Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends and Characteristics of 31 Provincial Capital Cities in China during 1957–2016
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiments
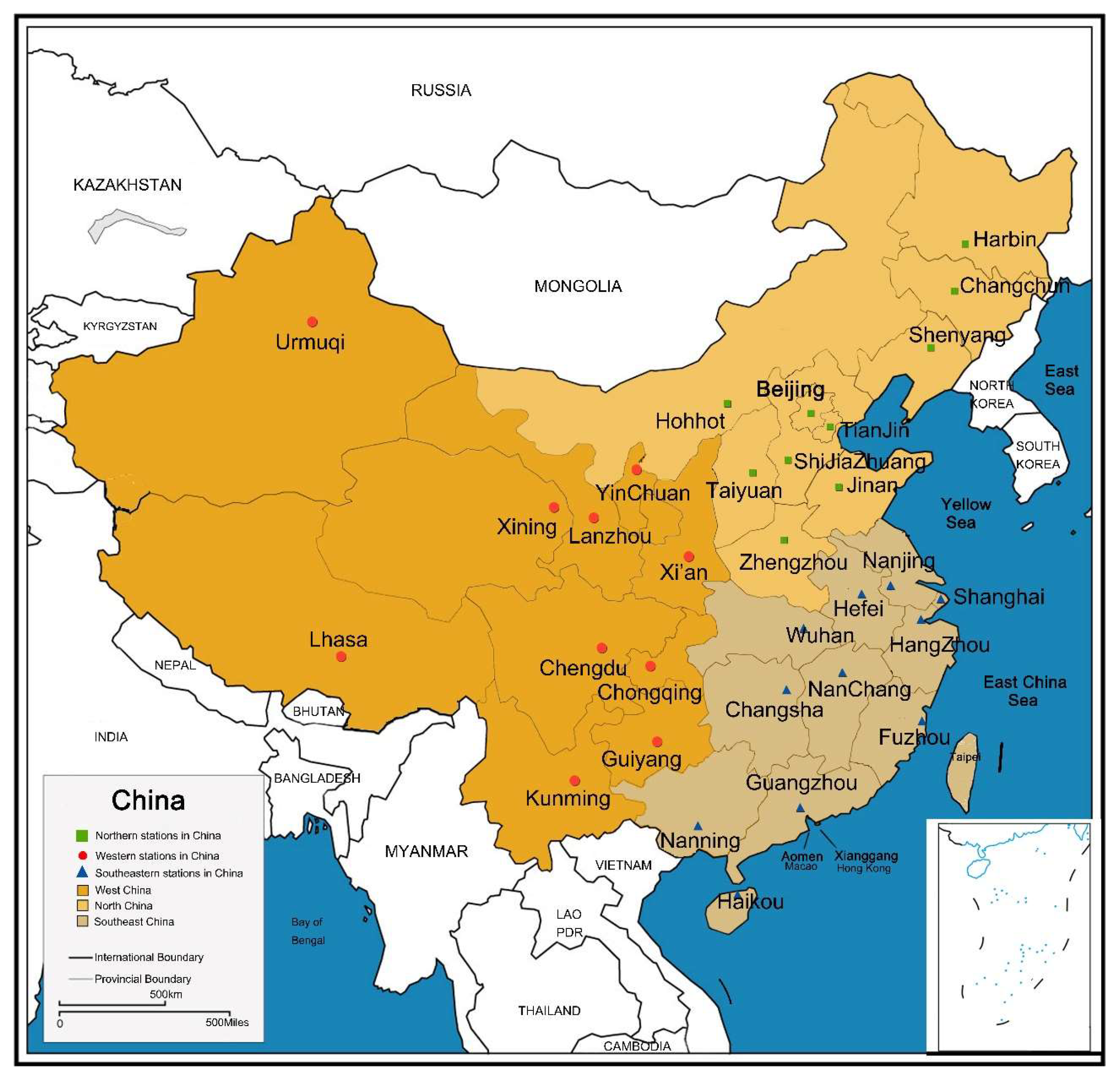
2.1. Data
2.2. Statistical Methods
2.2.1. Annual and Seasonal Mean Value of Atmospheric Visibility
2.2.2. Percentages of Atmospheric Visibility >20 Km and <10 Km Each Year
2.2.3. Lowest 20%, 50%, and Highest 20% Cumulative Percentiles of Atmospheric Visibility
2.2.4. Extinction Coefficient
2.2.5. Correlation Analysis
3. Results
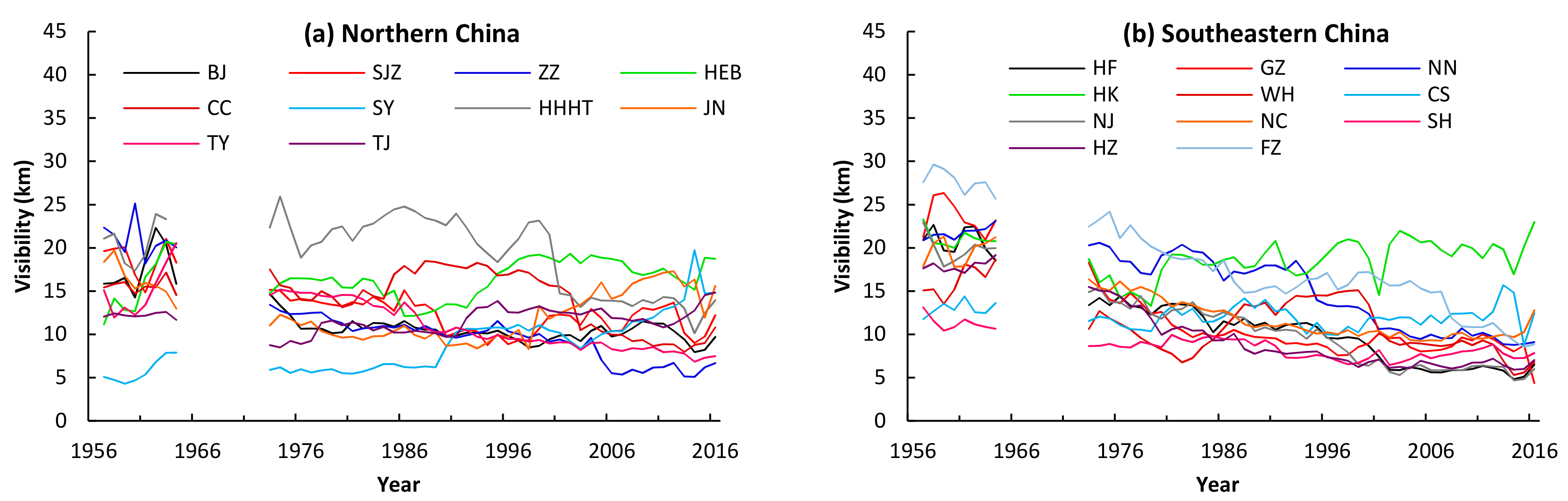
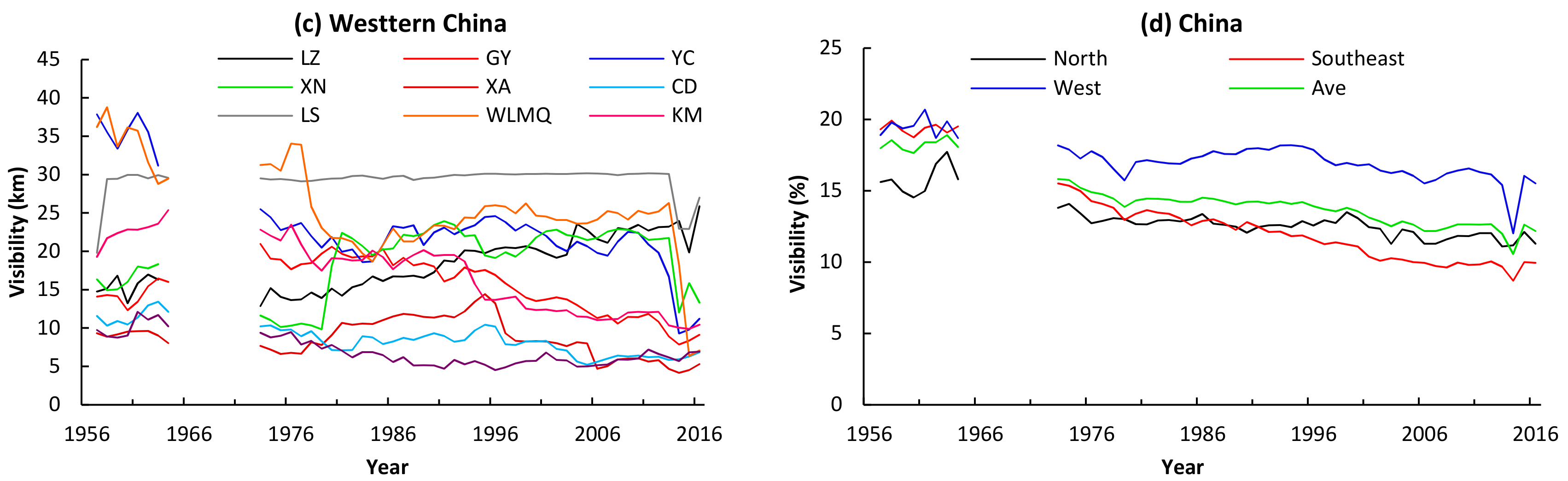
3.1. Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends
3.1.1. Annual Mean Values
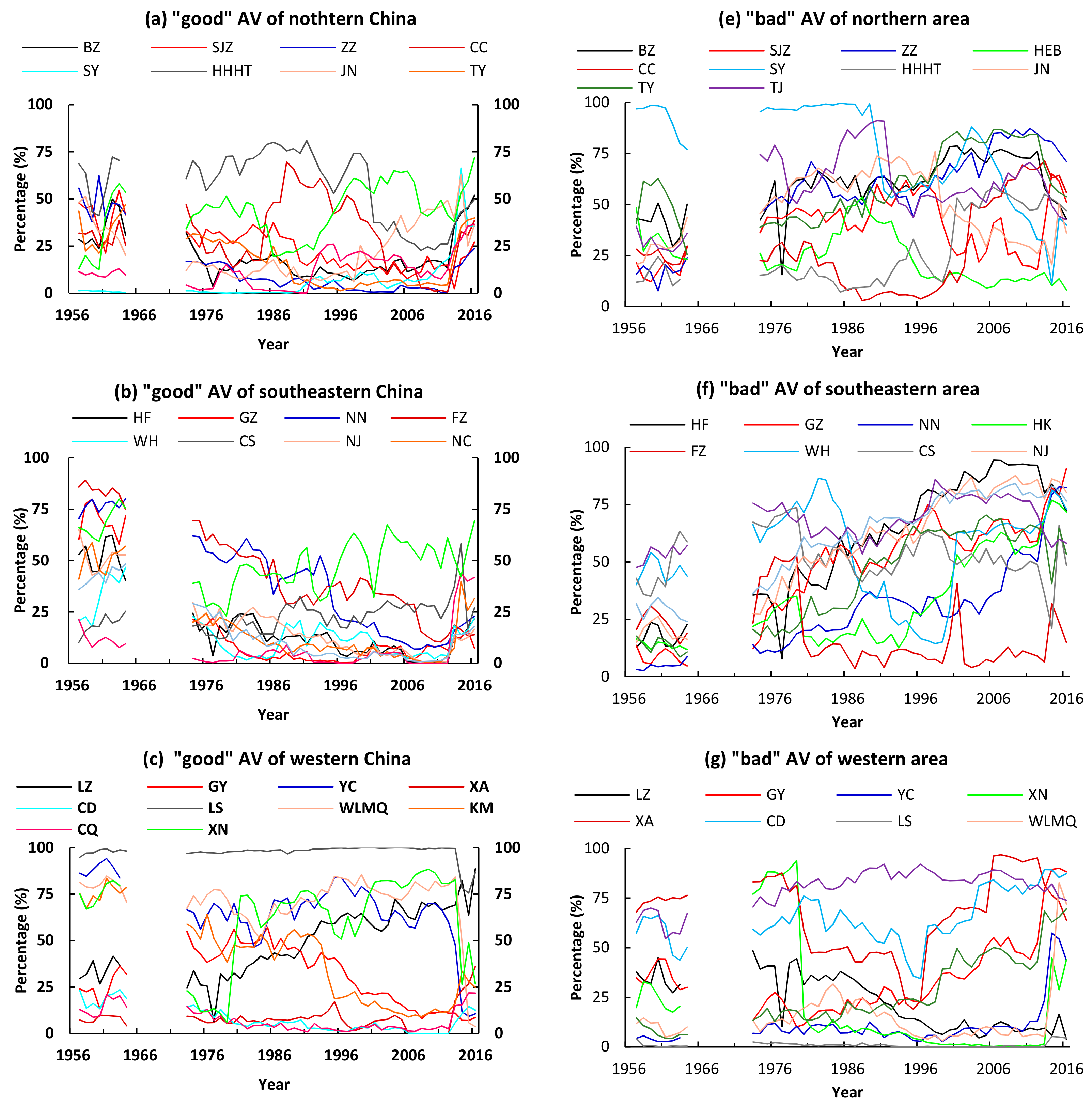
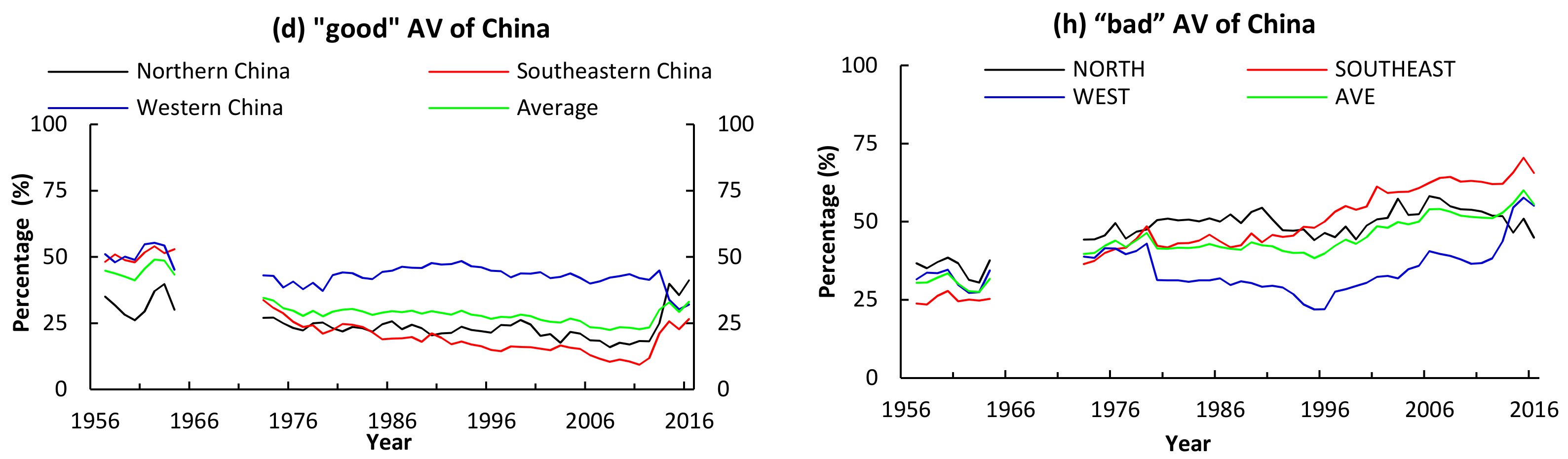
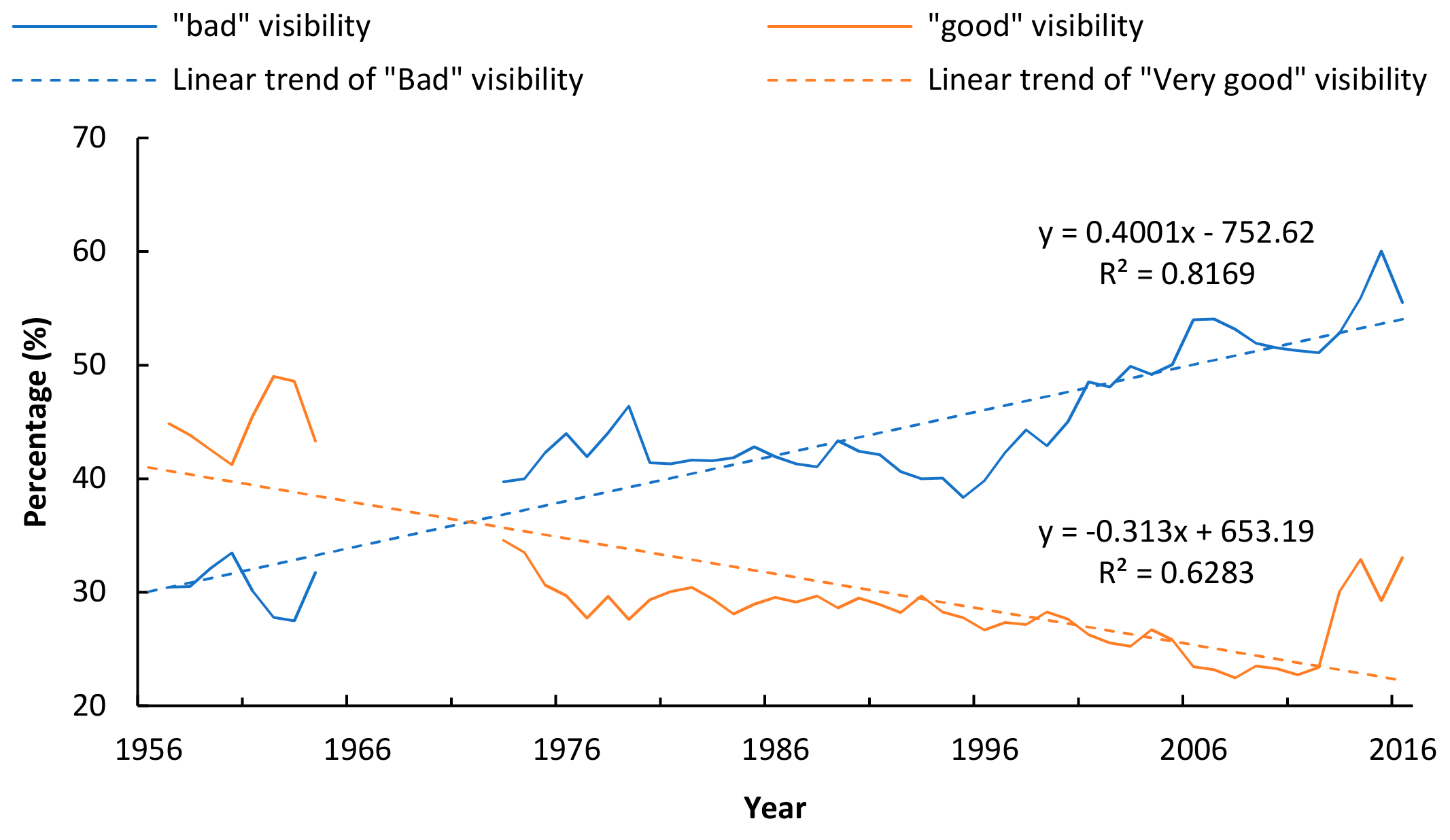
3.1.2. Percentages of ‘Good’ and ‘Bad’ Atmospheric Visibility
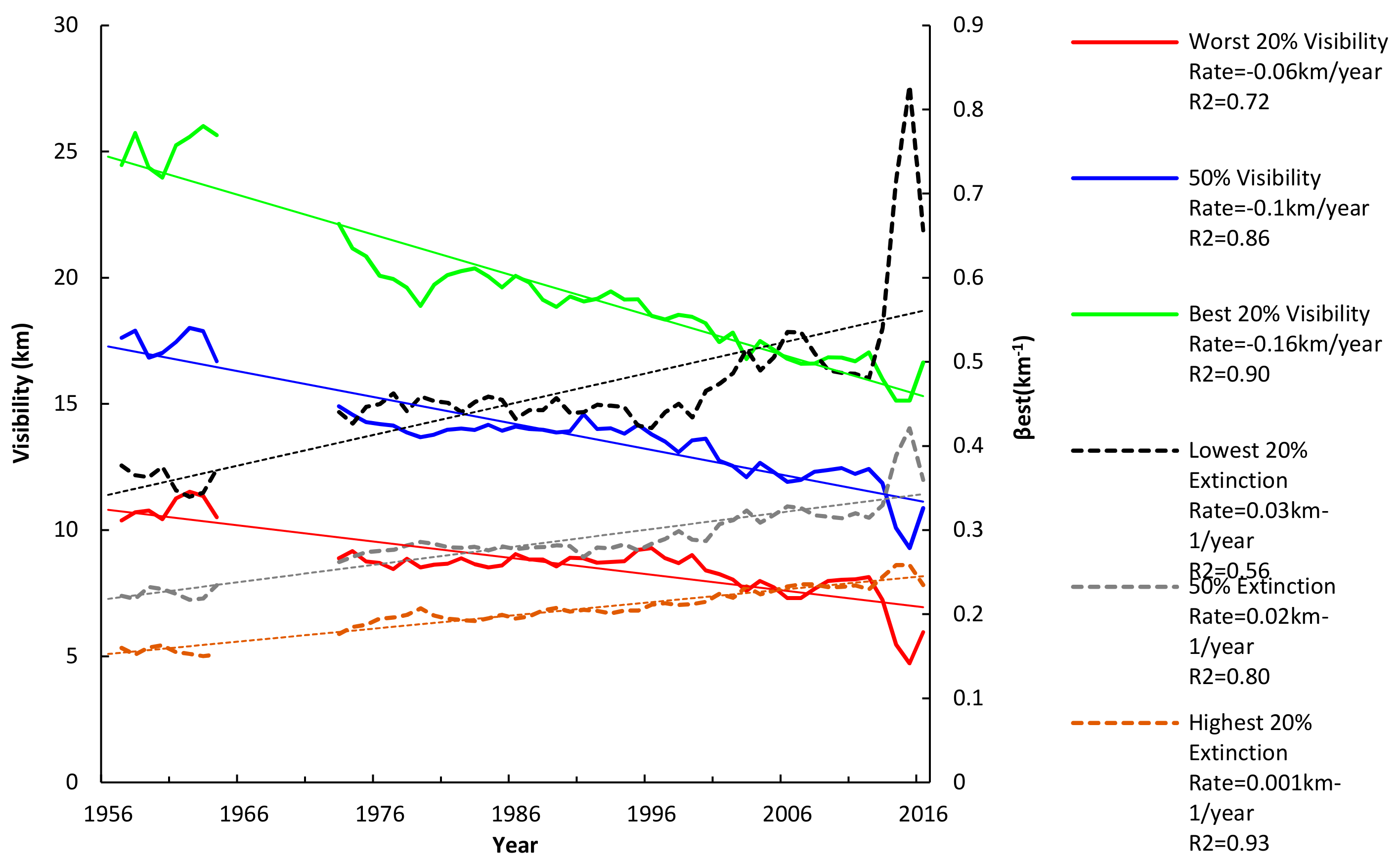
3.1.3. Cumulative Percentiles
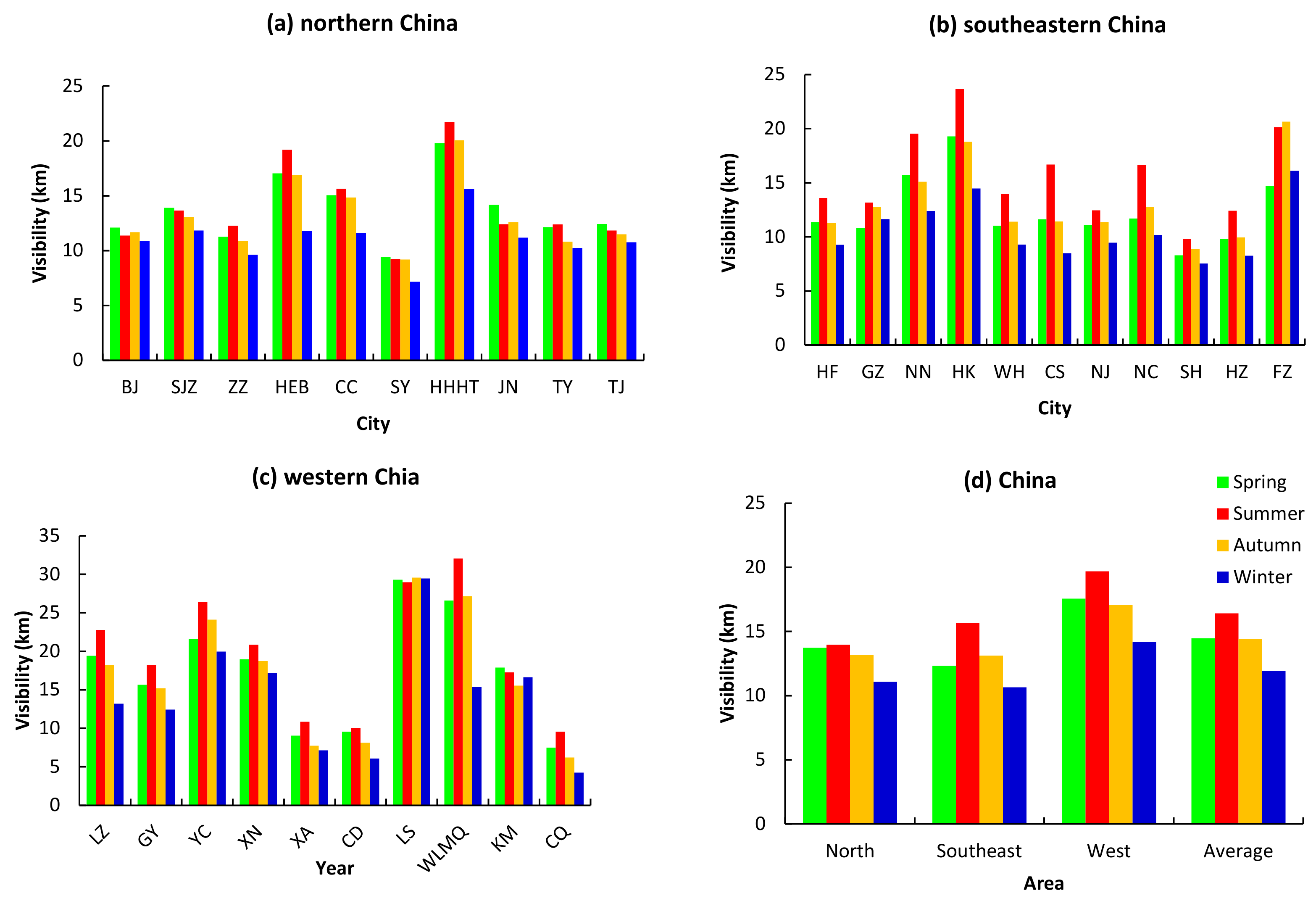
3.2. Seasonal Variation
3.3. Impact Factors
4. Discussion
4.1. Long-Term Trends of the Atmospheric Visibility in 31 Pccs of China
4.2. Seasonal Variation of Atmospheric Visibility in 31 PCCs of China
4.3. Special Characteristics of Atmospheric Visibility Trends in 31 PCCs of China
4.4. Factors Affecting Atmospheric Visibility
4.5. Application: Policy Recommendation
4.6. Limitation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koschmieder, H. Theorie der horizontalen Sichtweite Beit. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 1926, 12, 33–55. [Google Scholar]
- Environmental Protection Agency. Environmental Protection Agency Visibility in Mandatory Federal Class. I Areas; Office of Air Quality Planning and Standards Research Triangle Park: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, M.; Dorling, S. Visibility trends in the UK 1950–1997. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 3161–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Bloss, W.; Pope, F. 60 years of UK visibility measurements: Impact of meteorology and atmospheric pollutants on visibility. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 2085–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Du, K.; Wang, K.; Yuan, C.; Zhao, J. Long-term atmospheric visibility trend in Southeast China, 1973–2010. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Xing, Z.; Zhuang, B.; Du, K. Comparative study on long-term visibility trend and its affecting factors on both sides of the Taiwan Strait. Atmos. Res. 2014, 143, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Zhao, X. Long-term visibility trends and characteristics in the region of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei, China. Atmos. Res. 2011, 101, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fu, C.; Zhang, L.; Tang, J. Trends of visibility on sunny days in China in the recent 50 years. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, D.; Song, Y.; Liu, B. Visibility trends in six megacities in China 1973–2007. Atmos. Res. 2009, 94, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Quan, J.; Tie, X.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, D. Effects of meteorology and secondary particle formation on visibility during heavy haze events in Beijing, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 578–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Cao, J.; Tao, J.; Li, N.; Su, X.; Chen, L.W.A.; Wang, P.; Shen, Z.; Liu, S.; Dai, W. Long-term trends in visibility and at Chengdu, China. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Wang, Q.; Chow, J.C.; Wastson, J.G.; Tie, X.; Shen, Z.; Wang, P.; An, Z. Impacts of aerosol compositions on visibility impairment in Xi’an, China. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 59, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Tan, J.; Kan, H.; Zhao, N.; Song, W.; Song, G.; Chen, G.; Jiang, L.; Jiang, C.; Chen, R.; Chen, B. Visibility, air quality and daily mortality in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 3295–3300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thach, T.; Wong, C.; Chan, K.; Chau, Y.; Chung, Y.; Ou, C.; Yang, L.; Hedley, A. Daily visibility and mortality: Assessment of health benefits from improved visibility in Hong Kong. Environ. Res. 2010, 110, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, W.; Chen, R.; Song, W.; Kan, H. Daily visibility and hospital admission in Shanghai, China. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2011, 24, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Dickinson, R.E.; Liang, S. Clear sky visibility has decreased over land globally from 1973 to 2007. Science 2009, 323, 1468–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabetghadam, S.; Ahmadi-Givi, F.; Golestani, Y. Visibility trends in Tehran during 1958–2008. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.; Li, C.; Liu, Q. Visibility characteristics and the impacts of air pollutants and meteorological conditions over Shanghai, China. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2015, 187, 363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Huang, K.; Zhuang, G.; Fu, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, T.; Deng, C.; Fu, Q. A multi-year evolution of aerosol chemistry impacting visibility and haze formation over an Eastern Asia megacity, Shanghai. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, R.; Cao, J.; Chow, J.; Watson, J. Carbonaceous and Ionic Components of Atmospheric Fine Particles in Beijing and Their Impact on Atmospheric Visibility. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 492–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Tao, J.; Chan, C.; Cao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, R. Regression Analyses between Recent Air Quality and Visibility Changes in Megacities at Four Haze Regions in China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2012, 12, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Qiu, S.; Shang, J.; Wilfrid, O.M.F.; Liu, X.; Tian, H.; Boman, J. Impact of Relative Humidity and Water Soluble Constituents of PM2.5 on Visibility Impairment in Beijing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Yang, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, H. The contribution of socioeconomic factors to PM2.5 pollution in urban China. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 233, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, B.; Bi, J. Reforming China’s multi-level environmental governance: Lessons from the 11th Five-Year Plan. Environ. Sci. Policy 2012, 21, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, C.; Cheng, F.; Chang, S.; Lin, C.; Chou, C.C.K.; Chou, C.; Lin, Y. Analysis of the major factors affecting the visibility degradation in two stations. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2013, 63, 433–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Jin, A.Z.; Chafe, Z.A.; Pillarisetti, A.; Yu, T.; Shan, M.; Yang, X.; Li, H.; Liu, G.; Smith, K.R.; et al. The impact of household cooking and heating with solid fuels on ambient PM2.5 in peri-urban Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 165, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lin, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Duan, N.; Wu, X. Analysis of rural household energy consumption and renewable energy systems in Zhangziying town of Beijing. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.; Hirabayashi, S.; Bodine, A.; Greenfield, E. Tree and forest effects on air quality and human health in the United States. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayasooriya, V.M.; Ng, A.W.M.; Muthukumaran, S.; Perera, B.J.C. Green infrastructure practices for improvement of urban air quality. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 21, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irga, P.J.; Burchett, M.D.; Torpy, F.R. Does urban forestry have a quantitative effect on ambient air quality in an urban environment? Atmos. Environ. 2015, 120, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yli-Pelkonen, V.; Setälä, H.; Viippola, V. Urban forests near roads do not reduce gaseous air pollutant concentrations but have an impact on particles levels. Lands. Urban. Plan. 2017, 158, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Wang, P.; Ma, W.J.Z.; Zhu, S.; Pozzer, A.; Li, W. A high-resolution emission inventory of primary pollutants for the Huabei region, China. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 481–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quintana, P.J.E.; Khlighi, M.; Quinones, J.E.C.; Patel, Z.; Garcia, J.G.; Vergara, P.V.; Bryden, M.; Mantz, A. Traffic pollutants measured inside vehicles waiting in line at a major US-Mexico Port of Entry. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 622–623, 236–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, W.; Han, L. Understanding the dynamic of greenspace in the urbanized area of Beijing based on high resolution satellite images. Urban For. Urban Green. 2015, 14, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, F.; Grignetti, A.; Tinelli, A.; Lenz, A.; Ciccioli, P. General features of the Castelporziano test site. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manes, F.; Marando, F.; Capotorti, G.; Blasi, C.; Salvatori, E.; Fusaro, L.; Ciancarella, L.; Mircea, M.; Marchetti, M.; Chirici, G.; et al. Regulating Ecosystem Services of forests in ten Italian Metropolitan Cities: Air quality improvement by PM10 and O3 removal. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 67, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, P.E.J.; Maiheu, B.; Vankerkom, J.; Janssen, S. Improving local air quality in cities: To tree or not to tree? Environ. Pollut. 2013, 183, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmi, W.; Weber, C.; Riviere, E.; Blond, N.; Mehdi, L.; Nowak, D. Air pollution removal by trees in public green spaces in Strasbourg city, France. Urban For. Urban Green. 2016, 17, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Meteorological Administration. Observation and Forecasting Levels of Haze; China Meteorological Administration: Beijing, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S. Temporal and spatial visibility trends in the Sichuan Basin, China, 1973 to 2010. Atmos. Res. 2012, 112, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Environmental Protection Agency Regional Haze Regulations: Final Rule; EPA: Washington, DC, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, S. Characteristics and formation mechanism of a heavy air pollution episode caused by biomass burning in Chengdu, Southwest China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 473, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Lu, R.; Liu, C.; Yuan, L.; Shao, Y.; Zhu, B.; Lei, L. Seasonal variation of columnar aerosol optical properties and radiative forcing over Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 340–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Wu, J. The Different Characteristics of Sunny Visibility over Southwest China in Recent 50 Years. Proc. Environ. Sci. 2011, 10, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westervelt, D.; Horowitz, L.; Naik, V.; Tai, A.P.K.; Fiore, A.; Mauzerall, D. Quantifying PM2.5 meteorology sensitivities in a global climate model. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 142, 43–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, G.; Fu, J.; Jiang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Dong, D. Spatial Variation of the Relationship between PM2.5 Concentrations and Meteorological Parameters in China. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 684618, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteman, C.; Hoch, S.; Horel, J.; Charland, A. Relationship between particulate air pollution and meteorological variables in Utah’s Salt Lake Valley. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 94, 742–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dong, Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. Modern dust storms in China: An overview. J. Arid Environ. 2004, 58, 559–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Hu, J.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants in 31 provincial capital cities in China during 2013–2014. Environ. Int. 2014, 73, 413–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Wang, Y.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. Spatial and temporal variability of PM2.5 and PM10 over the North China Plain and the Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 95, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, S.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, T.; Chen, J.; Huang, G.; Li, X.; Wang, Q. Agricultural Fires and Their Potential Impacts on Regional Air Quality over China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 992–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yan, L.; Zhao, H. Seasonal Variations of Atmospheric Pollution and Air Quality in Beijing. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1753–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, K. Analyzing China’s productivity growth: Evidence from manufacturing industries. Econ. Syst. 2012, 36, 531–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escobedo, F.; Kroeger, T.; Wagner, J. Urban forests and pollution mitigation: Analyzing ecosystem services and disservices. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2078–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shu, M.; Ho, S.S.H.; Yu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhao, X. Effects of Chemical Composition of PM2.5 on Visibility in a Semi-rural City of Sichuan Basin. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, H.; Zhu, F.; Wang, S. Contribution to PM2.5 of Atmospheric Pollutant Emission from Thermal Power Sector and Emission Reduction Countermeasures. Electr. Power 2013, 46, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Grundström, M.; Pleijel, H. Limited effect of urban tree vegetation on NO2 and O3 concentrations near a traffic route. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 189, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Indicator | Effect | Sources |
|---|---|---|
| City size | ||
| Areas of urban built-up | Negative | [11,26] |
| Resident populations | Negative | [10,11,13] |
| Area of city paved roads | Negative | [8,11,12,25,27] |
| Industrial activities | ||
| Secondary industry GDP | Negative | [9,11,12] |
| Industrial dust Emission | Negative | [32,33] |
| Sulphur dioxide Emission | Negative | [32,33] |
| Industrial electricity consumption | Negative | [32,33] |
| Residents’ activities | ||
| Numbers of civilian vehicles | Negative | [8,11,12,25,27] |
| Total retail sales of consumer goods | Negative | [8,34] |
| Household electricity consumption | Negative | [34,35] |
| Urban greening | ||
| Rate of forest cover | Positive | [28,29,30,35] |
| Green Covered Area | Positive | [28,29,30,35] |
| Area of park | Positive | [28,29,30,35] |
| Area of green land | Positive | [30,31,36,37] |
| 1957–1964 | 1973–1976 | 1977–1986 | 1987–1996 | 1997–2006 | 2007–2016 | 1957–2016 | 60-Year Trend | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Northern China | ||||||||
| Beijing (BJ) | 16.25 | 12.72 | 10.89 | 10.22 | 9.60 | 10.33 | 11.37 | −1.26 |
| Shijiazhuang (SJZ) | 18.73 | 14.55 | 13.73 | 10.79 | 11.21 | 11.69 | 13.12 | −1.36 |
| Zhengzhou (ZZ) | 21.07 | 12.72 | 11.27 | 10.36 | 8.77 | 5.87 | 11.00 | −2.6 |
| Harbin (HEB) | 15.24 | 15.90 | 15.43 | 14.22 | 18.84 | 17.26 | 16.21 | 0.50 |
| Changchun (CC) | 15.47 | 15.64 | 14.84 | 17.73 | 13.86 | 9.19 | 14.28 | −1.06 |
| Shenyang (SY) | 5.59 | 5.90 | 5.96 | 9.09 | 10.04 | 12.55 | 8.55 | 1.43 |
| Hohhot (HHHT) | 19.99 | 22.37 | 22.45 | 21.77 | 17.31 | 13.41 | 19.19 | −1.62 |
| Jinan (JN) | 16.31 | 11.53 | 10.15 | 9.31 | 12.72 | 15.99 | 12.66 | 0.08 |
| Taiyuan (TY) | 14.75 | 14.87 | 13.90 | 10.36 | 8.96 | 8.13 | 11.37 | −1.53 |
| Tianjin (TJ) | 11.91 | 8.85 | 10.74 | 11.48 | 12.63 | 11.81 | 11.49 | 0.19 |
| Average | 15.39 | 13.50 | 12.94 | 12.53 | 12.39 | 11.62 | 12.92 | −0.71 |
| Southeastern China | ||||||||
| Hefei (HF) | 20.67 | 13.84 | 12.63 | 10.99 | 7.44 | 5.81 | 11.33 | −2.81 |
| Guangzhou (GZ) | 23.00 | 15.36 | 11.45 | 9.35 | 8.66 | 8.81 | 12.08 | −2.71 |
| Nanning (NN) | 21.34 | 19.86 | 18.52 | 16.78 | 11.30 | 9.67 | 15.63 | −2.52 |
| Haikou (HK) | 20.44 | 16.44 | 17.20 | 18.36 | 20.07 | 19.66 | 18.89 | 0.07 |
| Wuhan (WH) | 16.16 | 11.60 | 8.78 | 13.60 | 11.35 | 8.36 | 11.47 | −1.07 |
| Changsha (CS) | 13.07 | 11.62 | 11.71 | 12.31 | 11.37 | 12.66 | 12.15 | −0.06 |
| Nanjing (NJ) | 19.71 | 14.43 | 12.80 | 10.63 | 6.64 | 5.99 | 11.08 | −2.74 |
| Nanchang (NC) | 18.78 | 15.75 | 13.85 | 10.90 | 9.89 | 9.64 | 12.62 | −1.99 |
| Shanghai (SH) | 11.65 | 8.69 | 9.24 | 8.26 | 7.09 | 7.87 | 8.70 | −0.70 |
| Hangzhou (HZ) | 17.59 | 14.97 | 10.93 | 8.14 | 6.63 | 6.52 | 10.05 | −2.31 |
| Fuzhou (FZ) | 26.67 | 22.75 | 19.42 | 15.67 | 15.93 | 12.03 | 17.98 | −2.86 |
| Average | 19.01 | 15.03 | 13.32 | 12.27 | 10.58 | 9.73 | 12.91 | −1.79 |
| Western China | ||||||||
| Lanzhou (LZ) | 14.81 | 13.94 | 15.23 | 18.51 | 20.82 | 22.78 | 18.29 | 1.71 |
| Guiyang (GY) | 14.23 | 19.14 | 19.32 | 17.62 | 13.61 | 10.80 | 15.46 | −1.04 |
| Yinchuan (YC) | 33.73 | 23.98 | 20.96 | 23.04 | 21.73 | 19.28 | 23.18 | −2.45 |
| Xining (XN) | 16.83 | 10.77 | 17.38 | 21.99 | 21.41 | 21.07 | 19.20 | 1.39 |
| Xi’an (XA) | 9.01 | 7.05 | 9.64 | 12.26 | 7.90 | 5.60 | 8.73 | −0.50 |
| Chengdu (CD) | 11.41 | 10.02 | 8.21 | 9.13 | 7.13 | 6.02 | 8.39 | −1.00 |
| Lhasa (LS) | 27.57 | 29.40 | 29.52 | 29.82 | 30.09 | 29.39 | 29.35 | 0.22 |
| Urumqi (WLMQ) | 33.04 | 31.79 | 22.97 | 23.51 | 24.57 | 24.21 | 25.85 | −1.77 |
| Kuming (KM) | 22.16 | 22.44 | 18.99 | 17.87 | 12.38 | 11.34 | 16.79 | −2.43 |
| Chongqing (CQ) | 9.92 | 9.16 | 7.02 | 5.28 | 5.52 | 5.88 | 6.79 | −0.90 |
| Average | 19.16 | 17.77 | 16.92 | 17.90 | 16.52 | 15.64 | 17.19 | −0.64 |
| China | ||||||||
| Average | 17.97 | 15.42 | 14.36 | 14.17 | 13.08 | 12.25 | 14.30 | −1.07 |
| Category | Stations | Worst 20% | 50% | Highest 20% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visibility | Trend | Visibility | Trend | Visibility | Trend | ||
| North | BeiJing (BJ) | 4.96 | −0.45 | 10.29 | −0.74 | 15.48 | −2.64 |
| ShiJiaZhuang (SJZ) | 6.33 | −0.82 | 11.69 | −1.25 | 18.93 | −1.83 | |
| ZhengZhou (ZZ) | 6.29 | −1.58 | 10.08 | −2.23 | 15.53 | −3.55 | |
| Harbin (HEB) | 10.45 | 0.95 | 16.24 | 0.42 | 21.11 | 0.10 | |
| ChangChun (CC) | 9.95 | −0.65 | 14.42 | −1.04 | 17.71 | −3.39 | |
| ShenYang (SY) | 5.68 | 0.93 | 8.65 | 1.44 | 11.80 | 2.38 | |
| Hohhot (HHHT) | 11.98 | −1.00 | 19.26 | −2.48 | 27.43 | −1.37 | |
| JiNan (JN) | 5.75 | −0.15 | 11.86 | 0.04 | 18.73 | −0.46 | |
| TaiYuan (TY) | 6.72 | −0.76 | 10.57 | −0.87 | 14.93 | −2.80 | |
| TianJin (TJ) | 8.28 | 0.19 | 10.60 | −0.22 | 15.56 | 0.91 | |
| Average | 7.64 | −0.32 | 12.37 | −0.68 | 17.72 | −0.99 | |
| Southeast | HeFei (HF) | 6.06 | −1.63 | 10.29 | −2.51 | 16.23 | −3.97 |
| GuangZhou (GZ) | 7.34 | −2.24 | 12.17 | −2.84 | 15.96 | −3.69 | |
| NanNing (NN) | 9.90 | 0.65 | 15.19 | 0.49 | 21.32 | 0.37 | |
| HaiKou (HK) | 12.82 | 0.65 | 18.30 | 0.49 | 25.97 | 0.36 | |
| WuHan (WH) | 6.37 | −0.81 | 10.84 | −0.41 | 15.96 | −1.36 | |
| ChangSha (CS) | 4.49 | −0.71 | 10.44 | −0.11 | 19.01 | 0.74 | |
| NanJing (NJ) | 5.34 | −1.54 | 9.77 | −2.11 | 16.61 | −3.39 | |
| NanChang (NC) | 7.97 | −1.69 | 12.43 | −1.93 | 17.21 | −2.09 | |
| ShangHai (SH) | 4.44 | −0.37 | 9.31 | −0.24 | 12.08 | −1.00 | |
| HangZhou (HZ) | 4.31 | −1.13 | 8.88 | −2.21 | 14.99 | −3.21 | |
| FuZhou (FZ) | 10.43 | −2.52 | 17.42 | −3.57 | 25.16 | −3.94 | |
| Average | 7.26 | −1.30 | 12.28 | −1.69 | 18.27 | −2.35 | |
| West | LanZhou (LZ) | 10.14 | 1.76 | 18.91 | 2.84 | 26.61 | 1.81 |
| GuiYang (GY) | 8.94 | −0.60 | 14.32 | −0.97 | 22.40 | −1.93 | |
| YinChuan (YC) | 14.74 | −2.05 | 23.06 | −2.62 | 31.76 | −3.57 | |
| XiNing (XN) | 14.23 | −1.43 | 18.77 | −0.39 | 23.90 | −1.38 | |
| Xi’an (XA) | 4.20 | −0.33 | 8.41 | −0.55 | 12.43 | −0.38 | |
| ChengDu (CD) | 3.24 | −0.25 | 7.75 | −0.77 | 13.12 | −1.39 | |
| Lhasa (LS) | 29.37 | −0.01 | 29.83 | −0.19 | 30.02 | −0.19 | |
| WuLuMuQi (WLMQ) | 14.53 | −0.27 | 29.45 | −1.88 | 34.11 | −4.47 | |
| KuMing (KM) | 11.01 | −1.58 | 15.69 | −2.24 | 22.91 | −3.86 | |
| ChongQing (CQ) | 2.46 | −0.26 | 5.26 | −0.63 | 10.78 | −1.07 | |
| Average | 11.29 | −0.23 | 17.14 | −0.63 | 22.80 | −1.25 | |
| China | Average | 8.67 | −0.64 | 13.87 | −1.02 | 19.54 | −1.58 |
| Urban Size | Urban Greening | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Resident Populations | Areas of Urban Built-Up | Area of City Paved Roads | Rate of Forest Cover | Area of Green Land | Areas of Park | Green Covered Area | |
| Annual mean visibility | −0.379 * | −0.372 * | −0.464 ** | 0.010 | 0.094 | 0.144 | −0.085 |
| Bad visibility rate | 0.432 * | 0.436 * | 0.511 ** | −0.029 | −0.014 | −0.142 | 0.178 |
| Good visibility rate | −0.32 | −0.31 | −0.411 * | 0.022 | 0.101 | 0.118 | −0.094 |
| Residents’ activities | Industrial activities | ||||||
| Numbers of civilian vehicles | Total retail sales of consumer goods | Household electricity consumption | Secondary industry GDP | SO2 emission of industry | Industrial dust Emission | Industrial electricity consumption | |
| Annual mean visibility | −0.422 * | −0.375 * | −0.410 * | −0.444 * | −0.19 | −0.08 | −0.417 * |
| Bad visibility rate | 0.502 ** | 0.422 * | 0.469 ** | 0.508 ** | 0.21 | 0.11 | 0.469 ** |
| Good visibility rate | −0.342 * | −0.31 | −0.35 | −0.395 * | −0.18 | −0.07 | −0.371 * |
| Air Pollutants | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | PM10 | SO2 | CO | NO2 | O3 | |
| Annual mean visibility | −0.464 ** | −0.22 | −0.10 | −0.32 | −0.429 * | 0.10 |
| Bad visibility rate | 0.444* | 0.22 | −0.04 | 0.27 | 0.434 * | 0.01 |
| Good visibility rate | −0.436* | −0.21 | −0.16 | −0.32 | −0.384 * | 0.11 |
| Meteorological factors | ||||||
| Temperature | Air pressure | Humidity | Wind speed | Rain fall | Dew temperature point | |
| Annual mean visibility | −0.30 | −0.498** | −0.36 | 0.408 * | −0.21 | −0.21 |
| Bad visibility rate | 0.376 * | 0.456 * | 0.35 | −0.437 * | 0.25 | 0.15 |
| Good visibility rate | −0.28 | −0.467 ** | −0.33 | 0.406 * | −0.19 | −0.13 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fu, W.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, Q.; Qi, J.; Dang, E.; Wang, M.; Dong, J. Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends and Characteristics of 31 Provincial Capital Cities in China during 1957–2016. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080318
Fu W, Chen Z, Zhu Z, Liu Q, Qi J, Dang E, Wang M, Dong J. Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends and Characteristics of 31 Provincial Capital Cities in China during 1957–2016. Atmosphere. 2018; 9(8):318. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080318
Chicago/Turabian StyleFu, Weicong, Ziru Chen, Zhipeng Zhu, Qunyue Liu, Jinda Qi, Emily Dang, Minhua Wang, and Jianwen Dong. 2018. "Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends and Characteristics of 31 Provincial Capital Cities in China during 1957–2016" Atmosphere 9, no. 8: 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080318
APA StyleFu, W., Chen, Z., Zhu, Z., Liu, Q., Qi, J., Dang, E., Wang, M., & Dong, J. (2018). Long-Term Atmospheric Visibility Trends and Characteristics of 31 Provincial Capital Cities in China during 1957–2016. Atmosphere, 9(8), 318. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos9080318





