Abstract
The inter-comparison of regional air quality models is an effective way to understand uncertainty in ambient pollutant concentrations simulated using various model configurations, as well as to find ways to improve model performance. Based on the outcomes and experiences of Japanese projects thus far, a new model inter-comparison project called Japan’s study for reference air quality modeling (J-STREAM) has begun. The objective of J-STREAM is to establish reference air quality modeling for source apportionment and effective strategy making to suppress secondary air pollutants including PM2.5 and photochemical ozone in Japan through model inter-comparison. The first phase focuses on understanding the ranges and limitations in ambient PM2.5 and ozone concentrations simulated by participants using common input datasets. The second phase focuses on issues revealed in previous studies in simulating secondary inorganic aerosols, as well as on the three-dimensional characteristics of photochemical ozone as a new target. The third phase focuses on comparing source apportionments and sensitivities under heavy air pollution episodes simulated by participating models. Detailed understanding of model performance, uncertainty, and possible improvements to urban-scale air pollution involving secondary pollutants, as well as detailed sector-wise source apportionments over megacities in Japan are expected.
1. Introduction
Although air quality over Japan has been gradually improving, ambient concentrations of photochemical oxidants (mostly ozone) and PM2.5 still exceed Japanese Environmental Quality Standards [1]. These are secondary pollutants, formed in the atmosphere through complex photochemical reactions [2]. Nonlinear relationships with emissions of their precursors pose challenges to develop effective strategies to suppress their ambient concentrations. Three-dimensional air quality modeling, which involves a regional chemical transport model representing complex photochemical reactions, as well as a regional meteorology model and emission inventories, is a well-established tool to derive effective strategies. However, it requires great efforts to prepare input datasets, configure settings, and obtain reliable results. It would be useful to establish air quality modeling that can serve as a reference. We believe that model inter-comparison is a valuable way to establish reference air quality modeling based on collective participant experience and knowledge. Particularly, model inter-comparison is the only available way to check if the models are working well to evaluate sensitivities of specific emission sources on ambient pollutant concentrations because observations indicating them are hardly available.
2. History of Model Inter-Comparison Related to Japan
Inter-comparisons of regional chemical transport models have been performed in several research projects worldwide. Examples of the model inter-comparisons conducted for Asia and Japan are listed in Table 1. Initiated in 1998, the model inter-comparison study of long-range transport and sulfur deposition in East Asia (MICS-Asia) was a pioneer work of model inter-comparison for East Asia [3]. Its first phase focused on sulfur deposition. The concentrations and wet deposition amounts of sulfur dioxide and sulfate simulated by eight models were compared. Source-receptor relationships and critical factors affecting model performance were investigated. The targets were extended in the second phase of MICS-Asia initiated in 2003. O3 and its related precursors, aerosols, acid deposition, global inflow of pollutants and precursors to Asia, model sensitivities to aerosol parameterization, and emission fields were analyzed in detail [4]. The outcomes from the first and second phases of MICS-Asia have provided considerable valuable understanding and knowledge on model performance and possible improvements in East Asia. The third phase of MICS-Asia (MICS-Asia3) has started in 2010. The overall scope is model performance under highly polluted conditions. The role of long-range transport is jointly evaluated with the second phase of the task force on Hemispheric Transport of Air Pollution (HTAP2) [5], whereas model performance over polluted megacities in East Asia, including Beijing and Tokyo, is also included in the targets.

Table 1.
Outlines of model inter-comparisons conducted for Asia and Japan.
Inter-comparisons of regional chemical transport models have been also performed in Japan in 2008 at the beginning. Morino et al. [6] compared the ambient concentrations of O3 and PM2.5 components simulated by the four models applied to the monitoring campaign FAMIKA (Fine Aerosol Measurement and Modeling In Kanto Area) conducted in the Kanto area (Tokyo and surrounding prefectures) in summer 2007. All the models commonly underestimated concentrations of elemental carbon (EC) and organic aerosol (OA), whereas large variations were seen in the simulated fine particulate nitrate concentration among the models. The ensemble approach using the concentrations simulated by the four models was effective to achieve better results for the PM2.5 components, excepting OA [9]. In this first model inter-comparison performed in Japan, all the participating models were the Community Multiscale Air Quality (CMAQ) modeling system [10], but used different domains, different emission inputs, different meteorology inputs, and different boundary concentrations. Such a comparison is important because researchers usually choose their domains independently, and use their own tools to prepare the input datasets. Uncertainty originating from the modeling procedures of each researcher should be evaluated. On the other hand, this makes interpreting the differences in simulated values among the participating models difficult.
Based on their experience, a model inter-comparison project called the Urban Air Quality Model Inter-Comparison Study in Japan (UMICS) was conducted from 2010 to 2012. The objectives of UMICS were to investigate ranges in concentrations of PM2.5 components simulated by participating models, and to seek possible ways to improve model performance through extensive sensitivity analyses based on participant expertise. Common target domains were specified, and common emission inputs, meteorology inputs, and boundary concentrations were provided to the participants. Monitoring data of PM2.5 components obtained at several stations in the Kanto area were used to compare with simulated results. The first phase of UMICS focused on EC [7]. Seven different versions of CMAQ commonly underestimated the EC concentration. The results of sensitivity analyses implied that emissions and boundary concentrations were critical factors affecting model performance for EC, while Shimadera et al. [11] indicated that the model simulated the effect of long-range transport of EC well. RAQM2 [12] had a distinctive performance, which appeared to originate from the treatment of vertical diffusion. The second phase of UMICS focused on secondary inorganic aerosols [8]. Five CMAQs reproduced the sulfate concentration well, but significantly overestimated fine particulate nitrate concentrations. The results of sensitivity analyses implied that NH3 emissions and dry deposition velocities of gaseous NH3 and HNO3 are critical factors on model performance on fine particulate nitrate. The third phase of UMICS focused on OA [13,14]. Five CMAQs significantly underestimated OA concentrations. The results of sensitivity analyses implied that emissions of semi-volatile and condensable organic compounds are critical factors affecting model performance on OA.
Valuable findings obtained in UMICS have been carried over to subsequent modeling studies. In particular, issues related to semi-volatile and condensable organic compounds have been extensively studied in Japan [15] and worldwide, e.g., [16]. On the other hand, issues related to vertical diffusion and secondary inorganic aerosols remain unsolved. Although the implications of dry deposition velocities of NH3 and HNO3 were adapted to the air quality study in Japan [15,17], specific measurements are urgently required to increase our understanding of the behavior of fine particulate nitrate. In addition, photochemical ozone was not targeted, and comparisons with models other than CMAQ was scarce in UMICS. Moreover, the Japanese government has recognized the importance of reliable air quality modeling in order to consider effective strategies to suppress the concentrations of secondary pollutants. Therefore, we decided to initiate another model inter-comparison project called J-STREAM in 2016.
3. Objective of J-STREAM
The objective of J-STREAM is to establish reference air quality modeling for source apportionment and effective strategy-making to suppress secondary air pollutants, including PM2.5 and photochemical ozone in Japan. Our intentions for reference air quality modeling are as follows. Currently, both researchers and the government are trying to apply air quality modeling to consider effective strategies for improving air quality in Japan. It is important to develop a common understanding on how to use air quality modeling, and how to understand simulated results. There are many model settings, options, and a wide variety of model inputs. The possible range in simulated results under various configurations should be understood. At the same time, the limitations of results simulated by currently available models should be properly recognized, as no model has perfect performance. This could avoid excessive effort to obtain unrealistically improved model performance, and could avoid the development of ineffective strategies derived from a misunderstanding of model results.
Participants could have a motivation to check their model performances. They may be confident that their modeling has no errors if their results are within an acceptable range based on other participants. However, if the collective results commonly deviate from observed values, this implies common scientific challenges to improving currently available models. On the contrary, if results of some participants significantly differ from those of other participants, there may be problems in their modeling, or their models may have distinct performance due to specific embedded capabilities. Model inter-comparison could provide an opportunity to make such a judgment on a participant’s model performance. In addition, participants could obtain information and tips regarding the latest air quality modeling through comparisons and discussions with fellow participants. Findings and suitable model configurations will be documented as a reference for the future use of air quality modeling conducted by both researchers and the government.
We also endeavor to solve the remaining issues identified in previous model inter-comparison projects, as described above. Specific measurements will be conducted to see thermodynamic equilibrium, temporal variations, and deposition velocities of secondary inorganic aerosols and their related precursors. In addition, photochemical ozone has been added as a major target. High ozone concentrations in Japan are associated with not only chemical, but also various physical, processes. Meteorological patterns [18], vertical profiles [19], and transport from remote regions could all be critical factors. Three-dimensional characteristics of photochemical ozone and the role of various physical processes will be captured by measuring vertical profiles with ozonesondes and via monitoring at a remote island. These measurements could provide valuable datasets to validate and improve models that cannot be obtained by regular government monitoring. Moreover, there are large uncertainties in emission inventories available in Japan. Possible improvements will be applied based on deviations between observations and participants’ simulated results.
J-STREAM will have three phases for three years. The first phase focuses on understanding the ranges and limitations of current model results simulated by participants. Simulated concentrations of PM2.5 components, photochemical ozone, and related precursors are analyzed through comparisons with government monitoring data. The second phase will go into details of secondary inorganic aerosols and photochemical ozone by using data obtained in the specific measurements. The third phase will focus on model performance, as well as source sensitivities and apportionments, calculated by models for selected heavy pollution episodes.
J-STREAM could provide complementary understanding and knowledge to MICS-Asia3 activities. MICS-Asia3 will focus mainly on regional-scale transport and source apportionments of ambient pollutants in Asia, while J-STREAM will focus on urban-scale air pollution and detailed sector-wise source apportionments over megacities in Japan. MICS-Asia3 will mainly use the Acid Deposition Monitoring Network in East Asia (EANET) observations that monitor background ambient pollutant concentrations to evaluate model performance on regional transport around Japan, whereas J-STREAM will evaluate model performance on air pollution over megacities in Japan using ambient pollutant concentrations densely monitored there. The contributions of regional transport from the continent and various domestic emission sources to air quality over megacities in Japan will be clarified by combining understanding and knowledge obtained in MICS-Asia3 and J-STREAM. In addition, some researchers are participating in both MICS-Asia3 and J-STREAM. This could provide an opportunity to deepen our understanding on their model performance across both scales and to exchange their knowledge with other participants across both projects.
4. Methodology
The methodology for the first phase of J-STREAM is introduced in this section. It follows the concepts of previous UMICS, in which common domains were specified, and common input datasets were provided to all participants. The basic concept should be consistent for subsequent phases, but some changes may be applied based on progress and findings.
4.1. Target Periods
Fiscal year 2013 (from April 2013 to March 2014) was selected as the target period of the first phase because it was the latest year for which the databases required to prepare model inputs and to validate model results were available in Japan at the beginning of this study. In addition, January 2013 might be attractive for some participants, as heavy air pollution occurred in Beijing and surrounding areas, e.g., [20,21,22]. Therefore, the 15 months from January 2013 through March 2014 were set as the entire target period. Although the input datasets for all the days for the 15 months were prepared, participants were not forced to conduct their air quality simulations for the entire target period; they were requested to conduct their simulations at least for the five enhanced target periods listed in Table 2, which correspond to the periods of government monitoring of PM2.5 components throughout Japan in each season, introduced in detail in Section 4.6. They might be a bit short to evaluate seasonality, but their lengths were supposed to be optimal to encourage participants to conduct their simulations. Interested participants could extend their target periods using the available input datasets.

Table 2.
Dates of five enhanced target periods.
4.2. Target Domains
The four nested domains shown in Figure 1 were specified as the target domains. d01 covers the countries in East and Southeast Asia, to represent the transport of ambient pollutants from outside of Japan. Although it covers similar regions to domain 1 of MICS-Asia3, the standard longitude of the Lambert conformal coordinate is set to 139.8° E to minimize grid distortion around Japan. The mesh size is 45 × 45 km. d02 covers most of Japan. The mesh size is 15 × 15 km. d03 and d04 are independent; d03 covers major city clusters located in western Japan, including Osaka, Kobe, Kyoto, and Nagoya, which were not included as targets of previous UMICS, and d04 covers the Tokyo metropolitan area. These are the most populated areas in Japan, and air pollution at each is of concern. The mesh size of both domains is 5 × 5 km. All the domains have 30 consistent vertical layers from the ground to 100 hPa. The surface layer is approximately 53 m high. Participants did not have to conduct their air quality simulations in all domains; they were requested to conduct their simulations at least in d03 or d04, whereas some participants conducted their simulations in their own domains.
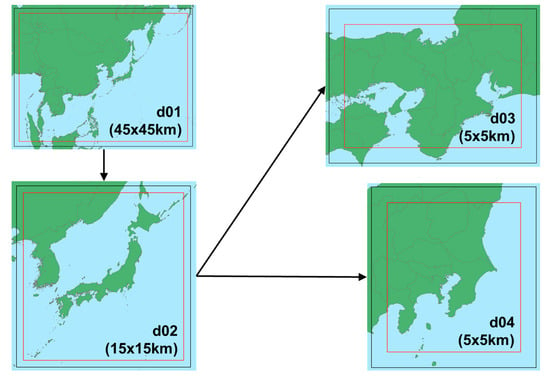
Figure 1.
Four nested target domains.
4.3. Emission Inputs
All the emission data and the flow applied to prepare a single input emission file for each day are shown in Figure 2. The emission datasets used for countries other than Japan were largely consistent with MICS-Asia3, with some minor differences. HTAP version 2.2 [23] was chosen for emissions of anthropogenic sources and ships to be consistent with MICS-Asia3 and HTAP2 simulations. The monthly values for 2010 were used, whereas no annual, weekly, and hourly variations were considered. The horizontal resolution is 0.1° × 0.1°. The vertical profile was consistent with MICS-Asia3. Global Fire Emissions Database (GFED) version 4.1 [24] was used for open biomass burning emissions. Their daily and three-hourly variations were used. The horizontal resolution is 0.25° × 0.25°. The vertical profile was consistent with MICS-Asia3. Hourly biogenic volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions were estimated by Model of Emissions of Gases and Aerosols from Nature (MEGAN) version 2.1 [25]. Constant volcanic SO2 emissions from Bulusan, Mayon, Barren Island, Karymsky, and Shiveluch, which are the volcanoes with distinct emission amounts in Aerosol Comparisons between Observations and Models (AeroCom) [26] located within d01, were taken into account.
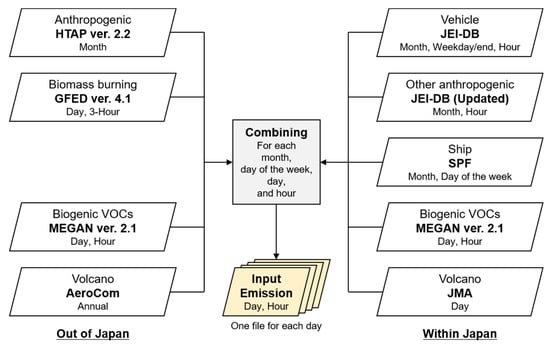
Figure 2.
Schematics of all the emission data and the flow used to prepare a single input emission file for each day.
The Japan Auto-Oil Program (JATOP) emission inventory database (JEI-DB) was used for anthropogenic emissions in Japan. Vehicles emissions were estimated by the JATOP emission inventory-vehicle emission estimation model (JEI-VEM) [27], which calculates hot running, cold start, evaporative (diurnal breathing loss, hot soak loss, and running loss), road dust, and tire wear emissions. Monthly, weekday/weekend, and hourly variations were represented. The horizontal resolution is approximately 1 × 1 km throughout Japan. The target year is 2010, and annual changes since then was not considered. Although anthropogenic emissions other than vehicles were also derived from JEI-DB, emission amounts and spatial allocations were recalculated with the updated activity database to represent 2013. Monthly and hourly variations were consistent with JEI-DB. The horizontal resolution was approximately 1 × 1 km throughout Japan. Ship emissions were provided from the Sasakawa Peace Foundation (SPF). They were estimated from activities obtained by the Automatic Identification System (AIS) and averaged for each day of the week and hour. The horizontal resolution was approximately 1 × 1 km within the range of available AIS information. Hourly biogenic VOC emissions within Japan were estimated by MEGAN version 2.1 [25]. SO2 emissions from four volcanoes (Asamayama, Asosan, Sakurajima, and Miyakejima) were derived from the Japan Meteorological Agency [28], which irregularly monitors SO2 emissions and plume heights at these four volcanoes. Constant SO2 emissions from two additional volcanoes (Satsuma-Iojima and Suwanosejima), where monitoring is not conducted by the Japan Meteorological Agency, were derived from AeroCom [26].
The horizontal distributions of annual mean NOX and primary PM2.5 emissions in d03 and d04 for fiscal year 2013 are shown in Figure 3. The highest emissions are located at the center of Tokyo in d04, and spread to surrounding cities along major roads. High emissions along the coast are mainly due to heavy industry. Emissions of similar magnitude are also seen around major cities in d03, indicating air pollution there is comparable to Tokyo. The influence of ship emissions is seen in both domains.
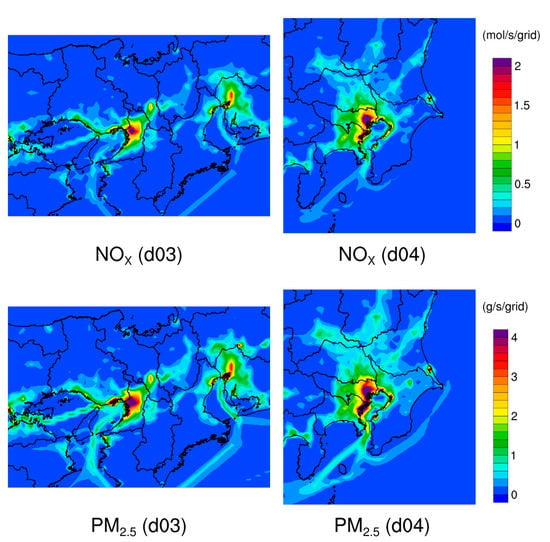
Figure 3.
Horizontal distributions of annual mean NOX and primary PM2.5 emissions in d03 and d04 for fiscal year 2013.
As a first trial in Japan, VOC emissions were adapted to multiple chemical mechanisms. Individual VOC species available in each emission database were speciated to SAPRC07 [29], SAPRC99 [30], CB05 [31], RACM2 [32], and RADM2 [33] mechanisms. This made evaluating the effects of different chemical mechanisms on simulated secondary pollutants possible.
The emissions from multiple emission sources described above were compiled into a single file for each day, domain, and four chemical mechanisms (SAPRC07, SAPRC99, CB05, and RACM2) in the CMAQ-ready format, as well as for one chemical mechanism (RADM2) in the WRF-Chem ready format. Participants can download files of suitable chemical mechanisms for any days and domains during the target period from the file servers, whereas some participants conducted their simulations using their own emission inputs.
Whereas the emission inputs described in this section were delivered as the best available datasets in the first phase of J-STREAM, they may result in poor model performance. If all the participating models overestimate or underestimate observed concentrations, that may be caused by problems in the emission inputs. Comparison of source apportionments derived by forward and receptor modeling, which will be conducted in the third phase of J-STREAM, could also give a suggestion to improve emission inputs [34]. The final target of J-STREAM in terms of emission inputs is to improve available emission inputs based on outcomes obtained in this study, and to establish emission datasets which could serve as a reference and give better model performance.
4.4. Meteorology Inputs
The common meteorology inputs for all target days and domains were generated in a simulation using the Weather Research and Forecasting (WRF)—Advanced Research WRF (ARW) version 3.7.1 [35]. Schemes and settings used in the simulation are listed in Table 3. The National Centers for Environmental Prediction (NCEP) Final (FNL) Operational Model Global Tropospheric Analyses (ds083.2) [36], and real-time, global, sea surface temperature (RTG_SST_HR) analyses [37] were used for the initial and boundary conditions as well as for grid nudging, but grid nudging in d03 and d04 was turned off because the horizontal resolution is much finer than the input analysis datasets. The output files were processed by the Meteorology Chemistry Interface Processor (MCIP) to generate files in the CMAQ-ready format. Participants can download files for any days and domains during the target period from the file servers, whereas some participants conducted their meteorology simulations with the WRF input datasets, also available from the file server.

Table 3.
Schemes and settings used in the WRF simulation.
The configuration described in this section were chosen based on experience from UMICS, but more suitable configurations will be explored in J-STREAM. Particularly, vertical profile of ozone, which is greatly affected by meteorological conditions, is one of the targets of the second phase of J-STREAM. Various actions including application of suitable urban canopy modeling [44], better boundary layer schemes, and reliable land use information will be explored in the second phase to derive a suitable configuration which could serve as a reference.
4.5. Initial and Boundary Concentrations
As mentioned above, participants were requested to conduct their air quality simulations at least for the enhanced target periods in d03 or d04. Initial concentrations on the beginning days of the enhanced target periods, as well as boundary concentrations for all days during the entire target period, were generated in the simulation using CMAQ version 5.0.2 [10] using the SAPRC07 chemical mechanism in d01 and d02. Boundary concentrations for d01 were obtained from the results of CHASER [45] for HTAP2 [46]. Initial and boundary concentrations of the inner domains were obtained from the results for the respective outer domains. Initial and boundary concentrations for chemical mechanisms other than SAPRC07 were obtained by converting species in SAPRC07 to those in other chemical mechanisms. Participants can download the files in the CMAQ-ready format for any days and domains during the target period from the file servers, whereas some participants prepared their boundary concentrations from other data sources, including the results of MOZART-4 [47].
4.6. Observation Data
The continuous monitoring data of ambient pollutant concentrations conducted by the government in Japan are used to validate model performance. There are two types of monitoring stations available in Japan: ambient air pollution monitoring stations (APMSs), and roadside air pollution monitoring stations (RAPMSs). The stations monitor ambient concentrations of the criteria pollutants including SO2, CO, suspended particulate matter (SPM, ≈PM7), NO2, photochemical oxidants, and PM2.5, for which Environmental Quality Standards (EQSs) have been specified, as well as NO and non-methane hydrocarbons (NMHCs) as related precursors. Photochemical oxidants and PM2.5 were monitored at 1152 and 492 APMSs, respectively, throughout Japan during fiscal year 2013. Hourly concentrations of all the pollutants monitored at all stations are available for download from the National Institute for Environmental Studies [48].
In addition, the monitoring data of ambient concentrations of PM2.5 components are used to validate model performance. This monitoring was started by the government after the implementation of the EQS for PM2.5 in 2009, aiming to increase scientific knowledge of PM2.5 and precursors in the atmosphere and to contribute to reliable source apportionments of PM2.5 for developing effective strategies to reduce ambient PM2.5 concentrations. The data from this monitoring should be useful for developing and validating air quality modeling and receptor modeling. The recommended target periods of two weeks are set in each season, and local governments are requested to conduct their monitoring at selected APMSs and RAPMSs that represent both polluted areas and background situations. Ambient PM2.5 samples are collected on filters daily, and components including ions (e.g., SO42−, NO3−, NH4+), inorganic elements (e.g., Na, Al, K, and Ca), and carbons (elemental carbon (EC) and organic carbon (OC)) are analyzed at a minimum to provide vital information for source apportionments. The monitoring was conducted at 101 APMSs, 32 RAPMSs, and 19 background sites for fiscal year 2013. Daily concentrations of all components monitored at all stations are available for download from the Ministry of the Environment [49].
Figure 4 shows the mean concentrations of PM2.5 components observed at all APMSs, RAPMSs, and background stations for fiscal year 2013 [50]. The observed differences between concentrations at the APMSs and RAPMSs are small. This implies that PM2.5 pollution in Japan is not a local issue affected by specific emission sources, but rather an urban or regional scale problem. Inorganic components, including SO42−, NO3−, and NH4+, contribute to approximately half of the total PM2.5 concentration. As such, it is important to tackle remaining issues in simulating inorganic components in J-STREAM. In addition, even background PM2.5 concentrations are equivalent to the EQS in Japan. The influence of not only domestic sources but also transboundary transport should be clarified by combining knowledge obtained from both J-STREAM and MICS-Asia3 to consider effective strategies to reduce ambient PM2.5 concentration over megacities in Japan.
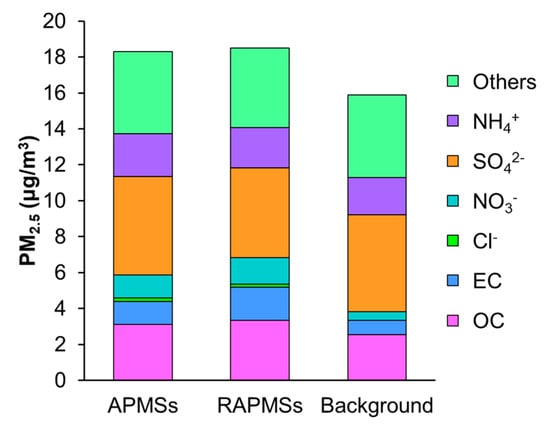
Figure 4.
Mean concentrations of PM2.5 components observed at all the APMSs, RAPMSs, and background stations for fiscal year 2013 [50].
4.7. Data Treatment
As described in this section, all common input datasets have been provided to participants. Participants, at least CMAQ users, can immediately begin their simulations using the provided datasets. Both the input datasets and the simulated results submitted from participants are stored on the file server, and participants are free to analyze them. Each dataset is essentially intended for use within J-STREAM. Participants who intend to use the datasets for other research purposes, or to analyze submitted modeling results themselves, are requested to introduce their results in J-STREAM first. Commercial use should be avoided. All the datasets, as well as the data processing tools required for a reference air quality modeling, will be open to the public at the end of J-STREAM.
5. Status
The configurations of the models participating in the first phase of J-STREAM are listed in Table 4. Simulation results from three models with 29 different configurations have been submitted thus far, far exceeding the number of participating models in previous UMICS. Most use CMAQ, reflecting that CMAQ is widely applied in Japan, including for regulatory purposes. However, differences in the versions, chemical mechanisms, aerosol modules, photolysis, emissions, meteorology, boundary concentrations, and target domains of participating CMAQs could allow us to establish a more reliable reference air quality modeling among the wide varieties of model configurations available in CMAQ. In addition, results from one comprehensive air quality model with extensions (CAMx) and three WRF-Chem [51] models have also submitted their results. Participation of a few more models are expected. They provide an opportunity to investigate the effects of different model frameworks and embedded modules, and to evaluate ranges and uncertainties in concentrations simulated by different models, something that cannot be evaluated in comparisons only among CMAQ. The results of detailed analyses will be introduced in forthcoming papers.

Table 4.
Configurations of models participating in the first phase of J-STREAM.
6. Future Direction
As mentioned in Section 3, the second phase of J-STREAM will focus on secondary inorganic aerosols, including uncertain temporal variations and deposition processes, and physical processes of photochemical ozone, by using data obtained from the specific measurements conducted in this study. Then, the third phase of J-STREAM will focus on source apportionments under heavy air pollution episodes. Reliable source apportionments are needed to develop effective strategies to suppress ambient PM2.5 and photochemical ozone concentrations in Japan. One of the purposes for government monitoring of PM2.5 components is to provide important information for reliable source apportionments, as described in Section 4.6. Now is the time to use the data obtained in this monitoring to derive reliable source apportionments. There are various methodologies using air quality modeling to calculate source apportionments, including ozone source apportionment technology (OSAT) [52] and particulate source apportionment technology (PSAT) [53], as well as source sensitivities including the brute force method and decoupled direct method (DDM) [54]. Although some of them have been already applied in Japan, e.g., [55,56,57,58,59,60], it is valuable to evaluate differences in source apportionments and sensitivities calculated by various models and methodologies. In addition, receptor modeling has also been applied to investigate source apportionments in Japan, e.g., [61]. Uranishi et al. [34] compared source apportionments obtained by air quality modeling and receptor modeling to investigate shortcomings in emissions of specific sources. We must now establish a common understanding on how to interpret the results of source apportionments and sensitivities calculated by various methodologies in order to develop effective strategies. This is a challenging task. The observation data could become a target for model performance validation to reproduce ambient pollutant concentrations, whereas a single answer may not exist for source apportionments and sensitivities. While consistency between simulated and observed concentrations lends confidence to model performance, it does not guarantee the accuracy of sensitivity, nor source apportionment results [62]. We will seek a solution for that through model inter-comparison.
Although many participating models listed in Table 4 have submitted their modeling results to the first phase, other interested researchers are still welcome to participate in J-STREAM. This could provide opportunities to evaluate their air quality modeling over megacities in Japan that have various emission sources and are also located downwind of rapidly growing Asian countries. Please contact the authors for detailed information.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Environment Research and Technology Development Fund (5-1601) of the Environmental Restoration and Conservation Agency. JEI-DB was provided from the Japan Petroleum Energy Center (JPEC). The ship emissions around Japan were produced by SPF (formerly the Ocean Policy Research Foundation (OPRF)) in the project to evaluate air quality improvements due to Emission Control Areas (ECA). We appreciate the cooperation of many participants in J-STREAM.
Author Contributions
Satoru Chatani is the leader of the J-STREAM project, and prepared emission inputs and wrote this paper. Kazuyo Yamaji managed the model inter-comparison, and prepared the initial, boundary, and meteorological inputs. Tatsuya Sakurai is in charge of specific measurements of ozone. Hiroshi Hayami and Syuichi Itahashi are in charge of specific measurements of inorganic aerosol and sub-model development. Hikari Shimadera gave suggestions based on UMICS. Kyo Kitayama conducted a detailed investigation of the chemical mechanisms.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Wakamatsu, S.; Morikawa, T.; Ito, A. Air pollution trends in Japan between 1970 and 2012 and impact of urban air pollution countermeasures. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 7, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Z.; Dabdub, D.; Seinfeld, J.H. Chemical coupling between atmospheric ozone and particulate matter. Science 1997, 277, 116–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Calori, G.; Hayami, H.; Uno, I.; Cho, S.Y.; Engardt, M.; Kim, S.B.; Ichikawa, Y.; Ikeda, Y.; Woo, J.H.; et al. The MICS-Asia study: Model intercomparison of long-range transport and sulfur deposition in East Asia. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmichael, G.R.; Sakurai, T.; Streets, D.; Hozumi, Y.; Ueda, H.; Park, S.U.; Fung, C.; Han, Z.; Kajino, M.; Engardt, M.; et al. MICS-Asia II: The model intercomparison study for Asia phase II methodology and overview of findings. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 3468–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galmarini, S.; Koffi, B.; Solazzo, E.; Keating, T.; Hogrefe, C.; Schulz, M.; Benedictow, A.; Griesfeller, J.J.; Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Carmichael, G.; et al. Technical note: Coordination and harmonization of the multi-scale, multi-model activities HTAP2, AQMEII3, and MICS-Asia3: Simulations, emission inventories, boundary conditions, and model output formats. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 1543–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morino, Y.; Chatani, S.; Hayami, H.; Sasaki, K.; Mori, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Ohara, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Kobayashi, S. Inter-comparison of chemical transport models and evaluation of model performance for O3 and PM2.5 prediction—Case study in the Kanto area in summer 2007. J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 45, 212–226. [Google Scholar]
- Chatani, S.; Morino, Y.; Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Mori, Y.; Sasaki, K.; Kajino, M.; Yokoi, T.; Morikawa, T.; Ohara, T. Multi-model analyses of dominant factors influencing elemental carbon in Tokyo metropolitan area of Japan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Chatani, S.; Morino, Y.; Mori, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Yamaji, K.; Ohara, T. Sensitivity analyses of factors influencing CMAQ performance for fine particulate nitrate. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2014, 64, 374–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morino, Y.; Chatani, S.; Hayami, H.; Sasaki, K.; Mori, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Ohara, T.; Hasegawa, S.; Kobayashi, S. Evaluation of ensemble approach for O3 and PM2.5 simulation. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 4, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, D.; Schere, K.L. Review of the governing equations, computational algorithms, and other components of the models-3 community multiscale air quality (CMAQ) modeling system. Appl. Mech. Rev. 2006, 59, 51–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Morino, Y.; Ohara, T.; Chatani, S.; Hasegawa, S.; Kaneyasu, N. Analysis of summertime atmospheric transport of fine particulate matter in Northeast Asia. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2013, 49, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajino, M.; Inomata, Y.; Sato, K.; Ueda, H.; Han, Z.; An, J.; Katata, G.; Deushi, M.; Maki, T.; Oshima, N.; et al. Development of the RAQM2 aerosol chemical transport model and predictions of the northeast asian aerosol mass, size, chemistry, and mixing type. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 11833–11856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Chatani, S.; Morikawa, T.; Morino, Y.; Mori, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Nakatsuka, S.; Ohara, T. Urban air quality model inter-comparison study in Japan (UMICS) for improvement of PM2.5 simulation. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2017, in press. [Google Scholar]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Chatani, S.; Morikawa, T.; Morino, Y.; Ohara, T.; Mori, Y.; Yamaji, K.; Nakatsuka, S. Comprehensive Sensitivity Analyses on Air Quality Model Performance for PM2.5 Simulation. In Proceedings of the 16th International Conference on Harmonisation within Atmospheric Dispersion Modelling for Regulatory Purposes, Varna, Bulgaria, 8–11 September 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Morino, Y.; Nagashima, T.; Sugata, S.; Sato, K.; Tanabe, K.; Noguchi, T.; Takami, A.; Tanimoto, H.; Ohara, T. Verification of chemical transport models for PM2.5 chemical composition using simultaneous measurement data over Japan. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2009–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, A.L.; Donahue, N.M.; Shrivastava, M.K.; Weitkamp, E.A.; Sage, A.M.; Grieshop, A.P.; Lane, T.E.; Pierce, J.R.; Pandis, S.N. Rethinking organic aerosols: Semivolatile emissions and photochemical aging. Science 2007, 315, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itahashi, S.; Uno, I.; Osada, K.; Kamiguchi, Y.; Yamamoto, S.; Tamura, K.; Wang, Z.; Kurosaki, Y.; Kanaya, Y. Nitrate transboundary heavy pollution over East Asia in winter. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 3823–3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikado, H. Summertime behavior of the precursors (non-methane hydrocarbons and nitrogen oxides) related with high concentrations of ozone in the Tokyo metropolitan area. J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 50, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kiriyama, Y.; Shimadera, H.; Itahashi, S.; Hayami, H.; Miura, K. Evaluation of the effect of regional pollutants and residual ozone on ozone concentrations in the morning in the inland of the kanto region. Asian J. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 9, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.L.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Fu, P.Q.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Yin, Y. Investigation of the sources and evolution processes of severe haze pollution in Beijing in January 2013. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2014, 119, 4380–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uno, I.; Sugimoto, N.; Shimizu, A.; Yumimoto, K.; Hara, Y.; Wang, Z.F. Record heavy PM2.5 air pollution over China in January 2013: Vertical and horizontal dimensions. Sola 2014, 10, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.J.; Duan, F.K.; Su, H.; Ma, Y.L.; Cheng, Y.; Zheng, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, T.; Kimoto, T.; Chang, D.; et al. Exploring the severe winter haze in Beijing: The impact of synoptic weather, regional transport and heterogeneous reactions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 2969–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssens-Maenhout, G.; Crippa, M.; Guizzardi, D.; Dentener, F.; Muntean, M.; Pouliot, G.; Keating, T.; Zhang, Q.; Kurokawa, J.; Wankmuller, R.; et al. HTAP_v2.2: A mosaic of regional and global emission grid maps for 2008 and 2010 to study hemispheric transport of air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 11411–11432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Werf, G.R.; Randerson, J.T.; Giglio, L.; van Leeuwen, T.T.; Chen, Y.; Rogers, B.M.; Mu, M.; van Marle, M.J.E.; Morton, D.C.; Collatz, G.J.; et al. Global fire emissions estimates during 1997–2016. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2017, 9, 697–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guenther, A.B.; Jiang, X.; Heald, C.L.; Sakulyanontvittaya, T.; Duhl, T.; Emmons, L.K.; Wang, X. The model of emissions of gases and aerosols from nature version 2.1 (megan2.1): An extended and updated framework for modeling biogenic emissions. Geosci. Model Dev. 2012, 5, 1471–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, T.; Heil, A.; Chin, M.; Pan, X.; Streets, D.; Schultz, M.; Kinne, S. Anthropogenic, biomass burning, and volcanic emissions of black carbon, organic carbon, and SO2 from 1980 to 2010 for hindcast model experiments. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 2012, 24895–24954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatani, S.; Morikawa, T.; Nakatsuka, S.; Matsunaga, S.; Minoura, H. Development of a framework for a high-resolution, three-dimensional regional air quality simulation and its application to predicting future air quality over Japan. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 1383–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Japan Meteorological Agency. Available online: http://www.data.jma.go.jp/svd/vois/data/tokyo/volcano.html (accessed on 27 October 2017).
- Carter, W.P.L. Development of the SAPRC-07 chemical mechanism. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5324–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.P.L. Documentation of the SAPRC-99 Chemical Mechanism for Voc Reactivity Assessment; California Environmental Protection Agency: Sacramento, CA, USA, 2000.
- Whitten, G.Z.; Heo, G.; Kimura, Y.; McDonald-Buller, E.; Allen, D.T.; Carter, W.P.L.; Yarwood, G. A new condensed toluene mechanism for carbon bond CB05-TU. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 5346–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goliff, W.S.; Stockwell, W.R.; Lawson, C.V. The regional atmospheric chemistry mechanism, version 2. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, W.R.; Middleton, P.; Chang, J.S.; Tang, X. The second generation regional acid deposition model chemical mechanism for regional air quality modeling. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1990, 95, 16343–16367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uranishi, K.; Ikemori, F.; Nakatsubo, R.; Shimadera, H.; Kondo, A.; Kikutani, Y.; Asano, K.; Sugata, S. Identification of biased sectors in emission data using a combination of chemical transport model and receptor model. Atmos. Environ. 2017, 166, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skamarock, W.C.; Klemp, J.B.; Dudhia, J.; Gill, D.O.; Barker, D.M.; Duda, M.G.; Huang, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Power, J.G. A Description of the Advanced Research WRF Version 3; NCAR/TN-475+STR; National Center for Atmospheric Research: Boulder, CO, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- National Centers for Environmental Prediction/National Weather Service/NOAA/U.S. Department of Commerce. NCEP FNL Operational Model Global Tropospheric Analyses, Continuing from July 1999; Research Data Archive at the National Center for Atmospheric Research, Computational and Information Systems Laboratory: Boulder, CO, USA, 2000.
- Gemmill, W.; Katz, B.; Li, X. The Daily Real-Time, Global Sea Surface Temperature—High Resolution Analysis: RTG_SST_HR; Environmental Modeling Center: Camp Springs, MD, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Hong, S.Y.; Dudhia, J.; Chen, S.H. A revised approach to ice microphysical processes for the bulk parameterization of clouds and precipitation. Mon. Weather Rev. 2004, 132, 103–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mlawer, E.J.; Taubman, S.J.; Brown, P.D.; Iacono, M.J.; Clough, S.A. Radiative transfer for inhomogeneous atmospheres: RRTM, a validated correlated-k model for the longwave. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 1997, 102, 16663–16682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudhia, J. Numerical study of convection observed during the winter monsoon experiment using a mesoscale two-dimensional model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1989, 46, 3077–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakanishi, M.; Niino, H. An improved mellor–yamada level-3 model: Its numerical stability and application to a regional prediction of advection fog. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2006, 119, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Dudhia, J. Coupling an advanced land surface-hydrology model with the penn state-NCAR MM5 modeling system. Part I: Model implementation and sensitivity. Mon. Weather Rev. 2001, 129, 569–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kain, J.S. The kain-fritsch convective parameterization: An update. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2004, 43, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusaka, H.; Kondo, H.; Kikegawa, Y.; Kimura, F. A simple single-layer urban canopy model for atmospheric models: Comparison with multi-layer and slab models. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2001, 101, 329–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudo, K.; Takahashi, M.; Kurokawa, J.; Akimoto, H. Chaser: A global chemical model of the troposphere—1. Model description. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2002, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Carmichael, G.R.; Pierce, R.B.; Jo, D.S.; Park, R.J.; Flemming, J.; Emmons, L.K.; Bowman, K.W.; Henze, D.K.; Davila, Y.; et al. Impact of intercontinental pollution transport on north american ozone air pollution: An HTAP phase 2 multi-model study. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 5721–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons, L.K.; Walters, S.; Hess, P.G.; Lamarque, J.F.; Pfister, G.G.; Fillmore, D.; Granier, C.; Guenther, A.; Kinnison, D.; Laepple, T.; et al. Description and evaluation of the model for ozone and related chemical tracers, version 4 (MOZART-4). Geosci. Model Dev. 2010, 3, 43–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Institute for Environmental Studies. Available online: https://www.nies.go.jp/igreen/ (accessed on 29 August 2017).
- Ministry of the Environment. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/air/osen/pm/monitoring.html (accessed on 29 August 2017).
- Ministry of the Environment. Available online: http://www.env.go.jp/air/osen/jokyo_h25/rep08_h25.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2017).
- Grell, G.A.; Peckham, S.E.; Schmitz, R.; McKeen, S.A.; Frost, G.; Skamarock, W.C.; Eder, B. Fully coupled “online” chemistry within the WRF model. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 6957–6975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, A.M.; Yarwood, G.; Ortmann, J.P.; Wilson, G.M. Comparison of source apportionment and source sensitivity of ozone in a three-dimensional air quality model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2953–2964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagstrom, K.M.; Pandis, S.N.; Yarwood, G.; Wilson, G.M.; Morris, R.E. Development and application of a computationally efficient particulate matter apportionment algorithm in a three-dimensional chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 5650–5659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Wilkinson, J.G.; Russell, A.G. Fast, direct sensitivity analysis of multidimensional photochemical models. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 2859–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatani, S.; Morikawa, T.; Nakatsuka, S.; Matsunaga, S. Sensitivity analyses of domestic emission sources and transboundary transport on PM2.5 concentrations in three major Japanese urban areas for the year 2005 with the three-dimensional air quality simulation. J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 46, 101–110. [Google Scholar]
- Ikeda, K.; Yamaji, K.; Kanaya, Y.; Taketani, F.; Pan, X.; Komazaki, Y.; Kurokawa, J.-I.; Ohara, T. Source region attribution of PM2.5 mass concentrations over Japan. Geochem. J. 2015, 49, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, S.; Hayami, H.; Uno, I. Comprehensive study of emission source contributions for tropospheric ozone formation over East Asia. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2015, 120, 331–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, S.; Hayami, H.; Yumimoto, K.; Uno, I. Chinese province-scale source apportionments for sulfate aerosol in 2005 evaluated by the tagged tracer method. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 220, 1366–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagashima, T.; Sudo, K.; Akimoto, H.; Kurokawa, J.; Ohara, T. Long-term change in the source contribution to surface ozone over Japan. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8231–8246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaji, K.; Uno, I.; Irie, H. Investigating the response of east asian ozone to chinese emission changes using a linear approach. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 55, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Fushimi, A.; Morino, Y.; Iijima, A.; Yonemochi, S.-I.; Hayami, H.; Hasegawa, S.; Tanabe, K.; Kobayash, S. Source apportionment of ambient fine particle using a receptor model combined with radiocarbon content in Northern Kanto area. J. Jpn. Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 46, 156–163. [Google Scholar]
- Cohan, D.S.; Napelenok, S.L. Air quality response modeling for decision support. Atmosphere 2011, 2, 407–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).