Analysis on Effectiveness of SO2 Emission Reduction in Shanxi, China by Satellite Remote Sensing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Data and Method
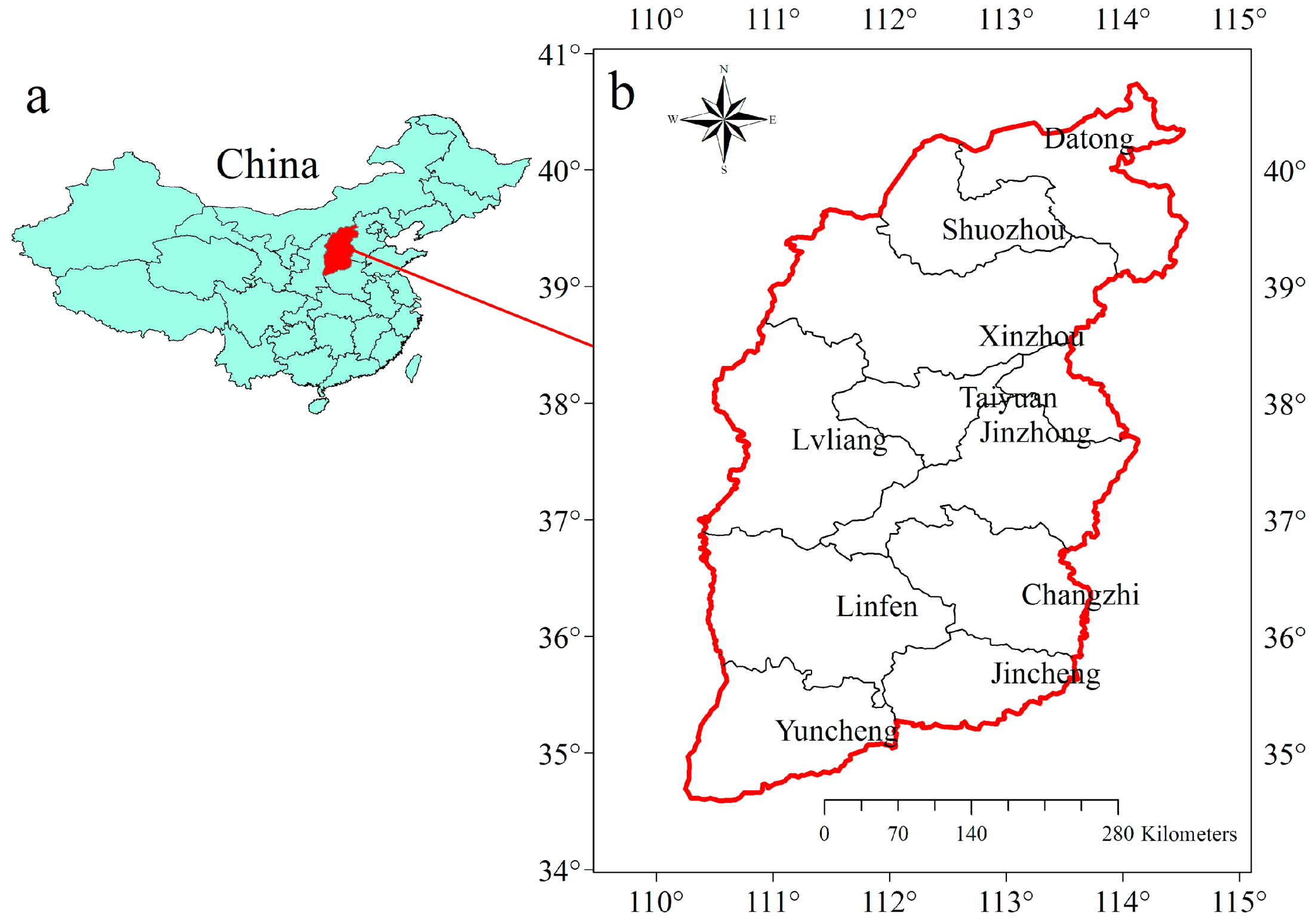
2.1. Site Description
2.2. OMI SO2 Data and Processing
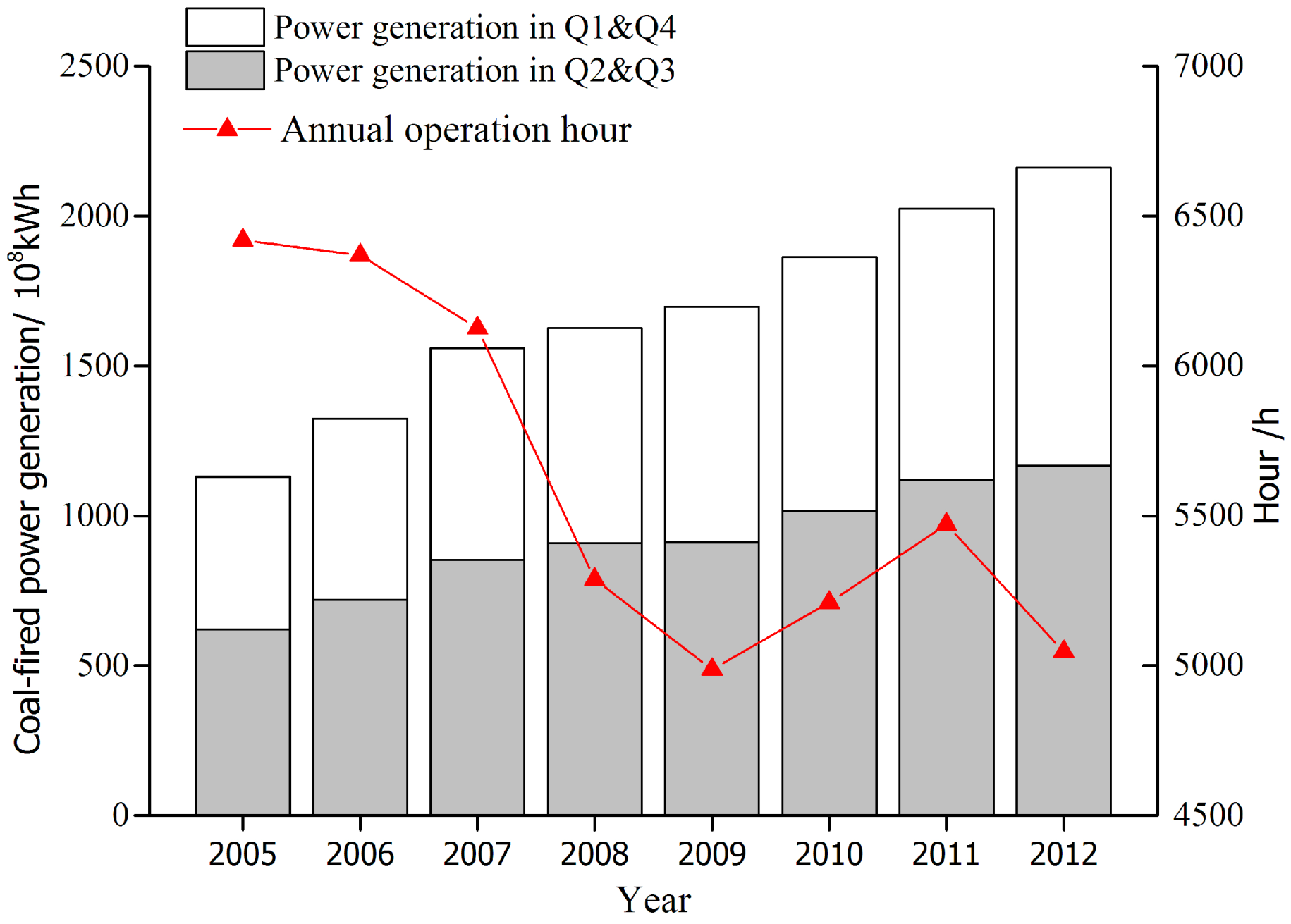
2.3. SO2 Emission Estimation
3. Results and Discussion
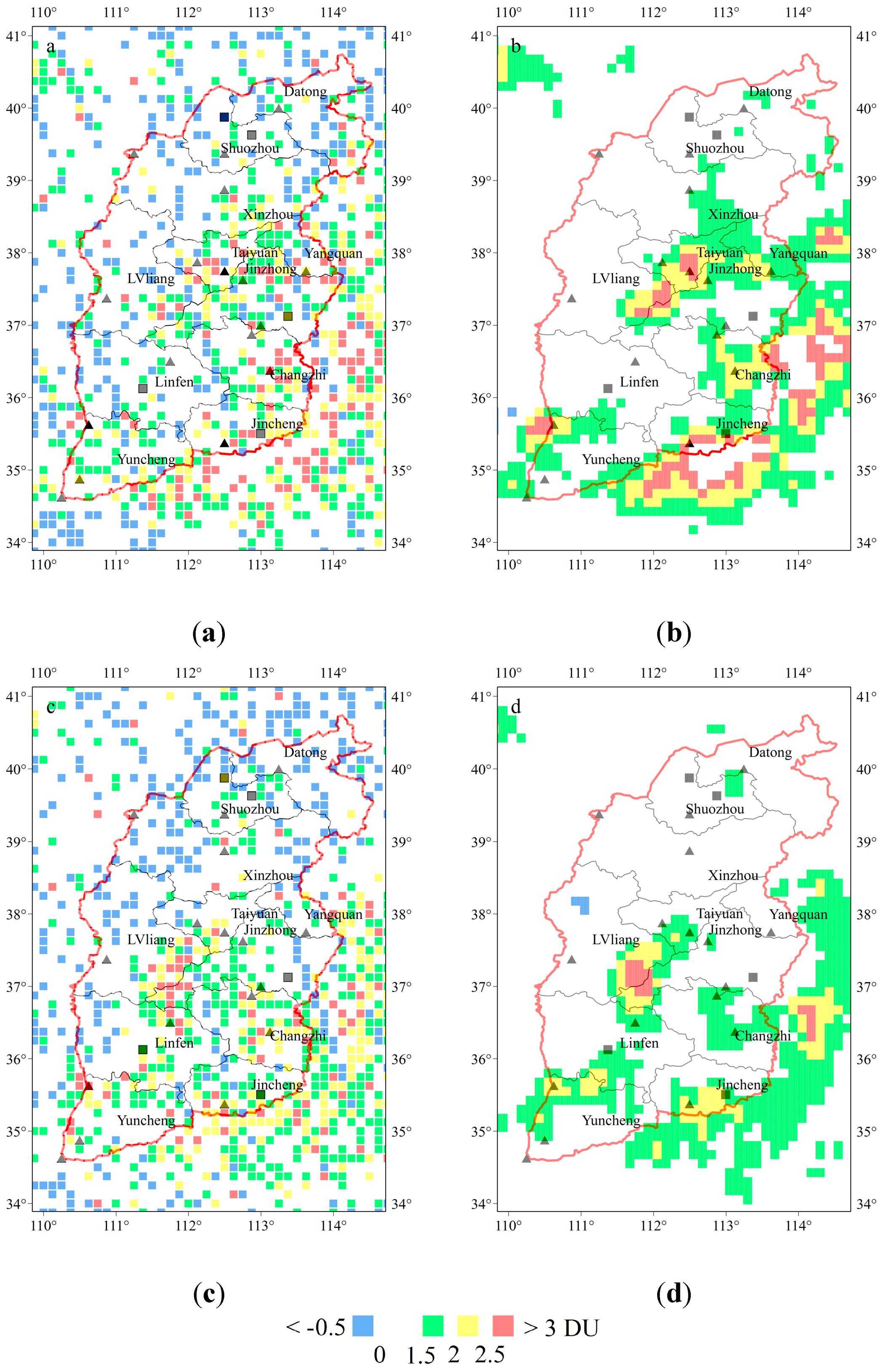
3.1. Spatial-Temporal Variation Characteristics of SO2
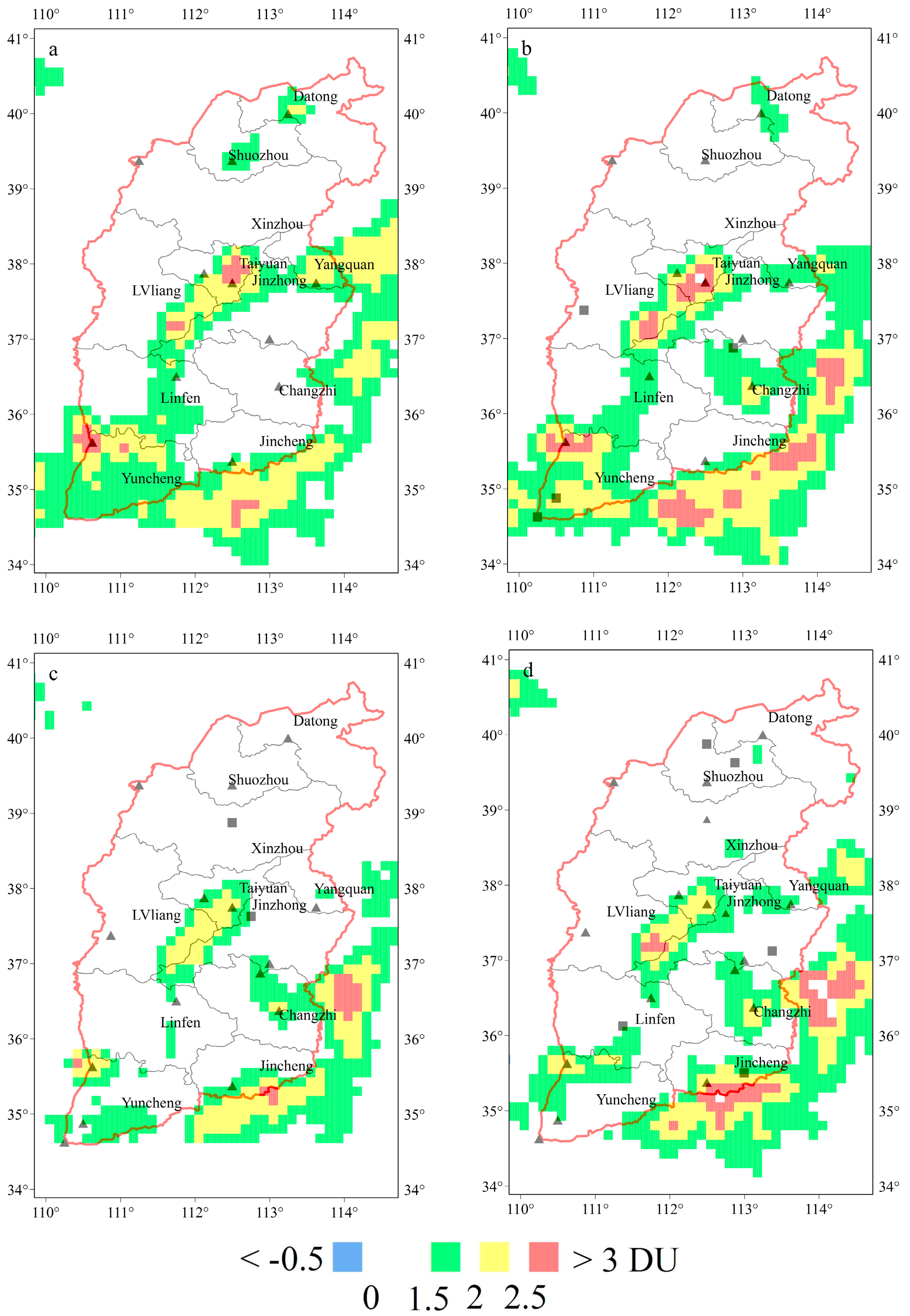
3.2. Evolution of SO2 over Selected Regions
| Location | Operated Time | SO2/DU | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |||
| Changzhi * | 36.375°N, 113.125°E | 2005 | 1.159 | 1.490 | 1.793 | 2.243 | 2.032 | 1.836 | 2.281 | 1.791 |
| Yushe | 37°N, 113°E | 2005 | 0.987 | 1.145 | 1.147 | 1.274 | 1.402 | 1.286 | 1.458 | 1.509 |
| Datong * | 40°N, 113.25°E | 2005 | 2.232 | 1.511 | 1.950 | 1.242 | 0.795 | 0.866 | 1.167 | 1.398 |
| Yangcheng * | 35.375°N, 112.5°E | 2005 | 2.249 | 1.156 | 0.958 | 1.628 | 1.665 | 1.681 | 2.651 | 2.036 |
| Shuozhou * | 39.375°N, 112.5°E | 2005 | 1.616 | 1.795 | 1.486 | 0.679 | 1.532 | 1.028 | 1.200 | 1.297 |
| Taiyuan * | 37.75°N, 112.5°E | 2005 | 2.395 | 2.660 | 3.030 | 2.474 | 2.219 | 1.739 | 2.587 | 1.673 |
| Hequ * | 39.375°N, 111.25°E | 2005 | 0.990 | 1.106 | 0.898 | 0.786 | 0.993 | 0.844 | 0.774 | 0.637 |
| Pingding * | 37.75°N, 113.625°E | 2005 | 2.232 | 1.745 | 1.739 | 1.597 | 1.449 | 1.281 | 1.988 | 1.085 |
| Hejin * | 35.625°N, 110.625°E | 2005 | 2.377 | 2.606 | 2.420 | 2.608 | 2.120 | 2.589 | 2.436 | 2.090 |
| Huozhou | 36.125°N, 111.375°E | 2006 | 1.582 | 1.661 | 1.670 | 1.505 | 1.105 | 1.219 | 1.303 | 1.481 |
| Gujiao | 37.875°N, 112.125°E | 2006 | 1.853 | 1.403 | 1.782 | 2.268 | 1.899 | 1.386 | 1.691 | 1.217 |
| Wuxiang | 36.875°N, 112.875°E | 2007 | 1.004 | 1.017 | 1.442 | 1.603 | 1.812 | 1.651 | 1.800 | 1.743 |
| Yongji | 34.875°N, 110.5°E | 2007 | 1.767 | 1.953 | 2.348 | 1.973 | 1.302 | 1.625 | 1.349 | 1.468 |
| Ruicheng | 34.625°N, 110.25°E | 2008 | 1.577 | 1.527 | 1.811 | 1.732 | 1.587 | 1.212 | 1.372 | 1.098 |
| Liulin | 37.375°N, 110.875°E | 2008 | 0.948 | 0.937 | 0.848 | 1.044 | 1.186 | 0.767 | 1.214 | 0.981 |
| Jinzhong | 37.625°N, 112.75°E | 2010 | 1.900 | 2.013 | 2.218 | 1.771 | 1.610 | 1.175 | 1.953 | 1.400 |
| Yuanping | 38.875°N, 112.5°E | 2010 | 0.849 | 0.937 | 0.997 | 0.768 | 0.832 | 0.917 | 1.307 | 1.268 |
| LinFen | 36.5°N, 111.75°E | 2011 | 1.652 | 1.755 | 1.910 | 1.442 | 1.163 | 1.573 | 1.124 | 1.871 |
| Zezhou | 35.5°N, 113°E | 2011 | 1.984 | 1.200 | 1.233 | 1.902 | 1.727 | 1.954 | 2.119 | 1.897 |
| Zuoquan | 37.125°N, 113.375°E | 2012 | 0.519 | 0.731 | 0.589 | 0.464 | 0.566 | 0.331 | 1.171 | 0.641 |
| Youyu | 39.875°N, 112.5°E | 2012 | 0.798 | 1.000 | 0.827 | 0.222 | 0.959 | 0.875 | 0.773 | 1.021 |
| Shanyin | 39.625°N, 112.875°E | 2012 | 1.247 | 1.727 | 1.165 | 1.035 | 0.879 | 0.894 | 1.030 | 1.223 |
3.3. SO2 Emission by Inventory
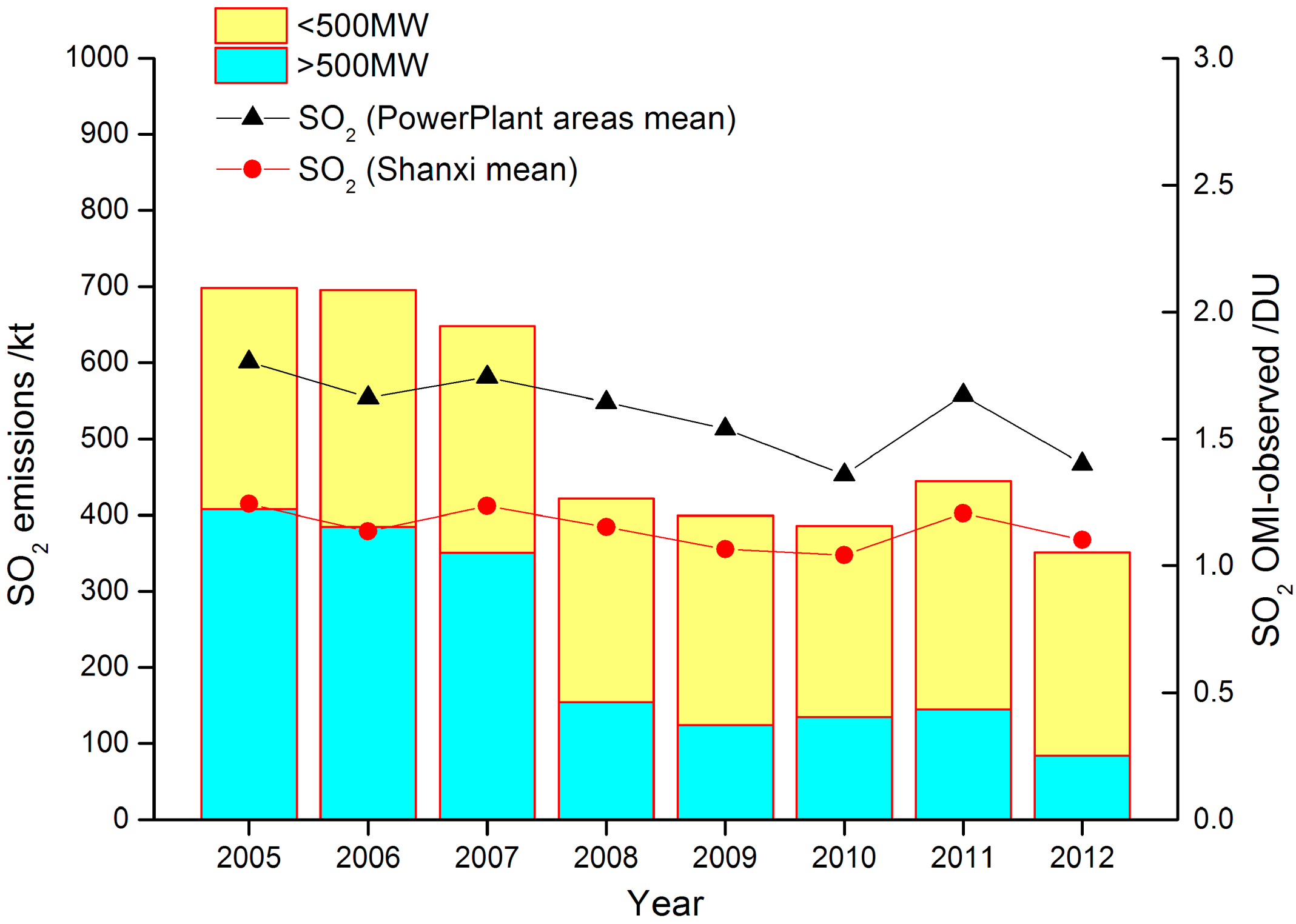
3.4. Other Emission Sources Contributed to SO2 Pollution

4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- National Bureau of Statistics. In China Statistical Yearbook 2005–2012; China Statistics Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese)
- Jaeglé, L.; Jacob, D.J.; Wang, Y.; Weinheimer, A.J.; Ridley, B.A.; Campos, T.L.; Sachse, G.W.; Hagen, D.E. Sources and chemistry of NOx in the upper troposphere over the United States. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 1705–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strouda, C.; Madronicha, S.; Atlasa, E.; Ridleya, B.; Flockea, F.; Weinheimera, A.; Talbotb, B.; Frieda, A.; Werta, B.; Shetter, R.; et al. Photochemistry in the arctic free troposphere: NOx budget and the role of odd nitrogen reservoir recycling. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 3351–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badr, O.; Probert, S.D. Atmospheric sulphur: Trends, sources, sinks and environmental impacts. Appl. Energy 1994, 47, 1–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Duan, L.; Xing, J.; Larssen, T.; Nielsen, C.P.; Hao, J. Soil acidification in China: Is controlling SO2 emissions enough? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 8021–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Akimoto, H.; Kurokawa, J.; Horii, N.; Yamaji, K.; Yan, X.; Hayasaka, T. An Asian emission inventory of anthropogenic emission sources for the period 1980–2020. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2007, 7, 4419–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Yin, H.; Ai, N.; Huang, Z. Historical analysis of SO2 pollution control policies in China. Environ. Manag. 2009, 43, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G.; Carmichael, G.R.; He, K.B.; Huo, H.; Kannari, A.; Klimont, Z.; Park, I.S.; Reddy, S.; Fu, J.S.; et al. Asian emissions in 2006 for the NASA INTEX-B mission. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2009, 9, 5131–5153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Streets, D.G. Sulfur dioxide and primary carbonaceous aerosol emissions in China and India, 1996–2010. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 9839–9864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreifels, J.J.; Fu, Y.; Wilson, E.J. Sulfur dioxide control in China: Policy evolution during the 10th and 11th Five-Year Plans and lessons for the future. Energy Policy. 2012, 48, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, J.C.; Schoeberl, M.R.; Douglass, A.R.; Gleason, J.F.; Krotkov, N.A.; Gille, J.C.; Pickering, K.E.; Livesey, N. Satellite observations of changes in air quality during the 2008 Beijing Olympics and Paralympics. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, N.; Valks, P.; Loyola, D.; Cheng, Y.F.; Zimmer, W. Space-Based measurements of air quality during the World Expo 2010 in Shanghai. Environ. Res. Lett. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonds, M.; Xiao, H.; Levine, S.P. Optical remote sensing for air pollutants-review. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1994, 55, 953–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, R.V. Satellite remote sensing of surface air quality. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 7823–7843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Levizzani, V.; Bauer, P. A review of satellite meteorology and climatology at the start of the twenty-first century. Prog. Phys. Geogr. 2009, 33, 474–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krueger, A.J.; Walter, L.S.; Schnetzler, C.C.; Doiron, S.D. TOMS measurement of the sulfur dioxide emitted during the 1985 Nevado del Ruiz eruptions. J. Volcanol. Geotherm. Res. 1990, 41, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bluth, G.J.; Doiron, S.D.; Schnetzler, C.C.; Krueger, A.J.; Walter, L.S. Global tracking of the SO2 clouds from the June, 1991 Mount Pinatubo eruptions. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1992, 19, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisinger, M.; Burrows, J.P. Tropospheric sulfur dioxide observed by the ERS-2 GOME instrument. Geophys. Res. Lett. 1998, 25, 4177–4180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, W.; Erbertseder, T.; Ruppert, T.; van Roozendael, M.; Verdebout, J.; Balis, D.; Meleti, C.; Zerefos, C. On the retrieval of volcanic sulfur dioxide emissions from GOME backscatter measurements. J. Atmos. Chem. 2005, 50, 295–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bovensmann, H.; Burrows, J.P.; Buchwitz, M.; Frerick, J.; Noël, S.; Rozanov, V.V.; Chance, K.V.; Goede, P.H. SCIAMACHY: Mission objectives and measurement modes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1999, 56, 127–150. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, C.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; O’Byrne, G.; Krotkov, N.; Richter, A.; Huey, L.G.; Holloway, J.S. Retrieval of vertical columns of sulfur dioxide from SCIAMACHY and OMI: Air mass factor algorithm development, validation, and error analysis. J. Geophys. Res. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Carn, S.A.; Krueger, A.J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Yang, K.; Levelt, P.F. Sulfur dioxide emissions from Peruvian copper smelters detected by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.; Krotkov, N.A.; Krueger, A.J.; Carn, S.A.; Bhartia, P.K.; Levelt, P.F. Retrieval of large volcanic SO2 columns from the aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument: Comparison and limitations. J. Geophys. Res. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgoulias, A.K.; Balis, D.; Koukouli, M.E.; Meleti, C.; Bais, A.; Zerefos, C. A study of the total atmospheric sulfur dioxide load using ground-based measurements and the satellite derived Sulfur Dioxide Index. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 43, 1693–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carn, S.A.; Krueger, A.J.; Krotkov, N.A.; Yang, K.; Evans, K. Tracking volcanic sulfur dioxide clouds for aviation hazard mitigation. Nat. Hazards 2009, 51, 325–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Martin, R.V.; van Donkelaar, A.; Lee, H.; Dickerson, R.R.; Hains, J.C.; Krotkov, N.; Richter, A.; Vinnikov, K.; Schwab, J.J. SO2 emissions and lifetimes: Estimates from inverse modeling using in situ and global, space-based (SCIAMACHY and OMI) observations. J. Geophys. Res. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioletov, V.E.; McLinden, C.A.; Krotkov, N.; Yang, K.; Loyola, D.G.; Valks, P.; Theys, N.; Van Roozendael, M.; Nowlan, C.R.; Chance, K.; et al. Application of OMI, SCIAMACHY, and GOME-2 satellite SO2 retrievals for detection of large emission sources. J. Geophys. Res.: Atmos. 2013, 118, 11399–11418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Ding, A.; Gao, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Lei, H.; Jin, D.; Qi, Y. Aircraft measurements of the vertical distribution of sulfur dioxide and aerosol scattering coefficient in China. Atmos Environ. 2010, 44, 278–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, C.; Loughner, C.P.; Li, Z.; Krotkov, N.A.; Yang, K.; Wang, L.; Zheng, Y.; Bao, X.; Zhao, G.; et al. SO2 over central China: Measurements, numerical simulations and the tropospheric sulfur budget. J. Geophys. Res. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zha, Y.; Gao, J.; Jiang, J. Monitoring of SO2 column concentration change over China from Aura OMI data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2012, 33, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, S.; Carmichael, G.R.; Cheng, Y.F.; Wei, C.; Chin, M.; Diehl, T.; Tan, Q. Sulfur dioxide emissions in China and sulfur trends in East Asia since 2000. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 6311–6331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Liu, K.; Zhou, J.; Lu, L.; Hao, J.; Qiu, P.; Gao, J.; Zhu, C.; Wang, K.; Hua, S. Atmospheric emission inventory of hazardous trace elements from China’s coal-fired power plants—Temporal trends and spatial variation characteristics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Xu, J.; Yang, J.; Zhao, X.; Wei, W.; Cheng, D.; Pan, X.; Su, J. Understanding haze pollution over the southern Hebei area of China using the CMAQ model. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 56, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Tan, S.C.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Shi, G.Y.; Zhang, M.X.; Che, H.Z. A multisource observation study of the severe prolonged regional haze episode over eastern China in January 2013. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 907–815. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, J.; Tie, X.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Gao, Y.; Zhao, D. Characteristics of heavy aerosol pollution during the 2012–2013 winter in Beijing, China. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 88, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- General Office of the State Council. Urgent Circular on Assuring the Supply of Electricity for Civil Living and Generation and Utilization of Electricity in Regular Order. Available online: http://www.gov.cn/zwgk/2010-11/23/content_1751457.htm (accessed on 30 July 2014). (In Chinese)
- Fioletov, V.E.; McLinden, C.A.; Krotkov, N.; Moran, M.D.; Yang, K. Estimation of SO2 emissions using OMI retrievals. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Streets, D.G.; de Foy, B.; Krotkov, N.A. Ozone monitoring instrument observations of interannual increases in SO2 emissions from Indian coal-fired power plants during 2005–2012. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 13993–14000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhang, Q.; Krotkov, N.A.; Streets, D.G.; He, K.; Tsay, S.C.; Gleason, J.F. Recent large reduction in sulfur dioxide emissions from Chinese power plants observed by the Ozone Monitoring Instrument. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. HJ/T178–2005 Flue Gas Circulation Fluidized Bed Desulfurization Project Technical Specification of Thermal Power Plant; China Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. HJ/T179–2005 Flue Gas Limestone/Limegypsum Desulfurization Project Technical Specification of Thermal Power Plant; China Environment Science Press: Beijing, China, 2005. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Department of Environmental Protection of Shanxi. 2005 Report on the State of Environment in Shanxi: Atmosphere. Available online: http://www.sxhb.gov.cn/news.do?action=info&id=4101 (accessed on 30 July 2014). (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Circular on Publishing the Key Projects for Atmospheric Pollution Reduction such as Desulfurization and Denitration Devices of Coal-Fired Equipments. Available online: http://www.mep.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201305/t20130506_251654.htm (accessed on 30 July 2014). (In Chinese)
- Editorial Committee of China Electric Power Yearbook. China Electric Power Yearbook 2005–2013; China Electric Power Press: Beijing, China, 2013. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Krotkov, N.A.; Carn, S.A.; Krueger, A.J.; Bhartia, P.K.; Yang, K. Band Residual Difference Algorithm for Retrieval of SO2 From the Aura Ozone Monitoring Instrument (OMI). IEEE Trans. Geosci. Remote Sens. 2006, 44, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotkov, N.A.; McClure, B.; Dickerson, R.R.; Carn, S.A.; Li, C.; Bhartia, P.K.; Yang, K.; Krueger, A.J.; Li, Z.; Levelt, P.F.; et al. Validation of SO2 retrievals from the Ozone Monitoring Instrument over NE China. J. Geophys. Res. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMI Row Anomaly Team. Background Information about the Row Anomaly in OMI. Available online: http://www.knmi.nl/omi/research/product/rowanomaly-background.php (accessed on 30 July 2014).
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Duan, L.; Lei, Y.; Cao, P.; Hao, J. Primary air pollutant emissions of coal-fired power plants in China: Current status and future prediction. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8442–8452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, S.; Nielsen, C.P.; Li, X.; Hao, J. Establishment of a database of emission factors for atmospheric pollutants from Chinese coal-fired power plants. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 1515–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, W. The generated and control measures on the glass furnace flue gas discussion on the origin and regulation steps of SO2 in flue gas. Glass 2009, 6, 23–25. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- National Development and Reform Commission/Ministry of Environmental Protection. Measures on the Management of the Desulfured Electricity Price of Coal-Fired Generation Units and the Operation of Desulfurization Devices. Available online: http://www.zhb.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/gwy/200910/W020070613292631585823.pdf (accessed on 30 July 2014). (In Chinese)
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Circular on Punishments for Companies with Prominent Problems on Flue Gas Desulfurization Devices in 2013. Available online: http://www.mep.gov.cn/gkml/hbb/bgg/201406/t20140612_276862.htm (accessed on 30 July 2014). (In Chinese)
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Song, H.; Yang, M. Analysis on Effectiveness of SO2 Emission Reduction in Shanxi, China by Satellite Remote Sensing. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 830-846. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040830
Song H, Yang M. Analysis on Effectiveness of SO2 Emission Reduction in Shanxi, China by Satellite Remote Sensing. Atmosphere. 2014; 5(4):830-846. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040830
Chicago/Turabian StyleSong, Huaxiang, and Minhua Yang. 2014. "Analysis on Effectiveness of SO2 Emission Reduction in Shanxi, China by Satellite Remote Sensing" Atmosphere 5, no. 4: 830-846. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040830
APA StyleSong, H., & Yang, M. (2014). Analysis on Effectiveness of SO2 Emission Reduction in Shanxi, China by Satellite Remote Sensing. Atmosphere, 5(4), 830-846. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5040830




