Construction of a NOx Emission Prediction Model for Hybrid Electric Buses Based on Two-Layer Stacking Ensemble Learning
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Calculation of Related Supplementary Parameters
2.3. Data Preprocessing
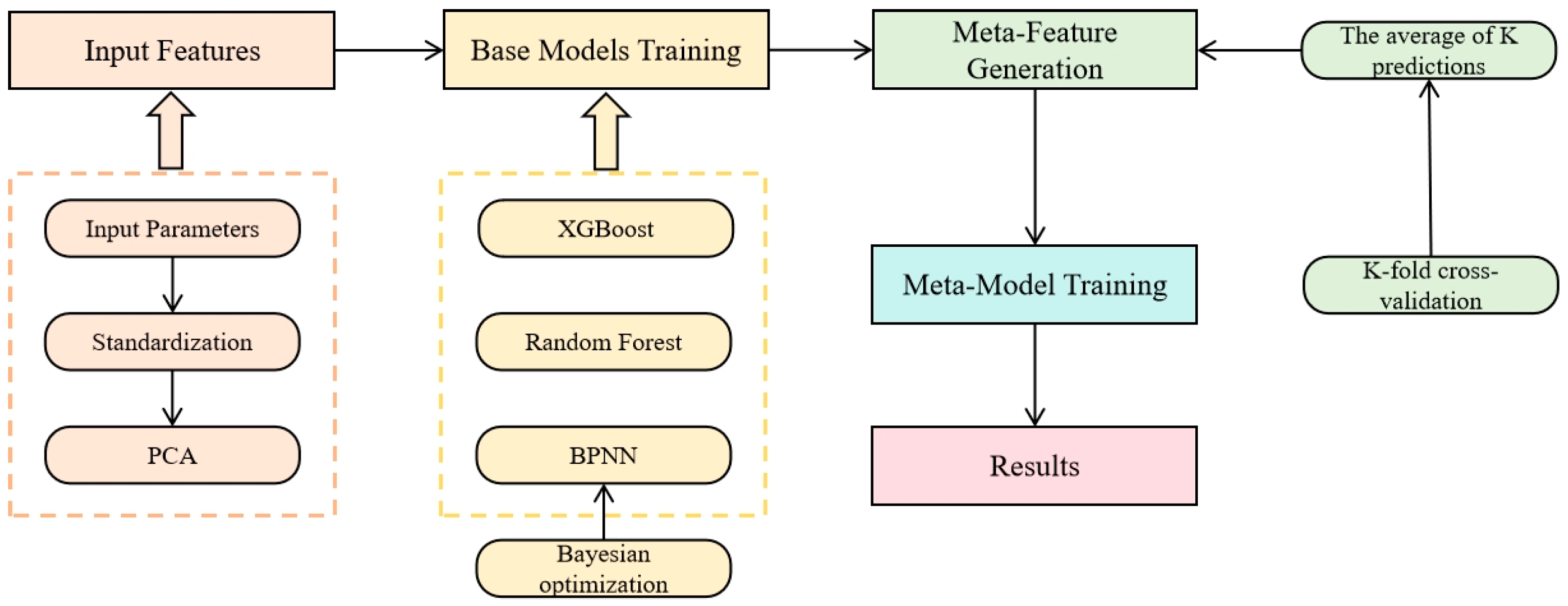
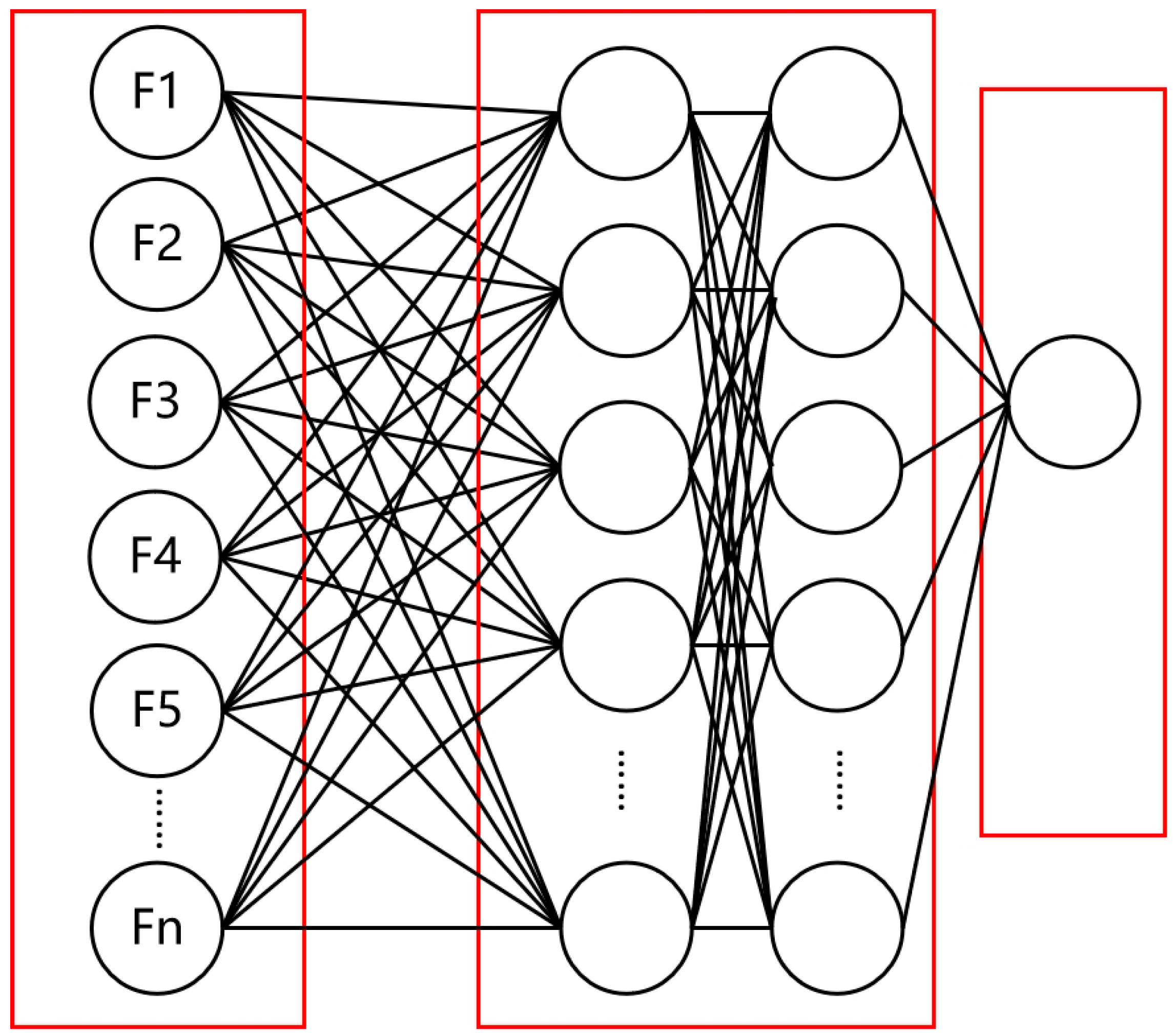
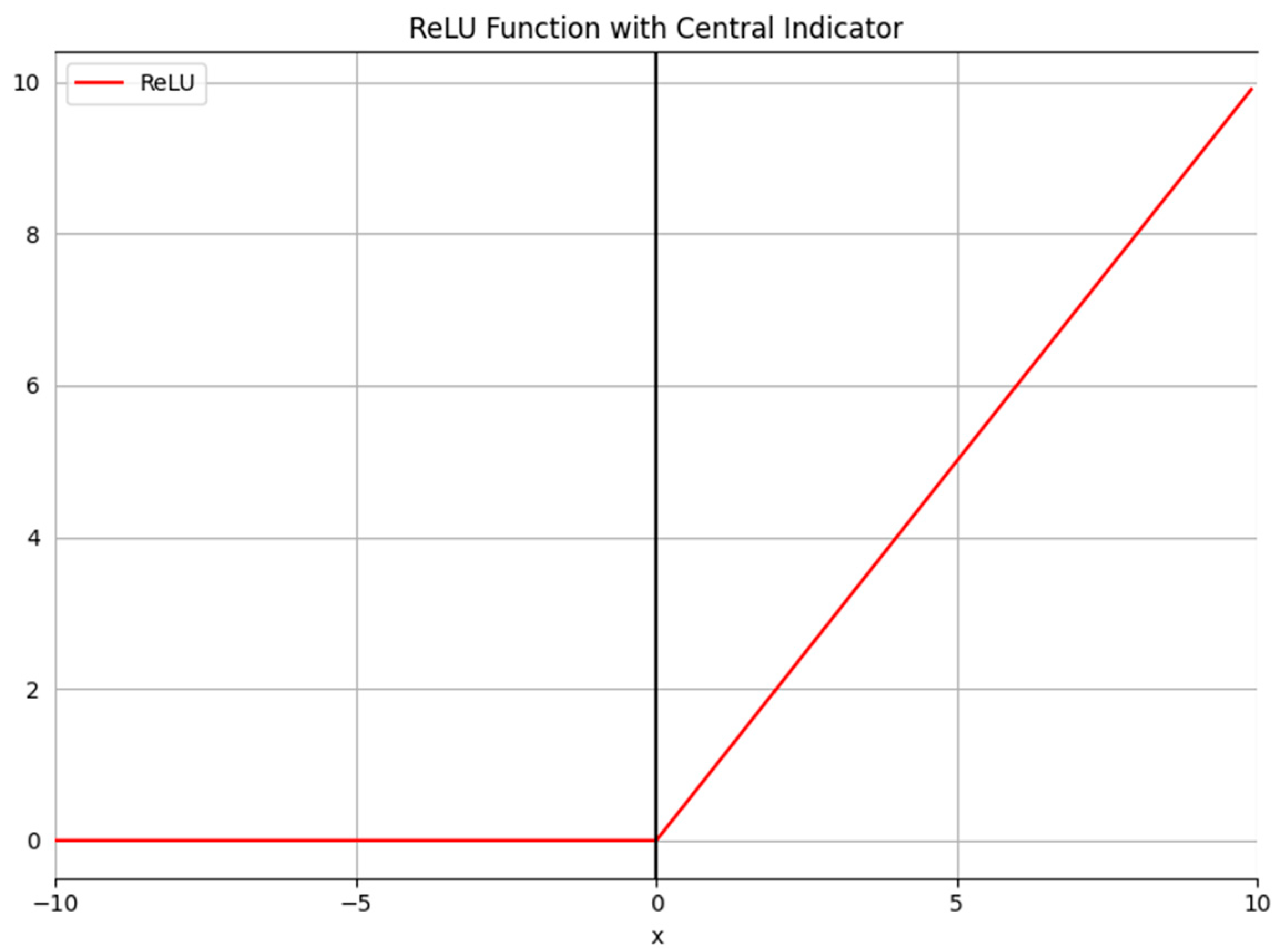
2.4. Two-Layer Stacking Ensemble Learning Model
2.5. Model Evaluation Methods
3. Results and Discussions
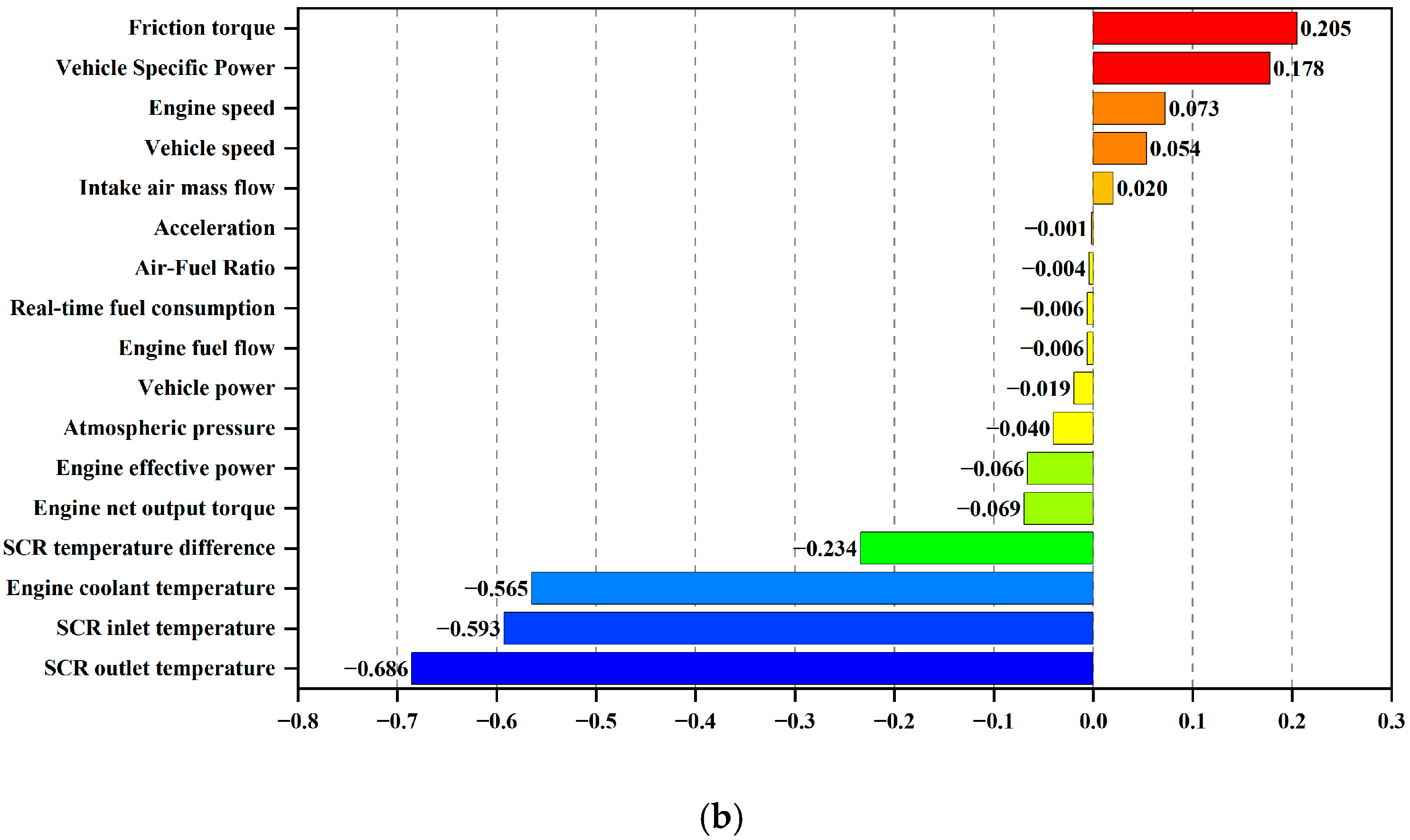
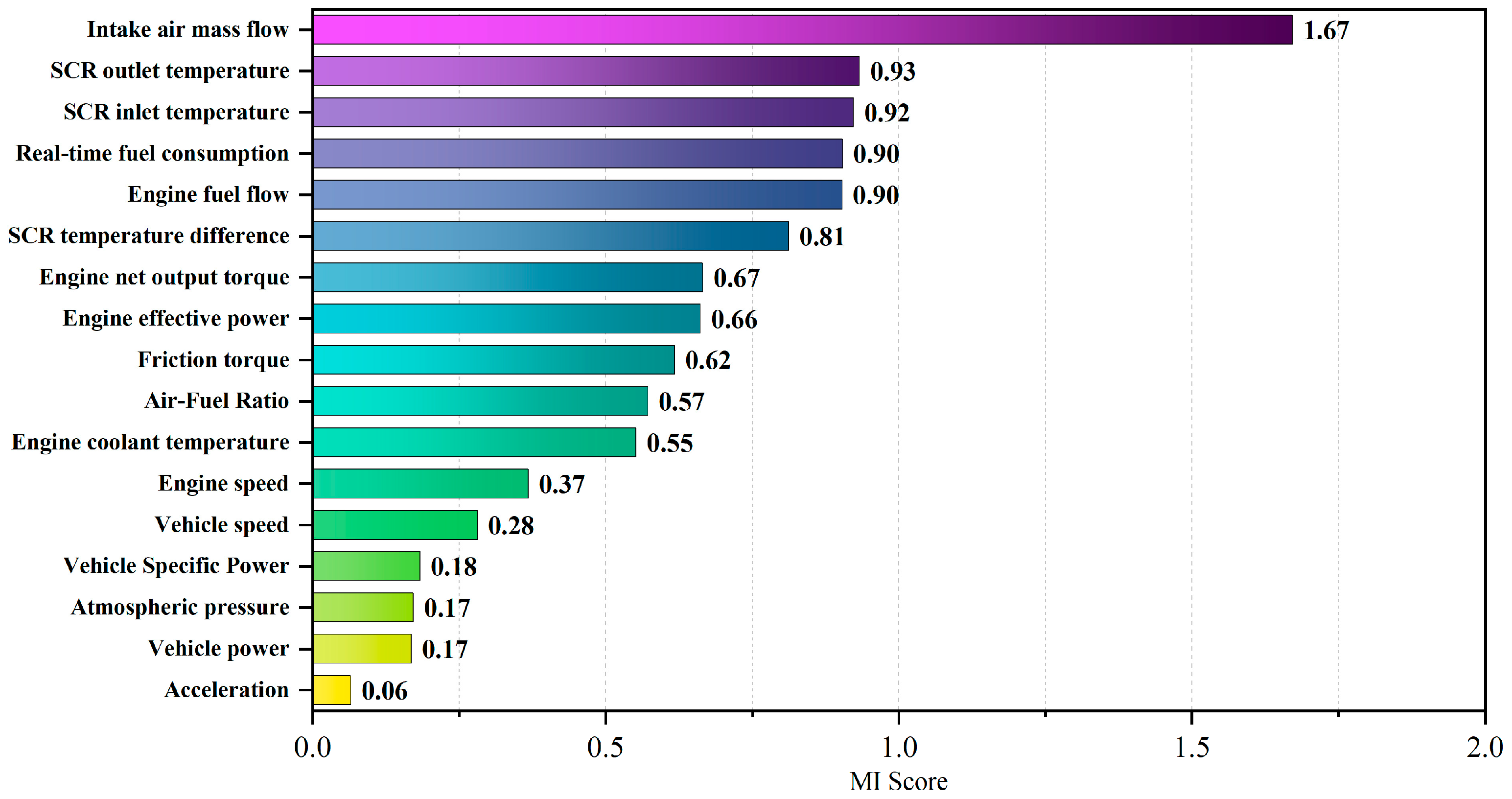
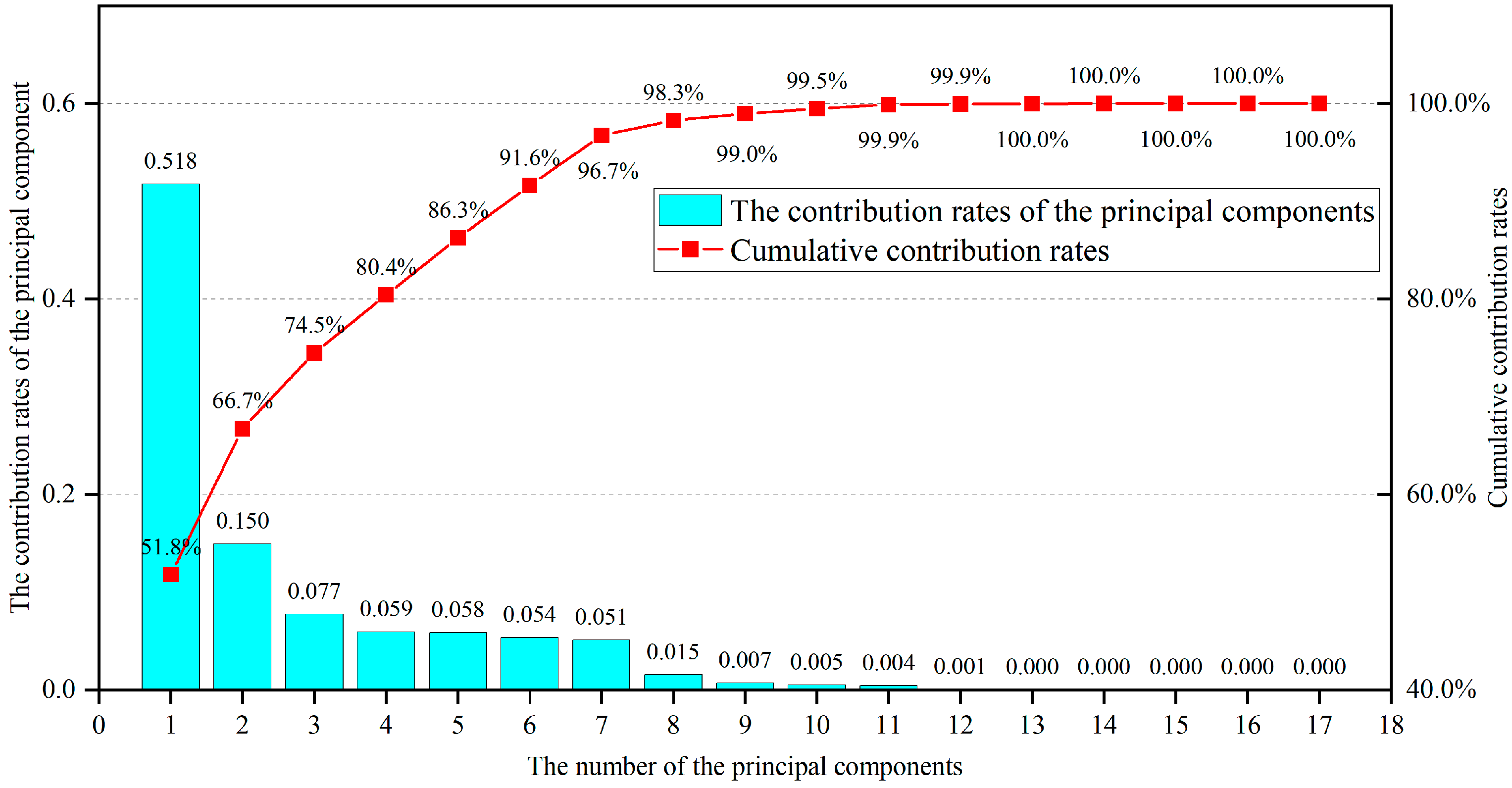
3.1. Input Feature Analysis
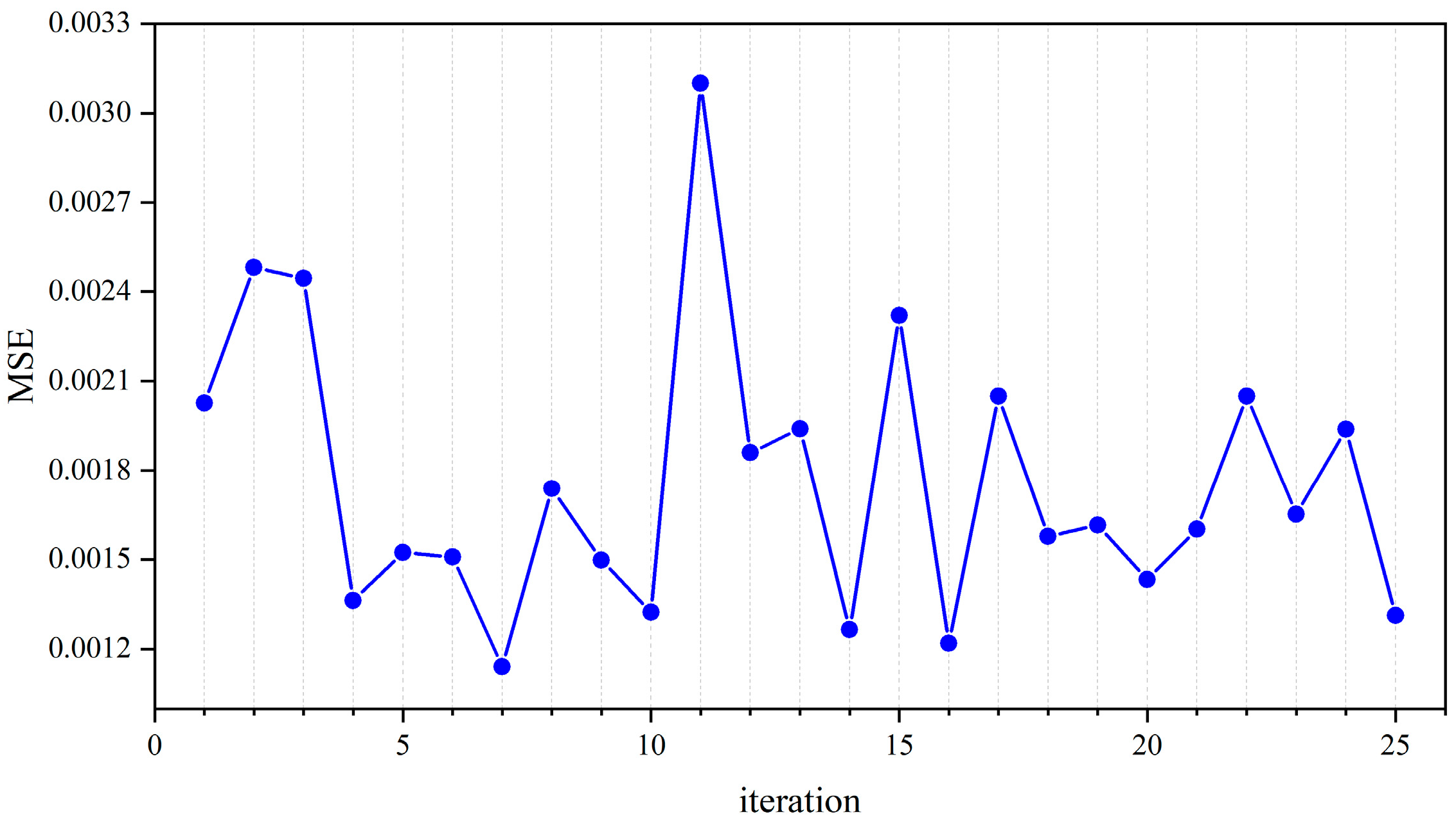
3.2. Model Optimization Results
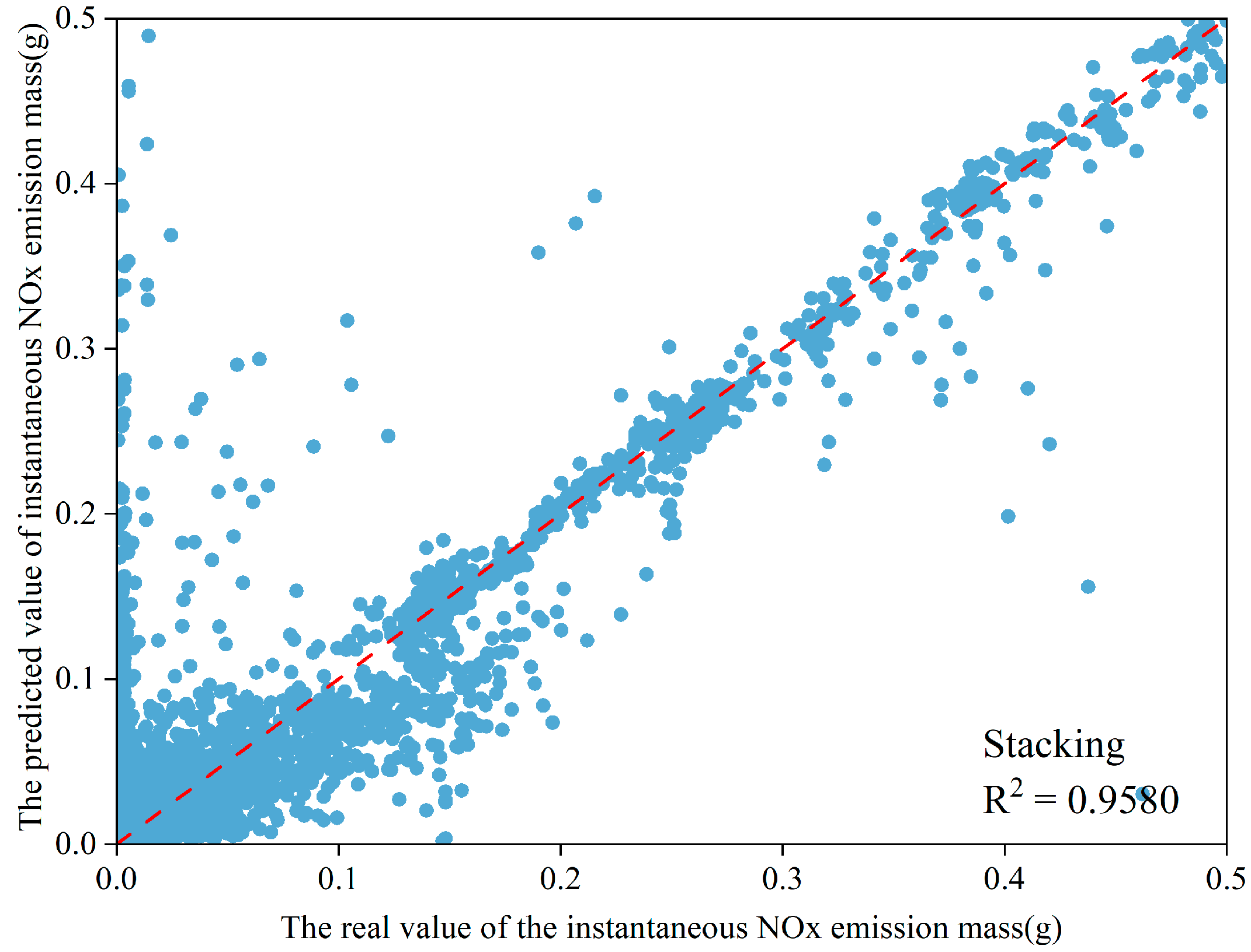
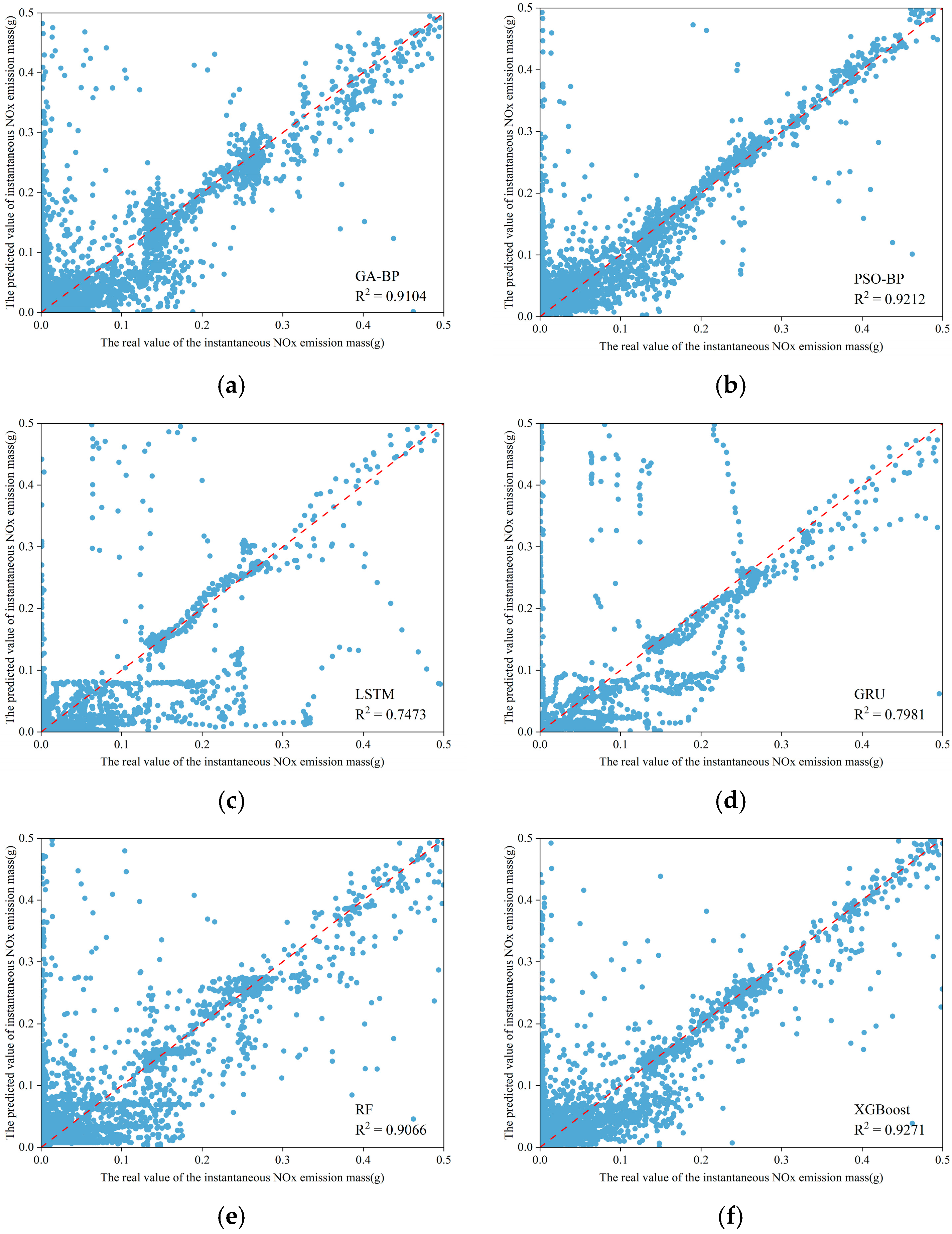
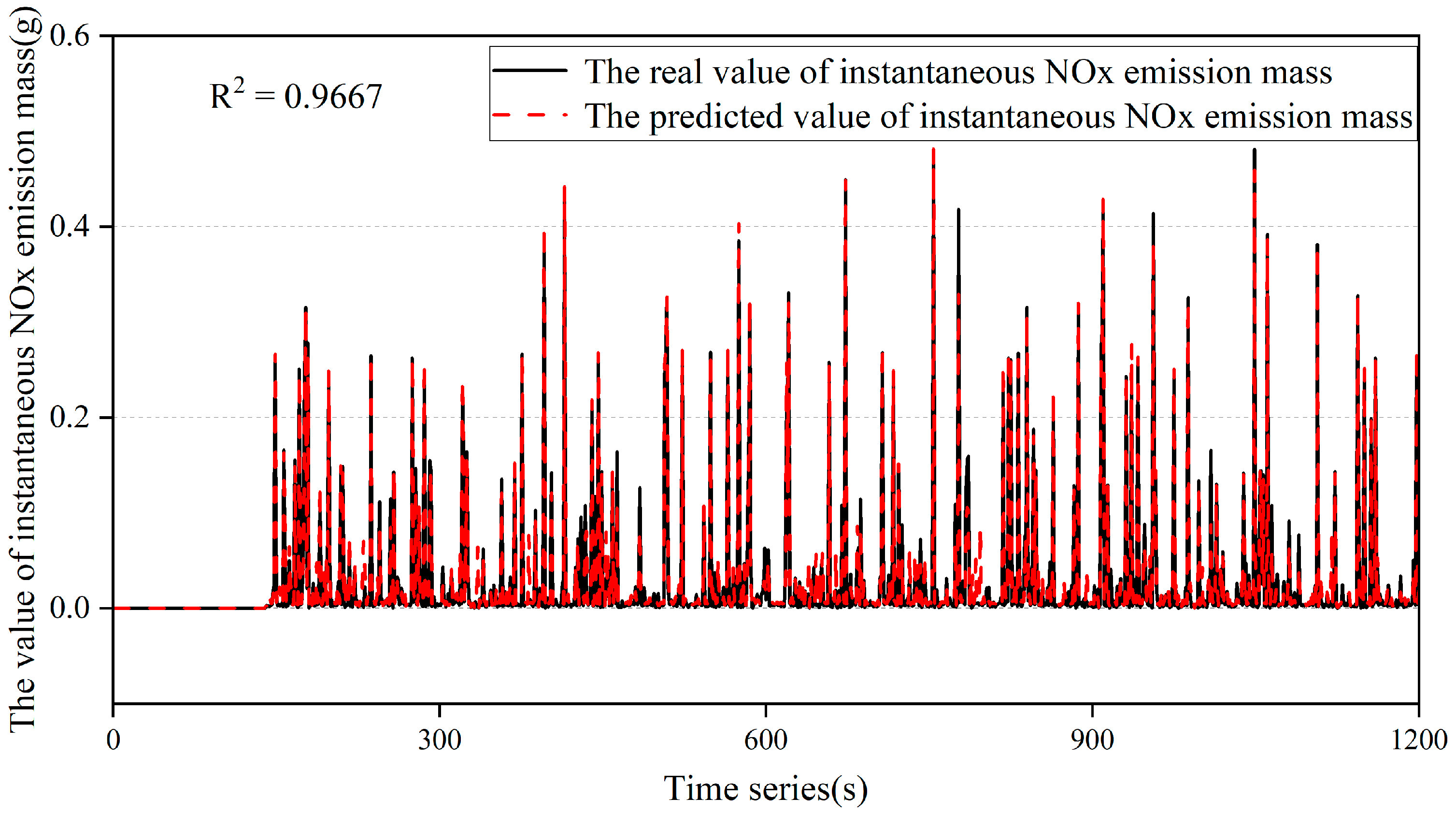
3.3. Model Prediction Results Comparison and Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ANN | artificial neural network |
| BPNN | Back Propagation Neural Network |
| CO | carbon monoxide |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| GA | Genetic Algorithm |
| GBDT | Gradient Boosting Decision Tree |
| GRU | Gated Recurrent Unit |
| LightGBM | Light Gradient Boosting Machine |
| LSTM | Long Short-Term Memory |
| MAE | mean absolute error |
| MI | Mutual Information |
| MSE | mean square error |
| NOx | nitrogen oxides |
| OBD | on-board diagnostic |
| PCA | principal component analysis |
| PEMS | portable emission measurement system |
| PM | particulate matter |
| PSO | Particle Swarm Optimization |
| R2 | coefficient of determination |
| RF | Random Forest |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| RNN | recurrent neural network |
| SCR | selective catalytic reduction |
| XGBoost | eXtreme Gradient Boosting |
References
- Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China. China Mobile Source Environmental Management Annual Report 2023; Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2023. (In Chinese)
- Zhang, S.; Zhao, P.; He, L.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; He, W.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, S.; Hu, Q.; et al. On-board monitoring (OBM) for heavy-duty vehicle emissions in China: Regulations, early-stage evaluation and policy recommendations. Sci. Total. Environ. 2020, 731, 139045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; He, L.; He, W.; Zhao, P.; Wang, P.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, S. Evaluating on-board sensing-based nitrogen oxides (NOX) emissions from a heavy-duty diesel truck in China. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 216, 116908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Yin, H.; Wang, Y.; Wang, H.; He, C.; Liang, J.; He, D.; Yin, H.; He, K. Assessing heavy-duty vehicles (HDVs) on-road NOx emission in China from on-board diagnostics (OBD) remote report data. Sci. Total. Environ. 2022, 846, 1572099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Shi, K.; Qin, H.; Xu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Yin, J.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, Q.; et al. A comprehensive OBD data analysis framework: Identification and factor analysis of high-emission heavy-duty vehicles. Environ. Pollut. 2025, 368, 125751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, P.; Cheng, X.; Yang, S.; Ruan, E.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, C. Artificial neural network models for forecasting the combustion and emission characteristics of ethanol/gasoline DFSI engines with combined injection strategy. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 54, 104007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seetharaman, S.; Suresh, S.; Shivaranjani, R.; Dhamodaran, G.; Js, F.J.; Alharbi, S.A.; Pugazhendhi, A.; Varuvel, E.G. Prediction, optimization, and validation of the combustion effects of diisopropyl ether-gasoline blends: A combined application of artificial neural network and response surface methodology. Energy 2024, 305, 132185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odufuwa, O.Y.; Tartibu, L.K.; Kusakana, K. Artificial Neural Network Modelling for Predicting Efficiency and Emissions in Mini-Diesel Engines: Key Performance Indicators and Environmental Impact Analysis. Fuel 2025, 387, 134294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mohan, I.; Lata, D.B. Modelling to Predict Performance and Emission Parameters of Hydrogen, Additive and Nano-Particles Blended Fuel in a Dual-Fuel Diesel Engine through Artificial Neural Network. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 80, 599–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, A.R.d.S.; Franco, D.G.d.B.; Junior, J.C.Z.; Spada, A.B.D. Artificial intelligence applied to truck emissions reduction: A novel emissions calculation model. Transp. Res. Part D Transp. Environ. 2024, 138, 104533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machavaram, R. Optimizing energy expenditure in agricultural autonomous ground vehicles through a GPU-accelerated particle swarm optimization-artificial neural network framework. Clean. Energy Syst. 2024, 9, 100130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.; Park, S. Optimizing model parameters of artificial neural networks to predict vehicle emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2022, 294, 119508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Hua, L.; Pan, J.; Xiao, Y. Prediction of cold start emissions for hybrid electric vehicles based on genetic algorithms and neural networks. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 420, 138403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.-T.; Lu, J.-H.; Jhang, D.-S. Features Importance Analysis of Diesel Vehicles’ NOx and CO2 Emission Predictions in Real Road Driving Based on Gradient Boosting Regression Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 13044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, K.; Yu, H.; Feng, K.; Ding, H. NOx Emission prediction of heavy-duty diesel vehicles based on Bayesian optimization -Gated Recurrent Unit algorithm. Energy 2024, 292, 130559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Awad, O.I.; Liu, S.; Shuai, S.; Wang, Z. NOx emissions prediction based on mutual information and back propagation neural network using correlation quantitative analysis. Energy 2020, 198, 117286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, N.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J.; Chang, J.; Yang, Z.; Ma, C.; Jia, Z.; Ren, C.; Wu, L.; et al. Super-learner model realizes the transient prediction of CO2 and NOx of diesel trucks: Model development, evaluation and interpretation. Environ. Int. 2022, 158, 106977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chang, H.; Wen, Z.; Ge, Y.; Hao, L.; Wang, X.; Tan, J. Prediction of Real Driving Emission of Light Vehicles in China VI Based on GA-BP Algorithm. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; He, C. Prediction of Transient NOx Emission from Diesel Vehicles Based on Deep-Learning Differentiation Model with Double Noise Reduction. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arsie, I.; Cricchio, A.; De Cesare, M.; Lazzarini, F.; Pianese, C.; Sorrentino, M. Neural network models for virtual sensing of NOx emissions in automotive diesel engines with least square-based adaptation. Control. Eng. Pract. 2017, 61, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HJ857-2017; Measurement Method and Technical Specification for PEMS Test of Exhaust Pollutants from Heavy-Duty Diesel and Gas Fuelled Vehicles. Ministry of Ecological Environment: Beijing, China, 2017. (In Chinese)
- Maino, C.; Misul, D.; Di Mauro, A.; Spessa, E. A deep neural network based model for the prediction of hybrid electric vehicles carbon dioxide emissions. Energy AI 2021, 5, 100073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshua, R.K.A.; Subramanian, K. Comparative performance and emission analysis of internal combustion engine and battery electric vehicle under modified Indian drive cycle. Process. Saf. Environ. Prot. 2024, 190, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Niu, T.; Huang, X.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Y.; Hao, J. Evaluating real-world CO2 and NOX emissions for public transit buses using a remote wireless on-board diagnostic (OBD) approach. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 218, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J. Principles of Automotive Engines; China Machine Press: Beijing, China, 2013; 16p. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Luo, Y.; Deng, X.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, M.; Grieneisen, M.L.; Di, B. Satellite-Based Estimates of Daily NO2 Exposure in China Using Hybrid Random Forest and Spatiotemporal Kriging Model. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 4180–4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Hu, J.; Yan, F.; Turkson, R.F.; Lin, F. A novel optimal support vector machine ensemble model for NOX emissions prediction of a diesel engine. Measurement 2016, 92, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameter Name | Specification |
|---|---|
| Traveling range | urban |
| Type of fuel | diesel-electric |
| Emission standard | China VI |
| Powertrain | Series |
| Rated engine speed (rpm) | 2300 |
| Maximum engine torque (N·m) | 700 |
| Rated engine power (kW) | 140 |
| Vehicle weights (kg) | 18,000 |
| Windward area (m2) | 8.16 |
| Battery capacity (kW·h) | 86.44 |
| Index | Input Features | Unit | Abbreviations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Vehicle speed | km/h | v |
| 2 | Atmospheric pressure | kPa | Patm |
| 3 | Engine net output torque | N·m | Ttq |
| 4 | Friction torque | N·m | Tfric |
| 5 | Engine speed | rpm | N |
| 6 | Engine fuel flow | L/h | Ffuel |
| 7 | Intake air mass flow | kg/h | Fair |
| 8 | SCR inlet temperature | °C | TSCR-in |
| 9 | SCR outlet temperature | °C | TSCR-out |
| 10 | Engine coolant temperature | °C | Tcool |
| 11 | Acceleration | m/s2 | a |
| 12 | Real-time fuel consumption | L/s | FC |
| 13 | Air-to-Fuel Ratio | / | AFR |
| 14 | Vehicle power | kW | Pe |
| 15 | Vehicle Specific Power | kW/t | VSP |
| 16 | Engine effective power | kW | Pme |
| 17 | SCR temperature difference | °C | ΔTSCR |
| Optimization Parameters | Search Range | Optimized Values |
|---|---|---|
| Batch size | 16~128 | 106 |
| Units of Hidden Layer 1 | 32~256 | 105 |
| Units of Hidden Layer 2 | 16~128 | 67 |
| Learning rate | 0.0001~0.01 | 0.0019 |
| Model | MAE | RMSE | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| GA-BP | 0.0132 | 0.0359 | 0.9104 |
| PSO-BP | 0.0093 | 0.0577 | 0.9212 |
| LSTM | 0.0128 | 0.0577 | 0.7473 |
| GRU | 0.0126 | 0.0516 | 0.7981 |
| RF | 0.0111 | 0.0402 | 0.9066 |
| XGBoost | 0.0084 | 0.0340 | 0.9271 |
| Stacking | 0.0066 | 0.0270 | 0.9580 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qi, J.; Zou, X.; He, R. Construction of a NOx Emission Prediction Model for Hybrid Electric Buses Based on Two-Layer Stacking Ensemble Learning. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050497
Qi J, Zou X, He R. Construction of a NOx Emission Prediction Model for Hybrid Electric Buses Based on Two-Layer Stacking Ensemble Learning. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(5):497. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050497
Chicago/Turabian StyleQi, Jiangyan, Xionghui Zou, and Ren He. 2025. "Construction of a NOx Emission Prediction Model for Hybrid Electric Buses Based on Two-Layer Stacking Ensemble Learning" Atmosphere 16, no. 5: 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050497
APA StyleQi, J., Zou, X., & He, R. (2025). Construction of a NOx Emission Prediction Model for Hybrid Electric Buses Based on Two-Layer Stacking Ensemble Learning. Atmosphere, 16(5), 497. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16050497







