Spatial–Temporal Variations of Air Pollutants and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors During 2014 to 2022 in Jiangsu Province, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
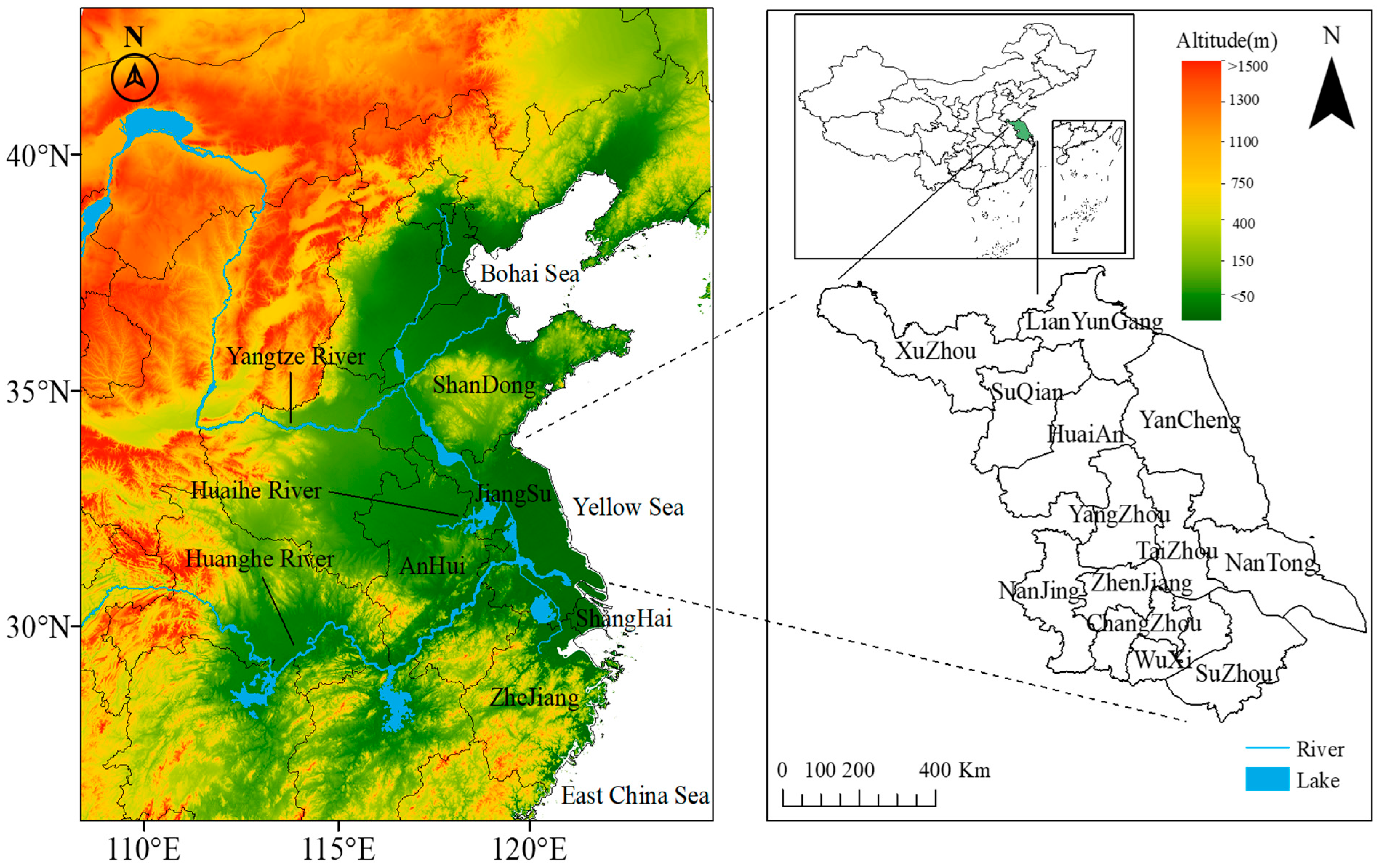
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Source
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Analyses
3.1. Temporal–Spatial Distribution of Pollutants
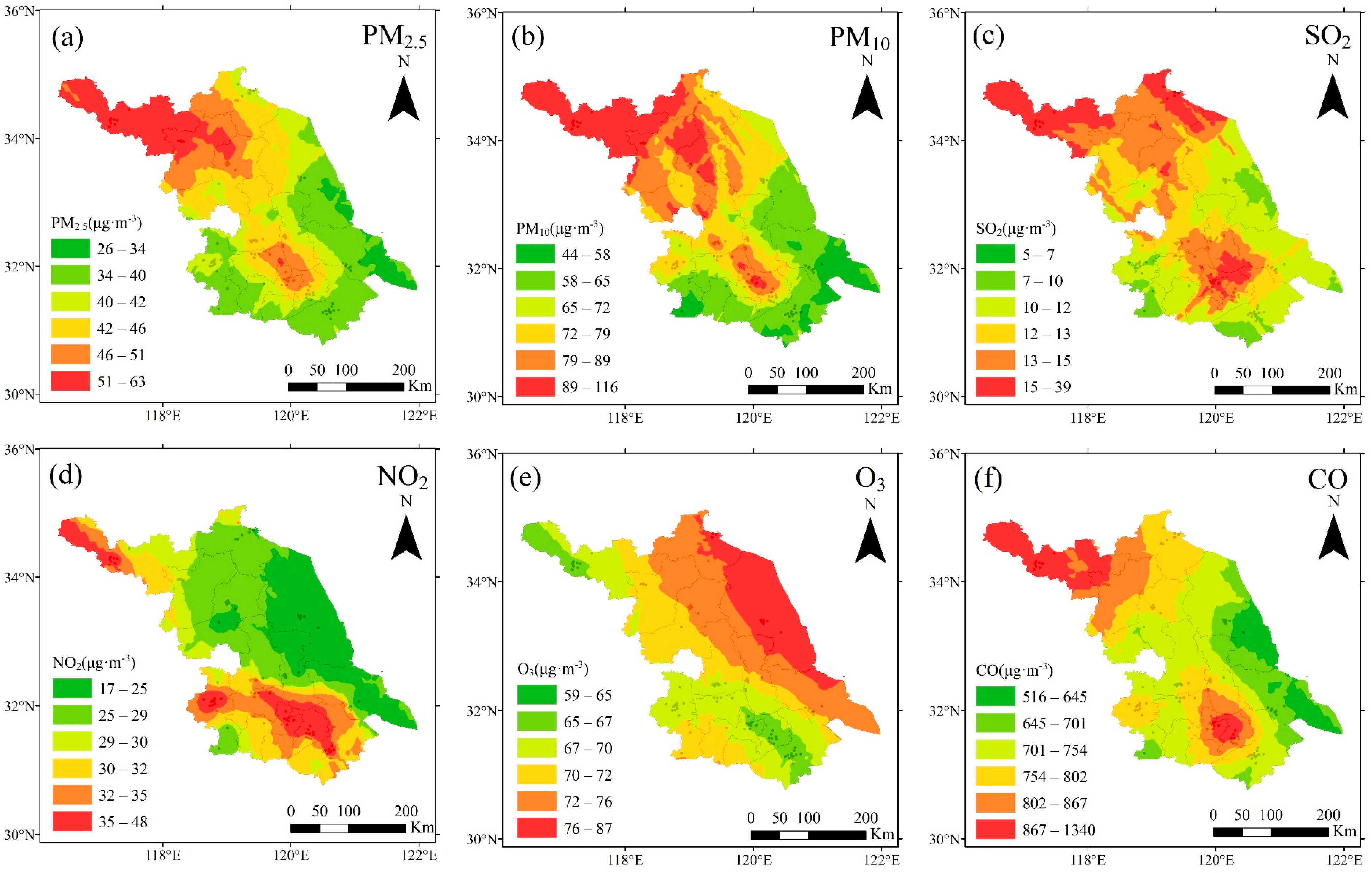
3.1.1. Average Distribution of Pollutants and Meteorological Elements During 2014 to 2022
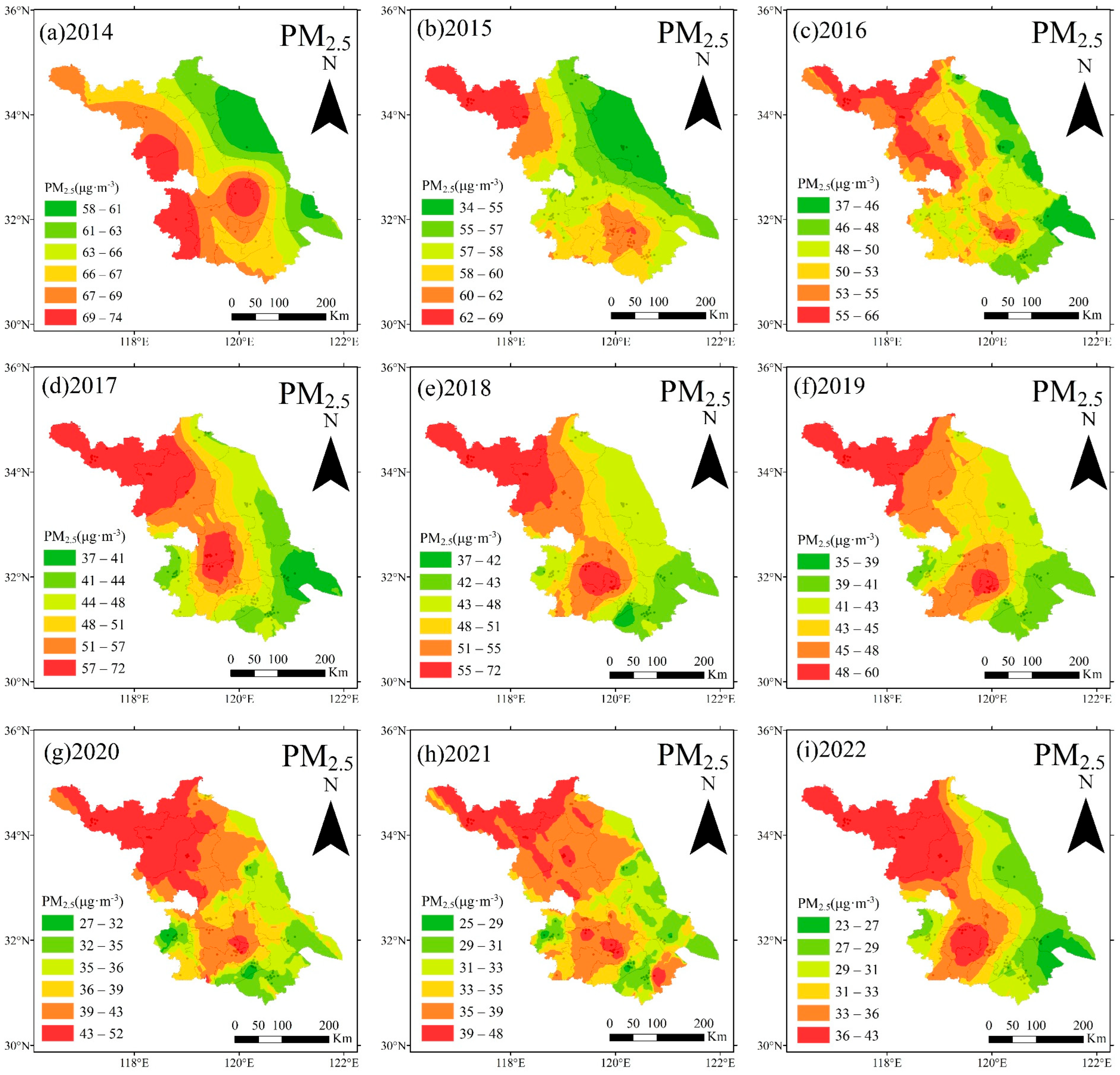
3.1.2. Annual Variation in Pollutant Distribution Characteristics
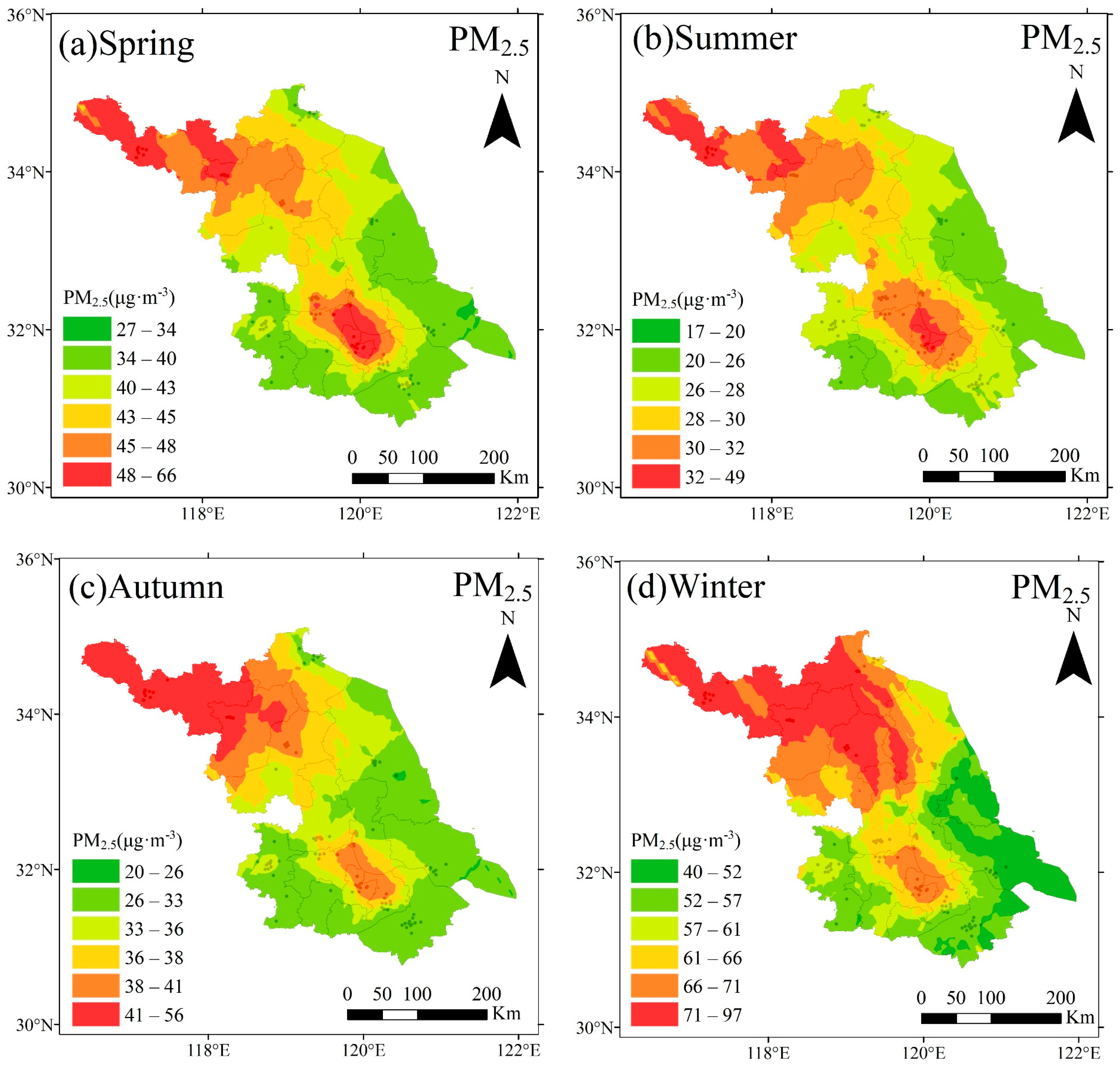
3.1.3. Seasonal Variation in Pollutant Distribution Characteristics
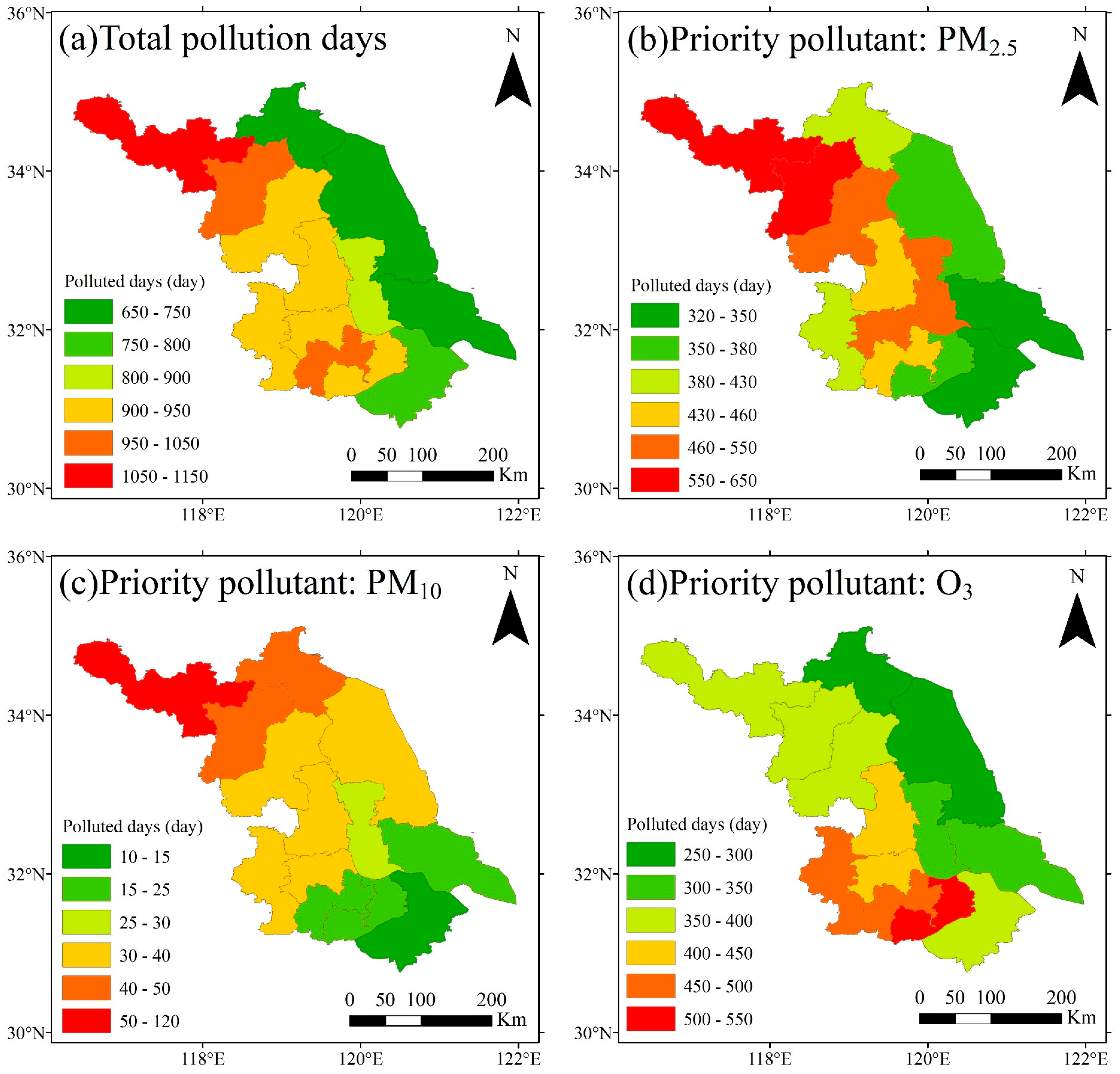
3.2. Distribution of Pollution Days
3.2.1. Distribution Characteristics of Total Pollution Days During 2014 to 2022
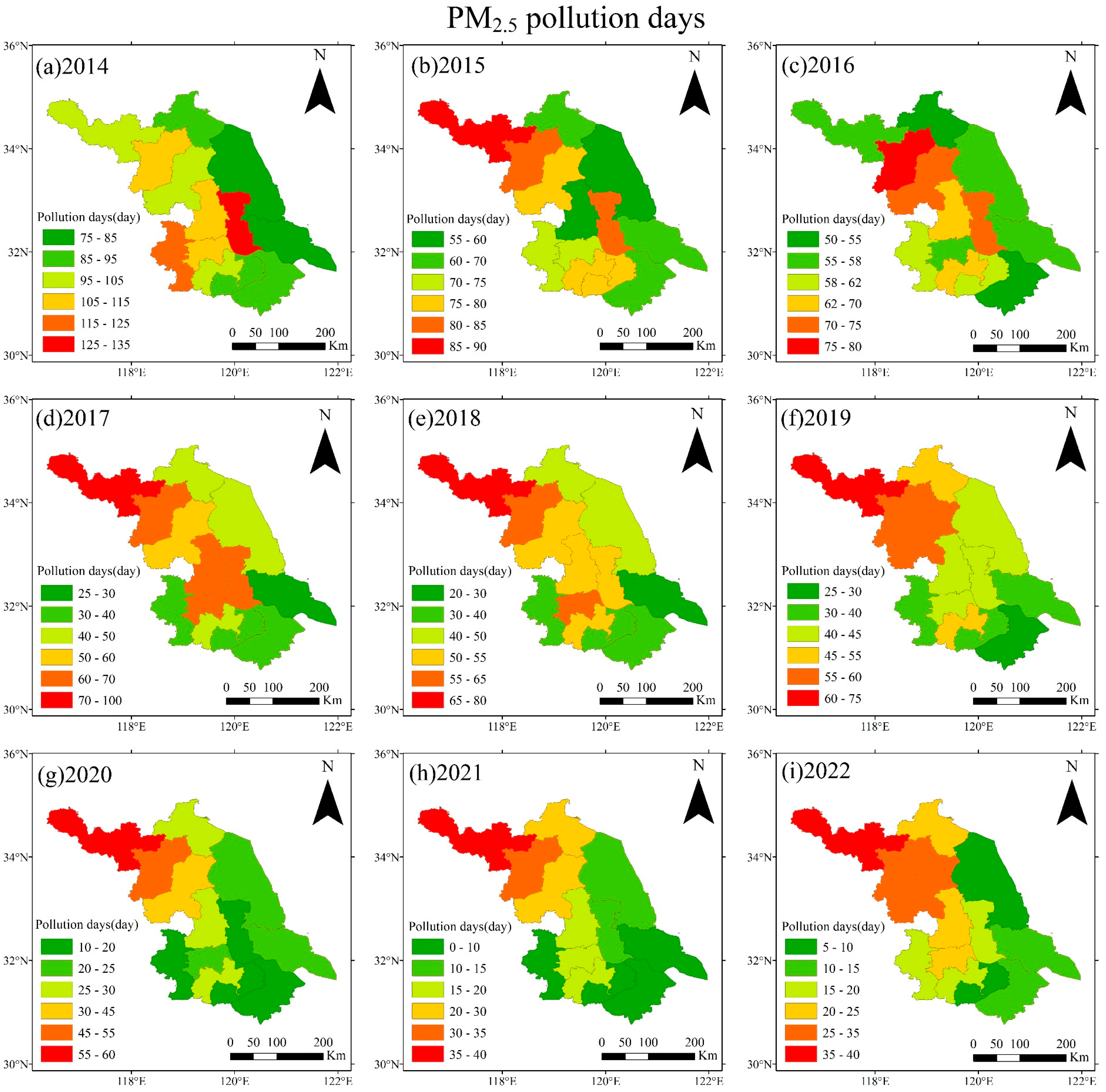
3.2.2. Annual Variation in Pollution Days Distribution Characteristics
3.2.3. Seasonal Variation in Pollution Days Distribution Characteristics
3.3. Impacts of Meteorological Factors on Pollutants
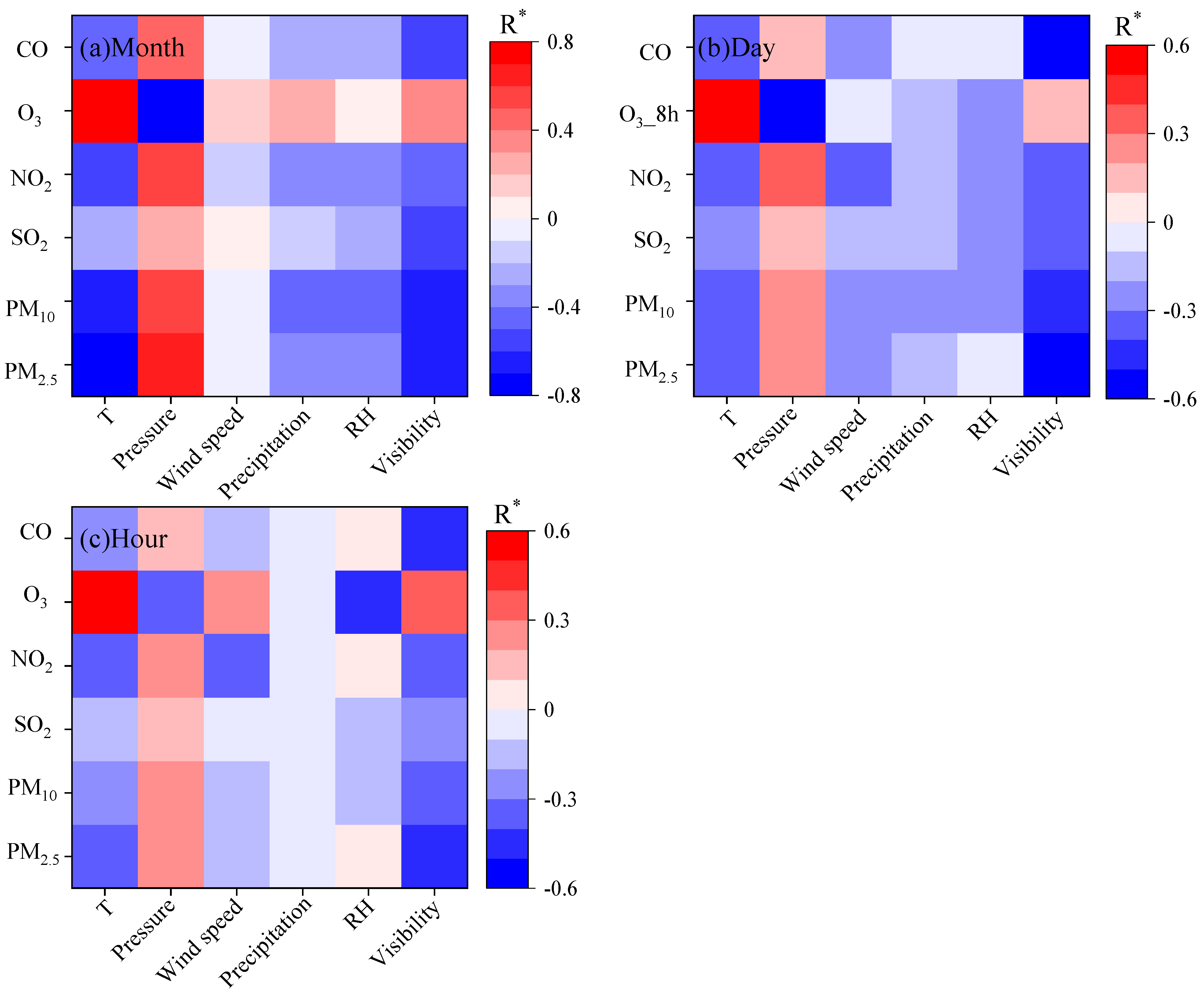
3.3.1. Correlation Between Pollutants and Meteorological Factors
3.3.2. Impacts of Precipitation, Wind Speed and Direction
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lovett, G.M.; Tear, T.H.; Evers, D.C.; Findlay, S.E.G.; Cosby, B.J.; Dunscomb, J.K.; Driscoll, C.T.; Weathers, K.C. Effects of Air Pollution on Ecosystems and Biological Diversity in the Eastern United States. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1162, 99–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoatey, P.; Baawain, M.S. Effects of pollution on freshwater aquatic organisms. Water Environ. Res. 2019, 91, 1272–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, G.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xue, T.; Zhao, H.; Tong, D.; Zheng, B.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; et al. Drivers of PM2.5 air pollution deaths in China 2002–2017. Nat. Geosci. 2021, 14, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, T.; Guo, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z.; Abramson, M.J.; Heyworth, J.; Hales, S.; Woodward, A.; Bell, M.; Guo, Y.; et al. Health and related economic benefits associated with reduction in air pollution during COVID-19 outbreak in 367 cities in China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, X.; Zeng, X.; Knibbs, L.D.; Zhang, Y.; Jalaludin, B.; Dharmage, S.C.; Morawska, L.; Guo, Y.; et al. Individual and joint associations of long-term exposure to air pollutants and cardiopulmonary mortality: A 22-year cohort study in Northern China. Lancet Reg. Health West. Pac. 2023, 36, 100776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Guo, B.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Yang, L.; Silang, Y.; Hong, F.; et al. Long-term Exposure to Ambient PM2.5 and Its Components Associated with Diabetes: Evidence from a Large Population-Based Cohort from China. Diabetes Care 2023, 46, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Xu, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; Dai, L.; Zhang, T.; Agathokleous, E.; Calatayud, V.; Paoletti, E.; Mukherjee, A.; Agrawal, M.; et al. Ozone pollution threatens the production of major staple crops in East Asia. Nat. Food 2022, 3, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Feng, Z.; Dai, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tan, Y. Ground-level ozone pollution in China: A synthesis of recent findings on influencing factors and impacts. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 063003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Wang, W.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; Wei, C.; Li, Y.; Deng, F.; Baccarelli, A.A.; et al. Ozone pollution and hospital admissions for cardiovascular events. Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 1622–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Li, X.; Cheng, Y.; Parrish, D.; Ni, R.; Tan, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, S.; et al. Ozone pollution mitigation strategy informed by long-term trends of atmospheric oxidation capacity. Nat. Geosci. 2024, 17, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominski, F.; JBranco, J.; Buonanno, G.; Stabile, L.; Silva, M.; Andrade, A. Effects of air pollution on health: A mapping review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Guo, S.; Peng, J.; Wu, Z. Insight into characteristics and sources of PM2.5 in the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei region, China. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2015, 2, 257–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T. Air pollution in China: Scientific challenges and policy implications. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2017, 4, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, J.S.; Monks, P.S. Estimating daily surface NO2 concentrations from satellite data—A case study over Hong Kong using land use regression models. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 17, 8211–8230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottalico, F.; Travaglini, D.; Chirici, G.; Garfì, V.; Giannetti, F.; De Marco, A.; Fares, S.; Marchetti, M.; Nocentini, S.; Paoletti, E.; et al. A spatially-explicit method to assess the dry deposition of air pollution by urban forests in the city of Florence, Italy. Urban For. Urban Green. 2017, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimissis, A.; Philippopoulos, K.; Tzanis, C.G.; Deligiorgi, D. Spatial estimation of urban air pollution with the use of artificial neural network models. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, G.; Wang, S.; Ma, M.; Ni, C.; Shang, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J. Characteristics of air pollution in different zones of Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 612, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yao, T.; Fung, J.C.H.; Lu, X.; Lau, A.K.H. Application of air parcel residence time analysis for air pollution prevention and control policy in the Pearl River Delta region. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 658, 744–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, B.; Zhang, L.; Luo, R. Spatiotemporal variations of PM2.5 and PM10 concentrations between 31 Chinese cities and their relationships with SO2, NO2, CO and O3. Particuology 2015, 20, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Ning, M.; Lei, Y.; Sun, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, J. Defending blue sky in China: Effectiveness of the “Air Pollution Prevention and Control Action Plan” on air quality improvements from 2013 to 2017. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 252, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, J.; Song, L.; Ma, L.; Luo, M.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D. Quantification of secondary particle loading during a heavy air pollution event in Beijing: A simplified method based on coal emission indicators. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 215, 116896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; Wu, G. Two air pollution events in the coastal city of Tianjin, north China plain. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1780–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Zhu, J.; Liao, H.; Li, J.; Liang, M.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X. Co-occurrence of ozone and PM2.5 pollution in the Yangtze River Delta over 2013–2019: Spatiotemporal distribution and meteorological conditions. Atmos. Res. 2021, 249, 105363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.; Lan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Chan, P.; Hong, Y.; Feng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Liang, G. Process analysis of regional aerosol pollution during spring in the Pearl River Delta region, China. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 829–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Jiao, M.; Huang, G.; Xia, B. Spatial-temporal heterogeneity of air pollution and its relationship with meteorological factors in the Pearl River Delta, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 254, 118415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Yu, Y.; Yin, D.; Qin, D.; He, J.; Dong, L. Spatial patterns and temporal variations of six criteria air pollutants during 2015 to 2017 in the city clusters of Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 624, 540–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Wang, S. Formation mechanism of a severe air pollution event: A case study in the Sichuan Basin, Southwest China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 246, 118135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Song, Y.; Kwan, M.P.; Huang, B.; Xu, B. How do people in different places experience different levels of air pollution? Using worldwide Chinese as a lens. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 238, 874–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalisa, E.; Fadlallah, S.; Amani, M.; Nahayo, L.; Habiyaremye, G. Temperature and air pollution relationship during heatwaves in Birmingham, UK. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2018, 43, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhu, J.; Liao, H.; Yang, Y.; Yue, X. Meteorological influences on PM2.5 and O3 trends and associated health burden since China’s clean air actions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 744, 140837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamińska, J.A. The use of random forests in modelling short-term air pollution effects based on traffic and meteorological conditions: A case study in Wrocław. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 217, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Wang, Z.; Cui, L.; Fu, H.; Zhang, L.; Kong, L.; Chen, W.; Chen, J. Air pollution characteristics in China during 2015–2016: Spatiotemporal variations and key meteorological factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 648, 902–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.; Gong, S.; Yu, Y.; Yu, L.; Wu, L.; Mao, H.; Li, R. Air pollution characteristics and their relation to meteorological conditions during 2014–2015 in major Chinese cities. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 223, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Dynamic effect analysis of meteorological conditions on air pollution: A case study from Beijing. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhan, Y.; Wang, B.; Li, Z.; Qin, Y.; Zhang, K. Spatiotemporally mapping of the relationship between NO2 pollution and urbanization for a megacity in Southwest China during 2005–2016. Chemosphere 2019, 220, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- QX/T 152-2012; Meteorological Industry Standard of the People’s Republic of China: Division of Climate and Seasons. Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- HJ 633-2012; Technical Regulation on Ambient Air Quality Index (on trial). The Ministry of Environmental Protection of People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Wang, H.; Lyu, X.; Guo, H.; Wang, Y.; Zou, S.; Ling, Z.; Wang, X.; Jiang, F.; Zeren, Y.; Pan, W.; et al. Ozone pollution around a coastal region of South China Sea: Interaction between marine and continental air. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 4277–4295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caicedo, V.; Delgado, R.; Luke, W.T.; Ren, X.; Kelley, P.; Stratton, P.R.; Dickerson, R.R.; Berkoff, T.A.; Gronoff, G. Observations of bay-breeze and ozone events over a marine site during the OWLETS-2 campaign. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 263, 118669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, T.; Ma, D.; Song, R.; Zhang, M.; Gao, L.; Li, S.; Zhuang, B.; Li, M.; Xie, M. Impacts of regional emission reduction and global climate change on air quality and temperature to attain carbon neutrality in China. Atmos. Res. 2022, 279, 106384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, T.; Jiang, F.; Liao, J.; Cai, Y.; Yin, C.; Zhu, J.; Han, Y. Studies on a severe dust storm in East Asia and its impact on the air quality of Nanjing, China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2013, 13, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Cui, Y.; He, Q.; Guo, L.; Gao, X.; Feng, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Seasonal Variations of Carbonyls and Their Contributions to the Ozone Formation in Urban Atmosphere of Taiyuan, China. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Song, Z.; Huang, J.; Zhang, P.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Guan, X.; Ge, J.; Zhou, X. Estimation of Atmospheric PM 10 Concentration in China Using an Interpretable Deep Learning Model and Top-of-the-Atmosphere Reflectance Data from China’s New Generation Geostationary Meteorological Satellite, FY-4A. JGR Atmos. 2022, 127, e2021JD036393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Alatalo, J.M.; Jiang, B. Air quality characteristics during 2016–2020 in Wuhan, China. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 8477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anglada, J.M.; Martins-Costa, M.; Ruiz-López, M.F.; Francisco, J.S. Spectroscopic signatures of ozone at the air–water interface and photochemistry implications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 11618–11623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB/T 28592-2012; Grade of Precipitation: General Administration of Quality Supervision. Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.


| Precipitation Grade | Precipitation (mm) | PM2.5 (μg·m−3) | PM10 (μg·m−3) | SO2 (μg·m−3) | NO2 (μg·m−3) | O3 (μg·m−3) | CO (μg·m−3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Scattered rain | <0.1 | 49.3 | 85.2 | 15.5 | 35.6 | 72.7 | 832.2 |
| Light rain | 0.1–9.9 | 39.3 | 61.4 | 11.1 | 29.5 | 60.1 | 778.2 |
| Moderate rain | 10.0–24.9 | 29.2 | 45 | 9.6 | 26 | 59.8 | 743.6 |
| Heavy rain | 25.0–49.9 | 23.4 | 37 | 8.9 | 23.4 | 62 | 710.2 |
| Torrential rain | 50.0–99.9 | 21.3 | 33.4 | 9 | 23.1 | 59.8 | 699.2 |
| Severe torrential rain | 100.0–249.9 | 16.6 | 26.3 | 8.9 | 22.3 | 53.9 | 674.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Wang, H.; Ke, Y.; Yin, Y.; Zhou, X.; Chen, J.; Chen, K.; Guo, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, K.; et al. Spatial–Temporal Variations of Air Pollutants and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors During 2014 to 2022 in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091079
Wu Z, Wang H, Ke Y, Yin Y, Zhou X, Chen J, Chen K, Guo J, Wang J, Wang K, et al. Spatial–Temporal Variations of Air Pollutants and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors During 2014 to 2022 in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(9):1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091079
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zihao, Honglei Wang, Yue Ke, Yan Yin, Xuedong Zhou, Jinghua Chen, Kui Chen, Jun Guo, Jia Wang, Keqing Wang, and et al. 2025. "Spatial–Temporal Variations of Air Pollutants and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors During 2014 to 2022 in Jiangsu Province, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 9: 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091079
APA StyleWu, Z., Wang, H., Ke, Y., Yin, Y., Zhou, X., Chen, J., Chen, K., Guo, J., Wang, J., Wang, K., & Wu, Y. (2025). Spatial–Temporal Variations of Air Pollutants and Its Relationship with Meteorological Factors During 2014 to 2022 in Jiangsu Province, China. Atmosphere, 16(9), 1079. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16091079







