Dynamic Characteristics of Key Meteorological Elements and Their Impacts on Major Crop Yields in Albic Soil Region of Sanjiang Plain in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Area and Methodology
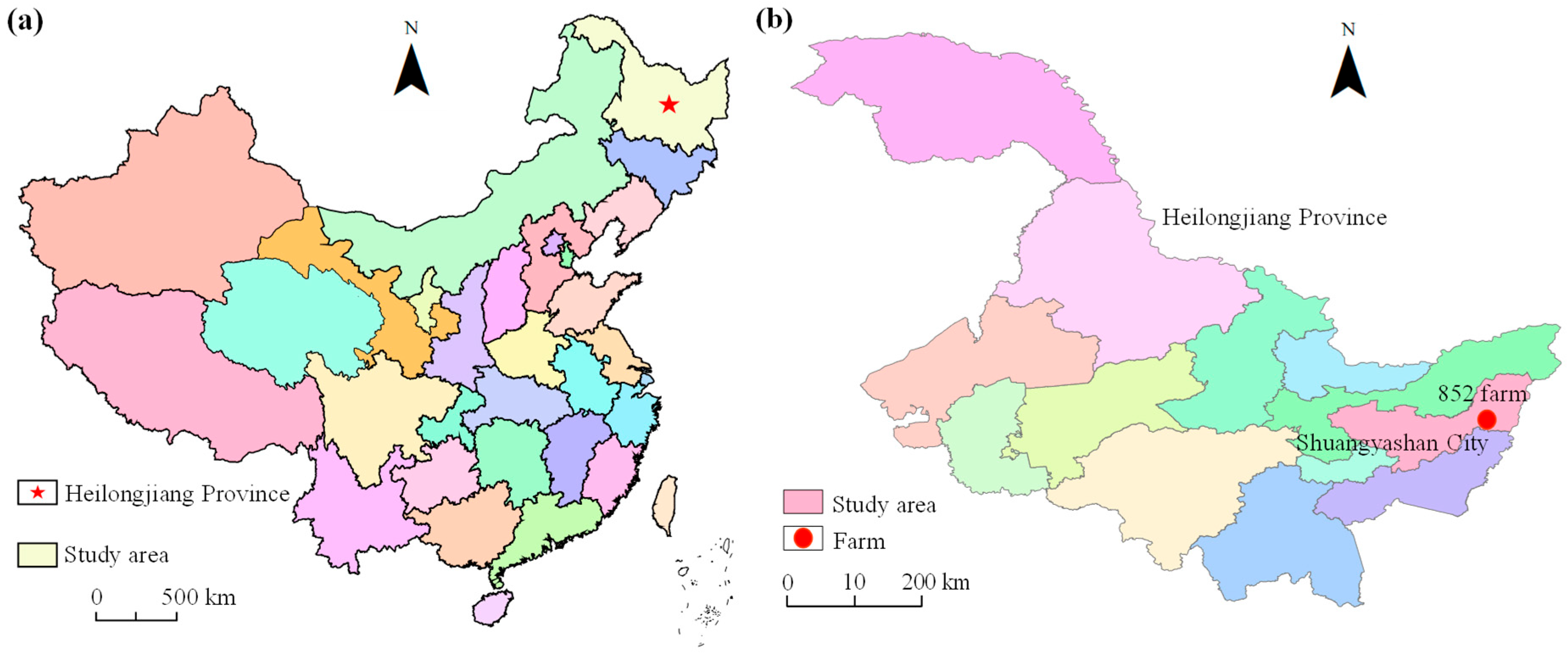
2.1. Overview of Study Area
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Measurement Items and Methods
2.4. Data Processing
3. Results and Analysis
3.1. Multi-Timescale Dynamic Variations in Meteorological Factors
3.1.1. Temporal Scale Variation Characteristics of Meteorological Factors
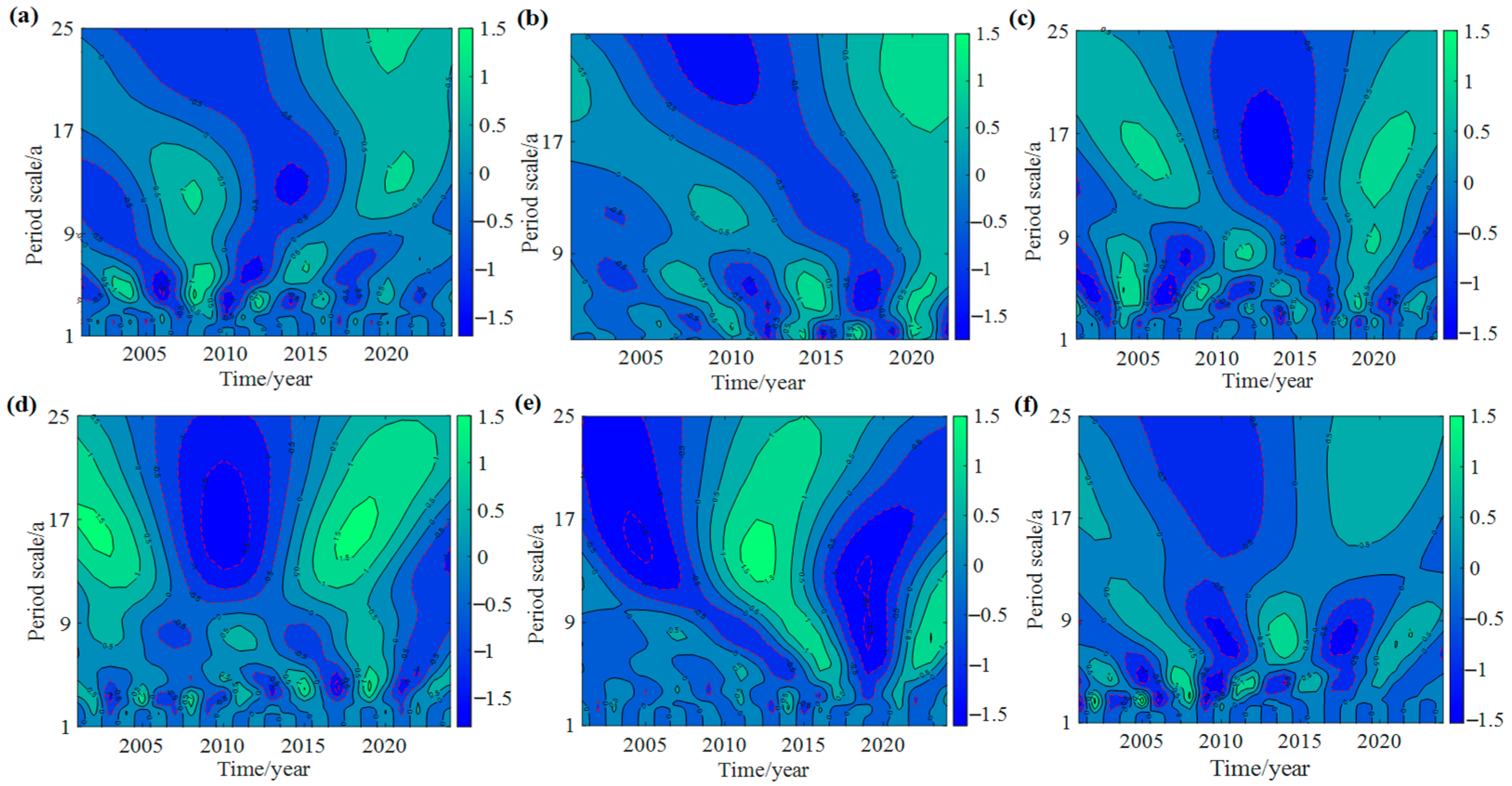
3.1.2. Evolutionary Patterns of Meteorological Factors at Periodic Scales
3.2. Dynamic Development of Yield for Different Crops
3.2.1. Comparison of Crop-Planting Structures
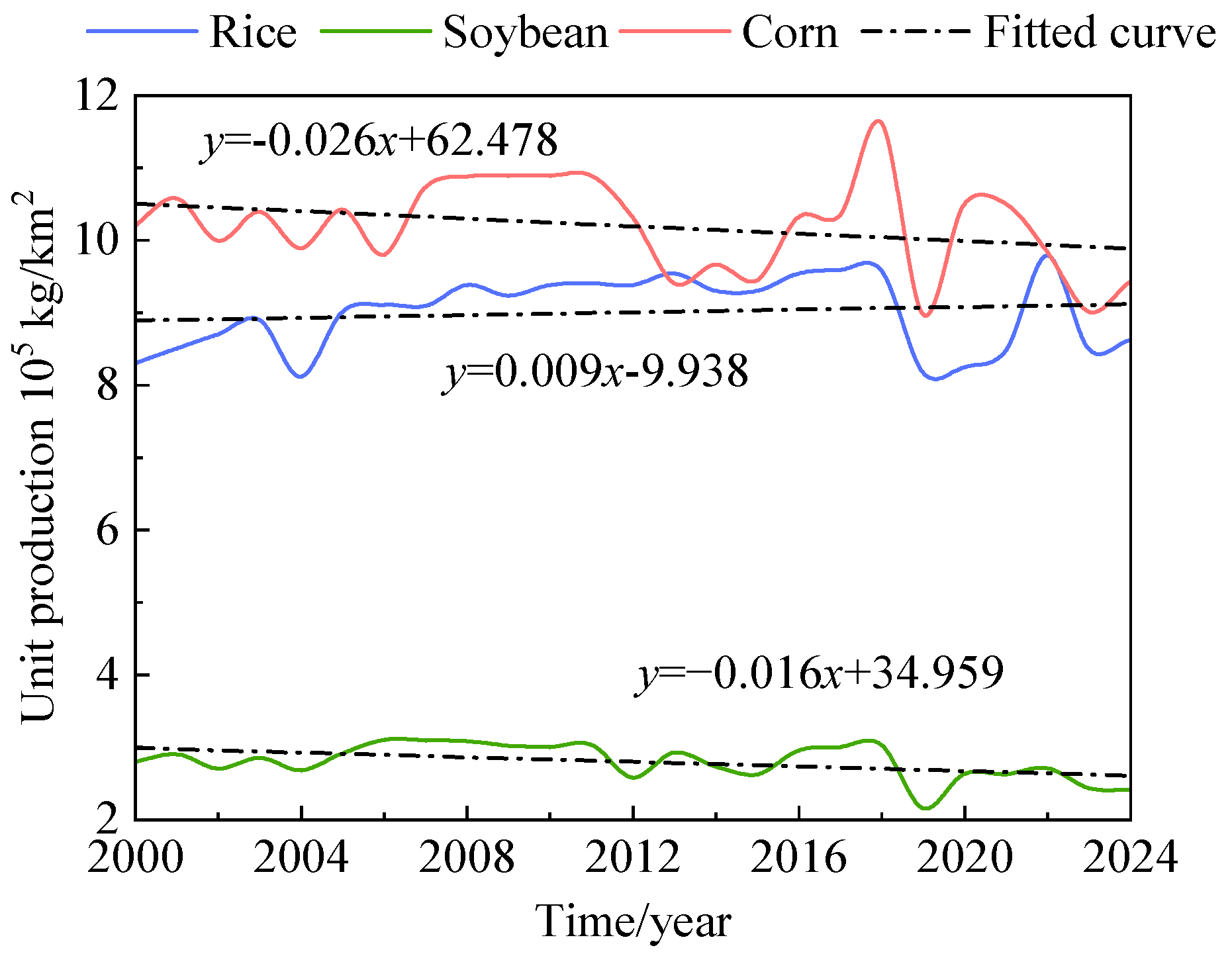
3.2.2. Temporal Dynamics of Different Crop Yields
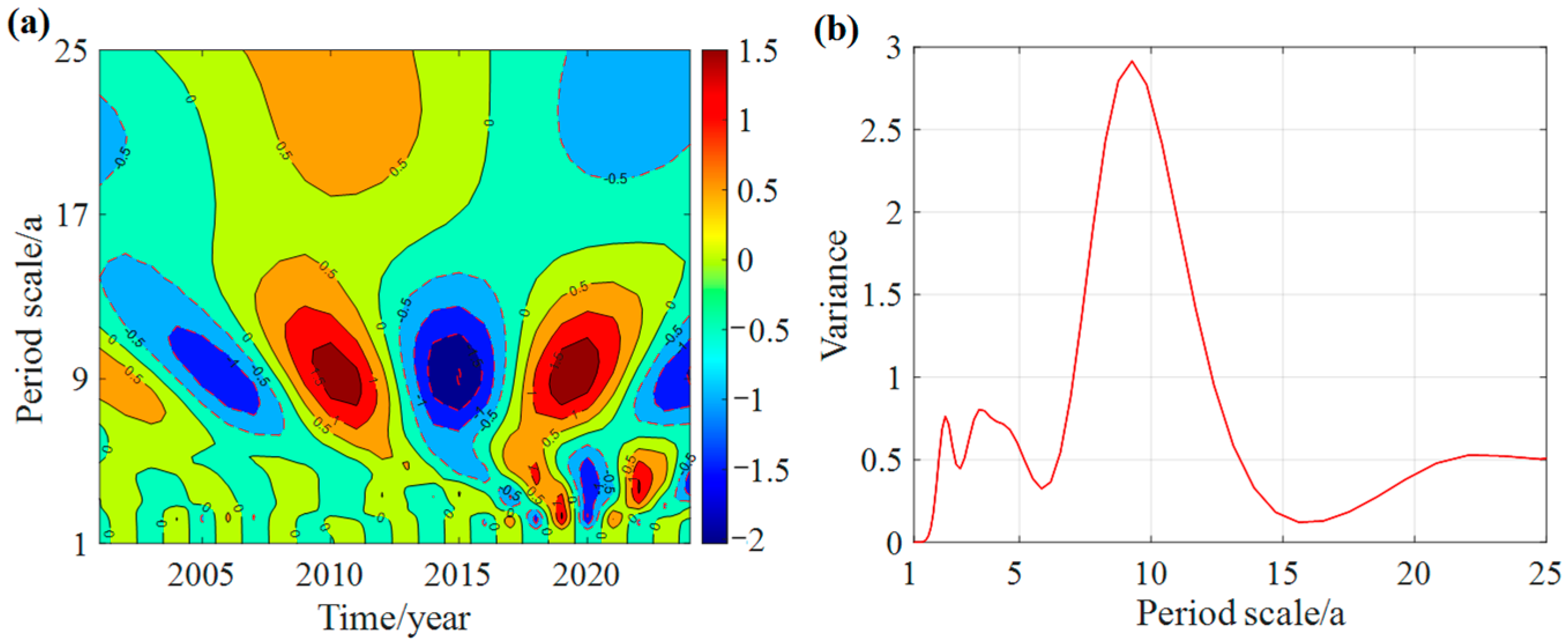
3.2.3. Periodic Evolution Patterns of Different Crops
3.3. Crop and Meteorological Factor Correlation Analysis
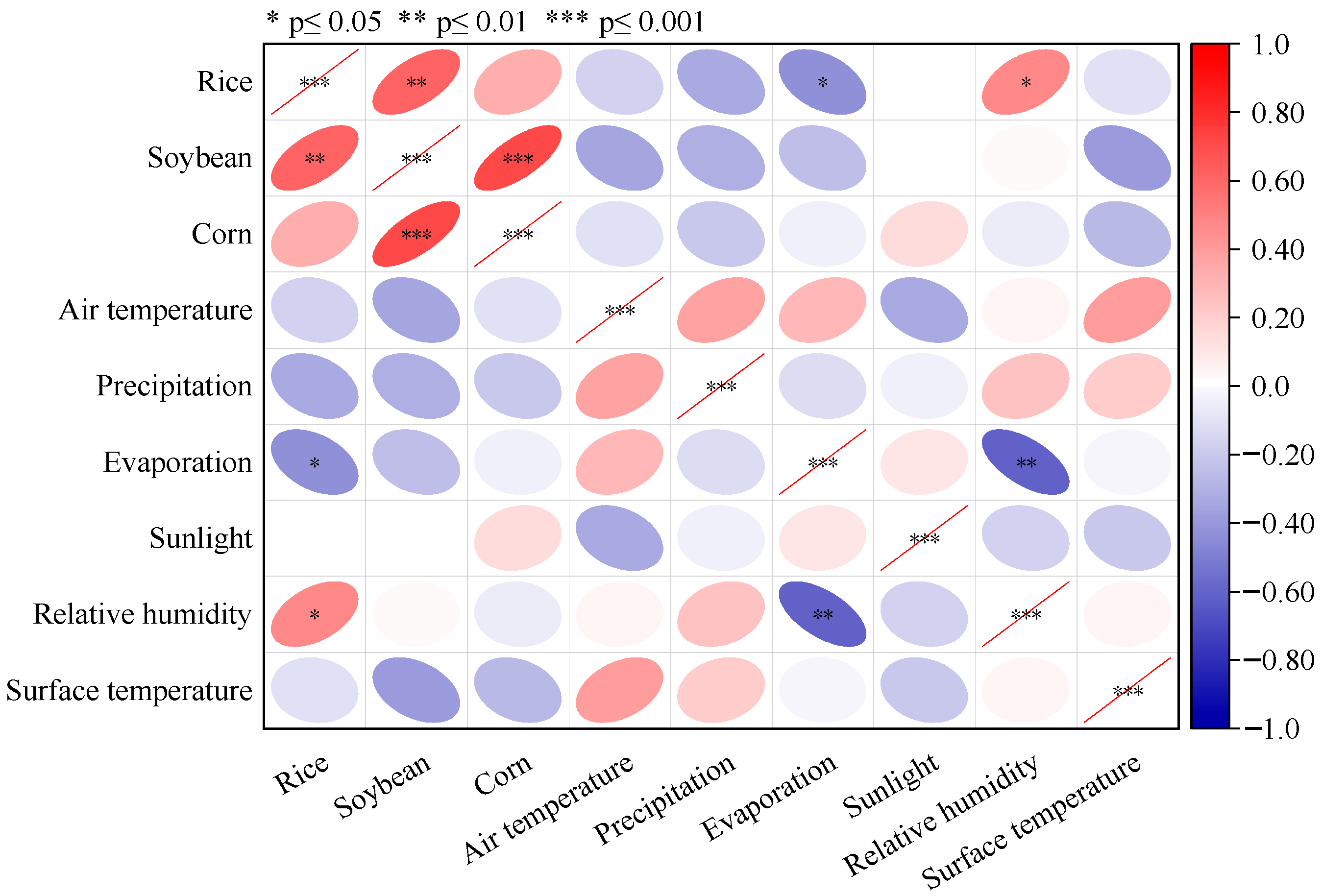
3.3.1. Correlation Analysis
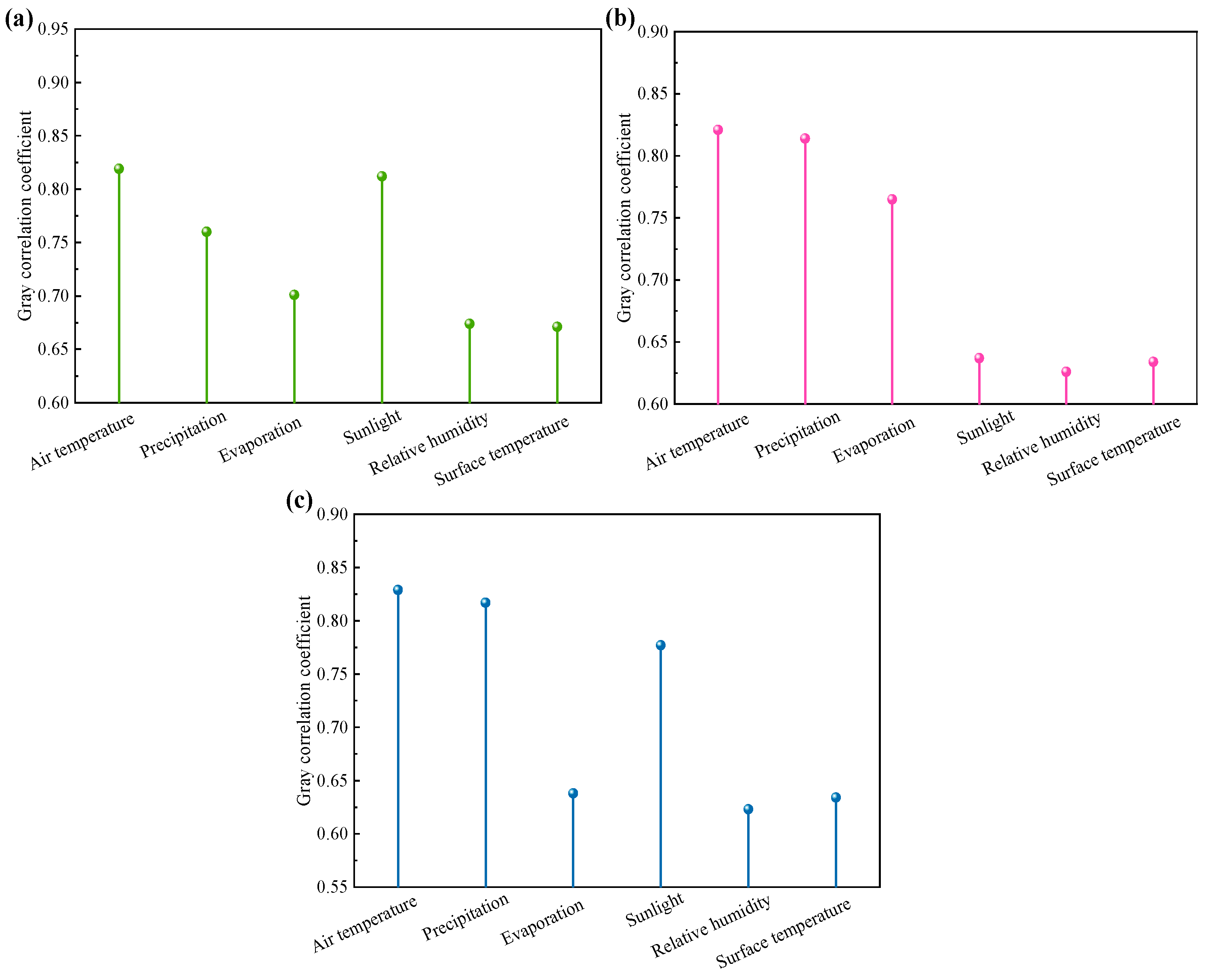
3.3.2. Grey Relational Analysis
3.4. Crop Yield Response Mechanisms to Climate Change
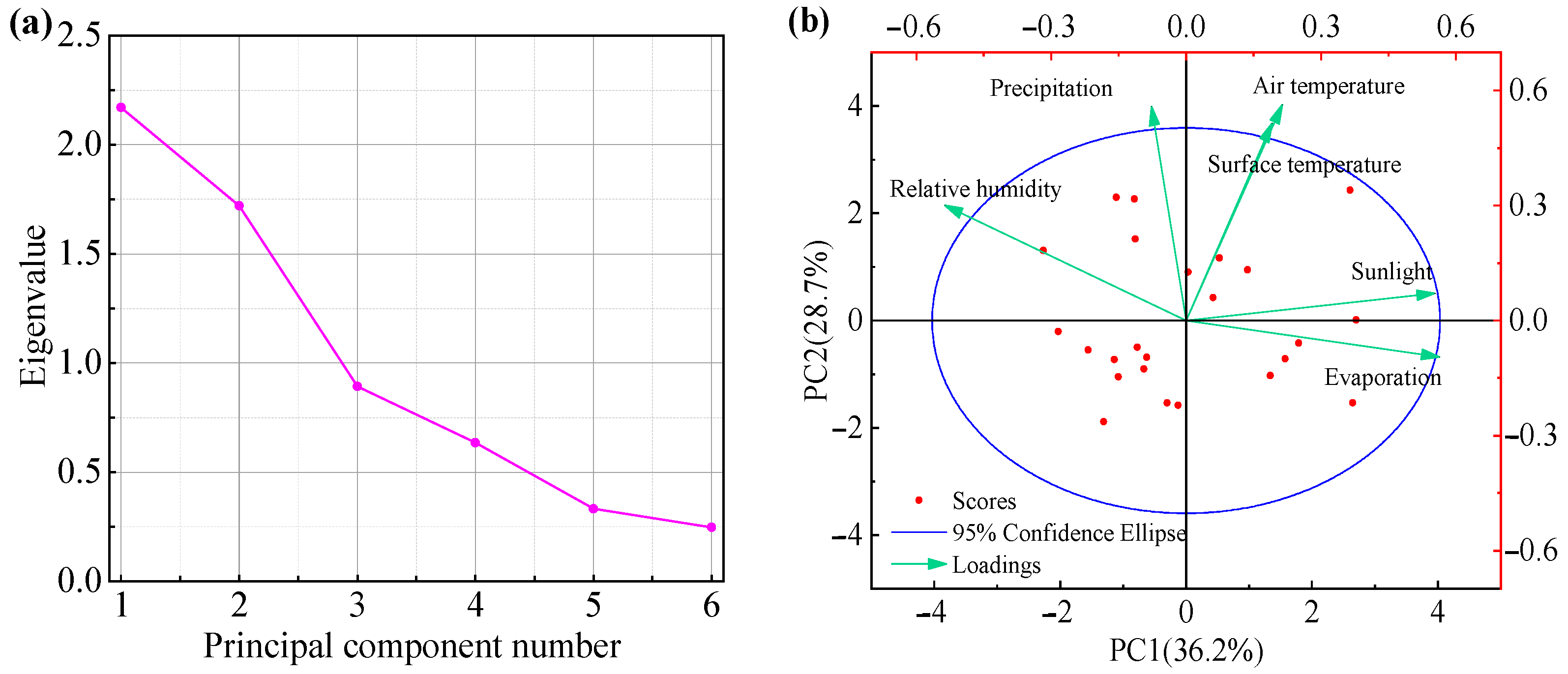
3.4.1. Quantification of Key Meteorological Factors
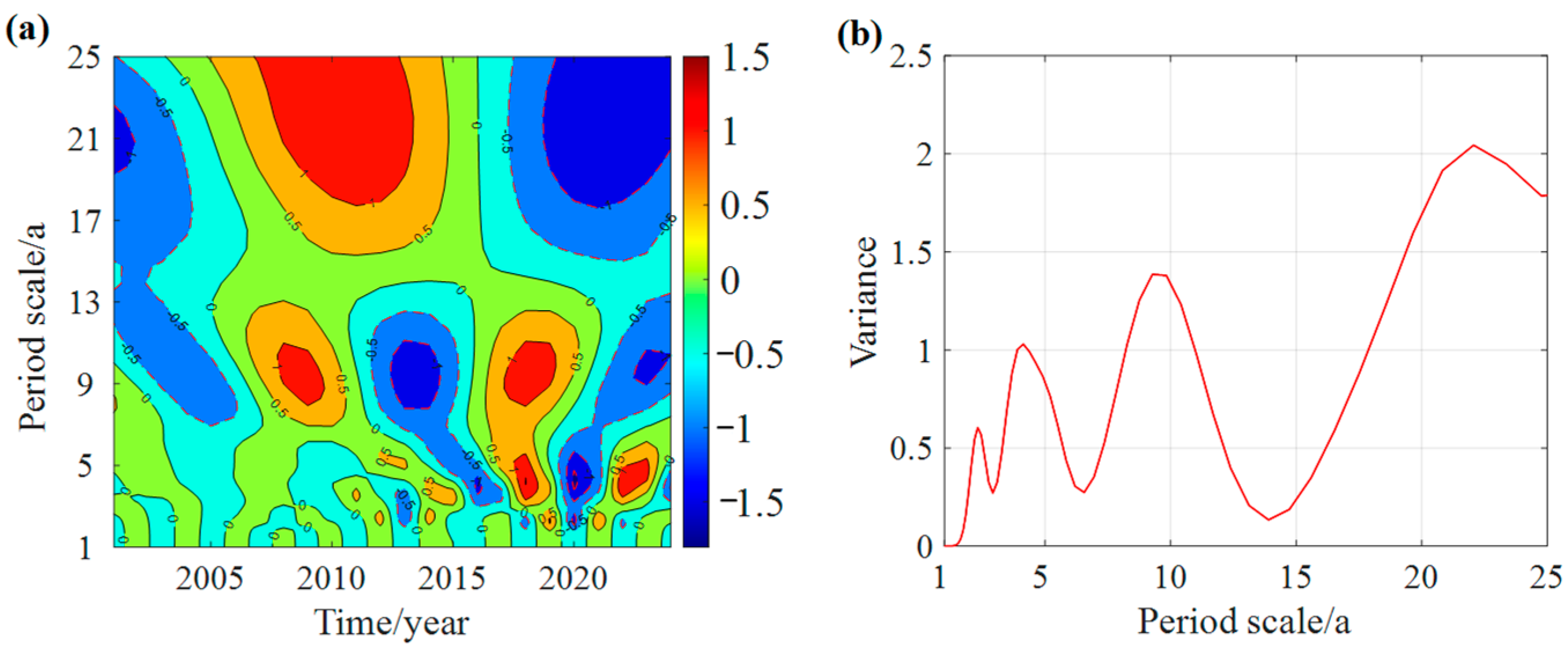
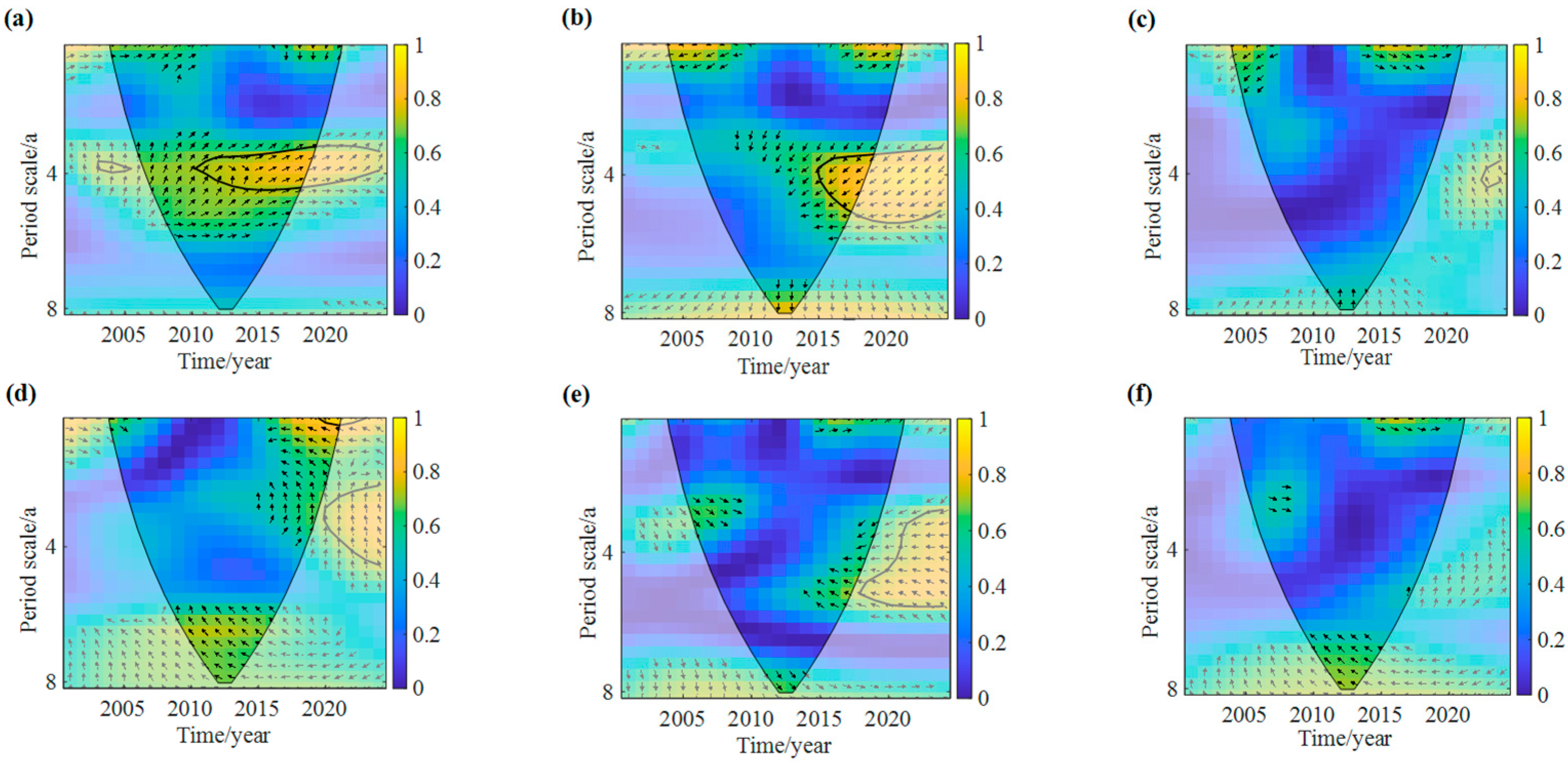
3.4.2. Time–Frequency Coupling Relationship Between Crop Yield and Meteorological Factors
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- (1)
- Trend characteristics: Among the six meteorological variables, only precipitation showed a statistically significant increasing trend. Air temperature, surface temperature, and relative humidity exhibited nonsignificant upward trends, while evaporation and sunlight duration declined slightly without significance. The crop yields for rice, soybean, and corn also showed overall upward trends, but none were statistically significant.
- (2)
- Periodic coherence: Both meteorological factors and crop yields exhibited dominant periodicities of around 22 and 8 years. These shared cycles revealed strong multi-scale time–frequency coherence, indicating that climate variability plays a long-term regulatory role in agricultural production.
- (3)
- Key drivers: Air temperature was the most influential factor for all three crops, followed by precipitation and sunlight duration. Rice was primarily affected by air temperature and sunlight, while soybean and corn were more sensitive to changes in air temperature and precipitation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, Y.; Tilman, D.; Jin, Z.; Smith, P.; Barrett, C.B.; Zhu, Y.G.; Burney, J.; D’Odorico, P.; Fantke, J.; Fargione, J. Climate change exacerbates the environmental impacts of agriculture. Science 2024, 385, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnakumar, S.; Sreevidhya, V.; Vivek, S.; Priya, V. Drought vulnerability assessment using GIS and remote sensing techniques: A case study in part of Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Indian Soc. Remote Sens. 2025, 53, 1077–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, H.Y.; Qian, L. Performances of different yield-detrending methods in assessing the impacts of agricultural drought and flooding: A case study in the middle-and-lower reach of the Yangtze River, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2024, 296, 108812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Kumar, J.; Redhu, M.; Kumar, P.; Godara, M.; Ghiyal, P.; Fu, P.; Rahimi, M. Estimation of rice yield using multivariate analysis techniques based on meteorological parameters. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, K.K.; Song, X.-P.; Kumari, A.; Jagadesh, M.; Singh, S.K.; Bhatt, R.; Singh, M.; Seth, C.S.; Li, Y. Climate change adaptation: Challenges for agricultural sustainability. Plant Cell Environ. 2025, 48, 2522–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, L.; Bittner, C.; Wollenberg, E.; Adair, E.C. Climate change adaptation and mitigation in agriculture: A review of the evidence for synergies and tradeoffs. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 013005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yao, H.; Li, Z.; Wu, F.; Liu, B.; Wu, Y.; Chun, K.P.; Octavianti, T.; Cui, X.; Xu, Y. A bibliometric analysis of global research on climate change and agriculture from 1985 to 2023. Agronomy 2024, 14, 2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bwire, D.; Watanabe, F.; Suzuki, S.; Suzuki, K. Improving irrigation water use efficiency and maximizing vegetable yields with drip irrigation and poly-mulching: A climate-smart approach. Water 2024, 16, 3458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, B.; Dou, X. Climate change, agricultural transformation and climate smart agriculture development in China. Heliyon 2024, 10, e40008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.Z.; Zhao, X.Y.; Yong, J.W.H.; Sehar, S.; Adil, M.F.; Riaz, M.; Verma, K.K.; Li, M.Y.; Huo, J.L.; Yang, S.; et al. Slow-release boron fertilizer improves yield and nutritional profile of Beta vulgaris L. grown in Northeast China by increasing boron supply capacity. Front. Plant Sci. 2024, 15, 1441226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, E.J.; Zhao, X.L.; Qin, W.; Jiao, J.; Han, J.Q.; Zhang, M. Temporal impacts of dryland-to-paddy conversion on soil quality in the typical black soil region of China: Establishing the minimum data set. Catena 2023, 231, 107303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Chen, W.F.; Li, L.N. Disentangling the relative effects of climate change and anthropogenic activities on paddy expansion in the northern Sanjiang Plain of China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.J.; Yu, Y.; Lv, G.Y.; Hao, Y.B.; Wang, L.L.; Ma, J.T.; Jiang, Y.B.; Zou, J.H.; Li, J.Y.; Wang, Q.J. Construction and effect analysis of a mixed actinomycete flora for straw returning to albic soil in Northeast China. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xie, H.; Li, D.; Hu, X.; Liu, C.; Kurshid, B.; Xu, Y.; Song, C.; Dai, C.; Khan, S.; et al. Projected high-resolution ETo spatiotemporal variation under future climate change and paddy area expansion in the Sanjiang Plain, Northeast China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2023, 50, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Shixuan, E.; Du, G.; Chen, Z. Analysis of climatic basis for the change of cultivated land area in Sanjiang Plain of China. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 862141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Jiang, B.Z.; Liu, G.H.; Zhang, H.; Nie, F.; Sun, Q.; Ji, M.Y. Applicability of spatial interpolation methods to predict total phosphorus in the typical irrigated areas of the Sanjiang Plain. Chin. J. Eco-Agric. 2021, 29, 1405–1416. [Google Scholar]
- Sootahar, M.K.; Zeng, X.; Su, S.; Wang, Y.N.; Bai, L.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, X.J. The effect of fulvic acids derived from different materials on changing properties of albic black soil in the Northeast Plain of China. Molecules 2019, 24, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.; Hao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Hao, F. Changes in climate-crop yield relationships affect risks of crop yield reduction. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2021, 304, 108401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, E.; Zhao, J.; Pullens, J.W.M.; Yang, X. The compound effects of drought and high temperature stresses will be the main constraints on corn yield in Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 812, 152461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baig, I.A.; Irfan, M.; Salam, M.A.; Iik, C. Addressing the effect of meteorological factors and agricultural subsidy on agricultural productivity in India: A roadmap toward environmental sustainability. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 30, 15881–15898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhan, C.; Liang, C.; Zhao, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H. Differential responses of crop yields to multi-timescale drought in mainland China: Spatiotemporal patterns and climate drivers. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 906, 167559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.K.; Liu, Y.S.; Shao, Y.J.; Zhang, L.F. Impact of climate change on crop-cropland coupling relationship: A case study of the Loess Plateau in China. Chin. Geogr. Sci. 2025, 35, 92–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.J.; Luo, C.; Kong, D.P.; Yu, Y.F.; Zang, D.Q.; Wang, F. Spatial and temporal variations in soil organic matter and their influencing factors in the Songnen and Sanjiang Plains of China (1984–2021). Land 2024, 13, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.W.; Wang, J.J.; Sun, X.; McLaughlin, N.B.; Jia, S.X.; Liang, A.Z.; Zhang, S.X. The driving mechanism of soil organic carbon biodegradability in the black soil region of Northeast China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 884, 163835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, F.J.; Zhang, Z.B.; Jiang, F.H.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, Q.J.; Li, L.L.; Peng, X.H. Spatial distribution of the buried depth and thickness of albic soil albic layer in Sanjiang Plain and its influencing factors. Acta Pedol. Sin. 2025, 62, 362–374. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, S.Z.; Wang, M.Y.; Gao, X.; Zhao, W.Q.; Miao, P.W.; Liu, Y.N.; Zhang, R.T.; Wang, X.; Sui, X.; Li, M.H. The diversity and composition of soil microbial communities differ in three land use types of the Sanjiang Plain, Northeastern China. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.H.; Deng, H.B.; Sun, R. Analysis of spatiotemporal variation in precipitation on the Loess Plateau from 1961 to 2016. Sustainability 2025, 16, 11119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Gao, D.; Chen, X. Detection of canopy chlorophyll content of corn based on continuous wavelet transform analysis. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 2741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.F.; Jamshidi, S.; Gu, L.L.; Li, Y.Y. Drought dynamics in California and Mississippi: A wavelet analysis of meteorological to agricultural drought transition. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 370, 122883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.L.; Bai, G.Y.; Liu, H.X. Groundwater dynamics clustering and prediction based on grey relational analysis and LSTM model: A case study in Beijing Plain, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 56, 102011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parding, K.M.; Benestad, R.E.; Dyrrdal, A.V.; Haugen, J.E. A principal-component-based strategy for regionalisation of precipitation intensity-duration-frequency (IDF) statistics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 719–3732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.H.; Li, H.H.; Yang, M.; Zhang, T.X. Study on response process and time delay effect of groundwater dynamic in northeastern margin of Tibetan Plateau. Water 2023, 15, 2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Wang, X.Y.; Liu, D. Multi-time scale analysis of precipitation series in 51a of 852 Farm. J. Heilongjiang Hydraul. Eng. Coll. 2009, 36, 79–81. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.L.; Liu, J.G.; Cui, W.H.; Zhang, B.F. Elevation regulates the response of climate heterogeneity to climate change. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2024, 51, e2024GL109483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solecki, W.; Roberts, D.; Seto, K.C. Strategies to improve the impact of the IPCC Special Report on Climate Change and Cities. Nat. Clim. Change 2024, 14, 85–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S. Study on Characteristics of Climate Change and Its Impact on Agricultural Production in the Sanjiang Plain. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Li, M. Study on Thermal and Precipitation Zoning Characteristics and Suitable Cultivation Methods in the Northeast Plain. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, X.L.; Li, H.L.; Zhang, Y.H.; Meng, X.Z. Characteristics and influencing factors of water requirements of major crops in the Sanjiang Plain from 2000 to 2015. Arid Land Geogr. 2019, 42, 854–866. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C.S. Characteristics of Extreme Temperature and Precipitation and Their Impacts on Spring Corn Yield in Heilongjiang Province. Master’s Thesis, Northeast Agricultural University, Harbin, China, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Bouteska, A.; Sharif, T.; Bhuiyan, F.; Tesfaye, S. Impacts of the changing climate on agricultural productivity and food security: Evidence from Ethiopia. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 449, 141793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.Z.; Zhao, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, L.L.; Zhang, Y.L.; Sun, Y.; Ji, J.H.; Hao, X.Y.; Liu, S.Q.; Sun, N. Effect of different fertilization on soil fertility, biological activity, and corn yield in the albic soil area of China. Plants 2025, 14, 810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priatmadi, B.J.; Septiana, M.; Saidy, A.R. Growth performance and yield of rice grown in three different types of soil collected from rice fields with coal fly ash application. Plant Soil Environ. 2023, 69, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Meteorological Elements | Z-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Air temperature | 1.256 | 0.051 |
| Precipitation | 0.571 | 0.001 |
| Evaporation | −0.967 | 0.053 |
| Sunlight | −0.906 | 0.060 |
| Relative humidity | 0.422 | 0.055 |
| Surface temperature | 2.307 | 0.100 |
| Meteorological Elements | Main Period/a |
|---|---|
| Air temperature | 23, 12, 8 |
| Precipitation | 22, 12, 8 |
| Evaporation | 22, 13, 8 |
| Sunlight | 22, 12, 8 |
| Relative humidity | 23, 13, 8 |
| Surface temperature | 23, 12, 7 |
| Crop | MK Statistics | Results |
|---|---|---|
| Rice | Z-value | 1.796 |
| p-value | 0.335 | |
| Soybean | Z-value | 0.739 |
| p-value | 0.144 | |
| Corn | Z-value | 2.257 |
| p-value | 0.277 |
| Meteorological Elements | Rice | Ranking | Soybean | Ranking | Corn | Ranking |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Air temperature | 0.819 | 1 | 0.821 | 1 | 0.829 | 1 |
| Precipitation | 0.760 | 3 | 0.814 | 2 | 0.817 | 2 |
| Evaporation | 0.701 | 4 | 0.765 | 3 | 0.638 | 4 |
| Sunlight | 0.812 | 2 | 0.637 | 4 | 0.777 | 3 |
| Relative humidity | 0.674 | 5 | 0.626 | 6 | 0.623 | 6 |
| Surface temperature | 0.671 | 6 | 0.634 | 5 | 0.634 | 5 |
| Factor | Eigenvalue | Extraction of Principal Components After Rotation | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eigenvalue | Variance Explanation Ratio % | Cumulative % | Eigenvalue | Variance Explanation Ratio % | Cumulative % | |
| 1 | 2.171 | 36.178 | 36.178 | 215.070 | 35.845 | 35.845 |
| 2 | 1.720 | 28.659 | 64.837 | 173.953 | 28.992 | 64.837 |
| 3 | 0.893 | 14.885 | 79.722 | |||
| 4 | 0.635 | 10.585 | 90.307 | |||
| 5 | 0.333 | 5.551 | 95.858 | |||
| 6 | 0.248 | 4.142 | 100 | |||
| Factor | Factor1 | Factor2 |
|---|---|---|
| Air temperature | −0.405 | 0.411 |
| Precipitation | 0.389 | 0.451 |
| Evaporation | −0.141 | 0.010 |
| Sunlight | 0.256 | 0.206 |
| Relative humidity | 0.052 | 0.148 |
| Surface temperature | 0.044 | 0.132 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Li, H.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Q.; Zou, J.; Jiang, Y.; Zhou, C. Dynamic Characteristics of Key Meteorological Elements and Their Impacts on Major Crop Yields in Albic Soil Region of Sanjiang Plain in China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080984
Li J, Li H, Wang Q, Meng Q, Zou J, Jiang Y, Zhou C. Dynamic Characteristics of Key Meteorological Elements and Their Impacts on Major Crop Yields in Albic Soil Region of Sanjiang Plain in China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(8):984. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080984
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jingyang, Huanhuan Li, Qiuju Wang, Qingying Meng, Jiahe Zou, Yu Jiang, and Chunwei Zhou. 2025. "Dynamic Characteristics of Key Meteorological Elements and Their Impacts on Major Crop Yields in Albic Soil Region of Sanjiang Plain in China" Atmosphere 16, no. 8: 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080984
APA StyleLi, J., Li, H., Wang, Q., Meng, Q., Zou, J., Jiang, Y., & Zhou, C. (2025). Dynamic Characteristics of Key Meteorological Elements and Their Impacts on Major Crop Yields in Albic Soil Region of Sanjiang Plain in China. Atmosphere, 16(8), 984. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080984




