Comparison between Vegetation and Rainfall of Bioclimatic Ecoregions in Central Africa
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Data
3. Method
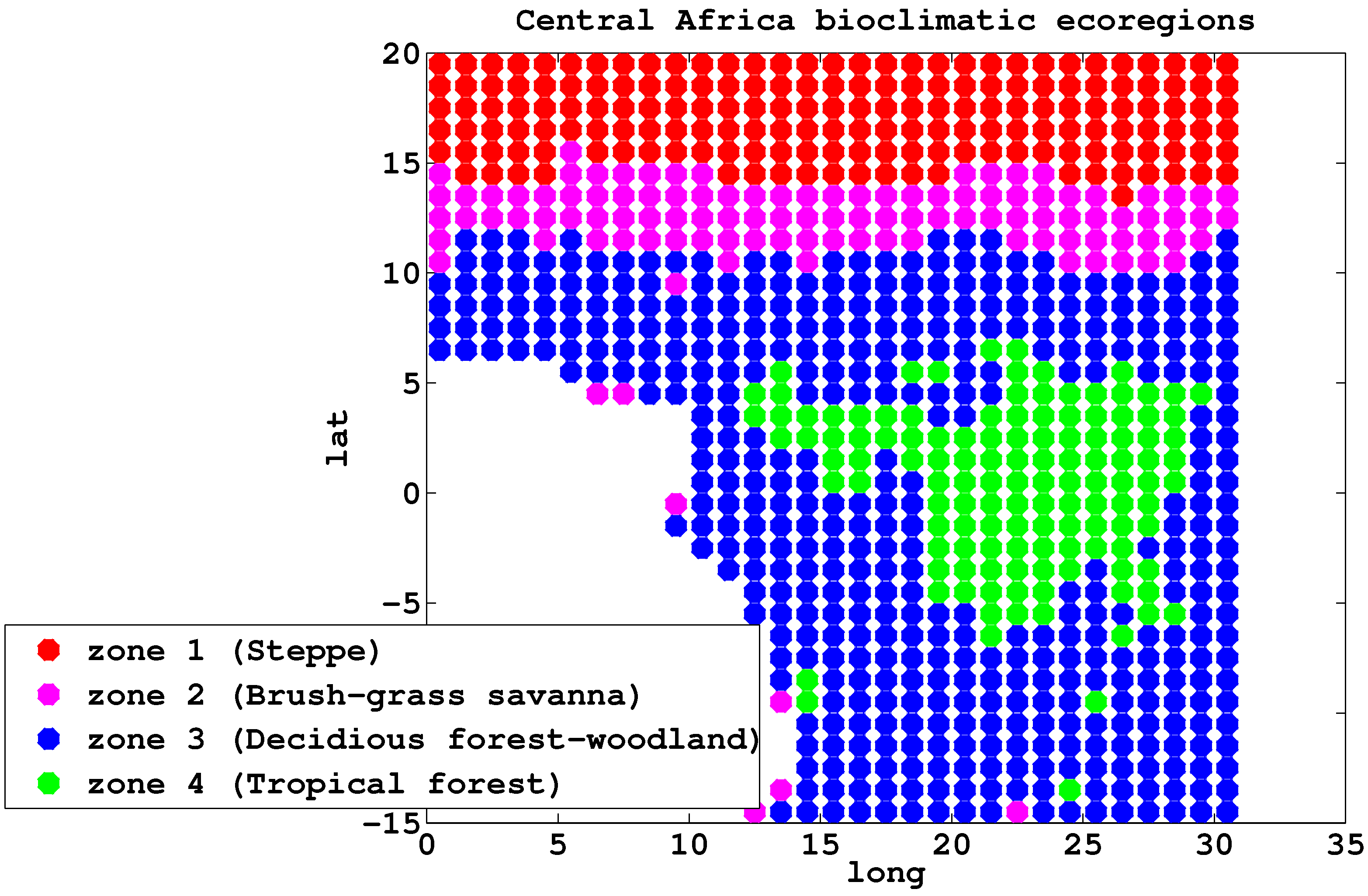
3.1. Vegetation Partitioning
3.2. Formatting GPCP and NDVI Data
4. Result and Discussion
4.1. Spatial NDVI Pattern
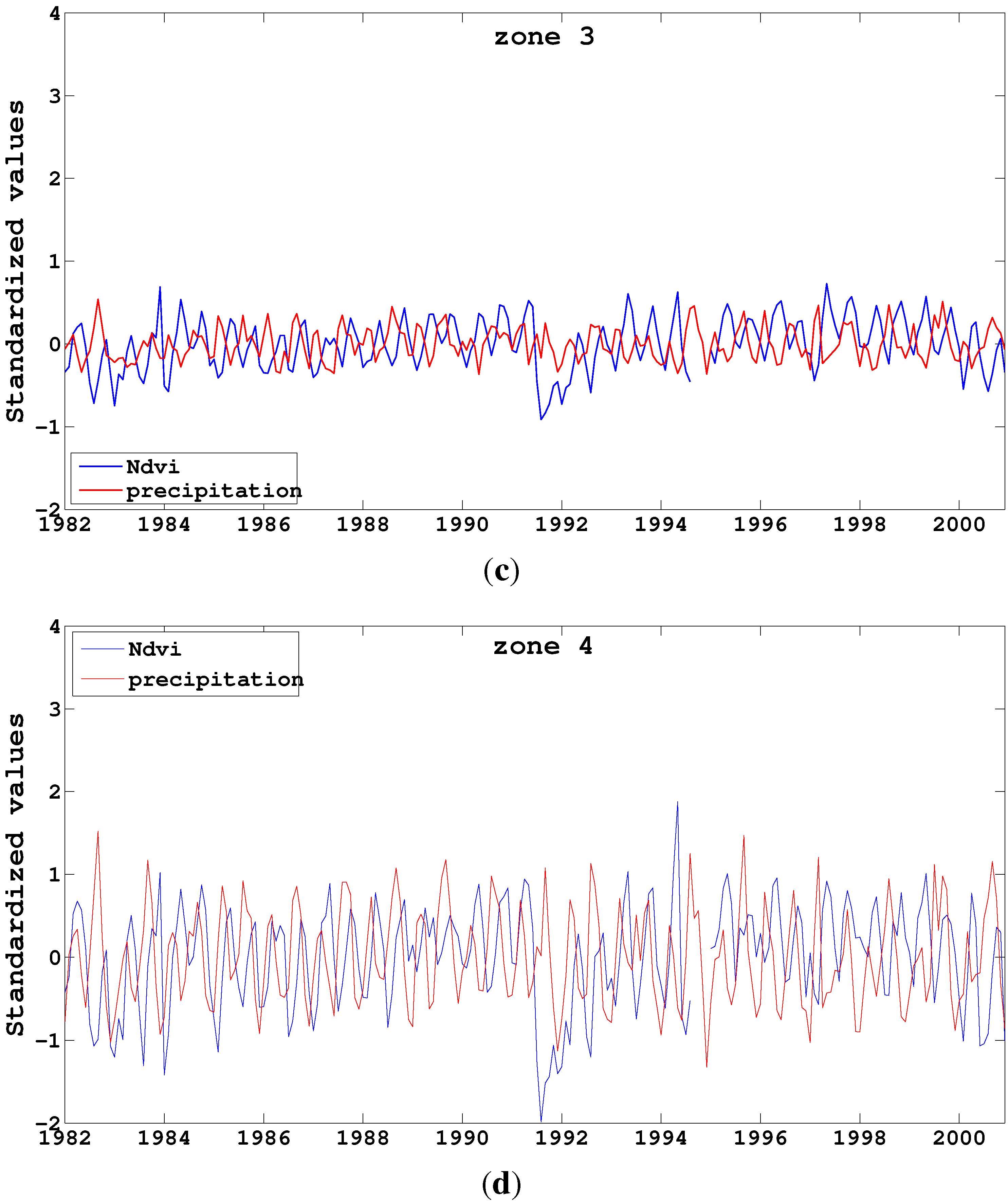
4.2. Interannual Variability

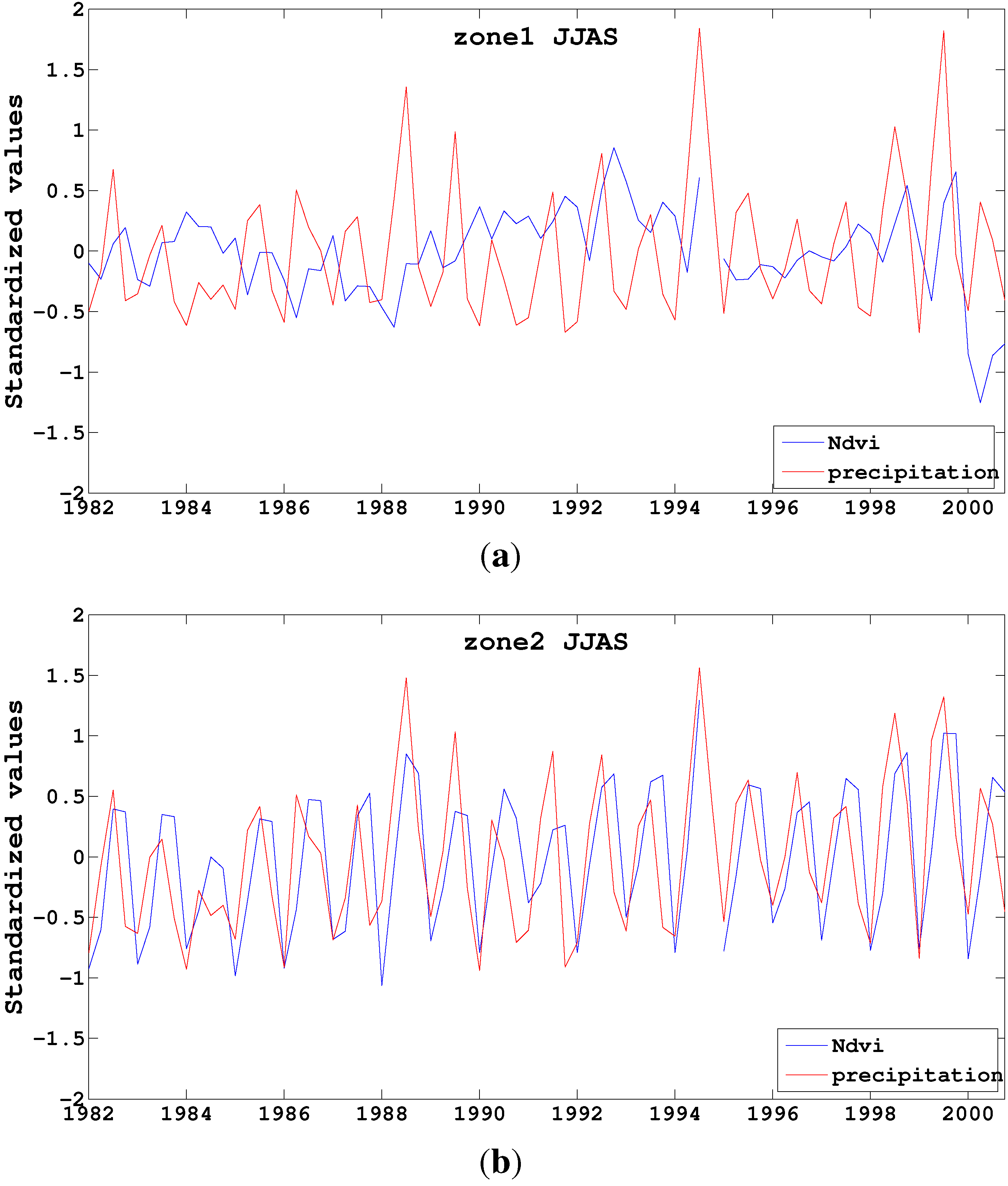
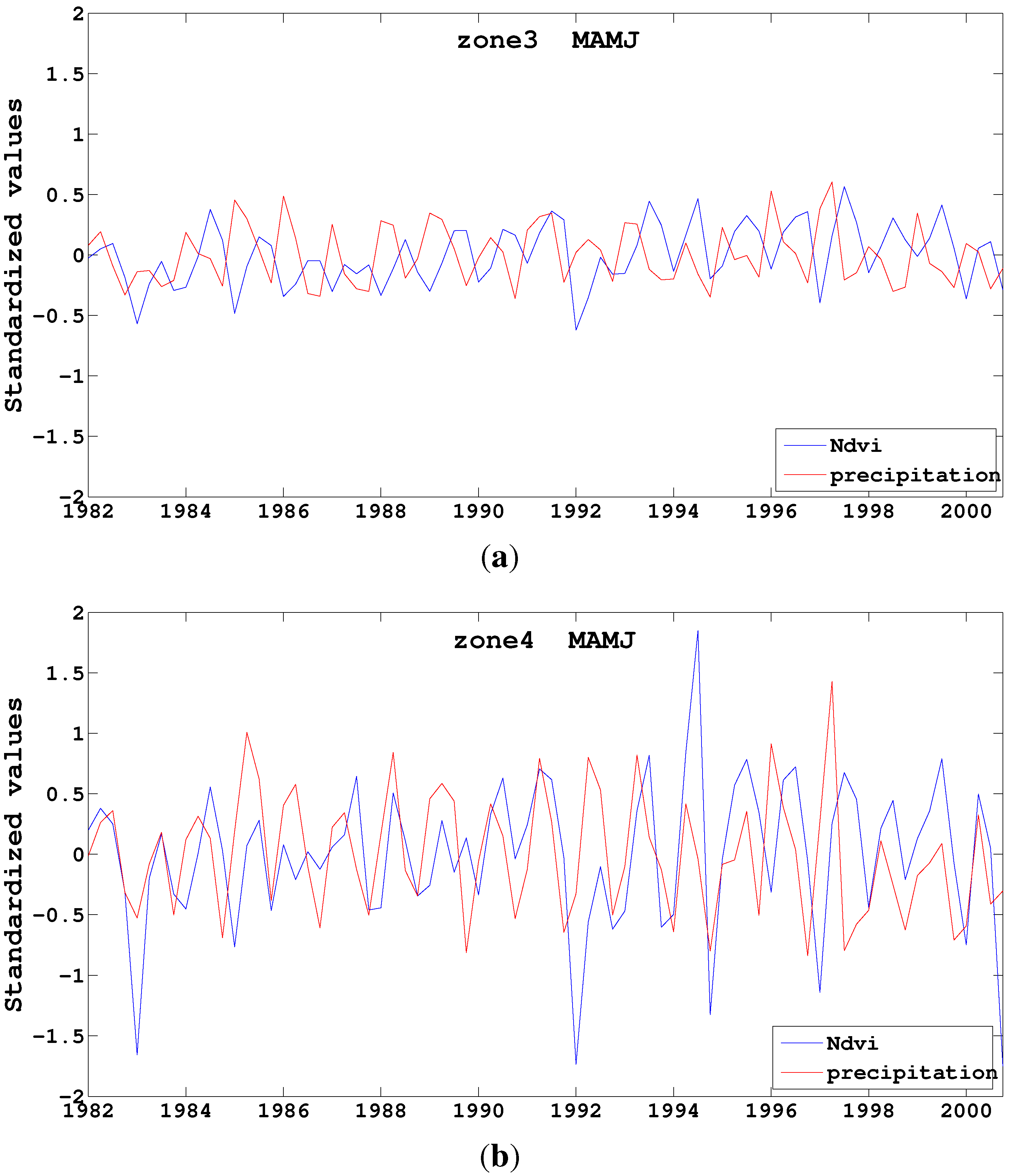
4.3. Intra-Annual and Seasonal Variability


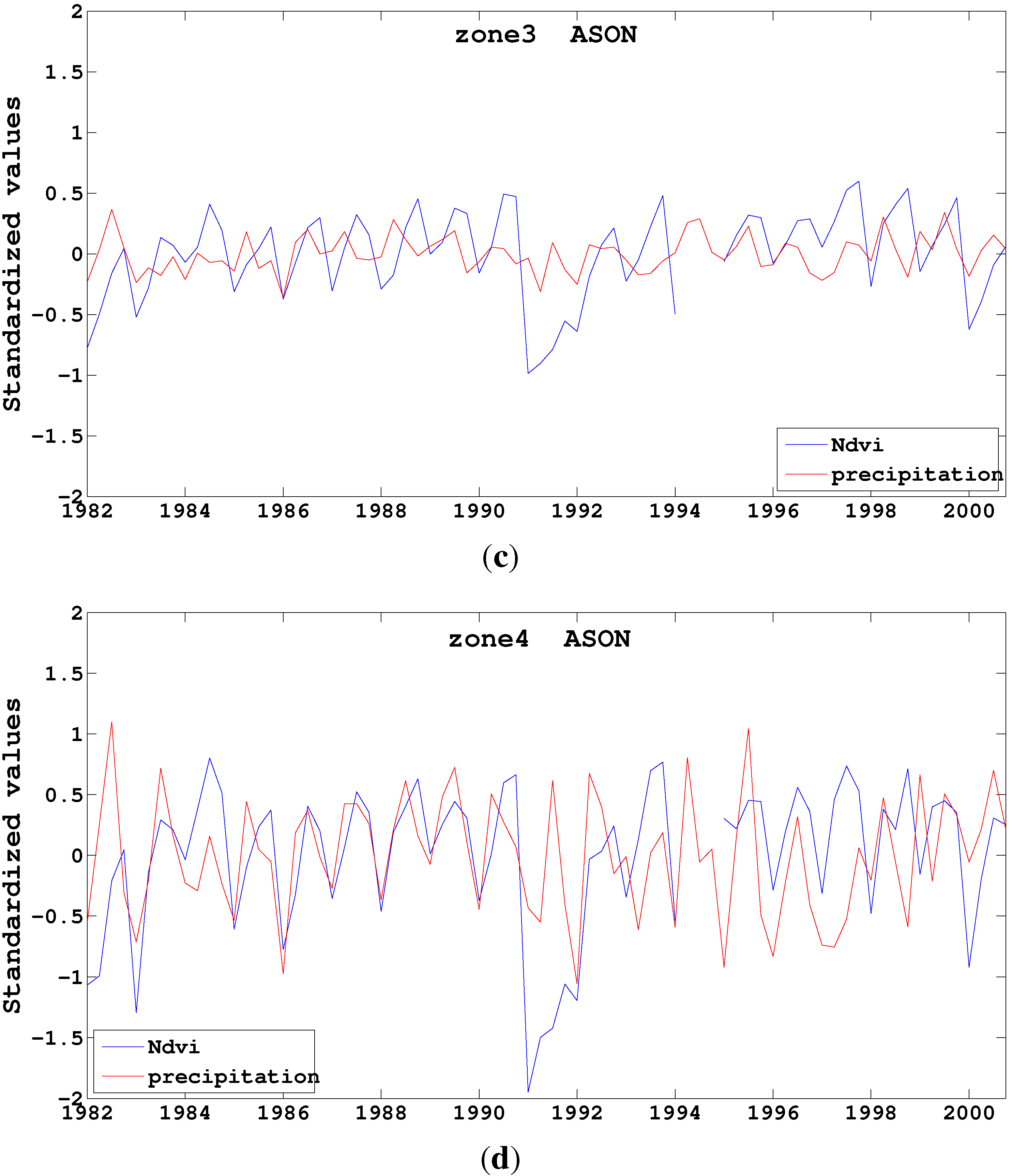
4.4. Correlation between Monthly NDVI and Precipitation
| Bioclimatic Ecoregions | nc | Time Lag | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (−1) | (0) | (1) | (2) | (3) | ||
| semi-desert and steppe | 224 | 0.2725 | 0.4030 | 0.2560 | 0.1672 | 0.0210 |
| brush-grass savannah | 224 | 0.9016 | 0.6514 | 0.9022 | 0.7532 | 0.4363 |
| deciduous forest-woodland | 224 | 0.4327 | 0.0860 | 0.4169 | 0.2965 | 0.1107 |
| tropical forest | 224 | 0.4402 | 0.4050 | 0.4387 | 0.0058 | 0.4686 |
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, L.; Dawes, W.R.; Walker, G.R. Predicting the Effect of Vegetation Changes on Catchment Average Water Balance; Technical Report 99/12; CRC for Catchment Hydrology: Clayton, VIC, Australia, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Sellers, P.J.; Tucker, C.J.; Collatz, G.J.; Los, S.; Justice, C.O.; Dazlich, D.A.; Randall, D.A. A global 1 × 1 degree NDVI data set for climate studies. Part 2—The adjustment of the NDVI and generation of global fields of terrestrial biophysical parameters. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3519–3545. [Google Scholar]
- Raich, J.W.; Schlesinger, W.H. The global carbon dioxide flux in soil respiration and its relationship to vegetation and climate. Tellus 1992, 44B, 81–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, C.S.; Randerson, J.T.; Field, C.B.; Matson, P.A.; Vitousek, P.M.; Mooney, H.A.; Klooster, S.A. Terrestrial ecosystem production: A process model based on global satellite and surface data. Glob. Biogeochem. Cy. 1993, 7, 811–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tans, P.P.; Fung, I.Y.; Takahashi, T. Observational constraints on the global atmosphere CO2 budget. Science 1990, 247, 1431–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prince, S.D.; Justice, C.O.; Moore, B. Remote Sensing of NPP; IGBP DIS Working Paper #10; IGBP-DIS: Paris, France, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Prince, S.D. A model of regional primary production for use with coarse resolution satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 1313–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, S.; Kergoat, L.; Viovy, N.; Dedieu, G. Global-scale assessment of vegetation phenology using NOAA/AVHRR satellite measurements. J. Clim. 1997, 10, 1154–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzali, S.; Menenti, M. Mapping vegetation-soil-climate complexes in southern Africa using temporal Fourier analysis of NOAA-AVHRR NDVI data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 21, 973–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diouf, A.; Lambin, E. Monitoring land-cover changes in semi-arid regions: Remote sensing data and field observations in the Ferlo, Senegal. J. Arid Environ. 2001, 48, 129–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawabata, A.; Ichii, K.; Yamaguchi, Y. Global monitoring of interannual changes in vegetation activities using NDVI and its relationships to temperature and precipitation. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, T.R.; Merchant, J.W.; Brown, J.F.; Ohlen, D.O.; Reed, B.C.; Olson, P.; Hutchinson, J. Seasonal land-cover regions of the United States. Ann. Assoc. Am. Geogr. 1995, 85, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Price, K.P.; Rich, P.M. Spatial patterns of NDVI in response to precipitation and temperature in the central Great Plains. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2000, 22, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.Y.; Zhuang, D.F.; Luo, D.; Xiao, X. Land-cover classification of China: Integrated analysis of AVHRR imagery and geophysical data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2003, 24, 2485–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptue, T.A.T.; De Jong, R.S.M.; Roujean, J.L.; Favier, C.; Mering, C. Ecosystem mapping at the African continent scale using a hybrid clustering approach based on 1-km resolution multi-annual data from SPOT/VEGETATION. Remote Sens. Environ. 2011, 115, 452–464. [Google Scholar]
- Verhegghen, A.; Mayaux, P.; de Wasseige, C.; Defourny, P. Mapping Congo Basin forest types from 300 m and 1 km multi-sensor time series for carbon stocks and forest areas estimation. Biogeosci. Discuss 2012, 9, 7499–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannari, A.; Morin, D.; Bonn, F. A review of vegetation indices. Remote Sens. Rev. 1995, 13, 95–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobo, A.; Marti, J.J.I.; Gimenez-Cassina, C.C. Regional scale hierarchical classification of temporal series of AVHRR vegetation index. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 3167–3193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, A.M.; Travis, D.; Arnold, D.; Brinegar, R. Climatic-scale vegetation- cloud interactions during drought using satellite data. Int. J. Climatol. 1994, 14, 593–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carleton, A.M.; O’Neal, M.O. Satellite-derived land surface climate “signal” for the Midwest USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1995, 16, 3195–3202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambin, E.F. Change detection at multiple temporal scales: Seasonal and annual variations in landscape variables. Photogramm. Eng. Remote Sens. 1996, 62, 931–938. [Google Scholar]
- Lambin, E.F.; Ehrlich, D. The surface temperature-vegetation index space for land cover and land-cover change analysis. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1996, 17, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, S.E.; Davenport, M.L.; Malo, A.R. A comparison of the vegetation response to rainfall in the Sahel and East Africa, using normalized difference vegetation index from NOAA AVHRR. Clim. Chang. 1990, 17, 209–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Yang, L.; Merchant, W. An assessment of AVHRR/NDVI-ecoclimatological relations in Nebraska, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1997, 18, 2161–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, D.M.; Dinerstein, E.; Wikramanayake, E.D.; Burgess, N.D.; Powell, G.V.; Underwood, E.C.; D’amico, J.A.; Itoua, I.; Strand, H.E.; Morrison, J.C.; et al. Terrestrial ecoregions of the world: A new map of life on earth: A new global map of terrestrial ecoregions provides an innovative tool for conserving biodiversity. BioScience 2001, 51, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camberlin, P.N.M.; Philippon, N.; Richard, Y. Determinants of the interannual relationships between remote sensed photosynthetic activity and rainfall in tropical Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2006, 106, 199–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaptue, T.A.T.; Roujean, J.L.; Faroux, S. ECOCLIMAP-II: An ecosystem classification and land surface parameter database of Western Africa at 1 km resolution for the African Monsoon Multidisciplinary Analysis (AMMA) project. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigot, S. Les Precipitations et La Convection Profonde en Afrique Centrale: Cycle Saisonnier. Variabilite Interannuelle et Impact sur la Vegetation. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Bourgogne, Dijon, France, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Kaptue, A. Cartographie des Ecosytemes et Parametres Biophysiques Pour l’etude des Flux Hydriques sur le Continent Africain. Ph.D. Thesis, Universite de Toulouse III-Paul Sabatier, Toulouse, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chander, G.; Markham, B.L.; Helder, D.L. Summary of current radiometric calibration coefficients for Landsat MSS, TM, ETM+, and EO-1 ALI sensors. Remote Sens. Environ. 2009, 113, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.; Newcomb, W.; Dregne, H. AVHRR data sets for determination of desert spatial extent. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 3547–3565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tucker, C.J.; Pinzon, J.E.; Brown, M.E.; Slayback, D.A.; Pak, E.W.; Mahoney, R.; Vermote, E.F.; El Saleous, N. An extended AVHRR 8-km NDVI dataset compatible with MODIS and SPOT vegetation NDVI data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 4485–4498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adler, R.; Huffman, G.; Chang, A.; Ferraro, R.; Xie, P.; Janowiak, J.; Rudolf, B.; Schneider, U.; Curtis, S.; Bolvin, D.; et al. The version-2 Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) monthly precipitation analysis (1979–Present). J. Hydrometeorol. 2003, 4, 1147–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.; Adler, R.F.; Bolvin, D.T.; Gu, G. Improving the global precipitation record: GPCP version 2.1. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2009, 36, L17808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mennis, J. Exploring relationships between ENSO and vegetation vigour in the South-East USA using AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2001, 22, 3077–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holben, B.N. Characteristics of maximum-value composite images from temporal AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1986, 7, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soufflet, V.; Tanre, D.; Begue, A.; Podaire, A.; Deschamps, P.Y. Atmospheric effects on NOAA AVHRR data over Sahelian regions. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 1189–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, C.; Eck, T.F.; Tanre, D.; Holben, D.N. The effect of water vapour on the NDVI derived for the Sahelian region from NOAA AVHRR data. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1991, 12, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinter, P. Solar angle independence in the relationship between absorbed PAR and remotely sensed data for alfalfa. Remote Sens. Environ. 1993, 46, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.D. Time Series Analysis; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1994; Volume 2. [Google Scholar]
- Andres, L.; Salas, W.A.; Skole, D. Fourier analysis of multitemporal AVHRR data applied to a land cover classification. Int. J. Remote Sens. 1994, 15, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzali, S.; Menenti, M. Mapping isogrowth zones on continental scale using temporal fourier analysis of AVHRR-NDVI data. Int. J. Appl. Earth Geoinf. 1999, 1, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immerzeel, W.W.; Quiroz, R.A.; de Jong, S.M. Understanding precipitation patterns and land use interaction in Tibet using harmonic analysis of SPOT VGT-S10 NDVI time series. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2005, 26, 2281–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moody, A.; Johnson, D.M. Land-surface phenologies from AVHRR using the discrete fourier transform. Remote Sens. Environ. 2001, 75, 305–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; John, C.; Hodges.; Crystal, B.; Schaaf.; Mark, A.; Friedl.; Alan, H.; Strahler, A.H.; Gao, F. Global Vegetation Phenology from AVHRR and MODIS Data. In Proceedings of the Geoscience and Remote Sensing Symposium (IGARSS’01), Sydney, Australia, 9–13 July 2001; Volume 5, pp. 2262–2264.
- Martiny, N.; Camberlin, P.; Richard, Y.; Philippon, N. Compared regimes of NDVI and rainfall in semi-arid regions of Africa. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2006, 27, 5201–5223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malo, A.R.; Nicholson, S. A study of rainfall and vegetation dynamics in the African Sahel using normalized difference vegetation index. J. Arid Environ. 1990, 19, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Rousvel, S.; Armand, N.; Andre, L.; Tengeleng, S.; Alain, T.S.; Armel, K. Comparison between Vegetation and Rainfall of Bioclimatic Ecoregions in Central Africa. Atmosphere 2013, 4, 411-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4040411
Rousvel S, Armand N, Andre L, Tengeleng S, Alain TS, Armel K. Comparison between Vegetation and Rainfall of Bioclimatic Ecoregions in Central Africa. Atmosphere. 2013; 4(4):411-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4040411
Chicago/Turabian StyleRousvel, Sonfack, Nzeukou Armand, Lenouo Andre, Siddi Tengeleng, Tchakoutio Sandjon Alain, and Kaptue Armel. 2013. "Comparison between Vegetation and Rainfall of Bioclimatic Ecoregions in Central Africa" Atmosphere 4, no. 4: 411-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4040411
APA StyleRousvel, S., Armand, N., Andre, L., Tengeleng, S., Alain, T. S., & Armel, K. (2013). Comparison between Vegetation and Rainfall of Bioclimatic Ecoregions in Central Africa. Atmosphere, 4(4), 411-427. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos4040411




