Scaling Flux Tower Observations of Sensible Heat Flux Using Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
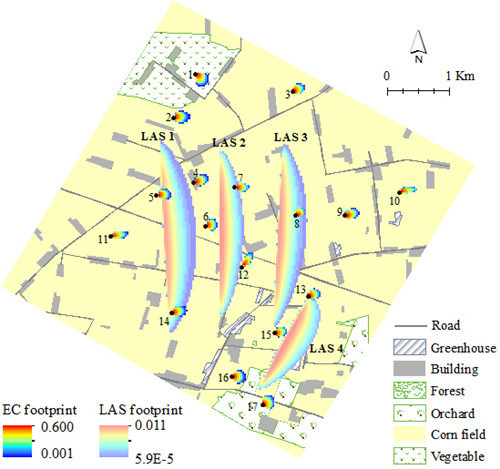
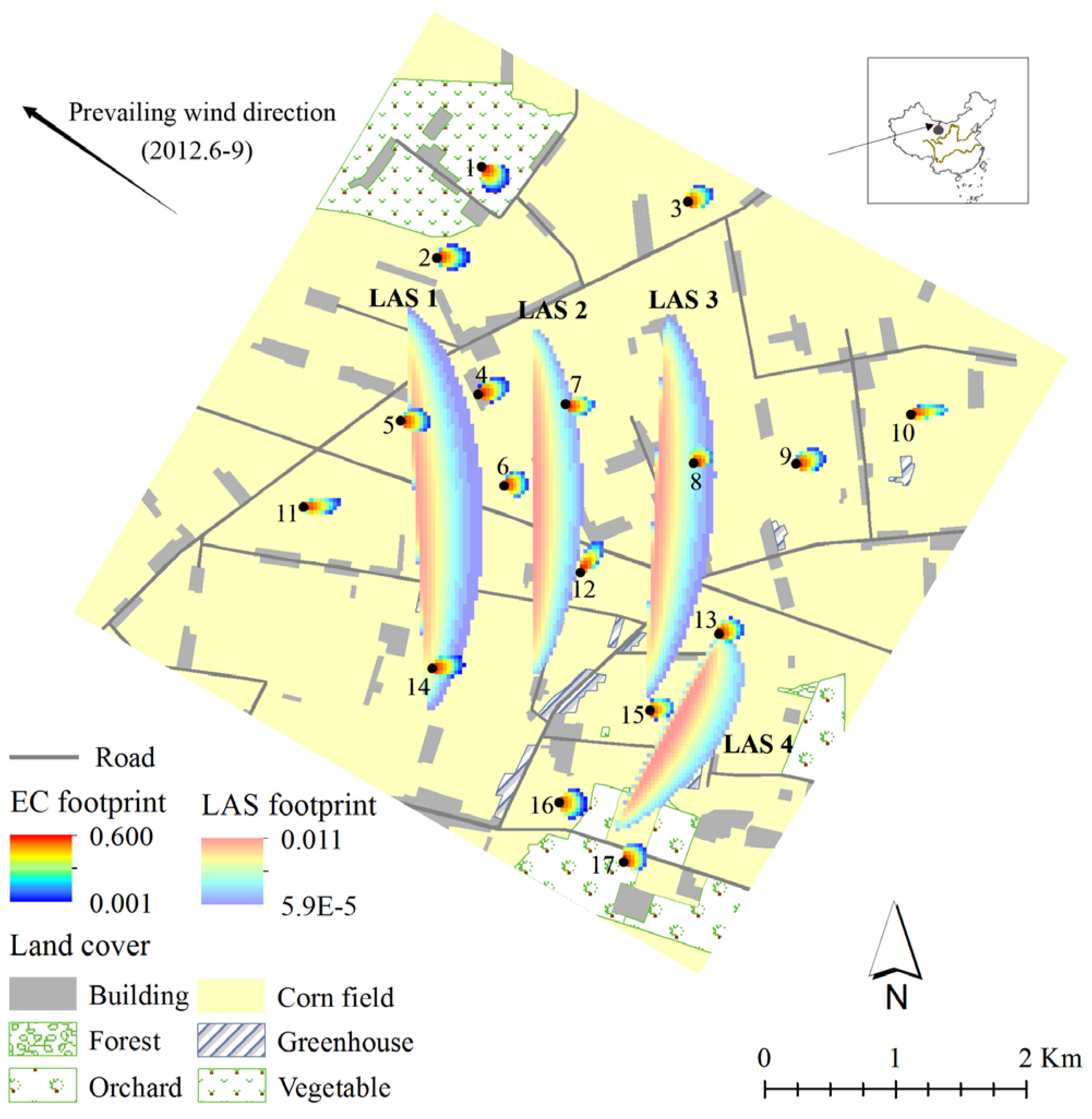
2.1. Study Area and Data Description
2.2. Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging
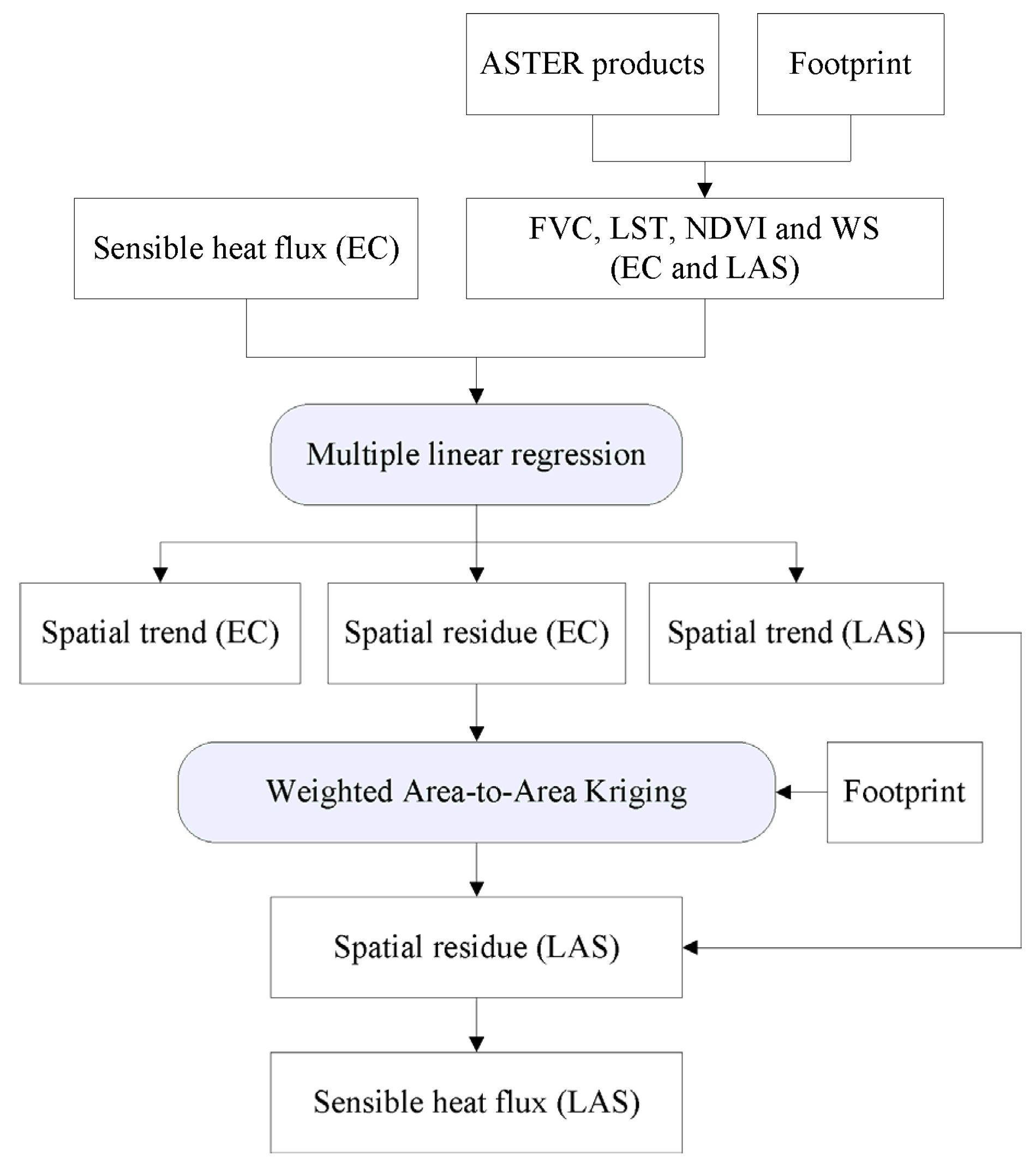
2.2.1. Spatial Trend Extraction
2.2.2. Weighted Area-to-Area Kriging
2.2.3. Point-to-Point Variogram Reconstruction
3. Results and Discussion
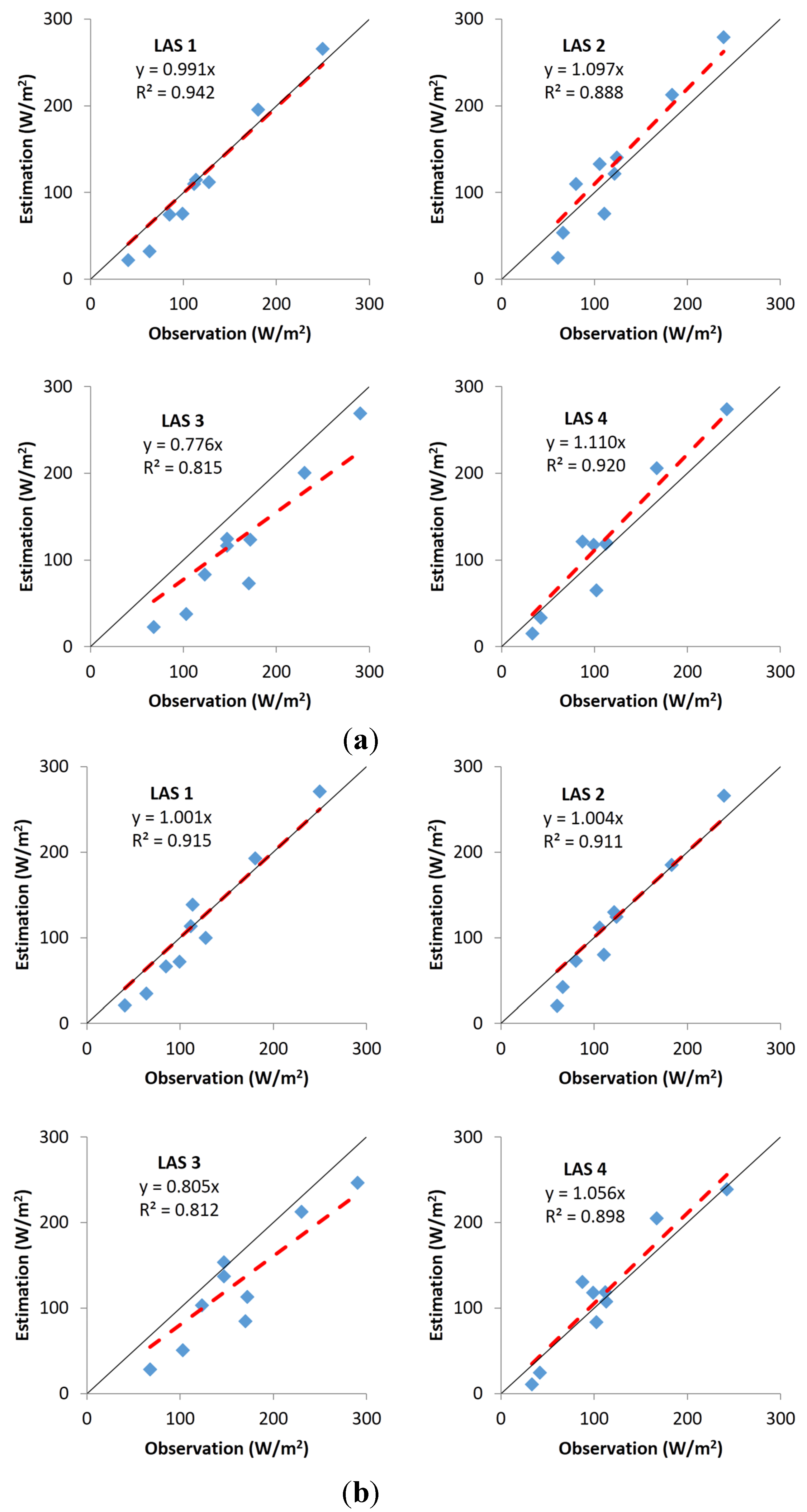
| Model | LAS 1 | LAS 2 | LAS 3 | LAS 4 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slope | RMSE | MBE | Slope | RMSE | MBE | Slope | RMSE | MBE | Slope | RMSE | MBE | |
| Area-weighted [31] | 0.965 | 23.7 | −13.3 | 0.923 | 27.0 | −18.5 | 0.704 | 59.7 | −56.6 | 0.910 | 25.5 | −13.5 |
| Footprint-weighted [31] | 0.996 | 30.0 | −12.2 | 0.924 | 27.9 | −18.6 | 0.726 | 54.4 | −51.6 | 0.917 | 26.6 | −13.5 |
| Multiple linear regression | 0.991 | 17.5 | −7.7 | 1.097 | 23.6 | −4.6 | 0.776 | 43.0 | −33.4 | 1.110 | 25.7 | 8.0 |
| ATA RK [20] | 0.961 | 17.6 | −11.2 | 1.006 | 23.5 | −6.3 | 0.784 | 48.0 | −40.4 | 1.040 | 20.7 | 1.6 |
| WATA RK | 1.001 | 21.0 | −6.8 | 1.004 | 21.1 | −6.4 | 0.805 | 44.5 | −30.6 | 1.056 | 23.4 | 4.4 |
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baldocchi, D.D.; Vogel, C.A.; Hall, B. Seasonal variation of carbon dioxide exchange rates above and below a boreal jack pine forest. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1997, 83, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, K.B.; Baldocchi, D.D. Seasonal and interannual variability of energy fluxes over a broadleaved temperate deciduous forest in North America. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2000, 100, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.M.; Xu, Z.W.; Wang, W.Z.; Jia, Z.Z.; Zhu, M.J.; Bai, J.; Wang, J.M. A comparison of eddy-covariance and large aperture scintillometer measurements with respect to the energy balance closure problem. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1291–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mito, C.O.; Boiyo, R.K.; Laneve, G. A simple algorithm to estimate sensible heat flux from remotely sensed MODIS data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 6109–6121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.J.; Hall, F.G.; Asrar, G.; Strebel, D.E.; Murphy, R.E. An overview of the first international satellite land surface climatology project (ISLSCP) field experiment (FIFE). J. Geophys. Res. 1992, 97, 18345–18371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhoff, A.L.; Paz, A.R.; Aragao, L.E.O.C.; Mu, Q.; Malhi, Y.; Collischonn, W.; Rocha, H.R.; Running, S.W. Assessment of the MODIS global evapotranspiration algorithm using eddy covariance measurements and hydrological modelling in the Rio Grande basin. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2013, 58, 1658–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batra, N.; Islam, S.; Venturini, V.; Bisht, G.; Jiang, L. Estimation and comparison of evapotranspiration from MODIS and AVHRR sensors for clear sky days over the Southern Great Plains. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 103, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.; Tasumi, M.; Morse, A.; Trezza, R. A Landsat-based energy balance and evapotranspiration model in Western US water rights regulation and planning. Irrig. Drain. Syst. 2005, 19, 251–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, B.; Li, J.; Shaomin, L.; Ziwei, X.; Guangcheng, H.; Mingjia, Z.; Lisheng, S. Characterizing the footprint of eddy covariance system and large aperture scintillometer measurements to validate satellite-based surface fluxes. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 943–947. [Google Scholar]
- Hemakumara, H.M.; Chandrapala, L.; Moene, A.F. Evapotranspiration fluxes over mixed vegetation areas measured from large aperture scintillometer. Agric. Water Manag. 2003, 58, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moene, A.F.; Hartogensis, O.K.; Beyrich, F. Developments in Scintillometry. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2009, 90, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruber, M.; Fochesatto, G. A New Sensitivity Analysis and Solution Method for Scintillometer Measurements of Area-Averaged Turbulent Fluxes. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2013, 149, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André, J.; Bougeault, P.; Goutorbe, J. Regional estimates of heat and evaporation fluxes over non-homogeneous terrain. Examples from the HAPEX-MOBILHY programme. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 1990, 50, 77–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halldin, S.; Gryning, S.; Gottschalk, L.; Jochum, A.; Lundin, L.; van de Griend, A.A. Energy, water and carbon exchange in a boreal forest landscape—NOPEX experiences. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 98–99, 5–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyrich, F.; Mengelkamp, H. Evaporation over a Heterogeneous Land Surface: EVA_GRIPS and the LITFASS-2003 Experiment—An Overview. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2006, 121, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellers, P.; Hall, F.; Ranson, K.J.; Margolis, H.; Kelly, B.; Baldocchi, D.; den Hartog, G.; Cihlar, J.; Ryan, M.G.; Goodison, B.; et al. The Boreal Ecosystem–Atmosphere Study (BOREAS): An Overview and Early Results from the 1994 Field Year. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1995, 76, 1549–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gottschalk, L.; Batchvarova, E.; Gryning, S.; Lindroth, A.; Melas, D.; Motovilov, Y.; Frech, M.; Heikinheimo, M.; Samuelsson, P.; Grelle, A.; et al. Scale aggregation—comparison of flux estimates from NOPEX. Agric. For. Meteorol. 1999, 98–99, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gryning, S.; Halldin, S.; Lindroth, A. Area averaging of land surface-atmosphere fluxes in NOPEX: Challenges, results and perspectives. Boreal Environ. Res. 2002, 7, 379–387. [Google Scholar]
- Ezzahar, J.; Chehbouni, A.; Hoedjes, J.C.B.; Chehbouni, A. On the application of scintillometry over heterogeneous grids. J. Hydrol. 2007, 334, 493–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, S. Upscaling sensible heat fluxes with area-to-area regression Kriging. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2015, 12, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistical analysis of health data with different levels of spatial aggregation. Spat. Spatio-Temporal Epidemiol. 2012, 3, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotway, C.A.; Young, L.J. Combining incompatible spatial data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 2002, 97, 632–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakidis, P.C. A geostatistical framework for area-to-point spatial interpolation. Geogr. Anal. 2004, 36, 259–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Cheng, G.; Liu, S.; Xiao, Q.; Ma, M.; Jin, R.; Che, T.; Liu, Q.; Wang, W.; Qi, Y.; et al. Heihe watershed allied telemetry experimental research (HiWATER): Scientific objectives and experimental design. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2013, 94, 1145–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, X.; Shi, S.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Z.; Xu, T.; Wang, W.; Ma, M. Intercomparison of surface energy flux measurement systems used during the HiWATER-MUSOEXE. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 13140–13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, D.; Zhan, W. Intercomparison of methods for estimating land surface temperature from a Landsat-5 TM image in an arid region with low water vapour in the atmosphere. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2011, 33, 2582–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastiaanssen, W.G.M.; Cheema, M.J.M.; Immerzeel, W.W.; Miltenburg, I.J.; Pelgrum, H. Surface energy balance and actual evapotranspiration of the transboundary Indus Basin estimated from satellite measurements and the ETLook model. Water Resour. Res. 2012, 48, W11512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matheron, G. The intrinsic random functions and their applications. Adv. Appl. Probab. 1973, 5, 439–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isaaks, E.H.; Srivastava, R.M. Applied Geostatistics; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Truong, P.N.; Heuvelink, G.B.M.; Pebesma, E. Bayesian area-to-point kriging using expert knowledge as informative priors. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2014, 30, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y. Research on Area-to-Area Regression Kriging for Scaling of Sensible Heat Flux. Master’s Thesis, The University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zeweldi, D.; Gebremichael, M.; Wang, J.; Sammis, T.; Kleissl, J.; Miller, D. Intercomparison of Sensible Heat Flux from Large Aperture Scintillometer and Eddy Covariance Methods: Field Experiment over a Homogeneous Semi-arid Region. Bound.-Layer Meteorol. 2010, 135, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foken, T.; Aubinet, M.; Finnigan, J.J.; Leclerc, M.Y.; Mauder, M.; Paw, K.T. Results of a panel discussion about the energy balance closure correction for trace gases. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 92, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Long, D.; Guan, H.; Liang, W.; Simmons, C.; Batelaan, K. Comparison of three dual-source remote sensing evapotranspiration models during the MUSOEXE-12 campaign: Revisit of model physics. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 3145–3165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Liang, S.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Fisher, J.B.; Zhang, X.; Jia, K.; Zhao, X.; Qin, Q.; Zhao, B.; et al. MODIS-driven estimation of terrestrial latent heat flux in China based on a modified Priestley–Taylor algorithm. Agric. Forest Meteorol. 2013, 171–172, 187–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Wang, J.; Ge, Y.; Liu, M.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Xu, T. Scaling Flux Tower Observations of Sensible Heat Flux Using Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1032-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6081032
Hu M, Wang J, Ge Y, Liu M, Liu S, Xu Z, Xu T. Scaling Flux Tower Observations of Sensible Heat Flux Using Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging. Atmosphere. 2015; 6(8):1032-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6081032
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Maogui, Jianghao Wang, Yong Ge, Mengxiao Liu, Shaomin Liu, Ziwei Xu, and Tongren Xu. 2015. "Scaling Flux Tower Observations of Sensible Heat Flux Using Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging" Atmosphere 6, no. 8: 1032-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6081032
APA StyleHu, M., Wang, J., Ge, Y., Liu, M., Liu, S., Xu, Z., & Xu, T. (2015). Scaling Flux Tower Observations of Sensible Heat Flux Using Weighted Area-to-Area Regression Kriging. Atmosphere, 6(8), 1032-1044. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos6081032