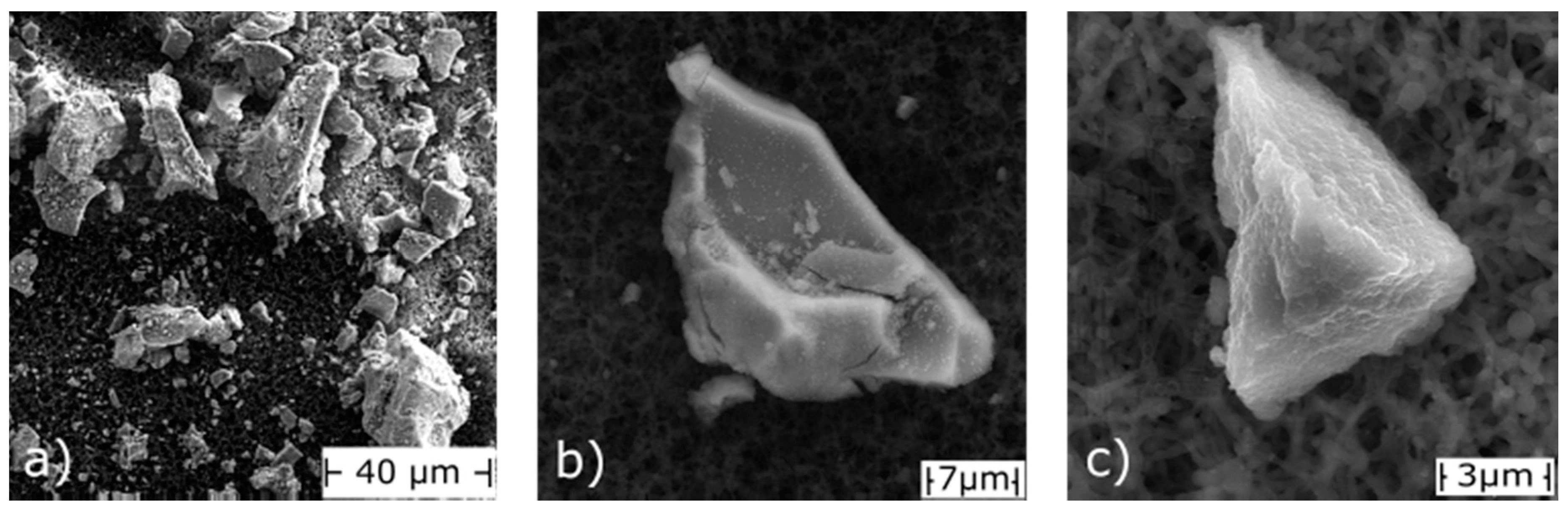
3.1. Physical Characterization
3.2. Carrier Material Selection
3.3. Optimization of Pumice Loading
3.4. Fixed Bed Adsorption
4. Conclusions
- BET analyses quantified surface areas of 300 m2/g for the fine fraction, equivalent to those of conventional GFH. Therefore, similar equilibrium adsorption capacities can be expected. The material consists of 30% (by mass) particles below 63 µm and very few particles above 120 µm.
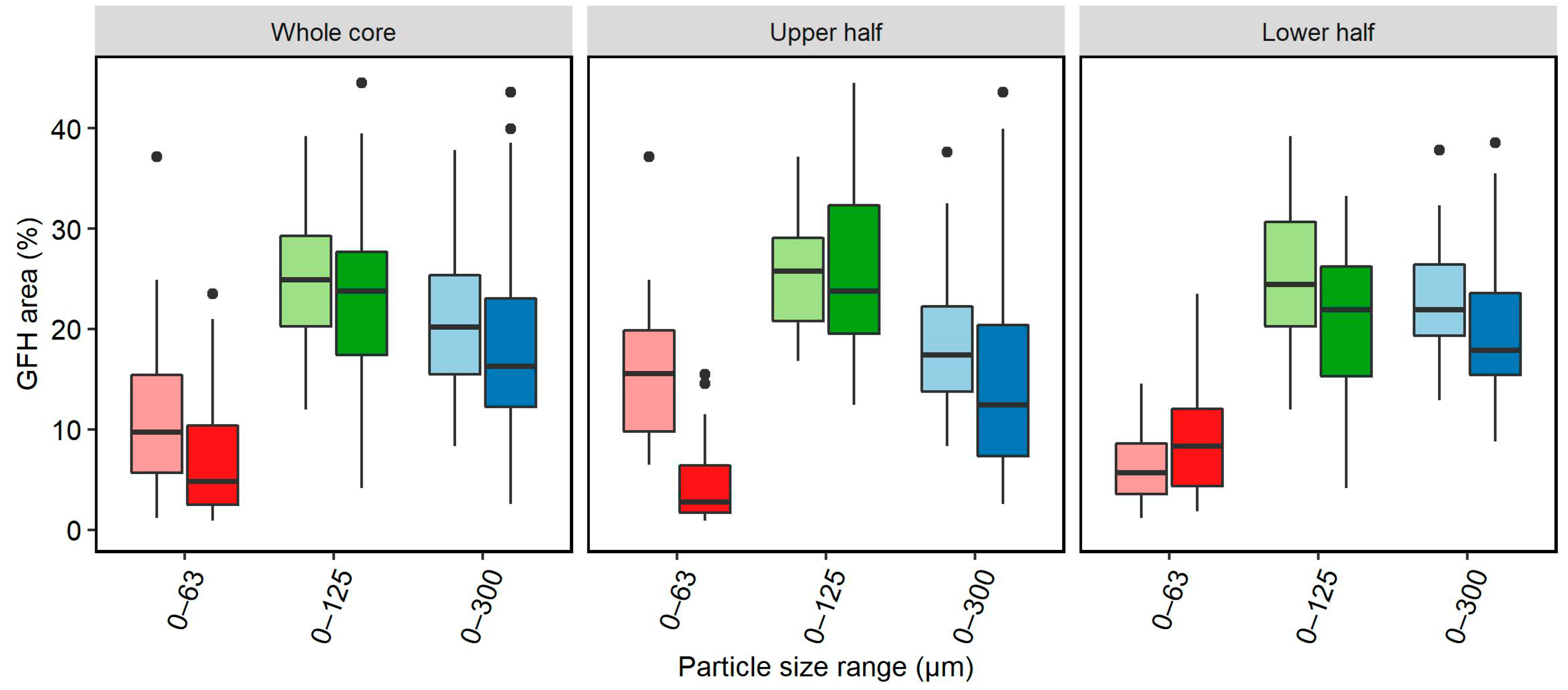
- For the utilization of µGFH in fixed-bed filtration, pumice proved to be a good carrier material. High embedment of the adsorbent (approximately 60 mg/g) and a homogeneous distribution could be observed when the pumice was pre-washed with deionized water (pH set to 8.5). The use of a concentrated stock suspension containing particle sizes 0–125 µm with pH set to 8.5 led to a homogeneous distribution on the carrier material.
- A method of image analysis of cross sections of frozen filter bed cores proved applicable for distribution analysis of fine fraction particle embedment in filter columns filled with a carrier material.
- A laboratory-scale fixed-bed filter with embedded µGFH showed breakthrough curves for phosphate similar to those of conventional GFH fixed-bed adsorbers. The use of µGFH did not lead to accelerated intra-particle diffusion. Loadings of 24 mg/g P were reached.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Driehaus, W.; Jekel, M.; Hildebrandt, U. Granular ferric hydroxide—A new adsorbent for the removal of arsenic from natural water. J. Water Serv. Res. Technol. 1998, 47, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlich, A.; Schimmelpfennig, S.; Baumgarten, B.; Genz, A.; Amy, G.; Worch, E.; Jekel, M. Predicting anion breakthrough in granular ferric hydroxide (GFH) adsorption filters. Water Res. 2008, 42, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sperlich, A.; Werner, A.; Genz, A.; Amy, G.; Worch, E.; Jekel, M. Breakthrough behavior of granular ferric hydroxide (GFH) fixed-bed adsorption filters: Modeling and experimental approaches. Water Res. 2005, 39, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genz, A.; Baumgarten, B.; Goernitz, M.; Jekel, M. NOM removal by adsorption onto granular ferric hydroxide: Equilibrium, kinetics, filter and regeneration studies. Water Res. 2008, 42, 238–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhl, A.S.; Altmann, J.; Zietzschmann, F.; Meinel, F.; Sperlich, A.; Jekel, M. Integrating Micro-Pollutant Removal by Powdered Activated Carbon into Deep Bed Filtration. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2014, 225, 1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altmann, J.; Ruhl, A.S.; Sauter, D.; Pohl, J.; Jekel, M. How to dose powdered activated carbon in deep bed filtration for efficient micropollutant removal. Water Res. 2015, 78, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haberer, K.; Normann-Schmidt, S. The Haberer Process: Combining Contact Flocculation, Filtration and PAC Adsorption. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 1991, 83, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löwenberg, J.; Zenker, A.; Krahnstöver, T.; Boehleret, M.; Baggenstosal, M.; Koch, G.; Wintgens, T. Upgrade of deep bed filtration with activated carbon dosage for compact micropollutant removal from wastewater in technical scale. Water Res. 2016, 94, 246–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.-K.; Keller, A.A. Removal of Arsenic and Phosphate from Aqueous Solution by Metal (Hydr-)oxide Coated Sand. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Badruzzaman, M.; Westerhoff, P.; Knappe, D.R.U. Intraparticle diffusion and adsorption of arsenate onto granular ferric hydroxide (GFH). Water Res. 2004, 38, 4002–4012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatnagar, A.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, Y.; Shin, Y.; Jeon, B.-H.; Kang, J.-W. Bromate removal from water by granular ferric hydroxide (GFH). J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 170, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, E.; Bhatnagar, A.; Ji, M.; Jung, W.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, S.-J.; Lee, G.; Song, H.; Choi, J.-Y.; Yang, J.-S.; et al. Defluoridation from aqueous solutions by granular ferric hydroxide (GFH). Water Res. 2009, 43, 490–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahr, C. Entfernung von Uran aus Trinkwasser durch Adsorption an Granuliertem Eisenhydroxid (GEH). Ph.D. Thesis, Technical University Berlin, Berlin, Germany, December 2012. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Jekel, M. Wasseraufbereitung: Grundlagen und Verfahren, 2nd ed.; Czekalla, C., Ed.; Deutscher Industrieverlag: München, Deutschland, 2017; Volume 6. (In German) [Google Scholar]
- Saha, B.; Bains, R.; Greenwood, F. Physicochemical characterization of granular ferric hydroxide (GFH) for arsenic(V) sorption from water. Separ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 40, 2909–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregg, S.J.; Sing, K.S. Adsorption, Surface Area and Porosity, 2nd ed.; Acad. Press: London, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. Products Used for Treatment of Water Intended for Human Consumption—Inorganic Supporting and Filtering Materials—Methods of Test (EN 12902). 2005. Available online: https://www.beuth.de/de/norm/din-en-12902/72862226 (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Rueden, C.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2002, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deutsches Institut für Normung e.V. Wasserbeschaffenheit—Bestimmung von Phosphor—Photometrisches Verfahren Mittels Ammoniummolybdat—Methods of Test (EN 6878). Available online: https://www.beuth.de/de/norm/din-en-iso-6878/71312882 (accessed on 4 September 2018).
- Patel, A. Desorption von Phosphat in GEH-Festbettfiltern: Einfluss von pH-Wert und Calcium. Master’s Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2016. (In German). [Google Scholar]
- Sperlich, A. Phosphate Adsorption onto Granular Ferric Hydroxide (GFH) for Wastewater Reuse. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, July 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Kersten, M.; Karabacheva, S.; Vlasova, N.; Branscheid, R.; Schurk, K.; Stanjek, H. Surface complexation modeling of arsenate adsorption by akagenéite (β-FeOOH)-dominant granular ferric hydroxide. Colloid Surf. A 2014, 448, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Material | Product (Supplier) | Main Component | Particle Size (mm) | Bulk Density (kg/m3) | Grain Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthracite | Hydroanthrasit-P (Rheinkalk Akdolit) | Carbon (92%) | 1.4–2.5 | 718 | 1250 |
| Coke | Filter coke H Type II (Evers GmbH) | Carbon (88%) | 1.4–2.5 | 523 | 1667 |
| Pumice | EVERZIT BI (Evers GmbH) | SiO2 (55%) | 0.8–1.5 | 375 | 1250 |
| Sand | Quartz sand (Sand-Schulz) | SiO2 (98%) | 1.0–2.0 | 1485 | 2625 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hilbrandt, I.; Ruhl, A.S.; Jekel, M. Conditioning Fixed-Bed Filters with Fine Fractions of Granulated Iron Hydroxide (µGFH). Water 2018, 10, 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101324
Hilbrandt I, Ruhl AS, Jekel M. Conditioning Fixed-Bed Filters with Fine Fractions of Granulated Iron Hydroxide (µGFH). Water. 2018; 10(10):1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101324
Chicago/Turabian StyleHilbrandt, Inga, Aki S. Ruhl, and Martin Jekel. 2018. "Conditioning Fixed-Bed Filters with Fine Fractions of Granulated Iron Hydroxide (µGFH)" Water 10, no. 10: 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101324
APA StyleHilbrandt, I., Ruhl, A. S., & Jekel, M. (2018). Conditioning Fixed-Bed Filters with Fine Fractions of Granulated Iron Hydroxide (µGFH). Water, 10(10), 1324. https://doi.org/10.3390/w10101324





