Abstract
Air pollution is causing a global health, climate, and environmental crisis. Air quality (AQ) in hyper-arid regions, such as the Arabian Peninsula, remains under-explored, posing significant concerns for public health and the scientific community. Both long-term and short-term exposure to high pollutant levels, whether from anthropogenic or natural sources, can pose serious health risks. This paper offers a comprehensive review and meta-analysis of urban AQ literature published in the region over the past decade (2013–June 2025). We aim to provide guidance and highlight key directions for future research in the field. This paper examines key pollutants, emission sources, implications of urban sources, and the most studied countries, methodologies, limitations, and recommendations from different case studies. Our analysis reveals a significant research gap highlighting insufficient recent literature. Saudi Arabia was the most studied country with 20 papers, followed by the broader Arabian Peninsula (sixteen), Qatar (twelve), the United Arab Emirates and Iraq (seven each), Kuwait (four), Oman (three), Jordan, and Bahrain (one each). The primary methods employed included measurements and sampling (28%) and remote sensing (24%), with a focus on pollutants such as dust (23.1%), NOx/NO2/NO (17.2%), PM2.5 (17.6%), and PM10 (12%). Industrial emissions (27%) and natural dust (24%) were identified as significant emission sources. Monitoring methods included grab sampling (19%), integrated sampling (34%), and continuous monitoring (47%). Notably, 13.3% of AQ sensors were linked to a station, 27.6% were self-referenced, and 59.1% did not specify calibration methods. The findings highlight the need for further research, regular calibration of air quality monitors, and the integration of advanced modeling approaches. Moreover, we recommend exploring the links between air pollution and urban development to ensure cleaner air and contribute to the global dialogue on sustainable and cross-border AQ solutions.
1. Introduction
Long-term personal exposure to air pollution and short-term exposure to high concentrations of air pollutants are pressing concerns in scientific research and public health discourse [1,2]. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), around 99% of the world’s population breathes air containing pollutant concentrations that exceed the WHO’s global guideline limits [3]. Globally, air pollution is responsible for more than 6.7 million premature deaths annually, with vulnerable groups such as children, pregnant women, older adults, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions being at greater risk [1,4]. The health impacts of air pollution include but are not limited to lung cancer [5,6], respiratory diseases, heart infections [7,8], heart attacks, strokes, and asthma [9,10]. Beyond health impacts, air pollution also harms the environment through global warming [11], the formation of acid rain [12], ozone depletion [13], and weather variability [14]. However, not all pollutants have the same impact. In fact, the recent updates to air quality (AQ) guidelines published by the WHO in September 2021 are significantly stricter for specific critical air pollutants. For instance, for particulate matter with an aerodynamic diameter of 2.5 μm (PM2.5) or less, the annual average limit is now 5 µg/m3; for particulate matter up to 10 μm (PM10), the limit is 15 µg/m3; and for nitrogen dioxide (NO2), the limit is 10 µg/m3 [3]. These limits and other information for different pollutants are detailed in the WHO’s 2021 report [3].
In urban areas, adhering to these guidelines often presents substantial challenges [15,16]. The high population density in urban areas is closely linked to elevated emissions from various sources, including natural gas and fuel oil used for home heating [17,18], extensive vehicle traffic [19,20,21], and intense levels of product manufacturing and industrial activities [22,23,24]. These factors contribute to the complexity of reducing pollutant levels by targeting and meeting the recommended guidelines. In addition, countries in the Arabian Peninsula (i.e., Bahrain, Kuwait, Iraq, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, and Jordan) must deal with natural sources. The region’s unique desert environment introduces additional complexities to AQ management [25]. This region is characterized by high temperatures and varying humidity levels, with low humidity in deserts and high humidity in coastal areas [26], as well as frequent dust storms [27], rapid urbanization [28], economic growth [29], increased energy consumption [30], and industrialization. These factors collectively have a significant impact on AQ [31].
Over the past 10 years, significant attention has been given to urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula. The existing studies provide a comprehensive overview of urban-focused AQ research, demonstrating that while substantial progress has been made, further studies are still needed to fully understand and address the region’s unique challenges. Rapid urbanization and population growth in the Arabian Peninsula have led to increased vehicular traffic, making transportation a major source of air pollution. Studies have consistently linked urban pollution to vehicle emissions, as seen in Saudi Arabia [1,32], Qatar [25,29,31], and Kuwait [33], highlighting the need for effective traffic management to mitigate air pollutants. The region’s reliance on oil production, refining, and manufacturing has led to significant industrial emissions. For instance, the industrial zones in Kuwait release significant SO2 and NO2 emissions, necessitating real-time monitoring and stricter regulations on cement, metal, and stone-cutting industries [34,35]. Additionally, the frequent sand and dust storms, driven by arid desert conditions, exacerbate air pollution by increasing PM pollution across the region [29], with high aerosol optical depth (AOD) [36].
In this study, we aim to provide a comprehensive review and meta-analysis of published papers on urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula from 2013 to June 2025. Given the growing significance of the issue, as highlighted in the background literature, we also seek to offer insights and directions for future research in the region. To achieve this aim, we addressed the most studied air pollutants, potential emission sources, most understudied areas, and the types of AQ monitoring devices and models most frequently used. Additionally, we examined data collection methods, spatial and temporal coverage, the calibration and accuracy of monitoring devices, the implications of urban sources on AQ, and key limitations and recommendations provided in the reviewed literature. This study contributes to advancing the current understanding of urban AQ and guiding future research and policy development to improve AQ management practices worldwide but with a focus on the Arabian Peninsula. We developed and applied a thematic methodology to extract consistent information from each reviewed study. This includes (1) assessing the current state and identifying significant research gaps, (2) evaluating essential tools and elements in material and experimental design, and (3) analyzing case studies and their resulting outcomes. Our study is the first to systematically review the rapidly expanding field of urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula over the past decade. The developed methodology is highly transferable to other systematic reviews, minimizing author biases and focusing on knowledge extracted from the literature. This methodology provides quantitative and qualitative references for future applications to improve urban AQ globally. It is relevant to AQ researchers, scholars, and experts at all levels working to improve public health and protect the environment by addressing urban air pollution.
2. Methodology
2.1. Study Area
The Arabian Peninsula (Figure 1), located in the southwestern part of Asia in the subtropical belt between 12° and 35° N latitude and 30° and 60° W longitude, is the largest peninsula in the world, covering approximately 3.2 million Km2 [26]. The Red Sea borders it to the west, the Arabian Sea to the south, the Gulf of Oman to the southeast, and the Persian Gulf to the northeast, with the Syrian Desert and Mesopotamian Plain to the north (Figure 1) [26,29]. The region has diverse geographical features, including vast deserts such as the Rub’ al Khali, the largest continuous sand desert globally [29]. The climate of the Arabian Peninsula is predominantly arid [37], with extreme heat during summer and minimal rainfall [38]; coastal areas experience milder temperatures and higher humidity compared to the interior, where harsh desert conditions prevail [26,29]. The southwestern highlands receive more rainfall due to their elevation [26,39].
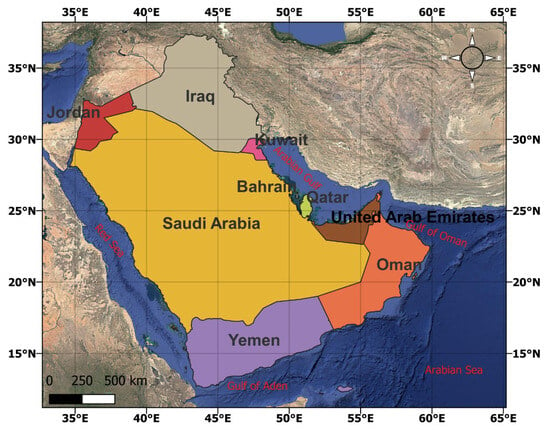
Figure 1.
Map of the study area, Arabian Peninsula.
The Arabian Peninsula consists of six countries, with parts of three additional countries extending onto it. The nations on the peninsula include Saudi Arabia, Oman, Kuwait, Qatar, Yemen, and the UAE. The southern areas of Jordan, Iraq, and Bahrain are also geopolitically associated with the peninsula [26,40]. The area encounters significant environmental challenges such as desertification, climate change, and declining AQ [26,29,40]. The region’s AQ is affected by natural factors (i.e., desert dust) and human activities (i.e., emissions from vehicles and industries). These activities encompass the rapidly expanding urban population, which leads to higher vehicle usage and emissions, industrialization, construction, emissions from ships in the Arabian Gulf, and the exploitation of natural resources [26,29,40]. These combined factors negatively affect AQ in the region, posing long-term public health and environmental sustainability concerns.
This study area was chosen due to a combination of several critical factors that uniquely impact urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula. The region experiences intense anthropogenic pressure from rapid urban development (e.g., Riyadh, Dubai, and Doha), major infrastructure projects, and high vehicular density, contributing to increased NO2, PM2.5, and other pollutants. Additionally, natural phenomena such as frequent dust storms (e.g., the seasonal Shamal winds in Kuwait and eastern Saudi Arabia) significantly elevate particulate matter concentrations. The region’s reliance on desalination plants, oil refineries, and energy-intensive cooling systems further compounds pollution. These complex and region-specific drivers make the Arabian Peninsula an essential and scientifically valuable setting for targeted AQ assessment and synthesis.
2.2. Thematic Analysis Method
The thematic analysis research methodology identifies, analyzes, and provides consistent knowledge within various data sources, including interviews, transcripts, questionnaires, scientific publications, and news articles [41]. Braun and Clarke [41] described a thematic analysis framework in psychological studies, consisting of six steps, which served as the guiding structure for our method. Wang et al. [42] also employed this thematic analysis approach in the review of studies utilizing low-cost sensors for AQ monitoring on a global scale. Drawing from the foundational frameworks of Wang et al. [42] and Braun and Clarke [41], we developed a novel thematic methodology (Figure 2) to address (1) the current state of urban AQ and identify significant research gaps, (2) the essential tools and components involved in urban AQ studies’ material and experimental design, and (3) the analysis of urban AQ through case studies and the resulting outcomes. To ensure that the comprehensive review aligned with our objectives (outlined in the introduction), self-contained questions were developed for each stage. They were then answered through a meta-analysis. By addressing these questions, we provided critical insights into urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula, offering valuable guidance for enhancing public health and environmental protection through the mitigation of urban air pollution.
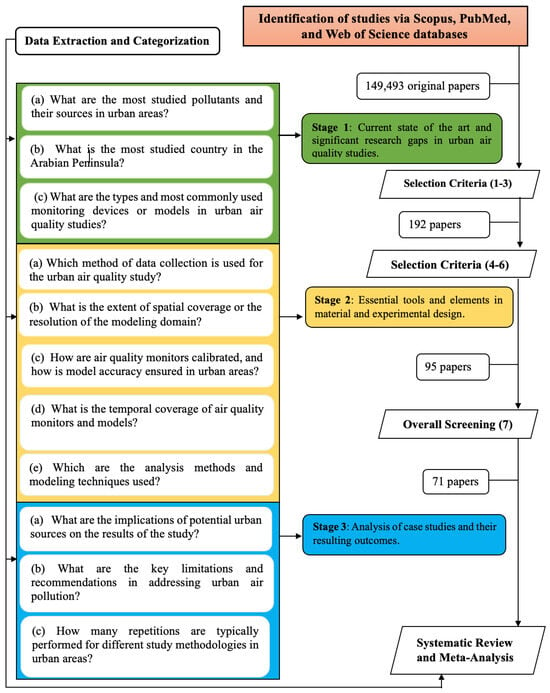
Figure 2.
Framework for the systematic review and meta-analysis study.
2.3. Data Search, Extraction, and Screening Criteria
To gather the datasets for this study, we primarily utilized the Web of Science (WoS) and searched for peer-reviewed articles containing specific keyword terms, including “urban air quality”, “urban air pollution”, “Arabian Peninsula”, “Gulf countries”, “Bahrain”, “Kuwait”, “Iraq”, “Oman”, “Qatar”, “Saudi Arabia”, “United Arab Emirates”, “Yemen”, and “Jordan”. The representative connection network based on all keywords from the consulted review papers is presented in Figure 3. It is crucial to highlight the following: (1) This systematic review specifically targets research on urban AQ within the Arabian Peninsula, encompassing both qualitative and quantitative full-length original research articles, as well as academic reviews, theoretical discussions, and case studies indexed in the WoS. (2) We excluded non-peer-reviewed materials such as reports from government bodies, organizations, newspapers, media outlets, and other online sources. The database of papers was reviewed multiple times to avoid repetitions or duplicates. The following inclusion criteria were adopted for selecting the papers:
Figure 3.
Interconnection (network-based) of all keywords from the consulted review papers.
- (1)
- Full-length original research articles: We prioritized comprehensive, original research articles, which provide in-depth analysis and contribute new findings to the field. This criterion excludes brief reports, opinion pieces, editorials, and reviews, as our focus was on obtaining robust, data-driven studies that offer substantial evidence and insights into urban AQ.
- (2)
- English language: English was chosen as the required language for the selected studies to ensure consistency in terminology, facilitate peer review, and enable the wider dissemination of findings. This also allows for easier cross-referencing with other studies in the field, as English is the predominant language in international scientific publications.
- (3)
- Publication date between 2013 and June 2025: We focused on papers published within the last decade to capture the most current research, trends, and advancements in urban AQ. This period was selected to ensure that the review reflects recent developments in methodologies, technologies, and regulatory frameworks that have shaped the field.
- (4)
- Transparent methodology: The inclusion of studies with well-defined and transparent methodologies was crucial to ensure the validity and reliability of our results. This criterion encompassed a variety of methodological approaches such as sample collection, environmental monitoring, dispersion modeling, satellite data analysis, and systematic reviews. By including diverse methodologies, the review aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the different techniques used to study urban AQ and their respective outcomes.
- (5)
- Urban AQ focus: The focus on urban AQ was chosen to address the specific environmental challenges faced by cities, particularly in densely populated and industrialized regions. These studies are essential for understanding the impact of urbanization on AQ, identifying key pollutants, and evaluating the effectiveness of air pollution measures in urban settings.
- (6)
- Studies in the Arabian Peninsula region (i.e., Bahrain, Kuwait, Iraq, Oman, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Yemen, and Jordan): The geographical focus on the Arabian Peninsula was chosen due to the unique environmental, climatic, and socioeconomic factors that influence AQ in this region. These factors include high temperatures, frequent dust storms, rapid urbanization, and reliance on fossil fuels. The review aims to address region-specific urban AQ issues and provide insights directly applicable to these countries by concentrating on this region.
- (7)
- Overall screening based on title, abstract, and conclusion: This step was designed to efficiently filter out irrelevant or low-quality studies and ensure that only those with a clear focus on urban AQ and a strong research basis were selected for further review. By concentrating carefully on the evaluation of the title, abstract, and conclusion, we ensured that the chosen studies were directly relevant to the research objectives and provided valuable contributions to the systematic review.
In our preliminary search, the database platforms yielded 149,493 original studies. We utilized additional resources such as Scopus and PubMed to ensure the inclusion of all relevant studies. Based on selection criteria 1 to 3, we narrowed this down to 192 papers. Following criteria 4 to 6, 95 papers advanced to the following stage. Finally, based on criteria 7, only 71 papers progressed to the last review stage for meta-analysis (Figure 2). Ultimately, all 71 studies were confirmed to be indexed. All 71 scientific articles are thoroughly discussed and cited in this systematic review paper [2,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86,87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94,95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103,104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111,112,113,114,115,116].
2.4. Meta-Analysis and Data Categorization
After selecting 71 scientific articles for review, we conducted multiple evaluation rounds to ensure consistency and precision in our analysis. The meta-analysis systematically synthesized findings from diverse urban AQ studies, emphasizing the extraction of insights regarding AQ challenges in hyper-arid regions, i.e., the Arabian Peninsula. Each question was addressed during the meta-analysis using a thematic framework (Figure 2), which organized the findings into key categories. These categories included identifying the most studied air pollutants and areas, potential emission sources, monitoring devices, AQ models, data collection methods, spatial and temporal coverage, calibration, regional number of publications per year, and frequency of regional repetitive methodologies.
For each category, Table 1 illustrates the thematic classes, normalized responses, and conceptual descriptions and definitions utilized throughout this study to minimize discrepancies and improve data consistency. This systematic approach enabled the identification of critical research gaps, the assessment of tools and methods used in AQ studies and the evaluation of case studies to extract meaningful insights into urban AQ trends and challenges in the region.

Table 1.
Normalized responses and definitions for thematic and meta-analysis methods in urban AQ studies.
3. Results and Discussion
The results presented in Table 2 summarize the systematic review, while those in Table 3 represent the meta-analysis of urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula based on the 71 papers that met the criteria outlined in the methodology section.

Table 2.
Summary of the systematic review results on urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula.

Table 3.
Summary of meta-analysis results on urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula.
3.1. Current State of the Art and Significant Research Gaps
3.1.1. Most Studied Air Pollutants
During our review and meta-analysis, we compiled air pollutant data (Figure 4a) from studies published between 2013 and early (June) 2025 (Figure 4b). The analysis highlighted AQ concerns in the Arabian Peninsula. These results indicated that dust, NOx, and particulate matter (PM) remain the most studied pollutants in the Arabian Peninsula, reflecting ongoing concerns regarding AQ management.
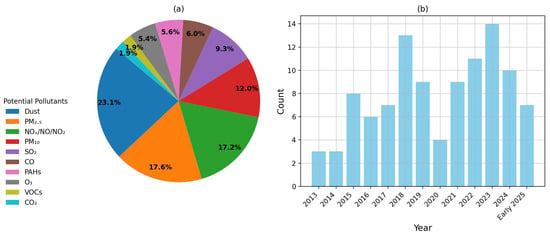
Figure 4.
(a) Frequency of potential air pollutants (b) for all studies published between 2013 and early (June) 2025 in the Arabian Peninsula.
Dust emerged as the most frequently reported pollutant with 16 occurrences (23.1%), reflecting the region’s arid environment and frequent dust storms. Studies such as Kaku et al. [68] and Shaltout et al. [75] confirm that mineral dust significantly influences AQ, particularly during extreme weather events that increase atmospheric aerosol concentrations. The persistence of dust as a primary air pollutant has been further emphasized by Modaihsh and Mahjou [71], who documented high deposition rates in urban areas, particularly near construction zones. Nitrogen oxides (NOx/NO/NO2), with twelve occurrences (17.2%), represent another major pollutant. Gasmi et al. [27] identified traffic emissions as a dominant source of NOx, pointing to the role of vehicular congestion in pollutant accumulation. Additionally, Omidvarborna et al. [35] highlighted NOx as a key contributor to air pollution across the region, reinforcing its significance in regional studies. Particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10) was also frequently studied, with twelve occurrences (17.6%) and nine occurrences (12%), respectively. The widespread occurrence of particulate matter across the reviewed studies indicates that it is a pollutant of growing concern, particularly given its association with both natural sources, such as dust storms, and anthropogenic emissions from industrial activities and traffic. The focus on PM in AQ research reflects its complex behavior in the atmosphere, its ability to interact with other pollutants [30], and its contribution to regional haze and visibility reduction [83].
Other pollutants, including sulfur dioxide (SO2) with seven occurrences (9.3%), carbon monoxide (CO) with four occurrences (6%), and ozone (O3) with four occurrences (5.4%), polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) with four occurrences (5.6%), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and carbon dioxide (CO2) with 1 occurrence (1.9%) each, were reported less frequently. The lower frequency of VOCs and CO2 in the reviewed studies suggests that while these pollutants contribute to atmospheric chemistry, they may not have been a primary focus of AQ assessments in the region. Nevertheless, the consistency of findings across different studies underscored the importance of continued monitoring and mitigation as essential components of AQ management in the Arabian Peninsula.
3.1.2. Potential Emission Sources of Air Pollutants and Their Implication for Urban AQ
This study highlighted the significant influence of various urban sources on AQ outcomes in the Arabian Peninsula. The analysis of the potential emission sources of air pollutants in the Arabian Peninsula, as presented in Figure 5a, revealed several key findings. Industrial emissions are the most frequent source, with 19 occurrences (27%), underscoring the significant role of industrial activities such as petrochemical plants, oil refineries, and cement industries in contributing to regional air pollution. These findings reflect the need for enhanced regulatory measures and pollution control technologies to mitigate the impact of industrial activities on the region’s AQ [32,63,68,80].
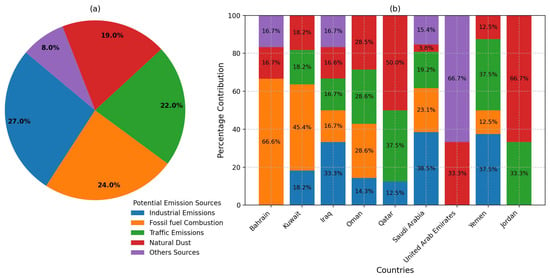
Figure 5.
(a) Overall distribution of potential emission sources in the Arabian Peninsula. (b) Distribution of potential emission sources by country.
Natural dust sources also play a major role, with 17 occurrences (24%). This reflects the significant influence of desert dust from sources like the Arabian Desert. The prevalence of natural dust highlights the region’s unique climatic and geographical factors that exacerbate air pollution, particularly during dust storms [2,36,45,54]. Fossil fuel combustion follows closely with 16 occurrences (22%). This category includes emissions from urban activities and oil refineries, indicating that energy production and transportation are substantial sources of pollutants and require comprehensive strategies to mitigate their impact [32,49,61]. These findings suggested that reducing fossil fuel use and improving energy efficiency are vital for mitigating air pollution.
Traffic emissions are reported 13 times (19%), illustrating their contribution to urban air pollution [30,49,70,72,80]. Other sources, including second air pollutants, marine air masses, biogenic sources, and unidentified sources account for six occurrences (8%) [67,76]. The distribution of potential emissions by country is presented in Figure 5b.
3.1.3. Most Studied Areas in the Arabian Peninsula
Among the 71 reviewed studies, Saudi Arabia emerges as the most extensively studied country, with twenty occurrences, followed by Qatar with twelve, the UAE and Iraq with seven each, Kuwait with four, Oman with three, and the broader Arabian Peninsula region with sixteen, as illustrated in Figure 6.

Figure 6.
Number of consulted studies per country and in the Arabian Peninsula (the red line represents the separation between countries and the region).
The importance of Saudi Arabia in these studies reflects its critical role in regional urban AQ research, partly due to its surface area size, its diverse geographic and climatic conditions [77], and its significant industrial activities. These factors contribute to a complex pollution landscape, with key sources such as oil refineries [51], petrochemical plants, and heavy traffic emissions concentrated in major cities [46] and industrial hubs [75]. The focus on Saudi Arabia underscores its importance in understanding air pollution within the Arabian Peninsula and highlights the necessity of targeted interventions in these high-impact areas to improve AQ across the region. In contrast, other countries such as Qatar, the UAE, Kuwait, and Oman are less frequently studied despite being home to considerable industrial [29] and urban development [84], which contribute to air pollution. The relatively lower number of studies in these countries suggests that while they might share similar pollution challenges as those of Saudi Arabia, they have not received equivalent research attention. This disparity points to potential research gaps that need to be addressed to ensure an inclusive understanding of AQ across the Arabian Peninsula. By expanding research efforts in these underrepresented areas, we can gain a more complete picture of regional air pollution dynamics, which is essential for developing effective AQ management strategies. The Arabian Peninsula, with 15 occurrences, draws attention due to its unique environmental and atmospheric conditions, offering valuable insights into regional AQ studies. Focusing on these broader regions is valuable for identifying general trends and common challenges, but it may overlook the unique conditions and specific pollution sources in individual countries. In addition, countries like Iraq, Jordan, and Bahrain, each with only one occurrence, are notably underrepresented in the literature. This lack of attention limits our understanding of the full extent of air pollution issues in these areas and hampers efforts to implement region-wide solutions.
The findings from this review highlighted the need for a more balanced and comprehensive approach to urban AQ studies across the Arabian Peninsula. Expanding research efforts to cover less-studied areas will enable the development of a more holistic understanding of air pollution in the region, ultimately leading to better-informed policies and more effective interventions. The overall distribution of related studies across the reviewed countries is presented in Table 2, further emphasizing the current research landscape and the areas in need of greater focus.
3.1.4. AQ Monitoring Devices and Models (Types and Most Used)
This study revealed insights into the types of AQ monitoring devices (Figure 7a) and models (Figure 7b) used in the Arabian Peninsula. Among the studies that used measurement and sampling methods, the results showed that fixed monitoring stations are predominantly used, accounting for 16 occurrences (80%). This prevalence highlights the reliance on stationary devices for continuous and long-term AQ assessments across the region. Mobile monitoring devices are less frequently used with three occurrences (16.8%), suggesting that while adopting these more flexible and location-specific tools is possible, they are not as widespread. The combination of mobile and fixed monitoring approaches is the least common, observed only in one occurrence (3.2%), indicating that integrated strategies that leverage the strengths of both methods are still in their infancy within the region. The findings showed a limited use of AQ models in urban AQ studies. Models like CALPUFF [43], AERMOD [34], WRF, WRF–CHIMERE [28,40], WRF–Chem [75], and MM5-CMAQ [28] have been utilized in the region for predicting how pollutants spread under different environmental conditions. The AERMOD model, which is widely recognized for its application in industrial source modeling [85,86], appears only once, suggesting that this type of modeling is not a primary focus in the Arabian Peninsula. Similarly, CALINE4, designed for predicting pollutant dispersion near roadways [25], also appears only once, indicating limited exploration of traffic-related pollution using this model. The CALPUFF model, which is suitable for simulating the long-range transport of pollutants [86,87], is slightly more common with two occurrences, reflecting some interest in understanding pollutant dispersion over larger areas. WRF–Chem, a sophisticated model that couples weather forecasting with chemical transport modeling [75,88], is also observed three times, pointing to a growing but limited use of advanced atmospheric modeling techniques in the region. Overall, these results suggested that while fixed monitoring stations dominate AQ assessment in the Arabian Peninsula, the use of advanced AQ models remains relatively underdeveloped.

Figure 7.
(a) Types of AQ monitoring devices and (b) models used in the Arabian Peninsula.
3.2. Essential Tools and Elements in Material and Experimental Design
The results presented in Figure 8a highlight the overall information about the methodologies currently used for assessing urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula.

Figure 8.
(a) Overall methodology, (b) calibration techniques, and (c) measurement and sampling methods used in the Arabian Peninsula.
Measurements and sampling methods emerge as the most frequently employed methodology, with 20 occurrences (28%). This category encompasses a broad range of general measurement techniques [32,33,46,50,55,89] and sample collection methods [44,56,58,70], focusing on pollutants such as dust, aerosols, and particulate matter. It also includes specific dust or aerosol sampling techniques, essential for directly assessing the environmental concentration and distribution of pollutants. The prominence of this methodology highlights the importance of on-the-ground data collection in understanding AQ, as it provides the empirical evidence needed for accurate analysis and modeling. Satellite data and remote sensing follow, with 17 occurrences (24%). This methodology involves the use of satellite data and remote sensing techniques, such as MODIS [36,45,52,54], AERONET [49,54,69], CALIPSO [54], and OMI [49], which allow for large-scale monitoring of AQ over vast geographic areas. Satellite measurements in the Arabian Peninsula provide critical insights into the spatial distribution of pollutants, especially in regions that are difficult to access for ground-based measurements [25,52,57,61]. The high frequency of this method reflects its importance in providing comprehensive and continuous data that complement ground-based observations. Statistical methods, with 13 occurrences (19%), include various receptor modeling techniques such as Positive Matrix Factorization (PMF) [30,47,67,77,78], Conditional Probability Function (CPF) [31], and Chemical Mass Balance (CMB) [65], as well as Principal Component Analysis (PCA) [53], Multiple Linear Regression (MLR) [53], and other descriptive approaches [30,31,65,72]. These techniques are essential for identifying pollution sources, understanding pollutant behavior, and making predictions based on the collected data. AQ and dispersion models appear with twelve occurrences (16.6%), while trajectory models appear with four occurrences (6%), involving the analysis of air mass movements using tools like HYSPLIT and other air mass trajectory models [46,74,76]. These models help track the origin and movement of air pollutants, which is essential for understanding long-range transport and identifying the sources of contaminants over time. Questionnaires and surveys with two occurrences (3%), while critical reviews [35] and other specialized instruments [2] appear with one occurrence (1.5% and 1.9%, respectively). Other specialized instruments, such as Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS) [65] and fast-response spectrometers [67], are also used for more targeted and detailed chemical analyses of urban air pollutants in the Arabian Peninsula.
A noteworthy development is the expansion of regional initiatives led by spearheaded by governmental and institutional bodies such as the Royal Commission for Riyadh City (RCRC) (Add Ref), the National Center for Meteorology (NCM) UAE (Add Ref), and Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (Add Ref), and the Environment Abu Dhabi (EAD) (Add Ref). These institutions have made substantial contributions by establishing real-time monitoring networks, developing AQ forecasting systems, launching public-facing applications (e.g., the RCRC AQ app), (Ref App), and conducting comprehensive assessments of urban air pollution. Although these outputs are not peer-reviewed in the traditional academic sense therefore, excluded from the core meta-analysis, they play a vital role in shaping the region’s AQ landscape. They contribute essential data, support evidence-based policy decisions, and foster greater public engagement with environmental issues. Future work would benefit from closer integration of institutional data sources with peer-reviewed research to produce a more comprehensive and policy-relevant understanding of AQ trends and challenges across the Arabian Peninsula.
It is also essential to mention that during our meta-analysis, we did not only focus on the methodologies used but also considered specific critical elements related to the overall methodology in each paper. These include:
Spatial and Temporal Coverage: The results presented in Table 2 highlight varying levels of spatial and temporal coverage across all consulted studies. While some focus on specific urban areas [43,46,67,90] provides detailed local insights into urban status based on AQ, others adopt a broader regional approach, capturing a wide range of urban and peri-urban environments [28,57,58,59,62,69]. The temporal coverage also varies, with some studies providing long-term monitoring data spanning several years [2,30,57] while others focus on short-term campaigns lasting a few months at most [51,56,67,68,71]. This diversity in coverage is crucial for capturing the dynamics of urban AQ across different scales and time frames.
Resolution of the Modeling Domain: The resolution of the modeling domain in the reviewed studies varies significantly, ranging from fine-scale, especially for AERMOD [34] and CALPUFF [43]. High-resolution models like WRF–Chem, as utilized by Fountoukis et al. [40] and Shaltout et al. [75], focused on specific urban areas and significantly contributed to urban AQ studies. It is essential to mention that, in AQ modeling studies [19,85], the choice of a good model [21,39] is essential for decision making and environmental management strategies [86,91].
Calibration and Accuracy of Monitoring Devices: Among the studies that used measurement and sampling methods, twelve occurrences (59.1%) did not mention the devices’ calibration methods while six occurrences (27.6%) used self-calibration and two occurrences (13.3%) used station calibration methods (Figure 8b). However, some studies provided protocols for sampling and sampling techniques, including grab sampling with four occurrences (19%), integrated sampling with seven occurrences (34%), and continuous monitoring with nine occurrences (47%) (Figure 8c), especially for satellite data and remote sensing, which typically include specific resolution and instrument calibration protocols. Monitoring device calibration is a critical step in ensuring data accuracy and reliability [92,93,94]. This study emphasizes the importance of regular calibration using reference-grade instruments or established calibration protocols [92], which is essential for maintaining the validity of data collected from low-cost sensors prone to drift over time. This need for regular calibration was also identified as a gap in the literature reviewed here.
3.3. Analysis of Case Studies and Their Resulting Outcomes
In each paper, we investigated the limitations and recommendations highlighted by the authors for addressing urban air pollution, summarized in Table 2. Most of these recommendations were made to inform AQ management and regulatory decisions. Several limitations are identified across the studies, including the scarcity of long-term data [72]. Multiple studies emphasized the importance of expanding monitoring efforts [30] to include not only well-developed urban centers but also peripheral and rural areas [80,81], where data scarcity has led to gaps in understanding the true extent of air pollution [43,44]. Further recommendations from studies highlighted that future research on urban AQ should prioritize the development of more monitoring networks [35] that combine ground-based [43] and remote sensing data [36]. A review also highlighted the necessity of standardizing methodologies and calibration procedures across studies to ensure the reliability and comparability of AQ data [39]. Another study also highlighted the need for innovative urban AQ techniques to address emerging challenges [76]. In addition, a need for advanced modeling techniques to more accurately capture the complexities of pollutant dispersion in urban environments, as evidenced by Al-Fadhli et al. [34] and Fountoukis et al. [40], was recommended. Future studies should focus on integrating health impact assessments [43] to better understand the public health implications of air pollution [53]. Policymakers were encouraged to adopt a multi-faceted approach that includes stricter emission controls [27], the promotion of cleaner technologies [63], and the implementation of sustainable urban planning practices [69] to mitigate the adverse effects of air pollution in the Arabian Peninsula. The implications of these findings extended to policy-making, where there is a pressing need for stricter regulation of industrial emissions and traffic-related pollution [36,67].
The review analysis also underscored the importance of public awareness and education in addressing AQ issues. Increasing community engagement and educating the public about the health risks associated with air pollution can lead to more significant support for AQ management initiatives and encourage behavioral changes that contribute to reducing pollution levels. Studies suggest that public participation in AQ monitoring and management could be a valuable tool in enhancing the effectiveness of these efforts [43,44]. The review further emphasizes integrating AQ data with other environmental and socioeconomic factors to develop more comprehensive urban planning strategies for transportation management, public health initiatives, industrial growth, and population density [44,67]. Another significant recommendation from the review analysis is the need for enhanced cross-border collaboration among countries in the Arabian Peninsula. Air pollution does not respect national boundaries, and transboundary pollution is a critical issue in the region, particularly due to the movement of dust [49] and other pollutants across borders [36]. Collaborative research, monitoring, and policy-making efforts can help address these shared challenges more effectively. Establishing regional frameworks for AQ management and data sharing could lead to more coordinated and impactful actions to reduce pollution levels across the Arabian Peninsula.
Compared to other global regions where urban AQ has been more extensively studied, such as South Asia, North Africa, and Europe, the Arabian Peninsula exhibits a distinct and underexplored set of environmental and anthropogenic factors. In South Asia, particularly in countries like India and Bangladesh, severe urban air pollution is primarily attributed to dense populations, coal-based energy production, the extensive use of biomass for cooking, and high vehicular emissions [95,96,97]. Seasonal variations in pollution levels are also influenced by agricultural burning and the South Asian monsoon system, which affect pollutant dispersion. In North Africa, urban centers such as Cairo and Algiers face high pollutant concentrations from traffic congestion, industrial zones, and increasing energy demand, compounded by Saharan dust intrusions [1,70,98]. Although North Africa shares some climatic features with the Arabian Peninsula, differences in urban planning, population density, and emission sources create distinct air quality dynamics. In contrast, while grappling with air pollution from transportation, industrial activity, and domestic heating, European cities benefit from comprehensive regulatory frameworks like the EU Ambient Air Quality Directives and more advanced air quality monitoring systems [99]. Efforts to transition to cleaner energy and enforce emission limits have led to measurable improvements in AQ across many European urban areas [99].
4. Concluding Remarks
In this paper, we performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of urban AQ studies to address the current state of the art, identify significant gaps, evaluate essential tools and elements in materials and experimental design, and analyze case studies and their outcomes in the Arabian Peninsula. A summary is provided below:
Current state of the art and significant research gaps in urban AQ research: (1) The results revealed a consistent pattern of pollution sources and impacts, with anthropogenic sources, particularly industrial emissions, traffic emissions, fossil fuel combustion, and natural dust being the most significant contributors to poor AQ. (2) The results highlighted that the Arabian Peninsula’s unique geographical features, such as vast desert areas, contribute to natural dust emissions, a significant component of PM10 and PM2.5 in the region. (3) While current methodologies provide valuable insights, there is a clear need for more comprehensive monitoring networks and improved modeling techniques to better understand and address the complexities of urban air pollution in the region. (4) The findings provided a comprehensive literature overview, highlighting extensive research on urban air pollution in Saudi Arabia. However, urban AQ studies in Qatar, the UAE, Kuwait, Oman, Iraq, Jordan, and Bahrain remain limited, indicating a need for further research in these countries. (5) Furthermore, the review identifies gaps in the existing research, particularly regarding the study of certain pollutants and sources. For instance, VOCs and PAHs, linked to severe health effects, are less frequently studied in the region despite their potential presence due to industrial activities and vehicular emissions. Similarly, the contribution of emerging sources, such as construction activities and waste burning, is not well-documented, indicating a need for future research to address these gaps.
Essential tools and elements in material and experimental design: (1) The findings highlighted significant limitations in the current body of research, particularly concerning the uneven spatial and temporal coverage of AQ monitoring across the Arabian Peninsula. This inconsistency hinders comprehensive conclusions about AQ trends in the region. (2) The variability in the accuracy and calibration of monitoring devices across studies poses challenges, leading to potential data inconsistencies. These issues underscore the urgent need for standardized methodologies and calibration procedures to ensure the reliability and comparability of AQ data. (3) Future research should prioritize the development of expanded monitoring networks that integrate ground-based and remote sensing data to overcome current limitations. Furthermore, incorporating health impact assessments in studies will also be vital for understanding the public health implications of air pollution.
Case studies and their outcomes: (1) The review advocates for a multidisciplinary approach that integrates environmental science, public health, urban planning, transportation networks, industry, and policymaking to address the complex interactions between air pollution, human health, and urban development in the Arabian Peninsula. It highlights the need for targeted interventions to reduce emissions from the critical sources identified. (2) The review suggests that future research should focus on the long-term impacts of air pollution on public health and the long-range transboundary transport of dust pollution in the Arabian Peninsula. (3) The review highlights the importance of raising public awareness about the health risks associated with air pollution and the need for community engagement in AQ management efforts. (4) The transboundary nature of air pollution, driven by atmospheric circulations that transport pollutants across borders, requires regional cooperation, collaborative policies, data sharing, and cross-border monitoring systems to effectively address this challenge. This would provide valuable insights into the long-term health risks associated with urban air pollution in the region and inform the development of more effective public health interventions.
We acknowledge several limitations in this review of urban AQ research in the Arabian Peninsula. One major limitation is the scarcity of publicly available data, unlike in the European Union (EU), where real-time data from government monitoring stations is freely accessible (EEA Air Quality Index (https://airindex.eea.europa.eu/AQI/index.html accessed on 28 June 2025)). Another limitation is the inclusion of only English-language publications, which may have introduced bias by excluding many local reports not published in English. While we aimed for comprehensive coverage, some relevant studies may have been inadvertently excluded, particularly when applying selection criteria (4) to (7), potentially omitting literature that could have provided additional insights. Nevertheless, we believe the extracted data offers a representative overview of the current research on urban AQ in the Arabian Peninsula. Despite these limitations, our findings reflect prevailing knowledge in the field and provide a solid foundation for understanding the region’s challenges and developments related to urban AQ. In addition, we recommend awareness campaigns and practical initiatives to be implemented in the region to increase public access to AQ information. For instance, mobile applications and web-based tools can be developed to inform the public about real-time AQ conditions and forecasts.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, E.I. and B.K.; methodology, E.I. and B.K.; software, E.I.; validation, E.I., M.M., B.K., F.P. and O.P.; investigation, M.M., B.K., F.P. and O.P.; resources, E.I.; data curation, E.I.; writing—original draft preparation, E.I.; writing—review and editing, E.I., M.M., B.K., F.P. and O.P.; visualization, M.M., B.K., F.P. and O.P.; supervision, M.M.; project administration, M.M. and F.P.; funding acquisition, M.M. and F.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by Tamkeen under the New York University Abu Dhabi Research Institute to Mubadala Arabian Center for Climate and Environmental Sciences (ACCESS), grant number: Award CG009.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in this study are included in the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Malekpour, M.-R.; Masinaei, M.; Moghaddam, S.S.; Ghamari, S.-H.; Abbasi-Kangevari, Z.; Rezaei, N.; Rezaei, N.; Mokdad, A.H.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Effect of Air Pollution on Disease Burden, Mortality, and Life Expectancy in North Africa and the Middle East: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet Planet. Health 2023, 7, e358–e369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faridi, S.; Yousefian, F.; Roostaei, V.; Harrison, R.M.; Azimi, F.; Niazi, S.; Naddafi, K.; Momeniha, F.; Malkawi, M.; Moh’d Safi, H.A.; et al. Source Apportionment, Identification and Characterization, and Emission Inventory of Ambient Particulate Matter in 22 Eastern Mediterranean Region Countries: A Systematic Review and Recommendations for Good Practice. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 310, 119889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Irankunda, E.; Torok, Z.; Mereuta, A.; Gasore, J.; Ozunu, A. Aermod evaluation for modelling the dispersion of particulate matter (PM10) in complex topography of Kigali, Rwanda. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. 2024, 23, 249–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borger, D.R.; Goyal, L.; Yau, T.; Poon, R.T.; Ancukiewicz, M.; Deshpande, V.; Christiani, D.C.; Liebman, H.M.; Yang, H.; Kim, H.; et al. Circulating Oncometabolite 2-Hydroxyglutarate Is a Potential Surrogate Biomarker in Patients with Isocitrate Dehydrogenase-Mutant Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, A.J.; Brauer, M.; Burnett, R.; Anderson, H.R.; Frostad, J.; Estep, K.; Balakrishnan, K.; Brunekreef, B.; Dandona, L.; Dandona, R.; et al. Estimates and 25-Year Trends of the Global Burden of Disease Attributable to Ambient Air Pollution: An Analysis of Data from the Global Burden of Diseases Study 2015. The Lancet 2017, 389, 1907–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Amato, G. Environmental Urban Factors (Air Pollution and Allergens) and the Rising Trends in Allergic Respiratory Diseases. Allergy 2002, 57, 30–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisephane, I. Ambient Particulate Matter (PM) Evaluation in Gasabo District, Rwanda. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. World Policy 2019, 8, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, Y.; Yokogawa, S.; Shimazaki, K.; Win-Shwe, T.-T.; Irankunda, E. Assessing Personal PM2.5 Exposure Using a Novel Neck-Mounted Monitoring Device in Rural Rwanda. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrigan, P.J.; Fuller, R.; Acosta, N.J.R.; Adeyi, O.; Arnold, R.; Basu, N.; Baldé, A.B.; Bertollini, R.; Bose-O’Reilly, S.; Boufford, J.I.; et al. The Lancet Commission on Pollution and Health. The Lancet 2018, 391, 462–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frölicher, T.L.; Joos, F. Reversible and Irreversible Impacts of Greenhouse Gas Emissions in Multi-Century Projections with the NCAR Global Coupled Carbon Cycle-Climate Model. Clim. Dyn. 2010, 35, 1439–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terán, R.; Garcia Bustos, K.A.; Sanchez Vera, F.P.; Colina Andrade, G.J.; Pacheco Tanaka, D.A. Acid Precipitation Followed by Microalgae (Chlorella Vulgaris) Cultivation as a New Approach for Poultry Slaughterhouse Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2021, 335, 125284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurston, G.D.; Ito, K. Epidemiological Studies of Acute Ozone Exposures and Mortality. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 286–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camino, C.; Cuevas, E.; Basart, S.; Alonso-Pérez, S.; Baldasano, J.M.; Terradellas, E.; Marticorena, B.; Rodríguez, S.; Berjón, A. An Empirical Equation to Estimate Mineral Dust Concentrations from Visibility Observations in Northern Africa. Aeolian Res. 2015, 16, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irankunda, E.; Török, Z.; Mereuta, A.; Ozunu, A.; Gasore, J.; Kalisa, E.; Akimpaye, B.; Habineza, T.; Shyaka, O.; Munyampundu, G. Potential Source Identification of SO2 and Comparison Between Modelling Results with In-Situ Monitoring Data: Study Case, Road Networks of Kigali-Rwanda. Bull. Rom. Chem. Eng. Soc. 2022, 9, 131–142. [Google Scholar]
- Kalisa, E.; Irankunda, E.; Rugengamanzi, E.; Amani, M. Noise Levels Associated with Urban Land Use Types in Kigali, Rwanda. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irankunda, E.; Gasore, J. Assessing the Effects of Household Wood Burning on Particulate Matter in Rwanda. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Environ. Res. 2021, 10, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalaj, F.; Sattler, M. Modeling of VOCs and Criteria Pollutants from Multiple Natural Gas Well Pads in Close Proximity, for Different Terrain Conditions: A Barnett Shale Case Study. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 1239–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisephane, I.; Ozunu, A. Emission Flux and Dispersion Analysis of Particulate Matter (PM10) from Mining and Industrial Areas in Rusizi District-Rwanda. Water Air Soil Pollut. 2024, 235, 328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irankunda, E.; Ozunu, A. Assessment of Urban Air Pollution by PM10 and NO2 and Associated Impacts and Risks through Computational Analysis in Kigali, Rwanda. Energ. Ecol. Environ. 2024, 9, 680–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Török, Z.; Elisephane, I.; Ozunu, A. Modelling the Dispersion of Particulate Matter (PM10) via Wind Erosion from Opencast Mining—Moldova Nouă Tailings Ponds, Romania. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisephane, I.; Ishigaki, Y. The Effect Assessment of Industrial Activities on Air Pollution at Cimerwa and Its Surrounding Areas, Rusizi-District-Rwanda. Int. J. Sustain. Energy Environ. Res. 2020, 9, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irankunda, E.; Török, Z.; Mereuță, A.; Gasore, J.; Kalisa, E.; Akimpaye, B.; Habineza, T.; Shyaka, O.; Munyampundu, G.; Ozunu, A. The Comparison between In-Situ Monitored Data and Modelled Results of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2): Case-Study, Road Networks of Kigali City, Rwanda. Heliyon 2022, 8, e12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raheja, G.; Harper, L.; Hoffman, A.; Gorby, Y.; Freese, L.; O’Leary, B.; Deron, N.; Smith, S.; Auch, T.; Goodwin, M.; et al. Community-Based Participatory Research for Low-Cost Air Pollution Monitoring in the Wake of Unconventional Oil and Gas Development in the Ohio River Valley: Empowering Impacted Residents through Community Science. Environ. Res. Lett. 2022, 17, 065006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Naimi, N.; Balakrishnan, P.; Goktepe, I. Measurement and Modelling of Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) Emissions: A Marker for Traffic-Related Air Pollution in Doha, Qatar. Ann. GIS 2015, 21, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akasha, H.; Ghaffarpasand, O.; Pope, F.D. Climate Change, Air Pollution and the Associated Burden of Disease in the Arabian Peninsula and Neighbouring Regions: A Critical Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasmi, K.; Aljalal, A.; Al-Basheer, W.; Abdulahi, M. Analysis of NOx, NO and NO2 Ambient Levels in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia. Urban Clim. 2017, 21, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegum, S.N.; Gherboudj, I.; Chaouch, N.; Temimi, M.; Ghedira, H. Simulation and Analysis of Synoptic Scale Dust Storms over the Arabian Peninsula. Atmos. Res. 2018, 199, 62–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A. Air Pollution in the Arabian Peninsula (Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Qatar, Bahrain, and Oman): Causes, Effects, and Aerosol Categorization. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebare, S.R.; Aburizaiza, O.S.; Khwaja, H.A.; Siddique, A.; Hussain, M.M.; Zeb, J.; Khatib, F.; Carpenter, D.O.; Blake, D.R. Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of PM2.5 in Rabigh, Saudi Arabia. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2016, 16, 3114–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, W.; Iakovides, M.; Garaga, R.; Stephanou, E.G.; Kota, S.H.; Ying, Q.; Wolfson, J.M.; Koutrakis, P.; Guo, B. Source Apportionment of Organic Pollutants in Fine and Coarse Atmospheric Particles in Doha, Qatar. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 1277–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Q.; Alharbi, B.; Collett, J.; Kreidenweis, S.; Pasha, M.J. Measurements and Source Apportionment of Particle-Associated Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 137, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfoldy, B.; Mahfouz, M.M.K.; Yigiterhan, O.; Safi, M.A.; Elnaiem, A.E.; Giamberini, S. BTEX, Nitrogen Oxides, Ammonia and Ozone Concentrations at Traffic Influenced and Background Urban Sites in an Arid Environment. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Fadhli, F.M.; Alhajeri, N.S.; Aly, A.Z.; Allen, D.T. The Impact of Power Plant Emission Variability and Fuel Switching on the Air Quality of Kuwait. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 672, 593–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidvarborna, H.; Baawain, M.; Al-Mamun, A. Ambient Air Quality and Exposure Assessment Study of the Gulf Cooperation Council Countries: A Critical Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 437–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abuelgasim, A.; Bilal, M.; Alfaki, I.A. Spatiotemporal Variations and Long Term Trends Analysis of Aerosol Optical Depth over the United Arab Emirates. Remote Sens. Appl. Soc. Environ. 2021, 23, 100532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, J.A.; Paparella, F. The Marine Environment of the Emirates. In A Natural History of the Emirates; Burt, J.A., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 95–117. ISBN 978-3-031-37396-1. [Google Scholar]
- Paparella, F.; Burt, J.A. Climate of the United Arab Emirates: Present, Past and Impacts on Life. In A Natural History of the Emirates; Burt, J.A., Ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 65–94. ISBN 978-3-031-37396-1. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.R.; Attada, R.; Dasari, H.P.; Vellore, R.K.; Langodan, S.; Abualnaja, Y.O.; Hoteit, I. Aerosol Optical Depth Variability over the Arabian Peninsula as Inferred from Satellite Measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 187, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fountoukis, C.; Martín-Pomares, L.; Perez-Astudillo, D.; Bachour, D.; Gladich, I. Simulating Global Horizontal Irradiance in the Arabian Peninsula: Sensitivity to Explicit Treatment of Aerosols. Sol. Energy 2018, 163, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, V.; Clarke, V. Using Thematic Analysis in Psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 2006, 3, 77–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Paul, S.; deSouza, P.; Machida, Y.; Mora, S.; Duarte, F.; Ratti, C. Key Themes, Trends, and Drivers of Mobile Ambient Air Quality Monitoring: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2023, 57, 9427–9444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul-Wahab, S.A.; Fadlallah, S.O. A Study of the Effects of Vehicle Emissions on the Atmosphere of Sultan Qaboos University in Oman. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 98, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alahmad, B.; Al-Hemoud, A.; Kang, C.-M.; Almarri, F.; Kommula, V.; Wolfson, J.M.; Bernstein, A.S.; Garshick, E.; Schwartz, J.; Koutrakis, P. A Two-Year Assessment of Particulate Air Pollution and Sources in Kuwait. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 282, 117016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Alola, S.S.; Alkadi, I.I.; Alogayell, H.M.; Mohamed, S.A.; Ismail, I.Y. Air Quality Estimation Using Remote Sensing and GIS-Spatial Technologies along Al-Shamal Train Pathway, Al-Qurayyat City in Saudi Arabia. Environ. Sustain. Indic. 2022, 15, 100184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduwais, A.K.; Dasari, H.P.; Karumuri, R.K.; Gandham, H.; Alharbi, B.H.; Ashok, K.; Hoteit, I. Transport Mechanisms of Nocturnal Surface Ozone over Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 313, 120069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, M.A.; Alam, M.S.; Yin, J.; Stark, C.; Jang, E.; Harrison, R.M.; Shamy, M.; Khoder, M.I.; Shabbaj, I.I. Receptor Modelling Study of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alghamdi, M.A.; Hassan, S.K.; Al Sharif, M.Y.; Khoder, M.I.; Harrison, R.M. On the Nature of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Associated with Sporting Walkways Dust: Concentrations, Sources and Relative Health Risk. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 781, 146540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.; Nichol, J.E.; Bilal, M.; Qiu, Z.; Mazhar, U.; Wahiduzzaman, M.; Almazroui, M.; Islam, M.N. Classification of Aerosols over Saudi Arabia from 2004–2016. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 241, 117785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljahdali, M.O.; Alhassan, A.B.; Albeladi, M.N. Impact of Novel Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Lockdown on Ambient Air Quality of Saudi Arabia. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 28, 1356–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almatar, K.M. Towards Sustainable Green Mobility in the Future of Saudi Arabia Cities: Implication for Reducing Carbon Emissions and Increasing Renewable Energy Capacity. Heliyon 2023, 9, e13977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqasemi, A.S.; Hereher, M.E.; Kaplan, G.; Al-Quraishi, A.M.F.; Saibi, H. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown upon the Air Quality and Surface Urban Heat Island Intensity over the United Arab Emirates. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 767, 144330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuwayjiri, A.; Pirhadi, M.; Kalafy, M.; Alharbi, B.; Sioutas, C. Impact of Different Sources on the Oxidative Potential of Ambient Particulate Matter PM10 in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia: A Focus on Dust Emissions. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 150590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegum, S.N.; Gherboudj, I.; Chaouch, N.; Couvidat, F.; Menut, L.; Ghedira, H. Simulating Aerosols over Arabian Peninsula with CHIMERE: Sensitivity to Soil, Surface Parameters and Anthropogenic Emission Inventories. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 128, 185–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beegum, S.N.; Tuomiranta, A.; Gherboudj, I.; Flemming, J.; Ghedira, H. Simulation of Aerosol Deposition Flux over the Arabian Peninsula with CHIMERE-2017: Sensitivity to Different Dry Deposition Schemes. Atmos. Res. 2020, 241, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikkina, S.; Shukla, A.; Singh, S.K.; Karri, D.; Singh, N.D.; Sahoo, B. Link of the Short-Term Temporal Trends of Sr and Nd Isotopic Composition of Aeolian Dust over the Arabian Sea with the Source Emissions. Sci. Total. Environ. 2023, 892, 164680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bodenheimer, S.; Nirel, R.; Lensky, I.M.; Dayan, U. Relationship between AOD and Synoptic Circulation over the Eastern Mediterranean: A Comparison between Subjective and Objective Classifications. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 177, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cusack, M.; Arrieta, J.M.; Duarte, C.M. Source Apportionment and Elemental Composition of Atmospheric Total Suspended Particulates (TSP) Over the Red Sea Coast of Saudi Arabia. Earth Syst. Environ. 2020, 4, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitriou, K.; Kassomenos, P. Aerosol Contributions at an Urban Background Site in Eastern Mediterranean—Potential Source Regions of PAHs in PM10 Mass. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 598, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunford, C.E.; Martins, Q.E.; Mann, G.K.H.; Spalton, J.A.; Al Hikmani, H.; Robinson, N.P.; Almalki, A.; Gallacher, E.; Balme, G.A.; Robinson, H.S. Modelling Potential Habitat Suitability for Critically Endangered Arabian Leopards (Panthera Pardus Nimr) across Their Historical Range in Saudi Arabia. J. Nat. Conserv. 2022, 68, 126233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Kenawy, A.M.; Lopez-Moreno, J.I.; McCabe, M.F.; Domínguez-Castro, F.; Peña-Angulo, D.; Gaber, I.M.; Alqasemi, A.S.; Al Kindi, K.M.; Al-Awadhi, T.; Hereher, M.E.; et al. The Impact of COVID-19 Lockdowns on Surface Urban Heat Island Changes and Air-Quality Improvements across 21 Major Cities in the Middle East. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 288, 117802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farahat, A. Chapter 10—Air Quality in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) Countries. In Asian Atmospheric Pollution; Singh, R.P., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; pp. 201–226. ISBN 978-0-12-816693-2. [Google Scholar]
- Habeebullah, T.M. Risk Assessment of Poly Cyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in the Holy City of Makkah, Saudi Arabia. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Dev. 2013, 4, 139–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habeebullah, T.M. Modeling Particulate Matter (PM10) in Makkah, Saudi Arabia—A View Point of Health Impact. J. Clean Energy Technol. 2014, 2, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, S.H.; Schauer, J.J.; Heo, J.; Kadhim, A.K.H. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 Carbonaceous Aerosol in Baghdad, Iraq. Atmos. Res. 2015, 156, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H.; Kumar, P.; Kakosimos, K.E. The Impact of Local Fugitive Particulate Matter and Emission Inventories on Air Quality and Health in Dry and Arid Areas. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 824, 153799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, W.; Guo, B. Chemical Characterization and Source Apportionment of Fine and Coarse Atmospheric Particulate Matter in Doha, Qatar. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaku, K.C.; Reid, J.S.; Reid, E.A.; Ross-Langerman, K.; Piketh, S.; Cliff, S.; Al Mandoos, A.; Broccardo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. Investigation of the Relative Fine and Coarse Mode Aerosol Loadings and Properties in the Southern Arabian Gulf Region. Atmos. Res. 2016, 169, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logothetis, S.-A.; Salamalikis, V.; Kazantzidis, A. Aerosol Classification in Europe, Middle East, North Africa and Arabian Peninsula Based on AERONET Version 3. Atmos. Res. 2020, 239, 104893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovett, C.; Sowlat, M.H.; Saliba, N.A.; Shihadeh, A.L.; Sioutas, C. Oxidative Potential of Ambient Particulate Matter in Beirut during Saharan and Arabian Dust Events. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 188, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modaihsh, A.S.; Mahjou, M.O. Falling Dust Characteristics in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia During Winter Months. APCBEE Procedia 2013, 5, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawahda, A. Monitoring the Temporal Variations of PM2.5 and Gases Close to the Highway in Sohar, Oman. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2015, 72, 685–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayebare, S.R.; Aburizaiza, O.S.; Siddique, A.; Carpenter, D.O.; Hussain, M.M.; Zeb, J.; Aburiziza, A.J.; Khwaja, H.A. Ambient Air Quality in the Holy City of Makkah: A Source Apportionment with Elemental Enrichment Factors (EFs) and Factor Analysis (PMF). Environ. Pollut. 2018, 243, 1791–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, P.N.; Dumka, U.C.; Babu, K.N.; Mathur, A.K. Aerosol Characterization and Radiative Properties over Kavaratti, a Remote Island in Southern Arabian Sea from the Period of Observations. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 599–600, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaltout, A.A.; Boman, J.; Alsulimane, M.E. Identification of Elemental Composition of PM2.5 Collected in Makkah, Saudi Arabia, Using EDXRF. X-Ray Spectrom. 2017, 46, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yigiterhan, O.; Alfoldy, B.Z.; Giamberini, M.; Turner, J.C.; Al-Ansari, E.S.; Abdel-Moati, M.A.; Al-Maslamani, I.A.; Kotb, M.M.; Elobaid, E.A.; Hassan, H.M.; et al. Geochemical Composition of Aeolian Dust and Surface Deposits from the Qatar Peninsula. Chem. Geol. 2018, 476, 24–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutairi, M.; Al-Otaibi, N.; Saber, A.; Abdel Basset, H.; Morsy, M. Climatological Study of Air Pollutant Emissions in Saudi Arabia. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, T.; Li, X.; Al-Dulaimi, Q.; Daour, S.; Atashi, N.; Viana, M.; Alastuey, A.; Sogacheva, L.; Arar, S.; Al-Hunaiti, A.; et al. Particulate Matter Concentrations in a Middle Eastern City—An Insight to Sand and Dust Storm Episodes. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2780–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jassim, M.S.; Coskuner, G. Assessment of Spatial Variations of Particulate Matter (PM10 and PM2.5) in Bahrain Identified by Air Quality Index (AQI). Arab. J. Geosci. 2017, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsiouri, V.; Kakosimos, K.E.; Kumar, P. Concentrations, Sources and Exposure Risks Associated with Particulate Matter in the Middle East Area—A Review. Air Qual. Atmosphere Health 2015, 8, 67–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, G.; Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, X.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, S.; Liu, B.; He, B.-J. Delineating the Spatial-Temporal Variation of Air Pollution with Urbanization in the Belt and Road Initiative Area. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2021, 91, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rashidi, M.S.; Yassin, M.F.; Alhajeri, N.S.; Malek, M.J. Gaseous Air Pollution Background Estimation in Urban, Suburban, and Rural Environments. Arab. J. Geosci. 2018, 11, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daneshpajooh, N.; Arhami, M.; Azoji, H. PM Dispersion during Stable Winter Episodes in Tehran and Effect of Governmental Emission Regulations. Atmospheric Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1316–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Shamsi, N.S.A. Salinity and Drought Tolerance in Suaeda Vermiculata, A Habitat Indifferent Halophyte of the Hyper-Arid Deserts of the United Arab Emirates (UAE); University of Málaga: Málaga, Spain, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Cimorelli, A.J.; Perry, S.G.; Venkatram, A.; Weil, J.C.; Paine, R.J.; Wilson, R.B.; Lee, R.F.; Peters, W.D.; Brode, R.W. AERMOD: A Dispersion Model for Industrial Source Applications. Part I: General Model Formulation and Boundary Layer Characterization. J. Appl. Meteorol. Clim. 2005, 44, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartakovsky, D.; Broday, D.M.; Stern, E. Evaluation of AERMOD and CALPUFF for Predicting Ambient Concentrations of Total Suspended Particulate Matter (TSP) Emissions from a Quarry in Complex Terrain. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 179, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoatey, P.; Omidvarborna, H.; Affum, H.A.; Baawain, M. Performance of AERMOD and CALPUFF Models on SO2 and NO2 Emissions for Future Health Risk Assessment in Tema Metropolis. Hum. Ecol. Risk Assess. Int. J. 2019, 25, 772–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Patil, R.S.; Dikshit, A.K.; Kumar, R. Application of WRF Model for Air Quality Modelling and AERMOD—A Survey. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2017, 17, 1925–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alghamdi, A.S.; Harrington, J. Synoptic Climatology and Sea Surface Temperatures Teleconnections for Warm Season Heat Waves in Saudi Arabia. Atmos. Res. 2019, 216, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alduchov, O.A.; Eskridge, R.E. Improved Magnus Form Approximation of Saturation Vapor Pressure. J. Appl. Meteor. 1996, 35, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, S.R.; Egan, B.A.; Purdum, J.; Wagler, J. Comparison of AERMOD, ISC3, and ADMS Model Performance with Five Field Data Sets. In Proceedings of the Air & Waste Management Association’s 2000 Annual Conference, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 20–25 June 2000; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Han, P.; Mei, H.; Liu, D.; Zeng, N.; Tang, X.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y. Calibrations of Low-Cost Air Pollution Monitoring Sensors for CO, NO2, O3, and SO2. Sensors 2021, 21, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malings, C.; Tanzer, R.; Hauryliuk, A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Zimmerman, N.; Kara, L.B.; Presto, A.A.; Subramanian, R. Development of a General Calibration Model and Long-Term Performance Evaluation of Low-Cost Sensors for Air Pollutant Gas Monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmerman, N.; Presto, A.A.; Kumar, S.P.N.; Gu, J.; Hauryliuk, A.; Robinson, E.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Subramanian, R. A Machine Learning Calibration Model Using Random Forests to Improve Sensor Performance for Lower-Cost Air Quality Monitoring. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2018, 11, 291–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakti, A.D.; Anggraini, T.S.; Ihsan, K.T.N.; Misra, P.; Trang, N.T.Q.; Pradhan, B.; Wenten, I.G.; Hadi, P.O.; Wikantika, K. Multi-Air Pollution Risk Assessment in Southeast Asia Region Using Integrated Remote Sensing and Socio-Economic Data Products. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 854, 158825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuevas Agulló, E. Establishing a WMO Sand and Dust Storm Warning Advisory and Assessment System Regional Node for West Asia: Current Capabilities and Needs: Technical Report; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Lumbroso, D.; Brown, E.; Ranger, N. Stakeholders’ Perceptions of the Overall Effectiveness of Early Warning Systems and Risk Assessments for Weather-Related Hazards in Africa, the Caribbean and South Asia. Nat. Hazards 2016, 84, 2121–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Córdoba-Jabonero, C.; Sicard, M.; del Águila, A.; Jiménez, M.; Zorzano, M.-P. Performance of a Dust Model to Predict the Vertical Mass Concentration of an Extreme Saharan Dust Event in the Iberian Peninsula: Comparison with Continuous, Elastic, Polarization-Sensitive Lidars. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 214, 116828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntziachristos, L.; Samaras, Z. EMEP/EEA Air Pollutant Emission Inventory Guidebook 2019—Update October 2021. Passenger Cars, Light Commercial Trucks, Heavy-Duty Vehicles Including Buses and Motor Cycles. Available online: https://www.eea.europa.eu/publications/emep-eea-guidebook-2019/part-b-sectoral-guidance-chapters/1-energy/1-a-combustion/1-a-3-b-i/view (accessed on 19 March 2022).
- Abdulrahman, K. Air Quality Assessment by Daily Estimation of Ground-Level PM2.5 Concentrations over Baghdad City Using MODIS AOD Data. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alolayan, M.A.; Abraham, L.M.; Ramadan, A.A. Fate and Speciation of NOx in an Arid Climatic Region: Factors Assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohieldeen, Y.E.; Moosakutty, S.P.; Fountoukis, C.; Siddique, A.; Ayoub, M.A.; Alfarra, M.R. Assessment of Tropospheric NO2 Concentrations over Greater Doha Using Sentinel-5 TROPOspheric Monitoring Instrument (TROPOMI) Satellite Data: Temporal Analysis, 2018–2023. Environ. Pollut. 2024, 362, 124995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammedamin, J.K.; Shekha, Y.A. Indoor Sulfur Dioxide Prediction through Air Quality Modeling and Assessment of Sulfur Dioxide and Nitrogen Dioxide Levels in Industrial and Non-Industrial Areas. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Rikabi, R.J.; Alqaralosy, H.N.; Sultan, M.A. The Impact of Human Activities on Air Pollution in the Fallujah City, Al-Anbar Province—West Iraq. AJWEP 2024, 21, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.S.; Abuelgasim, A.; Al Hosani, N. Advancing Air Quality Forecasting in Abu Dhabi, UAE Using Time Series Models. Front. Environ. Sci. 2024, 12, 1393878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershadifar, H.; Saleh, A.; Koochaknejad, E.; Kor, K.; Agah, H.; Hamzeh, M.A.; Sharifinia, M. Suspended Particulate Matter in the Gulf of Oman: Spatial Variations in Concentration, Bulk Composition, and Particulate Metals Controlled by Physical and Biogeochemical Processes. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 950, 175396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuouelezz, W.; Ali, N.; Aung, Z.; Altunaiji, A.; Shah, S.B.; Gliddon, D. Exploring PM2.5 and PM10 ML Forecasting Models: A Comparative Study in the UAE. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 9797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, S.S.; Idoudi, S.; Alhamdan, N.; Ibrahim, R.H.; Surkatti, R.; Amhamed, A.; Alrebei, O.F. Comprehensive Review of Health Impacts of the Exposure to Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Carbon Dioxide (CO2), and Particulate Matter (PM). Journal of Hazardous Materials Advances 2025, 19, 100771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammadi, A.M.; Hussain, B.A.; Ghanim, M.; Hashim, B.M. Estimating Respiratory and Cardiovascular Health Risks Associated with PM2.5 Concentration in Major Populated Areas of Iraq with Examining Its Correlation to COVID-19. IGJ 2025, 58, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarragunta, Y.; Francis, D.; Fonseca, R.; Nelli, N. Evaluation of the WRF-Chem Performance for the Air Pollutants over the United Arab Emirates. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2025, 25, 1685–1709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Nadhairi, R.; Al Kalbani, M.; Al Khazami, S.; Al Hashmi, M.; Al Zadai, S.; Al-Rumhi, Y.; Al-Kindi, K.M. Air Quality and Health Risk Assessment during Middle Eastern Dust Storms: A Study of Particulate Matter. Air Qual Atmos Health 2025, 18, 587–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evaluation of the Air Quality Index for PM2.5 and PM10 in the Station of the Great Husseiny Park in the Holy City of Karbala. In Springer Proceedings in Earth and Environmental Sciences; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 219–230. ISBN 978-3-031-57392-7.
- Alzaid, A.S.; Anil, I.; Aga, O. Simulation and Assessment of Episodic Dust Storms in Eastern Saudi Arabia Using HYSPLIT Trajectory Model and Satellite Observations. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, S.; Shameer, M.; Alawadhi, H.; Hamdan, N.M. Source Apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 Pollutants near an Urban Roadside Site Using Positive Matrix Factorization. Environmental Advances 2024, 17, 100573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shihab, A.S. Meteorological Effects on Particulate Matter PM10, PM2.5 Concentrations with Diurnal and Seasonal Variations in Cities Neighboring Desert Lands. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 11293–11321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogra, S.; Khamidi, M.F. Applicability of Vegetation to Reduce Traffic-Borne PM2.5 Concentration in Roadside User Zones in Hot Arid Climates: The Case of Central Doha, Qatar. Buildings 2024, 14, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).