Source Apportionment of Sulfate and Nitrate over the Pearl River Delta Region in China
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Model and Methods
2.1. Model Description
2.2. Particulate Source Apportionment Technology (PSAT)
3. Results and Discussion
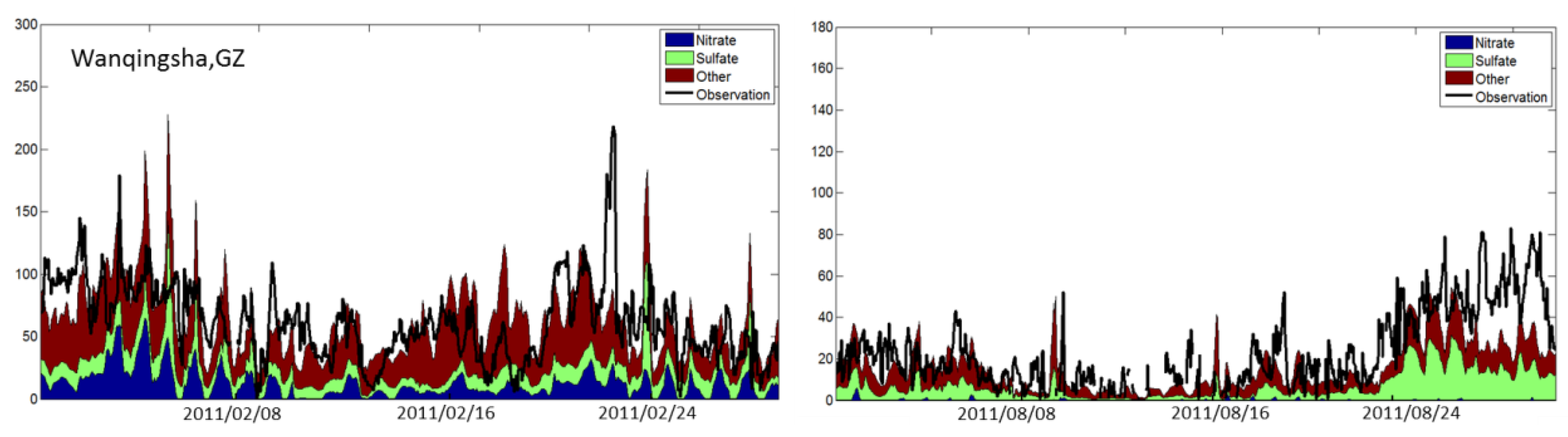
3.1. Model Evaluation
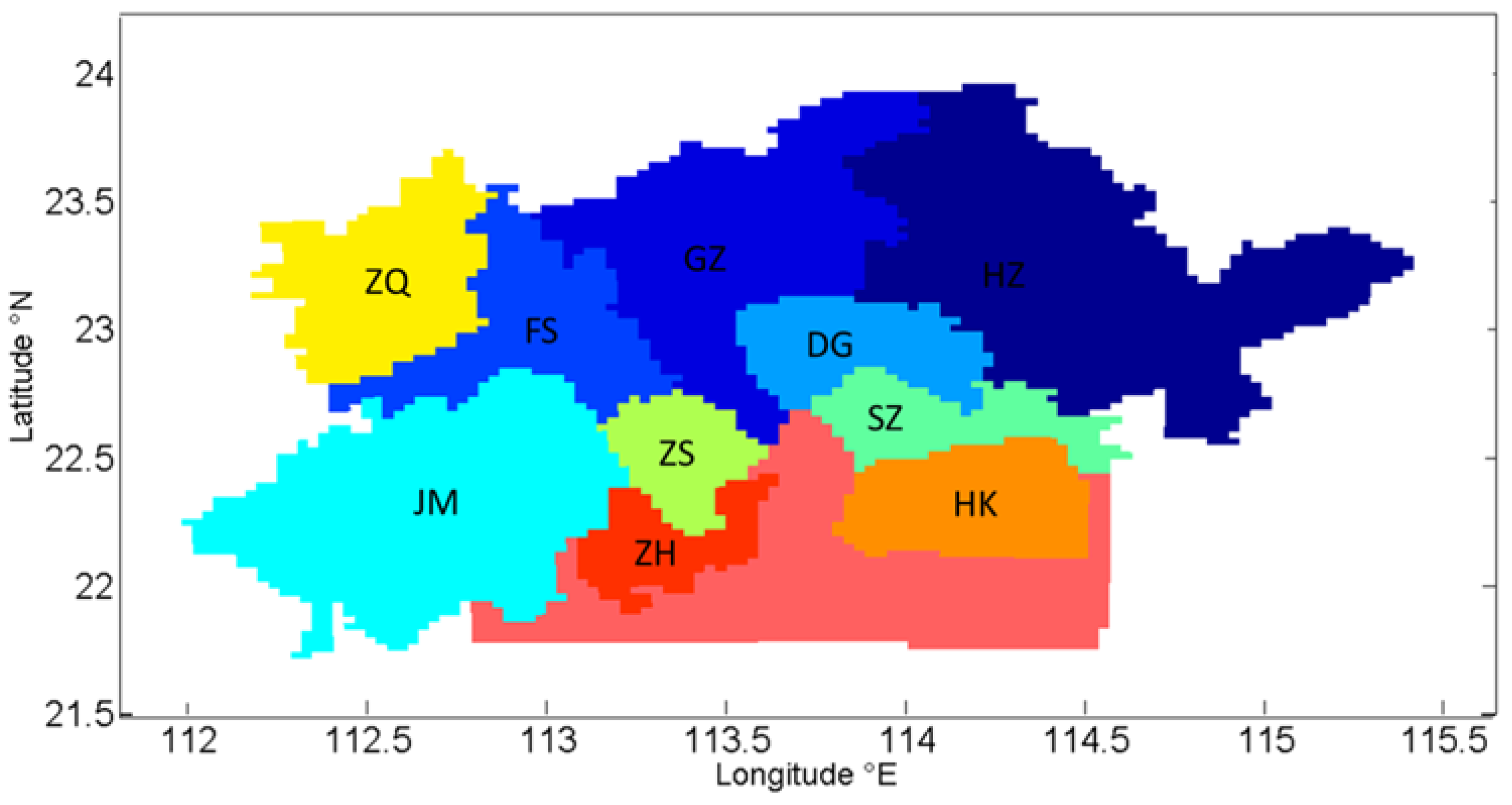
3.2. Local, Regional and Super-Regional Contribution
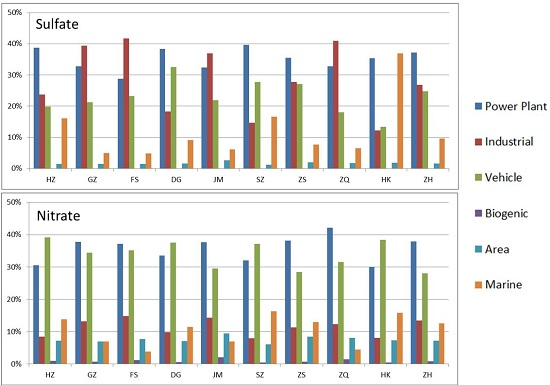
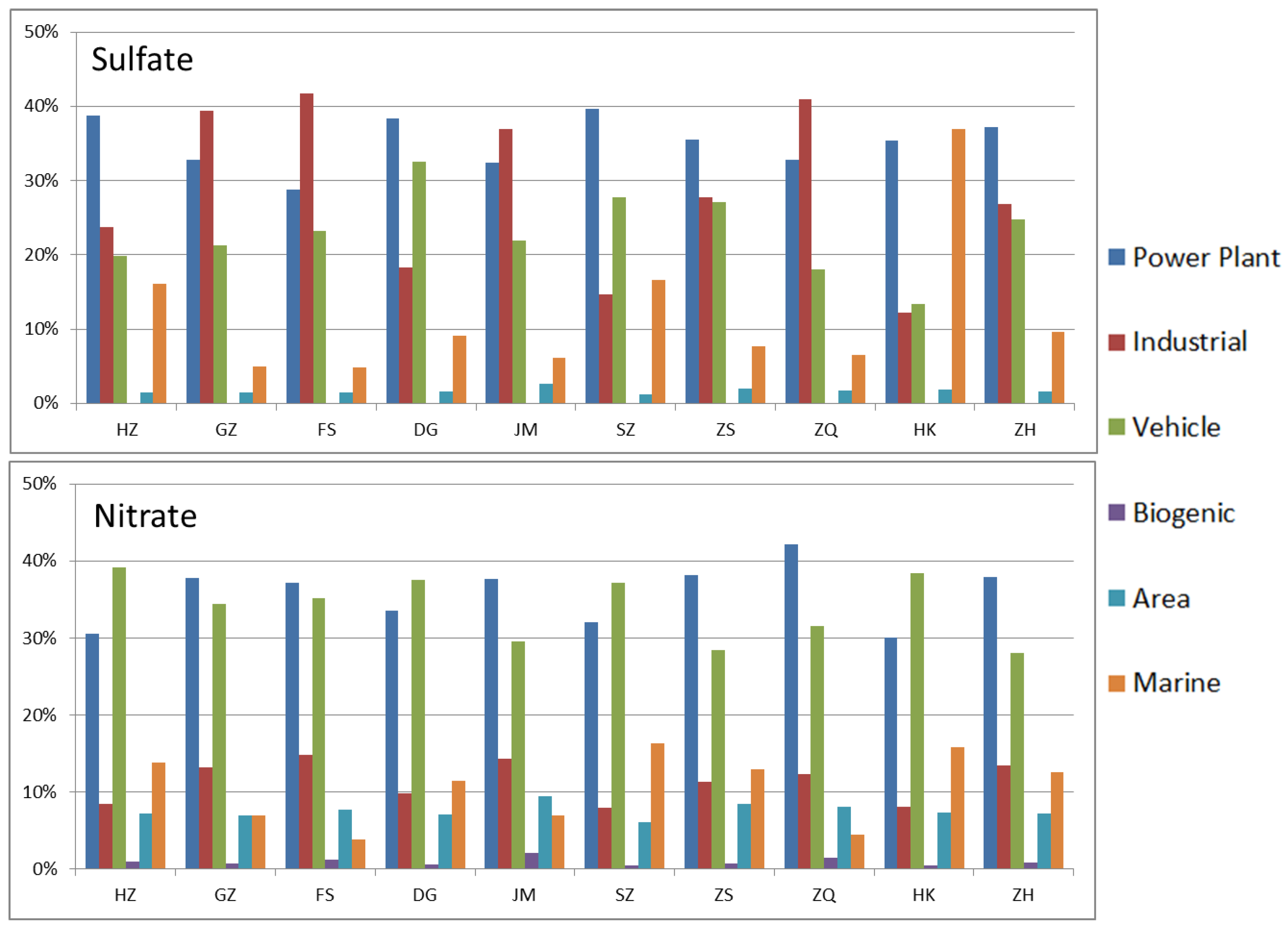
3.3. Source Category Contribution
3.4. Source Apportionment in City Center
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix
References
- Lu, X.; Fung, J.C.H.; Wu, D. Modeling wet deposition of acid substances over the PRD region in China. Atmosp. Environ. 2015, 122, 819–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, J.C.; Lau, A.K.; Fung, J.C.; Chen, F. Investigation of enhanced cross-city transport and trapping of air pollutants by coastal and urban land-sea breeze circulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2006, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lau, A.H.; Fung, J.H.; Zheng, J.Y.; Zhong, L.J.; Louie, P.K.K. Ozone source apportionment (OSAT) to differentiate local regional and super-regional source contributions in the Pearl River Delta region, China. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2012, 117, D15–D16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Fung, J.C.H.; Yao, T.; Lau, A.K.H. A study of control policy in the Pearl River Delta region by using the particulate matter source apportionment method. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 76, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Ma, H.; Lau, A.K.H.; Chan, P.W.; Yu, J.Z.; Xue, J. Enhancement in secondary particulate matter production due to mountain trapping. Atmos. Res. 2014, 147, 227–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yao, T.; Li, Y.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lau, A.K.H. Source apportionment and health effect of NOx over the Pearl River Delta region in southern China. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 212, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Lau, A.K.H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.Z.; Louie, P.K.; Fung, J.C. Identification and spatiotemporal variations of dominant PM10 sources over Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Griffith, S.M.; Yu, X.; Lau, A.K.; Yu, J.Z. Effect of nitrate and sulfate relative abundance in PM2.5 on liquid water content explored through half-hourly observations of inorganic soluble aerosols at a polluted receptor site. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.H.; Bian, Q.; Ng, W.M.; Louie, P.K.; Yu, J.Z. Characterization of PM2.5 major components and source investigation in suburban Hong Kong: A one year monitoring study. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2014, 14, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Li, J.; Ying, Q.; Yu, J.Z.; Wu, D.; Cheng, Y.; Jiang, J. Source apportionment of PM2.5 nitrate and sulfate in China using a source-oriented chemical transport model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 62, 228–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J.; Lam, Y.; Gao, Y.; Jacob, D.; Carouge, C.; Dolwick, P.; Jang, C. Recent study of U.S. ozone background concentrations using GEOS-Chem. In Proceedings of the 5th GEOS-Chem Meeting, Cambridge, MA, USA, 2–5 May 2011.
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
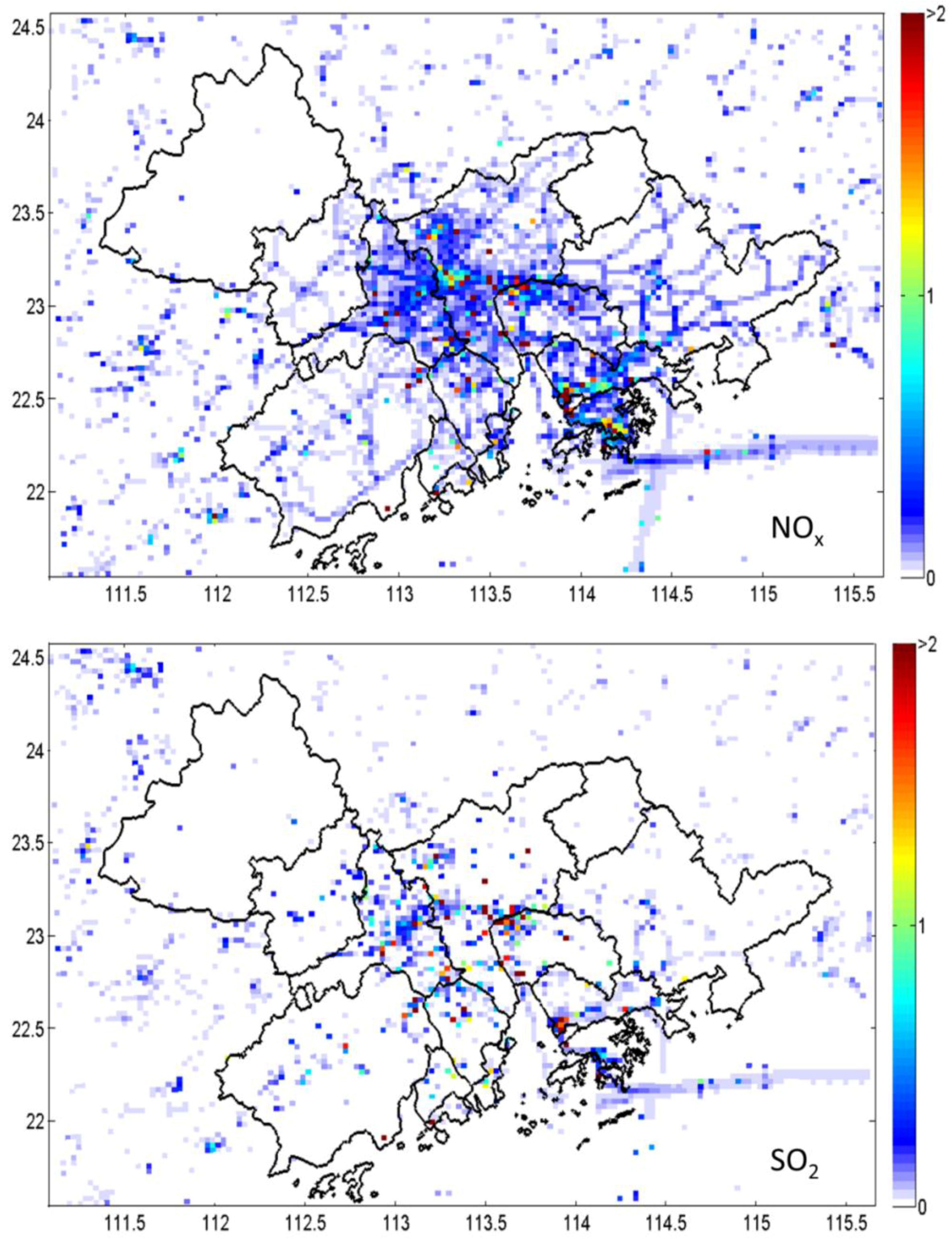
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, L.; Che, W.; Zheng, Z.; Yin, S. A highly resolved temporal and spatial air pollutant emission inventory for the Pearl River Delta region, China and its uncertainty assessment. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5112–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarwood, G.; Morris, R.E.; Wilson, G.M. Particulate matter source apportionment technology (PSAT) in the CAMx photochemical grid model. In Air Pollution Modeling and Its Application XVII; Springer US: New York, NY, USA, 2007; pp. 478–492. [Google Scholar]
- Kwok, R.H.; Fung, J.C.; Lau, A.K.; Fu, J.S. Numerical study on seasonal variations of gaseous pollutants and particulate matters in Hong Kong and Pearl River Delta Region. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. (1984–2012) 2010, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimadera, H.; Hayami, H.; Chatani, S.; Morino, Y.; Mori, Y.; Morikawa, T.; Ohara, T. Sensitivity analysis of influencing factors on PM2.5 nitrate simulation. In Proceedings of the 11th Annual CMAS Conference, Chapel Hill, NC, USA, 15–17 October 2012.
- Contini, D.; Cesari, D.; Genga, A.; Siciliano, M.; Ielpo, P.; Guascito, M.R.; Conte, M. Source apportionment of size-segregated atmospheric particles based on the major water-soluble components in Lecce (Italy). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 248–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, Q.; Kleeman, M. Regional contributions to airborne particulate matter in central California during a severe pollution episode. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 1218–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contini, D.; Cesari, D.; Conte, M.; Donateo, A. Application of PMF and CMB receptor models for the evaluation of the contribution of a large coal-fired power plant to PM10 concentrations. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 560, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becagli, S.; Sferlazzo, D.M.; Pace, G.; Sarra, A.D.; Bommarito, C.; Calzolai, G.; Ghedini, C.; Lucarelli, F.; Meloni, D.; Monteleone, F.; et al. Evidence for heavy fuel oil combustion aerosols from chemical analyses at the island of Lampedusa: A possible large role of ships emissions in the Mediterranean. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2012, 12, 3479–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesari, D.; Genga, A.; Ielpo, P.; Siciliano, M.; Mascolo, G.; Grasso, F.M.; Contini, D. Source apportionment of PM2.5 in the harbour–industrial area of Brindisi (Italy): Identification and estimation of the contribution of in-port ship emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 497, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffith, S.M.; Huang, X.H.; Louie, P.K.K.; Yu, J.Z. Characterizing the thermodynamic and chemical composition factors controlling PM2.5 nitrate: Insights gained from two years of online measurements in Hong Kong. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 864–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

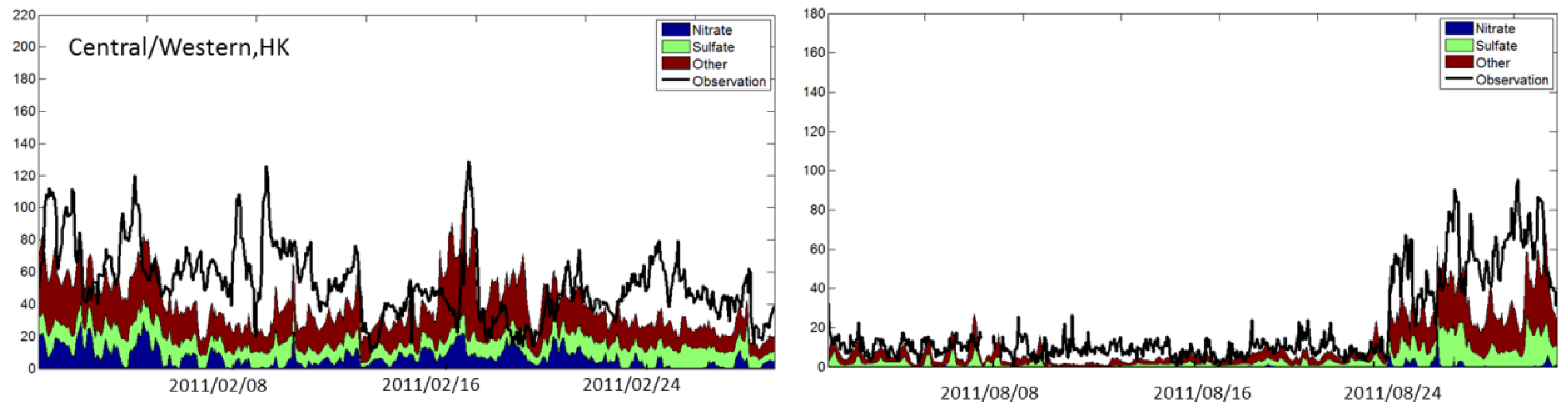
| RMSE | NMB | IOA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| February | Wind speed | 1.8 | 0.29 | 0.70 |
| Wind direction | - | −0.16 | 0.88 | |
| Temperature (2m) | 3 | 0.12 | 0.81 | |
| August | Wind speed | 1.4 | 0.37 | 0.68 |
| Wind direction | - | 0.05 | 0.88 | |
| Temperature (2m) | 2.2 | −0.009 | 0.73 | |
| PM2.5 | RMSE | IOA | NMB | Mean-Sim | Mean-OBS |
| February | 20.1 | 0.68 | −0.012 | 44.2 | 43.5 |
| August | 17.1 | 0.76 | −0.24 | 19.9 | 26.0 |
| Sulfate | RMSE | IOA | NMB | Mean-Sim | Mean-OBS |
| February | 6.1 | 0.60 | −0.19 | 10.6 | 13.2 |
| August | 4.9 | 0.81 | −0.35 | 4.2 | 6.6 |
| Nitrate | RMSE | IOA | NMB | Mean-Sim | Mean-OBS |
| February | 6.0 | 0.43 | 0.62 | 5.2 | 3.2 |
| August | 1.5 | 0.29 | −0.51 | 0.4 | 0.8 |
| Sulfate | ||||||
| February | August | |||||
| Local | Regional | S-Regional | Local | Regional | S-Regional | |
| HZ | 0.4 (4%) | 0.2 (2%) | 10.0 (94%) | 0.3 (6%) | 1.1 (23%) | 3.4 (71%) |
| GZ | 1.5 (12%) | 1.3 (10%) | 9.5 (78%) | 1.3 (19%) | 1.6 (23%) | 4.0 (58%) |
| FS | 1.6 (11%) | 3.0 (22%) | 9.3 (67%) | 1.0 (14%) | 1.8 (26%) | 4.1 (60%) |
| DG | 1.2 (10%) | 1.3 (11%) | 9.7 (79%) | 0.9 (16%) | 1.4 (24%) | 3.6 (60%) |
| JM | 1.0 (8%) | 1.9 (16%) | 9.0 (76%) | 0.6 (12%) | 0.8 (15%) | 3.9 (74%) |
| SZ | 1.3 (11%) | 0.7 (7%) | 9.8 (82%) | 1.2 (22%) | 1.0 (19%) | 3.3 (60%) |
| ZS | 0.7 (6%) | 2.5 (20%) | 9.3 (74%) | 0.4 (8%) | 1.2 (23%) | 3.5 (69%) |
| ZQ | 0.8 (6%) | 2.7 (21%) | 9.2 (73%) | 0.4 (6%) | 1.9 (27%) | 4.7 (67%) |
| HK | 0.4 (4%) | 0.5 (5%) | 10.0 (92%) | 0.7 (16%) | 0.5 (12%) | 3.1 (73%) |
| ZH | 0.6 (5%) | 1.6 (14%) | 9.3 (81%) | 0.3 (7%) | 0.7 (15%) | 3.3 (77%) |
| Nitrate | ||||||
| February | August | |||||
| Local | Regional | S-Regional | Local | Regional | S-Regional | |
| HZ | 0.7 (12%) | 0.2 (4%) | 5.0 (85%) | 0.1 (13%) | 0.4 (49%) | 0.3 (38%) |
| GZ | 1.7 (17%) | 3.2 (33%) | 4.8 (50%) | 0.2 (22%) | 0.5 (54%) | 0.2 (24%) |
| FS | 1.7 (14%) | 5.4 (44%) | 5.2 (42%) | 0.2 (23%) | 0.4 (49%) | 0.2 (28%) |
| DG | 0.8 (10%) | 2.7 (34%) | 4.3 (55%) | 0.04 (11%) | 0.2 (58%) | 0.1 (31%) |
| JM | 0.9 (9%) | 4.3 (47%) | 4.1 (44%) | 0.2 (25%) | 0.2 (31%) | 0.3 (44%) |
| SZ | 1.0 (13%) | 1.4 (19%) | 5.0 (68%) | 0.1 (14%) | 0.2 (51%) | 0.1 (35%) |
| ZS | 0.6 (5%) | 5.4 (50%) | 4.9 (45%) | 0.1 (11%) | 0.4 (64%) | 0.2 (25%) |
| ZQ | 0.8 (7%) | 5.5 (48%) | 5.2 (45%) | 0.1 (8%) | 0.6 (60%) | 0.3 (32%) |
| HK | 0.6 (10%) | 0.8 (14%) | 4.6 (76%) | 0.1 (30%) | 0.2 (40%) | 0.1 (30%) |
| ZH | 0.5 (6%) | 3.9 (49%) | 3.6 (45%) | 0.1 (15%) | 0.3 (59%) | 0.1 (26%) |
| February | ||||||
| Sulfate | Nitrate | |||||
| HZ | HK (24%) | SZ (21%) | DG (20%) | SZ (34%) | DG (22%) | GZ (21%) |
| GZ | DG (28%) | HK (21%) | SZ (18%) | DG (24%) | SZ (24%) | HK (19%) |
| FS | GZ (49%) | HK (12%) | JM (9%) | GZ (38%) | HK (12%) | DG (11%) |
| DG | SZ (31%) | HZ (31%) | HK (18%) | HZ (34%) | SZ (34%) | HK (20%) |
| JM | GZ (27%) | FS (21%) | HK (15%) | GZ (29%) | FS (22%) | DG (12%) |
| SZ | HK (36%) | HZ (30%) | DG (23%) | HK (40%) | HZ (39%) | DG (17%) |
| ZS | HK (23%) | SZ (17%) | ZH (14%) | HK (24%) | GZ (20%) | SZ (20%) |
| ZQ | FS (34%) | GZ (19%) | JM (14%) | FS (28%) | GZ (26%) | JM (15%) |
| HK | SZ (55%) | HZ (20%) | DG (11%) | SZ (47%) | HZ (34%) | DG (11%) |
| ZH | HK (26%) | DG (15%) | SZ (14%) | HK (21%) | GZ (20%) | SZ (20%) |
| August | ||||||
| Sulfate | Nitrate | |||||
| HZ | HK (36%) | DG (21%) | SZ (18%) | HK (39%) | SZ (27%) | DG (17%) |
| GZ | DG (30%) | HK (16%) | FS (14%) | DG (21%) | HK (16%) | FS (14%) |
| FS | GZ (27%) | JM (16%) | DG (15%) | JM (37%) | GZ (17%) | ZH (15%) |
| DG | SZ (32%) | HK (27%) | GZ (15%) | SZ (27%) | HK (25%) | GZ (13%) |
| JM | HK (21%) | FS (17%) | ZH (16%) | FS (27%) | ZH (27%) | GZ (20%) |
| SZ | HK (62%) | DG (13%) | GZ (7%) | HK (51%) | GZ (13%) | DG (10%) |
| ZS | ZH (23%) | HK (19%) | GZ (18%) | HK (20%) | ZH (20%) | GZ (19%) |
| ZQ | FS (23%) | GZ (16%) | JM (16%) | JM (38%) | FS (16%) | ZH (12%) |
| HK | SZ (41%) | DG (20%) | GZ (15%) | SZ (39%) | GZ (16%) | DG (14%) |
| ZH | HK (25%) | GZ (18%) | DG (16%) | GZ (25%) | SZ (21%) | DG (14%) |
| February-Sulfates | GZ | SZ | HK |
| Local | 32% | 16% | 6% |
| Regional | 9% | 6% | 3% |
| Super-regional | 59% | 78% | 91% |
| August-Sulfates | GZ | SZ | HK |
| Local | 32% | 25% | 23% |
| Regional | 18% | 20% | 10% |
| Super-regional | 47% | 55% | 67% |
| February-Nitrates | GZ | SZ | HK |
| Local | 27% | 15% | 12% |
| Regional | 34% | 14% | 9% |
| Super-regional | 39% | 71% | 79% |
| August-Nitrates | GZ | SZ | HK |
| Local | 33% | 24% | 11% |
| Regional | 47% | 43% | 49% |
| Super-regional | 20% | 33% | 40% |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, X.; Fung, J.C.H. Source Apportionment of Sulfate and Nitrate over the Pearl River Delta Region in China. Atmosphere 2016, 7, 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7080098
Lu X, Fung JCH. Source Apportionment of Sulfate and Nitrate over the Pearl River Delta Region in China. Atmosphere. 2016; 7(8):98. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7080098
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Xingcheng, and Jimmy C. H. Fung. 2016. "Source Apportionment of Sulfate and Nitrate over the Pearl River Delta Region in China" Atmosphere 7, no. 8: 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7080098
APA StyleLu, X., & Fung, J. C. H. (2016). Source Apportionment of Sulfate and Nitrate over the Pearl River Delta Region in China. Atmosphere, 7(8), 98. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos7080098