CALIPSO Overpasses During Three Atmospheric Pollen Events Detected by Hirst-Type Volumetric Samplers in Two Urban Cities in Greece
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
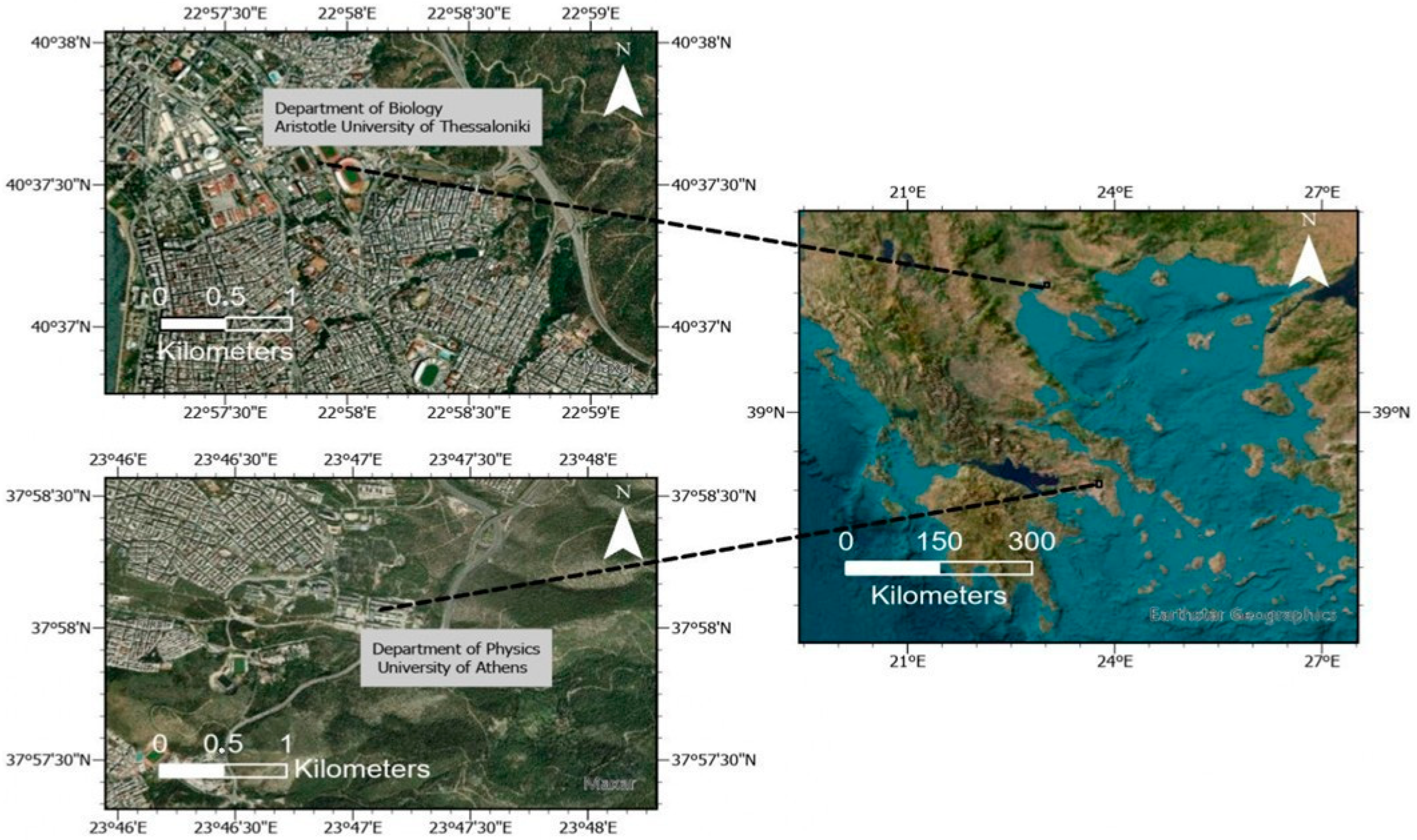
2.1. Sites Description
2.2. Pollen Data
2.3. Space-Based Lidar
2.4. Models
3. Results
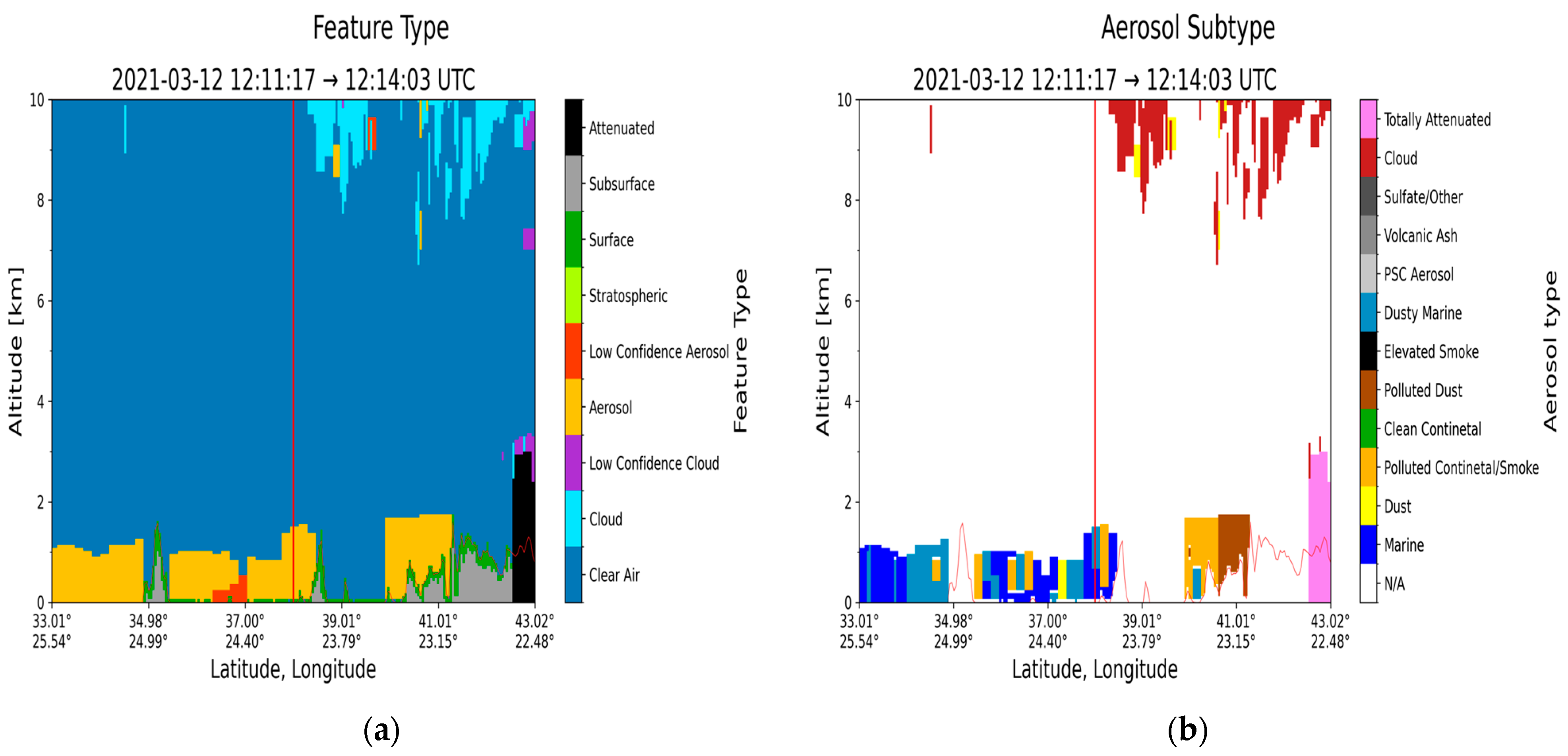
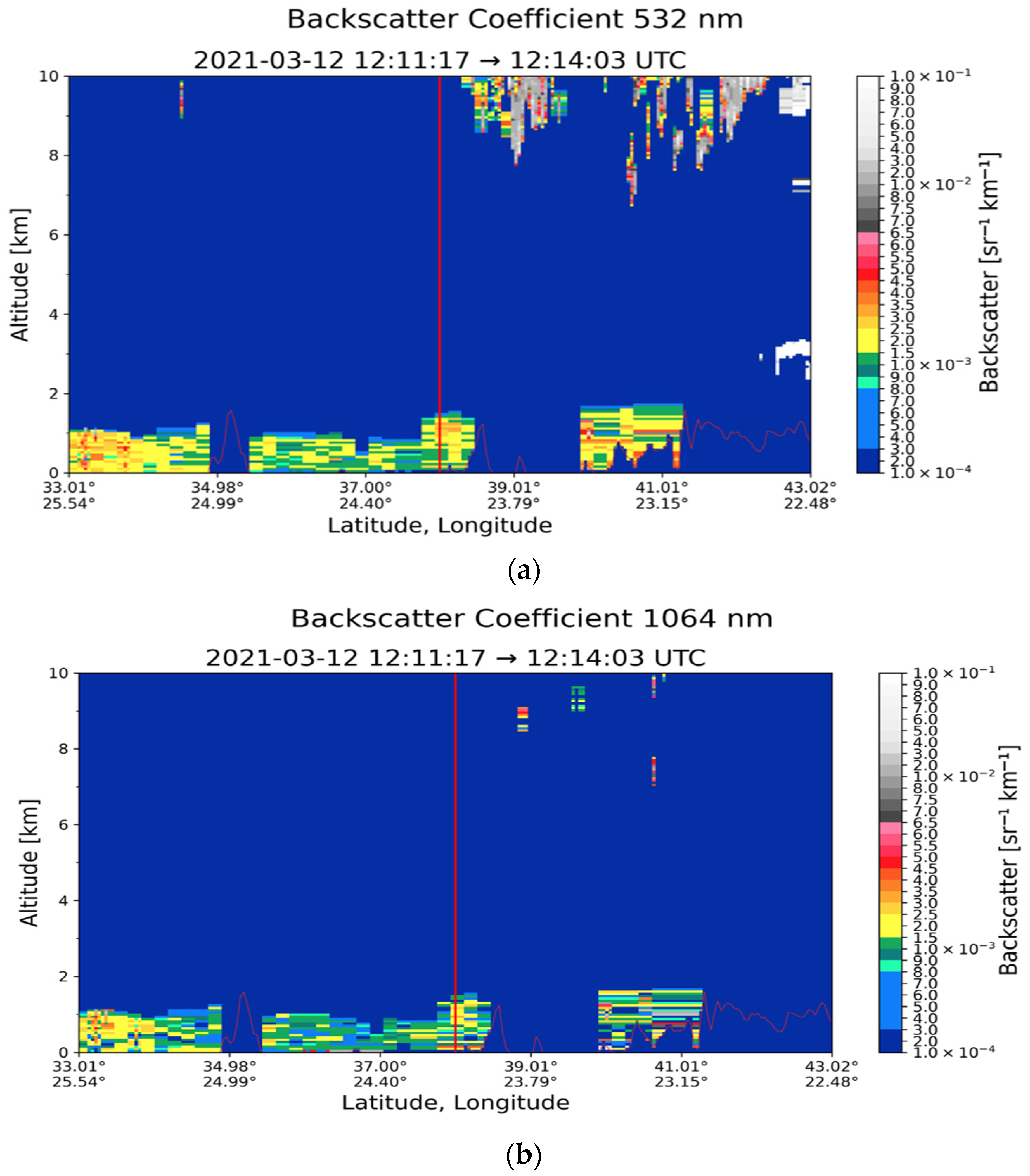
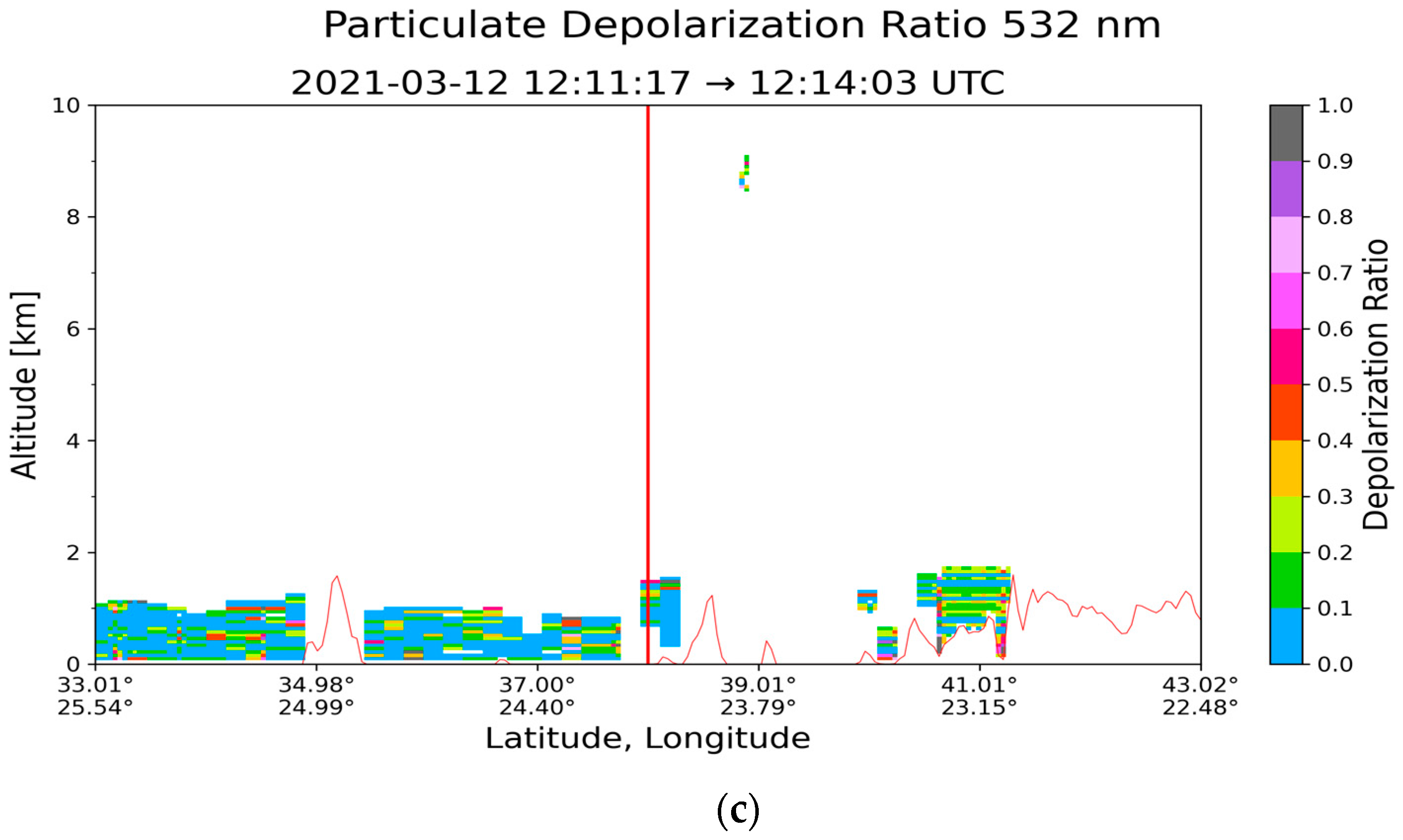
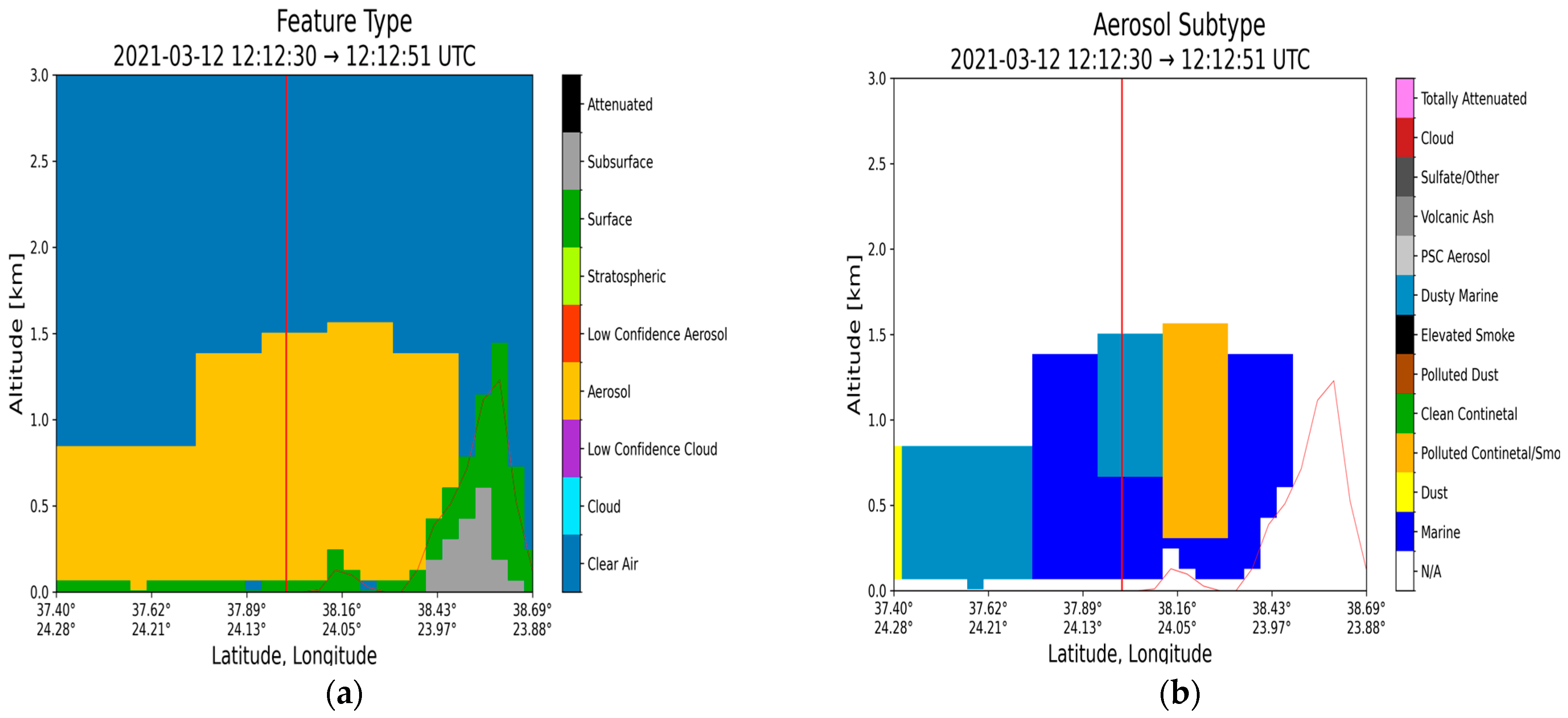
3.1. Case Study in Athens: 12 March 2021
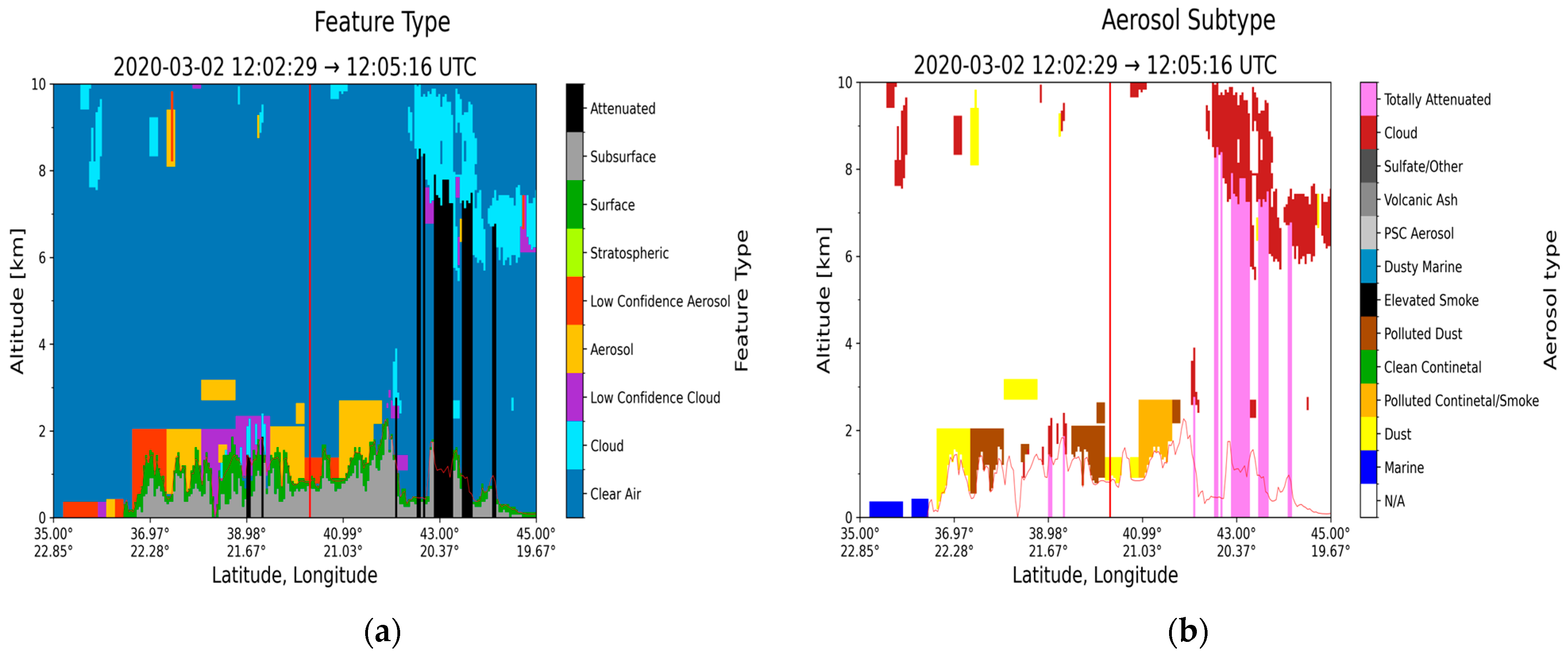
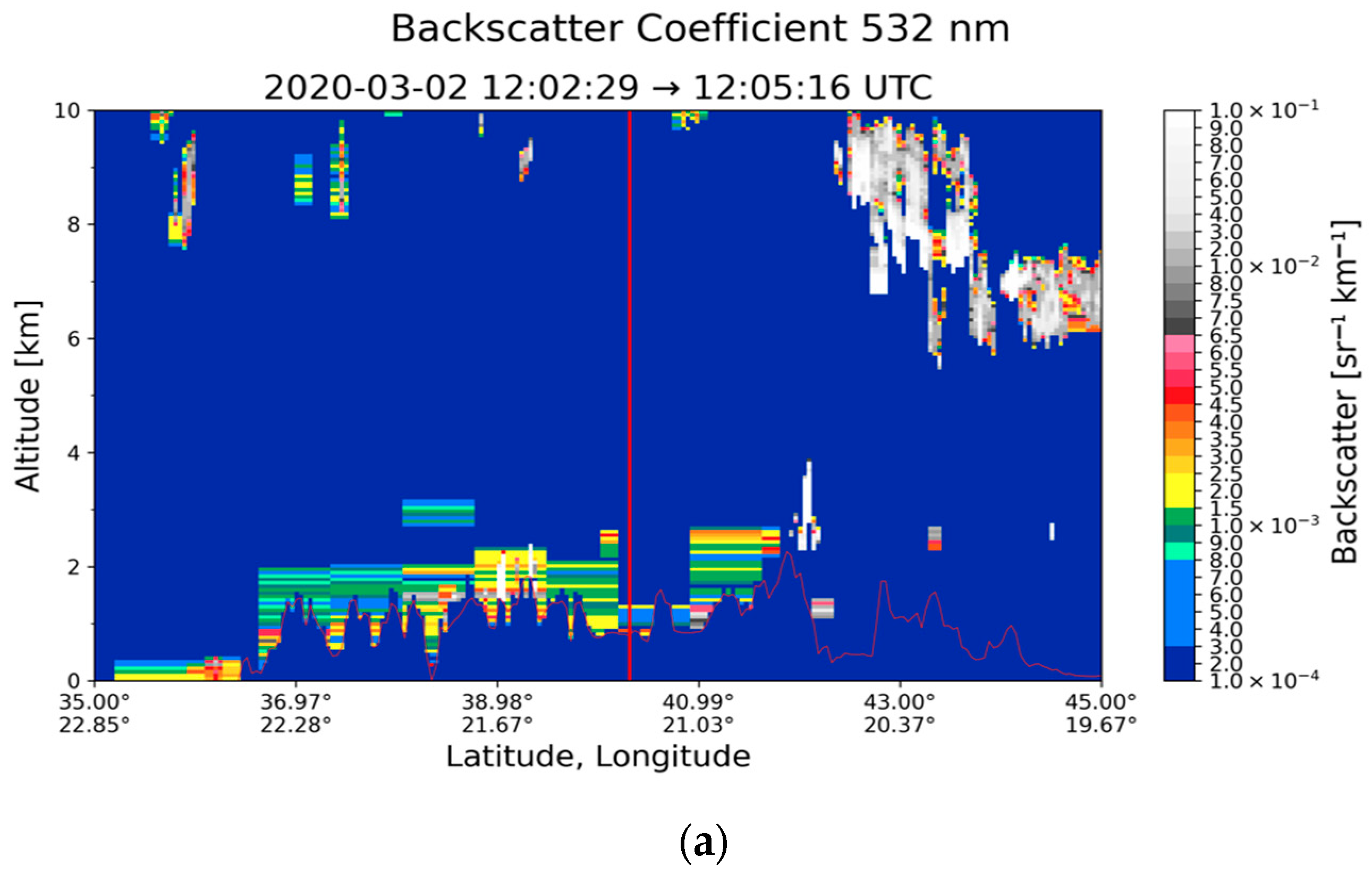
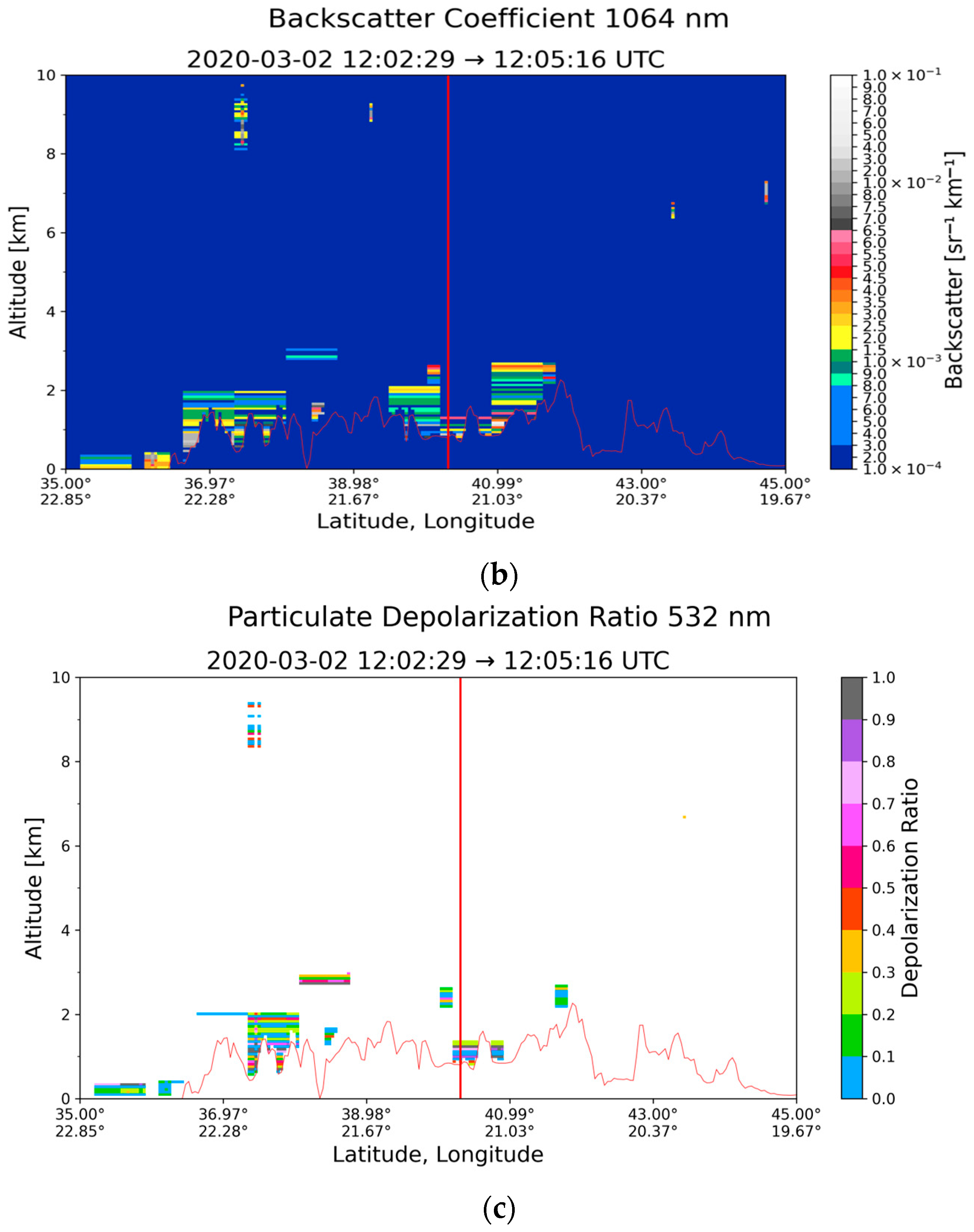
3.2. Case Study in Thessaloniki: 2 March 2020
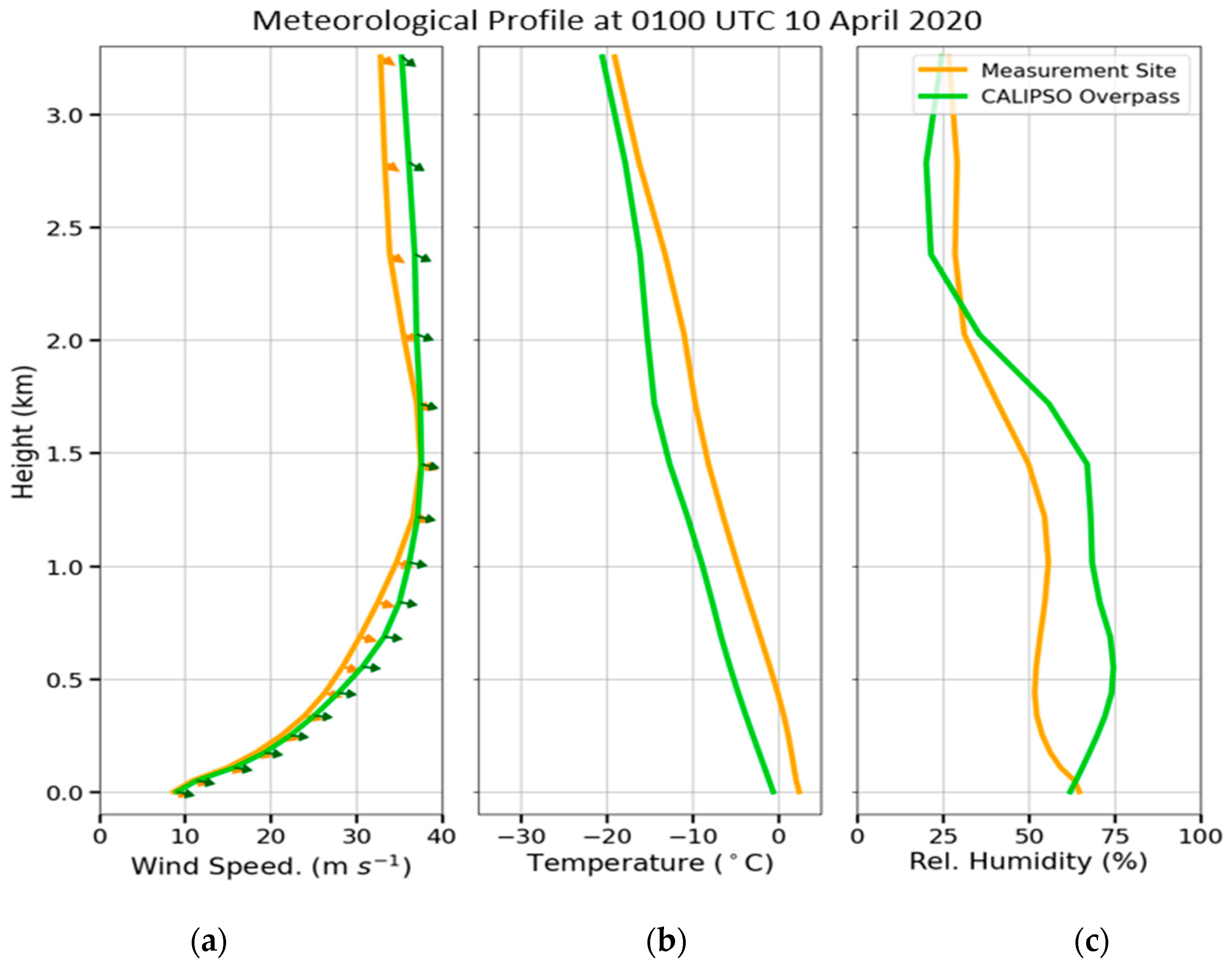
3.3. Case Study in Thessaloniki: 10 April 2020
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A


References
- IPCC: Climate Change. The Physical Science Basis. In Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change; Stocker, T.F., Qin, D., Plattner, G.K., Tignor, M., Allen, S.K., Boschung, J., Nauels, A., Xia, Y., Bex, V., Midgley, P.M., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WHO. World Health Report. A Vision for Global Health, Shaping the Future; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Bousquet, J.; Khaltaev, N.; Cruz, A.A.; Denburg, J.; Fokkens, W.J.; Togias, A.; Zuberbier, T.; Baena-Cagnani, C.E.; Canonica, G.W.; Van Weel, C.; et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma (ARIA). Allergy 2008, 63, 8–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gisler, A.; Eeftens, M.; de Hoogh, K.; Vienneau, D.; Salem, Y.; Yammine, S.; Jakob, J.; Gorlanova, O.; Decrue, F.; Gehrig, R.; et al. Pollen exposure is associated with risk of respiratory symptoms during the first year of life. Allergy 2022, 77, 3606–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, P.S.; Steiner, A.L.; O’Neill, M.S.; Baptist, A.P.; Gronlund, C.J. Chronic and infectious respiratory mortality and short-term exposures to four types of pollen taxa in older adults in Michigan, 2006–2017. BMC Public Health 2025, 25, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisgrill, L.; Fyhrquist, N.; Ndika, J.; Paalanen, L.; Berger, A.; Laatikainen, T.; Karisola, P.; Haahtela, T.; Alenius, H. Bet v 1 triggers antiviral-type immune signalling in birch-pollen-allergic individuals. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2022, 52, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tossavainen, T.; Martikainen, M.-V.; Loukola, H.; Roponen, M. Common Pollen Modulate Immune Responses against Viral-Like Challenges in Airway Coculture Model. J. Immunol. Res. 2023, 2023, 639092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, C.W. Pollen Overload: Seasonal Allergies in a Changing Climate. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, A70–A75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, I.R.; Jones, N.R.; Agnew, M.; Goodess, C.M.; Giorgi, F.; Hamaoui-Laguel, L.; Semenov, M.A.; Solomon, F.; Storkey, J.; Vautard, R.; et al. Erratum: “Climate Change and Future Pollen Allergy in Europe. Environ. Health Perspect. 2018, 126, 079002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, D.D.; Schevin, P.; Ferrier, J.; Jolly, D.; Andreasen, T.; Ascanius, S.E.; Hendriksen, S.E.; Poulsen, U. Long-distance pollen transport from North America to Greenland in spring. J. Geophys. Res. Biogeosciences 2008, 113, G02013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skjøth, C.A.; Sommer, J.; Stach, A.; Smith, M.; Brandt, J. The long-range transport of birch (Betula) pollen from Poland and Germany causes significant pre-season concentrations in Denmark. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 1204–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damialis, A.; Kaimakamis, E.; Konoglou, M.; Akritidis, I.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Gioulekas, D. Estimating the abundance of airborne pollen and fungal spores at variable elevations using an aircraft: How high can they fly? Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczepanek, K.; Myszkowska, D.; Worobiec, E.; Piotrowicz, K.; Ziemianin, M.; Bielec-Bąkowska, Z. The long-range transport of Pinaceae pollen: An example in Kraków (southern Poland). Aerobiologia 2017, 33, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayr, D.; Plaza, M.P.; Gilles, S.; Kolek, F.; Leier-Wirtz, V.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Damialis, A. Pollen long-distance transport associated with symptoms in pollen allergics on the German Alps: An old story with a new ending? Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 881, 163310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, P.; Negrini, M.G.; Cesari, G.; Griffith, M. Evidence for long range transport of biological and anthropogenic aerosol particles in the atmosphere. Grana 1984, 23, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Blohn, N.; Mitra, S.K.; Diehl, K.; Borrmann, S. The ice nucleating ability of pollen: Part III: New laboratory studies in immersion and contact freezing modes including more pollen types. Atmos. Res. 2005, 78, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.; Quick, C.; Matthias-Maser, S.; Mitra, S.K.; Jaenicke, R. The ice nucleating ability of pollen Part I: Laboratory studies in deposition and condensation freezing modes. Atmos. Res. 2001, 58, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diehl, K.; Matthias-Maser, S.; Jaenicke, R.; Mitra, S.K. The ice nucleating ability of pollen: Part II. Laboratory studies in immersion and contact freezing modes. Atmos. Res. 2002, 61, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffiths, P.T.; Borlace, J.S.; Gallimore, P.J.; Kalberer, M.; Herzog, M.; Pope, F.D. Hygroscopic growth and cloud activation of pollen: A laboratory and modeling study. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2012, 13, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope, F.D. Pollen grains are efficient cloud condensation nuclei. Environ. Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 044015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, A.L.; Brooks, S.D.; Deng, C.; Thornton, D.C.O.; Pendleton, M.W.; Bryant, V. Pollen as atmospheric cloud condensation nuclei. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2015, 42, 3596–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PalDat—A Palynological Database (2000 Onwards). Available online: https://www.paldat.org (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Buters, J.T.M.; Antunes, C.; Galveias, A.; Bergmann, K.C.; Thibaudon, M.; Galán, C.; Schmidt-Weber, C.; Oteros, J. Pollen and spore monitoring in the world. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2018, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwarakanath, D.; Milic, A.; Beggs, P.; Wraith, D.; Davies, J. A global survey addressing sustainability of pollen monitoring. World Allergy Organ. J. 2024, 17, 100997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirst, J.M. An automatic volumetric spore trap. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1952, 39, 157–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, K.A.; Bennett, K.D. Principles and methods for automated palynology. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weber, R.W. Pollen Identification. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1998, 80, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabey, A.M.; Gallagher, M.W.; Whitehead, J.; Dorsey, J.R.; Kaye, P.H.; Stanley, W.R. Measurements and comparison of primary biological aerosol above and below a tropical forest canopy using a dual channel fluorescence spectrometer. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 4453–4466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, N.J.; Krentz, C.E.; Könemann, T.; Han, T.T.; Mainelis, G.; Pöhlker, C.; Huffman, J.A. Systematic characterization and fluorescence threshold strategies for the wideband integrated bioaerosol sensor (WIBS) using size-resolved biological and interfering particles. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2017, 10, 4279–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šauliene, I.; Šukiene, L.; Daunys, G.; Valiulis, G.; Vaitkevicius, L.; Matavulj, P.; Brdar, S.; Panic, M.; Sikoparija, B.; Clot, B.; et al. Automatic pollen recognition with the Rapid-E particle counter: The first-level procedure, experience and next steps. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 3435–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oteros, J.; Pusch, G.; Weichenmeier, I.; Heimann, U.; Möller, R.; Röseler, S.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Schmidt-Weber, C.; Buters, J.T.M. Automatic and Online Pollen Monitoring. Int. Arch. Allergy Imm. 2015, 167, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvageat, E.; Zeder, Y.; Auderset, K.; Calpini, B.; Clot, B.; Crouzy, B.; Konzelmann, T.; Lieberherr, G.; Tummon, F.; Vasilatou, K. Real-time pollen monitoring using digital holography. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2020, 13, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, K.; Kawashima, S. Estimation of pollen counts from light scattering intensity when sampling multiple pollen taxa—Establishment of an automated multi-taxa pollen counting estimation system (AME system). Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2021, 14, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, S.; Shang, X.; Giannakaki, E.; Filioglou, M.; Saarto, A. Detection and characterization of birch pollen in the atmosphere using a multiwavelength Raman polarization lidar and Hirst-type pollen sampler in Finland. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2019, 19, 14559–14569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.M.; Müller, D.; Lee, H.; Choi, T.J. Influence of biogenic pollen on optical properties of atmospheric aerosols observed by lidar over Gwangju, South Korea. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 69, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.M.; Lee, H.; Mueller, D.; Lee, K.; Shin, D.; Shin, S.; Choi, T.J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, K.R. Investigation of the diurnal pattern of the vertical distribution of pollen in the lower troposphere using LIDAR. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2013, 13, 7619–7629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassen, K. Boreal tree pollen sensed by polarization lidar: Depolarizing biogenic chaff. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2008, 35, L18810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sicard, M.; Izquierdo, R.; Alarcón, M.; Belmonte, J.; Comerón, A.; Baldasano, J.M. Near-surface and columnar measurements with a micro pulse lidar of atmospheric pollen in Barcelona, Spain. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 6805–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohlmann, S.; Shang, X.; Vakkari, V.; Giannakaki, E.; Leskinen, A.; Lehtinen, K.E.J.; Pätsi, S.; Komppula, M. Lidar depolarization ratio of atmospheric pollen at multiple wavelengths. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 7083–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mona, L.; Liu, Z.; Müller, D.; Omar, A.; Papayannis, A.; Pappalardo, G.; Sugimoto, N.; Vaughan, M. Lidar measurements for desert dust characterization: An overview. Adv. Meteorol. 2012, 36, 356265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Lou, M.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, H.; He, J.; Xu, H.; Wang, F.; Min, M.; et al. Trans-Pacific transport of dust aerosols from East Asia: Insights gained from multiple observations and modeling. Environ. Pol. 2017, 230, 1030–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senghor, H.; Machu, É.; Hourdin, F.; Gaye, A.T. Seasonal cycle of desert aerosols in western Africa: Analysis of the coastal transition with passive and active sensors. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2017, 17, 8395–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Han, Y.; Voulgarakis, A.; Wang, T.; Li, M.; Wang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhuang, B.; Li, S. An agricultural biomass burning episode in eastern China: Transport, optical properties, and impacts on regional air quality. J. Geophys. Res.-Atmos. 2017, 122, 2304–2324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, H.; Ginoux, P.; Shen, J. Global dust optical depth climatology derived from CALIOP and MODIS aerosol retrievals on decadal timescales: Regional and interannual variability. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 13369–13395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, L.; Tao, M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, L.; Lin, C.; Tao, J.; Wang, J.; Yu, C. Climatology of aerosol types and their vertical distribution over East Asia based on CALIPSO lidar measurements. Int. J. Climatol. 2022, 42, 6042–6054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, T.; Anchule, A.; Sorek-Hamer, M.; Latif, M.T. Vertical stratification of aerosols over South Asian cities. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 309, 119776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukurov, K.A.; Simonenkov, D.V.; Nevzorov, A.V.; Rashki, A.; Hamzeh, N.H.; Abdullaev, S.F.; Shukurova, L.M.; Chkhetiani, O.G. CALIOP-Based Evaluation of Dust Emissions and Long-Range Transport of the Dust from the Aral−Caspian Arid Region by 3D-Source Potential Impact (3D-SPI) Method. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, R.; Higurashi, A.; Oikawa, E.; Fujikawa, M.; Ishimoto, H.; Nishizawa, T. Global 3-D distribution of aerosol composition by synergistic use of CALIOP and MODIS observations. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2023, 16, 3835–3863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.C.; Mytilinaios, M.; Foskinis, R.; Kyrou, C.; Papayannis, A.; Pyrri, I.; Giannoutsou, E.; Adamakis, I.D. Bioaerosol detection over Athens, Greece using the laser induced fluorescence technique. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 133906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, E.K.; Yannitsaros, A.G. Atmospheric pollen in the area of Athens. Acta Allergol. 1977, 32, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioulekas, D.; Balafoutis, C.; Damialis, A.; Papakosta, D.; Gioulekas, G.; Patakas, D. Fifteen years’ record of airborne allergenic pollen and meteorological parameters in Thessaloniki, Greece. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2004, 48, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ELSTAT: Resident Population Census. Hellenic Statistical Authority. 2021. Available online: https://elstat-outsourcers.statistics.gr/census_results_2022_en.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Pielke, R.A.; McNider, R.T.; Segal, M.; Mahrer, Y. The use of a mesoscale numerical model for evaluations of pollutant transport and diffusion in coastal regions and over irregular terrain. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1983, 64, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassomenos, P.; Kotroni, V.; Kallos, G. Analysis of climatological and air quality observations from Greater Athens Area. Atmos. Environ. 1995, 29, 3671–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drosoglou, T.; Koukouli, M.E.; Raptis, I.P.; Kazadzis, S.; Pseftogkas, A.; Eleftheratos, K.; Zerefos, C. Nitrogen dioxide spatiotemporal variations in the complex urban environment of Athens, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 314, 120115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pateraki, S.; Fameli, K.M.; Assimakopoulos, V.; Bairachtari, K.; Zagkos, A.; Stavraka, T.; Bougiatioti, A.; Maggos, T.; Mihalopoulos, N. Differentiation of the Athens Fine PM Profile during Economic Recession (March of 2008 Versus March of 2013): Impact of Changes in Anthropogenic Emissions and the Associated Health Effect. Atmosphere 2020, 11, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varotsos, C.; Ondov, J.; Efstathiou, M. Scaling properties of air pollution in Athens, Greece and Baltimore, Maryland. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 4041–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economopoulou, A.A.; Economopoulos, A.P. Air Pollution in Athens Basin and Health Risk Assessment. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2002, 80, 277–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touloumi, G.; Samoli, E.; Katsouyanni, K. Daily mortality and “winter type” air pollution in Athens, Greece—A time series analysis within the APHEA project. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1996, 50 (Suppl. S1), S47–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flocas, H.; Kelessis, A.; Helmis, C.; Petrakakis, M.; Zoumakis, M.; Pappas, K. Synoptic and local scale atmospheric circulation associated with air pollution episodes in an urban Mediterranean area. Theor. Appl. Climatol. 2009, 95, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmis, C.G.; Tombrou, M.; Asimakopoulos, D.N.; Soilemes, A.; Güsten, H.; Moussiopoulos, N.; Hatzaridou, A. Thessaloniki 91 field measurement campaign. I. Wind field and atmospheric boundary layer structure over greater Thessaloniki area under light background flow. Atmos. Environ. 1997, 31, 1101–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussiopoulos, N.; Vlachokostas, C.H.; Tsilingiridis, G.; Douros, I.; Hourdakis, E.; Naneris, C.; Sidiropoulos, C. Air quality status in Greater Thessaloniki Area and the emission reductions needed for attaining the EU air quality legislation. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 1268–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, X.; Giannakaki, E.; Bohlmann, S.; Filioglou, M.; Saarto, A.; Ruuskanen, A. Optical characterization of pure pollen types using a multi-wavelength Raman polarization lidar. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2020, 20, 15323–15339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwendemann, A.B.; Wang, G.; Mertz, M.L.; McWilliams, R.T.; Thatcher, S.L.; Osborn, J.M. Aerodynamics of saccate pollen and its implications for wind pollination. Am. J. Bot. 2007, 94, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhondnezhad, S.; Nejadsattari, T.; Sattarian, A.; Asri, Y.; Bagheriieh, N.M. Pollen morphology of the genus Carpinus L. (Corylaceae) in Iran. Iran. J. Bot. 2011, 17, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bricchi, E.; Frenguelli, G.; Mincigrucci, G. Experimental results about Platanus pollen deposition. Aerobiologia 2000, 16, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winker, D.M.; Pelon, J.; Coakley, J.A., Jr.; Ackerman, S.A.; Charlson, R.J.; Colarco, P.R.; Flamant, P.; Fu, Q.; Hoff, R.M.; Kittaka, C.; et al. The CALIPSO mission: A global 3D view of aerosols and clouds. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2010, 91, 1211–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaughan, M.; Powell, K.; Kuehn, R.; Young, S.; Winker, D.; Hostetler, C.; Hunt, W.; Liu, Z.; McGill, M.; Getzewich, B. Fully Automated Detection of Cloud and Aerosol Layers in the CALIPSO Lidar Measurements. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 2034–2050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Vaughan, M.; Winker, D.; Kittaka, C.; Getzewich, B.; Kuehn, R.; Omar, A.; Powell, K.; Trepte, C.; Hostetler, C. The CALIPSO lidar cloud and aerosol discrimination: Version 2 algorithm and initial assessment 15 of performance. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1198–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, A.H.; Winker, D.M.; Kittaka, C.; Vaughan, M.A.; Liu, Z.; Hu, Y.; Trepte, C.R.; Rogers, R.R.; Ferrare, R.A.; Lee, K.P.; et al. The CALIPSO automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. J. Atmos. Ocean. Technol. 2009, 26, 1994–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Omar, A.H.; Tackett, J.L.; Vaughan, M.A.; Winker, D.M.; Trepte, C.R.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Poole, L.R.; Pitts, M.C.; et al. The CALIPSO version 4 automated aerosol classification and lidar ratio selection algorithm. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 11, 6107–6135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. Description of the HYSPLIT 4 Modeling System; NOAA Technical Memorandum ERL ARL-224; NOAA: Silver Spring, MD, USA, 1997.
- Draxler, R.R.; Hess, G.D. An overview of the hysplit_4 modeling system for trajectories, dispersion, and deposition. Aust. Meteorol. Mag. 1998, 47, 295–308. [Google Scholar]
- Pielke, R.A.; Cotton, W.R.; Walko, R.L.; Tremback, C.J.; Lyons, W.A.; Grasso, L.D.; Nicholls, M.E.; Moran, M.D.; Wesley, D.A.; Lee, T.J.; et al. A Comprehensive Meteorological Modeling System RAMS, Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 1992, 49, 69–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomos, S.; Kallos, G.; Kushta, J.; Astitha, M.; Tremback, C.; Nenes, A.; Levin, Z. An integrated modeling study on the effects of mineral dust and sea salt particles on clouds and precipitation. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 873–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyro, S.; Aas, W.; Soares, W.; Sofiev, M.; Berge, H.; Spindler, G. Modelling of sea salt concentrations over Europe: Key uncertainties and comparison with observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2011, 11, 10367–10388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manders, A.M.M.; Schaap, M.; Querol, X.; Albert, M.F.M.A.; Vercauteren, J.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Hoogerbrugge, R. Sea salt concentrations across the European continent. Atmos. Environ. 2010, 44, 2434–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, S.L.; Barrie, L.A.; Prospero, J.M.; Savoie, D.L.; Ayers, G.P.; Blanchet, J.-P.; Spacek, L. Modeling sea-salt aerosols in the atmosphere: 2. Atmospheric concentrations and fluxes. J. Geophys. Res. 1997, 102, 3819–3830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Roy, G.A.; Bernier, R. Lidar polarization discrimination of bioaerosols. Opt. Eng. 2010, 49, 116201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cholleton, D.; Rairoux, P.; Miffre, A. Laboratory Evaluation of the (355, 532) nm Particle Depolarization Ratio of Pure Pollen at 180.0° Lidar Backscattering Angle. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck, T.F.; Holben, B.N.; Reid, J.S.; Dubovik, O.; Smirnov, A.; O’neill, N.T.; Slutsker, I.; Kinne, S. Wavelength dependence of the optical depth of biomass burning, urban and desert dust aerosols. J. Geophys. Res. 1999, 104, 31333–31350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siomos, N.; Balis, D.S.; Voudouri, K.A.; Giannakaki, E.; Filioglou, M.; Amiridis, V.; Papayannis, A.; Fragkos, K. Are EARLINET and AERONET climatologies consistent? The case of Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 11885–11903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mylonaki, M.; Giannakaki, E.; Papayannis, A.; Papanikolaou, C.-A.; Komppula, M.; Nicolae, D.; Papagiannopoulos, N.; Amodeo, A.; Baars, H.; Soupiona, O. Aerosol type classification analysis using EARLINET multiwavelength and depolarization lidar observations. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2021, 21, 2211–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



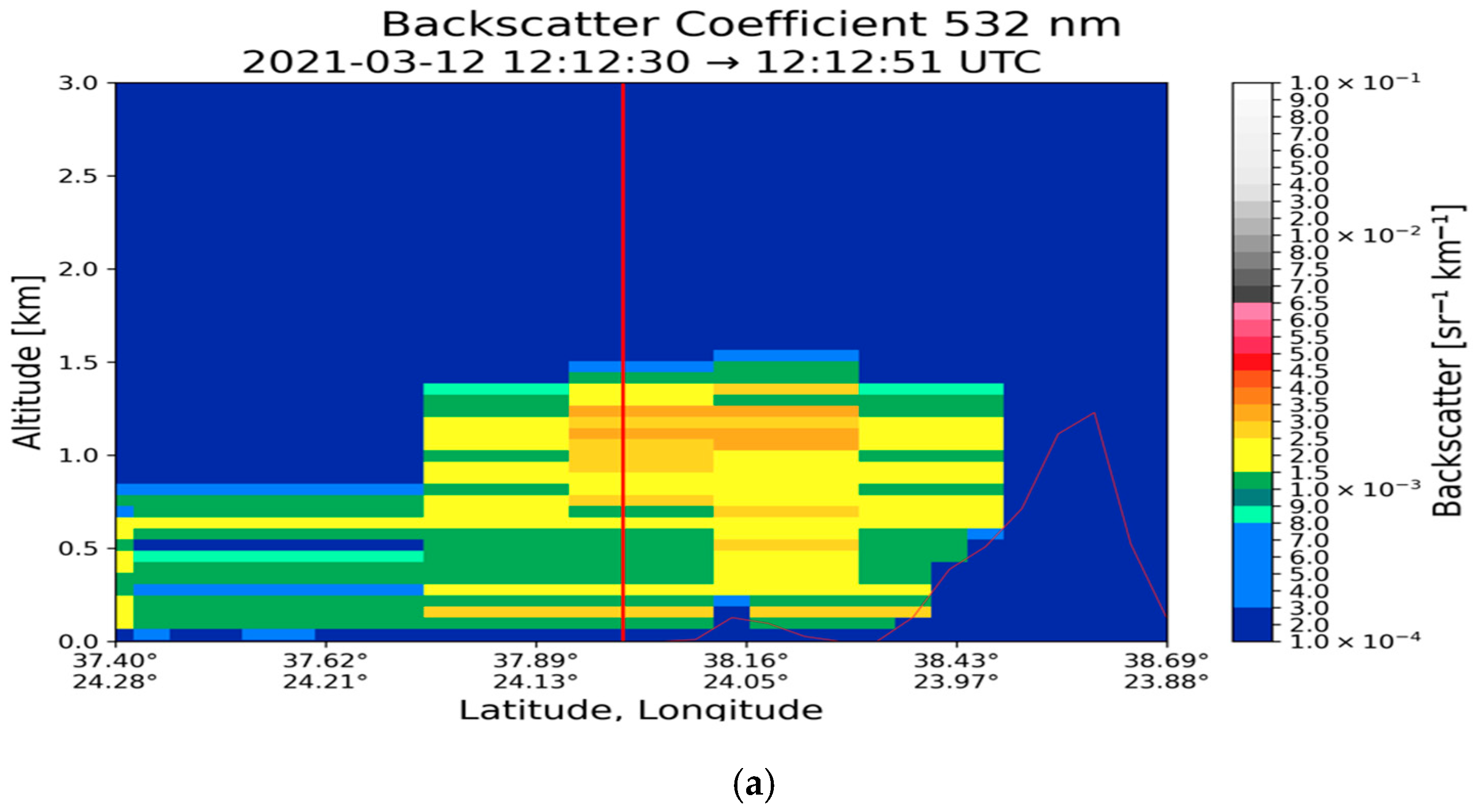
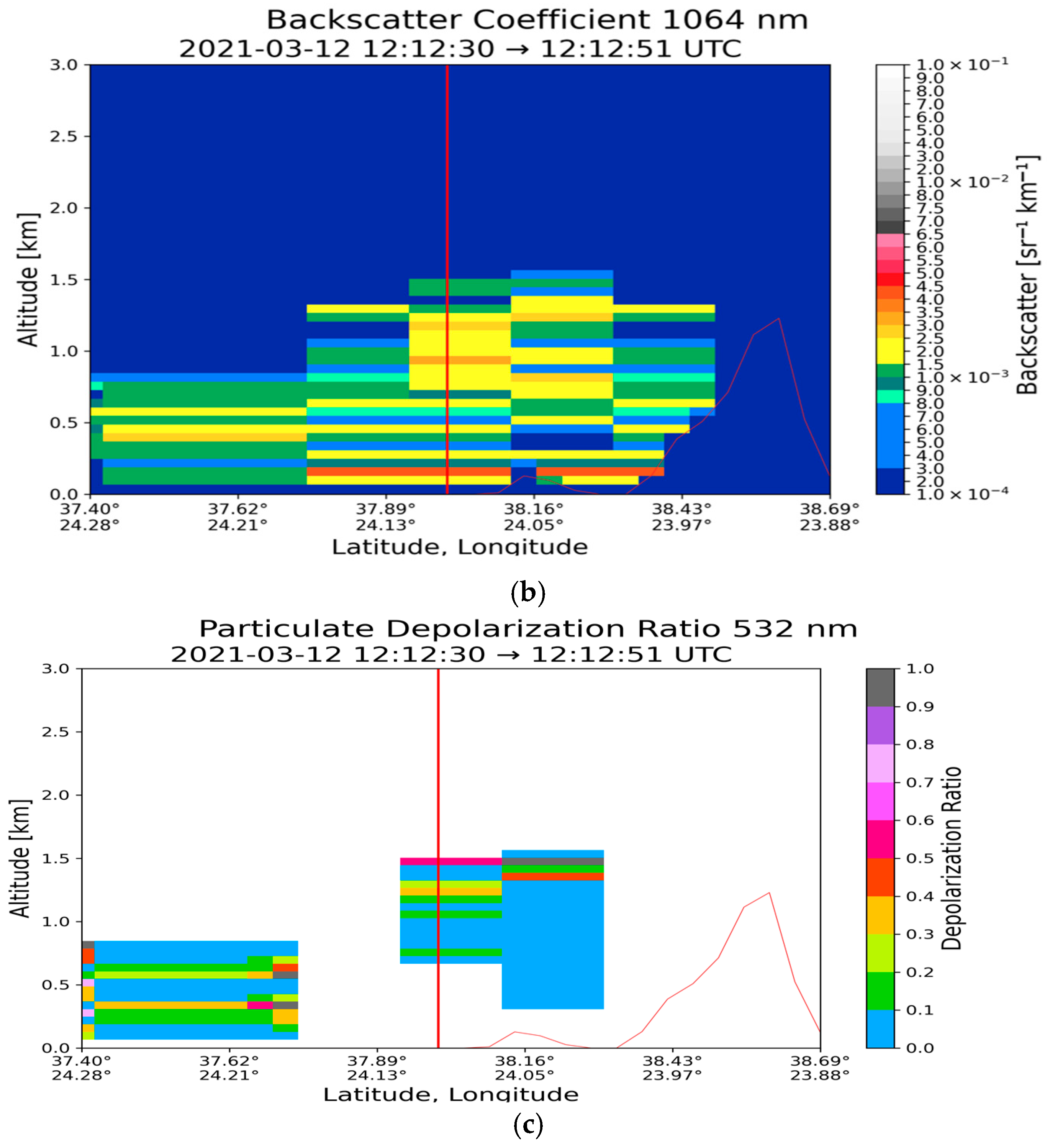

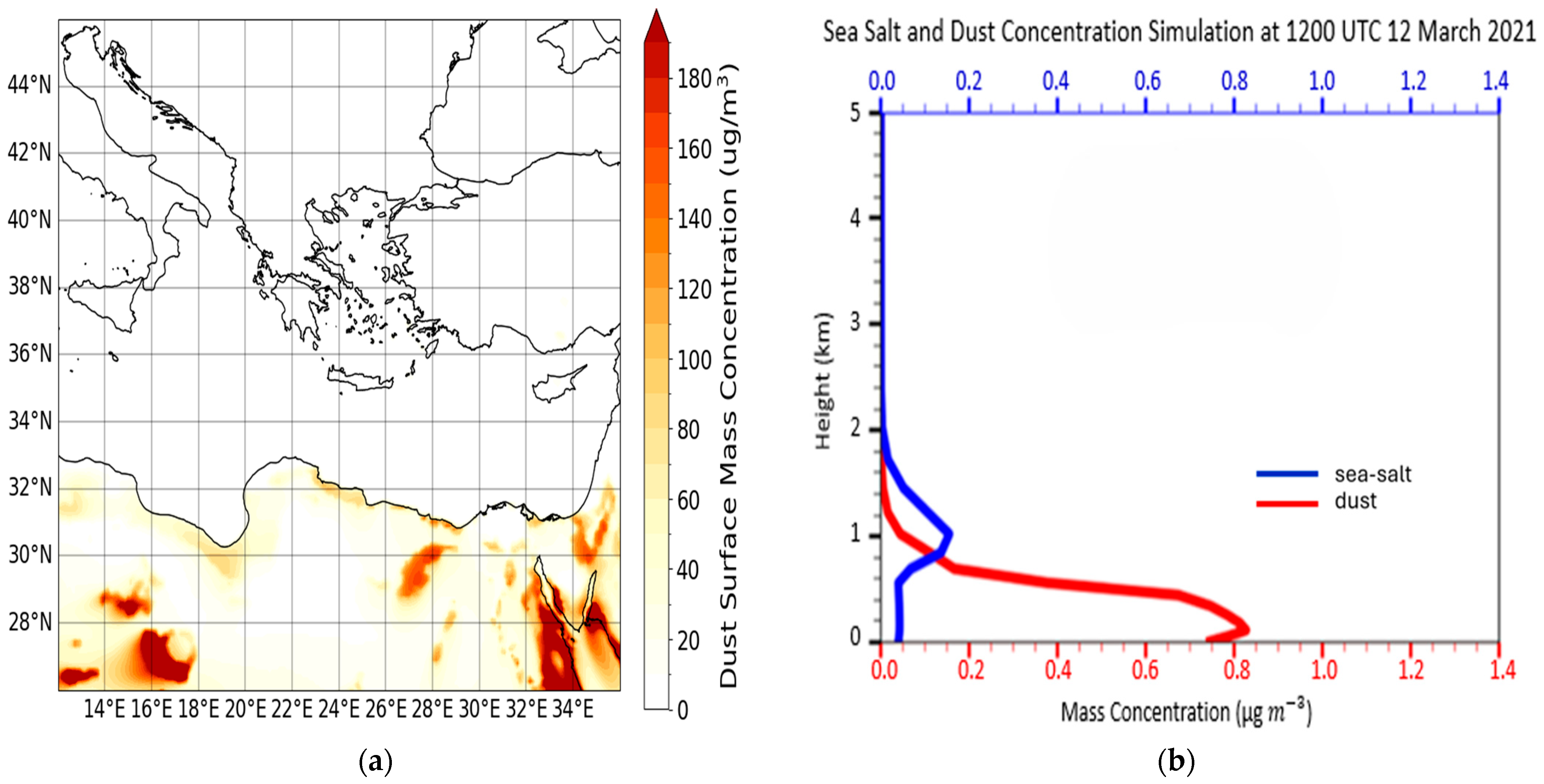
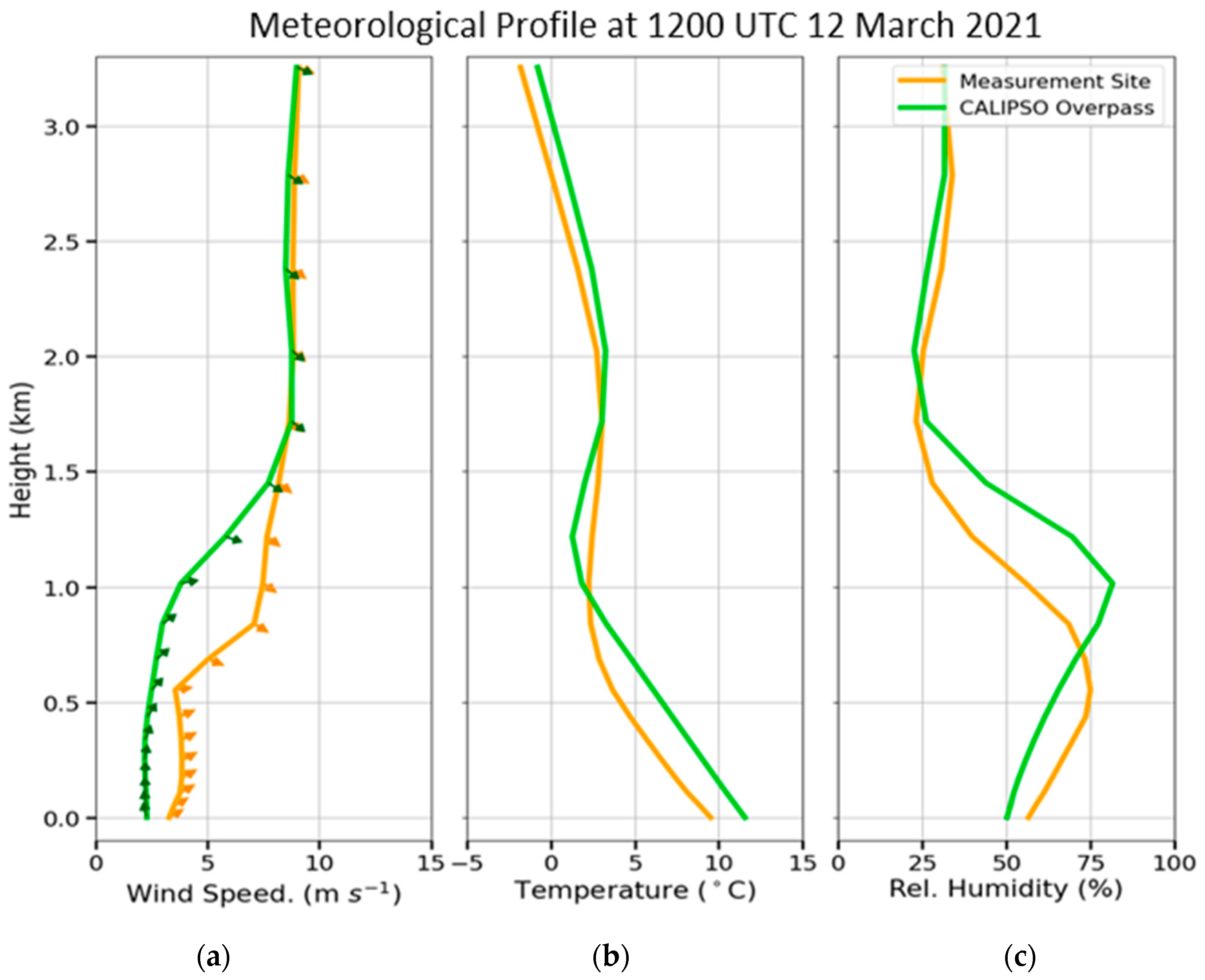

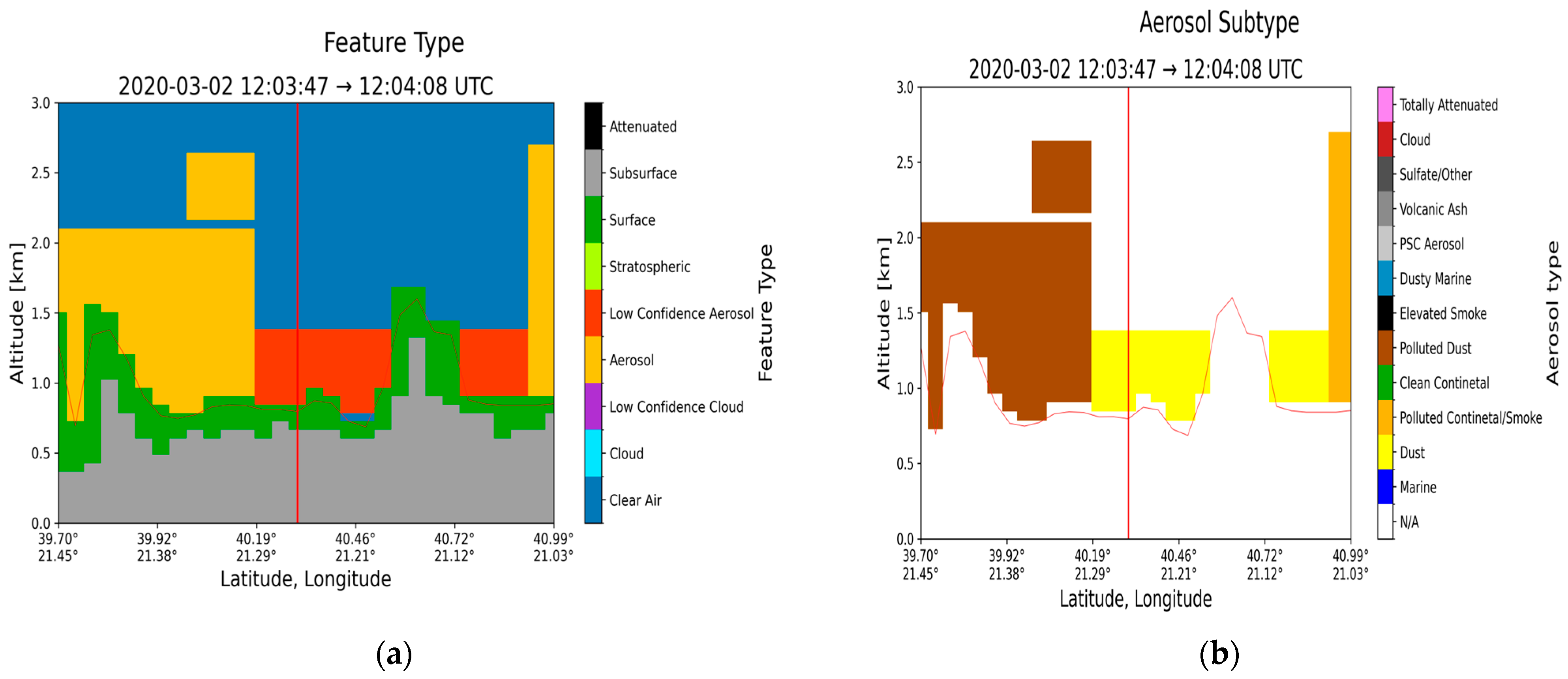
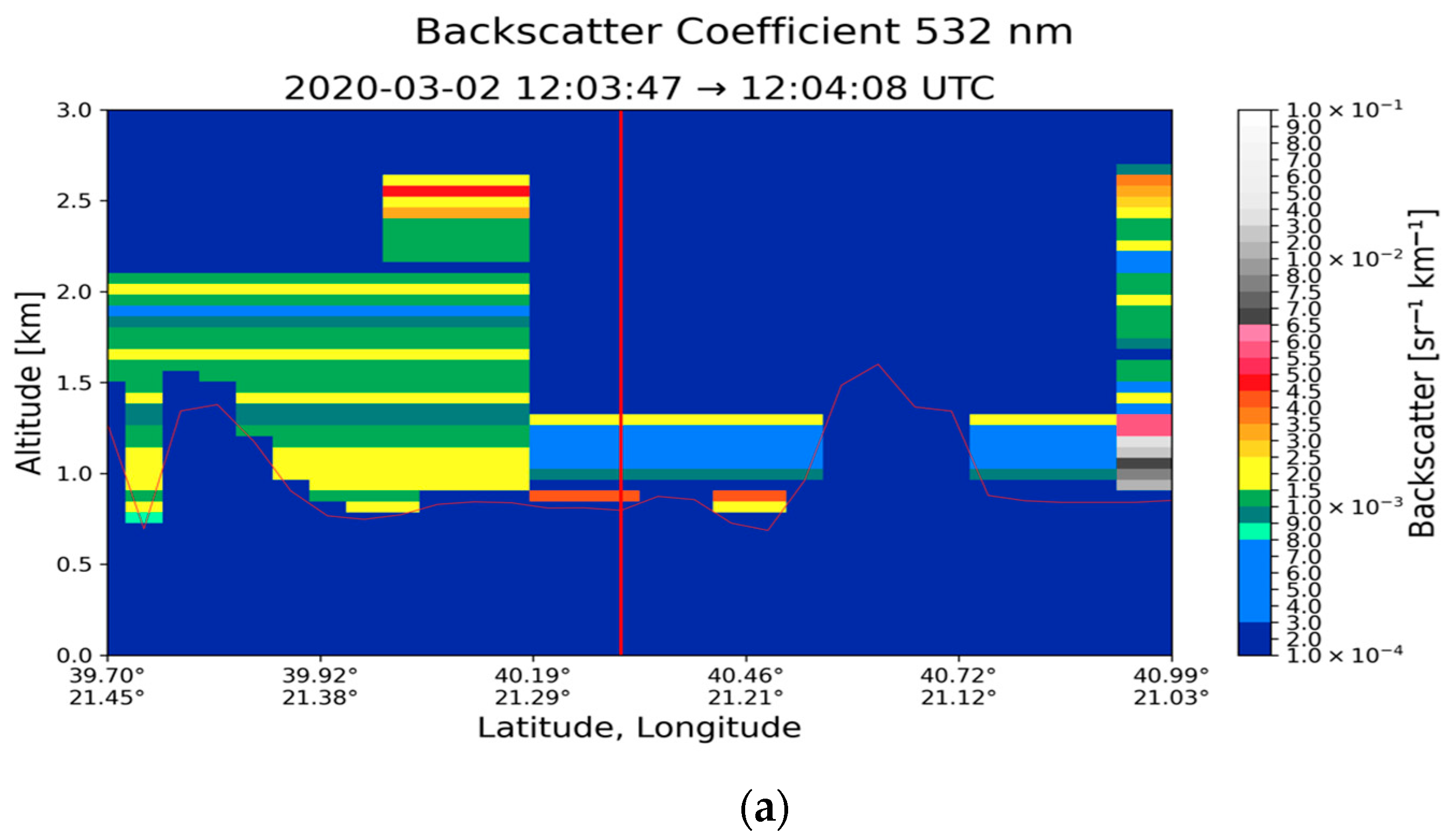
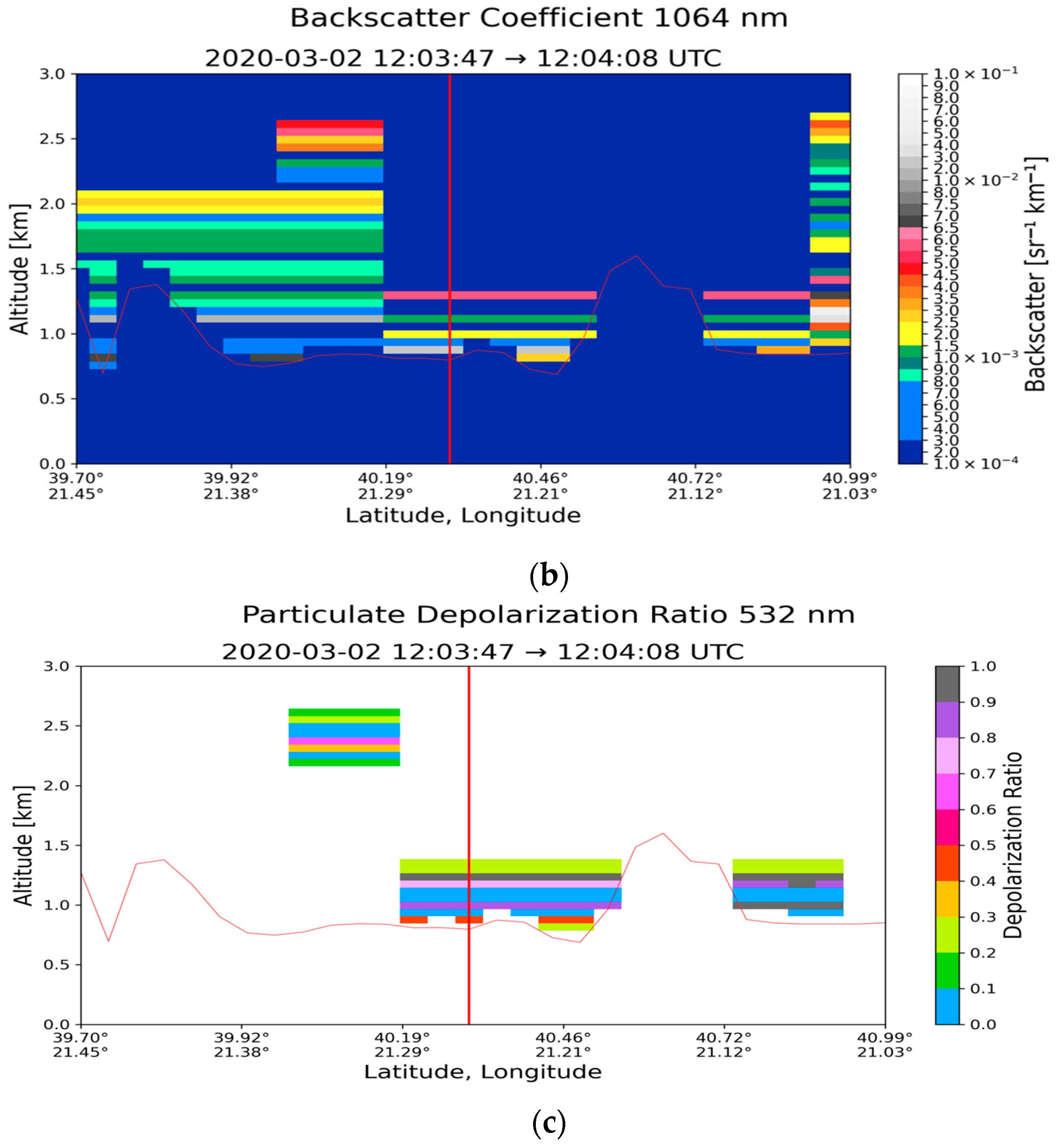
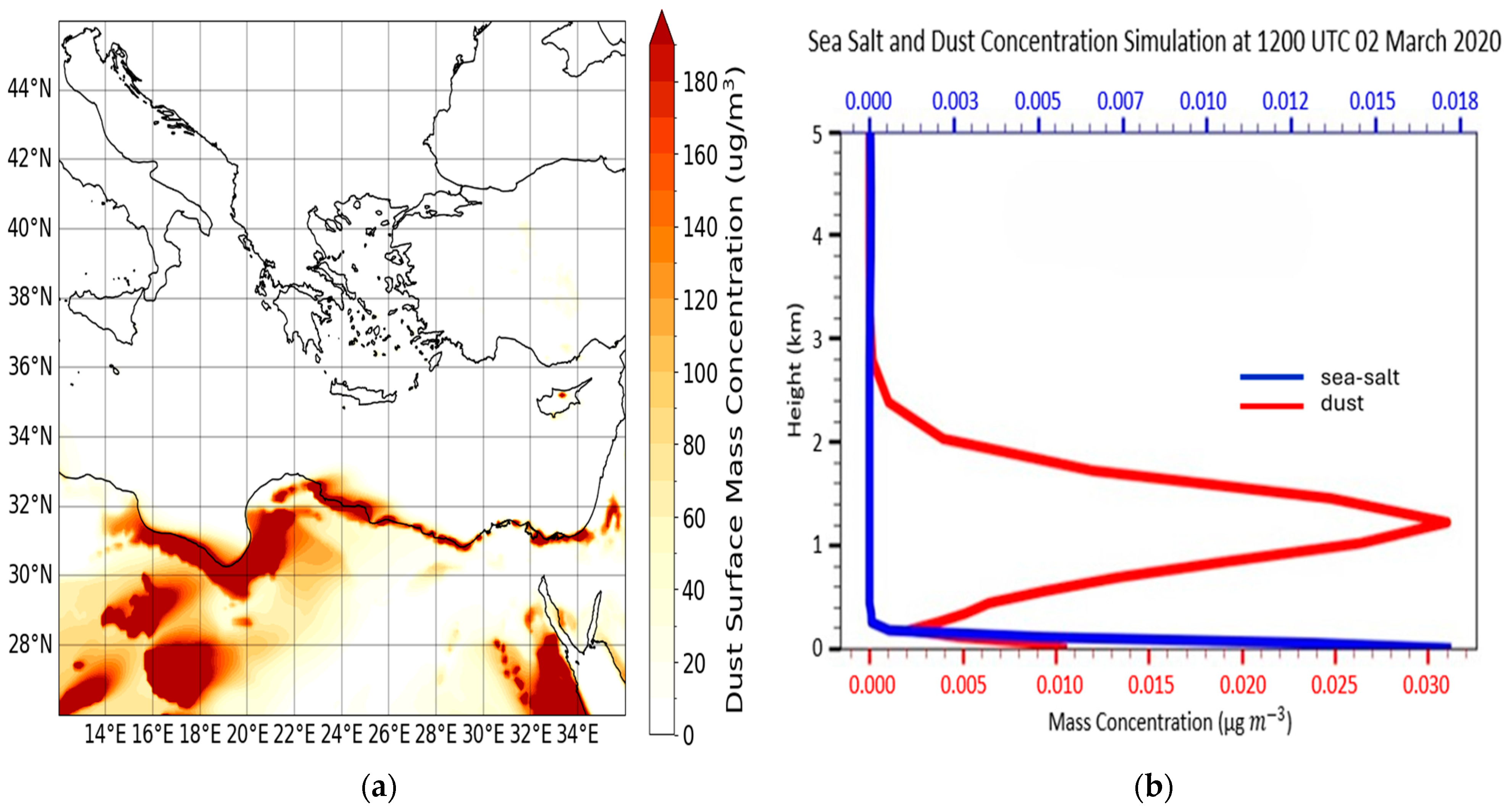
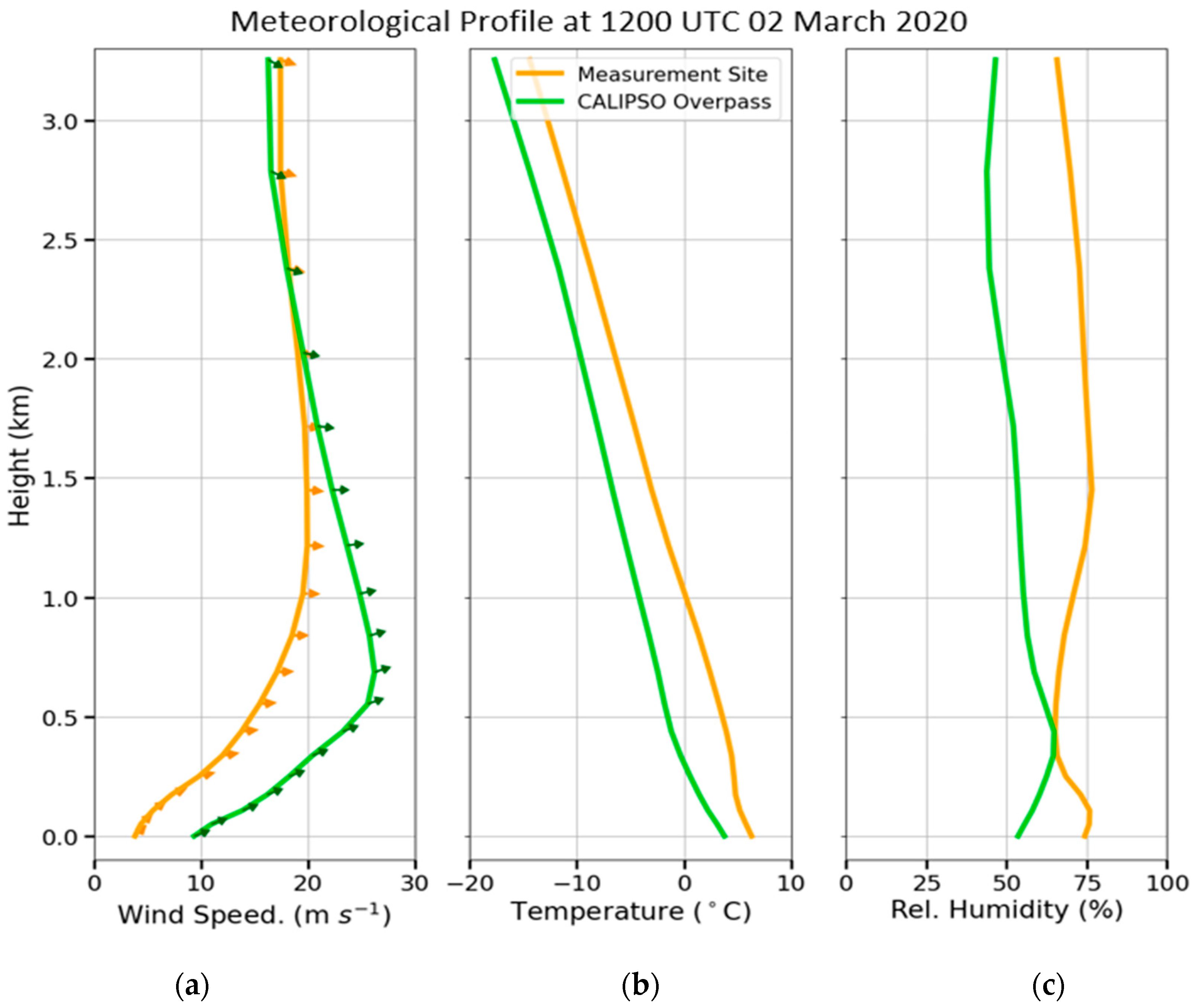
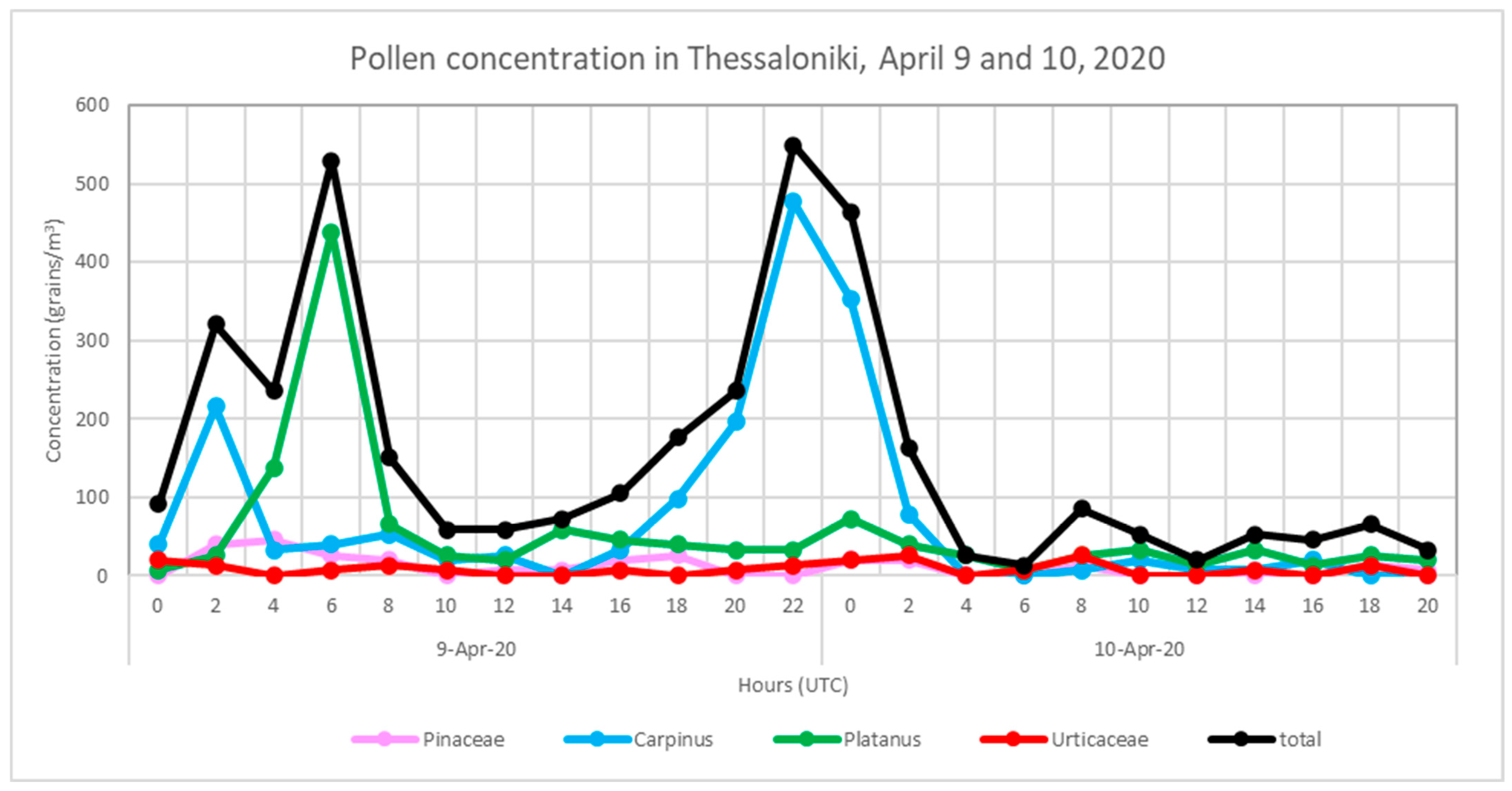
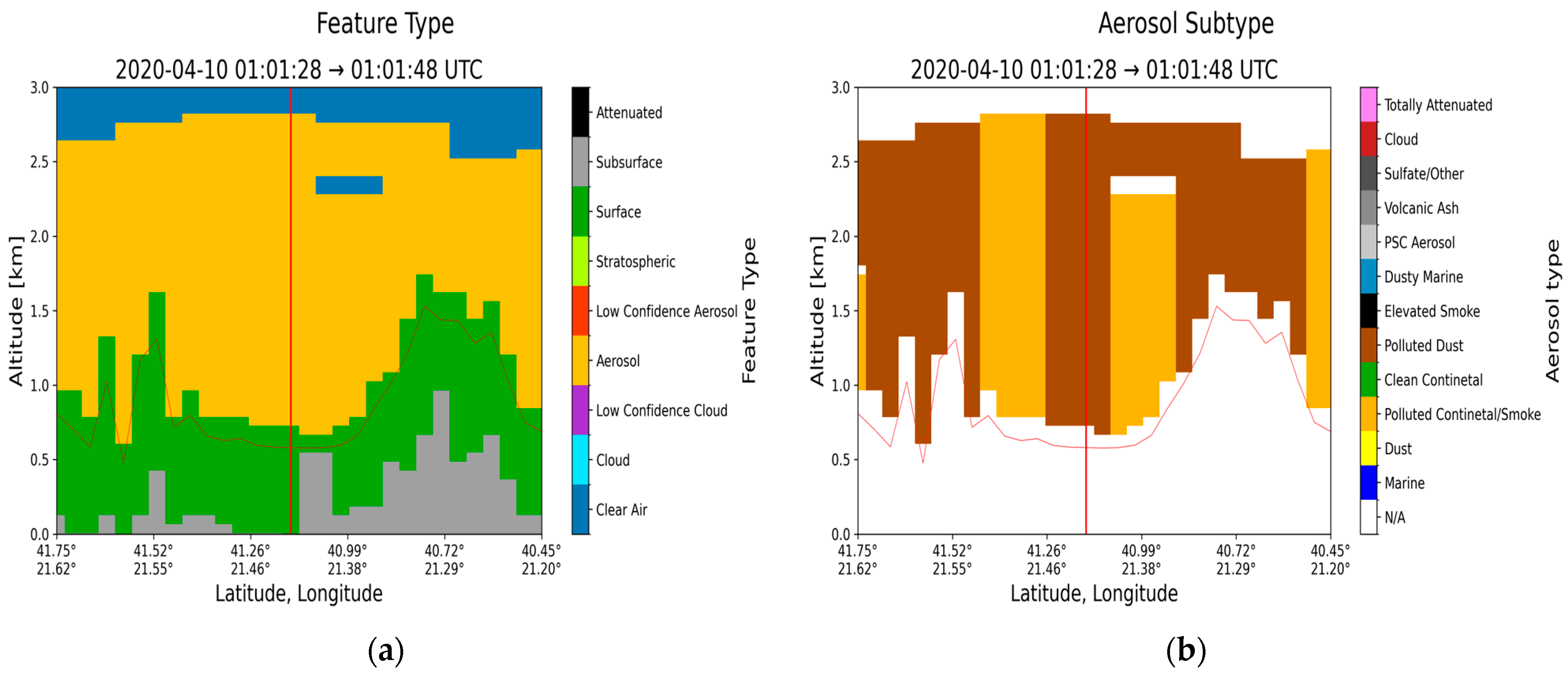
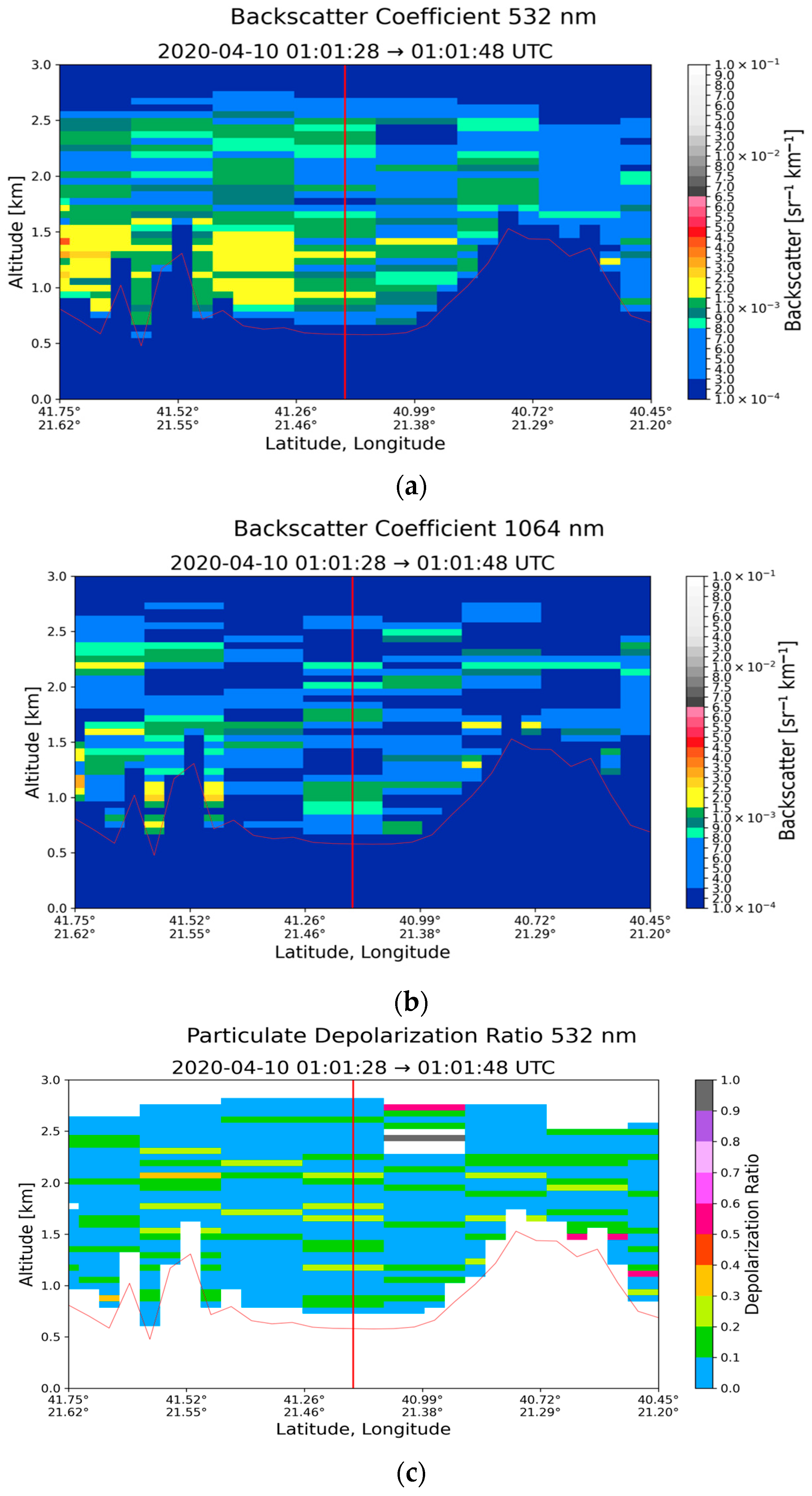

| Region | Date | Time CALIPSO Overpass (UTC) | Max Time Pollen (UTC) | Max Total Pollen Concentration (Grains m−3) | Dominant PollenType(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athens (37.97° N, 23.78° E) | 12 March 2021 | 12:12:40 | 10–12 | 409 | Pinaceae 69% Cupressaceae 24% |
| Thessaloniki (40.63° N, 22.96° E) | 2 March 2020 | 12:03:58 | 8–10 | 424 | Cupressaceae 97% |
| 10 April 2020 | 01:01:38 | 23 (9/4)–01 (10/4) | 464 | Carpinus 76% Platanus 15% |
| Region | Date | Layer Base Altitude (km) | Layer Top Altitude (km) | Depolarization Ratio (%) | Color Ratio | Feature Optical Depth 532 nm | Feature Optical Depth 1064 nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Athens (37.97° N, 23.78° E) | 12 March 2021 | 0.083 | 1.370 | 8.70 ± 6.26 | 0.652 ± 0.194 | 0.047 ± 0.012 | 0.034 ± 0.014 |
| Thessaloniki (40.63° N, 22.96° E) | 2 March 2020 | 0.801 | 1.340 | 28.30 ± 14.16 | 0.638 ± 0.362 | 0.030 ± 0.009 | 0.019 ± 0.007 |
| 10 April 2020 | 0.711 | 2.777 | 8.96 ± 6.87 | 0.456 ± 0.284 | 0.105 ± 0.044 | 0.039 ± 0.035 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Karageorgopoulou, A.; Giannakaki, E.; Stathopoulos, C.; Georgiou, T.; Marinou, E.; Amiridis, V.; Pyrri, I.; Gatou, M.-C.; Shang, X.; Charalampopoulos, A.; et al. CALIPSO Overpasses During Three Atmospheric Pollen Events Detected by Hirst-Type Volumetric Samplers in Two Urban Cities in Greece. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030317
Karageorgopoulou A, Giannakaki E, Stathopoulos C, Georgiou T, Marinou E, Amiridis V, Pyrri I, Gatou M-C, Shang X, Charalampopoulos A, et al. CALIPSO Overpasses During Three Atmospheric Pollen Events Detected by Hirst-Type Volumetric Samplers in Two Urban Cities in Greece. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(3):317. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030317
Chicago/Turabian StyleKarageorgopoulou, Archontoula, Elina Giannakaki, Christos Stathopoulos, Thanasis Georgiou, Eleni Marinou, Vassilis Amiridis, Ioanna Pyrri, Maria-Christina Gatou, Xiaoxia Shang, Athanasios Charalampopoulos, and et al. 2025. "CALIPSO Overpasses During Three Atmospheric Pollen Events Detected by Hirst-Type Volumetric Samplers in Two Urban Cities in Greece" Atmosphere 16, no. 3: 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030317
APA StyleKarageorgopoulou, A., Giannakaki, E., Stathopoulos, C., Georgiou, T., Marinou, E., Amiridis, V., Pyrri, I., Gatou, M.-C., Shang, X., Charalampopoulos, A., Vokou, D., & Damialis, A. (2025). CALIPSO Overpasses During Three Atmospheric Pollen Events Detected by Hirst-Type Volumetric Samplers in Two Urban Cities in Greece. Atmosphere, 16(3), 317. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16030317










