Abstract
(1) Background: The role of air pollutants as risk factors for tinnitus remains unclear. To address this gap in research, we conducted a nationwide retrospective cohort study in Taiwan by integrating patients’ clinical data with daily air quality data to evaluate the environmental risk factors associated with tinnitus. (2) Methods: The Taiwan National Health Research Database (NHIRD) includes medical records for nearly all residents of Taiwan. To assess pollution levels, we used daily air quality data from the Taiwan Environmental Protection Agency regarding SO2, CO, NO, NOX, and particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10). We merged the NHIRD data with air quality information based on the residents’ locations and the positions of air quality monitoring stations. Pollutant levels were then categorized into quartiles (Q1, Q2, Q3, and Q4). (3) Results: This study included 284,318 subjects. After controlling for covariates, the adjusted HR (95 CI%) for tinnitus increased with increasing SO2, CO, NO, NOX, PM2.5, and PM10 exposure levels, specifically from 1.24 (95 CI% = 1.18, 1.30) to 1.35 (95 CI% = 1.28–1.41); from 1.15 (95 CI% = 1.09, 1.21) to 1.90 (95 CI% = 1.81, 2.00); from 0.86 (95 CI% = 0.82, 0.91) to 1.69 (95 CI% = 1.62, 1.77); from 1.62 (95 CI% = 1.54, 1.71) to 1.69 (95 CI% = 1.60, 1.77); from 0.16 (95 CI% = 0.15, 0.18) to 2.70 (95 CI% = 2.57, 2.84); and from 2.53 (95 CI% = 2.38, 2.69) to 3.58 (95 CI% = 3.39, 3.78), respectively, compared to the Q1 concentrations for all air pollutants. (4) Conclusions: During the 15-year follow-up period, we found a significant positive correlation between air pollutant exposure and the risk of tinnitus.
1. Introduction
Due to the accelerating pace of industrialization and urban development in many countries worldwide, the degradation of air quality—particularly as a result of heavy vehicular traffic—has emerged as a pressing public health concern [1,2,3]. The growing number of automobiles, coupled with industrial emissions and inadequate urban planning, has led to elevated levels of airborne pollutants in densely populated regions [4,5]. Numerous studies have documented the detrimental effects of air pollution on human health, linking exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5 and PM10), nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), carbon monoxide (CO), and other pollutants with a broad spectrum of medical conditions. These include systemic inflammation, oxidative stress, and the exacerbation or development of chronic illnesses such as respiratory diseases (e.g., asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease), cardiovascular diseases, cerebrovascular events, and neurodegenerative disorders [6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. Among the range of health outcomes potentially influenced by environmental exposures is tinnitus, a prevalent and often persistent medical condition characterized by the perception of sound in the absence of an external auditory stimulus [14,15]. Tinnitus can manifest as ringing, buzzing, or hissing sensations, and although it may be transient or mild in some individuals, it can be chronic and debilitating in others [16,17]. Several risk factors have been associated with the onset or worsening of tinnitus, including lifestyle behaviors such as obesity, smoking, and alcohol consumption, as well as medical history variables such as head trauma, arthritis, and hypertension [18,19,20,21,22,23]. Despite being more common among older adults, tinnitus can affect individuals of all ages and has been identified as a symptom that significantly disrupts daily functioning and overall well-being [24,25,26]. Though tinnitus only severely affects a subset of those who experience it, its impact on quality of life can be substantial [25]. Affected individuals may report disturbances in emotional and psychological well-being, including symptoms of anxiety and depression, as well as challenges related to sleep, concentration, and communication [27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34]. In many cases, tinnitus necessitates lifestyle adjustments and contributes to a reduction in overall life satisfaction and perceived health [35]. While considerable research has focused on identifying biological, psychological, and environmental contributors to tinnitus, the condition’s multifactorial etiology continues to present challenges for clinicians and researchers alike [36].
Traditionally, air pollution and tinnitus have been treated as distinct public health issues. Air pollution, with its well-established links to mortality and morbidity across organ systems, has prompted global health initiatives aimed at emission reduction and environmental sustainability [37]. Tinnitus, on the other hand, has primarily been approached from an audiological and neurological standpoint. However, emerging evidence suggests that these two seemingly unrelated issues may share underlying mechanisms and health pathways. Recent epidemiological studies have begun to examine the association between exposure to air pollutants and auditory disorders, identifying links to conditions such as sudden sensorineural hearing loss and Meniere’s disease [38,39,40,41,42]. These findings point toward a possible influence of environmental factors—including air quality—on inner ear and neural auditory function [43,44].
Despite these advances, research specifically addressing the relationship between long-term exposure to air pollution and the incidence of tinnitus remains limited. The lack of large-scale, longitudinal data on this topic hinders the ability to draw definitive conclusions or implement evidence-based public health interventions. To address this gap in the literature, we conducted a nationwide retrospective cohort study in Taiwan, leveraging a comprehensive health database to examine whether chronic exposure to ambient air pollutants is associated with an elevated risk of developing tinnitus. This study contributes novel insights into the environmental determinants of tinnitus and can inform future public health policies aimed at mitigating the burden of this condition.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Sources
Two databases were used: the 2005 Longitudinal Generation Tracking Database (LGTD 2005) and the Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Database (TAQMD). The LGTD 2005 included two million residents randomly selected from the original 2005 registry for beneficiaries joining the Taiwan National Health Insurance (NHI) program. The NHI program in Taiwan was launched on 1 March 1995, and provides coverage to more than 23 million residents in Taiwan. Disease coding follows the International Classification of Diseases, Ninth Revision, Tenth Revision, and Clinical Modification (ICD-9-CM and ICD-10-CM). The Taiwan Environmental Protection Administration Executive Yuan established the TAQMD to record daily air pollution concentrations from 74 ambient air quality monitoring stations on Taiwan Island. We combined and stratified the LGTD 2005 and TAQMD by residential areas linked to nearby air quality monitoring stations. The living area of the insured persons was defined based on the treatment sought for acute upper respiratory tract infection (AURTI) (ICD-9-CM code 460; ICD-9-CM code J00). This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Research Ethics Committee of China Medical University Hospital (CMUH109-REC2-031(CR-3)).
2.2. Study Population, Outcome, and Comorbidities
The study cohort was determined according to the residential addresses of insured individuals on 1 January 2005, which served as the index date for the research. We excluded insurants with a history of tinnitus (ICD-9-CM codes: 388.30, 388.31, and 388.32; ICD-10-CM codes: H93.11, H93.12, H93.13, and H93.19) before the index date. The follow-up endpoints included either the date of withdrawal from the NHI program, the onset of tinnitus, or 31 December 2017. For each participant, daily average concentrations of air pollutants were computed from 2003 through the end of the observation period. These concentrations were then divided into four quartile-based levels: SO2 concentration (first quartile [Q1]: <3.64, second quartile [Q2]: 3.64–4.61, third quartile [Q3]: 4.62–5.30, and fourth quartile [Q4]: >5.30 ppb), CO concentration (first quartile [Q1]: <0.49, second quartile [Q2]: 0.50–0.61, third quartile [Q3]: 0.62–0.78, and fourth quartile [Q4]: >0.78 ppm), NO concentration (Q1: <4.15, Q2: 4.15–7.31, Q3: 7.32–10.0, and Q4: >10.0 ppb), NOx concentration (Q1: <21.7, Q2: 21.7–28.1, Q3: 28.2–37.8, and Q4: >37.8 ppb), PM2.5 concentration (Q1: <27.6, Q2: 27.6–29.1, Q3: 29.2–36.3, and Q4: >36.3 μg/m3), and PM10 concentration (Q1: <51.7, Q2: 51.7–55.6, Q3: 55.7–66.4, and Q4: >66.4 μg/m3). We considered sex, age, urbanization level, alcohol abuse or dependence, tobacco abuse or dependence, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), asthma, obesity, osteoporosis, temperature, and humidity as the confounding factors in this study.
2.3. Statistical Analysis
Categorical variables, including sex, urbanization level, comorbidities, and outcome, are expressed as numbers and percentages. Continuous variables, including age, temperature, humidity, and exposure to air pollutants, are presented as means and standard deviations. The incidence rate (IR) of tinnitus (per 1000 person-years) was calculated for different air pollutants. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to calculate hazard ratios for tinnitus in Q2–Q4 concentrations of air pollutants compared with concentrations in Q1. SAS software (version 9.4; SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) was used in this study, and a two-sided p-value of <0.05 was considered significant.
3. Results
A total of 223,544 participants were enrolled in this study (Table 1); 54.4% were female, and the average age was 39.6 ± 15.5 years. The highest level of urbanization (Level 1) accounted for 64.29% of the total. The percentage of participants with COPD, asthma, and osteoporosis were 26,453 (12.39%), 27,949 (13.09%), and 16,604 (7.78%), respectively. The daily average concentrations of SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10 were 4.66 ± 1.67 ppb, 0.68 ± 0.29 ppm, 10.2 ± 11.0 ppb, 32.4 ± 16.9 ppb, 31.7 ± 7.73 µg/m3, and 58.7 ± 12.4 µg/m3, respectively. At the end of the study, 9401 (4.4%) participants had developed tinnitus during the study period. The mean follow-up time was 16.1 ± 2.76 years.

Table 1.
Baseline demographics and air pollutant exposure by yearly average concentration in Taiwan, 2003–2021.
The incidence rates (IRs), crude hazard ratios (cHRs), and 95% confidence intervals of tinnitus for SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10 are presented in Table 2 and stratified into quartiles. The IR of tinnitus increased from Q1 to Q4 for SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10, specifically from 1.93 to 5.29; from 2.13 to 6.19; from 2.13 to 3.4; from 1.77 to 3.62; from 0.65 to 6.46; and from 1.10 to 6.19 per 1000 person-years, respectively.

Table 2.
Incidence rates and crude hazard ratios of tinnitus across quartiles of pollutant levels.
After controlling for age, sex, urbanization level, and comorbidities of alcohol abuse/dependence, tobacco abuse/dependence, COPD, asthma, temperature, and humidity, the adjusted HR (95 CI%) for tinnitus increased with increasing SO2, CO, NO, NOx, PM2.5, and PM10 exposure levels, specifically from 1.25 (95 CI% = 1.17, 1.34) to 2.75 (95 CI% = 2.60–2.91); from 1.11 (95 CI% = 1.044, 1.18) to 3.13 (95 CI% = 2.95, 3.33); from 1.31 (95 CI% = 1.23, 1.39) to 1.76 (95 CI% = 1.66, 1.86); from 1.57 (95 CI% = 1.47, 1.67) to 2.24 (95 CI% = 2.11, 2.39); from 1.29 (95 CI% = 1.17, 1.46) to 9.26 (95 CI% = 8.58, 9.99); and from 0.36 (95 CI% = 0.32, 0.41) to 5.23 (95 CI% = 4.89, 5.58), respectively, compared to the Q1 concentrations for all air pollutants (Table 3).

Table 3.
The risk of tinnitus in patients exposed to various air pollutants stratified by quartile of daily average concentration using Cox proportional hazard regression.
Figure 1 illustrates the positive association between exposure to higher concentrations of SO2, CO, NO, NOX, PM2.5, and PM10 and an increased incidence of tinnitus, relative to lower exposure levels. Across all pollutants examined, elevated ambient air pollution concentrations were consistently associated with an increased risk of tinnitus, suggesting a dose–response relationship.
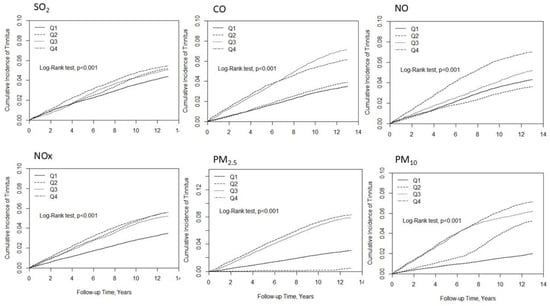
Figure 1.
Kaplan–Meier curves depicting the cumulative incidence of tinnitus over the follow-up period for each quartile of air pollutant exposure.
Pearson coefficients were highest between NOx and NO (r = 0.977) and NOx and CO (r = 0.940), moderate for SO2 with NOx (r = 0.640) and NO (r = 0.581), and strong between PM2.5 and PM10 (r = 0.923), with low correlations between gaseous and particulate pollutants (Table S1). Table S2 show the per-unit exposure–tinnitus associations. After adjustment, each 1 ppb increase in SO2 corresponded to aHR 1.25 (95% CI 1.23–1.26), each 1 ppm CO to aHR 2.25 (2.11–2.39), each 1 ppb NO and NOx to aHR 1.01 (1.008–1.01 and 1.01–1.012, respectively), each 1 µg/m3 PM2.5 to aHR 1.12 (1.11–1.12), and each 1 µg/m3 PM10 to aHR 1.06 (1.05–1.06). In median-stratified subgroup analyses, participants with pollutant levels at or above the median showed significantly higher adjusted tinnitus hazards across demographic and comorbidity strata (Tables S3–S8). In females versus males, aHRs were: SO2 ≥ 4.61 ppb (Table S3): 1.72 (1.63–1.82) vs. 1.44 (1.36–1.54); CO ≥ 0.61 ppm (Table S4): 1.67 (1.58–1.77) vs. 1.54 (1.44–1.64); NO ≥ 7.31 ppb (Table S5): 1.20 (1.14–1.27) vs. 1.13 (1.06–1.20); NOx ≥ 28.1 ppb (Table S6): 1.55 (1.47–1.64) vs. 1.44 (1.36–1.54); PM2.5 ≥ 29.1 µg/m3 (Table S7): 6.89 (6.37–7.46) vs. 6.01 (5.51–6.56); PM10 ≥ 55.6 µg/m3 (Table S8): 5.61 (5.20–6.04) vs. 4.83 (4.45–5.24). Across age, urbanization, and comorbidity subgroups, elevated pollutant exposures conferred 20–150% greater risk for gaseous pollutants and 4–17-fold for particulate matter. Effect sizes were generally larger in younger adults, females, and lower-urbanization areas, and modestly attenuated among participants with baseline respiratory or metabolic conditions.
4. Discussion
Accumulating evidence indicates that air pollution is associated with the incidence of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) [39,40,45,46,47]. However, it is still unclear whether air pollution is associated with the incidence of tinnitus. Tinnitus is defined as the perception of sound without additional external stimuli. It is usually accompanied by different types of SNHL, such as noise-induced and age-related SNHL. In the present study, we further tested the hypothesis of an association between air pollution and tinnitus using two large longitudinal databases to evaluate the risk of tinnitus in Taiwanese residents exposed to air pollution. During the 15-year follow-up period, we enrolled 284,318 residents (13,882 with tinnitus and 270,436 with SNHL) and found a significant positive correlation between air pollutant exposure and the risk of tinnitus.
Tinnitus has been associated with an increased incidence of depression and anxiety [48,49,50]. A previous study enrolled a total of 566 patients with tinnitus to evaluate depression and anxiety symptoms, both of which have been suggested as significant targets for the management of suicidal ideation [48]. Lin et al. also reported a significant association between tinnitus and the risk of depression in the adult population of the United States and suggested that the clinical management of tinnitus requires consideration of psychological factors [49]. Another prospective study evaluating 600 enrolled patients with mild-to-moderate tinnitus also indicated a significant correlation between the degree of SNHL and anxiety/depression scores in these patients [50]. Tinnitus has also been associated with an increased incidence of dementia [51,52,53]. Cheng et al. reported that in the young and middle-aged populations, pre-existing tinnitus increased the risk of developing early-onset dementia by 68%, indicating an urgent need for raising awareness of tinnitus as a potential harbinger for future dementia in these populations [51]. Notably, compared to dementia patients without any history of auditory symptoms, patients with tinnitus or hyperacusis had relatively preserved gray matter in the posterior superior temporal lobe but reduced gray matter in the orbitofrontal cortex and medial geniculate nucleus. Therefore, tinnitus may be a significant risk factor for dementia [53].
The concentrations of pollutants were divided into four quartile-based levels. The adjusted hazard ratio for PM2.5 in the second quartile (0.16; 95% CI: 0.15–0.18) was significantly low and inconsistent with the trends observed in higher quartiles. Several factors may contribute to this outcome. First, our data show that the study population was heavily concentrated near the upper limit of the first quartile (25.49 μg/m3) for PM2.5. As a result, the number of individuals exposed to PM2.5 levels in the second quartile—and who subsequently developed tinnitus—was lower compared to those exposed to other pollutants. Second, PM2.5 may have a threshold effect whereby health risks only begin to increase once exposure exceeds a certain level. However, the use of quartile-based categorization for pollutant exposure is methodologically limiting. Arbitrary cutoffs reduce interpretability, mask dose–response relationships, and limit comparability to established regulatory thresholds.
This cohort study was meticulously designed and featured an extended follow-up duration with adjustments for diverse confounding factors. However, this study had certain limitations. First, the primary constraints of the NHIRD study pertain to the absence of occupational noise exposure, stress, and information on healthy behaviors and dietary habits. The lack of these covariates does create potential bias. However, several studies suggested that urbanization is highly correlated with the above covariates [54,55,56,57,58]; therefore, we consider urbanization as a proxy covariate in multivariate analysis to minimize potential bias. The diagnostic criteria for alcohol abuse/dependence rely on drinking behavior and patient attitudes. Previous NHIRD studies have focused on COPD, asthma, and tobacco abuse/dependence instead of assessing smoking status [12,39,40,59,60,61,62,63]. Therefore, we regarded COPD, asthma, tobacco abuse/dependence, and alcohol abuse/dependence as surrogate variables for assessing smoking status and alcohol consumption. However, the reported prevalence of COPD, asthma, and tobacco abuse/dependence may be affected by underreporting.
Second, there could be surveillance bias at play, potentially linked to the level of urbanization and its association with medical accessibility. This could lead to the varying prevalence rates of tinnitus in urban and rural areas. Notably, the Taiwanese government has implemented a single-payer compulsory social insurance system that encompasses over 99% of residents. This system helps to equalize medical accessibility between urban and rural regions by offering free medical care [64,65]. Third, while indoor air pollutant levels are linked to building characteristics [66], their concentration was not assessable in this nationwide study. However, there is no evidence suggesting variations in building characteristics among locations with different air pollution levels in Taiwan, nor is there any evidence indicating that buildings cannot effectively block outdoor air pollutants [67,68]. Nevertheless, further research is needed to elucidate the influence of indoor air quality. Fourth, due to the Personal Data Protection Act, we are unable to obtain the study participants’ addresses and activity areas from the database. Therefore, the participants’ residential area was determined based on the location of the institution where they sought medical attention for acute upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs), throughout the study period. In the United States, URTIs represent the most prevalent category of infectious diseases, with adults experiencing an estimated three episodes annually [69]. Defining residential areas based on patterns of healthcare utilization, as employed in this study, is considered a more accurate approach than relying on administrative insurance registration data, particularly in evaluating accessibility to medical resources [70]. Furthermore, evidence supports the notion that individuals typically seek care for upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) within or near their residential zones, and that long-distance travel for such care is uncommon [71]. However. individuals without medical records during this period were excluded, and this group tended to reside in regions characterized by low levels of air pollutants. This could lead to an underestimation of the risk of tinnitus. Nevertheless, potential misclassification bias remains. Fifth, although this study featured a long follow-up period, misclassification resulting from tinnitus developing after the study period may have led to an underestimation of tinnitus risk. Finally, the air pollution levels in the residential areas of the NHIRD insurants were evaluated using data from the closest air quality monitoring stations to clinics or hospitals. This methodology may introduce bias into the findings, given that the measured air quality and urbanization levels could diverge from the actual values, especially in cases where participants have lengthy commutes between their homes and medical facilities. Therefore, additional personal air sampling should be conducted to confirm these observations.
5. Conclusions
This is the first nationwide, population-based cohort study investigating the association between air pollution and tinnitus. Our findings suggest that increased exposure to air pollution is associated with a higher risk of tinnitus. Future research should incorporate personal air sampling to validate and further explore these observations.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/atmos16050618/s1, Table S1. Pearson’s Correlation Coefficient among air pollutants; Table S2. The risk of Tinnitus in patients and associated HRs in participants exposed to daily average concentrations of various air pollutants; Table S3. Comparison of incidence and hazard ratio of Tinnitus stratified by gender, age, and comorbidity between SO2 < 4.61 (median) and SO2 ≧ 4.61 (median); Table S4. Comparison of incidence and hazard ratio of Tinnitus stratified by gender, age and comorbidity between CO < 0.61 (median) and CO ≧ 0.61 (median); Table S5. Comparison of incidence and hazard ratio of Tinnitus stratified by gender, age and comorbidity between NO < 7.31 (median) and NO ≧ 7.31 (median); Table S6. Comparison of incidence and hazard ratio of Tinnitus stratified by gender, age and comorbidity between NOx < 28.1 (median) and NOx ≧ 28.1 (median); Table S7. Comparison of incidence and hazard ratio of Tinnitus stratified by gender, age and comorbidity between PM2.5 < 29.1 (median) and PM2.5 ≧ 29.1 (median); Table S8. Comparison of incidence and hazard ratio of Tinnitus stratified by gender, age and comorbidity between PM10 < 55.6 (median) and PM10 ≧ 55.6 (median).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, K.-H.C., P.-Y.L., S.C.-S.T. and Y.-C.H.; methodology, K.-H.C. and C.-L.L.; software, K.-H.C. and C.-L.L.; validation, P.-Y.L., C.-Y.L., K.-H.C., Y.-K.C., Y.-C.H., I.-M.C., S.C.-S.T., D.-Y.C., C.-L.L., T.-H.L. and W.-L.C.; formal analysis, K.-H.C., Y.-K.C. and C.-L.L.; investigation, P.-Y.L., C.-Y.L., K.-H.C., Y.-K.C., Y.-C.H., I.-M.C., S.C.-S.T., D.-Y.C., C.-L.L., T.-H.L. and W.-L.C.; resources, D.-Y.C. and K.-H.C.; data curation, K.-H.C., Y.-K.C., S.C.-S.T. and Y.-C.H.; writing—original draft preparation, K.-H.C., P.-Y.L., S.C.-S.T. and Y.-C.H.; writing—review and editing, K.-H.C.; visualization, all authors; supervision, K.-H.C., P.-Y.L., S.C.-S.T. and Y.-C.H.; project administration, D.-Y.C. and S.C.-S.T.; funding acquisition, D.-Y.C. and S.C.-S.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study is supported in part by Taiwan Ministry of Health and Welfare Clinical Trial Center (MOHW113-TDU-B-212-114009), China Medical University Hospital (DMR-111-105; DMR-112-087; DMR-113-009; DMR-113-156; DMR-114-139), and Tungs’ Taichung Metroharbor Hospital (TTMHH-R1120012/R1130051/R1140020/R1140024/R140025/R140037/R1140083/R1140085).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The NHIRD safeguards patient personal information through encryption to ensure privacy protection and assigns researchers anonymous identification numbers linked to pertinent claims data such as gender, date of birth, medical services, and prescriptions. Consequently, accessing the NHIRD does not necessitate patient consent. This research project received approval for exemption from the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at China Medical University (Approval Number CMUH109-REC2-031(CR-3)), and the IRB explicitly waived the requirement for consent. All procedures adhered to the applicable guidelines and regulations. The requirement for informed consent was waived by the Ethics Committee of the Institutional Review Board (IRB) at China Medical University because of the retrospective nature of the study.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are accessible through the National Health Insurance Research Database (NHIRD) provided by the Taiwan National Health Insurance (NHI) Administration. However, due to the Personal Information Protection Act enforced by the Taiwan government, these data cannot be publicly released. If you wish to obtain these data, you can submit an official request through the NHIRD website at https://dep.mohw.gov.tw/DOS/lp-2506-113.html (accessed on 15 May 2025).
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Health Data Science Center, China Medical University Hospital, for providing administrative, technical, and funding support. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, the decision to publish, or the preparation of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| LGTD | Longitudinal Generation Tracking Database |
| TAQMD | Taiwan Air Quality Monitoring Database |
| IRR | incidence rate ratio |
| aHR | adjusted hazard ratio |
| cHR | crude hazard ratio |
| CI | confidence interval |
| SO2 | sulfur dioxide |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOx | nitrogen oxide |
| PM | particulate matter |
| NHIRD | National Health Insurance Research Database |
| COPD | chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
References
- Chang, K.H.; Hsu, P.Y.; Lin, C.J.; Lin, C.L.; Juo, S.H.; Liang, C.L. Traffic-related air pollutants increase the risk for age-related macular degeneration. J. Investig. Med. 2019, 67, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, F.J.; Fussell, J.C. Air pollution and public health: Emerging hazards and improved understanding of risk. Environ. Geochem. Health 2015, 37, 631–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Jia, Y.; Sun, Z.; Su, J.; Liu, Q.S.; Zhou, Q.; Jiang, G. Environmental pollution, a hidden culprit for health issues. Eco-Environ. Health 2022, 1, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piracha, A.; Chaudhary, M.T. Urban air pollution, urban heat island and human health: A review of the literature. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, S.; Ahmed, S.; Kaur-Sidhu, M.; Mor, S.; Ravindra, K. Health risks of major air pollutants, their drivers and mitigation strategies: A review. Air Soil Water Res. 2023, 16, 11786221231154659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, Z.J.; Kristiansen, L.C.; Andersen, K.K.; Olsen, T.S.; Hvidberg, M.; Jensen, S.S.; Ketzel, M.; Loft, S.; Sorensen, M.; Tjonneland, A.; et al. Stroke and long-term exposure to outdoor air pollution from nitrogen dioxide: A cohort study. Stroke 2012, 43, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisabeth, L.D.; Escobar, J.D.; Dvonch, J.T.; Sanchez, B.N.; Majersik, J.J.; Brown, D.L.; Smith, M.A.; Morgenstern, L.B. Ambient air pollution and risk for ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Ann. Neurol. 2008, 64, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oftedal, B.; Brunekreef, B.; Nystad, W.; Madsen, C.; Walker, S.E.; Nafstad, P. Residential outdoor air pollution and lung function in schoolchildren. Epidemiology 2008, 19, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turin, T.C.; Kita, Y.; Rumana, N.; Nakamura, Y.; Ueda, K.; Takashima, N.; Sugihara, H.; Morita, Y.; Ichikawa, M.; Hirose, K.; et al. Ambient air pollutants and acute case-fatality of cerebro-cardiovascular events: Takashima Stroke and AMI Registry, Japan (1988–2004). Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2012, 34, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahebari, M.; Esmailpour, M.; Esmaili, H.; Orooji, A.; Dowlatabadi, Y.; Nabavi Mahali, S.; Rajabi, E.; Salari, M. Influence of Air Pollutants on the Disease Activity and Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis, an Iranian Observational Longitudinal Study. Med. J. Islam. Repub. Iran. 2023, 37, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fang, X.Y.; Wu, J.; Fan, Y.G.; Leng, R.X.; Liu, B.; Lv, X.J.; Yan, Y.L.; Mao, C.; Ye, D.Q. Association of Combined Exposure to Ambient Air Pollutants, Genetic Risk, and Incident Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Prospective Cohort Study in the UK Biobank. Environ. Health Perspect. 2023, 131, 37008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.H.; Hsu, C.C.; Muo, C.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Liu, H.C.; Kao, C.H.; Chen, C.Y.; Chang, M.Y.; Hsu, Y.C. Air pollution exposure increases the risk of rheumatoid arthritis: A longitudinal and nationwide study. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Shim, J.Y.; Park, B.; Lee, Y.J. Long-term exposure to air pollution and the risk of non-lung cancer: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Perspect. Public Health 2020, 140, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krog, N.H.; Engdahl, B.; Tambs, K. The association between tinnitus and mental health in a general population sample: Results from the HUNT Study. J. Psychosom. Res. 2010, 69, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molaug, I.; Aarhus, L.; Mehlum, I.S.; Stokholm, Z.A.; Kolstad, H.A.; Engdahl, B. Occupational noise exposure and tinnitus: The HUNT Study. Int. J. Audiol. 2024, 63, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usmonov, S.; Usmonov, E. Tinnitus: Clinical, Pathological And Treatment Aspects. Frontline Med. Sci. Pharm. J. 2025, 5, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swain, S.K. Impact of tinnitus on quality of life: A review. Int. J. Adv. Med. 2021, 8, 1006–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallus, S.; Lugo, A.; Garavello, W.; Bosetti, C.; Santoro, E.; Colombo, P.; Perin, P.; La Vecchia, C.; Langguth, B. Prevalence and Determinants of Tinnitus in the Italian Adult Population. Neuroepidemiology 2015, 45, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veile, A.; Zimmermann, H.; Lorenz, E.; Becher, H. Is smoking a risk factor for tinnitus? A systematic review, meta-analysis and estimation of the population attributable risk in Germany. BMJ Open 2018, 8, e016589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shargorodsky, J.; Curhan, G.C.; Farwell, W.R. Prevalence and Characteristics of Tinnitus among US Adults. Am. J. Med. 2010, 123, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Lee, H.J.; An, S.Y.; Sim, S.; Park, B.; Kim, S.W.; Lee, J.S.; Hong, S.K.; Choi, H.G. Analysis of the prevalence and associated risk factors of tinnitus in adults. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, R.; Lugo, A.; Genitsaridi, E.; Trpchevska, N.; Akeroyd, M.A.; Cederroth, C.R.; Liu, X.; Schlee, W.; Garavello, W.; Gallus, S.; et al. Chapter 1—Modifiable lifestyle-related risk factors for tinnitus in the general population: An overview of smoking, alcohol, body mass index and caffeine intake. In Progress in Brain Research; Langguth, B., Kleinjung, T., Ridder, D.D., Schlee, W., Vanneste, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; Volume 263, pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Stephens, D. Detrimental effects of alcohol on tinnitus. Clin. Otolaryngol. Allied Sci. 1999, 24, 114–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandsson, S.I.; Hallberg, L.R. Prediction of quality of life in patients with tinnitus. Br. J. Audiol. 2000, 34, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, V.; Wilson, C.; Stephens, D. Quality of life and tinnitus. Hear. Balance Commun. 2004, 2, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cima, R.F.; Crombez, G.; Vlaeyen, J.W. Catastrophizing and fear of tinnitus predict quality of life in patients with chronic tinnitus. Ear Hear. 2011, 32, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, P.; Marcelos, C.; Mezzasalma, M.; Osterne, F.; De Lima, M.D.M.T.; Nardi, A. Tinnitus and its association with psychiatric disorders: Systematic review. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2014, 128, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hébert, S.; Mazurek, B.; Szczepek, A.J. Stress-related psychological disorders and tinnitus. In Tinnitus and Stress: An Interdisciplinary Companion for Healthcare Professionals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017; pp. 37–51. [Google Scholar]
- Trevis, K.J.; McLachlan, N.M.; Wilson, S.J. Cognitive mechanisms in chronic tinnitus: Psychological markers of a failure to switch attention. Front. Psychol. 2016, 7, 1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, S.; Padgham, N.D. More than ringing in the ears: A review of tinnitus and its psychosocial impact. J. Clin. Nurs. 2009, 18, 2927–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alster, J.; Shemesh, Z.; Ornan, M.; Attias, J. Sleep disturbance associated with chronic tinnitus. Biol. Psychiatry 1993, 34, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallam, R. Correlates of sleep disturbance in chronic distressing tinnitus. Scand. Audiol. 1996, 25, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazell, J.; Jastreboff, P.; Tinnitus, I. Auditory mechanisms: A model for tinnitus and hearing impairment. J. Otolaryngol. 1990, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Jastreboff, P.J. Phantom auditory perception (tinnitus): Mechanisms of generation and perception. Neurosci. Res. 1990, 8, 221–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadhwa, S.; Jain, S.; Patil, N. The role of diet and lifestyle in the tinnitus management: A comprehensive review. Cureus 2024, 16, e59344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoes, J.P.; Daoud, E.; Shabbir, M.; Amanat, S.; Assouly, K.; Biswas, R.; Casolani, C.; Dode, A.; Enzler, F.; Jacquemin, L. Multidisciplinary tinnitus research: Challenges and future directions from the perspective of early stage researchers. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 647285. [Google Scholar]
- Amann, M.; Kiesewetter, G.; Schöpp, W.; Klimont, Z.; Winiwarter, W.; Cofala, J.; Rafaj, P.; Höglund-Isaksson, L.; Gomez-Sabriana, A.; Heyes, C. Reducing global air pollution: The scope for further policy interventions. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. A 2020, 378, 20190331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.G.; Lee, C.H.; Yoo, D.M.; Min, C.; Park, B.; Kim, S.Y. Effects of short- and long-term exposure to air pollution and meteorological factors on Meniere’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.C.; Hsu, Y.C.; Lai, J.N.; Chou, R.H.; Fan, H.C.; Lin, F.C.; Zhang, R.; Lin, C.L.; Chang, K.H. Long-term exposure to air pollution and the risk of developing sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.-H.; Tsai, S.C.-S.; Lee, C.-Y.; Chou, R.-H.; Fan, H.-C.; Lin, F.C.-F.; Lin, C.-L.; Hsu, Y.-C. Increased risk of sensorineural hearing loss as a result of exposure to air pollution. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, M.J.; Park, S.K.; Kim, S.-Y.; Choi, Y.-H. Long-term exposure to ambient air pollutants and hearing loss in Korean adults. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 820, 153124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.M.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, D.J.; Uhm, T.W.; Yi, S.B.; Han, J.H.; Lee, I.W. Effects of meteorological factor and air pollution on sudden sensorineural hearing loss using the health claims data in Busan, Republic of Korea. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2019, 40, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gohari, N.; Dastgerdi, Z.H.; Mellati, A.; Emami, S.F. Air pollution and the auditory system at risk: A narrative review. Audit. Vestib. Res. 2025, 34, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Kulesza, R.J.; Mansour, Y.; Aiello-Mora, M.; Mukherjee, P.S.; González-González, L.O. Increased gain in the auditory pathway, Alzheimer’s disease continuum, and air pollution: Peripheral and central auditory system dysfunction evolves across pediatric and adult urbanites. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2019, 70, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Whitsel, E.; Avery, C.; Hughes, T.M.; Griswold, M.E.; Sedaghat, S.; Gottesman, R.F.; Mosley, T.H.; Heiss, G.; Lutsey, P.L. Variation in Population Attributable Fraction of Dementia Associated With Potentially Modifiable Risk Factors by Race and Ethnicity in the US. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2219672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Cao, L.; Lv, P.; Bai, S. Associations between household solid fuel use and hearing loss in a Chinese population: A population-based prospective cohort study. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 236, 113506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjdoost, F.; Ghaffari, M.E.; Azimi, F.; Mohammadi, A.; Fouladi-Fard, R.; Fiore, M. Association between air pollution and sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Environ. Res. 2023, 239, 117392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Ren, L.; Xue, X.; Yu, N.; Liu, P.; Shen, W.; Zhou, H.; Wang, B.; Zhou, J.; Yang, S.; et al. The Comorbidity of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Tinnitus Sufferers: A Network Analysis. Brain Sci. 2023, 13, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Wei, Y.; Lin, J.; Chen, C.; Lin, W.; Xu, Y. Association between depression and tinnitus in US adults: A nationally representative sample. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2023, 8, 1365–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Du, H.; You, H. Correlation between the Degree of Hearing Loss and the Levels of Anxiety and Depression in Patients with Tinnitus. Noise Health 2023, 25, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.F.; Xirasagar, S.; Yang, T.H.; Wu, C.S.; Kao, Y.W.; Lin, H.C. Risk of early-onset dementia among persons with tinnitus: A retrospective case-control study. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, Z.; Kolb, B.E.; Mohajerani, M.H. Age-related hearing loss and tinnitus, dementia risk, and auditory amplification outcomes. Ageing Res. Rev. 2019, 56, 100963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahoney, C.J.; Rohrer, J.D.; Goll, J.C.; Fox, N.C.; Rossor, M.N.; Warren, J.D. Structural neuroanatomy of tinnitus and hyperacusis in semantic dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2011, 82, 1274–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dale, L.M.; Goudreau, S.; Perron, S.; Ragettli, M.S.; Hatzopoulou, M.; Smargiassi, A. Socioeconomic status and environmental noise exposure in Montreal, Canada. BMC Public Health 2015, 15, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mucci, N.; Traversini, V.; Lorini, C.; De Sio, S.; Galea, R.P.; Bonaccorsi, G.; Arcangeli, G. Urban Noise and Psychological Distress: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 6621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochnik, D.; Buława, B.; Nagel, P.; Gachowski, M.; Budziński, M. Urbanization, loneliness and mental health model—A cross-sectional network analysis with a representative sample. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 24974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, A.; Shukla, S.P.; Shukla, A.K.; Manar, M.K.; Singh, S.K.; Mehrotra, M. A Comprehensive Review of Auditory and Non-Auditory Effects of Noise on Human Health. Noise Health 2024, 26, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Hubbard, R.A.; Himes, B.E. Neighborhood-level measures of socioeconomic status are more correlated with individual-level measures in urban areas compared with less urban areas. Ann. Epidemiol. 2020, 43, 37–43.e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, K.H.; Teng, C.J.; Hsu, Y.C.; Tsai, S.C.; Lin, H.J.; Hsieh, T.L.; Muo, C.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chou, R.H. Long-Term Exposure to Air Pollution Associates the Risk of Benign Brain Tumor: A Nationwide, Population-Based, Cohort Study in Taiwan. Toxics 2022, 10, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Hsieh, T.L.; Tsai, F.J.; Chang, K.H. Long-term exposure to air pollution and risk of Sarcopenia in adult residents of Taiwan: A nationwide retrospective cohort study. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 2172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.W.; Lin, H.J.; Tsai, S.C.; Lin, C.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Hsieh, T.L.; Chen, C.M.; Chang, K.H. Exposure to Air Pollutants Increases the Risk of Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Taiwan Residents. Toxics 2022, 10, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.C.; Chen, C.M.; Tsai, J.D.; Chiang, K.L.; Tsai, S.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Lin, C.L.; Hsu, C.Y.; Chang, K.H. Association between Exposure to Particulate Matter Air Pollution during Early Childhood and Risk of Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Taiwan. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 16138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, H.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Hsu, Y.C.; Chou, R.H.; Teng, C.J.; Chiu, C.H.; Hsu, C.Y.; Muo, C.H.; Chang, M.Y.; Chang, K.H. Increased risk of incident nasopharyngeal carcinoma with exposure to air pollution. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0204568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, N.; Yip, W.; Chang, H.J.; Chou, Y.J. Trends in rural and urban differentials in incidence rates for ruptured appendicitis under the National Health Insurance in Taiwan. Public Health 2006, 120, 1055–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siroux, V.; Pin, I.; Oryszczyn, M.P.; Le Moual, N.; Kauffmann, F. Relationships of active smoking to asthma and asthma severity in the EGEA study. Epidemiological study on the Genetics and Environment of Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2000, 15, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langer, S.; Bekö, G. Indoor air quality in the Swedish housing stock and its dependence on building characteristics. Build. Environ. 2013, 69, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blondeau, P.; Iordache, V.; Poupard, O.; Genin, D.; Allard, F. Relationship between outdoor and indoor air quality in eight French schools. Indoor Air 2005, 15, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boomhower, S.R.; Long, C.M.; Li, W.; Manidis, T.D.; Bhatia, A.; Goodman, J.E. A review and analysis of personal and ambient PM2.5 measurements: Implications for epidemiology studies. Environ. Res. 2022, 204, 112019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibaldi, R.A. Epidemiology of community-acquired respiratory tract infections in adults: Incidence, etiology, and impact. Am. J. Med. 1985, 78, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.; Chang, R. Geographical Analysis of ESRD Incidence and Environment. Master’s Thesis, Graduate Institute of Health Care Organization Administration, National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan, 2010. (In Chinese with English Abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Dong, X.; Zhou, R.; Shen, X.; Feng, R.; Cheng, J.; Chai, J.; Kadetz, P.; Wang, D. Health service utilization following symptomatic respiratory tract infections and influencing factors among urban and rural residents in Anhui, China. Prim. Health Care Res. Dev. 2019, 20, e150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).