Wavelet Coherence Analysis of PM10 Variability Due to Changes in Meteorological Factors in the Continental Climate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.3. Models
2.3.1. Spearman’s Rank Correlation
- If rs is close to +1.0, there is close positive agreement between the ranks of the X variable and those of the Y variable.
- If rs is close to −1.0, one of the variables tends to rank high, while the other tends to rank low.
- If rs is near zero, the ranks of the X and Y variables are nearly independent.
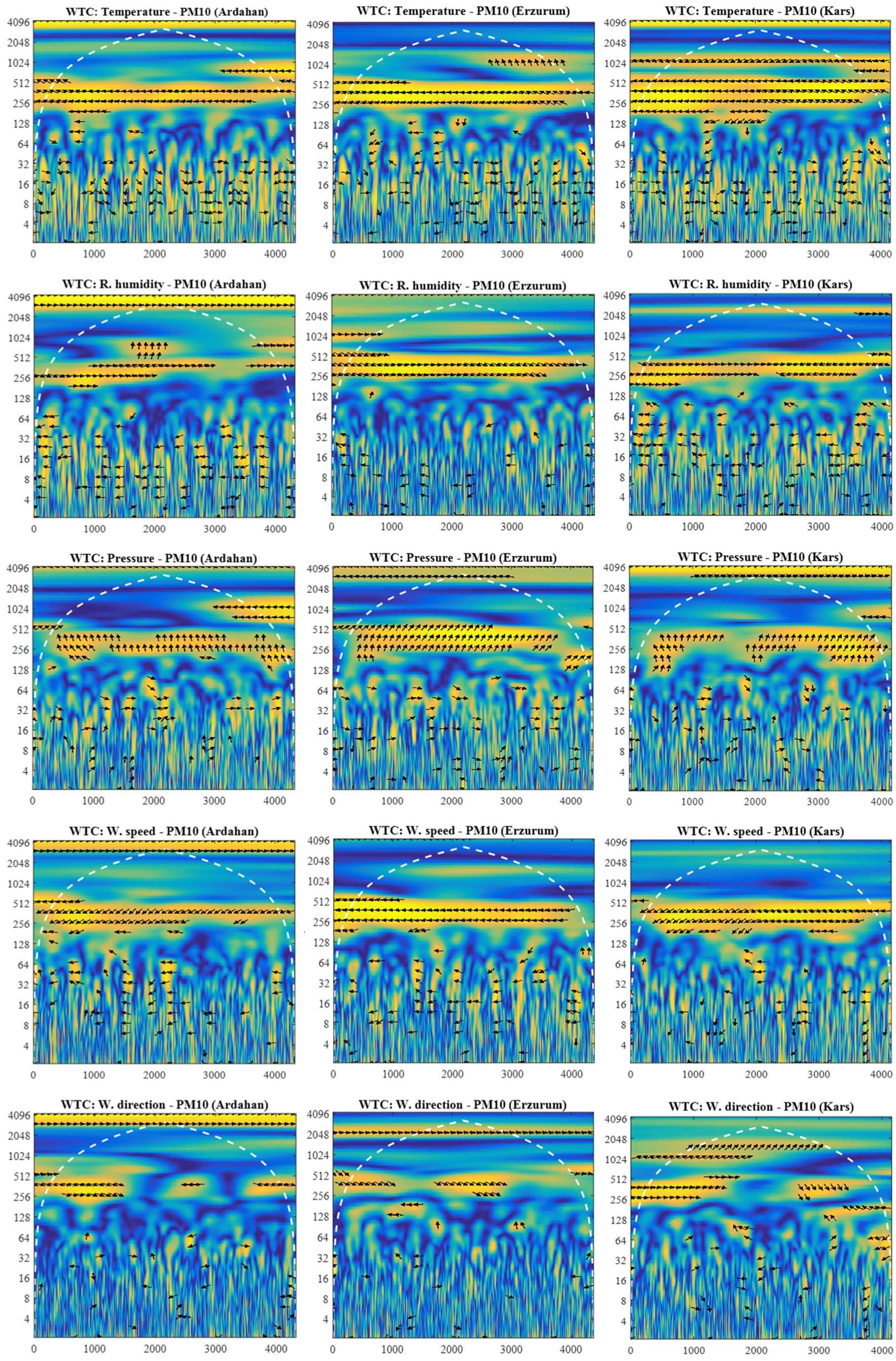
2.3.2. Wavelet Coherence Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Comparison Analyses of the Time Series Characteristics
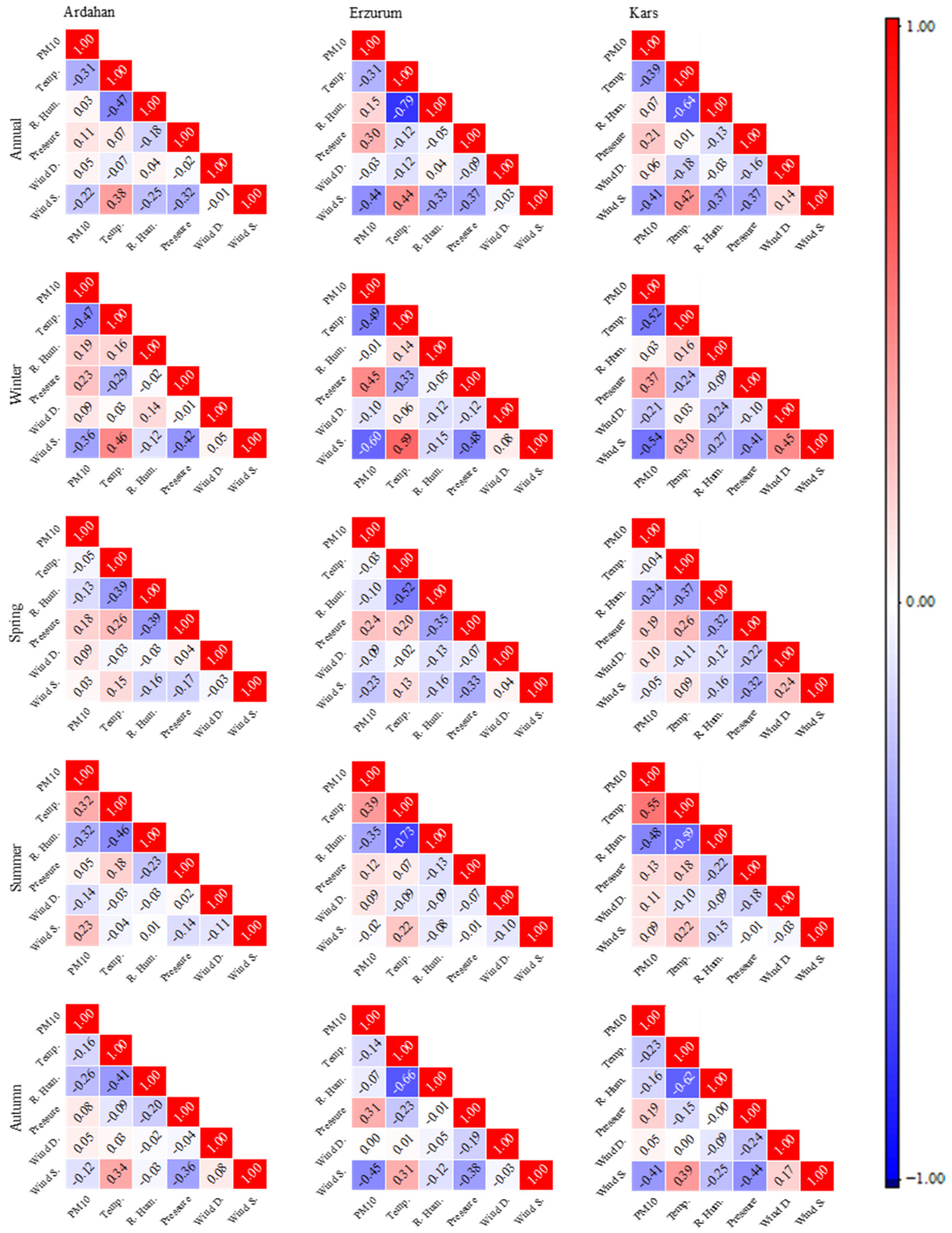
3.2. Spearman’s Rank Correlation Analysis
3.3. Wavelet Coherence Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ostro, B.; Chestnut, L.; Vichit-Vadakan, N.; Laixuthai, A. The Impact of Particulate Matter on Daily Mortality in Bangkok, Thailand. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 1999, 49, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancofiore, F.; Busilacchio, M.; Verdecchia, M.; Tomassetti, B.; Aruffo, E.; Bianco, S.; Di Tommaso, S.; Colangeli, C.; Rosatelli, G.; Di Carlo, P. Recursive Neural Network Model for Analysis and Forecast of PM10 and PM2.5. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2017, 8, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EU. Official Journal of the European Union; EU: Aberdeen, UK, 2008; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide; WHO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, J.D.; Nethery, E.; Brauer, M. Within-Urban Variability in Ambient Air Pollution: Comparison of Estimation Methods. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 1359–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinci, E.; Deniz, A.; Özdemir, E.T. The Relationship between PM10 and Meteorological Variables in the Mega City Istanbul. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2023, 195, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarigiannis, D.A.; Handakas, E.J.; Kermenidou, M.; Zarkadas, I.; Gotti, A.; Charisiadis, P.; Makris, K.; Manousakas, M.; Eleftheriadis, K.; Karakitsios, S.P. Monitoring of Air Pollution Levels Related to Charilaos Trikoupis Bridge. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 609, 1451–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltare, N.N.; Vahora, S.; Jani, K. Seasonal Analysis of Meteorological Parameters and Air Pollutant Concentrations in Kolkata: An Evaluation of Their Relationship. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 436, 140514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birim, N.G.; Turhan, C.; Atalay, A.S.; Gokcen Akkurt, G. The Influence of Meteorological Parameters on PM10: A Statistical Analysis of an Urban and Rural Environment in Izmir/Türkiye. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Shuo, W.; Zhao, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, W.; Arshad, A. Investigating the Relationship between Air Pollutants and Meteorological Parameters Using Satellite Data over Bangladesh. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali-Taleshi, M.S.; Riyahi Bakhtiari, A.; Hopke, P.K. Meteorologically Normalized Spatial and Temporal Variations Investigation Using a Machine Learning-Random Forest Model in Criteria Pollutants across Tehran, Iran. Urban Clim. 2024, 53, 101790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Xu, X.; Ma, X.; Wang, Z.; You, Q.; Shan, W.; Yang, Y.; Bo, X.; Yin, C. Application of Machine Learning to Predict Hospital Visits for Respiratory Diseases Using Meteorological and Air Pollution Factors in Linyi, China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2023, 30, 88431–88443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xie, J.; Li, C. Air Pollutants Concentrations Forecasting Using Back Propagation Neural Network Based on Wavelet Decomposition with Meteorological Conditions. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2016, 7, 557–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotse, S.Q.; Petra, M.I.; Dagar, L.; De Silva, L.C. Application of Computational Intelligence Techniques to Forecast Daily PM10 Exceedances in Brunei Darussalam. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2018, 9, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Qian, J.; Ou, C.Q.; Zhou, Y.X.; Guo, C.; Guo, Y. Spatial and Temporal Analysis of Air Pollution Index and Its Timescale-Dependent Relationship with Meteorological Factors in Guangzhou, China, 2001–2011. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, W.J.; Lin, Y.C. Investigation of the Main PM2.5 Sources and Diffusion Patterns and Corresponding Meteorological Conditions by the Wavelet Analysis Approach. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2021, 12, 101222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fattah, M.A.; Morshed, S.R.; Kafy, A.-A.; Rahaman, Z.A.; Rahman, M.T. Wavelet Coherence Analysis of PM2.5 Variability in Response to Meteorological Changes in South Asian Cities. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliengchuay, W.; Worakhunpiset, S.; Limpanont, Y.; Meeyai, A.C.; Tantrakarnapa, K. Influence of the Meteorological Conditions and Some Pollutants on PM10 Concentrations in Lamphun, Thailand. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2021, 19, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Zhan, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, Z. Spatiotemporal Variations of Particulate and Gaseous Pollutants and Their Relations to Meteorological Parameters: The Case of Xiangyang, China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Li, S.; Zhang, F. Multi-Scale Spatiotemporal Variations and Drivers of PM2.5 in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei from 2015 to 2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, S.P.; Silwal, A.; Baral, B.; Subedi, S.; Lamichhane, N.; Chapagain, N.P.; Adhikari, B. Influence of the Rainfall and Temperature Oscillation on Air Quality in Kathmandu Valley: The Wavelet Analysis. Environ. Eng. Res. 2023, 28, 220694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BARLİK, N. Effect of Meteorological Parameters on PM10 Concentrations in Ardahan by Wavelet Coherence Analysis. Celal Bayar Üniversitesi Fen Bilim. Derg. 2020, 17, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocak, S.; Turalioglu, F.S. Relationship Between Air Pollutants and Some Meteorological Parameters in Erzurum, Turkey. In Global Warming: Engineering Solutions; Dincer, I., Hepbasli, A., Midilli, A., Karakoc, T.H., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, USA, 2010; pp. 485–499. ISBN 978-1-4419-1017-2. [Google Scholar]
- Duru, O. Volcano Stratigraphy, Petrology and Geochemistry of The Kars Volcanic Plateau in The North of Çıldır (Ardahan City); İstanbul University Graduate Studies in Sciences: İstanbul, Turkey, 2012. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Keskin, M. Volcano-Stratigraphy and Evolution of Collision-Origin Volcanism in the Erzurum-Kars Plateau in Light of New K/Ar Age Findings, Northeastern Anatolia. MTA 1998, 120, 135–157. (In Turkish) [Google Scholar]
- Iyigun, C.; Türkeş, M.; Batmaz, I.; Yozgatligil, C.; Purutçuoǧlu, V.; Koç, E.K.; Öztürk, M.Z. Clustering Current Climate Regions of Turkey by Using a Multivariate Statistical Method. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2013, 114, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Çiçek, İ. Detailed Köppen-Geiger Climate Regions of Turkey<p>Türkiye’nin Detaylandırılmış Köppen-Geiger Iklim Bölgeleri. J. Hum. Sci. 2018, 15, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TSMS. Extreme Maximum, Minimum and Average Temperatures Measured in Long Period. Available online: https://www.mgm.gov.tr/eng/forecast-cities.aspx (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- TURKSTAT. Address Based Population Registration System Results. 2023. Available online: https://data.tuik.gov.tr/Bulten/Index?p=Adrese-Dayali-Nufus-Kayit-Sistemi-Sonuclari-2023-49684 (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- MoIT. Socio-Economic Development Ranking of Provinces and Regions SEGE-2017; MoIT: Ankara, Turkey, 2017. (In Turkish)
- MoIT. 81 Provinces Industrial Status Reports. Available online: https://www.sanayi.gov.tr/plan-program-raporlar-ve-yayinlar/81-il-sanayi-durum-raporlari (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- NAQMN (National Air Quality Monitoring Network). Available online: https://sim.csb.gov.tr/STN/STN_Report/StationDataDownloadNew (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- TSMS (Turkish State Meteorological Service). Available online: https://mevbis.mgm.gov.tr/mevbis/ui/index.html#/Login (accessed on 14 June 2024).
- Tian, H.; Kong, H.; Wong, C. A Novel Stacking Ensemble Learning Approach for Predicting PM2.5 Levels in Dense Urban Environments Using Meteorological Variables: A Case Study in Macau. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 5062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ma, J.; Zhang, W.; Li, L. Analysis and Prediction of the Meteorological Characteristics of Dust Concentrations in Open-Pit Mines. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.; Xin, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, W. Analysis of Dry-Wet Changes and the Driving Factors in Mainland China under Climate Change. Water 2023, 15, 2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowdy, S.; Wearden, S.; Chilko, D. Statistics for Research, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2004; ISBN 0-471-26735-X. [Google Scholar]
- Labat, D. Recent Advances in Wavelet Analyses: Part 1. A Review of Concepts. J. Hydrol. 2005, 314, 275–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.; Cao, J.; Ali, S.; Ullah, W.; Muhammad, S.; Hussain, I.; Abbas, H.; Hamal, K.; Sharma, S.; Akhtar, M.; et al. Wavelet Coherence of Monsoon and Large-Scale Climate Variabilities with Precipitation in Pakistan. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 9950–9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihanović, H.; Orlić, M.; Pasarić, Z. Diurnal Thermocline Oscillations Driven by Tidal Flow around an Island in the Middle Adriatic. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, S157–S168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhan Bashir, M.; Benghoul, M.; Numan, U.; Shakoor, A.; Komal, B.; Adnan Bashir, M.; Bashir, M.; Tan, D. Environmental Pollution and COVID-19 Outbreak: Insights from Germany. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 2020, 13, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grinsted, A.; Moore, J.C.; Jevrejeva, S. Nonlinear Processes in Geophysics Application of the Cross Wavelet Transform and Wavelet Coherence to Geophysical Time Series. Nonlinear Process. Geophys. 2004, 11, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdakovic, S.; Ademovic, A.; Nuhanovic, A. Correlation between Air Temperature and Electricity Demand by Linear Regression and Wavelet Coherence Approach: UK, Slovakia and Bosnia and Herzegovina Case Study. Arch. Electr. Eng. 2013, 62, 521–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, T.; Wang, E. Impacts of International Oil Price Fluctuations on China’s PM2.5 Concentrations: A Wavelet Analysis. Econ. Res. Istraz. 2019, 33, 2488–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguiar-Conraria, L.; Azevedo, N.; Soares, M.J. Using Wavelets to Decompose the Time-Frequency Effects of Monetary Policy. Phys. A Stat. Mech. Its Appl. 2008, 387, 2863–2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mott, R.; Vionnet, V.; Grünewald, T. The Seasonal Snow Cover Dynamics: Review on Wind-Driven Coupling Processes. Front. Earth Sci. 2018, 6, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, Y.S.; Toros, H.; Deniz, A.; Incecik, S. Influence of Meteorological Factors and Emission Sources on Spatial and Temporal Variations of PM10 Concentrations in Istanbul Metropolitan Area. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 5504–5513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Sun, W. Relationship between the Formation of PM2.5and Meteorological Factors in Northern China: The Periodic Characteristics of Wavelet Analysis. Adv. Meteorol. 2021, 2021, 9723676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, A.P.; Eckersley, R.J. Statistics for Biomedical Engineers and Scientists: How to Visualize and Analyze Data; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barmpadimos, I.; Hueglin, C.; Keller, J.; Henne, S.; Prévôt, A.S.H. Influence of Meteorology on PM10 Trends and Variability in Switzerland from 1991 to 2008. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 1813–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltaci, H.; Akkoyunlu, B.O.; Arslan, H.; Yetemen, O.; Ozdemir, E.T. The Influence of Meteorological Conditions and Atmospheric Circulation Types on PM10 Levels in Western Turkey. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2019, 191, 466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, P.; Sonwani, S.; Srivastava, A.; Jain, M.; Srivastava, A.; Bharti, A.; Rangra, D.; Mongia, N.; Tejan, S.; Bhardwaj, S. Impact of Crop Residue Burning in Haryana on the Air Quality of Delhi, India. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, S.; Hopke, P.K.; Pipal, A.S.; Srivastava, A.K.; Bisht, D.S.; Tiwari, S.; Singh, A.K.; Soni, V.K.; Attri, S.D. Intra-Urban Variability of Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10) and Its Relationship with Optical Properties of Aerosols over Delhi, India. Atmos. Res. 2015, 166, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zateroglu, M.T. Forecasting Particulate Matter Concentrations by Combining Statistical Models. J. King Saud Univ.-Sci. 2024, 36, 103090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Aishan, T.; Halik, Ü.; Betz, F.; Rezhake, R. Assessment of Air Quality before and during the COVID-19 and Its Potential Health Impacts in an Arid Oasis City: Urumqi, China. Stoch. Environ. Res. Risk Assess. 2023, 37, 1265–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
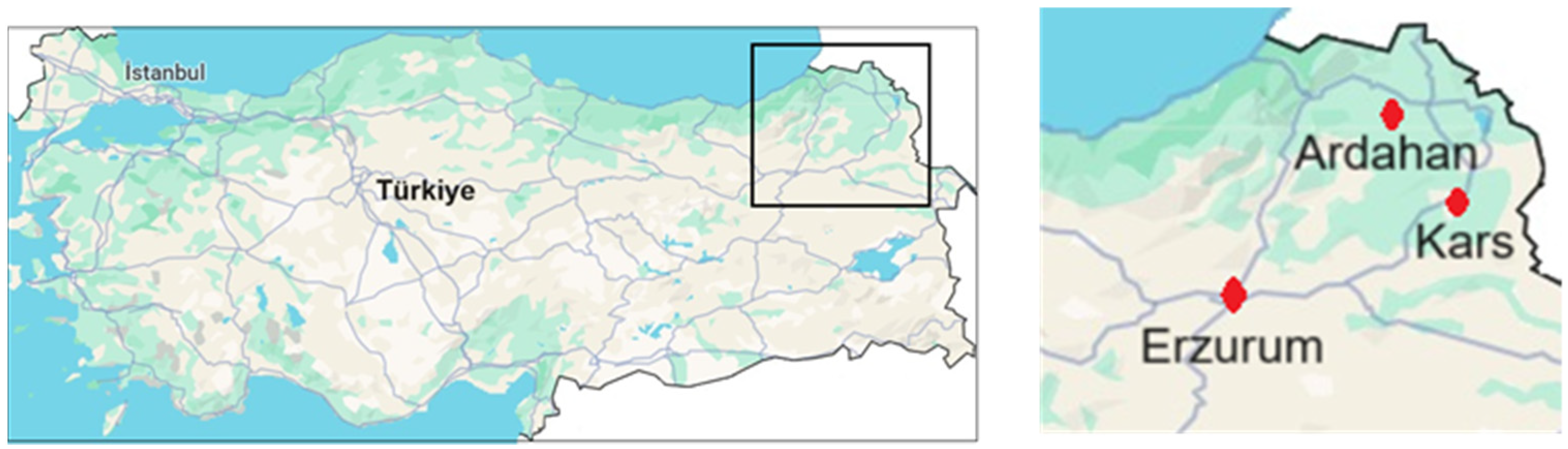
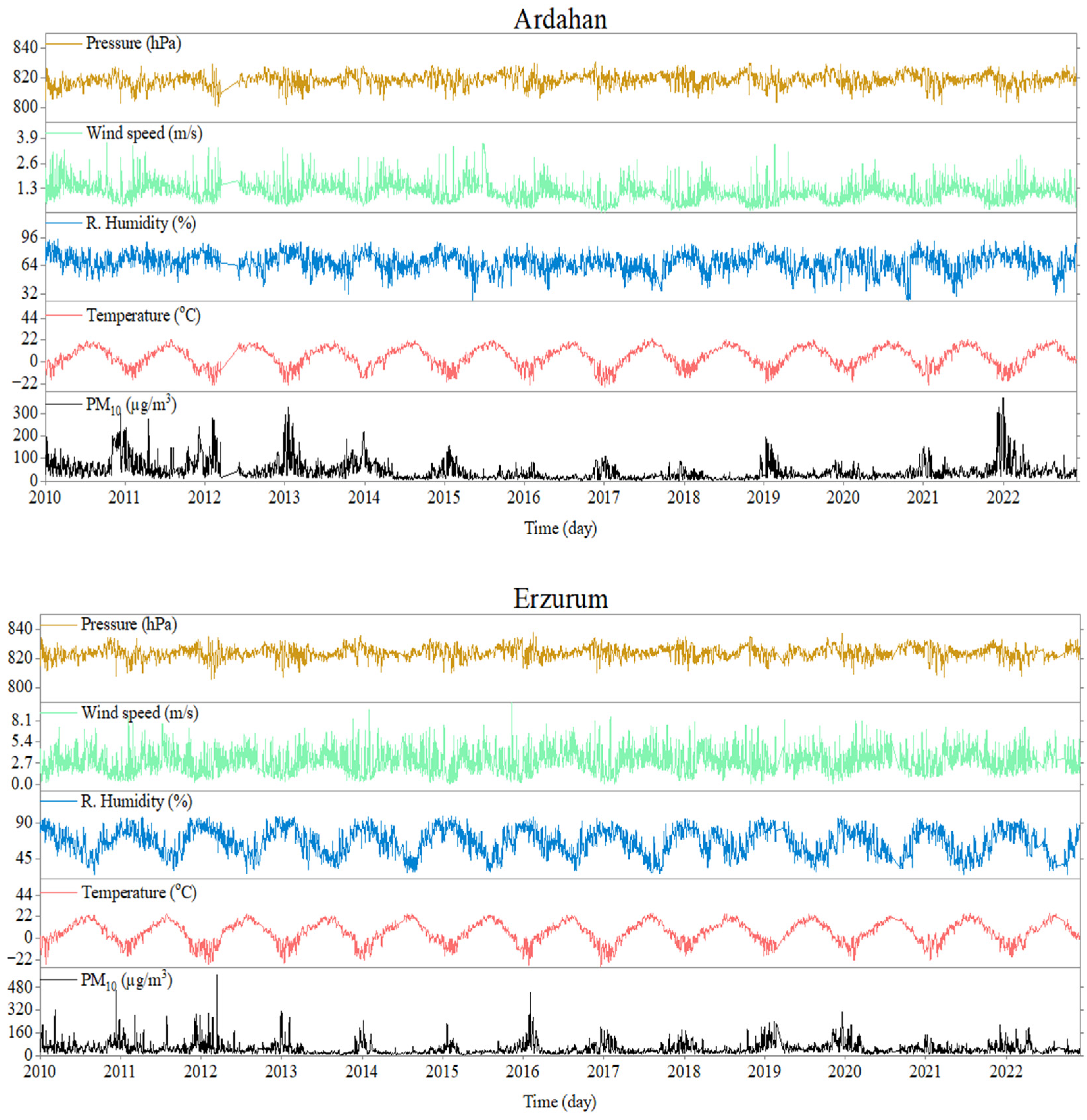
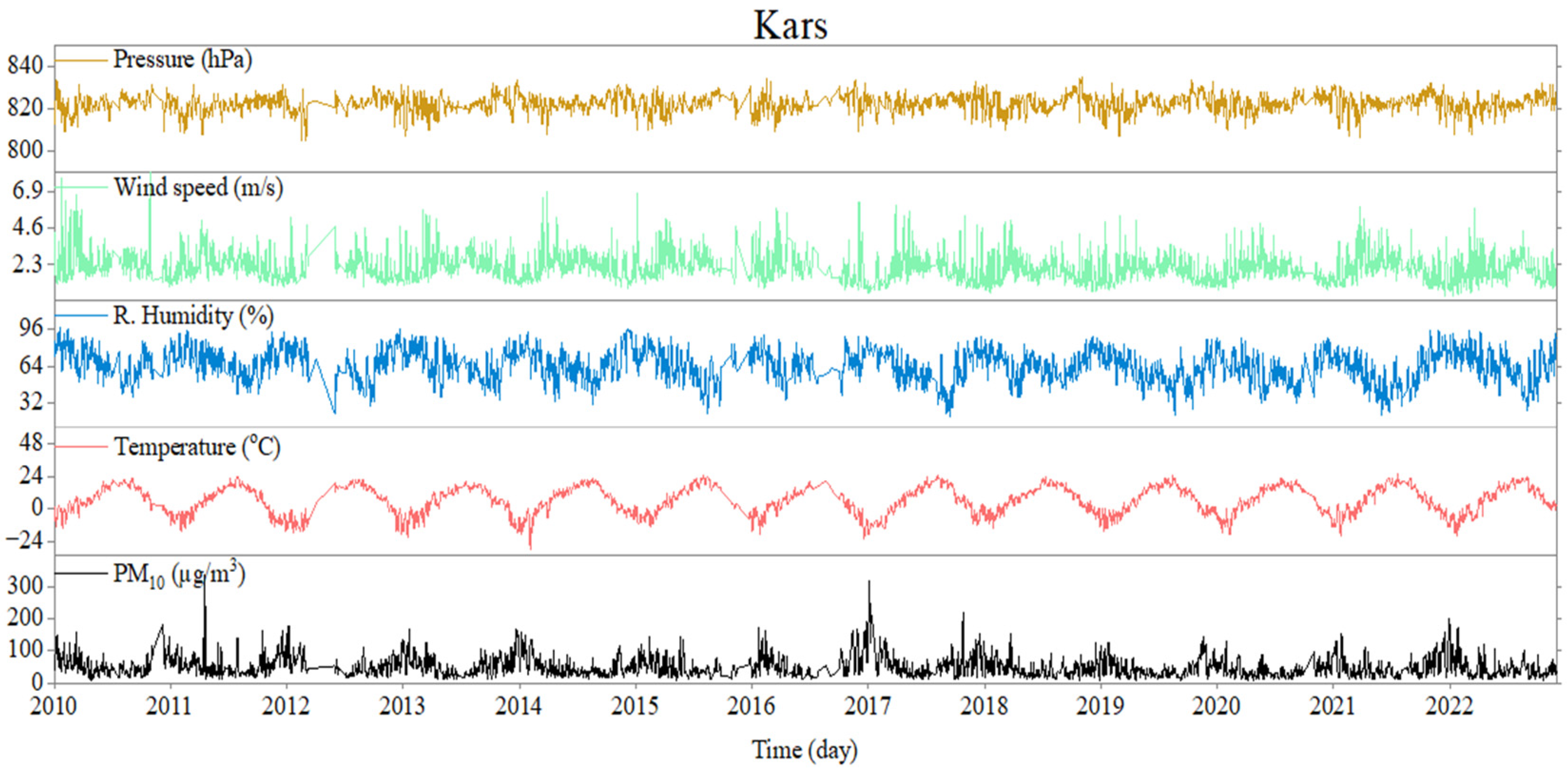

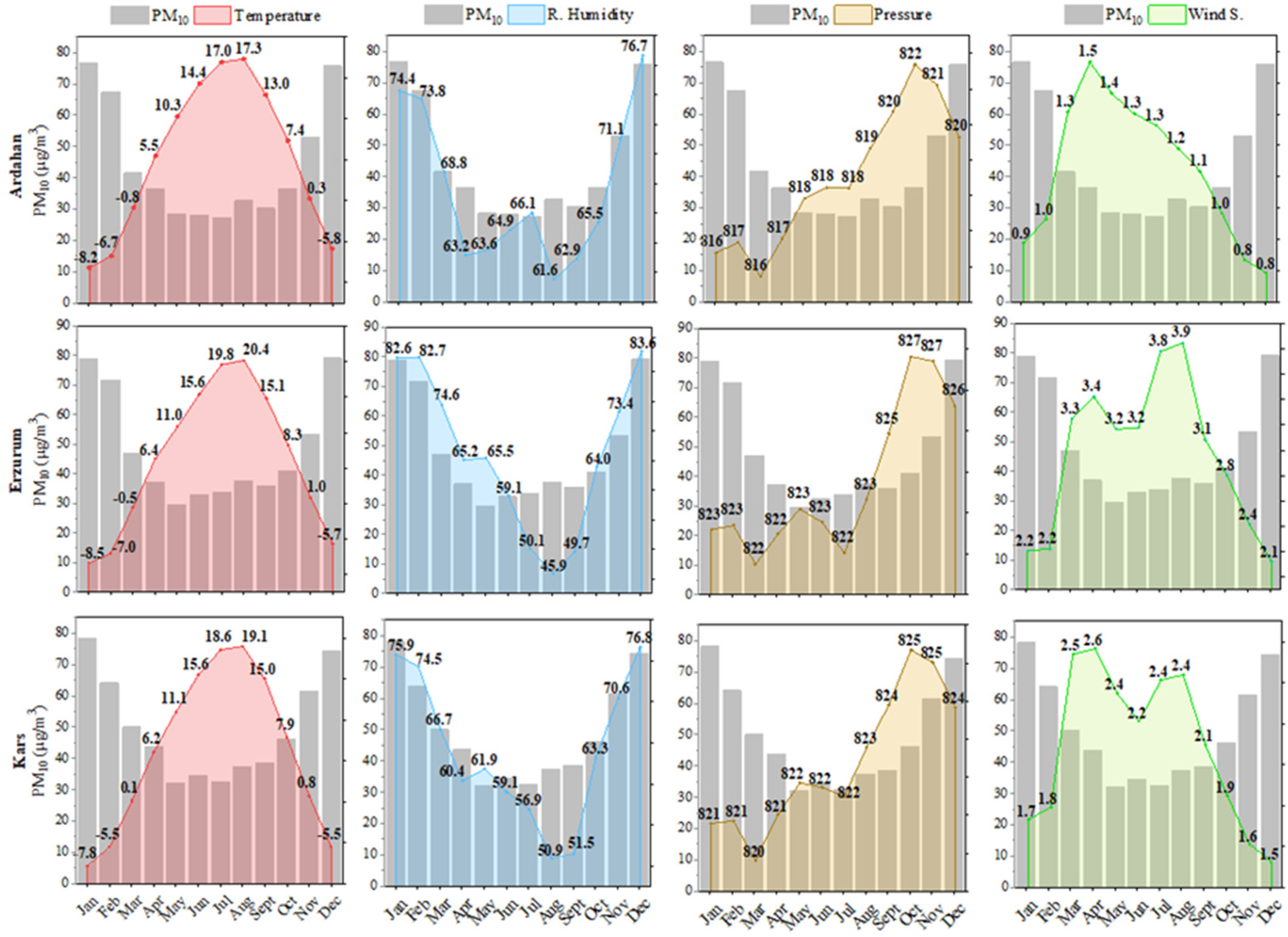
| City/Station | Area (km2) | Altitude of City Center Relative to Sea Level (m) | Coordinates | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Longitude (°, E) | Latitude (°, N) | |||
| Ardahan | 4934 | 1870 | 42.70 | 41.11 |
| Erzurum | 25,006 | 1890 | 41.30 | 39.92 |
| Kars | 10,193 | 1768 | 43.09 | 40.61 |
| Mean ± SD | Min | Max | Mean ± SD | Min | Max | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ardahan | ||||||
| Winter | Spring | |||||
| Temperature | −6.91 ± 5.97 | −25.1 | 6.1 | 4.91 ± 5.97 | −17.8 | 18.6 |
| R. humidity | 74.96 ± 8.03 | 34.5 | 95.0 | 65.28 ± 10.98 | 24.5 | 92.3 |
| Pressure | 817.6 ± 5.3 | 801.1 | 830.2 | 816.8 ± 3.9 | 800.5 | 828.1 |
| Wind speed | 0.88 ± 0.55 (NNE) | 0.0 | 3.6 | 1.38 ± 0.49 (NW) | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| PM10 | 73.35 ± 62.44 | 3.17 | 371.2 | 35.54 ± 6.28 | 3.83 | 276.8 |
| Summer | Autumn | |||||
| Temperature | 16.24 ± 2.75 | 7.9 | 23.5 | 6.90 ± 31.78 | −17 | 20.5 |
| R. humidity | 64.18 ± 9.15 | 29.0 | 85.3 | 66.47 ± 11.46 | 24.4 | 93.4 |
| Pressure | 818.6 ± 2.5 | 809.0 | 825.1 | 821.1 ± 3.3 | 808.5 | 830.6 |
| Wind speed | 1.25 ± 0.38 (NE) | 0.5 | 3.63 | 0.98 ± 0.43 (N) | 0.2 | 3.7 |
| PM10 | 29.37 ± 19.31 | 3.21 | 152.1 | 39.87 ± 31.78 | 2.36 | 208.8 |
| Erzurum | ||||||
| Winter | Spring | |||||
| Temperature | −7.07 ± 6.67 | −28.8 | 5.7 | 5.72 ± 6.03 | −16.1 | 18.0 |
| R. humidity | 82.96 ± 7.29 | 52.5 | 98.5 | 68.34 ± 12.22 | 31.2 | 97.4 |
| Pressure | 823.7 ± 5.3 | 805.8 | 837.4 | 822.5 ± 3.8 | 806.9 | 833.9 |
| Wind speed | 2.19 ± 1.56 (E) | 0.0 | 9.6 | 3.29 ± 1.33 (WSW) | 0.4 | 8.3 |
| PM10 | 76.89 ± 57.85 | 5.63 | 465.6 | 37.25 ± 30.37 | 4.49 | 324.5 |
| Summer | Autumn | |||||
| Temperature | 18.64 ± 3.23 | 9.0 | 26.1 | 7.85 ± 6.68 | −16.9 | 23.6 |
| R. humidity | 51.66 ± 11.77 | 25.4 | 86.9 | 62.86 ± 15.13 | 25.9 | 96.4 |
| Pressure | 822.7 ± 2.3 | 814.5 | 829.8 | 826.2 ± 3.1 | 814.7 | 835.1 |
| Wind speed | 3.61 ± 1.31 (ENE) | 0.4 | 7.7 | 2.76 ± 1.43 (E) | 0.0 | 10.9 |
| PM10 | 34.72 ± 20.17 | 3.53 | 279.9 | 43.79 ± 28.35 | 1.89 | 189.9 |
| Kars | ||||||
| Winter | Spring | |||||
| Temperature | −6.33 ± 5.42 | −29.9 | 5.7 | 5.70 ± 5.83 | −13.9 | 18.9 |
| R. humidity | 75.77 ± 9.06 | 44.3 | 97.7 | 63.11 ± 12.49 | 30.8 | 94.9 |
| Pressure | 821.9 ± 5.2 | 805.0 | 834.0 | 820.9 ± 4.0 | 804.8 | 832.0 |
| Wind speed | 1.68 ± 0.88 (S) | 0.3 | 7.8 | 2.49 ± 0.99 (S) | 0.5 | 6.9 |
| PM10 | 72.59 ± 37.84 | 8.28 | 321.1 | 52.28 ± 27.29 | 7.61 | 160.2 |
| Summer | Autumn | |||||
| Temperature | 17.79 ± 2.99 | 9.2 | 25.6 | 8.03 ± 6.80 | −13.3 | 23.6 |
| R. humidity | 55.58 ± 11.10 | 20.8 | 86.3 | 61.59 ± 13.97 | 21.0 | 95.5 |
| Pressure | 822.0 ± 2.6 | 812.9 | 829.5 | 824.8 ± 3.3 | 813.0 | 834.7 |
| Wind speed | 2.36 ± 0.61 (NNE) | 0.9 | 4.7 | 1.86 ± 0.73 (NNE) | 0.7 | 8.9 |
| PM10 | 34.80 ± 16.70 | 8.47 | 140.2 | 48.57 ± 27.72 | 6.25 | 220.2 |
| Station | Period | Temperature | R. Humidity | Pressure | Wind D. | Wind S. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ardahan | Annual (2010–2022) | −0.31 | 0.03 | 0.11 | 0.05 | −0.22 |
| Winter | −0.47 | 0.19 | 0.23 | 0.09 | −0.36 | |
| Spring | - | −0.13 | 0.18 | 0.09 | - | |
| Summer | 0.32 | −0.32 | - | −0.14 | 0.23 | |
| Autumn | −0.16 | −0.26 | 0.08 | - | −0.12 | |
| Erzurum | Annual (2010–2022) | −0.31 | 0.15 | 0.30 | −0.03 | −0.44 |
| Winter | −0.49 | - | 0.45 | −0.10 | −0.60 | |
| Spring | - | −0.10 | 0.24 | −0.10 | −0.23 | |
| Summer | 0.39 | −0.35 | 0.12 | 0.09 | - | |
| Autumn | −0.14 | −0.07 | 0.31 | - | −0.45 | |
| Kars | Annual (2010–2022) | −0.39 | 0.07 | 0.21 | 0.06 | −0.41 |
| Winter | −0.52 | - | 0.37 | −0.21 | −0.54 | |
| Spring | - | −0.34 | 0.19 | 0.10 | - | |
| Summer | 0.55 | −0.48 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.09 | |
| Autumn | −0.23 | −0.16 | 0.19 | - | −0.41 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barlik, N. Wavelet Coherence Analysis of PM10 Variability Due to Changes in Meteorological Factors in the Continental Climate. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030331
Barlik N. Wavelet Coherence Analysis of PM10 Variability Due to Changes in Meteorological Factors in the Continental Climate. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):331. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030331
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarlik, Necla. 2025. "Wavelet Coherence Analysis of PM10 Variability Due to Changes in Meteorological Factors in the Continental Climate" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030331
APA StyleBarlik, N. (2025). Wavelet Coherence Analysis of PM10 Variability Due to Changes in Meteorological Factors in the Continental Climate. Atmosphere, 16(3), 331. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030331





