Diagnosing Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon Variability Through Temperature Advection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methodology
2.1. Data
2.2. Methodology
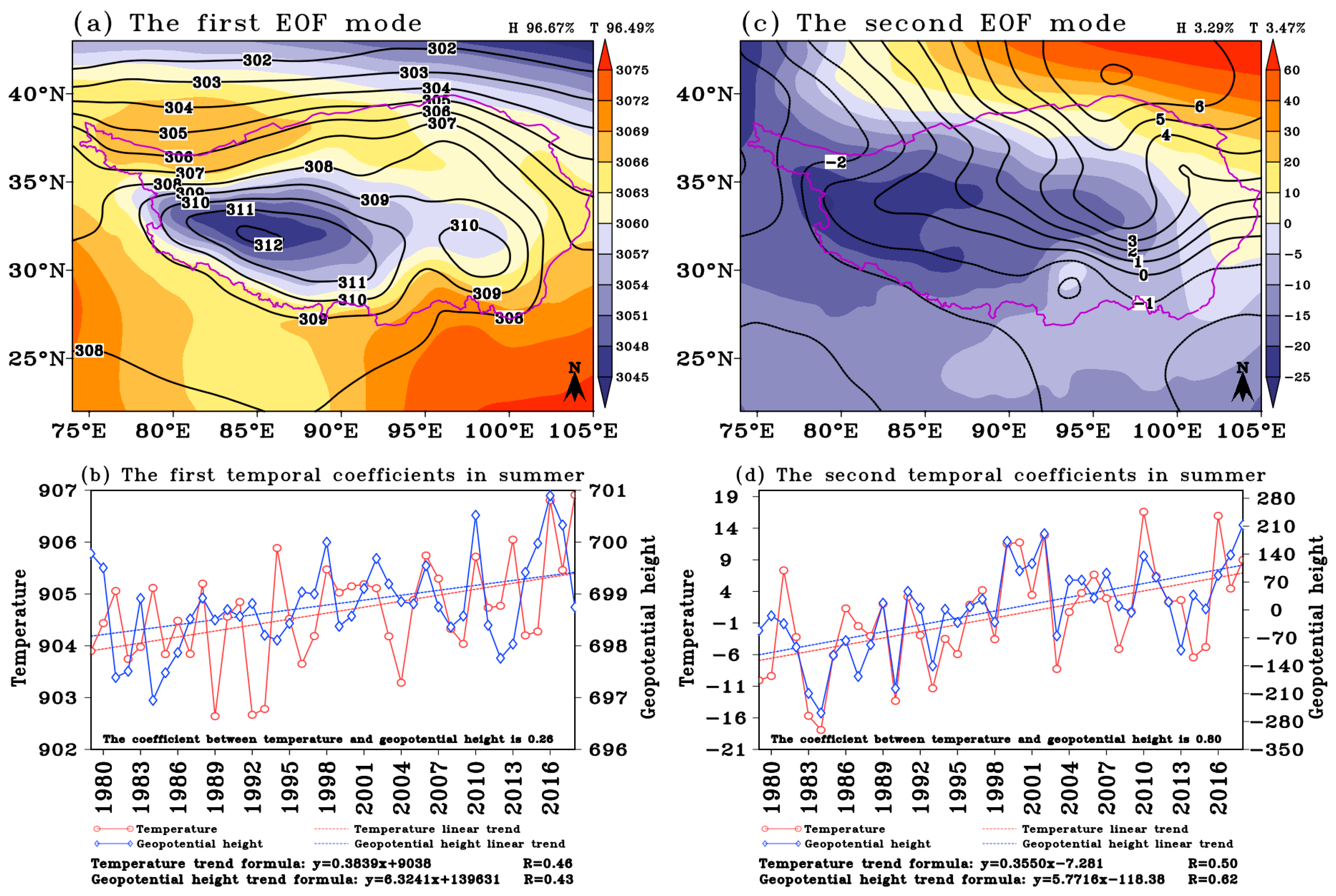
3. Asymmetric Structure of the Atmospheric Circulation
4. Ability of Temperature Advection to Describe the TPSM
4.1. Contrast Analysis and Evolution Characteristics of the Indices
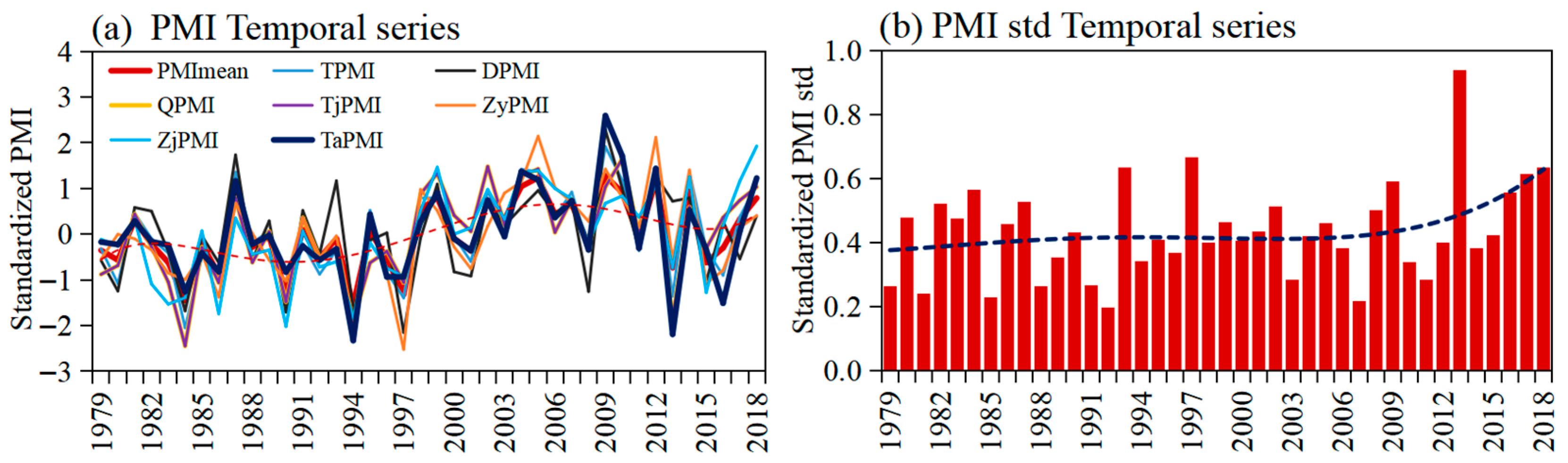
4.1.1. Variation Characteristics of the TPSM
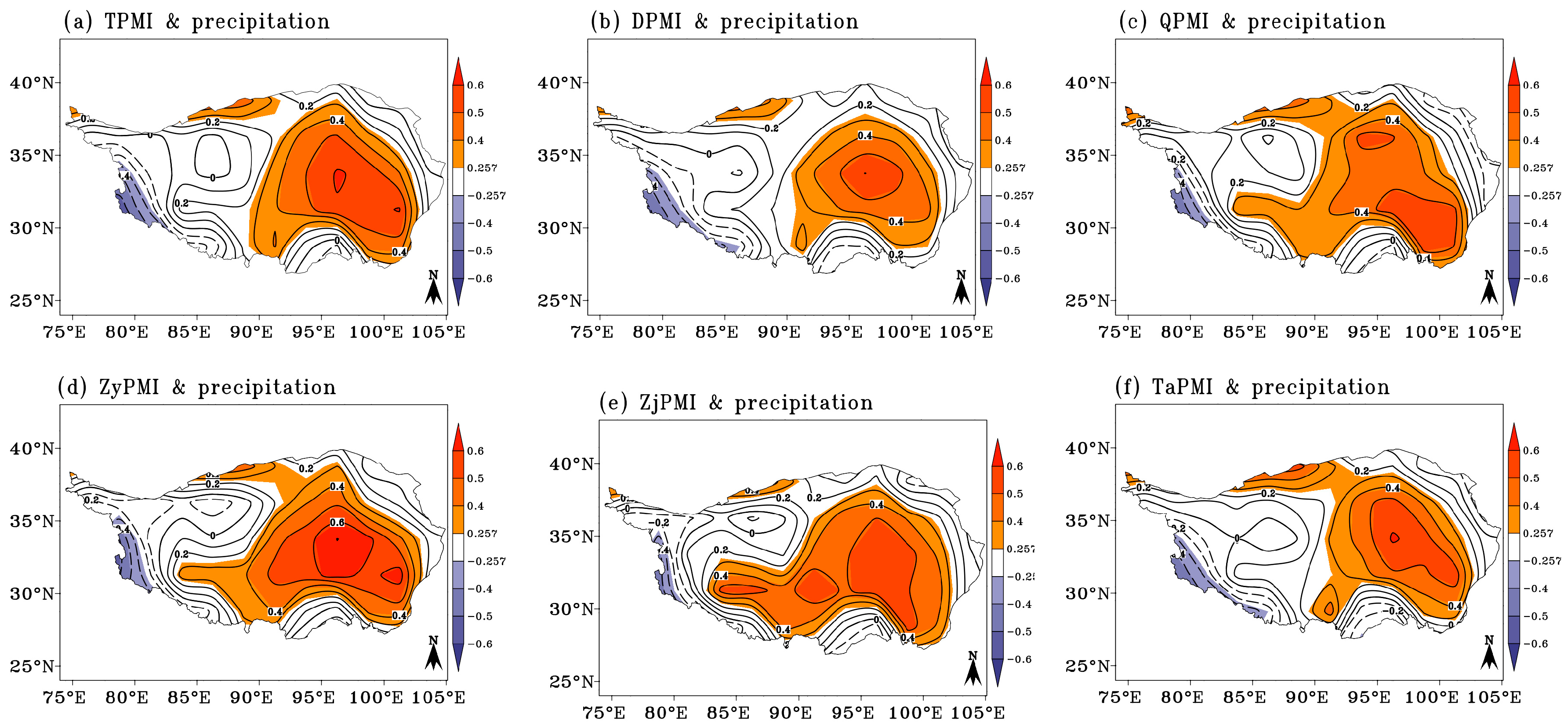
4.1.2. Correlation Analysis Between the TPSM and Precipitation
4.2. Composite Analysis of Weather Element Fields
4.3. Effect of TPSM on Regional Precipitation
4.4. Association of the TPSM with TT
5. Conclusions and Discussion
- (1)
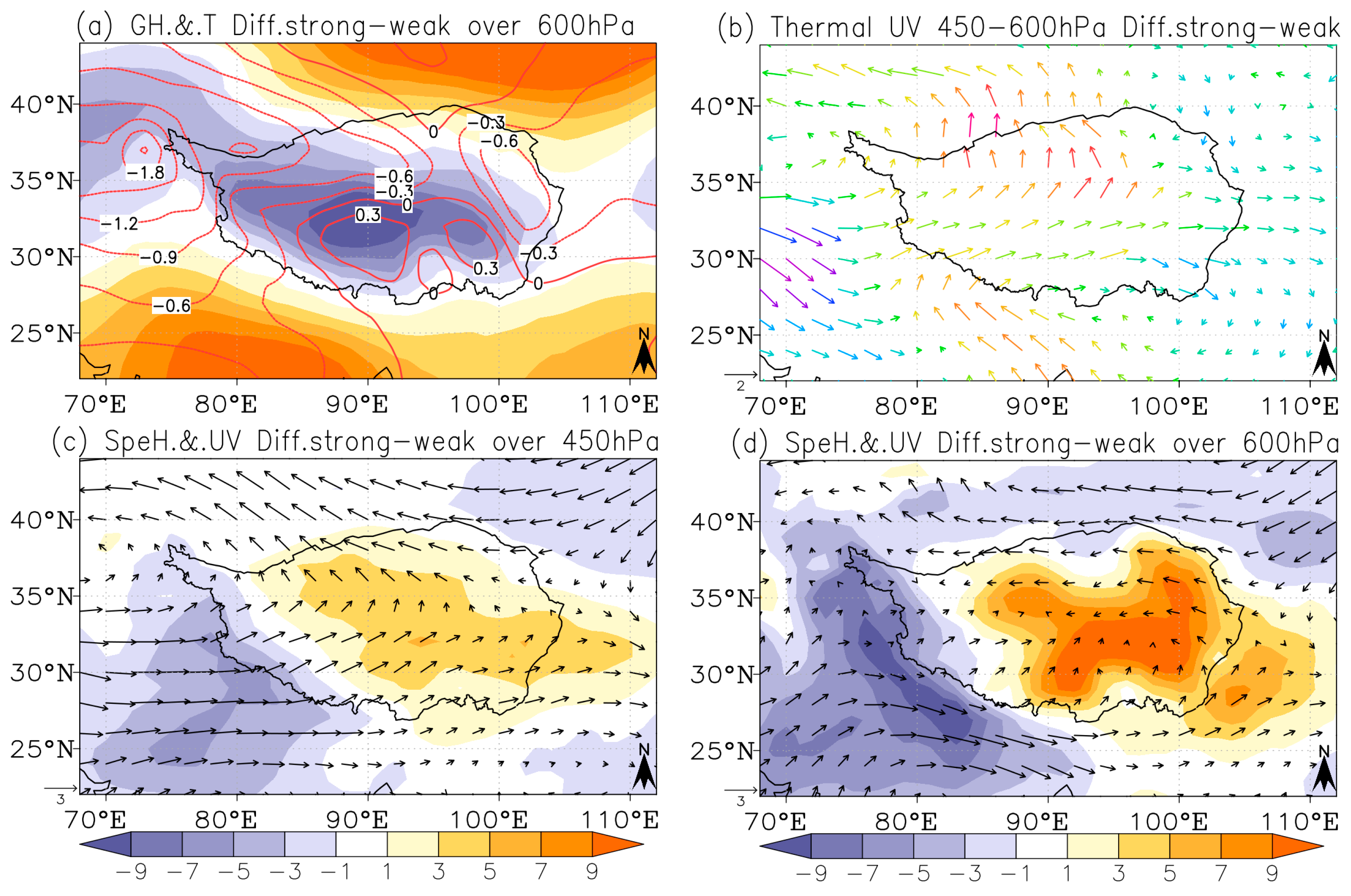
- During the summer, the main body of the plateau is controlled by a strong warm low-pressure system; the geopotential height field spatio-temporal evolution pattern is almost equal to the temperature field over time. The warm center never completely overlaps with the low center, which will cause the redistribution of temperature and pressure fields, leading to temperature advection and affecting the plateau summer monsoon. When the plateau monsoon region is dominated by warm advection, the plateau summer monsoon strengthens, and when cold advection dominates, the plateau summer monsoon weakens.
- (2)
- Not only is the interannual variability of the plateau monsoon indices very consistent and follows a significant fluctuating upward trend, but also the abrupt change time and the significant enhancement time of the plateau summer monsoon are relatively concentrated. TaPMI has the best correlation with TPMI, next between TaPMI and QPMI, and lower between TaPMI and DPMI. There are some differences in the fluctuation amplitude over time. During the summer, the main body of the plateau is controlled by a strong warm low-pressure system; the geopotential height field spatio-temporal evolution pattern is almost equal to the temperature field over time. The warm center never completely overlaps with the low center, which will cause the redistribution of temperature and pressure fields, leading to temperature advection and affecting the plateau summer monsoon. When the plateau monsoon region is dominated by warm advection, the plateau summer monsoon strengthens, and when cold advection dominates, the plateau summer monsoon weakens.
- (3)
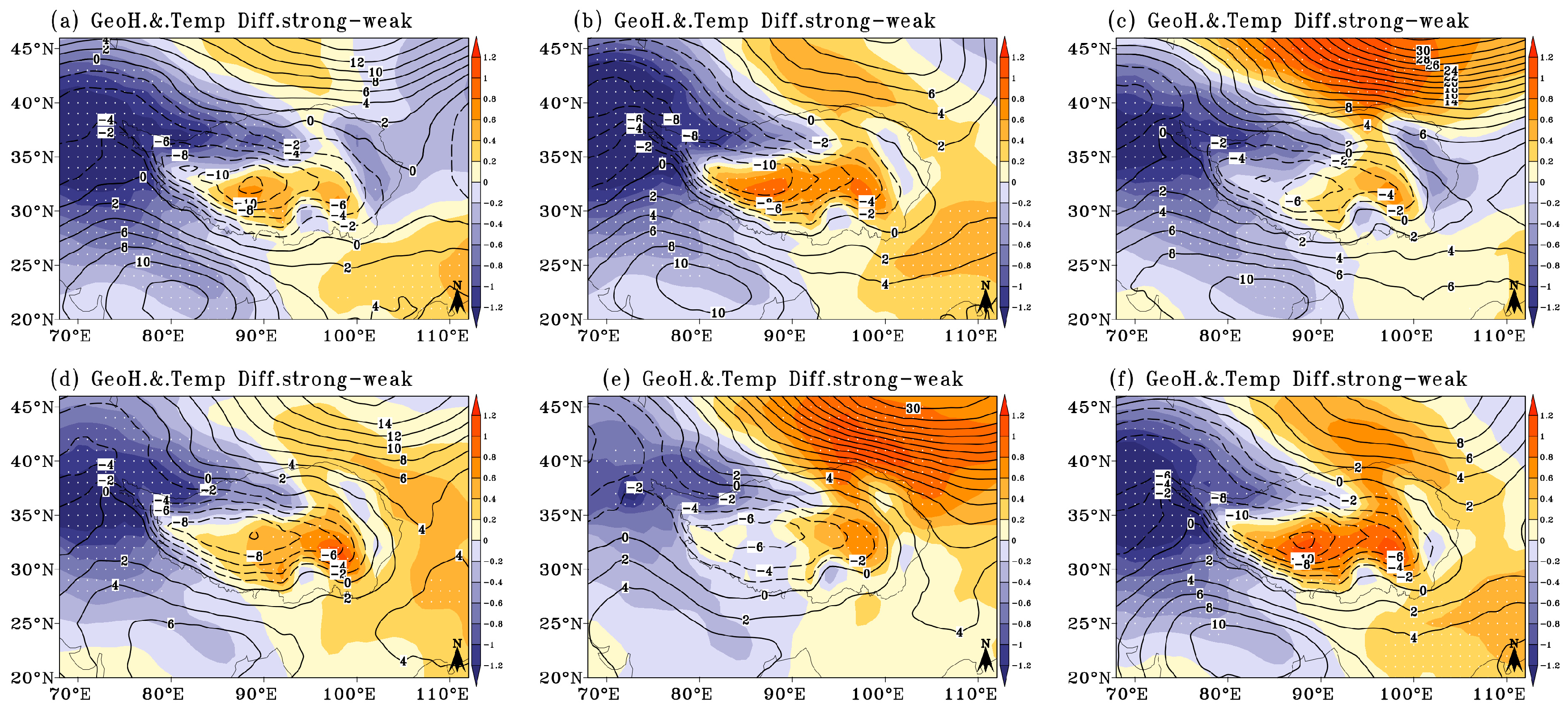
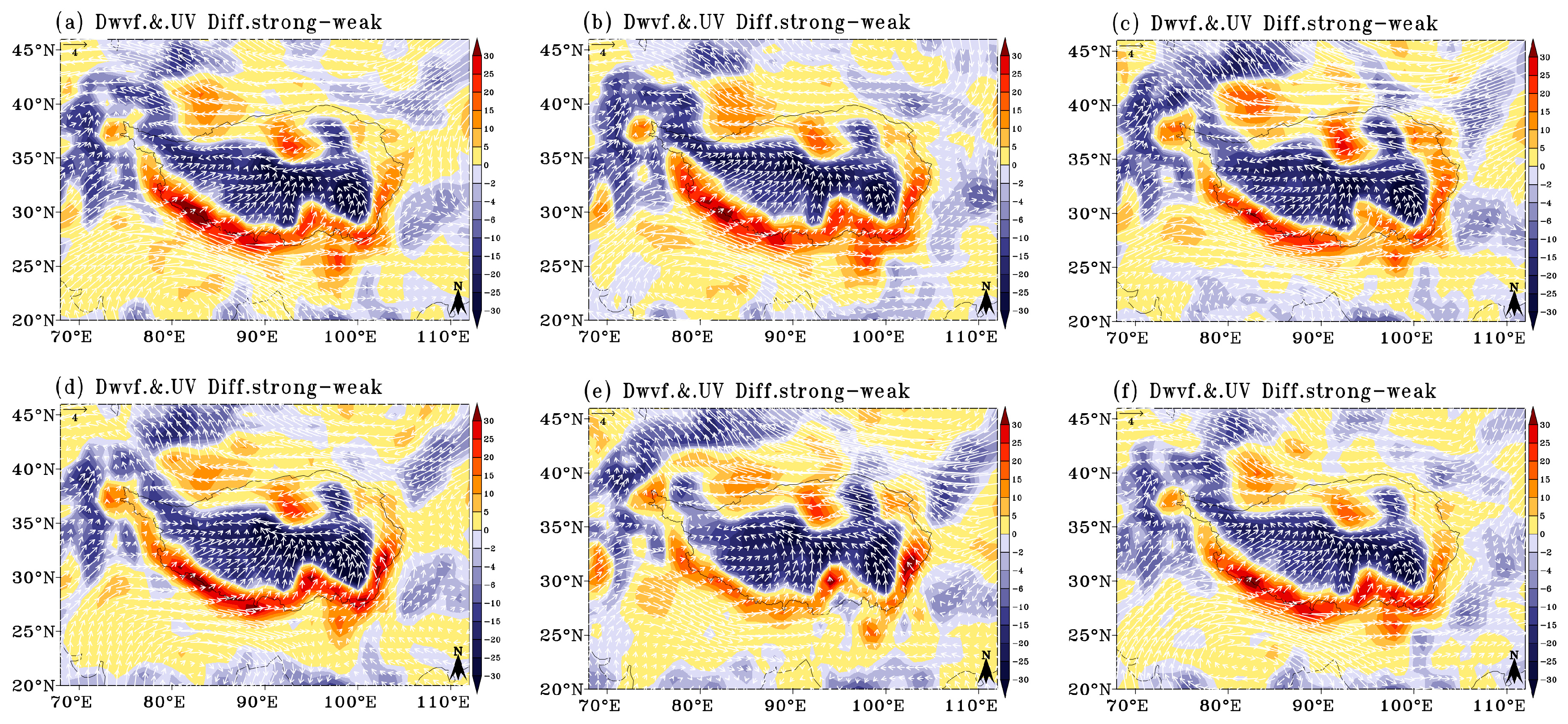
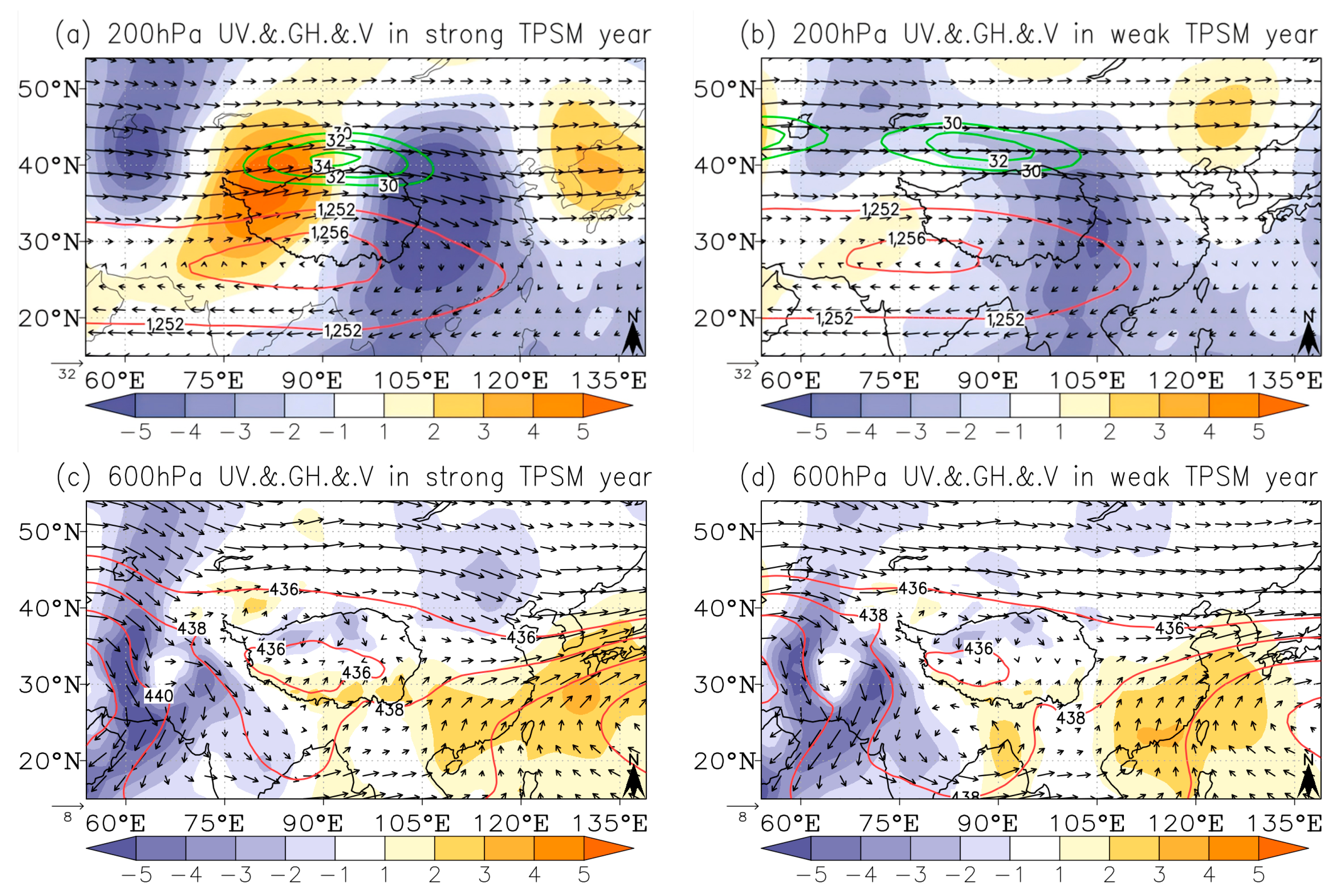
- The TaPMI effectively reflected meteorological elements and accurately represented climate variability. In strong plateau summer monsoon years, the warm low over the plateau is warmer and deeper, and the southern part of the plateau is dominated by enhanced southerlies associated with the cyclonic flow anomaly, which is shared by the water vapor flux convergence and leads to more precipitation in the main body of the plateau. In weak plateau summer monsoon years, the warm low over the plateau is colder and weaker, and the southern part of the plateau is dominated by enhanced northerlies associated with the anti-cyclonic flow anomaly, which is shared by the water vapor flux divergence and leads to less precipitation in the main body of the plateau.
- (4)
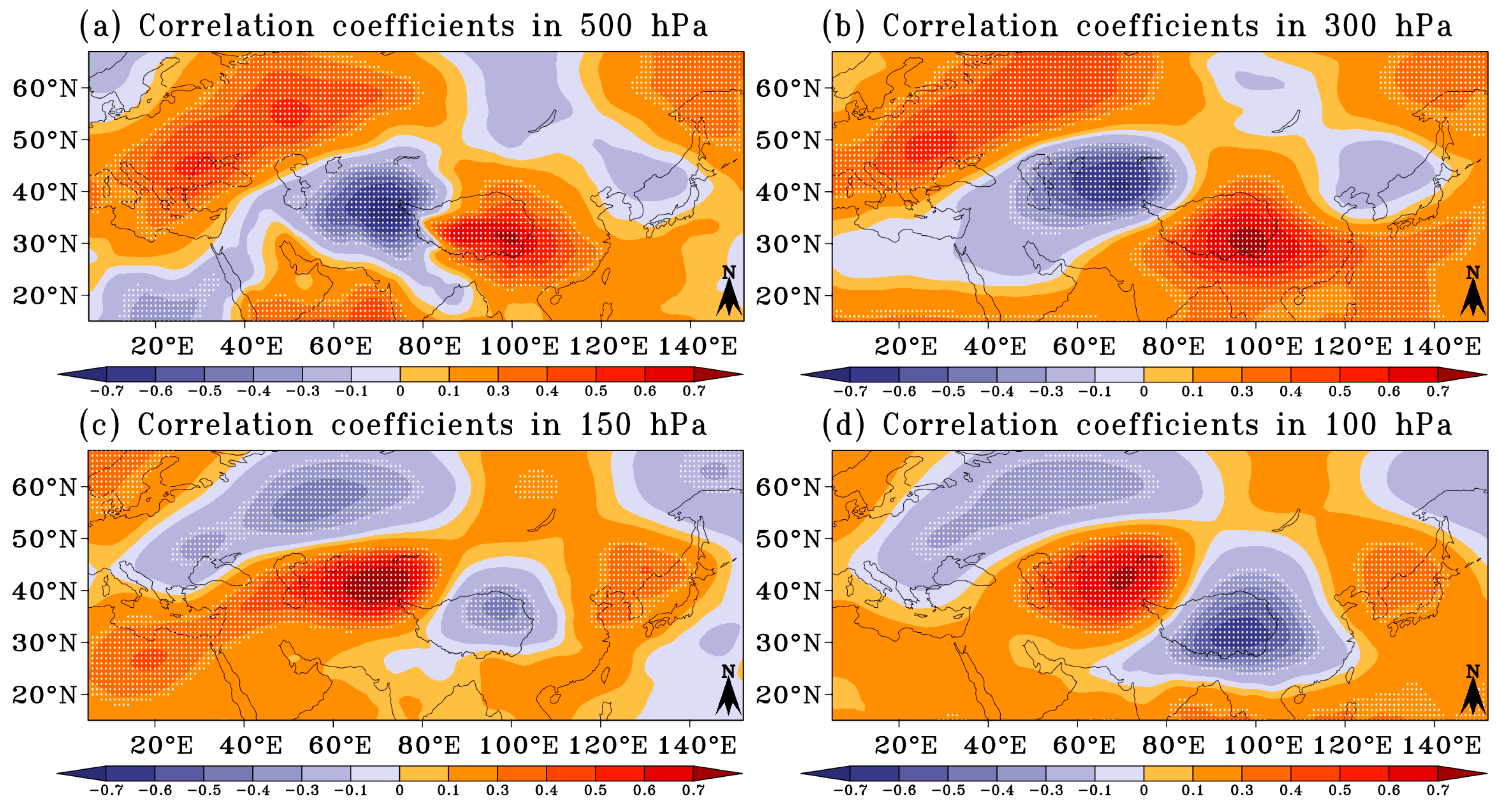
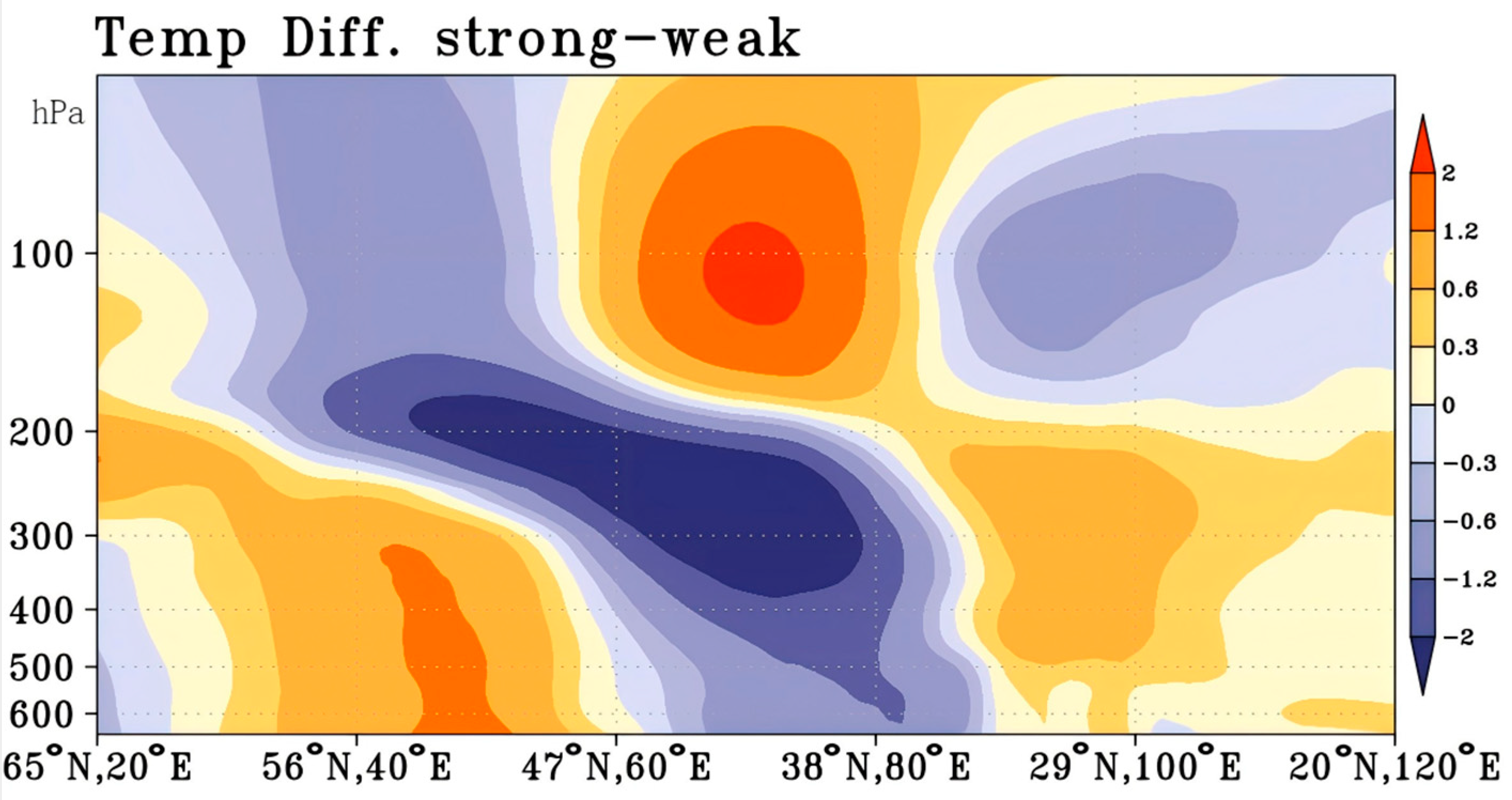
- There is a wave-like stable structure that appears over the Eurasian continent from the East European Plain to the plateau, and the correlation coefficients show a significant phase shift between the higher and lower levels in the vertical direction. In strong plateau summer monsoon years, the temperature over the Eastern European and Western Siberian plains, Southwest China and the seas east of Japan is warmer, and over the Turan Plain, Iranian plateau, central Arabian Peninsula and northern Sahara it is cooler than normal below 200 hPa and the opposite above 200 hPa. The distribution in weak plateau summer monsoon years is opposite to that in strong plateau summer monsoon years. In particular, within the plateau and western region, the dipolar pattern is distributed not only horizontally but also vertically.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Qiu, J. Tibetan plateau gets wired up for monsoon prediction. Nature 2014, 514, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Dong, B. Influence of the Tibetan Plateau uplift on the Asian monsoon-arid environment evolution. Chin. Sci. Bulletin. 2013, 58, 4277–4291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Guo, Q.; Guo, Z.; Yin, Z.; Dong, B.; Smith, R. Where were the monsoon regions and arid zones in Asia prior to the Tibetan Plateau uplift? Natl. Sci. Rev. 2015, 2, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Liu, Y.; You, Q.; Chen, G.; Bao, Q. Top-of-atmosphere radiation budget and cloud radiative effects over the Tibetan plateau and adjacent monsoon regions from CMIP6 simulations. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2021, 126, e2020JD034345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Wang, Z.; He, C.; Chen, D.; Yang, S. Future changes in South Asian summer monsoon circulation under global warming: Role of the Tibetan Plateau latent heating. Npj Clim. Atmos. Sci. 2024, 7, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.Z.; Luo, S.W.; Zhu, B.Z. The wind structure and heat balance in the lower troposphere over Tibetan Plateau and its surrounding. J. Meteorol. Res. 1957, 28, 108–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.Y.; Gao, Y.X. The monsoon phenomenon in Tibetan Plateau. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1962, 28, 111–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.C.; Shen, Z.B.; Chen, Y.Y. On climatic characteristics of the Xizang Plateau monsoon. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1979, 34, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.C.; Liang, J.; Shao, M.J.; Shi, G. Preliminary analysis on inter-annual variation of Plateau monsoon. Plateau Meteorol. 1984, 3, 76–82. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M. Some advances on the research of plateau monsoon (a reiview). Plateau Meteorol. 1993, 12, 95–101. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, M. Discussion on inter-decade oscillation of plateau monsoon and its causes. Sci. Meteorol. Sin. 1995, 15, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, D.M.; Li, Y.Q.; Bai, Y.Y.; De, D. The definition of plateau summer monsoon index and analysis on its characteristics. Plateau Mt. Meteorol. Res. 2009, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.; Ma, Z.F.; Fan, G.Z.; Chen, X.T. Relationship between a new plateau monsoon index and summer precipitation in Sichuan basin. Sci. Meteorol. Sinica. 2010, 30, 308–315. [Google Scholar]
- Xun, X.; Hu, Z.; Ma, Y. The dynamic plateau monsoon index and its association with general circulation anomalies. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 29, 1249–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Wang, H.; Zheng, R. New Variation Characteristics of Winter Monsoon over Qinghai-Xizang Plateau and Its Influences on Temperature over Southwest China. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Fan, G.Z.; Hua, W.; Wang, B.Y.; Zhu, L.H.; Zhou, D.W. Distribution Characteristics of Plateau Monsoon and a Contrastive Analysis of Plateau Monsoon Index. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 1517–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lv, S.; Ao, Y.; Ma, D. A New Plateau Monsoon Index Based on Wind Dynamicl Normalized Seasonality and Its Application. Plateau Meteorol. 2015, 34, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Wen, J.; Wang, X.; Jia, D.; Chen, J. Analysis of the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau monsoon evolution and its linkages with soil moisture. Remote Sens. 2016, 8, 493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.S.; Ma, Z.F.; Yan, S.Q. Discussion of Plateau monsoon index and its impact on precipitation in Sichuan Basin in midsummer. Plateau Meteror. 2017, 36, 886–899. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, S.; Lü, S.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X. An improvement of the Plateau monsoon index based on seasonal variation of wind and its comparison with other indexes. Aeta Meteorol. Sin. 2019, 77, 315–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, D.L.; Hu, Z. Relationship between the Snow Cover Day and Monsoon Index in Tibetan Plateau. Plateau Meteorol. 2010, 29, 1093–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Moore, G. On the relationship between Tibetan snow cover, the Tibetan plateau monsoon and the Indian summer monsoon. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2004, 31, L14204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, A.; Hu, J.; Xiao, Z. The Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon in the CMIP5 Simulations. J. Clim. 2013, 26, 7747–7766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, B.H.; Kripalani, R.H. Monsoon 2020: An interaction of upper tropospheric thermodynamics and dynamics over the Tibetan Plateau and the Western Pacific. Pure Appl. Geophys. 2021, 178, 3645–3654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Li, Z. Impacts of the Wave Train along the Asian Jet on the South China Sea Summer Monsoon Onset. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Hu, Z.; Ma, W.; Ma, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, H.; Han, X. Impacts of mid-high latitude atmospheric teleconnection patterns on interannual variation of the Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon. Atmos. Res. 2022, 275, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Fan, G.; Wang, B. Variation of Tibetan Plateau summer monsoon and its effect on precipitation in East China. Chin. J. Atmos. Sci. 2012, 36, 784–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cen, S.; Gong, Y.; Lai, X.; Qi, D. The relationship of the thermal contrast between the eastern Tibetan Plateau and itsnorthern side with the plateau monsoon and the precipitation in the Yangtze river basin in summer. Acia Meteorol. Sin. 2014, 72, 256–265. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, F.; Sielmann, F.; Zhu, X.; Fraedrich, K.; Zhi, X.; Peng, T.; Wang, L. The link between Tibetan Plateau monsoon and Indian summer precipitation: A linear diagnostic perspective. Clim. Dyn. 2017, 49, 4201–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Meng, L.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, A. The influence of the Tibetan Plateau monsoon on summer precipitation in Central Asia. Front. Earth Sci. 2022, 10, 771104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hu, Z.; Yu, H.; Sun, G.; Fan, W.; Niu, R.; Zhang, B. Tibetan Plateau Vortex Activity Its Relationship with the Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon Precipitation. Int. J. Climatol. 2024, 45, e8713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, D.; Li, Y. The major progress of the plateau monsoon study and its significant. Arid. Meteorol. 2007, 25, 74–79. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y. The observational basis of the 3rd Tibetan plateau atmospheric scientific experiment. Plateau Mt. Meteor. Res. 2011, 31, 77–82. [Google Scholar]
- Hersbach, H.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Hirahara, S.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Peubey, C.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D. The ERA5 global reanalysis. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2020, 146, 1999–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dee, D.P.; Uppala, S.; Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Poli, P.; Kobayashi, S.; Andrae, U.; Balmaseda, M.A.; Balsamo, G.; Bauer, D.P. The ERA-Interim reanalysis: Configuration and performance of the data assimilation system. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2011, 137, 553–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Gu, H.; Xie, J.; Xu, Y.P. How well do the ERA-Interim, ERA-5, GLDAS-2.1 and NCEP-R2 reanalysis datasets represent daily air temperature over the Tibetan Plateau? Int. J. Climatol. 2020, 41, 1484–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Liu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Muhammad, H.A.B.; Chi, W.; Wang, Z. Evaluation of spatial and temporal performances of ERA-Interim precipitation and temperature in mainland China. J. Clim. 2018, 31, 4347–4365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, A.J.; Berrisford, P.; Dee, D.P.; Hersbach, H.; Hirahara, S.; Thépaut, J.N. A reassessment of temperature variations and trends from global reanalyses and monthly surface climatological datasets. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2017, 143, 101–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, B.; Hersbach, H.; Simmons, A.; Berrisford, P.; Dahlgren, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; Schepers, D.; et al. The ERA5 global reanalysis: Preliminary extension to 1950. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2021, 147, 4186–4227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarek, M.; Brissette, F.P.; Arsenault, R. Evaluation of the ERA5 reanalysis as a potential reference dataset for hydrological modelling over North America. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 2527–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albergel, C.; Dutra, E.; Munier, S.; Calvet, J.C.; Munoz-Sabater, J.; de Rosnay, P.; Balsamo, G. ERA-5 and ERA-Interim driven ISBA land surface model simulations: Which one performs better? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2018, 22, 3515–3532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robert, A.; Mathew, S.; George, H.; Wang, J.J.; Gu, G.; David, B.; Long, C.; Udo, S.; Andreas, B.; Eric, N. The Global Precipitation Climatology Project (GPCP) Monthly Analysis (New Version 2.3) and a Review of 2017 Global Precipitation. Atmosphere 2018, 9, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, X.D.; Zhao, T.L.; Xu, H.X.; Mao, F.; Sun, H.; Wang, Y.H. Extreme precipitation events in East China and associated moisture transport pathways. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2016, 59, 1854–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.Y. Technology of Statistical Diagnosis and Prediction of Modern Climate; China Meteorological Press: Beijing, China, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Smadi, M.M.; Ahmed, Z. A Sudden Change in Rainfall Characteristics in Amman, Jordan During the Mid 1950s. Am. J. Environ. Sci. 2006, 2, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.S.; Bromwich, D.H. An Equivalent Isobaric Geopotential Height and Its Application to Synoptic Analysis and a Generalized ω Equation in σ Coordinates. Mon. Weather Rev. 2010, 127, 145–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Linz, M.; Chen, G. Interpreting Observed Temperature Probability Distributions Using a Relationship between Temperature and Temperature Advection. J. Clim. 2022, 35, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martineau, P.; Behera, S.K.; Nonaka, M.; Nakamura, H.; Kosaka, Y. Seasonally dependent increases in subweekly temperature variability over Southern Hemisphere landmasses detected in multiple reanalyses. Weather Clim. Dyn. 2024, 5, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garfinkel, C.I.; Rostkier Edelstein, D.; Morin, E.; Hochman, A.; Schwartz, C.; Nirel, R. Precursors of summer heat waves in the Eastern Mediterranean. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 150, 3757–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, G.; Li, D. Objective Identifying and Activity Characteristics of Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau Vortex. Plateau Meteorol. 2019, 1, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, S.; Yu, S.; Yang, D.; Zhang, L. Climate warming and growth of high-elevation inland lakes on the Tibetan Plateau. Glob. Planet. Change 2009, 67, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J. A unified monsoon index. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2002, 29, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, B.H.; Liang San, X. The changing relationship between the convection over the western Tibetan Plateau and the sea surface temperature in the northern Bay of Bengal. Tellus A Dyn. Meteorol. Oceanogr. 2018, 70, 1440869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaid, B.H.; Liang San, X. Influence of tropospheric temperature gradient on the boreal wintertime precipitation over East Asia. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2019, 30, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| TPMI | DPMI | QPMI | ZyPMI | ZjPMI | TaPMI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TPMI | 1 | |||||
| DPMI | 0.78 *** | 1 | ||||
| QPMI | 0.89 *** | 0.69 *** | 1 | |||
| ZyPMI | 0.85 *** | 0.72 *** | 0.74 *** | 1 | ||
| ZjPMI | 0.81 *** | 0.62 *** | 0.86 *** | 0.79 *** | 1 | |
| TaPMI | 0.93 *** | 0.67 *** | 0.82 *** | 0.78 *** | 0.73 *** | 1 |
| Indies | Strong Plateau Summer Monsoon Years | Weak Plateau Summer Monsoon Years |
|---|---|---|
| TPMI | 2018 (1.07), 2010 (1.18), 1987 (1.35), 2014 (1.36) 2005 (1.36), 2012 (1.37), 2004 (1.42), 2009 (1.91) | 1984 (−2.05), 1994 (−1.90), 1990 (−1.55) 1997 (−1.40), 2013 (−1.36), 1980 (−1.09) |
| DPMI | 2010 (1.00), 1999 (1.09), 1993 (1.17) 2012 (1.27), 1987 (1.73), 2009 (2.28) | 1997 (−2.16), 1990 (−1.71), 1994 (−1.68), 1984 (−1.68) 2008 (−1.26), 1980 (−1.25), 2015 (−1.03) |
| QPMI | 2018 (1.03), 2009 (1.03), 2012 (1.21), 2004 (1.27) 1999 (1.33), 2005 (1.42), 2002 (1.48), 2010 (1.65) | 1984 (−2.45), 1994 (−1.91), 2013 (−1.88), 1990 (−1.48) 1986 (−1.06), 1997 (−1.06), 1983 (−1.05) |
| ZyPMI | 2006 (1.02), 2004 (1.14), 2014 (1.40) 2009 (1.42), 2012 (2.11), 2005 (2.14) | 1997 (−2.52), 1994 (−1.91), 1986 (−1.38) 2015 (−1.08), 1990 (−1.03), 1984 (−1.00) |
| ZjPMI | 2006 (1.00), 2012 (1.07), 2017 (1.16), 2014 (1.25) 2004 (1.34), 2005 (1.39), 1999 (1.46), 2018 (1.92) | 1990 (−2.02), 1994 (−1.83), 1986 (−1.74), 1983 (−1.53) 1984 (−1.39), 2015 (−1.28), 1982 (−1.09) |
| TaPMI | 1987 (1.00), 2002 (1.03), 2010 (1.18), 2014 (1.20) 2012 (1.31), 2005 (1.60), 2004 (1.75), 2009 (1.76) | 1984 (−2.01), 1994 (−1.96), 2013 (−1.62) 1990 (−1.49), 1997 (−1.36), 2016 (−1.20) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xun, X.; Hu, Z.; Zhao, F.; Han, Z.; Zhang, M.; Li, R. Diagnosing Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon Variability Through Temperature Advection. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080973
Xun X, Hu Z, Zhao F, Han Z, Zhang M, Li R. Diagnosing Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon Variability Through Temperature Advection. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(8):973. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080973
Chicago/Turabian StyleXun, Xueyi, Zeyong Hu, Fei Zhao, Zhongqiang Han, Min Zhang, and Ruiqing Li. 2025. "Diagnosing Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon Variability Through Temperature Advection" Atmosphere 16, no. 8: 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080973
APA StyleXun, X., Hu, Z., Zhao, F., Han, Z., Zhang, M., & Li, R. (2025). Diagnosing Tibetan Plateau Summer Monsoon Variability Through Temperature Advection. Atmosphere, 16(8), 973. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16080973







