The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area
3. Data Sources and Factors Selection
3.1. Data Sources
3.2. Factor Selection
4. Land-Use Factor Processing
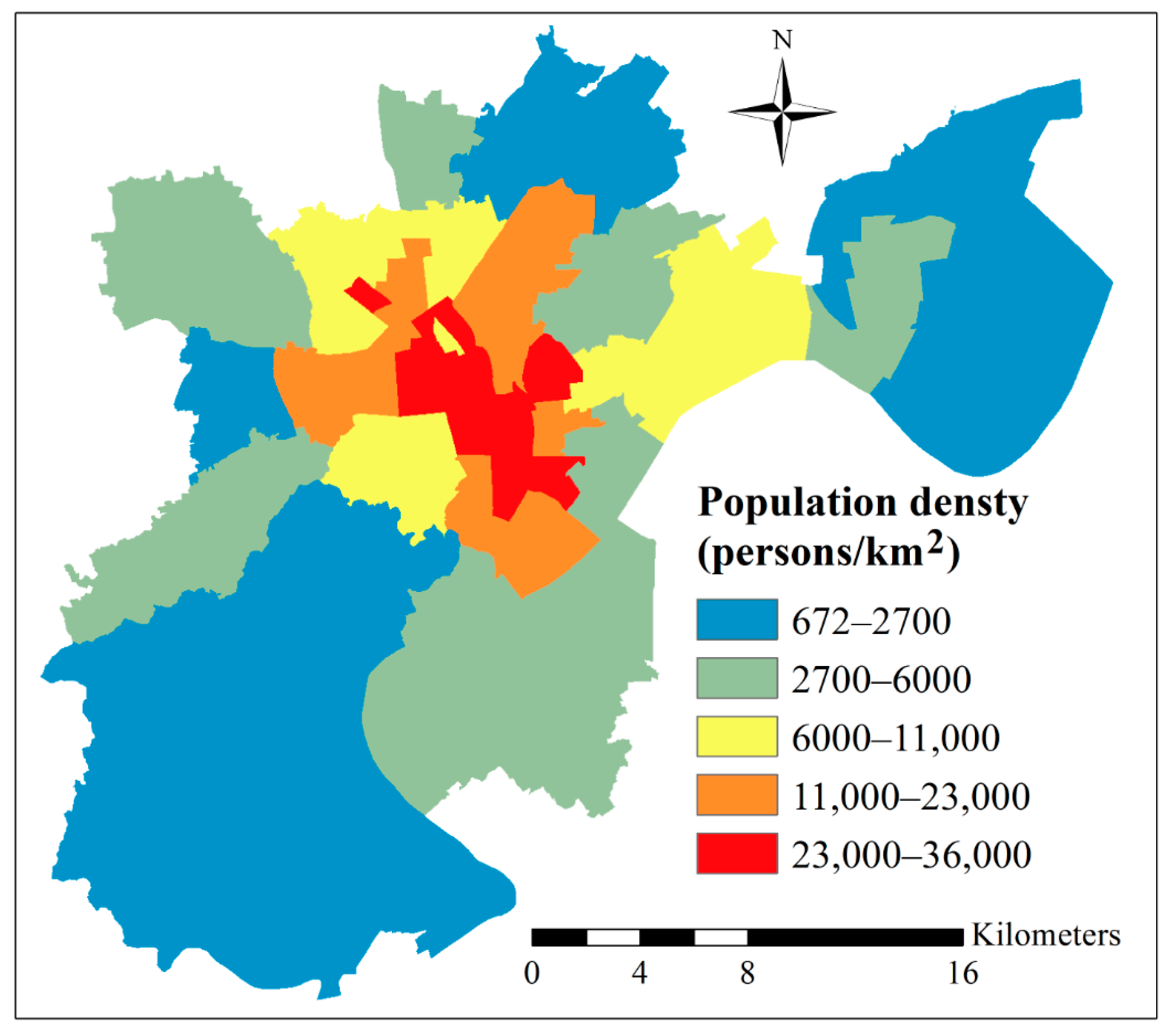
4.1. Population Density
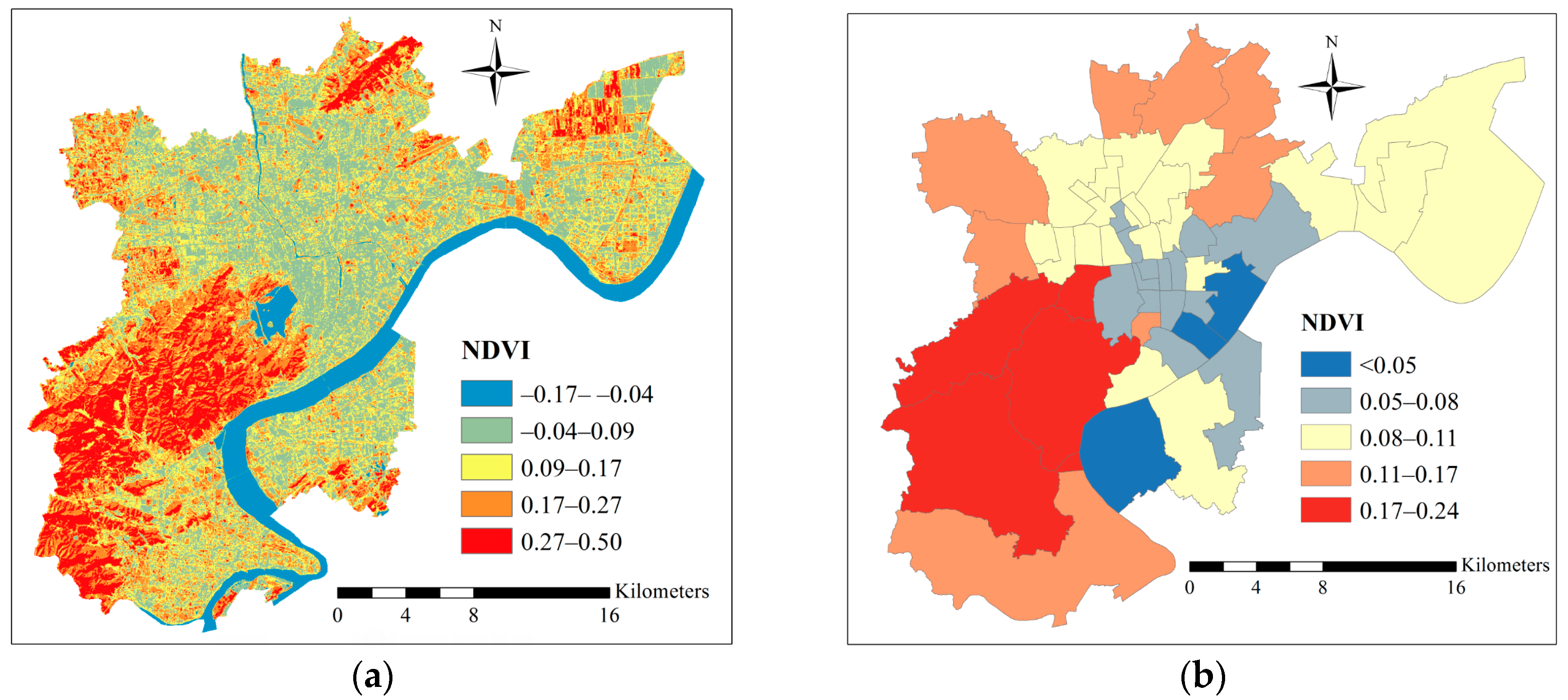
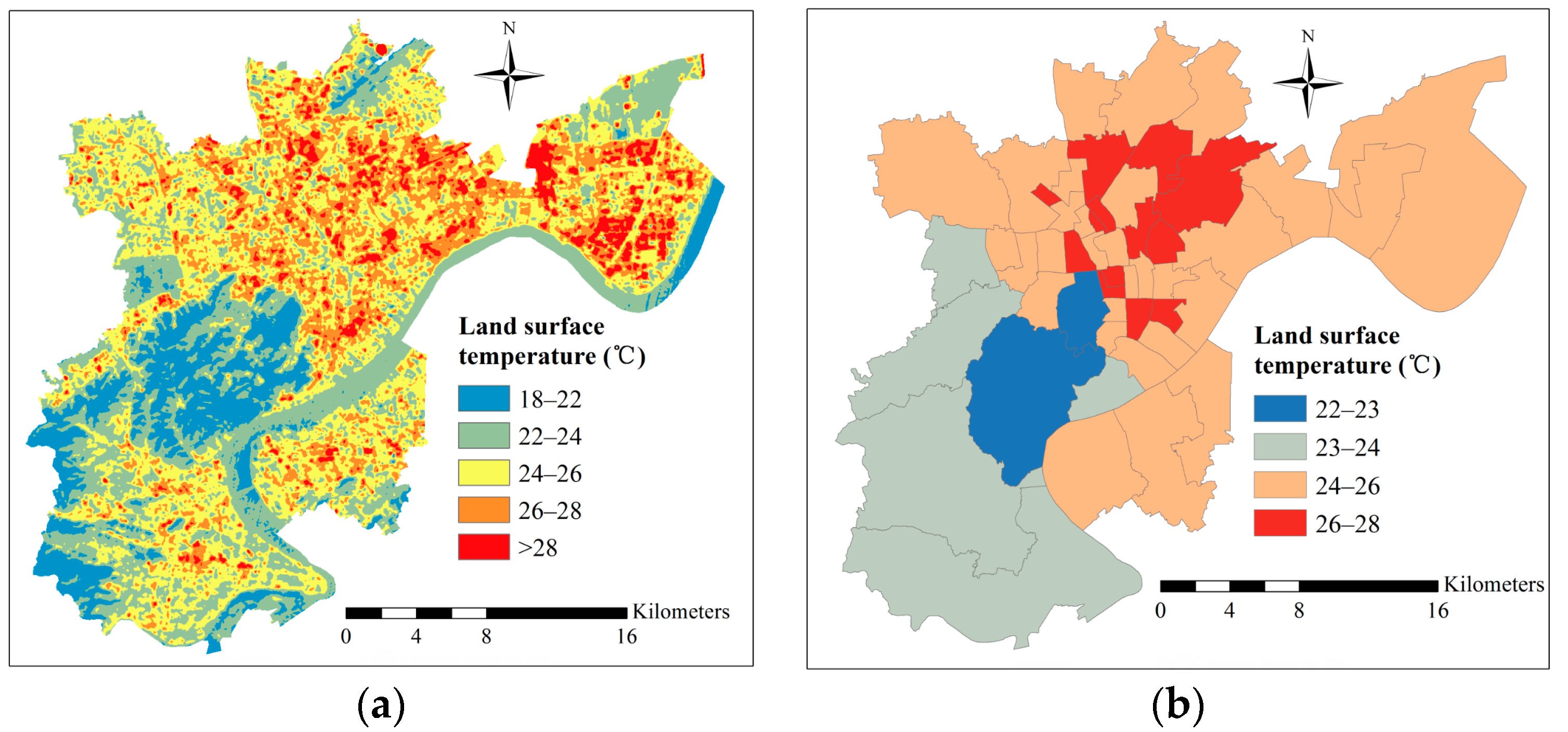
4.2. NDVI and LST
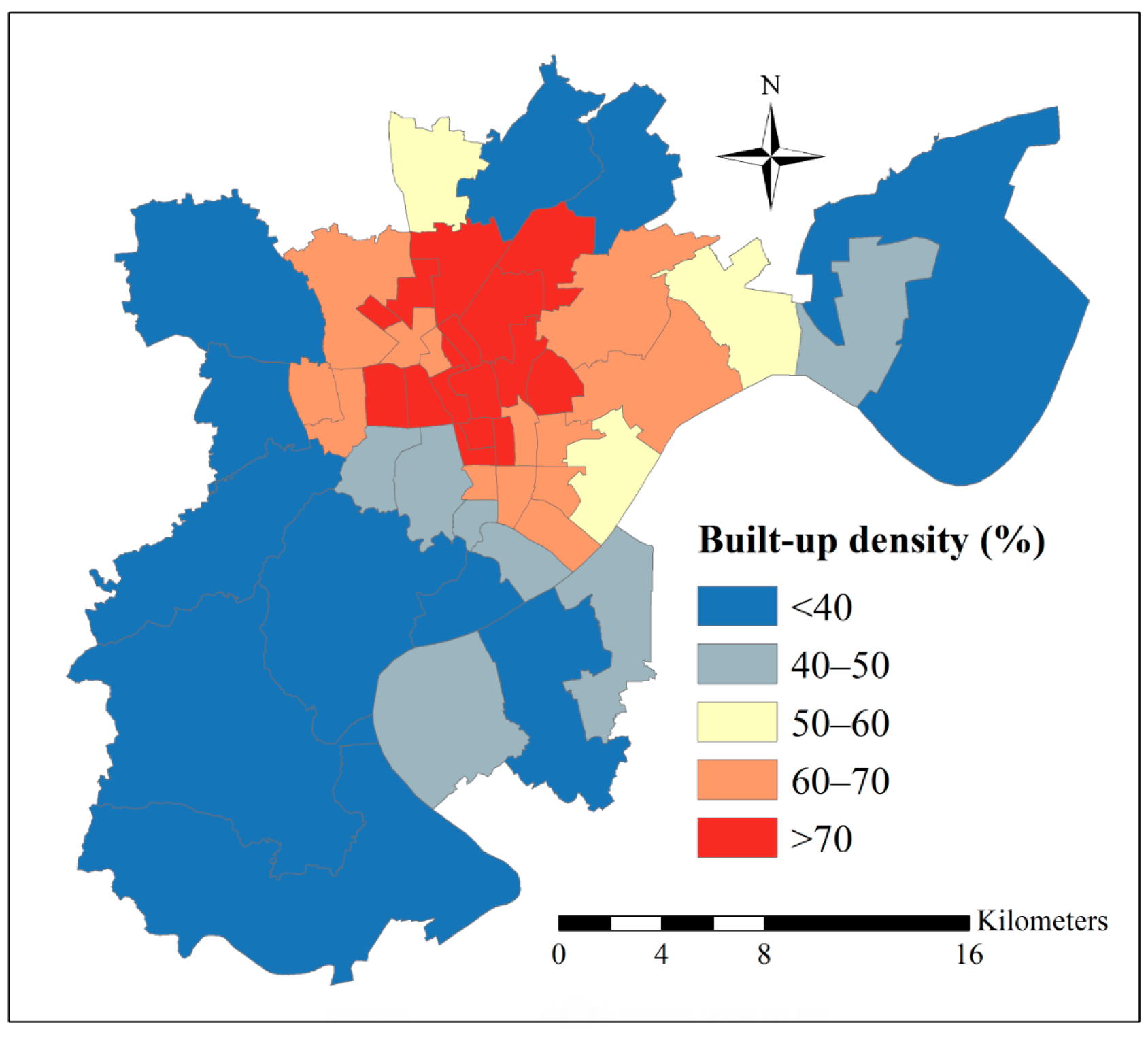
4.3. Urban Build-Up and Road Density
5. Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollution in Hangzhou City
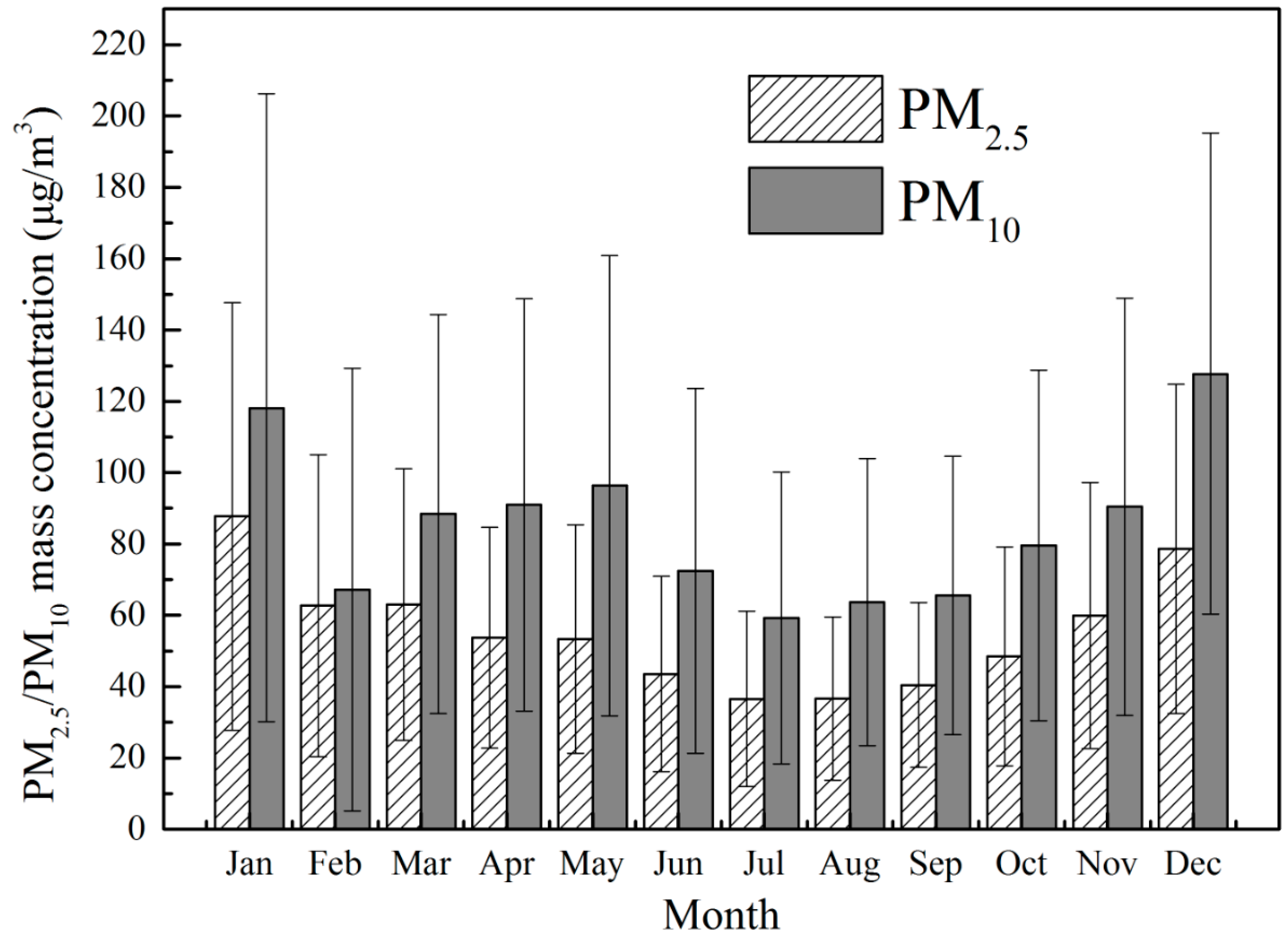
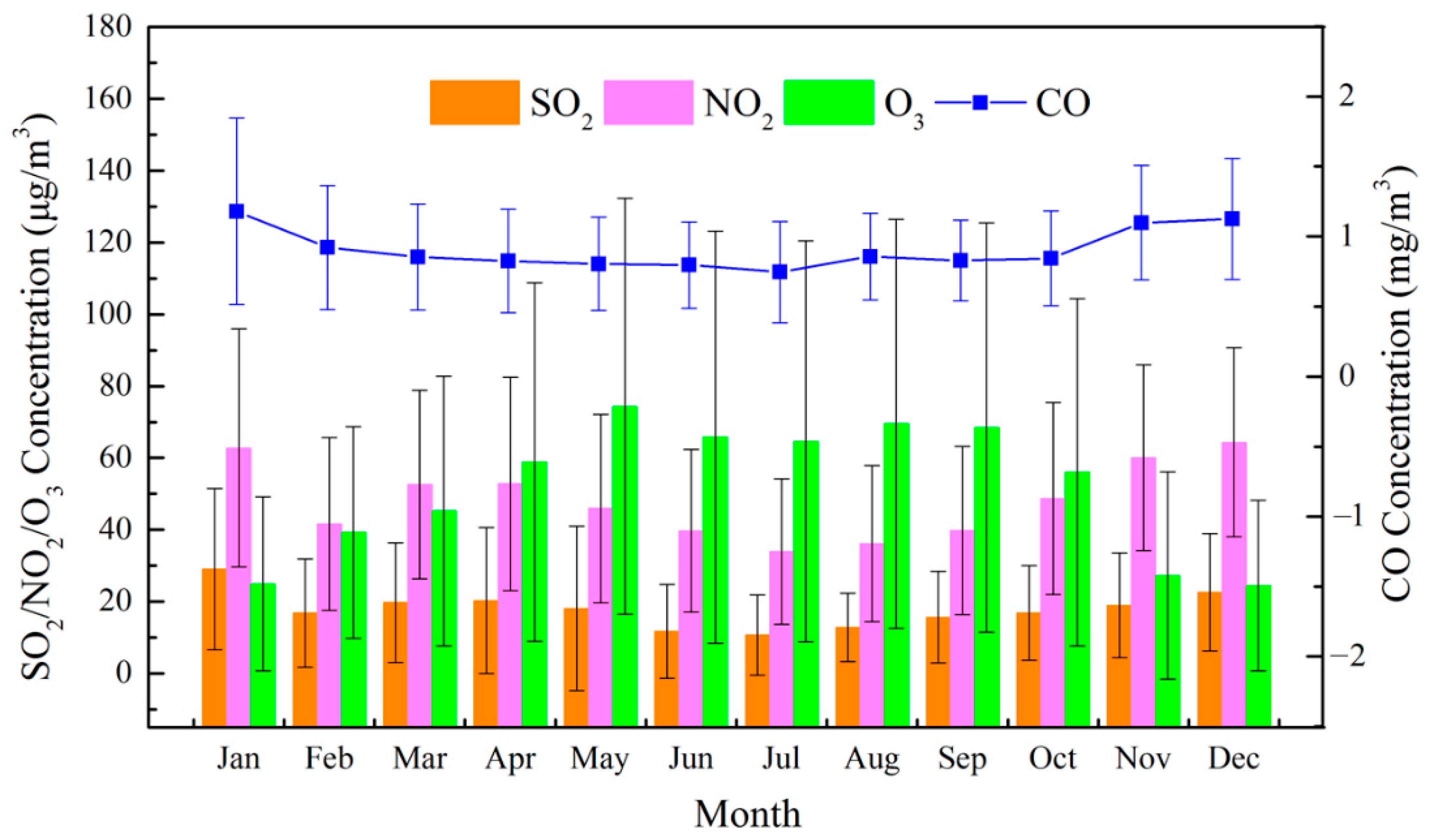
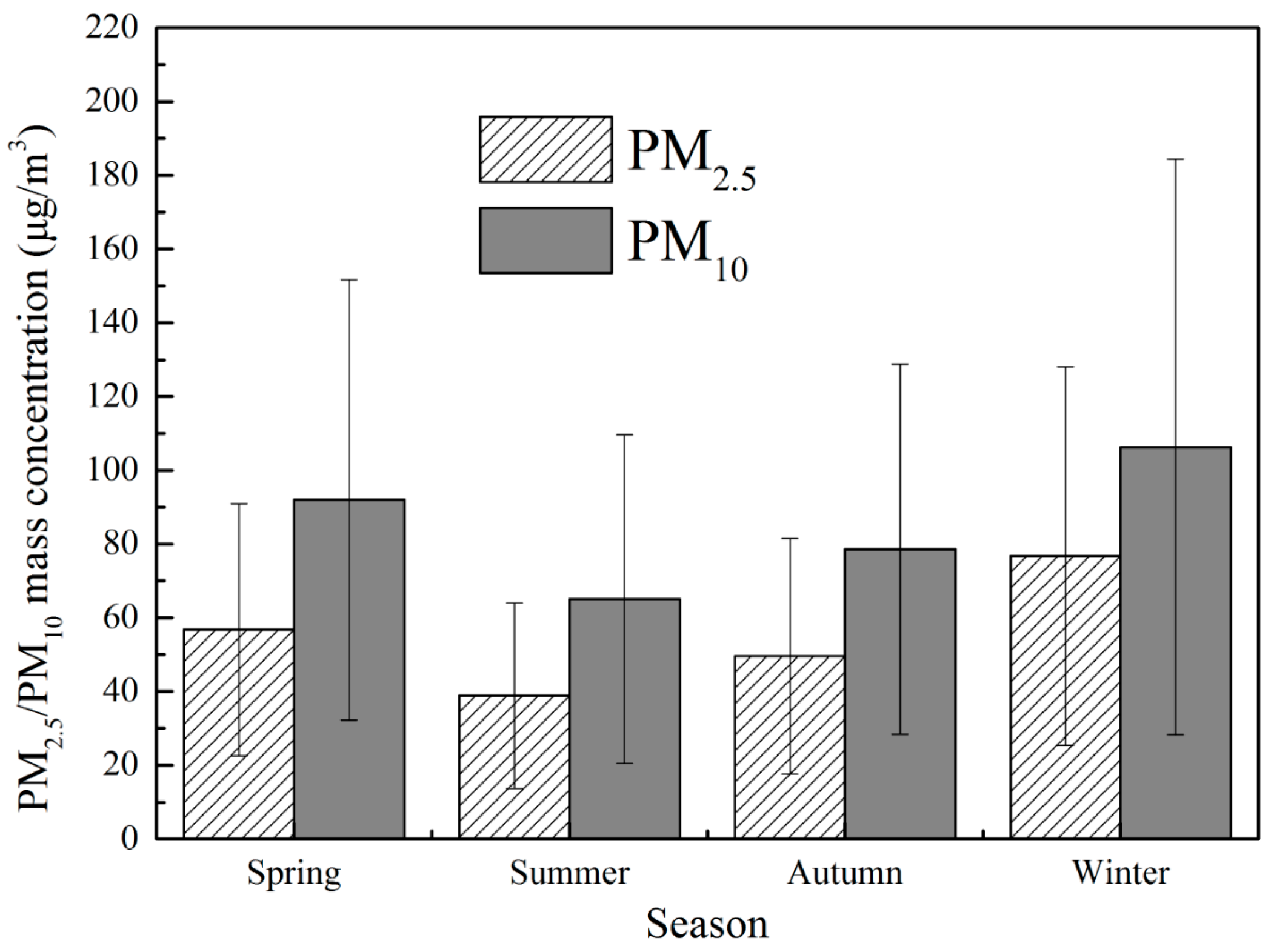
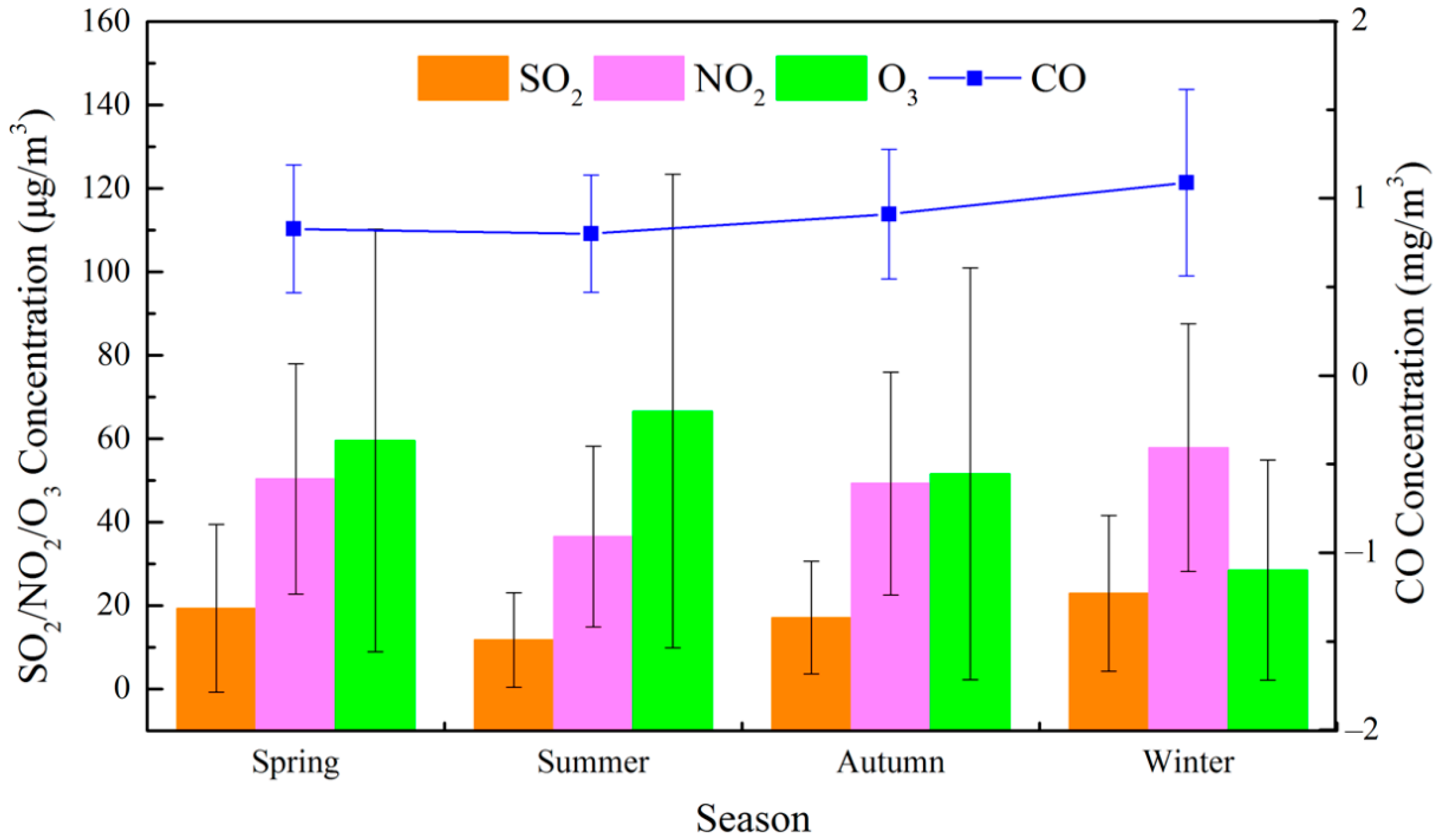
5.1. Temporal Distribution of Air Pollutants
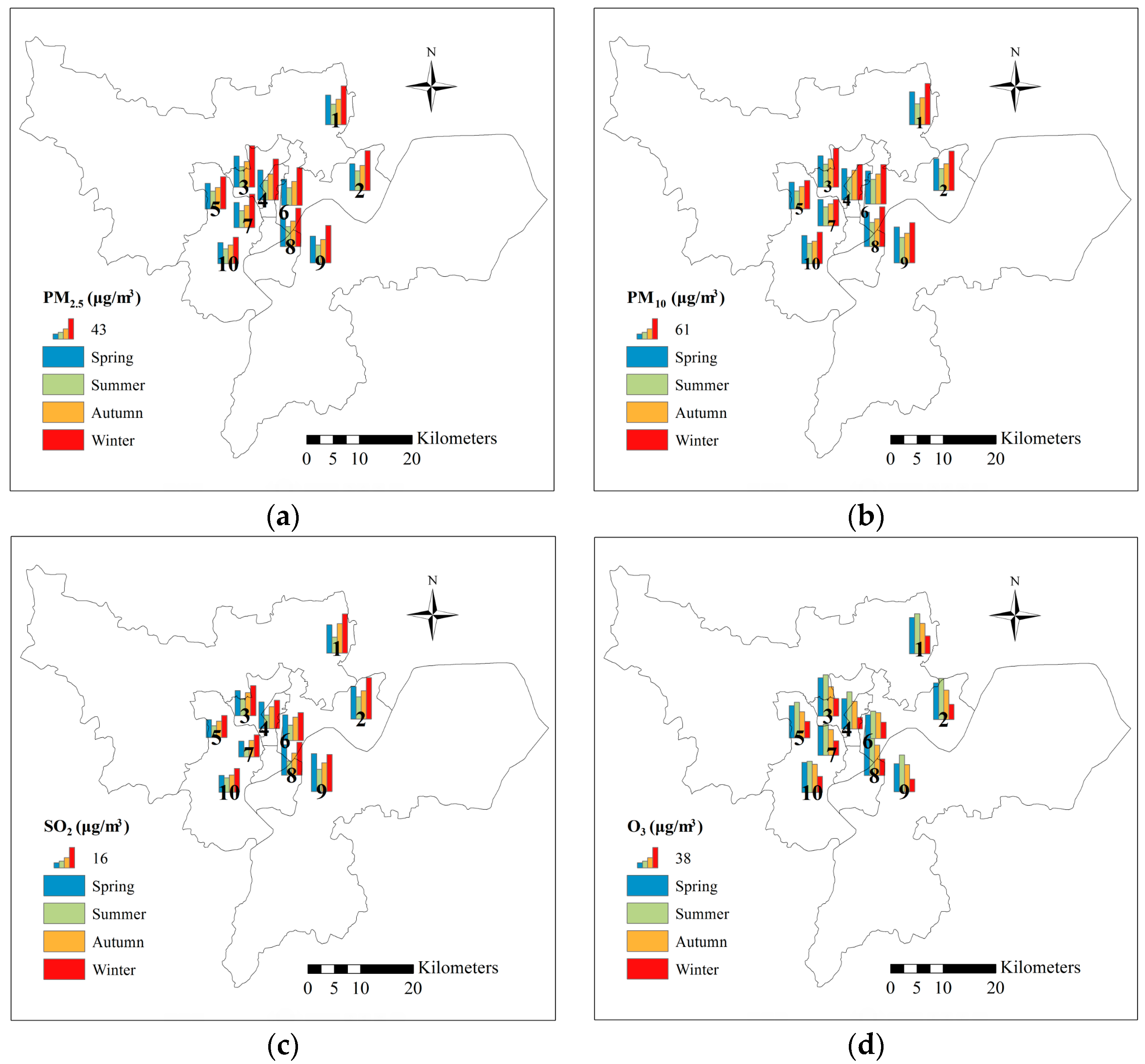
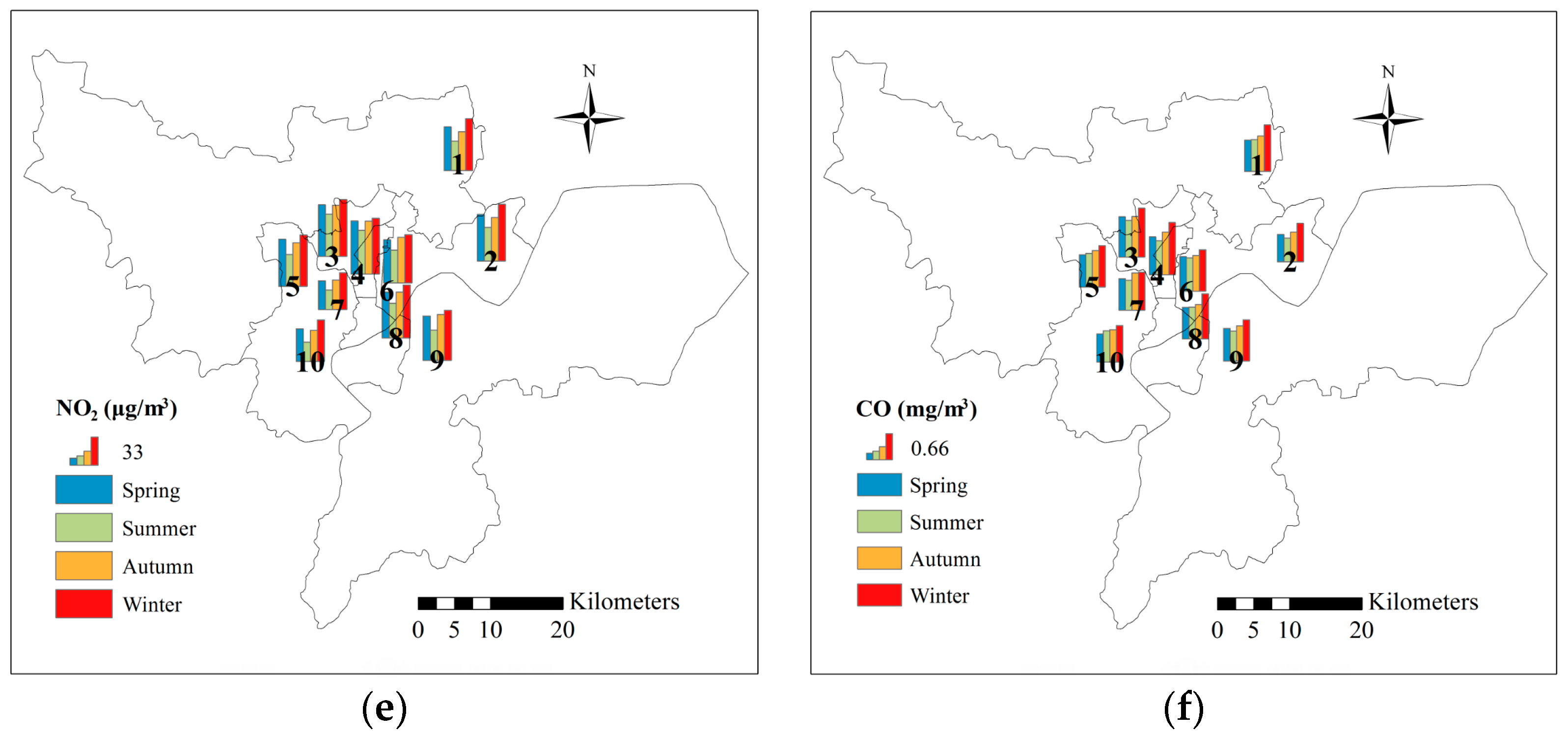
5.2. Spatial Distribution of Air Pollutants
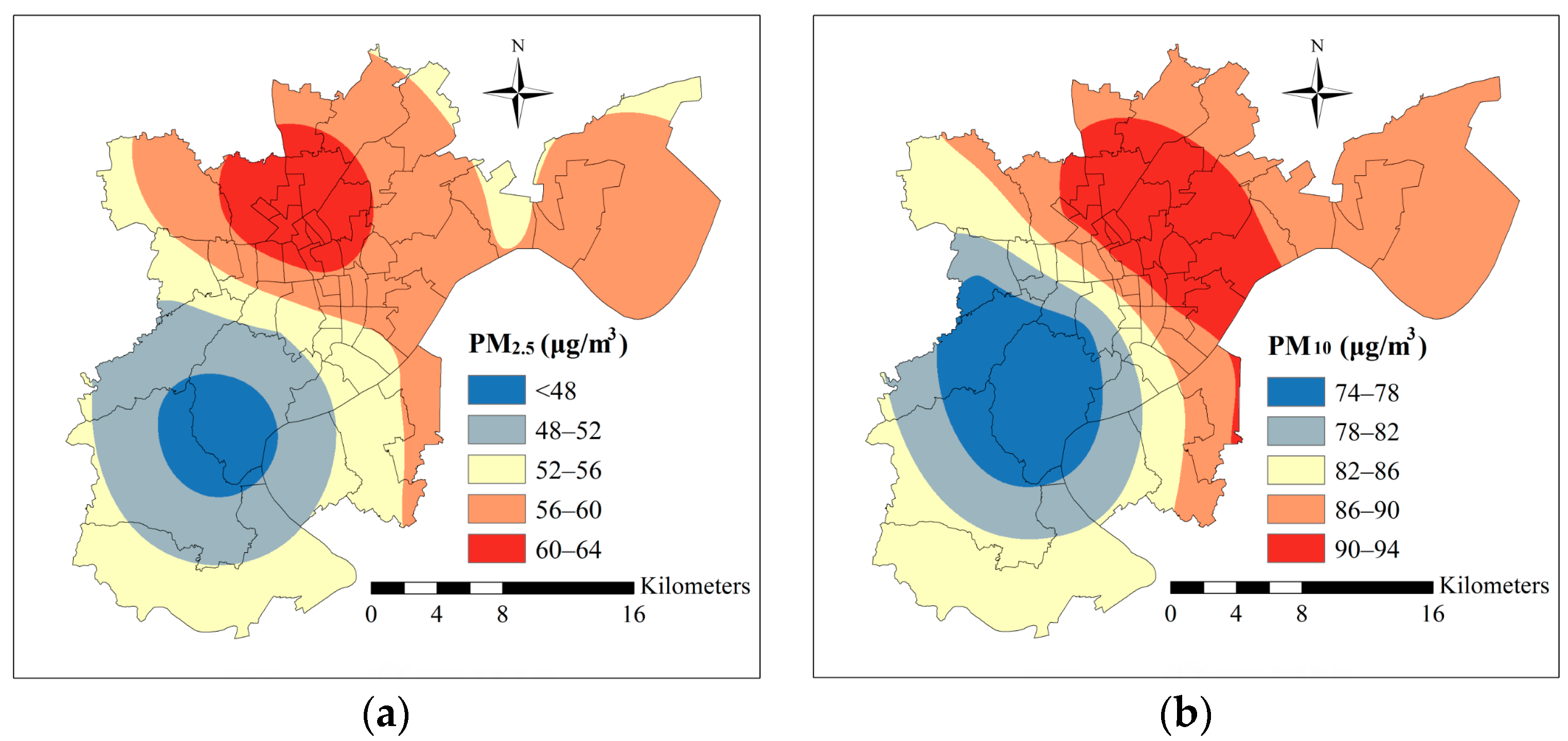
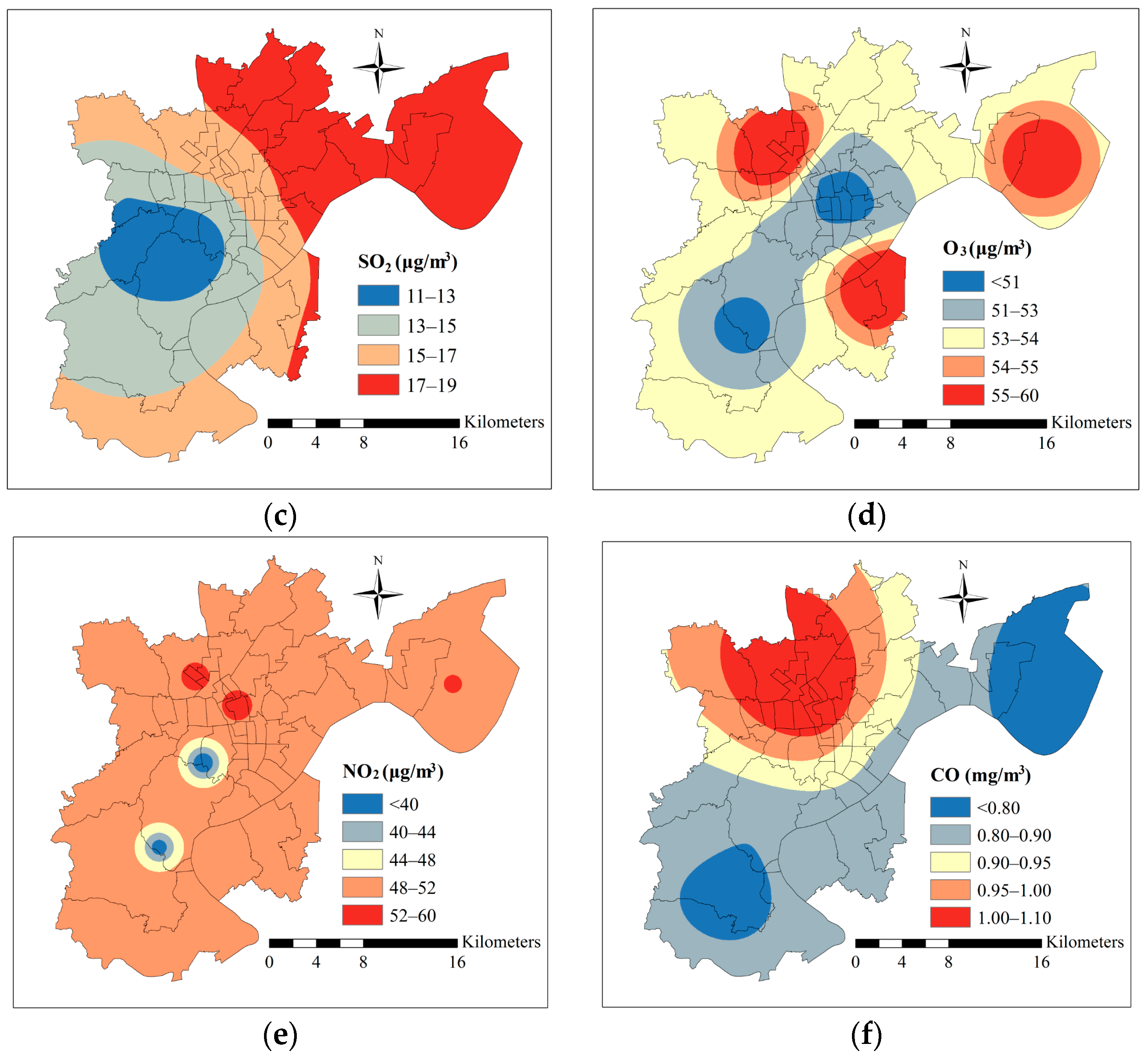
5.3. Spatial Interpolation of Air Pollutants
6. Results and Discussion
7. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflict of Interest
References
- Crutzen, P.J. Geology of mankind. Nature 2002, 415, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lelieveld, J.; Barlas, C.; Giannadaki, D.; Pozzer, A. Model calculated global, regional and megacity premature mortality due to air pollution. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7023–7037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.S.; Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Danaei, G.; Shibuya, K.; Adair-Rohani, H.; AlMazroa, M.A.; Amann, M.; Anderson, H.R.; Andrews, K.G.; et al. A comparative risk assessment of burden of disease and injury attributable to 67 risk factors and risk factor clusters in 21 regions, 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2010. Lancet 2013, 380, 2224–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Cesari, D.; Genga, A.; Siciliano, M.; Ielpo, P.; Guascito, M.; Conte, M. Source apportionment of size-segregated atmospheric particles based on the major water-soluble components in Lecce (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, J.; Duan, J.; Zhen, N.; He, K.; Hao, J. Chemical characteristics and source of size-fractionated atmospheric particle in haze episode in Beijing. Atmos. Res. 2016, 167, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, R.; Hanaoka, T.; Kanamori, Y.; Dai, H.; Masui, T. An impact assessment of sustainable technologies for the Chinese urban residential sector at provincial level. Environ. Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 065001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Yan, R.; Wang, S.; Li, P.; Chen, B.; Liu, W.; Zhang, X. Origin of air pollution during a weekly heavy haze episode in Hangzhou, China. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2014, 12, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, F.; Xu, Y.; Chen, J. Characterization of water-soluble inorganic ions in size-segregated aerosols in coastal city, Xiamen. Atmos. Res. 2011, 99, 546–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heald, C.L.; Spracklen, D.V. Land use change impacts on air quality and climate. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 4476–4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crutzen, P.J.; Andreae, M.O. Biomass burning in the tropics: Impact on atmospheric chemistry and biogeochemical cycles. Science 1990, 250, 1669–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houghton, R.; Hobbie, J.; Melillo, J.M.; Moore, B.; Peterson, B.; Shaver, G.; Woodwell, G. Changes in the carbon content of terrestrial biota and soils between 1860 and 1980: A net release of CO2 to the atmosphere. Ecol. Monogr. 1983, 53, 235–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cicerone, R.J.; Oremland, R.S. Biogeochemical aspects of atmospheric methane. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1988, 2, 299–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacFarling Meure, C.; Etheridge, D.; Trudinger, C.; Steele, P.; Langenfelds, R.; Van Ommen, T.; Smith, A.; Elkins, J. Law dome CO2, CH4 and N2O ice core records extended to 2000 years BP. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L14810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, J.; Matthews, E.; Fung, I. Methane emission from animals: A global high-resolution data base. Glob. Biogeochem. Cycles 1988, 2, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, H. Modeling impacts of increased urban vegetation on ozone air quality in the south coast air basin. Atmos. Environ. 1996, 30, 3423–3430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, W.; Zhou, J.; Luo, H.; Yang, C.; Zhao, J. Relationship between land use change and its urban air environmental impacts. Res. Soil Water Conserv. 2010, 17, 87–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Hankey, S.; Marshall, J.D. Land use regression models of on-road particulate air pollution (particle number, black carbon, PM2.5, particle size) using mobile monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 9194–9202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Hewson, M.G.; Bechle, M.J.; Marshall, J.D.; Barnett, A.G. A national satellite-based land-use regression model for air pollution exposure assessment in Australia. Environ. Res. 2014, 135, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Coorey, C.P.; Bechle, M.J.; Cowie, C.T.; Dirgawati, M.; Heyworth, J.S.; Marks, G.B.; Marshall, J.D.; Morawska, L.; Pereira, G.; et al. Independent validation of national satellite-based land-use regression models for nitrogen dioxide using passive samplers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 12331–12338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novotny, E.V.; Bechle, M.J.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. National satellite-based land-use regression: NO2 in the United States. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vienneau, D.; de Hoogh, K.; Bechle, M.J.; Beelen, R.; van Donkelaar, A.; Martin, R.V.; Millet, D.B.; Hoek, G.; Marshall, J.D. Western European land use regression incorporating satellite- and ground-based measurements of NO2 and PM10. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13555–13564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeganeh, B.; Hewson, M.G.; Clifford, S.; Knibbs, L.D.; Morawska, L. A satellite-based model for estimating PM2.5 concentration in a sparsely populated environment using soft computing techniques. Environ. Model. Softw. 2017, 88, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.P.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. Air quality and urban form in us urban areas: Evidence from regulatory monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7028–7035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bechle, M.J.; Millet, D.B.; Marshall, J.D. Effects of income and urban form on urban NO2: Global evidence from satellites. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4914–4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, J.; Wang, T.; Jiang, Z.; Zhuang, B.; Xie, M.; Yin, C.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, Y. WRF/Chem modeling of the impacts of urban expansion on regional climate and air pollutants in Yangtze River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 106, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Fu, X.; Hao, J. Long-term trend of haze pollution and impact of particulate matter in the Yangtze River Delta, China. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 182, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Z.; Wang, S.; Fu, X.; Watson, J.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Q.; Chen, C.; Xu, B.; Yu, J.; Chow, J. Impact of biomass burning on haze pollution in the Yangtze River Delta, china: A case study in summer 2011. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2014, 14, 4573–4585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.Y.; Li, X.X.; Tian, W.L.; Fu, A.Y.; Du, W.F.; Wang, C. Scenarios for vehicular air pollutant emissions abatement: A case study in Hangzhou, China. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. 2014, 15, 753–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Li, J.; Wu, D.; Xu, H. Chemical composition and source apportionment of the ambient PM2.5 in Hangzhou, China. Particuology 2015, 18, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ma, W.; Qian, J.; Cai, J.; Ye, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X. Effect of urbanization on the urban meteorology and air pollution in Hangzhou. J. Meteorol. Res. 2015, 29, 950–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.R.; Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Lu, S. A study of vertical distribution patterns of PM2.5 concentrations based on ambient monitoring with unmanned aerial vehicles: A case in Hangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xu, C.; Wang, Q.; Cheng, W. Potential sources and formations of the PM2.5 pollution in urban Hangzhou. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hangzhou Statistics Bureau. Hangzhou Statistical Yearbook 2014; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2014. (In Chinese)
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.S.; Liu, Z.J.; Wu, J.H.; Zhang, Y.F.; Han, S.Q.; Zheng, X.J.; Zhou, L.D.; Feng, Y.C.; Zhu, T. Characterization of chemical compositions in size-segregated atmospheric particles during severe haze episodes in three mega-cities of China. Atmos. Res. 2017, 187, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhou, Y. Modelling urban population densities in Beijing 1982–1990: Suburbanisation and its causes. Urban Stud. 1999, 36, 271–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, W.M.; Grossa, J. Environmental Geography: SCIENCE, Land Use, and Earth Systems, 3rd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hoek, G.; Beelen, R.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Gulliver, J.; Fischer, P.; Briggs, D. A review of land-use regression models to assess spatial variation of outdoor air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7561–7578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, J.D.; Nethery, E.; Brauer, M. Within-urban variability in ambient air pollution: Comparison of estimation methods. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, N.; Cowie, C.; Gillett, R.; Marks, G.B. Weighted road density: A simple way of assigning traffic-related air pollution exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5009–5014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oke, T.R. The energetic basis of the urban heat island. Q. J. R. Meteor. Soc. 1982, 108, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Q.; Yang, S. Urban air pollution patterns, land use, and thermal landscape: An examination of the linkage using GIS. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2006, 117, 463–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ottlé, C.; Stoll, M. Effect of atmospheric absorption and surface emissivity on the determination of land surface temperature from infrared satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1993, 14, 2025–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Guo, X.; Wu, Z. Land surface temperature retrieval from Landsat 8 TIRS-comparison between radiative transfer equation-based method, split window algorithm and single channel method. Remote Sens. Basel 2014, 6, 9829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hu, Z.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, S. Contamination characteristics and possible sources of PM10 and PM2.5 in different functional areas of Shanghai, China. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 68, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, R.C.; Shi, Y.; Chen, J.; Hu, Y.; Xu, C.; Hong, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, M. Using hourly measurements to explore the role of secondary inorganic aerosol in PM2.5 during haze and fog in Hangzhou, China. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2014, 31, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.W.; Tian, W.L.; Zhang, Q.Y. Development of motor vehicles emission inventory in Hangzhou. China Environ. Sci. 2012, 32, 1368–1374. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Burrough, P.A.; Mcdonnell, R.A.; Lloyd, C.D. Principles of Geographical Information Systems; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, L.; Wei, J.; Duan, D.; Guo, Y.; Yang, D.; Jia, C.; Mi, X. Impact of land-use and land-cover change on urban air quality in representative cities of china. J. Atmos. Sol. Terr. Phys. 2016, 142, 43–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Xie, W.; Li, W.; Li, J. Effects of urban landscape pattern on PM2.5 pollution—A Beijing case study. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, F.; Bauer, M.E. Comparison of impervious surface area and normalized difference vegetation index as indicators of surface urban heat island effects in Landsat imagery. Remote Sens. Environ. 2007, 106, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Chen, L.; Cai, J.; Zou, B.; Wu, C.F.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Kan, H. A land use regression model for estimating the NO2 concentration in Shanghai, China. Environ. Res. 2015, 137, 308–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
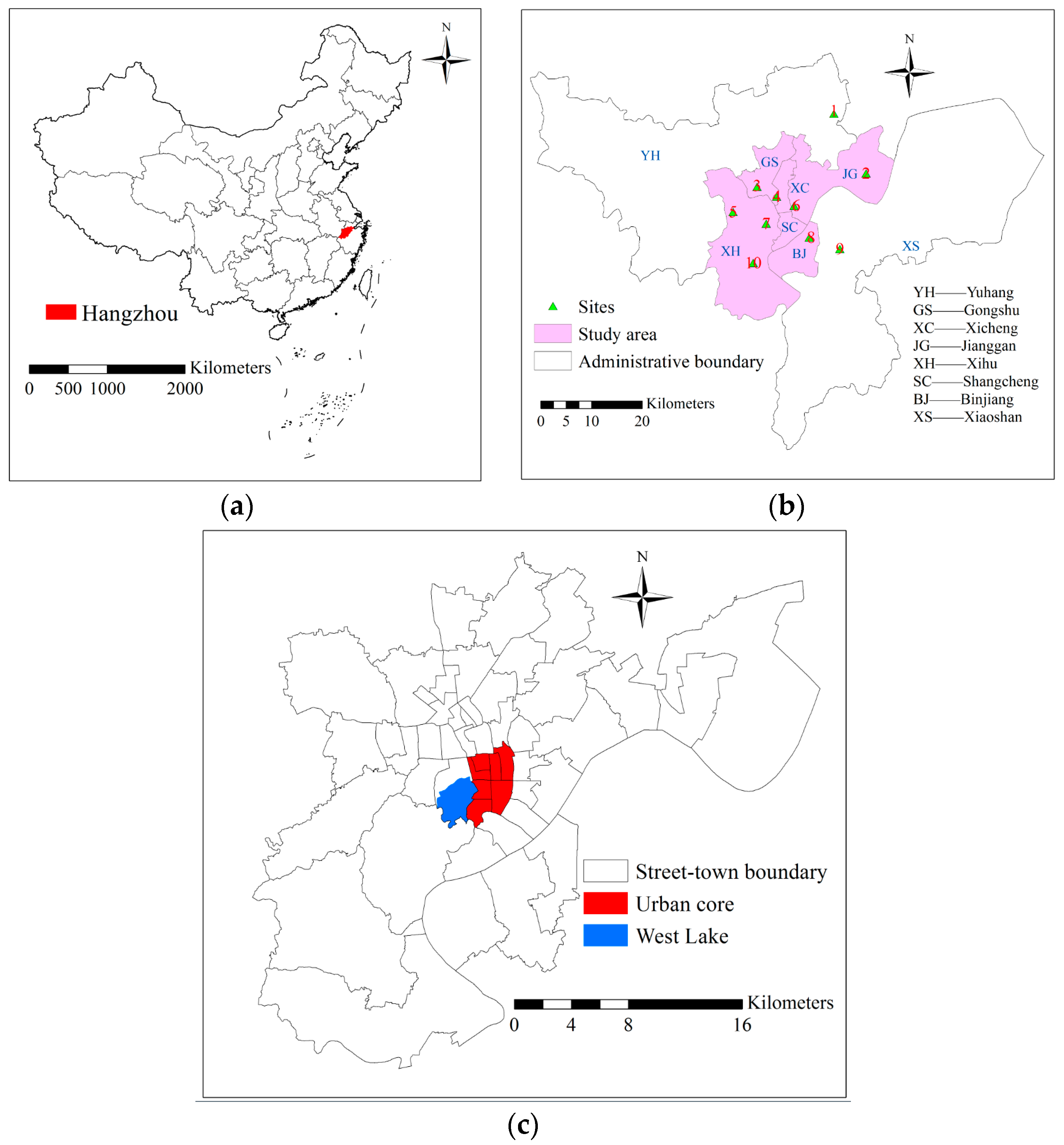

| Sites | Name of Site | Sites | Name of Site |
|---|---|---|---|
| Site 1 | Linpinzhen | Site 6 | Zhejiangnongda |
| Site 2 | Xiasha | Site 7 | Wolongqiao |
| Site 3 | Hemuxiaoxue | Site 8 | Binjiang |
| Site 4 | Chaohuiwuqu | Site 9 | Chengxiangzhen |
| Site 5 | Xixi | Site 10 | Yunqi |
| Air Pollutants | Land Use | ||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 | PM10 | SO2 | O3 | NO2 | CO | RD | CD | NDVI | LST | PD | |
| PM2.5 | — | ||||||||||
| PM10 | 0.780 ** | — | |||||||||
| SO2 | 0.437 ** | 0.750 ** | — | ||||||||
| O3 | 0.118 | −0.124 | 0.172 | — | |||||||
| NO2 | 0.730 ** | 0.560 ** | 0.223 | 0.098 | — | ||||||
| CO | 0.861 ** | 0.465 ** | −0.006 | 0.087 | 0.579 ** | — | |||||
| RD | 0.394 ** | 0.450 ** | 0.318 * | 0.024 | 0.475 ** | 0.204 | — | ||||
| BD | 0.784 ** | 0.667 ** | 0.191 | −0.246 | 0.628 ** | 0.688 ** | 0.447 ** | — | |||
| NDVI | −0.187 | −0.294 * | −0.068 | 0.263 | −0.294 * | −0.084 | −0.455 ** | −0.514 ** | — | ||
| LST | 0.670 ** | 0.685 ** | 0.487 ** | −0.113 | 0.461 ** | 0.471 ** | 0.509 ** | 0.772 ** | −0.312 * | — | |
| PD | 0.551 ** | 0.415 ** | −0.082 | −0.333 * | 0.562 ** | 0.566 ** | 0.531 ** | 0.816 ** | −0.606 ** | 0.615 ** | — |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, S.; Zhou, X.; Singh, R.P.; Wu, Y.; Ye, Y.; Wu, C. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere 2017, 8, 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8060110
Zheng S, Zhou X, Singh RP, Wu Y, Ye Y, Wu C. The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere. 2017; 8(6):110. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8060110
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Sheng, Xueyuan Zhou, Ramesh P. Singh, Yuzhe Wu, Yanmei Ye, and Cifang Wu. 2017. "The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China" Atmosphere 8, no. 6: 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8060110
APA StyleZheng, S., Zhou, X., Singh, R. P., Wu, Y., Ye, Y., & Wu, C. (2017). The Spatiotemporal Distribution of Air Pollutants and Their Relationship with Land-Use Patterns in Hangzhou City, China. Atmosphere, 8(6), 110. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos8060110








