Atmospheric Estrogenic Semi-Volatile Compounds and PAH in PM2.5 in Mexico City
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sampling Site
2.2. Sampling
2.3. Chemicals and Reagents
2.4. Extraction and Derivatization
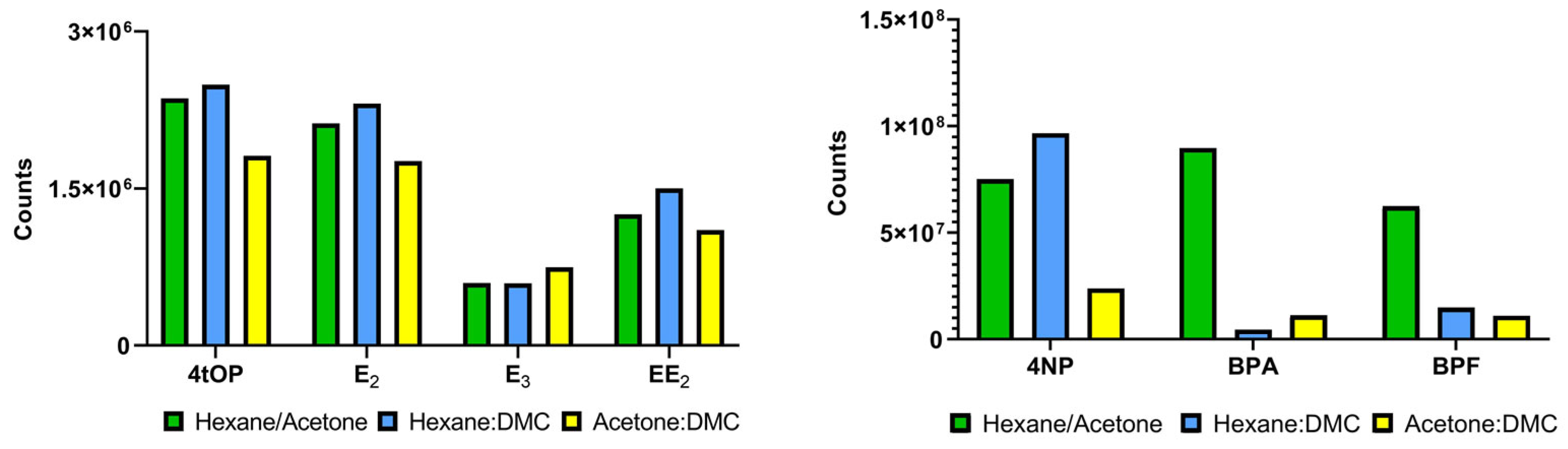
2.5. Method Validation and Extraction Optimization
2.6. Risk Assessment for Estrogenic Compounds
2.7. Carcinogenic and Mutagenic Potential Due to PAH
2.8. Chromatographic Analyses
2.9. Quality Assurance/Quality Control (QA/QC)
3. Results
3.1. Method Validation and Optimization
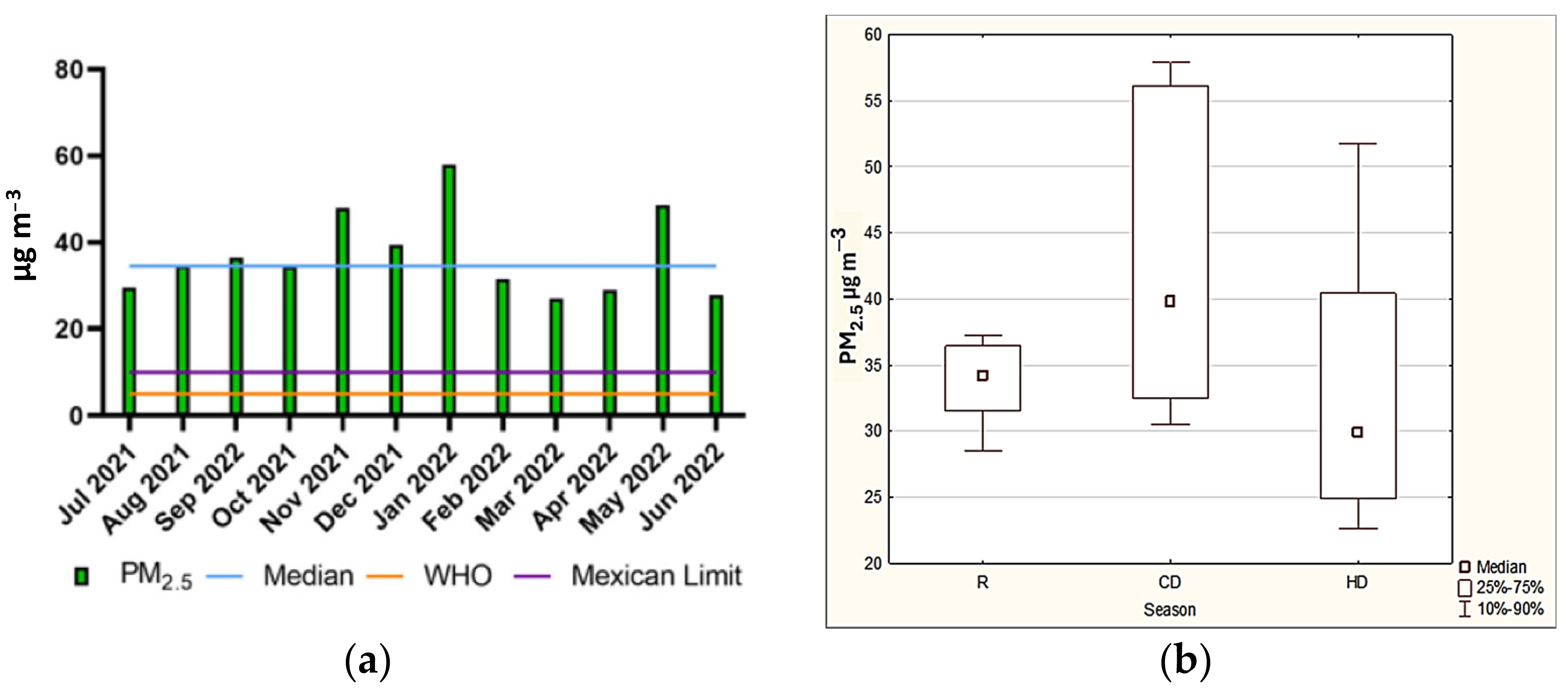
3.2. PM2.5 Concentration in the Mexico City Atmosphere
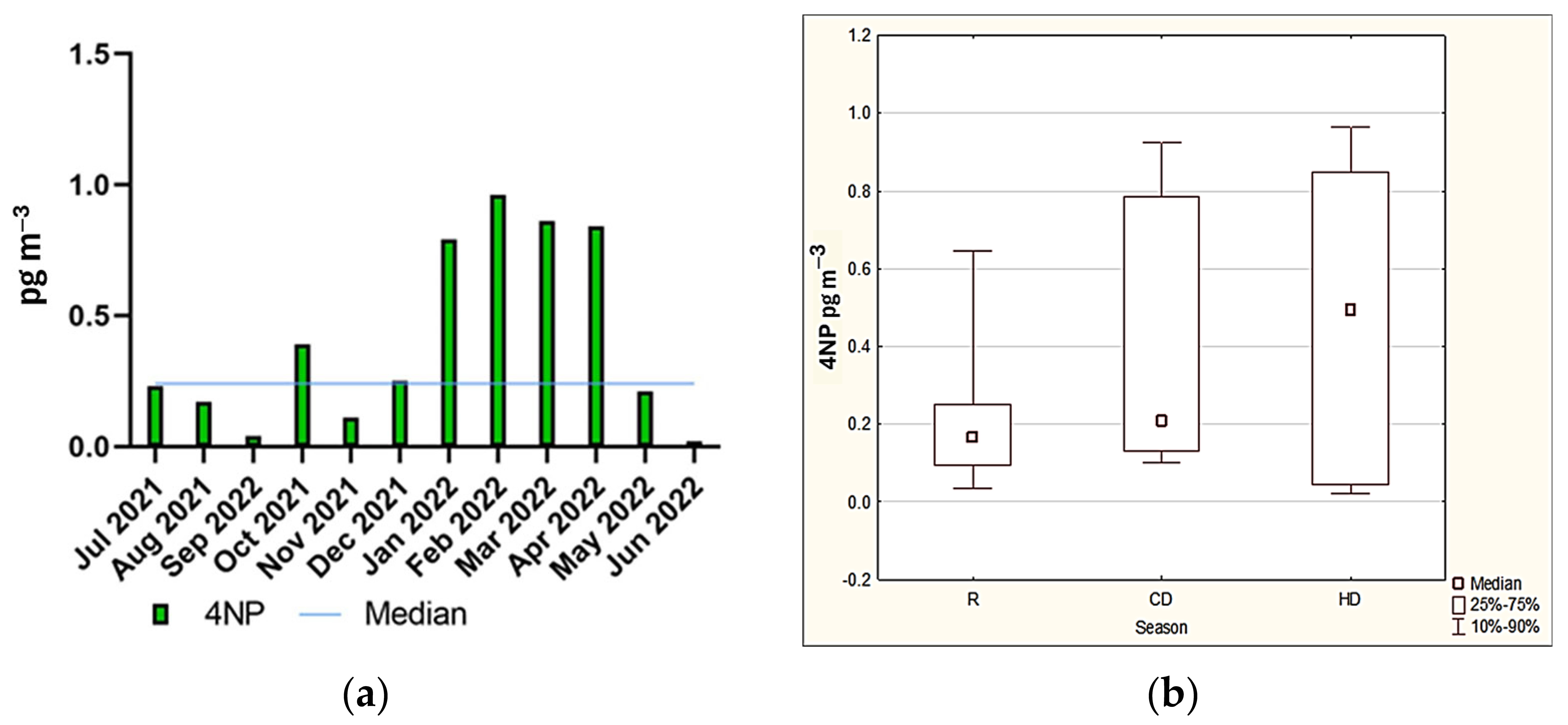
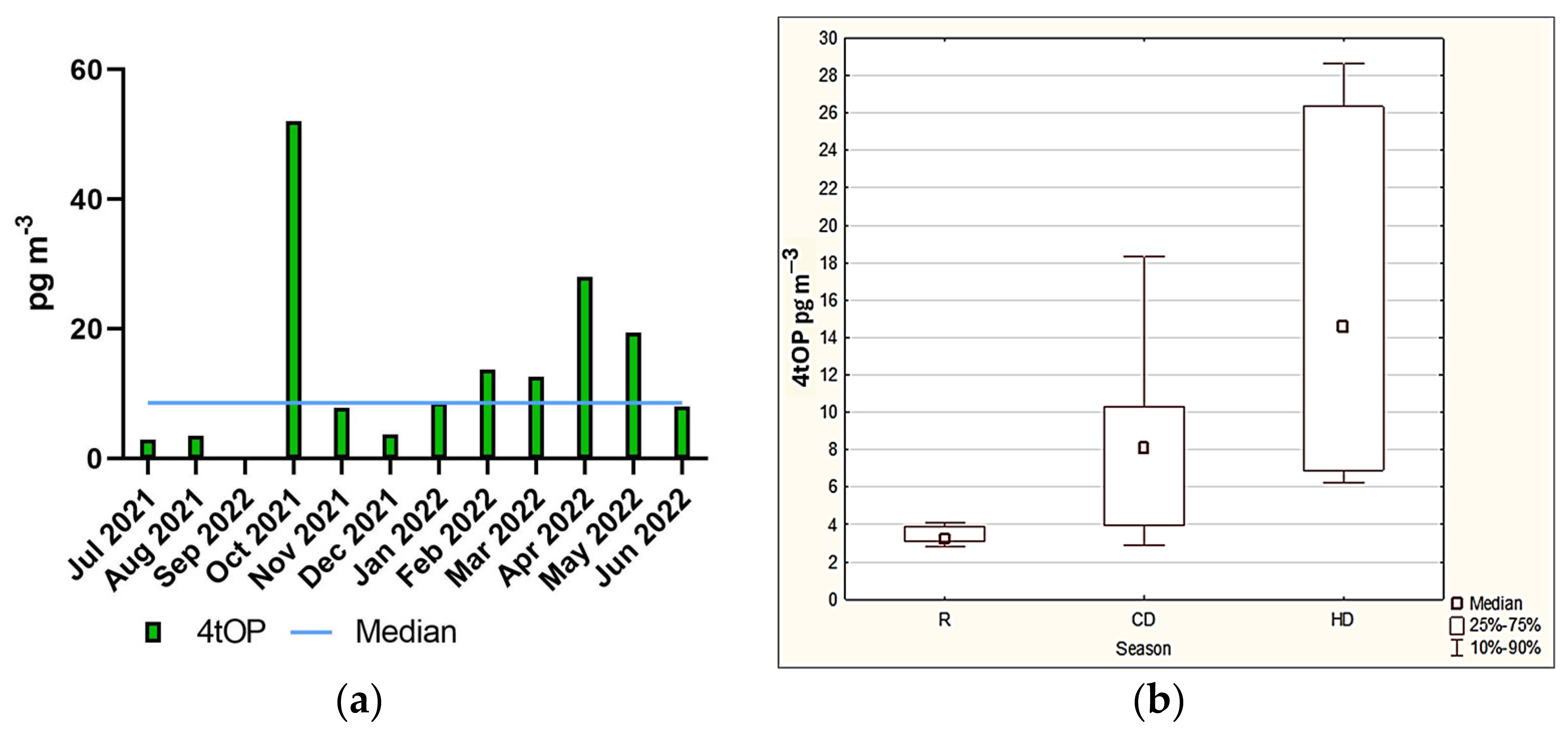
3.3. Estrogenic Semi-Volatile EDCs Concentrations Contained in PM2.5
3.4. Correlations Among Studied Compounds
3.5. Estrogenic Risk Assessment
3.6. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons
3.7. PAH Health Risk Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, M.U.; Liu, G.; Yousaf, B.; Ullah, H.; Abbas, Q.; Munir, M.A.M. A Systematic Review on Global Pollution Status of Particulate Matter-Associated Potential Toxic Elements and Health Perspectives in Urban Environment. Environ. Geochem. Health 2019, 41, 1131–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.O.; Thundiyil, J.G.; Stolbach, A. Clearing the Air: A Review of the Effects of Particulate Matter Air Pollution on Human Health. J. Med. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P. Overview of Air Pollution and Endocrine Disorders. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2018, 11, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Jin, Y.; Carlsten, C. Inflammatory Health Effects of Indoor and Outdoor Particulate Matter. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 833–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rovelli, S.; Cattaneo, A.; Nischkauer, W.; Borghi, F.; Spinazzè, A.; Keller, M.; Campagnolo, D.; Limbeck, A.; Cavallo, D.M. Toxic Trace Metals in Size-Segregated Fine Particulate Matter: Mass Concentration, Respiratory Deposition, and Risk Assessment. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 266, 115242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millán-Vázquez, F.; Sosa-Echevería, R.; Alarcón-Jiménez, A.L.; Figueroa-Lara, J.D.J.; Torres-Rodríguez, M.; Valle-Hernández, B.L.; Mugica-Álvarez, V. Temporal Variation and Potential Sources of Water-Soluble Inorganic Ions in PM2.5 in Two Sites of Mexico City. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, C.; Shen, H.; Su, S.; Shen, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Lin, N.; et al. Concentrations and Origins of Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Oxy-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Ambient Air in Urban and Rural Areas in Northern China. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 197, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, V.; Fang, T.; Xu, L.; Peltier, R.E.; Russell, A.G.; Ng, N.L.; Weber, R.J. Organic Aerosols Associated with the Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Water-Soluble PM2.5. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 4646–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gea, M.; Fea, E.; Racca, L.; Gilli, G.; Gardois, P.; Schilirò, T. Atmospheric Endocrine Disruptors: A Systematic Review on Oestrogenic and Androgenic Activity of Particulate Matter. Chemosphere 2024, 349, 140887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- US-EPA Environmental Protection Agency. Overview of Endocrine Disruption. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/endocrine-disruption/overview-endocrine-disruption (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Fu, P.; Kawamura, K. Ubiquity of Bisphenol A in the Atmosphere. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 3138–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgueiro-González, N.; López De Alda, M.; Muniategui-Lorenzo, S.; Prada-Rodríguez, D.; Barceló, D. Determination of 13 Estrogenic Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Atmospheric Particulate Matter by Pressurised Liquid Extraction and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 8913–8923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Xing, W.; Wang, Y.; Bai, P.; Tang, N. Exposure to Atmospheric Particulate Matter-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Their Health Effects: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Souza, T.L.d; sa Luz, J.Z.; de Almeida Roque, A.; Opuskevitch, I.; da Silva Ferreira, F.C.A.; de Oliveira Ribeiro, C.A.; Neto, F.F. Exploring the Endocrine Disrupting Potential of a Complex Mixture of PAHs in the Estrogen Pathway in Oreochromis Niloticus Hepatocytes. Aquat. Toxicol. 2024, 273, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderón-Moreno, G.M.; Vergara-Sánchez, J.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; García-Betancourt, M.L.; Domínguez-Patiño, M.L.; Moeller-Chávez, G.E.; Ronderos-Lara, J.G.; Arias-Montoya, M.I.; Montoya-Balbas, I.J.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A. Occurrence and Risk Assessment of Steroidal Hormones and Phenolic Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in Surface Water in Cuautla River, Mexico. Water 2019, 11, 2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peremiquel-Trillas, P.; Benavente, Y.; Martín-Bustamante, M.; Casabonne, D.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Gómez-Acebo, I.; Oliete-Canela, A.; Diéguez-Rodríguez, M.; Tusquets, I.; Amiano, P.; et al. Alkylphenolic Compounds and Risk of Breast and Prostate Cancer in the MCC-Spain Study. Environ. Int. 2019, 122, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- In, S.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Go, R.-E.; Hwang, K.-A.; Choi, K.-C. Benzophenone-1 and Nonylphenol Stimulated MCF-7 Breast Cancer Growth by Regulating Cell Cycle and Metastasis-Related Genes Via an Estrogen Receptor α-Dependent Pathway. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health Part A 2015, 78, 492–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivacqua, A.; Recchia, A.G.; Fasanella, G.; Gabriele, S.; Carpino, A.; Rago, V.; Gioia, M.L.D.; Leggio, A.; Bonofiglio, D.; Liguori, A.; et al. The Food Contaminants Bisphenol A and 4-Nonylphenol Act as Agonists for Estrogen Receptor in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells. Endocrine 2003, 22, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Montano, L.; Pironti, C.; Pinto, G.; Ricciardi, M.; Buono, A.; Brogna, C.; Venier, M.; Piscopo, M.; Amoresano, A.; Motta, O. Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs) in the Environment: Occupational and Exposure Events, Effects on Human Health and Fertility. Toxics 2022, 10, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vom Saal, F.S.; Vandenberg, L.N. Update on the Health Effects of Bisphenol A: Overwhelming Evidence of Harm. Endocrinology 2021, 162, bqaa171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, A.; Chakraborty, P. A Review on Sources and Health Impacts of Bisphenol A. Rev. Environ. Health 2020, 35, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrugia, F.; Aquilina, A.; Vassallo, J.; Pace, N.P. Bisphenol A and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Review of Epidemiologic, Functional, and Early Life Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.S.; Kwon, W.-S.; Lee, J.-S.; Yoon, S.-J.; Ryu, B.-Y.; Pang, M.-G. Bisphenol-A Affects Male Fertility via Fertility-Related Proteins in Spermatozoa. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 9169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, S.C.; Matthews, C.E.; Ou Shu, X.; Yu, K.; Gail, M.H.; Xu, X.; Ji, B.-T.; Chow, W.-H.; Cai, Q.; Li, H.; et al. Endogenous Estrogens, Estrogen Metabolites, and Breast Cancer Risk in Postmenopausal Chinese Women. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djw103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelles, J.L.; Hu, W.-Y.; Prins, G.S. Estrogen Action and Prostate Cancer. Expert Rev. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 6, 437–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolok, A.S.; Ali, J.M.; Rogan, E.G.; Bartelt-Hunt, S.L. The Fate of Synthetic and Endogenous Hormones Used in the US Beef and Dairy Industries and the Potential for Human Exposure. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2018, 5, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabuto, M.; Akiba, S.; Stevens, R.G.; Neriishi, K.; Land, C.E. A Prospective Study of Estradiol and Breast Cancer in Japanese Women. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2000, 9, 575–579. [Google Scholar]
- Barańska, A.; Kanadys, W. Oral Contraceptive Use and Breast Cancer Risk for BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Case–Control Studies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narod, S.A. Oral Contraceptives and the Risk of Breast Cancer in BRCA1 and BRCA2 Mutation Carriers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2002, 94, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanczyk, F.Z.; Archer, D.F.; Bhavnani, B.R. Ethinyl Estradiol and 17β-Estradiol in Combined Oral Contraceptives: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics and Risk Assessment. Contraception 2013, 87, 706–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Dong, S.; Wang, H.; Tao, S.; Kiyama, R. Biological Impact of Environmental Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (ePAHs) as Endocrine Disruptors. Environ. Pollut 2016, 213, 809–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, N.K.; Chuang, J.C.; Lyu, C. Levels of Persistent Organic Pollutants in Several Child Day Care Centers. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salapasidou, M.; Samara, C.; Voutsa, D. Endocrine Disrupting Compounds in the Atmosphere of the Urban Area of Thessaloniki, Greece. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3720–3729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, I.; Onuki, A.; Seto, H. Indoor Air Pollution by Alkylphenols in Tokyo. Indoor Air 2004, 14, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becouze, C.; Wiest, L.; Baudot, R.; Bertrand-Krajewski, J.-L.; Cren-Olivé, C. Optimisation of Pressurised Liquid Extraction for the Ultra-Trace Quantification of 20 Priority Substances from the European Water Framework Directive in Atmospheric Particles by GC–MS and LC–FLD–MS/MS. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 693, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkner, S.; Streck, G.; Herrmann, R. Development and Validation of a Method for Determination of Trace Levels of Alkylphenols and Bisphenol A in Atmospheric Samples. Chemosphere 2004, 54, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, H.A.; Calderón-Segura, M.E.; Gómez-Arroyo, S.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Amador-Muñoz, O. Composition and Mutagenicity of PAHs Associated with Urban Airborne Particles in Córdoba, Argentina. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.-L.; Zhu, F.-J.; Liu, L.-Y.; Jia, H.-L.; Yang, M.; Li, Y.-F. PAHs in Chinese Atmosphere: Gas/Particle Partitioning. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 693, 133623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, Y.; Chakradhari, S.; Patel, K.S.; Patel, R.K.; Yurdakul, S.; Saathoff, S.; Pablo, M.R. Distribution, variations, fate and sources of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and carbon in particulate matter, road dust, and sediments in Central India. Polycyclic Aromat. Compd. 2023, 1309–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villanueva, F.; Tapia, A.; Cabañas, B.; Martínez, E.; Albaladejo, J. Characterization of Particulate Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in an Urban Atmosphere of Central-Southern Spain. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2015, 22, 18814–18823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mugica, V.; Hernández, S.; Torres, M.; García, R. Seasonal Variation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon Exposure Levels in Mexico City. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2010, 60, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amador-Muñoz, O.; Martínez-Domínguez, Y.M.; Gómez-Arroyo, S.; Peralta, O. Current Situation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAH) in PM2.5 in a Receptor Site in Mexico City and Estimation of Carcinogenic PAH by Combining Non-Real-Time and Real-Time Measurement Techniques. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 703, 134526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI) México En Cifras. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/app/areasgeograficas/?ag=07000009#collapse-Resumen (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Instituto Nacional de Estadística y Geografía (INEGI) Conjunto de Datos: Vehículos de Motor Registrados En Circulación. Available online: https://www.inegi.org.mx/sistemas/olap/Proyectos/bd/continuas/transporte/vehiculos.asp?s=est%3Fc%3D13158 (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- SENASICA Padrón de Establecimientos Industriales y Mercantiles de Productos Veterinarios. Available online: https://datos.gob.mx/busca/dataset/padron-de-establecimientos-industriales-y-mercantiles-de-productos-veterinarios (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- Municipios.mx Azcapotzalco. Available online: http://www.municipios.mx/distrito-federal/azcapotzalco/ (accessed on 5 February 2024).
- US-EPA Ambient Air Sampling SESDPROC-303-R5. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/system/files/documents/2022-06/Ambient%20Air%20Sampling%28SESDPROC-303-R5%29_0.pdf (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Ronderos-Lara, J.G.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Alvarez, L.; Vergara-Sánchez, J.; Barba, V.; Guerrero-Alvarez, J.A. Distribution and Estrogenic Risk of Alkylphenolic Compounds, Hormones and Drugs Contained in Water and Natural Surface Sediments, Morelos, Mexico. Separations 2022, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Hernández, B.L.; Mugica-Álvarez, V.; Salinas-Talavera, E.; Amador-Muñoz, O.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Villalobos-Pietrini, R.; De Vizcaya-Ruíz, A. Temporal Variation of Nitro-Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in PM10 and PM2.5 Collected in Northern Mexico City. Sci. Total Environ. 2010, 408, 5429–5438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Céspedes, R.; Petrovic, M.; Raldúa, D.; Saura, Ú.; Piña, B.; Lacorte, S.; Viana, P.; Damià, B. Integrated Procedure for Determination of Endocrine-Disrupting Activity in Surface Waters and Sediments by Use of the Biological Technique Recombinant Yeast Assay and Chemical Analysis by LC-ESI-MS. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US-EPA Exposure Factors Handbook. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/expobox/about-exposure-factors-handbook (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Durant, J.L.; Busby, W.F.; Lafleur, A.L.; Penman, B.W.; Crespi, C.L. Human Cell Mutagenicity of Oxygenated, Nitrated and Unsubstituted Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Associated with Urban Aerosols. Mutat. Res./Genet. Toxicol. 1996, 371, 123–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nisbet, I.C.T.; LaGoy, P.K. Toxic Equivalency Factors (TEFs) for Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs). Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 1992, 16, 290–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US-EPA SW-846 Test Method 8000D: Determinative Chromatographic Separations. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/hw-sw846/sw-846-test-method-8000d-determinative-chromatographic-separations (accessed on 4 September 2024).
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Guidelines on Air Quality: Suspended Particles (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. Summary [WHO Global Air Quality Guidelines: Particulate Matter (PM2.5 and PM10), Ozone, Nitrogen Dioxide, Sulfur Dioxide and Carbon Monoxide. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240034228 (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Warhurst, A.M. An Environmental Assessment of Alkylphenol Ethoxylates and Alkylphenols. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/270362760_An_Environmental_Assessment_of_Alkylphenol_Ethoxylates_and_Alkylphenols (accessed on 31 January 2025).
- Dachs, J.; Van Ry, D.A.; Eisenreich, S.J. Occurrence of Estrogenic Nonylphenols in the Urban and Coastal Atmosphere of the Lower Hudson River Estuary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 2676–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, E.; Puttmann, W. Ocurrence of 4-Nonylphenol in Rain and Snow. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox Caroline Nonyl Phenol and Related Chemicals. Available online: https://www.cabidigitallibrary.org/doi/full/10.5555/19960504349 (accessed on 27 September 2024).
- US-EPA Nonylphenol (NP) and Nonylphenol Ethoxylates (NPEs) Action Plan [RIN 2070-ZA09]. Available online: https://www.epa.gov/sites/default/files/2015-09/documents/rin2070-za09_np-npes_action_plan_final_2010-08-09.pdf (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Bergé, A.; Cladière, M.; Gasperi, J.; Coursimault, A.; Tassin, B.; Moilleron, R. Meta-Analysis of Environmental Contamination by Alkylphenols. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2012, 19, 3798–3819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alothman, Z.A.; Badjah, A.Y.; Ali, I. Facile Synthesis and Characterization of Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Fast and Effective Removal of 4-tert-octylphenol Endocrine Disruptor in Water. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 275, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Ry, D.A.; Dachs, J.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Brunciak, P.A.; Nelson, E.D.; Eisenreich, S.J. Atmospheric Seasonal Trends and Environmental Fate of Alkylphenols in the Lower Hudson River Estuary. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2000, 34, 2410–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecinato, A.; Romagnoli, P.; Perilli, M.; Balducci, C. Nonylphenol and Bisphenol A in Ambient Particulates: A Preliminary Approach in Italy. Environ. Toxicol. Stud. J. 2017, 1, 3. Available online: https://www.imedpub.com/articles/nonylphenol-and-bisphenol-a-in-ambientparticulates-a-preliminary-approach-in-italy.php?aid=21159 (accessed on 29 January 2025).
- Graziani, N.S.; Carreras, H.; Wannaz, E. Atmospheric Levels of BPA Associated with Particulate Matter in an Urban Environment. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PubChem National Library of Medicine, National Center for Biotechnology Information. Available online: https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ (accessed on 2 October 2024).
- Rochester, J.R.; Bolden, A.L. Bisphenol S and F: A Systematic Review and Comparison of the Hormonal Activity of Bisphenol A Substitutes. Environ. Health Perspect. 2015, 123, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, A.; Ikhlas, S.; Ahmad, M. Occurrence, Toxicity and Endocrine Disrupting Potential of Bisphenol-B and Bisphenol-F: A Mini-Review. Toxicol. Lett. 2019, 312, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Wong, C.K.C.; Zheng, J.S.; Bouwman, H.; Barra, R.; Wahlström, B.; Neretin, L.; Wong, M.H. Bisphenol A (BPA) in China: A Review of Sources, Environmental Levels, and Potential Human Health Impacts. Environ. Int. 2012, 42, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltonen, K.; Pukkila, J. Determination of Bisphenol A in Air by High-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Electrochemical Detection. J. Chromatogr. A 1988, 439, 375–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidhu, S.; Gullett, B.; Striebich, R.; Klosterman, J.; Contreras, J.; DeVito, M. Endocrine Disrupting Chemical Emissions from Combustion Sources: Diesel Particulate Emissions and Domestic Waste Open Burn Emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 801–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simoneit, B.R.T.; Medeiros, P.M.; Didyk, B.M. Combustion Products of Plastics as Indicators for Refuse Burning in the Atmosphere. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 6961–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alliot, F.; Moreau-Guigon, E.; Bourges, C.; Desportes, A.; Teil, M.-J.; Blanchard, M.; Chevreuil, M. A Multi-Residue Method for Characterization of Endocrine Disruptors in Gaseous and Particulate Phases of Ambient Air. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 92, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Z.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, S.; Chen, H.; Xie, H.; Zeng, S. Novel Extraction for Endocrine Disruptors in Atmospheric Particulate Matter. Anal. Lett. 2015, 48, 1355–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Liu, B.; Rong, S.; Dai, S.Y.; Trasande, L.; Lehmler, H.-J. Association Between Bisphenol A Exposure and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open 2020, 3, e2011620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmler, H.-J.; Liu, B.; Gadogbe, M.; Bao, W. Exposure to Bisphenol A, Bisphenol F, and Bisphenol S in U.S. Adults and Children: The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013–2014. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 6523–6532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.S.; Soto, A.M. Bisphenol A: Perinatal Exposure and Body Weight. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2009, 304, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moriyama, K.; Tagami, T.; Akamizu, T.; Usui, T.; Saijo, M.; Kanamoto, N.; Hataya, Y.; Shimatsu, A.; Kuzuya, H.; Nakao, K. Thyroid Hormone Action Is Disrupted by Bisphenol A as an Antagonist. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 5185–5190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ropero, A.B.; Alonso-Magdalena, P.; García-García, E.; Ripoll, C.; Fuentes, E.; Nadal, A. Bisphenol-A Disruption of the Endocrine Pancreas and Blood Glucose Homeostasis. Int. J. Androl. 2008, 31, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubin, B.S.; Murray, M.K.; Damassa, D.A.; King, J.C.; Soto, A.M. Perinatal Exposure to Low Doses of Bisphenol A Affects Body Weight, Patterns of Estrous Cyclicity, and Plasma LH Levels. Environ. Health Perspect. 2001, 109, 675–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Food Safety Authority, EFSA Opinion of the Scientific Panel on Food Additives, Flavourings, Processing Aids and Materials in Contact with Food (AFC) Related to 2,2-BIS(4-HYDROXYPHENYL)PROPANE. Available online: https://data.europa.eu/doi/10.2903/j.efsa.2007.428 (accessed on 21 July 2024).
- Liao, C.; Liu, F.; Guo, Y.; Moon, H.-B.; Nakata, H.; Wu, Q.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of Eight Bisphenol Analogues in Indoor Dust from the United States and Several Asian Countries: Implications for Human Exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 9138–9145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Wan, Y.; Kannan, K. Occurrence of Bisphenols, Bisphenol A Diglycidyl Ethers (BADGEs), and Novolac Glycidyl Ethers (NOGEs) in Indoor Air from Albany, New York, USA, and Its Implications for Inhalation Exposure. Chemosphere 2016, 151, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackwell, B.R.; Wooten, K.J.; Buser, M.D.; Johnson, B.J.; Cobb, G.P.; Smith, P.N. Occurrence and Characterization of Steroid Growth Promoters Associated with Particulate Matter Originating from Beef Cattle Feedyards. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 8796–8803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdan, M.; Kumar, R.; Leung, S.W. The Environmental and Health Impacts of Steroids and Hormones in Wastewater Effluent, as Well as Existing Removal Technologies: A Review. Ecologies 2022, 3, 206–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC Chemical Agents and Related Occupations IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans. Available online: https://publications.iarc.fr/Book-And-Report-Series/Iarc-Monographs-On-The-Identification-Of-Carcinogenic-Hazards-To-Humans/Chemical-Agents-And-Related-Occupations-2012 (accessed on 25 December 2024).
- Azimi-Yancheshmeh, R.; Moeinaddini, M.; Feiznia, S.; Riyahi-Bakhtiari, A.; Savabieasfahani, M.; Van Hullebusch, E.D.; Asgari Lajayer, B. Seasonal and Spatial Variations in Atmospheric PM2.5-Bound PAHs in Karaj City, Iran: Sources, Distributions, and Health Risks. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2021, 72, 103020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, K.; Yoshida, S.; Nakayama, S.; Ito, R.; Okanouchi, N.; Nakazawa, H. Development of Stable Isotope Dilution Quantification Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry Method for Estimation of Exposure Levels of Bisphenol A, 4-Tert-Octylphenol, 4-Nonylphenol, Tetrabromobisphenol A, and Pentachlorophenol in Indoor Air. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2006, 51, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzmán, M.A.; Fernández, A.J.; Boente, C.; Márquez, G.; Sánchez De La Campa, A.M.; Lorenzo, E. Study of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons and Anhydro-Sugars in Ambient Air near Two Spanish Oil Refineries: COVID-19 Effects. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2023, 14, 101694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, C.; Xue, Z.; Fu, X.; Sultana, F.; Smith, L.J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, B. Impacts of Independence Day Fireworks on Pollution Levels of Atmospheric Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) in the U.S. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 743, 140774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, Z.; Yin, Y.; Chen, K.; Zhen, X.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, H.; Wang, H.; Kuang, X.; Cui, Y.; Dai, M.; et al. Concentration and Atmospheric Transport of PM2.5-Bound Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons at Mount Tai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 786, 147513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Barradas-Gimate, A.; Arias-Montoya, M.I.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A. Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) Associated with PM2.5 in Guadalajara, Mexico: Environmental Levels, Health Risks and Possible Sources. Environments 2018, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.; López-Márquez, R.; Murillo-Tovar, M.; Hernández-Mena, L.; Ospina-Noreña, E.; Sánchez-Salinas, E.; Waliszewski, S.; Montiel-Palma, S. Analysis of PAHs Associated with Particulate Matter PM2.5 in Two Places at the City of Cuernavaca, Morelos, México. Atmosphere 2015, 6, 1259–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Hernández, B.L.; Figueroa-Lara, J.D.J.; Torres-Rodríguez, M.; Ginéz-Hernández, N.; Álvarez-Lupercio, T.; Mugica-Álvarez, V. Levels, Sources and Risk Assessment of Carbonaceous and Organic Species Associated with PM2.5 in Two Small Cities of Morelos, Mexico. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
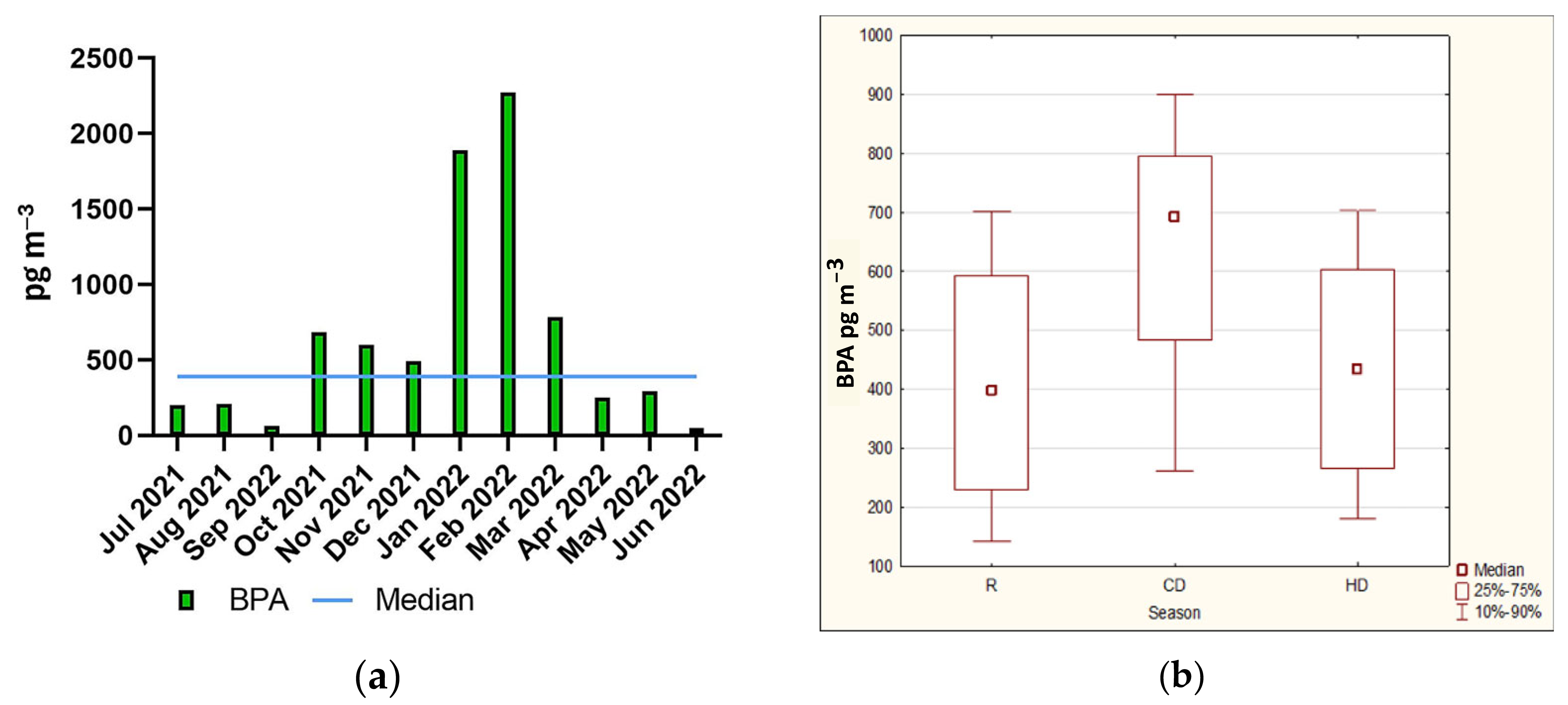
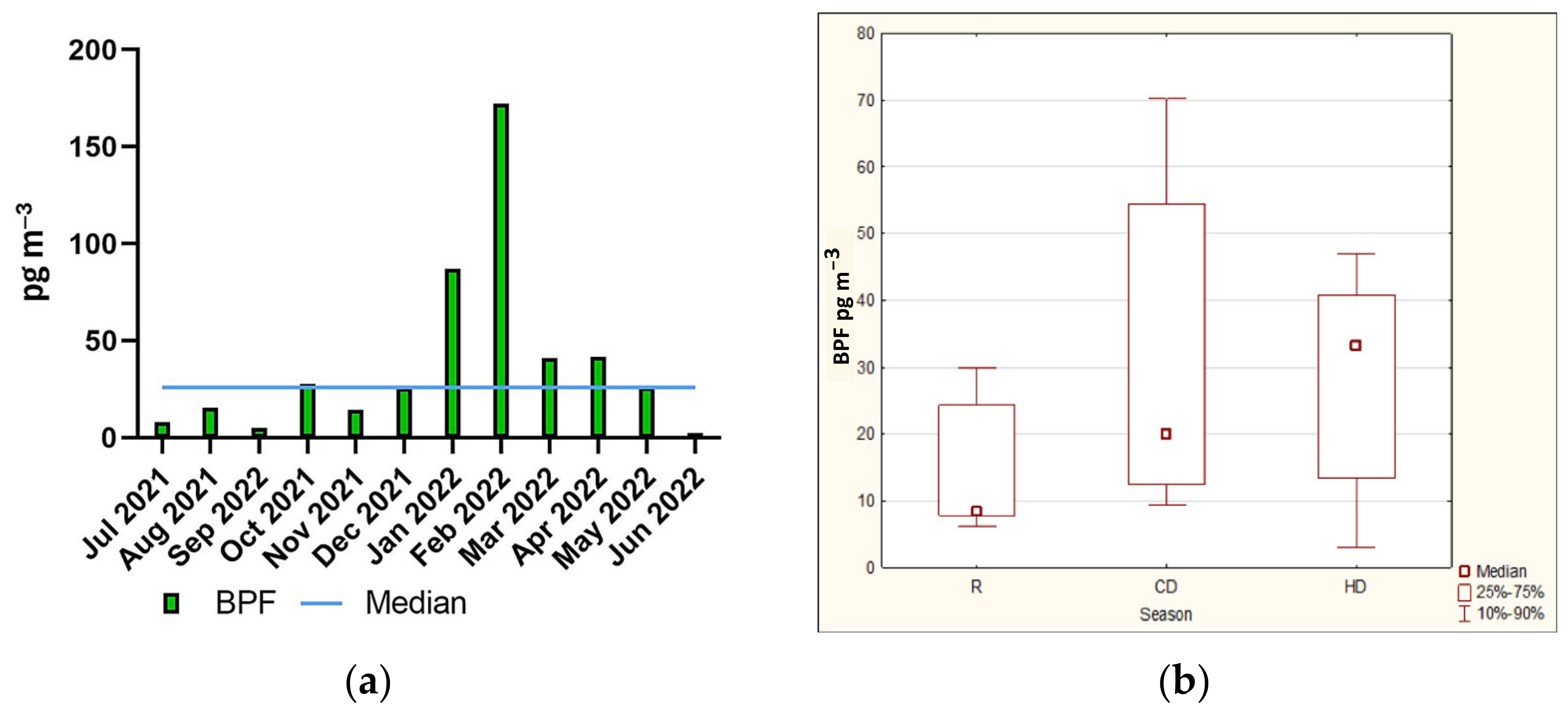

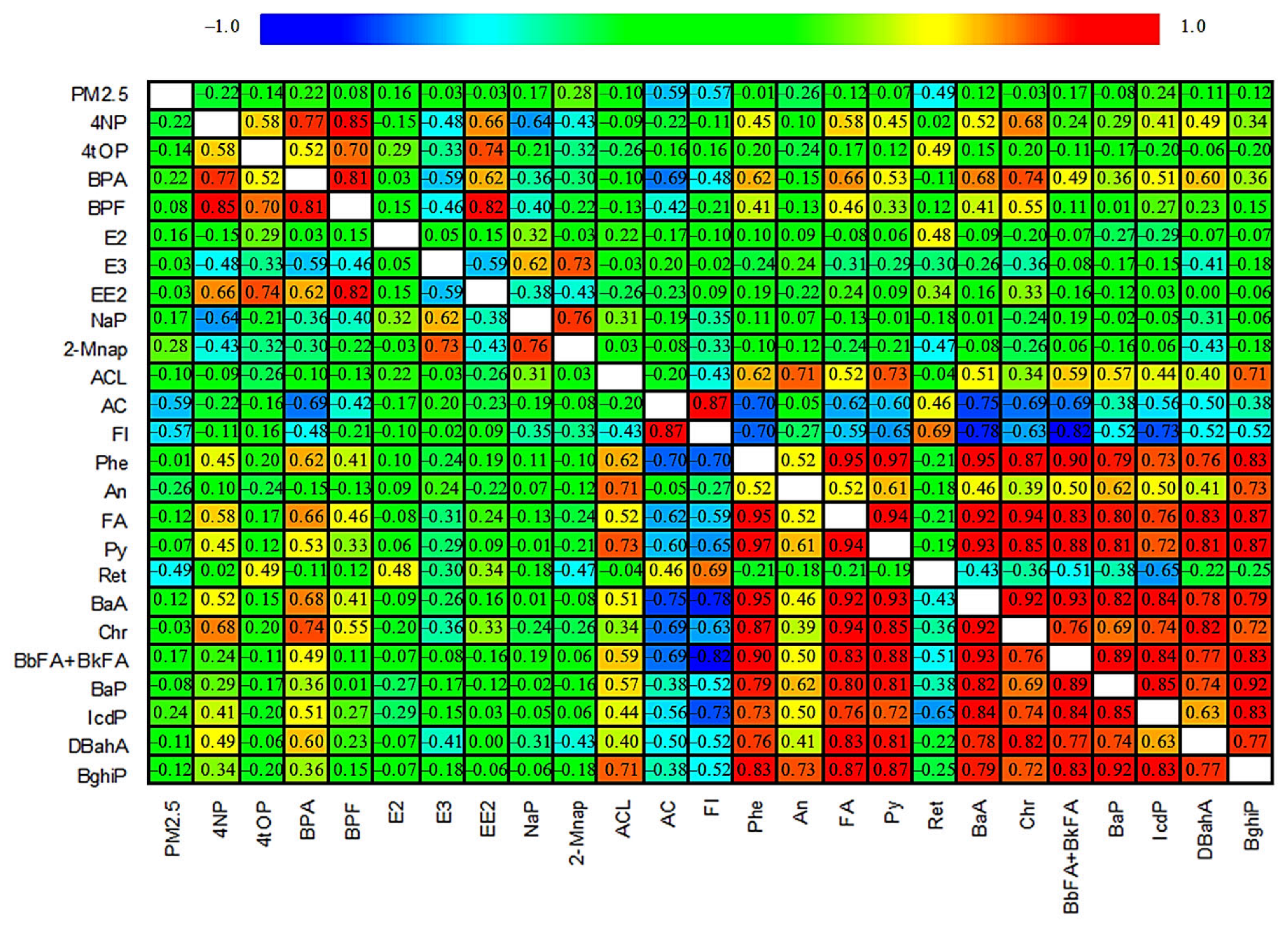
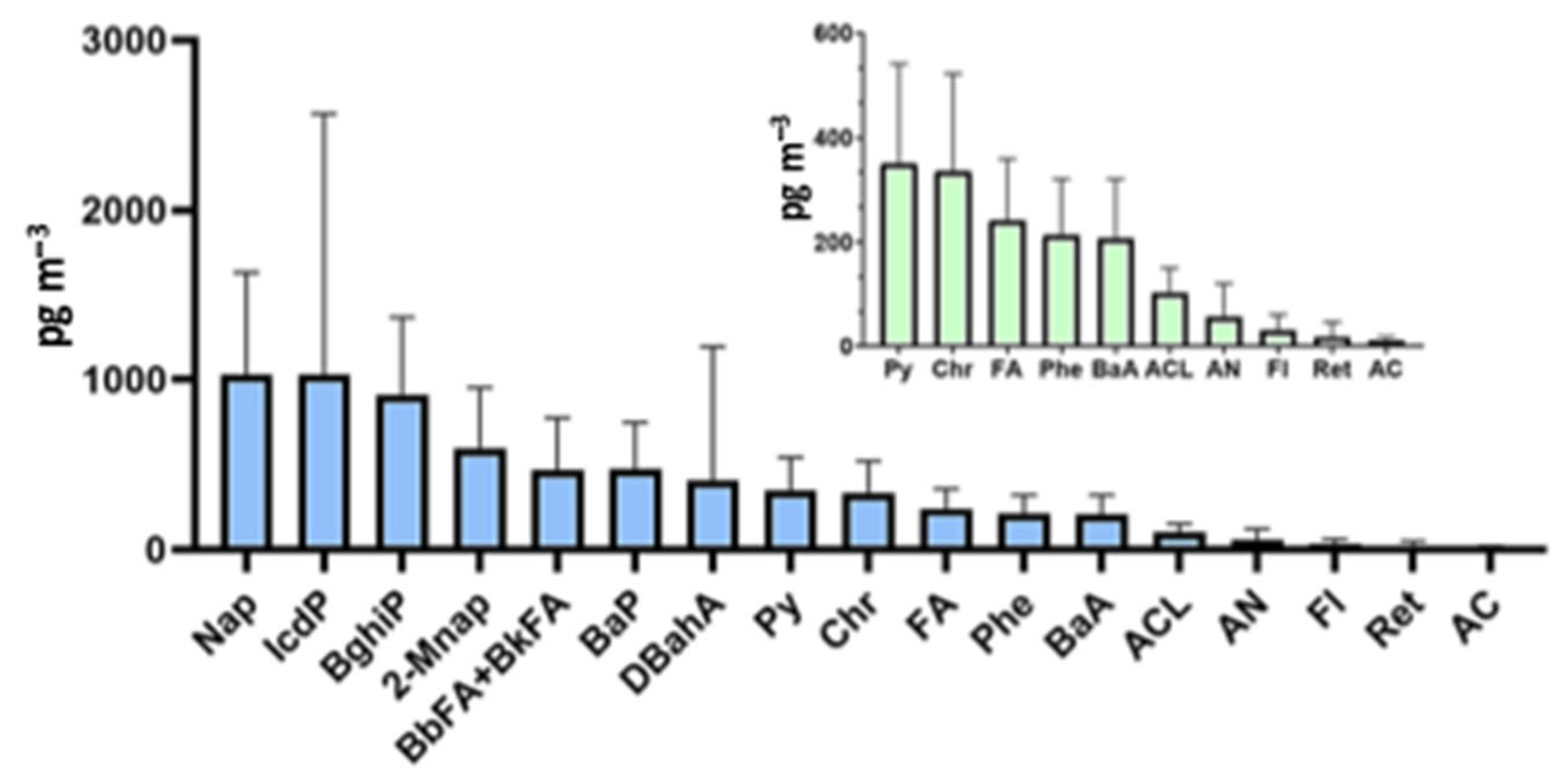
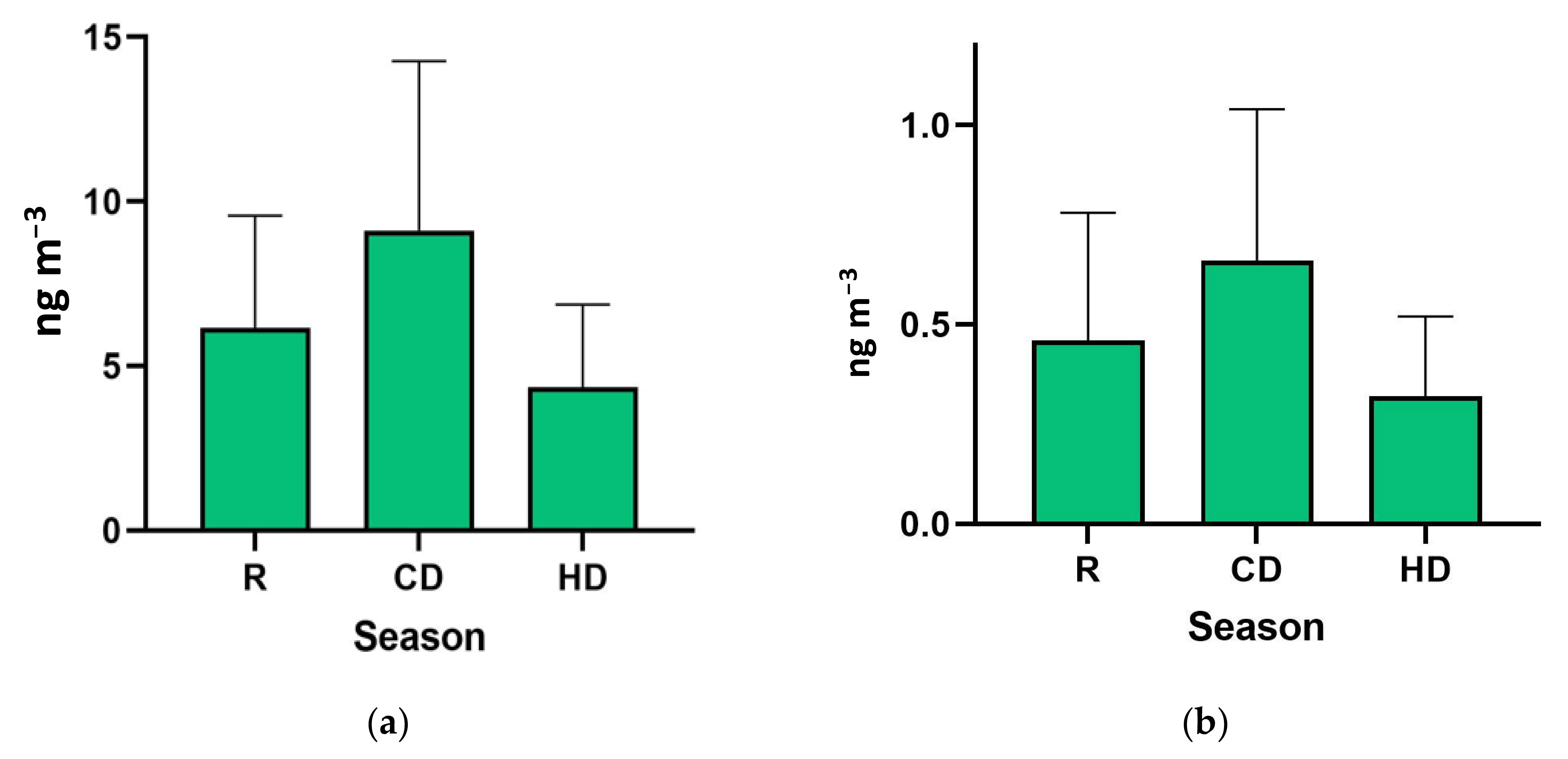
| Season | n | 4NP | 4tOP | BPA | E2 | E3 | EE2 | ΣEEQE2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seasonal EEQE2 (ng m−3) 1 | R | 8 | 8.31 × 10−7 | 2.12 × 10−5 | 5.47 × 10−5 | 7.65 × 10−2 | 2.35 × 10−2 | 2.79 × 10−3 | 1.03 × 10−1 |
| CD | 7 | 1.96 × 10−6 | 1.23 × 10−5 | 1.95 × 10−4 | 4.93 × 10−2 | 3.14 × 10−3 | 4.61 × 10−3 | 5.73 × 10−2 | |
| HD | 6 | 1.93 × 10−6 | 3.11 × 10−5 | 5.88 × 10−5 | 6.33 × 10−2 | 7.12 × 10−3 | 6.03 × 10−3 | 7.66 × 10−2 | |
| ΣEEQE2 (Annual) | 21 | 4.72 × 10−6 | 6.46 × 10−5 | 3.09 × 10−4 | 1.89 × 10−1 | 3.38 × 10−2 | 1.34 × 10−2 | 2.37 × 10−1 | |
| Estrogenicity contribution (%) by season 2 | Season | n | 4NP | 4tOP | BPA | E2 | E3 | EE2 | Total % |
| R | 8 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.05 | 74.35 | 22.86 | 2.71 | 100.000 | |
| CD | 7 | 0.00 | 0.02 | 0.34 | 86.09 | 5.49 | 8.05 | 100.00 | |
| HD | 6 | 0.00 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 82.71 | 9.30 | 7.88 | 100.00 |
| Compound | Country | Location | PM 1 (µm) | Concentration Range (pg m−3) | Average (pg m−3) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4tOP | Mexico | Urban (near industrial area) | 2.5 | 2.56–89.47 | 15.96 | This study |
| 4NP | 0.2–1.52 | 0.41 | ||||
| BPA | 49–2274 | 649 | ||||
| BPF | 0.88–283.14 | 24.32 | ||||
| E2 | 2.33–23.06 | 8.60 | ||||
| E3 | 0.54–21.18 | 4.90 | ||||
| EE2 | 0.96–7.98 | 3.93 | ||||
| 4NP | Germany | Urban | --- | 1.7–117 | --- | [36] |
| 4tOP | 0.3–4.2 | |||||
| BPA | 5–15 | |||||
| NP | Japan | Urban | --- | 8500–17,300 | 12,900 | [88] |
| 4tOP | ˂100–1100 | 600 | ||||
| BPA | 400–500 | 450 | ||||
| BPA | China | Urban | 2.5 | 70–2340 | 480 | [11] |
| 4NP | Greece | Industrial | 10 | 2500–10,900 | 4960 | [33] |
| 4tOP | BDL–20 | 10 | ||||
| BPA | BDL–47,300 | 13,200 | ||||
| BPF | Korea | Indoor | Dust | n.d.–107 2 | 0.50 2 | [82] |
| 4NP | Spain | Industrial Industrial Urban Industrial Industrial Industrial | 2.5 | n.d. | --- | [12] |
| 4tOP | ˂24 | |||||
| BPA | n.d.–108 | |||||
| E2 | n.d.–˂15 | |||||
| E3 | n.d. | |||||
| EE2 | n.d. | |||||
| E2 | USA | Cattle feedyards | 2.5 | --- | 0.008 2 | [84] |
| EE2 | 0.026 2 | |||||
| BPF | USA | Indoor (Home) | 2.5 1 | ˂LOQ–2220 2 | 133 2 | [83] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ronderos-Lara, J.G.; Millán-Vázquez, F.; Murillo-Tovar, M.A.; Saldarriaga-Noreña, H.A.; Valle-Hernández, B.L.; López-Velázquez, K.; Mugica-Álvarez, V. Atmospheric Estrogenic Semi-Volatile Compounds and PAH in PM2.5 in Mexico City. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020178
Ronderos-Lara JG, Millán-Vázquez F, Murillo-Tovar MA, Saldarriaga-Noreña HA, Valle-Hernández BL, López-Velázquez K, Mugica-Álvarez V. Atmospheric Estrogenic Semi-Volatile Compounds and PAH in PM2.5 in Mexico City. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):178. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020178
Chicago/Turabian StyleRonderos-Lara, José Gustavo, Fernando Millán-Vázquez, Mario Alfonso Murillo-Tovar, Hugo Albeiro Saldarriaga-Noreña, Brenda Liz Valle-Hernández, Khirbet López-Velázquez, and Violeta Mugica-Álvarez. 2025. "Atmospheric Estrogenic Semi-Volatile Compounds and PAH in PM2.5 in Mexico City" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020178
APA StyleRonderos-Lara, J. G., Millán-Vázquez, F., Murillo-Tovar, M. A., Saldarriaga-Noreña, H. A., Valle-Hernández, B. L., López-Velázquez, K., & Mugica-Álvarez, V. (2025). Atmospheric Estrogenic Semi-Volatile Compounds and PAH in PM2.5 in Mexico City. Atmosphere, 16(2), 178. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020178






