Characteristics and Sources of VOCs During a Period of High Ozone Levels in Kunming, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
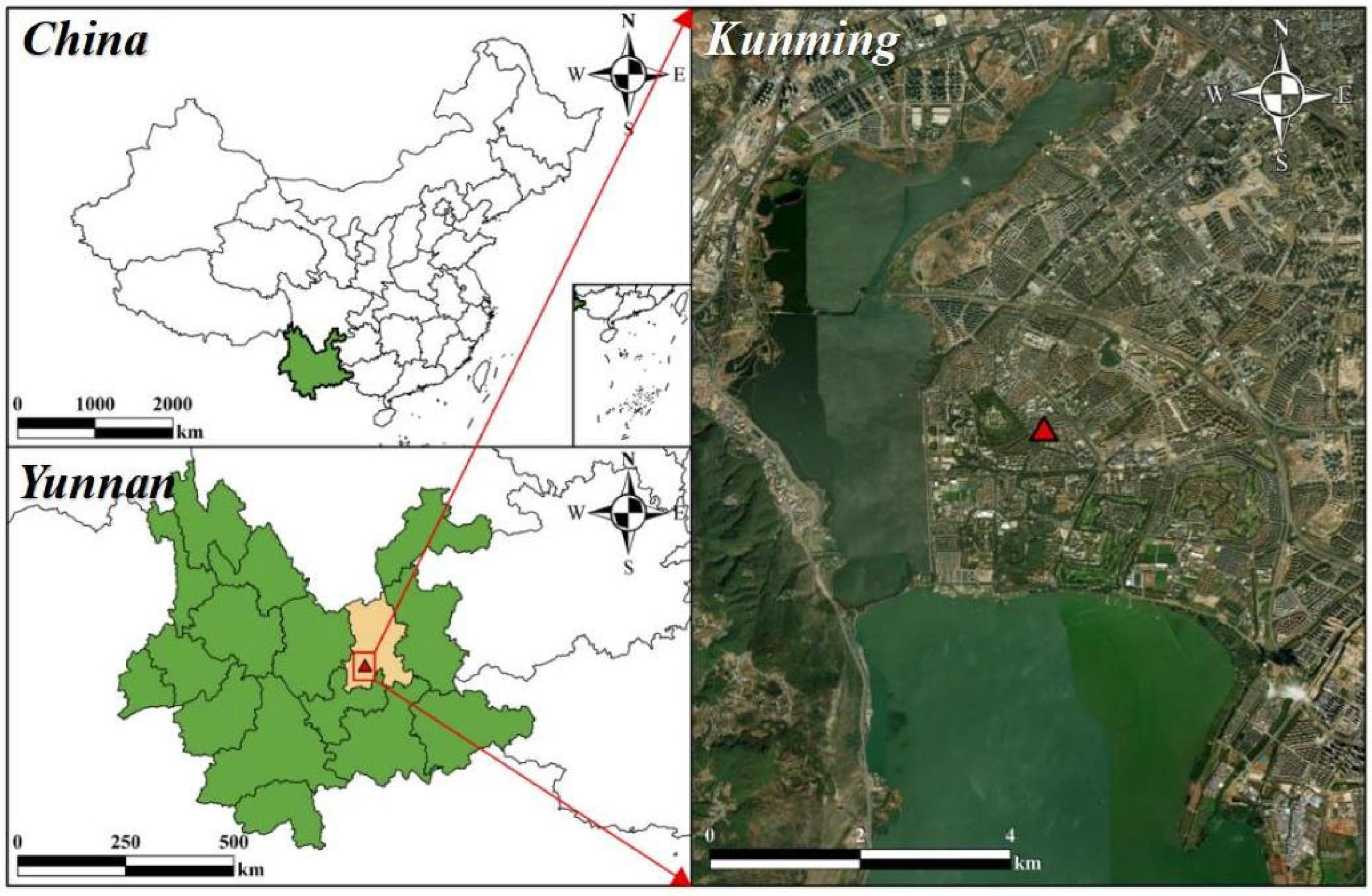
2.1. Study Site and Data Collection
2.2. OFP Analysis
2.3. EKMA Model
2.4. HYSPLIT Model
2.5. PMF Model
3. Results and Discussion
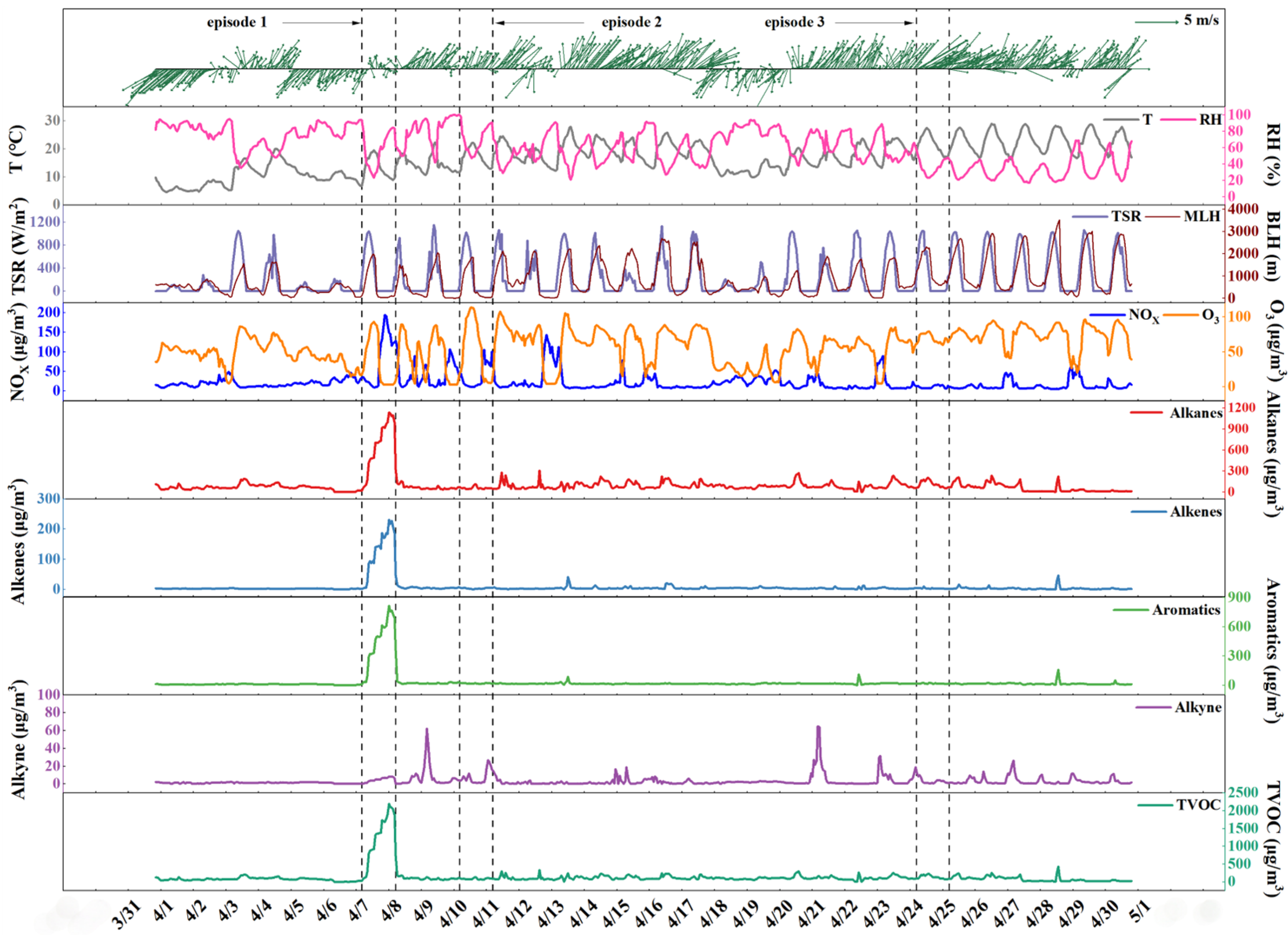
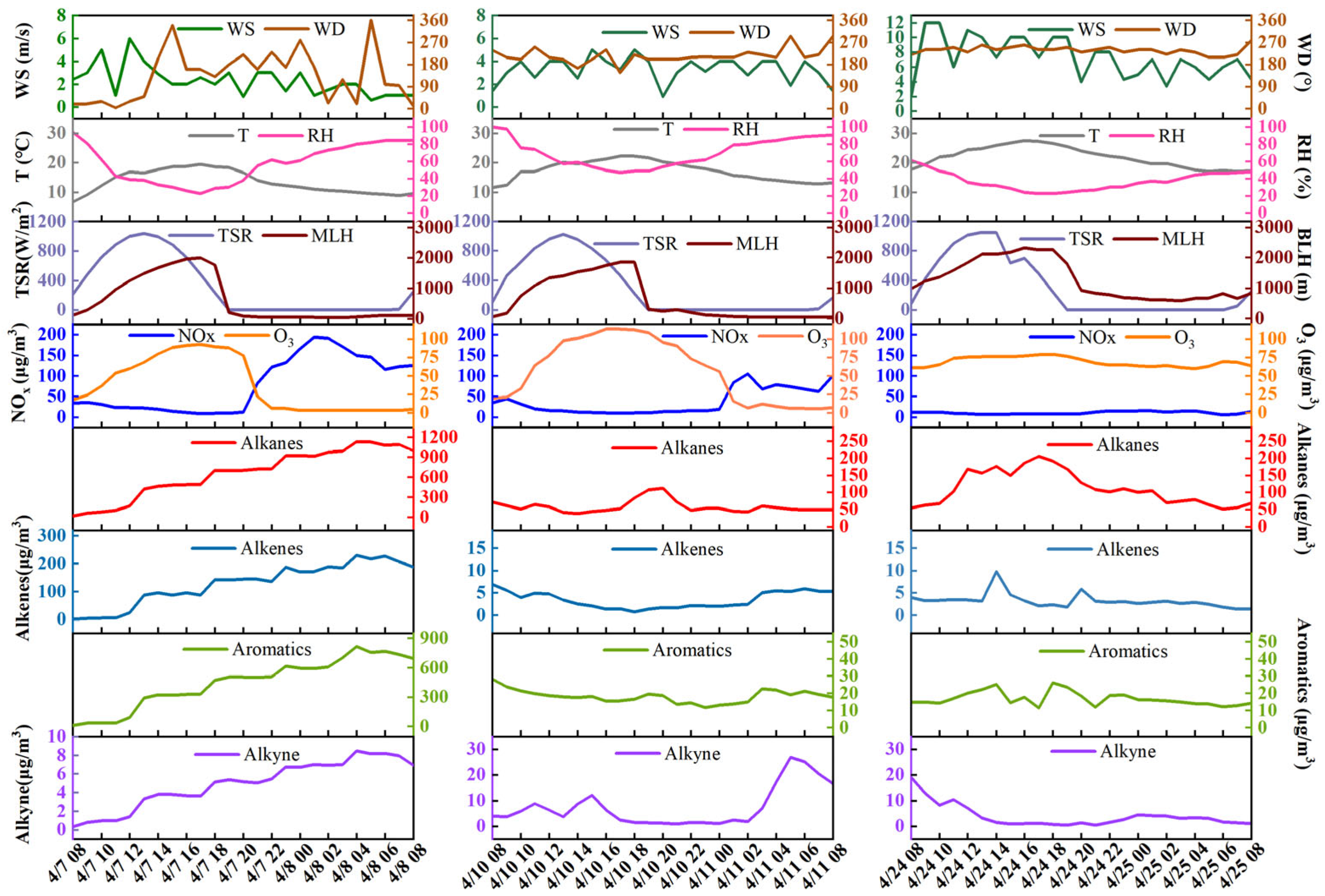
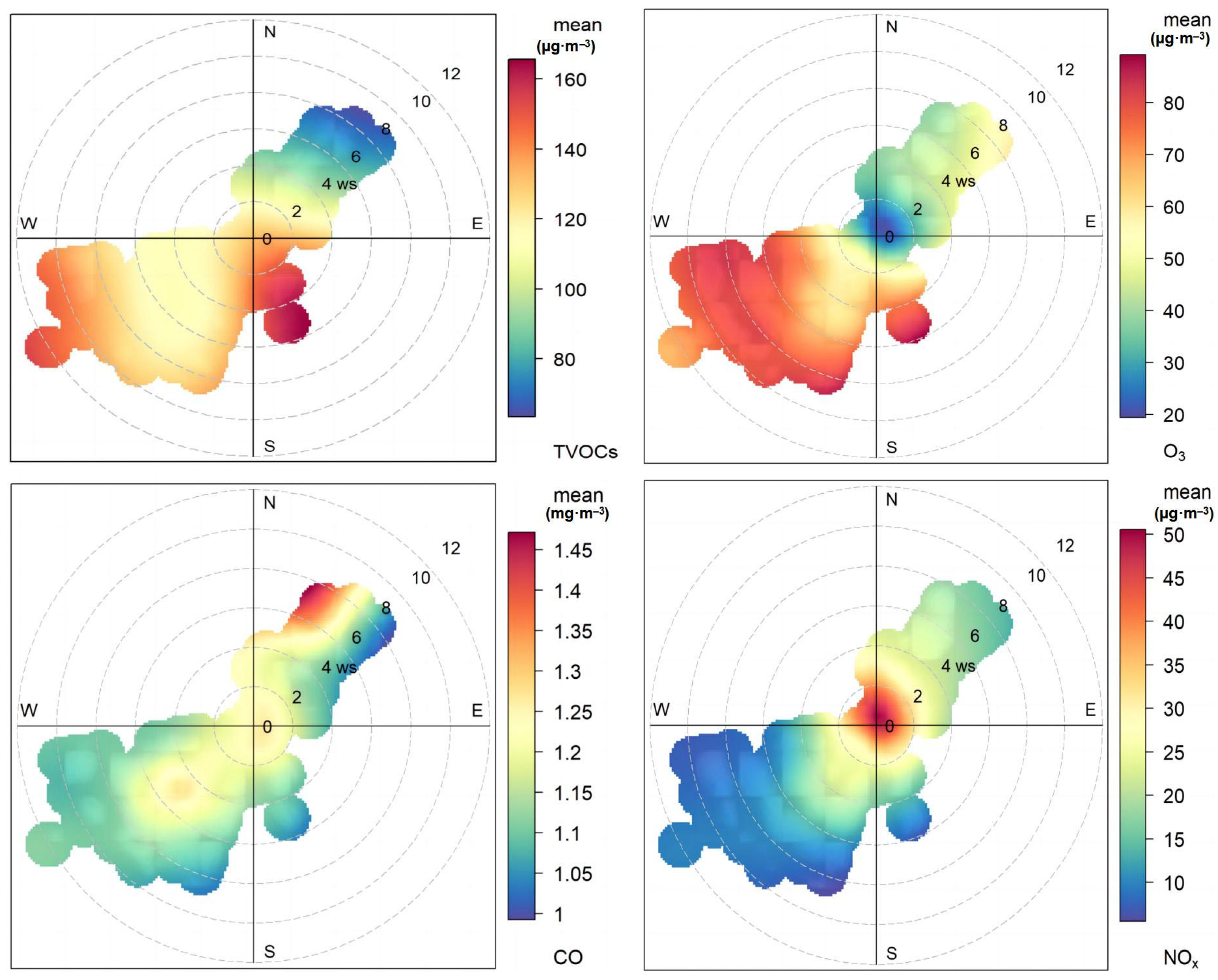
3.1. Hourly Variations of VOCs and Meteorological Parameters
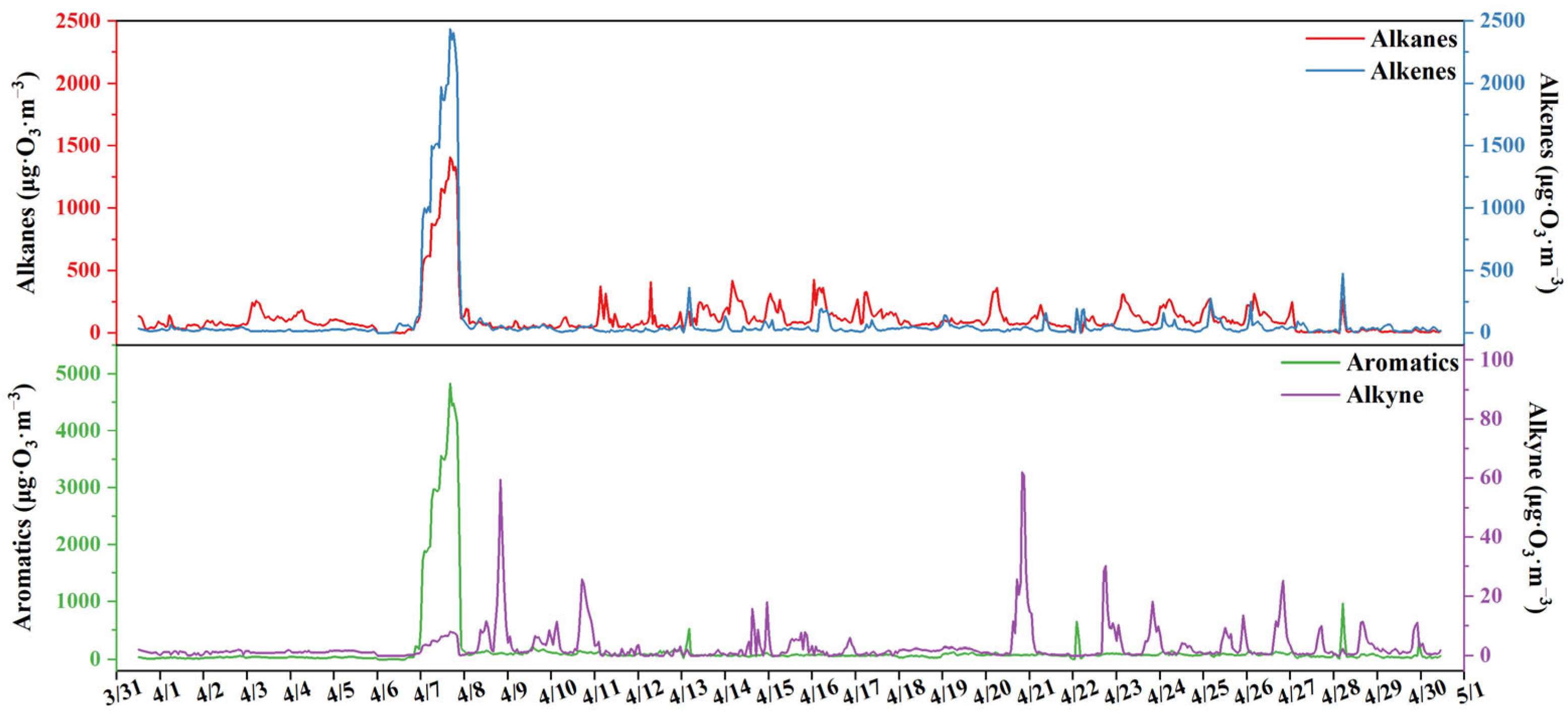
3.2. Ozone Formation Potential of VOCs
3.3. Ozone Sensitivity Analysis
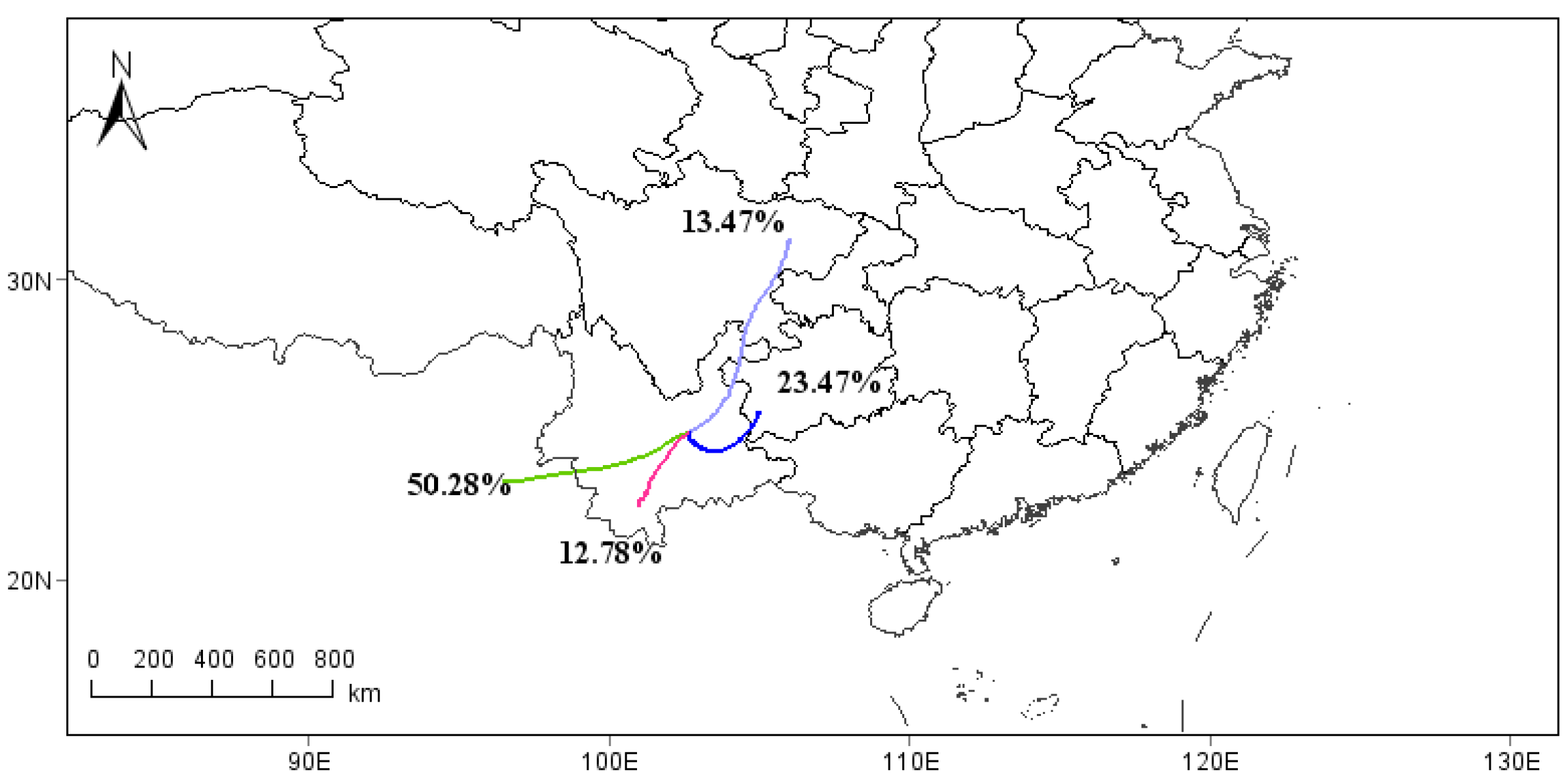
3.4. HYSPLIT Analysis
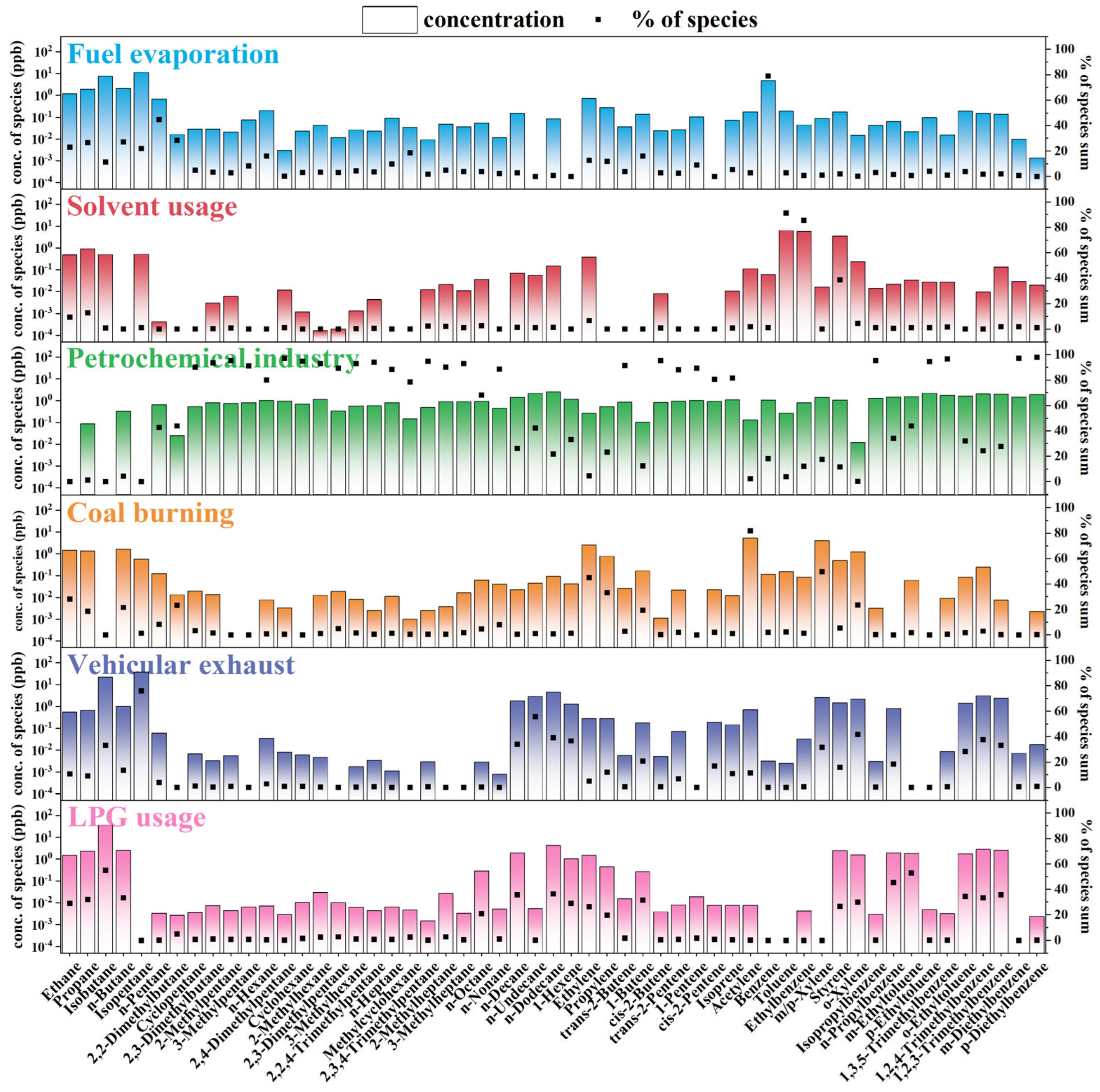
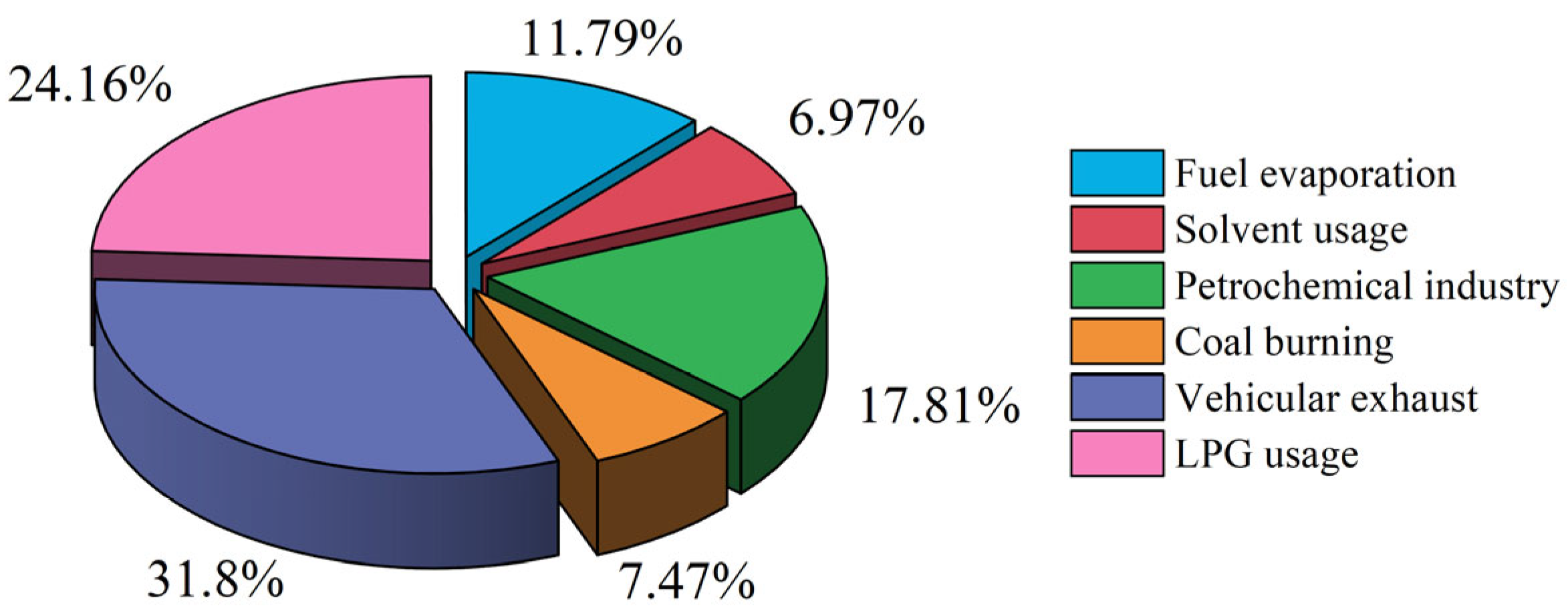
3.5. VOC Source Apportionment
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, M.; An, X.; Xing, L.; Li, G.; Tang, G.; He, J.; Long, X.; Zhao, S. Simulated Sensitivity of Ozone Generation to Precursors in Beijing during a High O3 Episode. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 38, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, F.; Azri, C. Surface O3 temporal variation, photolysis and accumulation in urban Tunis (North Africa) during January to December, 2016: Influence of meteorology and chemical precursors. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2023, 16, 2401–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, L.; Xiao, H.; Yi, H.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, J.; Huang, C.; He, M. Spatial Regionalization on Surface Ozone in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Asia-Pac. J. Atmos. Sci. 2021, 58, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Guo, F.; Xie, S. Diagnosing ozone–NOx–VOC sensitivity and revealing causes of ozone increases in China based on 2013–2021 satellite retrievals. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15035–15047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Duan, W.; Cheng, S.; Wang, X. Nonlinear and lagged effects of VOCs on SOA and O3 and multi-model validated control strategy for VOC sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 887, 164113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Shan, W.; Xiao, H. Recent Advances in Passive Air Sampling of Volatile Organic Compounds. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 602–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Tong, L.; Dai, X.; Xiao, H. Evaluation and Application of a Passive Air Sampler for Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 3047–3055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ring, A.M.; Dickerson, R.R.; Sebol, A.E.; Ren, X.; Benish, S.E.; Salawitch, R.J.; Galasyn, A.; Miller, P.J.; Canty, T.P. Anthropogenic VOCs in the Long Island Sound, NY Airshed and their role in ozone production. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 296, 119583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, B.; Pouyaei, A.; Choi, Y.; Rappenglueck, B. Influence of seasonal variability on source characteristics of VOCs at Houston industrial area. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 277, 119077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holland, R.; Khan, A.H.; Derwent, R.G.; Lynch, J.; Ahmed, F.; Grace, S.; Bacak, A.; Shallcross, D.E. Gas-phase kinetics, POCPs, and an investigation of the contributions of VOCs to urban ozone production in the UK. Int. J. Chem. Kinet. 2023, 55, 350–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berezina, E.; Moiseenko, K.; Skorokhod, A.; Pankratova, N.V.; Belikov, I.; Belousov, V.; Elansky, N.F. Impact of VOCs and NOx on Ozone Formation in Moscow. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim, D.S.; Gatti, L.V.; Corrêa, S.M.; Chiquetto, J.B.; Santos, G.M.; de Souza Rossatti, C.; Pretto, A.; Rozante, J.R.; Figueroa, S.N.; Pendharkar, J.; et al. Determining VOCs Reactivity for Ozone Forming Potential in the Megacity of São Paulo. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2460–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notario, A.; Bravo, I.; Adame, J.A.; Díaz-de-Mera, Y.; Aranda, A.; Rodríguez, A.; Rodríguez, D. Variability of oxidants (OX=O3+NO2), and preliminary study on ambient levels of ultrafine particles and VOCs, in an important ecological area in Spain. Atmos. Res. 2013, 128, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Bari, M.A.; Xing, Z.; Du, K. Ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in two coastal cities in western Canada: Spatiotemporal variation, source apportionment, and health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 706, 135970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bari, M.A.; Kindzierski, W.B. Ambient volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in Calgary, Alberta: Sources and screening health risk assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 631–632, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhat, M.; Afif, C.; Zhang, S.; Dusanter, S.; Delbarre, H.; Riffault, V.; Sauvage, S.; Borbon, A. Investigating the industrial origin of terpenoids in a coastal city in northern France: A source apportionment combining anthropogenic, biogenic, and oxygenated VOC. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 928, 172098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, S.G.; Frankel, A.; Hafner, H.R. Source apportionment of VOCs in the Los Angeles area using positive matrix factorization. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, T.K.; Yadav, P.; Kumar, M.; Lal, S.; Soni, K.; Yadav, L.; Saharan, U.S.; Sharma, S.K. Characteristics of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) at an urban site of Delhi, India: Diurnal and seasonal variation, sources apportionment. Urban Clim. 2023, 49, 101545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Marlier, M.E.; DeFries, R.S.; Westervelt, D.M.; Xia, K.R.; Fiore, A.M.; Mickley, L.J.; Cusworth, D.H.; Milly, G. Seasonal impact of regional outdoor biomass burning on air pollution in three Indian cities: Delhi, Bengaluru, and Pune. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 172, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prapatigul, P.; Sreshthaputra, S. Causes and solution of forest and agricultural burning in Northern, Thailand. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2022, 18, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar]
- Tala, W.; Janta, R.; Kraisitnitikul, P.; Chantara, S. Patterns and impact of volatile organic compounds on ozone and secondary organic aerosol formation: Implications for air pollution in Upper Southeast Asia. J. Hazard. Mater. Adv. 2025, 18, 100762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Ling, Y.; Liu, F.; Tong, L.; Yang, M.; Shi, Y.; Xue, Y.; Ye, H.; Xu, Y.; Huang, C.; et al. Characteristics and Source Apportionment of Volatile Organic Compounds in a Coastal Industrial Area: A Case Study in the Yangtze River Delta of China. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2024, 113, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Shi, Y.; Yang, M.; Tong, L.; Dai, X.; Liu, F.; Huang, C.; Zheng, J.; Li, J.; Xiao, H. Spatiotemporal distribution, source apportionment and health risk assessment of atmospheric volatile organic compounds using passive air samplers in a typical coastal area, China. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 423, 138741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Tong, L.; Luo, Q.; Ling, Y.; Gu, H.; Lv, Y.; Shi, A.; Liu, H.; Xiao, H.; Huang, C. Emission Characteristics and Health Risk Assessment of Volatile Organic Compounds in Key Industries: A Case Study in the Central Plains of China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China; General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Xie, S.; Gong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Liu, J. Characterization and Source Analysis of Pollution Caused by Atmospheric Volatile Organic Compounds in the Spring, Kunming, China. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbieri, M.V.; Peris, A.; Postigo, C.; Moya-Garces, A.; Monllor-Alcaraz, L.S.; Rambla-Alegre, M.; Eljarrat, E.; Lopez de Alda, M. Evaluation of the occurrence and fate of pesticides in a typical Mediterranean delta ecosystem (Ebro River Delta) and risk assessment for aquatic organisms. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 274, 115813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eun, D.-M.; Han, Y.-S.; Nam, I.; Chang, Y.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-H.; Gong, S.Y.; Youn, J.-S. Ambient volatile organic compounds in the Seoul metropolitan area of South Korea: Chemical reactivity, risks and source apportionment. Environ. Res. 2024, 251, 118749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Zhou, L.; Chen, D.; Luo, L.; Xiao, K.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Tan, Q.; Yang, F. Atmospheric oxidation capacity and secondary pollutant formation potentials based on photochemical loss of VOCs in a megacity of the Sichuan Basin, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 901, 166259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, M.; Chang, L.; Shin, S.-A.; Kim, K.; Choi, Y.; Lim, H.; Choi, S.-D.; Lee, G. Assessment of VOCs emission inventory in Seoul through spatiotemporal observations using passive and online PAMS measurements. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Yan, Q.; Han, S.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, R. Typical industrial sector-based volatile organic compounds source profiles and ozone formation potentials in Zhengzhou, China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 841–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, Z.; Dai, Y.; Du, G.; Han, J.; Hou, L.; Duan, E. Summer O3 pollution cycle characteristics and VOCs sources in a central city of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei area, China. Environ. Pollut. 2023, 323, 121293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, W.P.L. Development of an Improved Chemical Speciation Database for Processing Emissions of Volatile Organic Compounds for Air Quality Models. 2023. Available online: https://intra.engr.ucr.edu/~carter/emitdb/ (accessed on 9 March 2023).
- Shiu, C.-J.; Liu, S.C.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, J.-P.; Chou, C.C.K.; Lin, C.-Y.; Young, C.-Y. Photochemical production of ozone and control strategy for Southern Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 9324–9340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, L.; Liu, X.; Tan, Q.; Feng, M.; An, J.; Qu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M. Characteristics, source apportionment and contribution of VOCs to ozone formation in Wuhan, Central China. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 192, 55–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Li, J. Extending Ozone-Precursor Relationships in China From Peak Concentration to Peak Time. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2020, 125, e2020JD033670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Lang, Y.; Wang, T.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Guo, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, Y.; et al. Temporal and spatial variations in stable isotopic compositions of precipitation during the typhoon Lekima (2019), China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 762, 143143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, Z.; Tian, C.; Li, J.; Syed, J.H.; Zhang, W.; Fang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Nasir, J.; Mansha, M.; Rizvi, S.H.H.; et al. Isotopic Interpretation of Particulate Nitrate in the Metropolitan City of Karachi, Pakistan: Insight into the Oceanic Contribution to NO(x). Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 7787–7797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Hu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, J.; Li, F. Nitrate sources and its formation in precipitation during typhoons (In-fa and Chanthu) in multiple cities, East China. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 155949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Liu, B.; Bi, X.; Wu, J.; Liang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y.; Hopke, P.K. Dispersion Normalized PMF Provides Insights into the Significant Changes in Source Contributions to PM(2.5) after the COVID-19 Outbreak. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 9917–9927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warneke, C.; de Gouw, J.A.; Goldan, P.D.; Kuster, W.C.; Williams, E.J.; Lerner, B.M.; Jakoubek, R.; Brown, S.S.; Stark, H.; Aldener, M.; et al. Comparison of daytime and nighttime oxidation of biogenic and anthropogenic VOCs along the New England coast in summer during New England Air Quality Study 2002. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2004, 109, D10309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Lu, K.; Jiang, M.; Su, R.; Dong, H.; Zeng, L.; Xie, S.; Tan, Q.; Zhang, Y. Exploring ozone pollution in Chengdu, southwestern China: A case study from radical chemistry to O3-VOC-NOx sensitivity. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 636, 775–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.P.; Chen, N.; Guo, H.; Zhang, W.H.; Wang, N.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M. Ambient volatile organic compounds and their effect on ozone production in Wuhan, central China. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 200–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X.; Guo, H.; Zou, Q.; Li, K.; Xiong, E.; Zhou, B.; Guo, P.; Jiang, F.; Tian, X. Evidence for Reducing Volatile Organic Compounds to Improve Air Quality from Concurrent Observations and In Situ Simulations at 10 Stations in Eastern China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 15356–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Qiu, P.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Ma, W.; Yin, S.; Yu, Q.; Li, J.; Liu, X. Evolution and variations of atmospheric VOCs and O3 photochemistry during a summer O3 event in a county-level city, Southern China. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 272, 118942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milford, J.B.; Russell, A.G.; McRae, G.J. A new approach to photochemical pollution control: Implications of spatial patterns in pollutant responses to reductions in nitrogen oxides and reactive organic gas emissions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1989, 23, 1290–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Zhang, L.; Wen, Y.; Shi, K. Sensitivity analysis of O3 formation to its precursors-Multifractal approach. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 251, 118275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, D.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, C.; Chen, J.; Huang, H.; Zhuang, Z.; Choi, S.-D.; Hong, Y. Health risks and environmental influence of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in a residential area near an industrial park in Southeast China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2024, 15, 101966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z.; Lian, S.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Cheng, H. The chemical characteristics and sources of formaldehyde on O3 and non-O3 polluted days in Wuhan, central China. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Shao, M.; Fu, L.; Lu, S.; Zeng, L.; Tang, D. Source profiles of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) measured in China: Part I. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 6247–6260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, C.; Liu, P.; Ye, C.; Xue, C.; Zhao, D.; Sun, J.; Du, Y.; Chai, F.; et al. The levels, sources and reactivity of volatile organic compounds in a typical urban area of Northeast China. J. Environ. Sci. 2019, 79, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Zou, Q.; Jin, L.; Shen, Y.; Shen, J.; Xu, B.; Qu, F.; Zhang, F.; Xu, J.; Pei, X.; et al. Characteristics and sources of ambient Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) at a regional background site, YRD region, China: Significant influence of solvent evaporation during hot months. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 857, 159674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Yin, S.; Yuan, M.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Zhang, D.; Lu, X.; Zhang, R. Characteristics, source analysis and chemical reactivity of ambient VOCs in a heavily polluted city of central China. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Gao, M.; Xu, H.; Cai, R.; Feng, R.; He, K.; Sun, J.; Ho, S.S.H.; Shen, Z. Volatile organic compounds in typical coal chemical industrial park in China and their environmental and health impacts. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 338, 120825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.; Ling, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tong, L.; Xue, Y.; Liu, C.; Xiao, H.; Huang, C. Characteristics and Sources of VOCs During a Period of High Ozone Levels in Kunming, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070874
Huang C, Ling Y, Chen Y, Tong L, Xue Y, Liu C, Xiao H, Huang C. Characteristics and Sources of VOCs During a Period of High Ozone Levels in Kunming, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(7):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070874
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chuantao, Yufei Ling, Yunbo Chen, Lei Tong, Yuan Xue, Chunli Liu, Hang Xiao, and Cenyan Huang. 2025. "Characteristics and Sources of VOCs During a Period of High Ozone Levels in Kunming, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 7: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070874
APA StyleHuang, C., Ling, Y., Chen, Y., Tong, L., Xue, Y., Liu, C., Xiao, H., & Huang, C. (2025). Characteristics and Sources of VOCs During a Period of High Ozone Levels in Kunming, China. Atmosphere, 16(7), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16070874




