Diurnal Variation of Rainfall Associated with Tropical Depression in South China and its Relationship to Land-Sea Contrast and Topography
Abstract
:1. Introduction
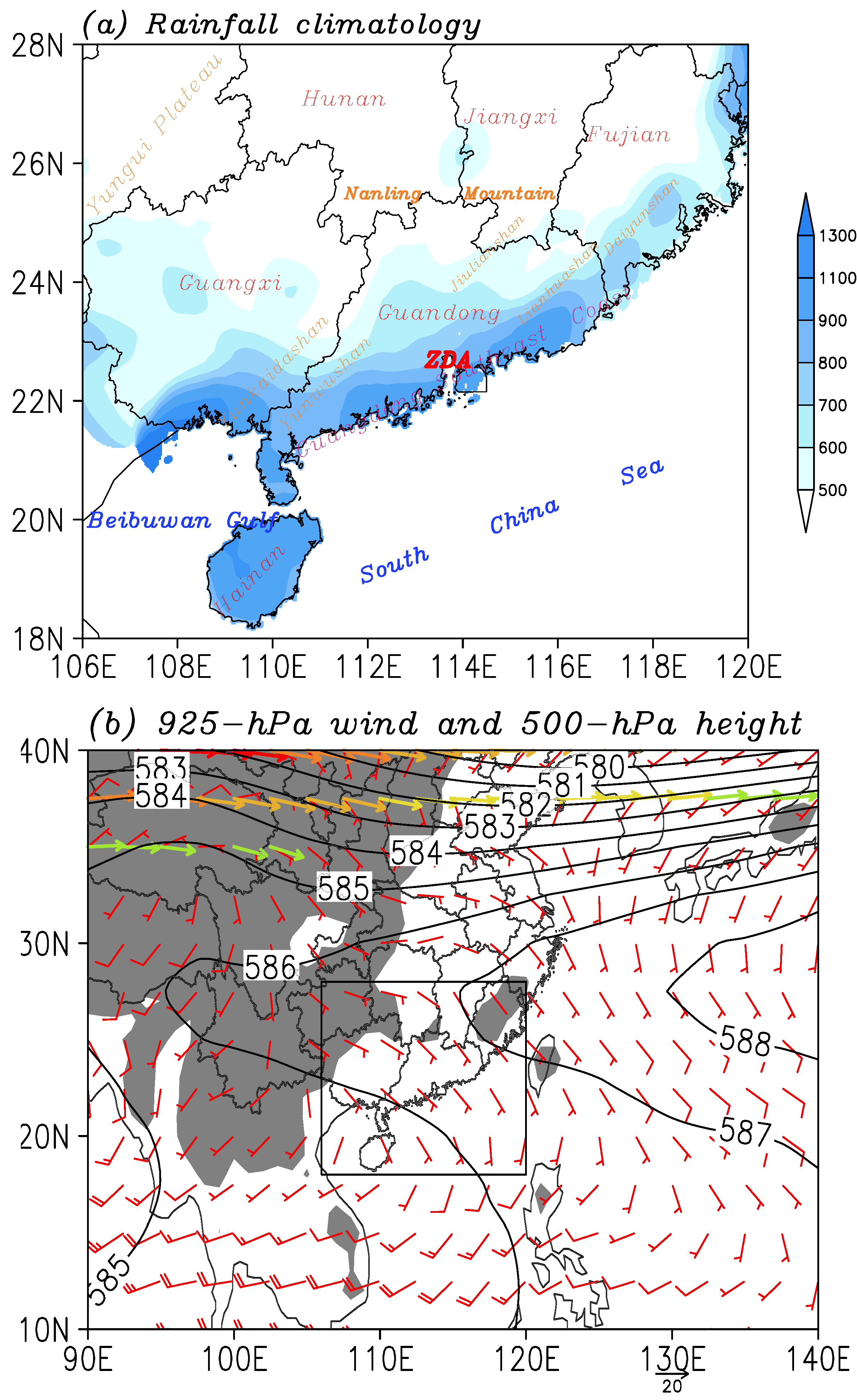
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Datasets and Processing
2.2. Model Configuration and Experimental Design
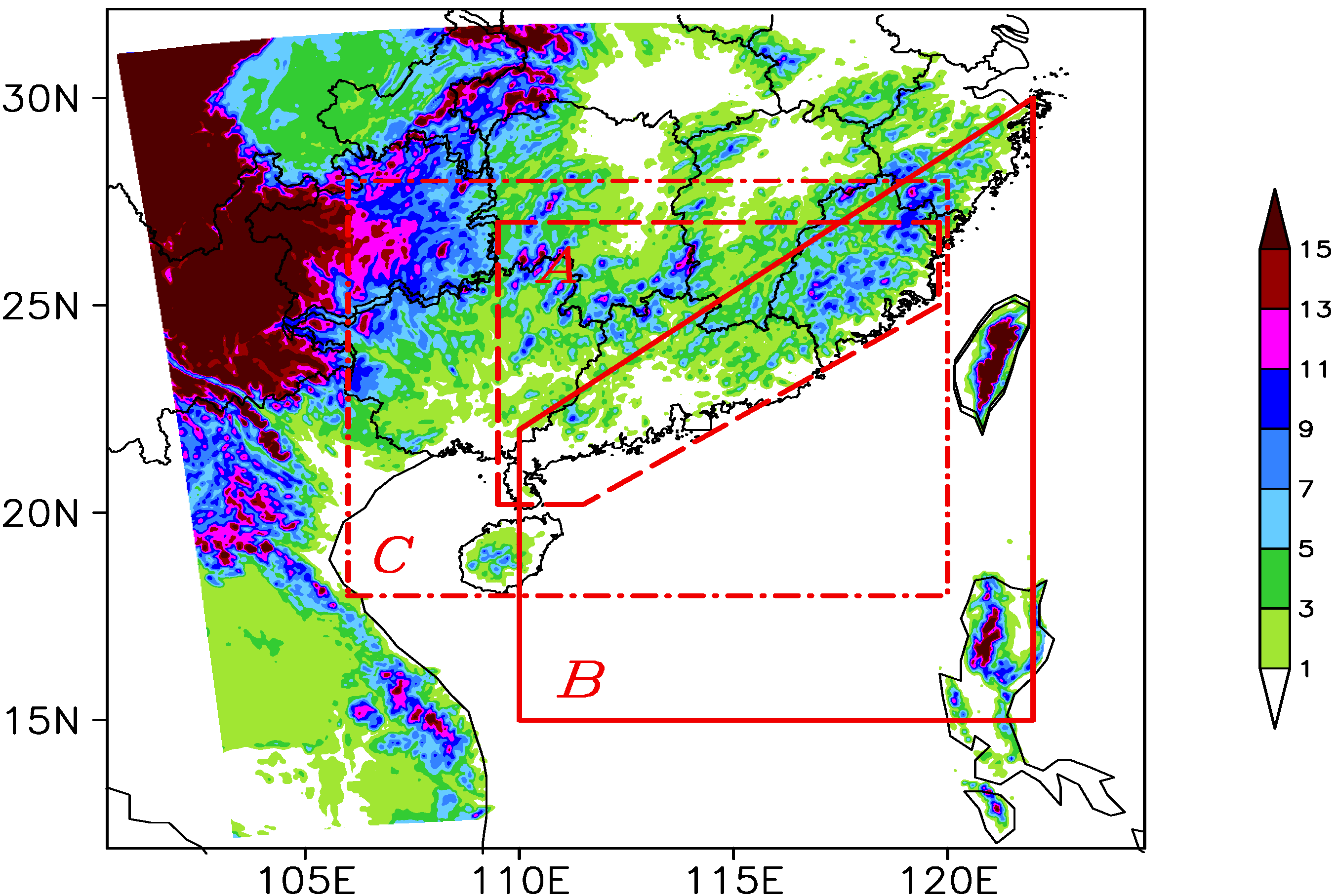
3. Diurnal Variations of Rainfall Associated with TD
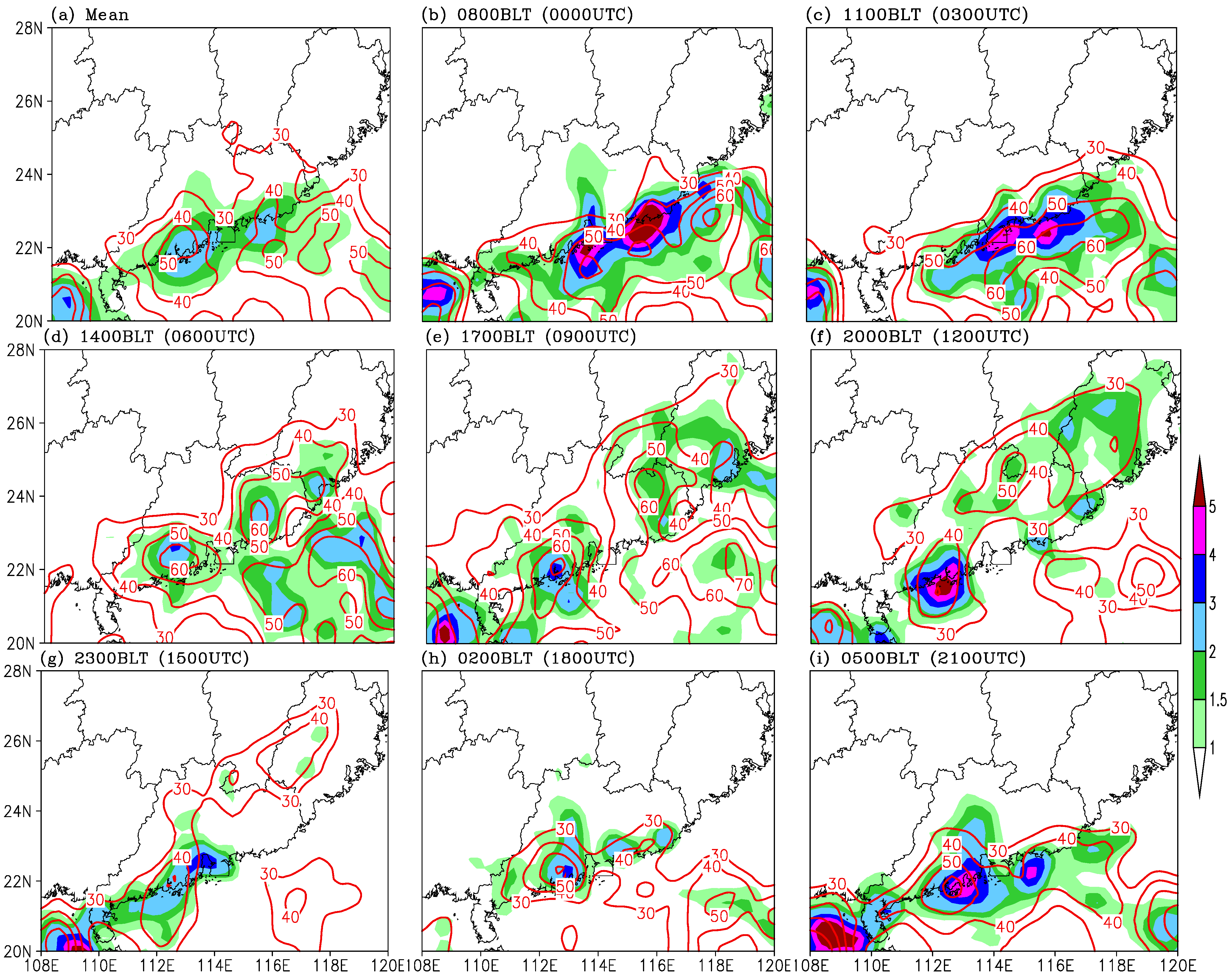
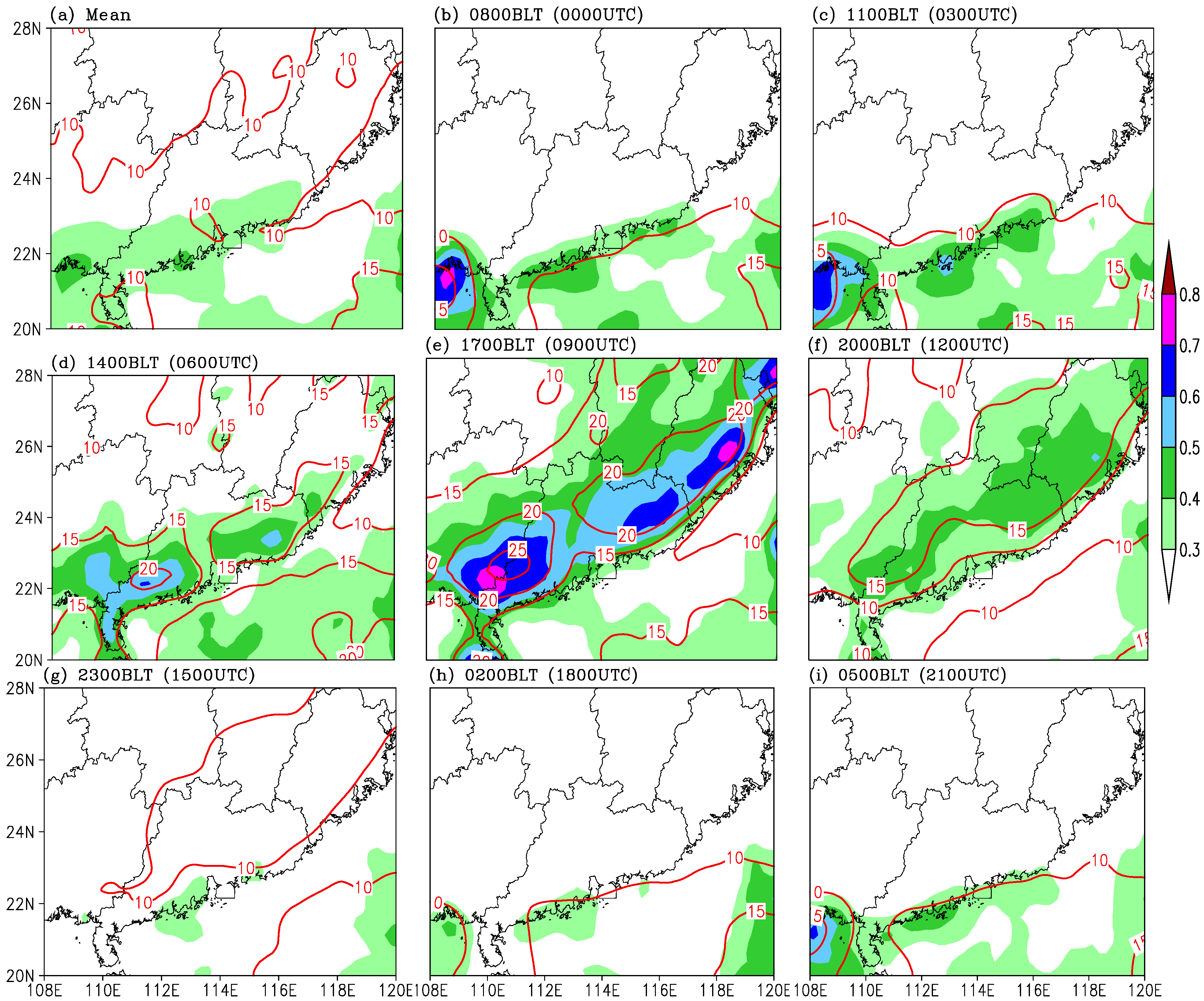
3.1. Diurnal Pattern of Precipitation Associated with TD in the Years 2000–2009
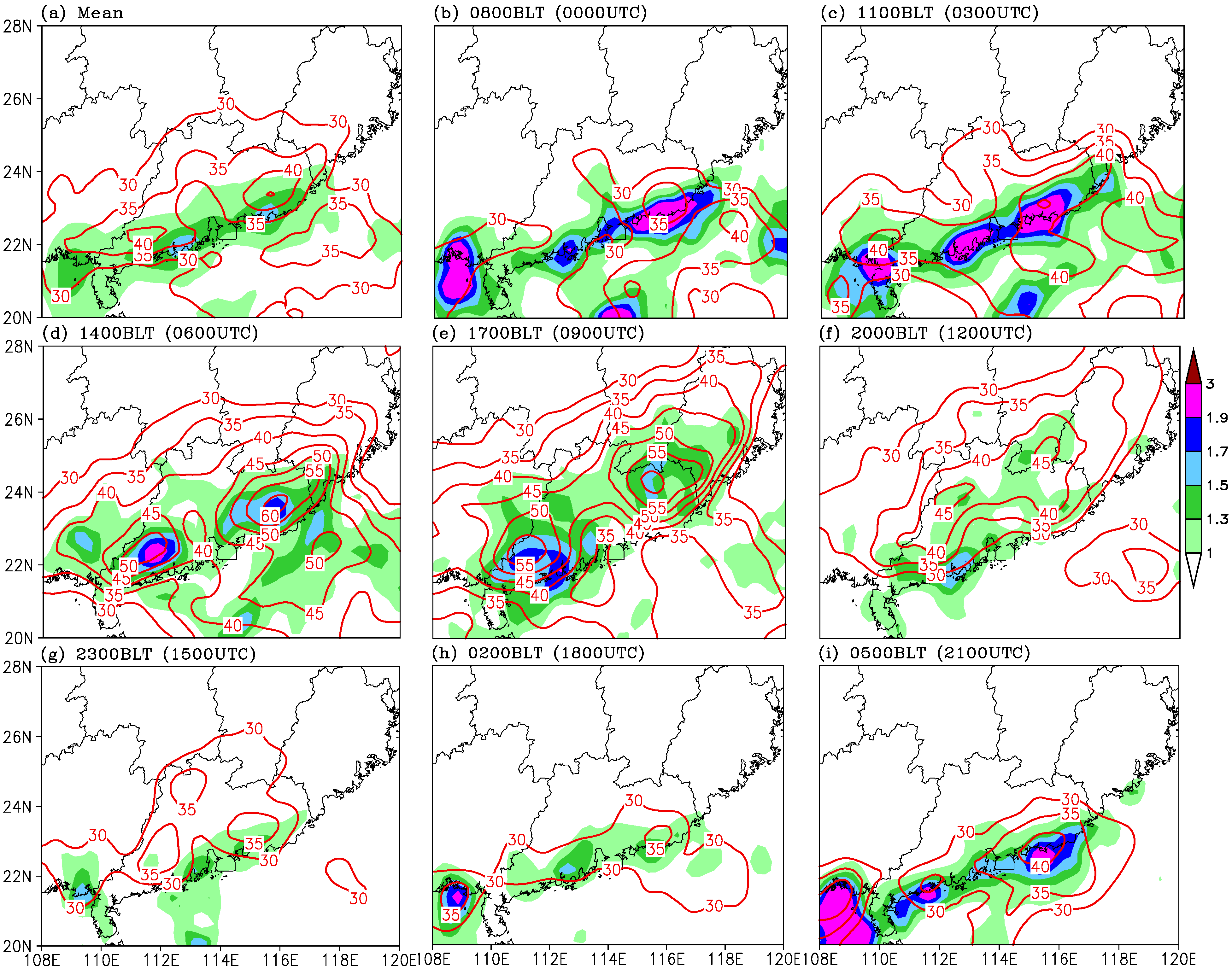
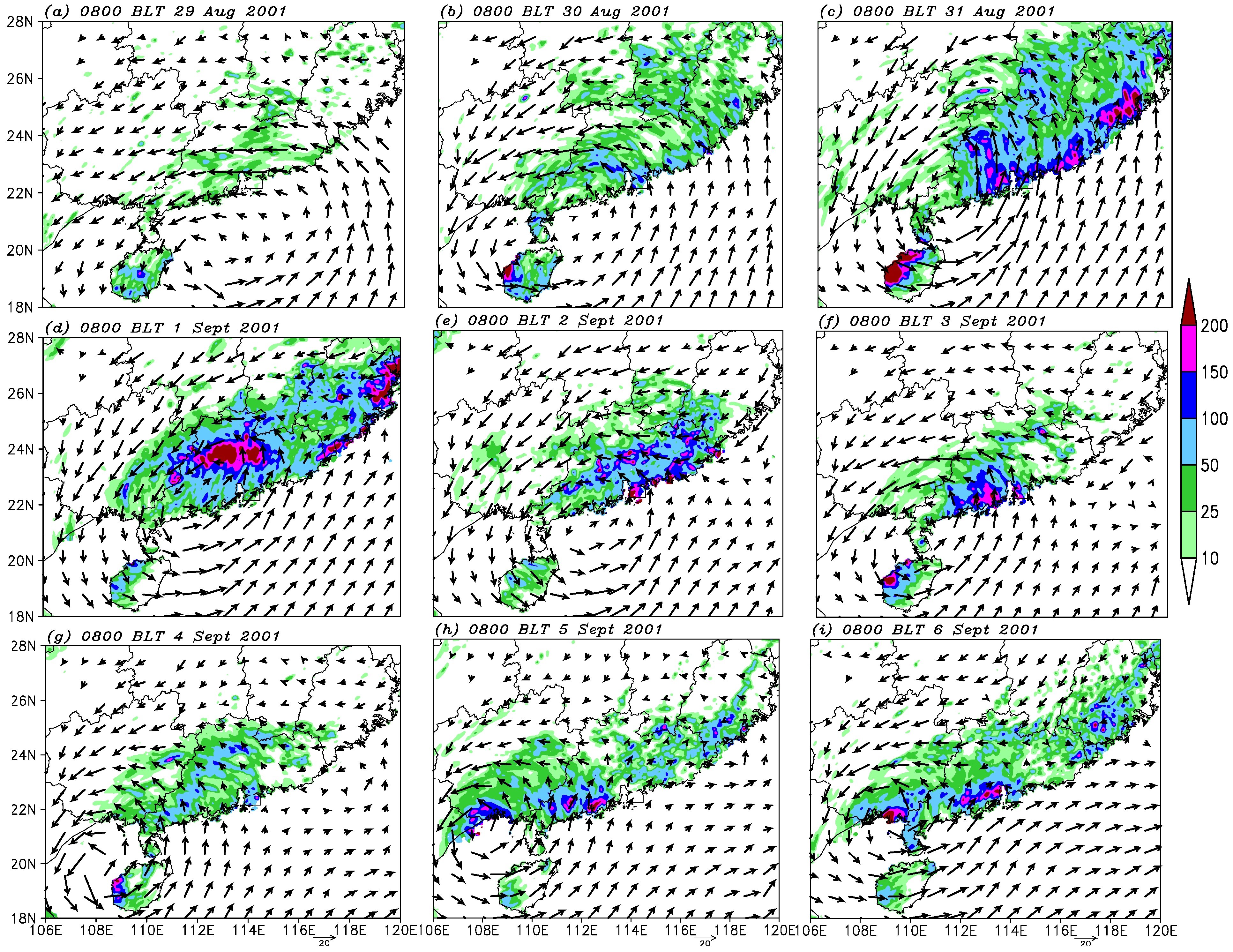
3.2. A Case Producing Continuous Heavy Rainfall in South China
3.2.1. Overview of Synoptic Circulation of TD “Fitow”

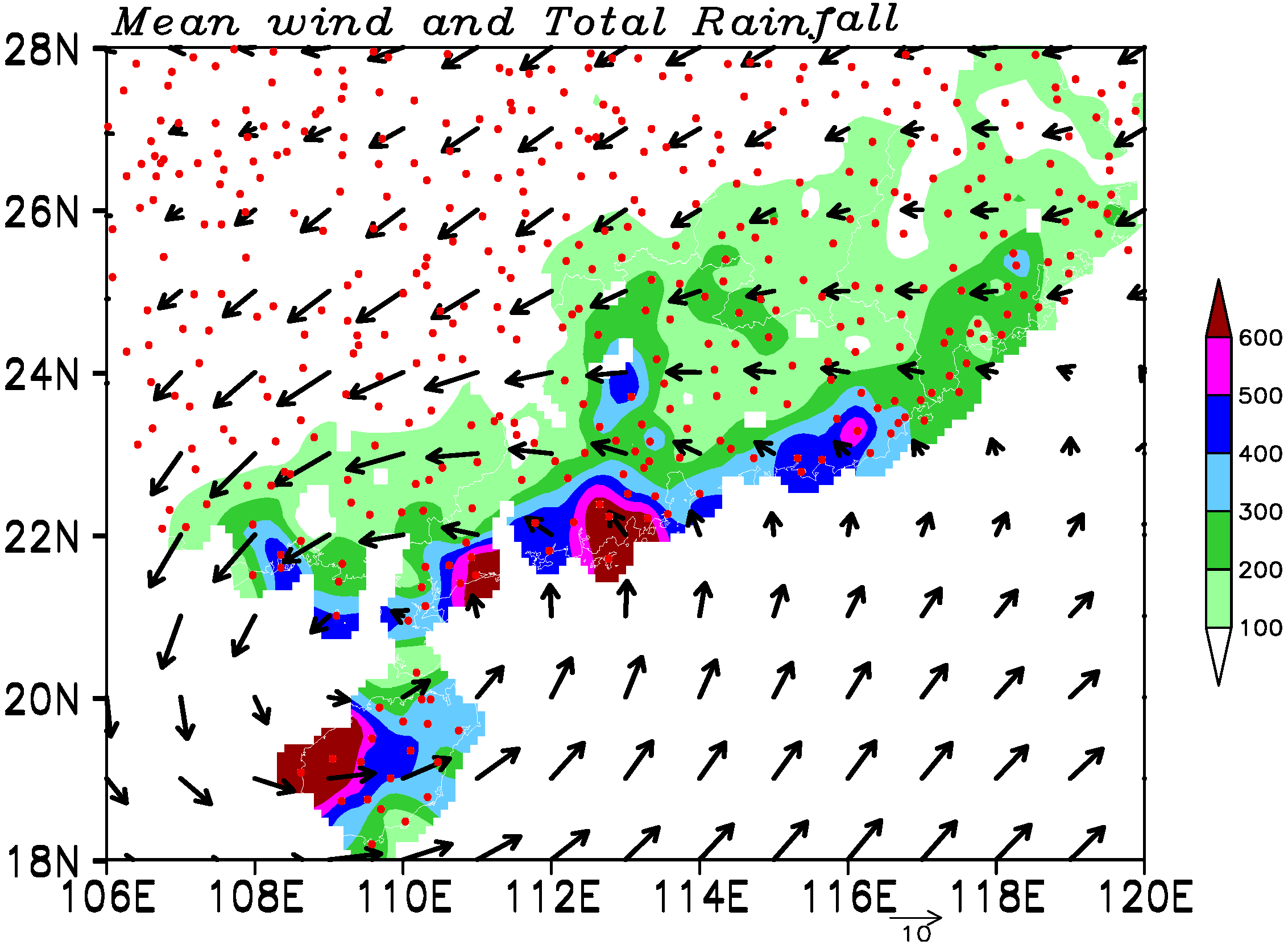
3.2.2. Representativeness of 10-Day Diurnal Rainfall Pattern
4. Numerical Experiment Results
4.1. Simulation Overview
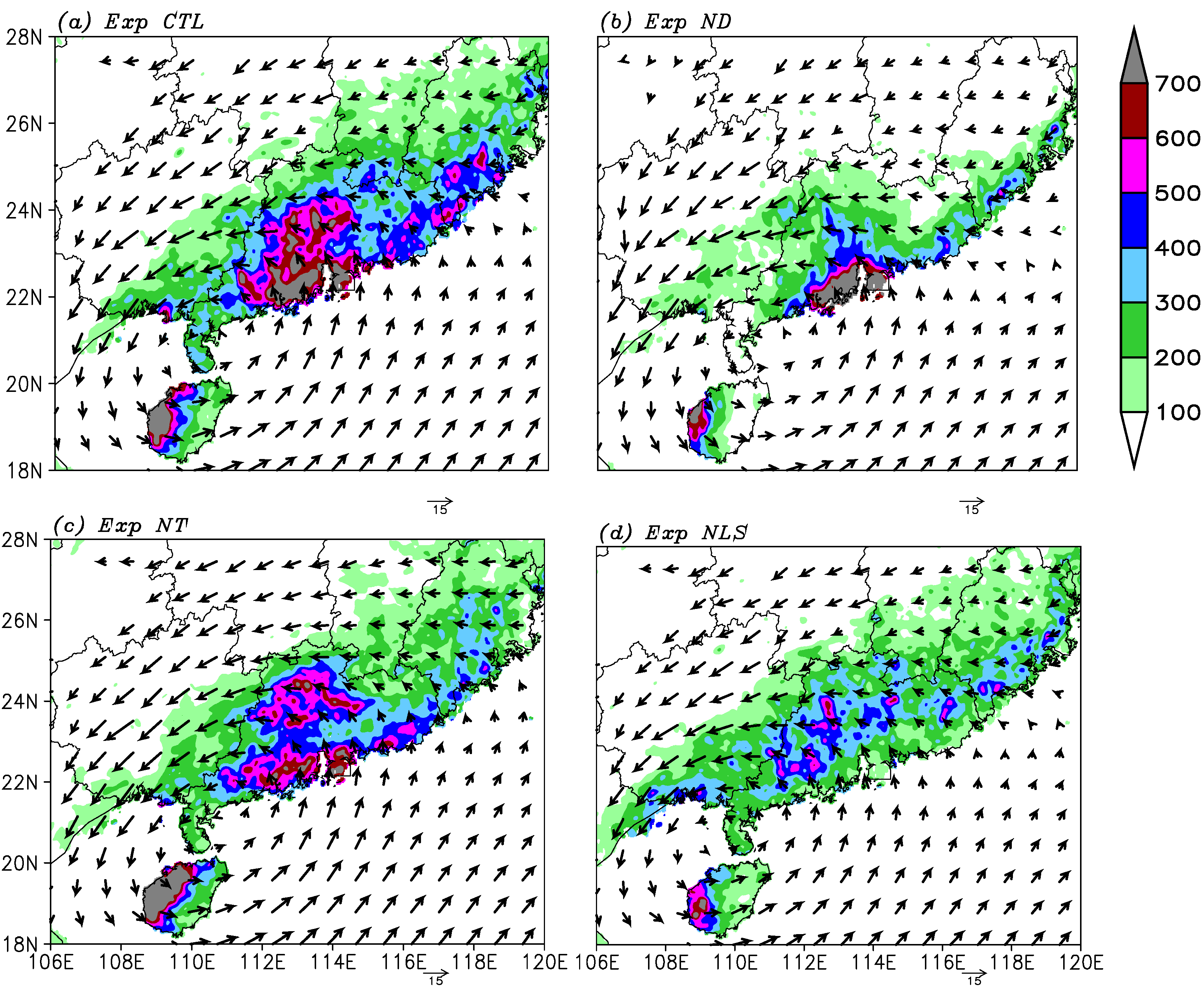
4.2. Diurnal Variation of Simulated Rainfall
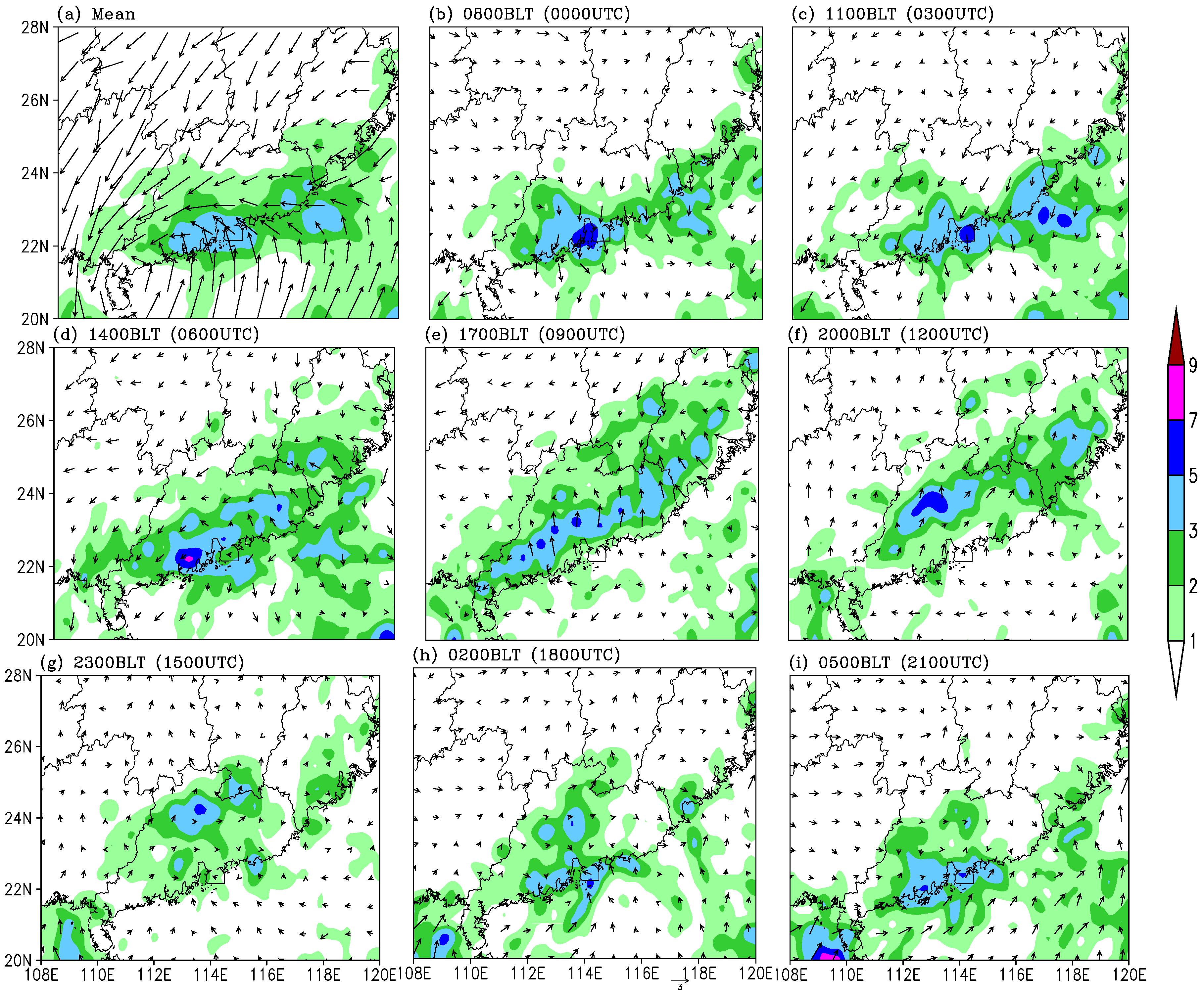
4.3. Diurnal Variation of Horizontal and Vertical Circulation along the Coastal Region
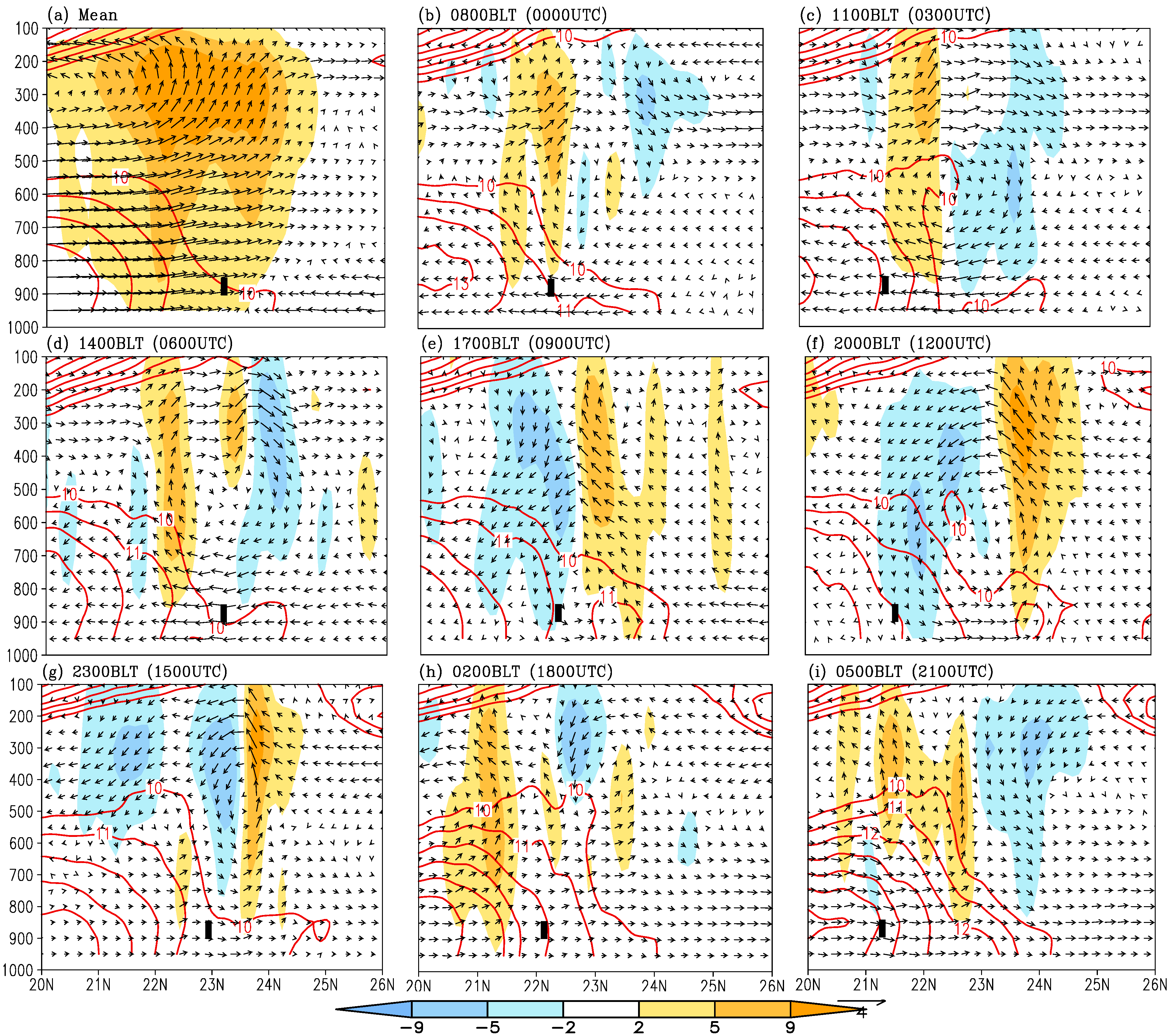
4.4. Effect of Diurnal Solar Radiation Forcing

4.5. Topographic Impacts
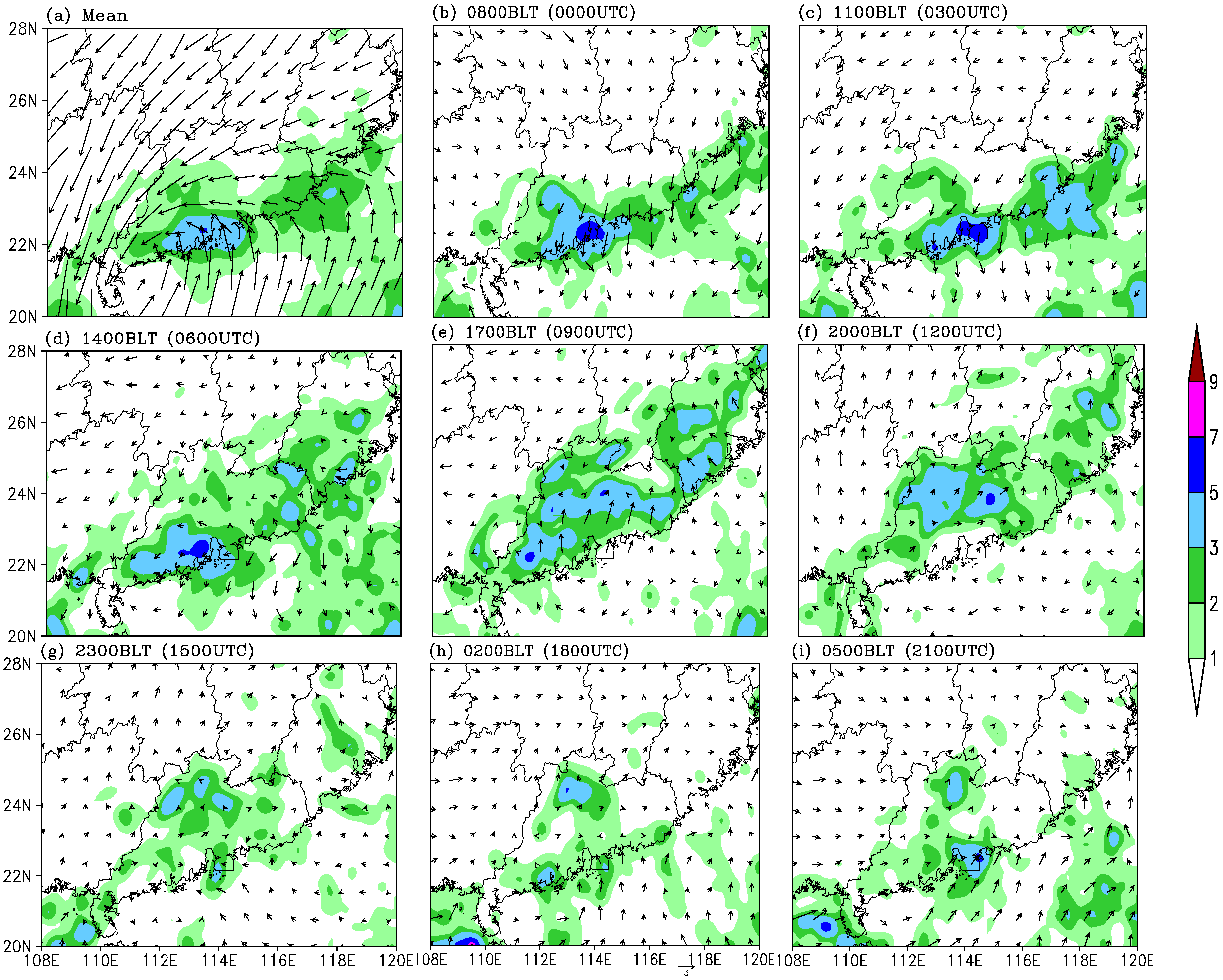
4.6. Role of Land-Sea Contrast
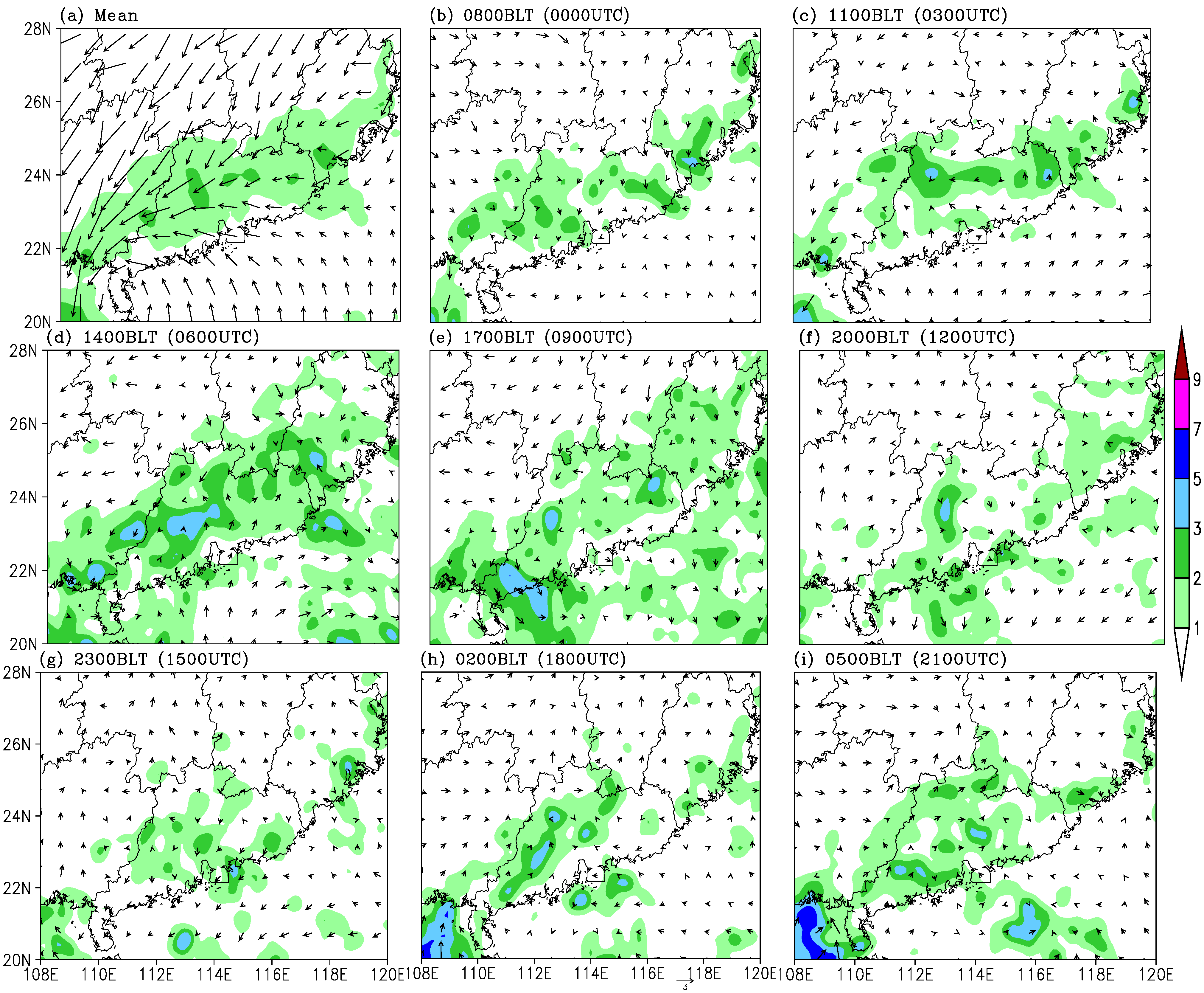
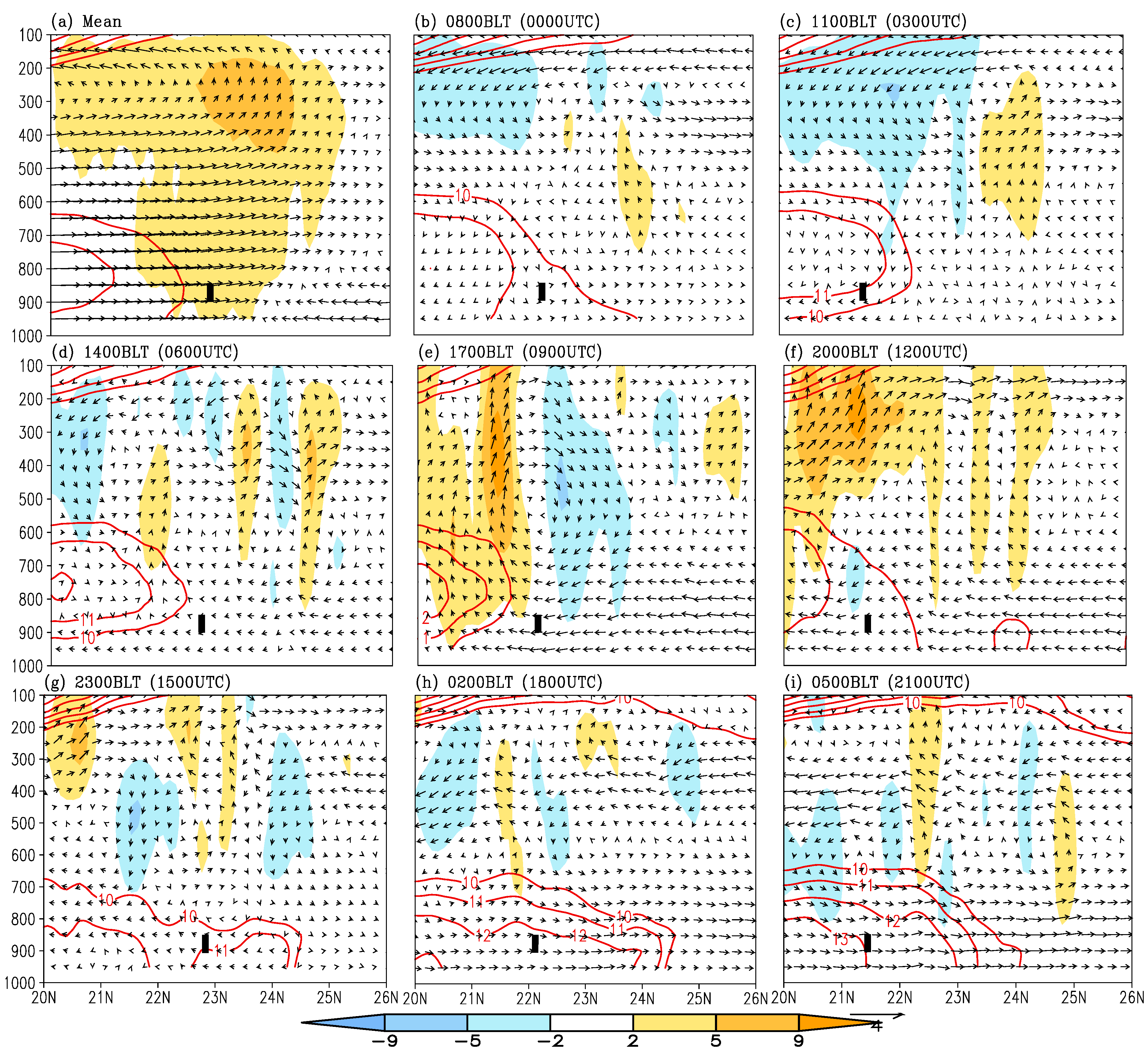
5. Discussions
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ding, Y.; Chan, J. The East Asian summer monsoon: An overview. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2005, 89, 117–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, S. Rainstorms in China; (in Chinese). Science Press: Beijing, China, 1980; pp. 255–256. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, Y. Summer monsoon rainfalls in China. J. Meteorol. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 70, 373–396. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, P. Climatological distribution and diurnal variation of mesoscale convective systems over China and its vicinity during summer. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 1574–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, R.; Zhou, T.; Xiong, A. Diurnal variations of summer precipitation over contiguous China. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L01704. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yu, R.; Zhou, T. Seasonal variations of the diurnal cycle of rainfall in the southern contiguous China. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 6036–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.Z.; Zhang, F. Diurnal variations of warm-season precipitation over Northern China. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2010, 138, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, X.; Zhang, F.; Sun, J. Diurnal variations of warm-season precipitation east of the Tibetan Plateau over China. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2011, 139, 2790–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhang, F. Impacts of mountain-plains solenoid on diurnal variation of rainfalls along the Mei-Yu front over the east China plains. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2012, 140, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R. Diurnal Cycle of Monsoon Convection. In The Global Monsoon System, Research and Forecast, 2nd ed.; Chang, C.-P., Ed.; World Scientific Publication: Singapore, 2010; pp. 257–276. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, G.; Sha, W.; Sawada, M.; Iwasaki, T. Influence of summer monsoon diurnal cycle on moisture transport and precipitation over eastern China. J. Geophy. Res. 2013, 118, 3163–3177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Carbone, R. Variability of warm season cloud episodes over East Asia based on GMS infrared brightness temperature observations. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2005, 133, 1478–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Yu, R.; Chen, H. Summer precipitation frequency, intensity, and diurnal cycle over China: A comparison of satellite data with rain gauge observations. J. Clim. 2008, 21, 3997–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Wang, C.; Chen, G.; Carbone, R. The role of diurnal solenoidal circulation on propagating rainfall episodes near the eastern Tibetan Plateau. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2010, 138, 2975–2989. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Yu, R.; Li, J. Why nocturnal long-duration rainfall presents an eastward-delayed diurnal phase of rainfall down the Yangtze River valley. J. Clim. 2010, 23, 905–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Slingo, J. The diurnal cycle in the tropics. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 784–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, C.; Park, M.; Choi, Y.; Takayabu, Y. Relationship between intraseasonal oscillation and diurnal variation of summer rainfall over the South China Sea. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Sha, W.; Iwasaki, T. Diurnal variation of precipitation over southeastern China: Spatial distribution and its seasonality. J. Geophys. Res. 2009, 114, D13103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Zisper, E. Diurnal variations of precipitation, deep convection, and lighting over and east of the eastern Tibetan Plateau. J. Clim. 2011, 24, 448–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, W.; Yu, R.; Zhang, M.; Lin, W.; Chen, H.; Li, J. Regimes of diurnal variation of summer rainfall over subtropical East China. J. Clim. 2012, 25, 3307–3320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Kimura, F. Diurnal cycle of convective instability around the central mountains in Japan during the warm season. J. Atmos. Sci. 2005, 62, 1626–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, T.; Musiake, K. Seasonal change of the diurnal cycle of precipitation over Japan and Malaysia. J. Appl. Meteorol. 1994, 33, 1445–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Hamada, J.; Mori, S. Diurnal variation of precipitable water over a mountainous area of Sumatra Island. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2003, 42, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, J. Why precipitation is mostly concentrated over islands in the maritime continent. J. Atmos. Sci. 2008, 65, 1428–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Hara, M.; Hamada, J.; Yamanaka, M. Why a large amount of rain falls over the sea in the vicinity of western Sumatra Island during nighttime. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2009, 48, 1345–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mapes, B.; Warner, T.; Xu, M. Diurnal patterns of rainfall in northwestern South America. Part III: Diurnal gravity waves and nocturnal convection offshore. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2003, 131, 830–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Schubert, S.; Suarez, M. Role of convection triggers in the simulation of the diurnal cycle of precipitation over the United States Great Plains in a general circulation model. J. Geophys. Res. 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannettone, J.; Barros, A. Probing regional orgraphic controls of precipitation and cloudiness in the central Andes using satellite data. J. Hydrometeorol. 2009, 10, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolini, M.; Skabar, G. Diurnal cycle in convergence patterns in the boundary layer east of the Andes and convection. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rickenbach, T.; Ferreira, R.; Guy, N.; Williams, E. Radar-observed squall line propagation and the diurnal cycle of convection in Niamey, Niger, during the 2006 African Monsoon and multidisciplinary analyses intensive observing period. J. Geophys. Res. 2009. [CrossRef]
- Dai, A. Global precipitation and thunderstorm frequencies. Part II: Diurnal variations. J. Clim. 2001, 14, 1112–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ping, F.; Luo, Z. Microphysical and radiative effects of ice clouds on diurnal variations of tropical convective and stratiform rainfall. Atmos. Res. 2009, 93, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, D.; Harshvardhan, D.; Corsetti, T. Diurnal variability of the hydrologic cycle in a general circulation model. J. Atmos. Sci. 1991, 48, 40–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Moncrieff, M. A numerical study of the diurnal cycle of tropical oceanic convection. J. Atmos. Sci. 1998, 55, 2329–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gray, W.; Jacobson, R. Diurnal variation of deep cumulus convection. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1977, 105, 1171–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; Lang, S.; Simpson, J.; Sui, C.; Ferrier, B.; Chou, M. Mechanisms of cloud–radiation interaction in the Tropics and midlatitudes. J. Atmos. Sci. 1996, 53, 2624–2651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, C.; Lau, K.; Takayabu, Y. Diurnal variation in tropical oceanic cumulus convection during TOGA COARE. J Atmos. Sci. 1997, 54, 639–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goddard Earth Sciences Data and Information Services Center. Available online: http://mirador.gsfc.nasa.gov (accessed on 1 June 2013).
- Yang, K.; Koike, T.; Stackhouse, P.; Mikovitz, C.; Cox, S. An assessment of satellite surface radiation products for highlands with Tibet instrumental data. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L22403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kummerow, C.; Ringerud, S.; Crook, J.; Randel, D.; Berg, W. An observationally generated a priori database for microwave rainfall retrievals. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2011, 28, 113–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Bolvin, D.; Nelkin, E.; Wolff, D.; Adler, R.; Gu, G.; Hong, Y.; Bowman, K.P.; Stocker, E. The TRMM multisatellite precipitation analysis: Quasi-global, multiyear, combined-sensor precipitation estimates at fine scale. J. Hydrometeorol. 2007, 8, 38–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Computer Information Service Laboratory Research Data Archive. Available online: http://rda.ucar.edu/datasets/ds083.2 (accessed on 1 July 2013).
- Hong, S.; Pan, H. Nonlocal boundary layer vertical diffusion in a medium-range forecast model. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1996, 124, 2322–2339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, G.; Field, P.; Rasmussen, R.; Hall, W. Explicit forecasts of winter precipitation using an improved bulk microphysics scheme. Part II: Implementation of a new snow parameterization. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2008, 136, 5095–5115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negri, A.; Bell, T. Sampling of the diurnal cycle of precipitation using TRMM. J Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2002, 19, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douglas, M.; Arturo, V.-M.; Rafael, G. Diurnal variation and horizontal extent of the low-level jet over the Northern Gulf of California. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1998, 126, 2017–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, J.; Mahrer, Y. A theoretical study of the land and sea breeze circulation. J. Atmos. Sci. 1971, 28, 532–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotunno, R. On the linear theory of the land and sea breeze. J. Atmos. Sci. 1983, 40, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahrer, Y.; Pielke, R. The effects of topography on sea and land breezes in a two-dimensional numerical model. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1977, 105, 1151–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fovell, R. Convective initiation ahead of sea-breeze front. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2005, 133, 264–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, Z.; Xiao, Z. A diagnostic and numerical study on a rainstorm in South China induced by a northward-propagating tropical system. Acta Meteorol. Sin. 2008, 22, 284–302. [Google Scholar]
- Cairns, B. Diurnal variations of cloud from ISCCP data. Atmos. Res. 1995, 37, 133–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook, N.; Klemp, J. Lifting by convergence lines. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000, 57, 873–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Moncrieff, M. A numerical study of the effects of ambient flow and shear on density currents. Mon. Wea. Rev. 1996, 124, 2282–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkam, D. Convective available potential energy (CAPE) in Northern Africa and tropical Atlantic and study of its connections with rainfall in Central and West Africa during Summer 1985. Atmos. Res. 2002, 62, 125–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladich, I.; Gallai, I.; Giaiotti, D.; Stel, F. On the diurnal cycle of deep moist convection in the southern side of the Alps analysed through cloud-to-ground lightning activity. Atmos. Res. 2011, 100, 371–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y. Numerical investigation of a localized extremely heavy rainfall event in complex topographic area during midsummer. Atmos. Res. 2012, 113, 22–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, K.; Keenan, T.; Holland, G.; Puri, K. Numerical simulation of the diurnal evolution of tropical island convection over the maritime continent. Mon. Wea. Rev. 2001, 129, 378–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, T.; Epifanio, C.; Zhang, F. Topographic effects on the tropical land and sea breeze. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 69, 130–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, Y. Diurnal Variation of Rainfall Associated with Tropical Depression in South China and its Relationship to Land-Sea Contrast and Topography. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 16-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5010016
Zhao Y. Diurnal Variation of Rainfall Associated with Tropical Depression in South China and its Relationship to Land-Sea Contrast and Topography. Atmosphere. 2014; 5(1):16-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5010016
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Yuchun. 2014. "Diurnal Variation of Rainfall Associated with Tropical Depression in South China and its Relationship to Land-Sea Contrast and Topography" Atmosphere 5, no. 1: 16-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5010016
APA StyleZhao, Y. (2014). Diurnal Variation of Rainfall Associated with Tropical Depression in South China and its Relationship to Land-Sea Contrast and Topography. Atmosphere, 5(1), 16-44. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos5010016



