Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
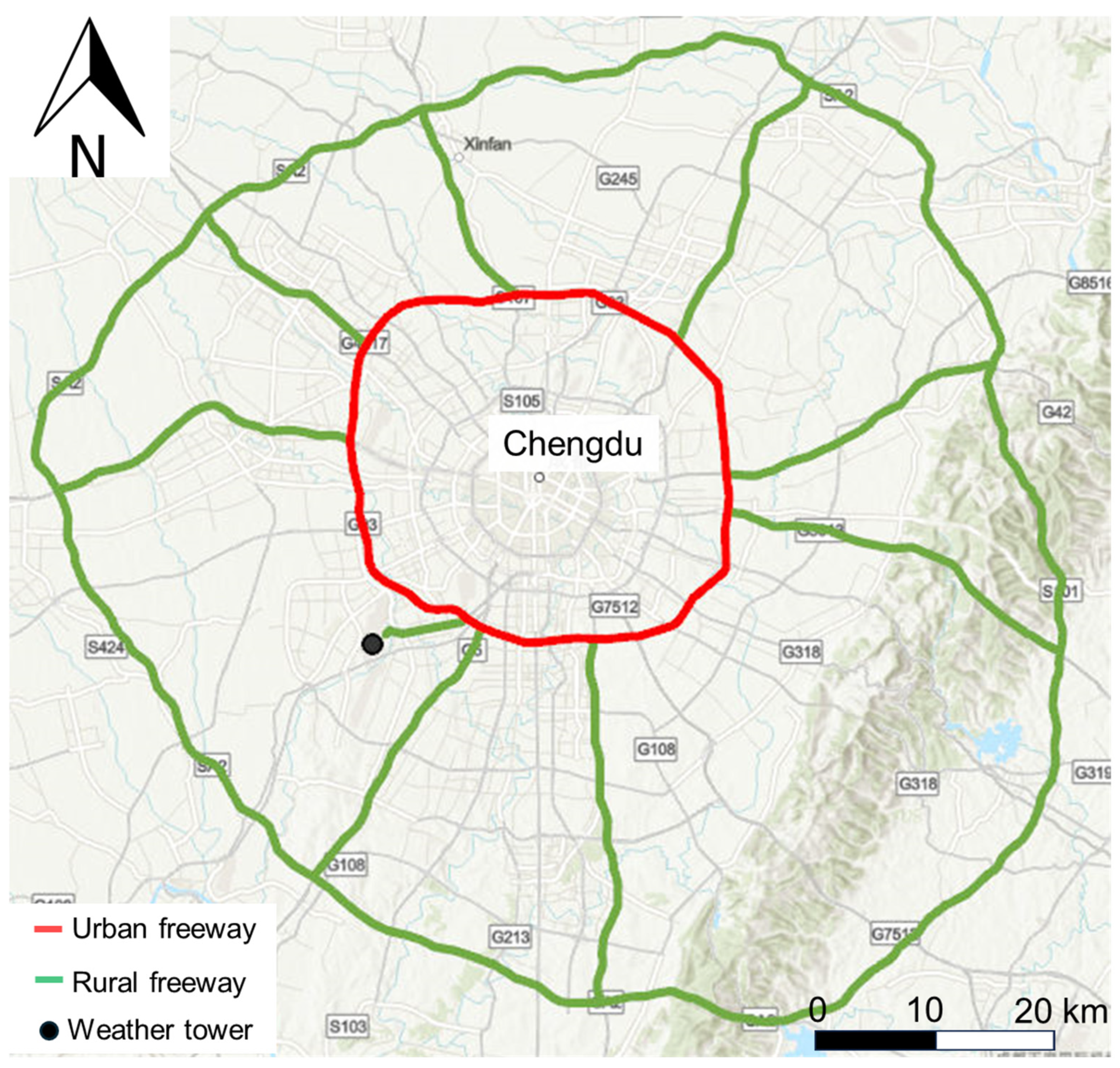
2.2. Study Domain and Monitoring Conditions
2.3. Quality Assurance and Data Processing
3. Results and Discussion
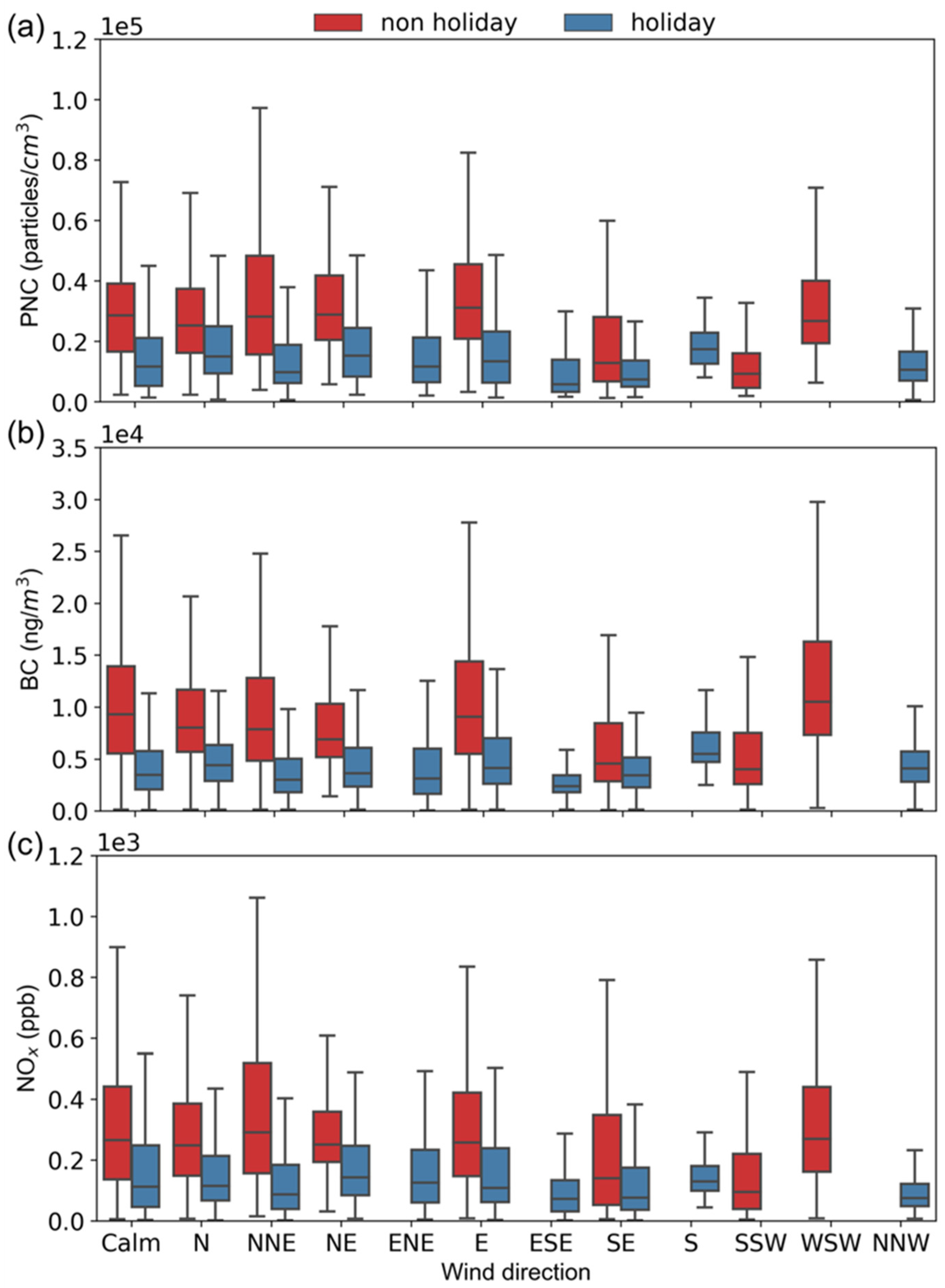
3.1. Monitoring Conditions
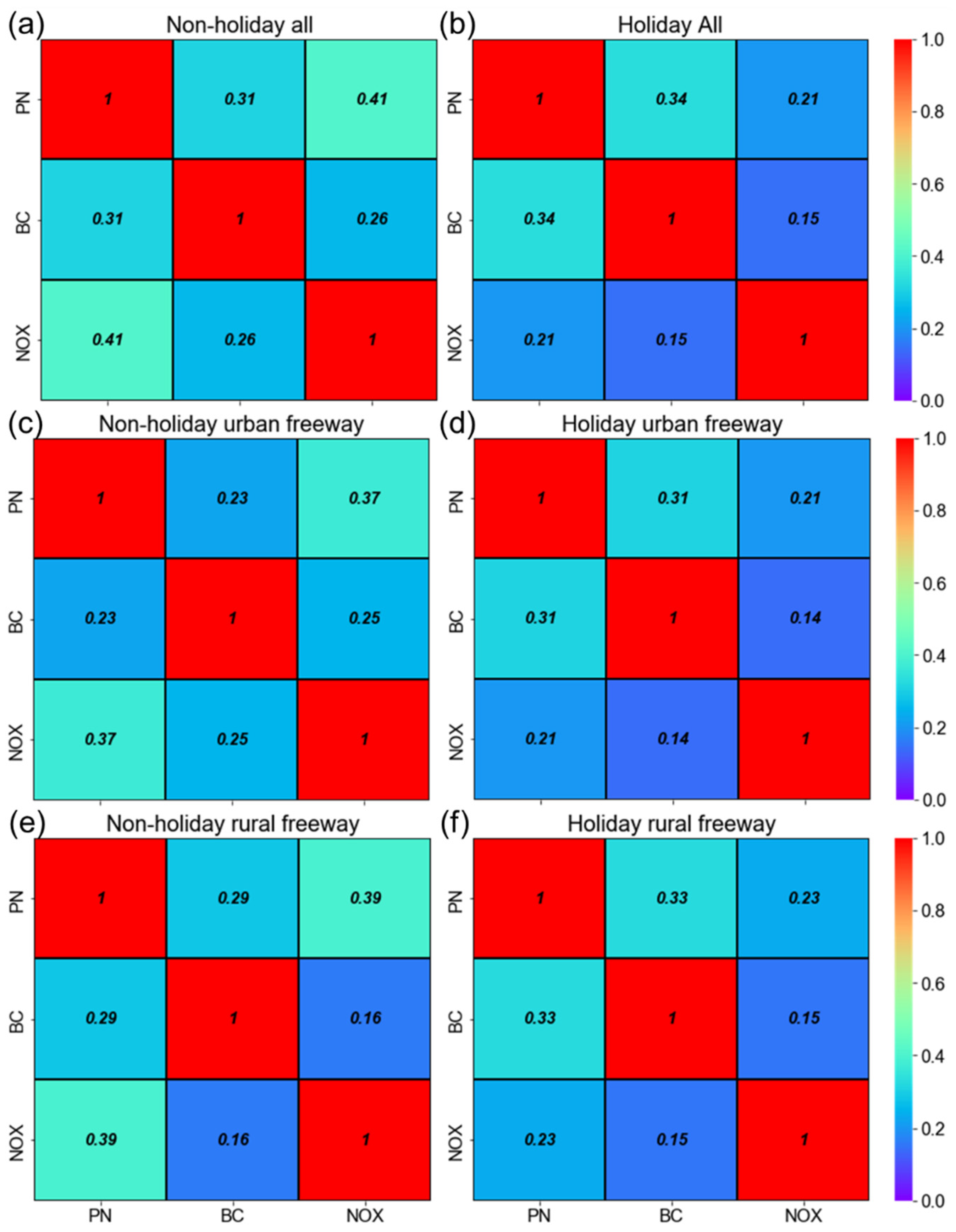
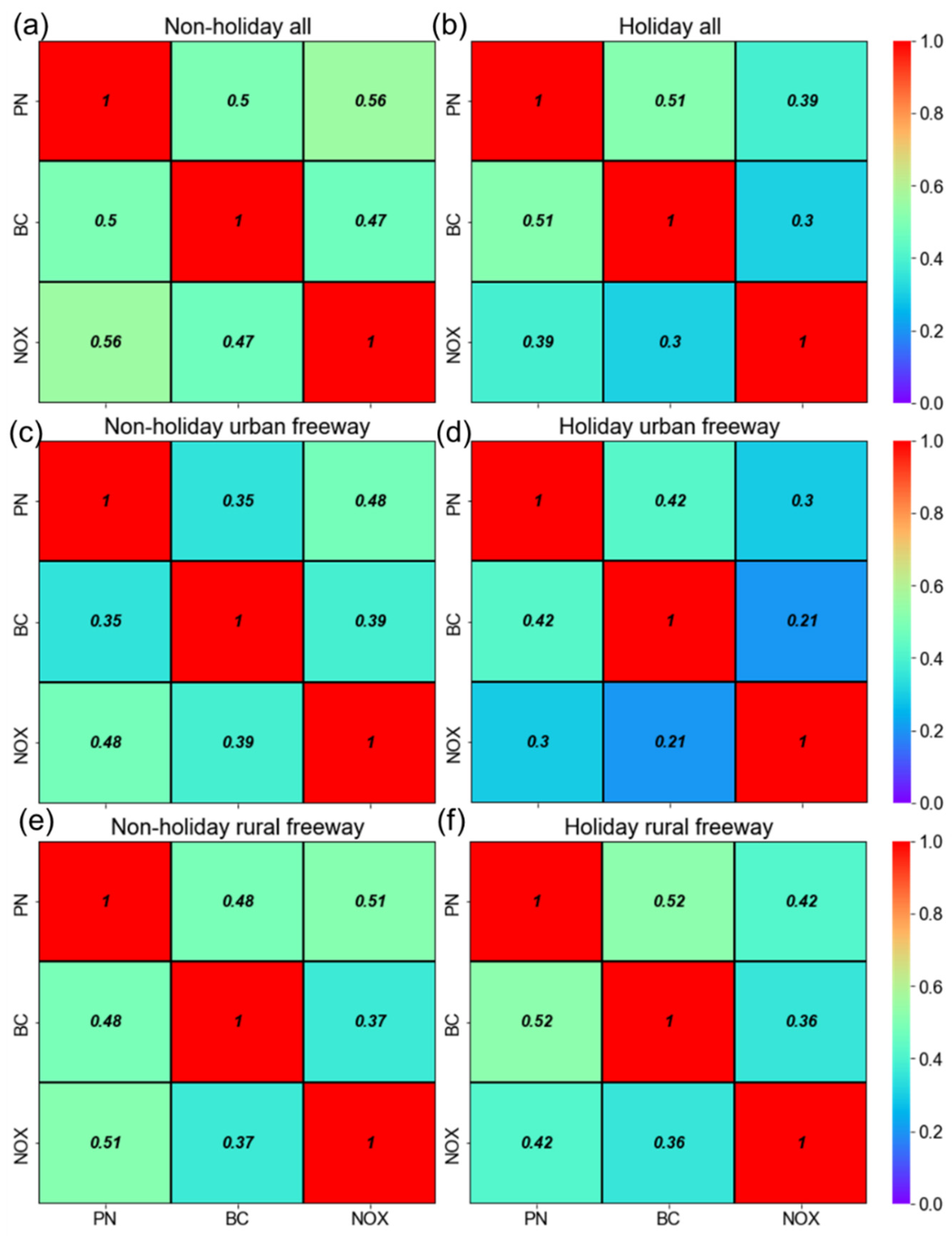
3.2. Traffic-Related Air Pollutants’ Intercorrelation
3.3. Temporal-Spatial Variations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TRAPs | Traffic-related air pollutants |
| PNC | Particle number concentration |
| BC | Black carbon |
| NOx | Nitrogen oxides |
| HDDV | Heavy-duty diesel vehicle |
| UFPs | Ultrafine particles |
References
- Panel, H. On the health effects of long-term exposure to traffic-related air pollution. In Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Selected Health Effects of Long-Term Exposure to Traffic-Related Air Pollution; Health Effects Institute: Boston, MA, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C.; Kim, S.; Sioutas, C. Concentration and size distribution of ultrafine particles near a major highway. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2002, 52, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban-Weiss, G.A.; McLaughlin, J.P.; Harley, R.A.; Lunden, M.M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Kean, A.J.; Strawa, A.W.; Stevenson, E.D.; Kendall, G.R. Long-term changes in emissions of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter from on-road gasoline and diesel vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krecl, P.; Targino, A.C.; Landi, T.P.; Ketzel, M. Determination of black carbon, PM2.5, particle number and NOx emission factors from roadside measurements and their implications for emission inventory development. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 186, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, D.; Paul, K.C.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Folle, A.D.; Wu, J.; Bronstein, J.M.; Ritz, B. Traffic-related air pollution and Parkinson’s disease in central California. Environ. Res. 2024, 240, 117434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, N.A.; Hoek, G.; Simic-Lawson, M.; Fischer, P.; Van Bree, L.; Ten Brink, H.; Keuken, M.; Atkinson, R.W.; Anderson, H.R.; Brunekreef, B. Black carbon as an additional indicator of the adverse health effects of airborne particles compared with PM10 and PM2.5. Environ. Health Perspect. 2011, 119, 1691–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delfino, R.J. Epidemiologic evidence for asthma and exposure to air toxics: Linkages between occupational, indoor, and community air pollution research. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olstrup, H.; Flanagan, E.; Persson, J.-O.; Rittner, R.; Krage Carlsen, H.; Stockfelt, L.; Xu, Y.; Rylander, L.; Gustafsson, S.; Spanne, M. The Long-Term Mortality Effects Associated with Exposure to Particles and NOx in the Malmö Diet and Cancer Cohort. Toxics 2023, 11, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Manchanda, C. High-resolution urban air pollution mapping. Science 2024, 385, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, J.S.; Messier, K.P.; Gani, S.; Brauer, M.; Kirchstetter, T.W.; Lunden, M.M.; Marshall, J.D.; Portier, C.J.; Vermeulen, R.C.; Hamburg, S.P. High-resolution air pollution mapping with Google street view cars: Exploiting big data. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 6999–7008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yim, S.H.L.; He, X.; Xia, X.; Ho, K.-F.; Yu, J.Z. High spatial resolution estimates of major PM2.5 components and their associated health risks in Hong Kong using a coupled land use regression and health risk assessment approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 907, 167932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Bossche, J.; Peters, J.; Verwaeren, J.; Botteldooren, D.; Theunis, J.; De Baets, B. Mobile monitoring for mapping spatial variation in urban air quality: Development and validation of a methodology based on an extensive dataset. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 105, 148–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.Z.; Gu, P.; Ye, Q.; Zimmerman, N.; Robinson, E.S.; Subramanian, R.; Apte, J.S.; Robinson, A.L.; Presto, A.A. Spatially dense air pollutant sampling: Implications of spatial variability on the representativeness of stationary air pollutant monitors. Atmos. Environ. X 2019, 2, 100012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambliss, S.E.; Pinon, C.P.; Messier, K.P.; LaFranchi, B.; Upperman, C.R.; Lunden, M.M.; Robinson, A.L.; Marshall, J.D.; Apte, J.S. Local-and regional-scale racial and ethnic disparities in air pollution determined by long-term mobile monitoring. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2109249118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Li, R.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.M.; Si, S.; Wu, X.; Wu, Y. Characterizing spatial variations of city-wide elevated PM10 and PM2.5 concentrations using taxi-based mobile monitoring. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 829, 154478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, T.; You, Y.; Si, S.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Evaluation of City-Scale Disparities in PM2.5 Exposure Using Hyper-Localized Taxi-Based Mobile Monitoring. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 56, 13584–13594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velizarova, M.; Dimitrova, R.; Hristov, P.O.; Burov, A.; Brezov, D.; Hristova, E.; Gueorguiev, O. Evaluation of Emission Factors for Particulate Matter and NO2 from Road Transport in Sofia, Bulgaria. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Poppel, M.; Peters, J.; Vranckx, S.; Van Laer, J.; Hofman, J.; Vandeninden, B.; Vanpoucke, C.; Lefebvre, W. Exploring the Spatial Variability of Air Pollution Using Mobile BC Measurements in a Citizen Science Project: A Case Study in Mechelen. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şahin, Ü.A.; Onat, B.; Akın, Ö.; Ayvaz, C.; Uzun, B.; Mangır, N.; Doğan, M.; Harrison, R.M. Temporal variations of atmospheric black carbon and its relation to other pollutants and meteorological factors at an urban traffic site in Istanbul. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2020, 11, 1051–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Wu, L.; Duan, Y.; Liang, L.; Li, Y. Identifying the O3 chemical regime inferred from the weekly pattern of atmospheric O3, CO, NOx, and PM10: Five-year observations at a center urban site in Shanghai, China. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 888, 164079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, K.M.; Zheng, H.; Xing, J.; Wu, Y.; Hao, J. Four-month changes in air quality during and after the COVID-19 lockdown in six megacities in China. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2020, 7, 802–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Ghaffarpasand, O.; Pope, F.D. Assessing the Impact of Calendar Events upon Urban Vehicle Behaviour and Emissions Using Telematics Data. Smart Cities 2024, 7, 3071–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, P.-H.; Chou, C.; Liang, J.-Y.; Chou, C.C.-K.; Shiu, C.-J. Air pollution “holiday effect” resulting from the Chinese New Year. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 2114–2124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, I. A national day with near zero emissions and its effect on primary and secondary pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 77, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brimblecombe, P.; Lai, Y. Effect of fireworks, Chinese new year and the COVID-19 lockdown on air pollution and public attitudes. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2020, 20, 2318–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Brimblecombe, P. Changes in air pollutants from fireworks in chinese cities. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.P. Air Pollution Meteorology and Dispersion; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1999; Volume 310. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, Y.T.; Xiang, S.; Noll, K.E. Evaluation of the Relationship between Momentum Wakes behind Moving Vehicles and Dispersion of Vehicle Emissions Using Near-Roadway Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2020, 54, 10483–10492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Brimblecombe, P.; Yu, Y.T.; Noll, K.E.; Liu, H.; Wu, Y.; Hao, K. An Integrated Field Study of Turbulence and Dispersion Variations in Road Microenvironments. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2024, 58, 20566–20576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Gao, P.; Xiang, S.; Zhu, H.; Chen, J.; Fu, Q. A Python toolkit for integrating geographic information system into regulatory dispersion models for refined pollution modeling. Environ. Model. Softw. 2024, 183, 106219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chengdu Bureau of Statistics. Chengdu Statistical Yearbook; Chengdu Bureau of Statistics: Chengdu, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ministry of Environmental Protection. Ambient Air Quality Standards (GB 3095-2012). 2012. Available online: https://www.chinesestandard.net/PDF.aspx/GB3095-2012 (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Wen, Y.; Yu, Y.T.; Li, Z.; Wallington, T.J.; Shen, W.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Q. Mobile Measurements of Carbonaceous Aerosol in Microenvironments to Discern Contributions from Traffic and Solid Fuel Burning. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 2021, 8, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Wang, H.; Yu, Y.T.; Wallington, T.J.; Shen, W.; Kirchner, U.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, Z. Variability of NO2/NOx Ratios in Multiple Microenvironments from On-Road and Near-Roadway Measurements. ACS EST Eng. 2022, 2, 1599–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Deng, Y.; Tan, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Wu, Y. Evaluating Ultrafine Particles and PM2.5 in Microenvironments with Health Perspectives: Variability in Concentrations and Pollutant Interrelationships. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2023, 23, 230046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mejía, J.F.; Morawska, L.; Mengersen, K. Spatial variation in particle number size distributions in a large metropolitan area. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2008, 8, 1127–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morawska, L.; Thomas, S.; Bofinger, N.; Wainwright, D.; Neale, D. Comprehensive characterization of aerosols in a subtropical urban atmosphere: Particle size distribution and correlation with gaseous pollutants. Atmos. Environ. 1998, 32, 2467–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinds, W.C. Aerosol Technology: Properties, Behavior, and Measurement of Airborne Particles; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Drinovec, L.; Močnik, G.; Zotter, P.; Prévôt, A.; Ruckstuhl, C.; Coz, E.; Rupakheti, M.; Sciare, J.; Müller, T.; Wiedensohler, A. The “dual-spot” Aethalometer: An improved measurement of aerosol black carbon with real-time loading compensation. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2015, 8, 1965–1979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Bureau of Statistics of China. Major Figures on 2020 Population Census of China. 2020. Available online: https://www.chinayearbooks.com/major-figures-on-2020-population-census-of-china.html (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Chengdu Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. Municipal Planning of Chengdu 2011–2020. Chengdu Municipal Bureau of Planning and Natural Resources. 2021. Available online: https://mpnr.chengdu.gov.cn/ghhzrzyj/ztgh/2019-07/14/content_39be6057b8194c4d89afde1e26625a69.shtml (accessed on 27 January 2025).
- Brimblecombe, P.; Townsend, T.; Lau, C.F.; Rakowska, A.; Chan, T.L.; Močnik, G.; Ning, Z. Through-tunnel estimates of vehicle fleet emission factors. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 123, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Characterization of Dispersion and Ultrafine-particle Emission Factors Based on Near-roadway Monitoring Part I: Light Duty Vehicles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2410–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Hu, Z.; Noll, K.E. Characterization of Dispersion and Ultrafine-particle Emission Factors Based on Near-roadway Monitoring Part II: Heavy Duty Vehicles. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2019, 19, 2421–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, C.F.; Rakowska, A.; Townsend, T.; Brimblecombe, P.; Chan, T.L.; Yam, Y.S.; Močnik, G.; Ning, Z. Evaluation of diesel fleet emissions and control policies from plume chasing measurements of on-road vehicles. Atmos. Environ. 2015, 122, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, X.; Zheng, X.; Wen, Y.; Wu, Y. Mitigation potential of black carbon emissions from on-road vehicles in China. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 278, 116746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.P.; Perkins, J.; Zamore, W.; Levy, J.I.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. Spatial and temporal differences in traffic-related air pollution in three urban neighborhoods near an interstate highway. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 99, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patton, A.P.; Collins, C.; Naumova, E.N.; Zamore, W.; Brugge, D.; Durant, J.L. An hourly regression model for ultrafine particles in a near-highway urban area. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 3272–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crouse, D.L.; Goldberg, M.S.; Ross, N.A. A prediction-based approach to modelling temporal and spatial variability of traffic-related air pollution in Montreal, Canada. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5075–5084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, E.A.; Schaal, L.; Sasakura, M.; Crampton, R.; Gould, T.R.; Hartin, K.; Sheppard, L.; Larson, T.; Simpson, C.D.; Yost, M.G. Correlations between short-term mobile monitoring and long-term passive sampler measurements of traffic-related air pollution. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 132, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Hu, Z.; Zhai, W.; Wen, D.; Noll, K.E. Concentration of Ultrafine Particles near Roadways in an Urban Area in Chicago, Illinois. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 895–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Ketzel, M.; Ellermann, T.; Wåhlin, P.; Jensen, S.; Fang, D.; Massling, A. Particle number, particle mass and NO x emission factors at a highway and an urban street in Copenhagen. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2010, 10, 2745–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hilker, N.; Wang, J.M.; Jeong, C.-H.; Healy, R.M.; Sofowote, U.; Debosz, J.; Su, Y.; Noble, M.; Munoz, A.; Doerksen, G. Traffic-related air pollution near roadways: Discerning local impacts from background. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2019, 12, 5247–5261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Wang, D.; Tian, M.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the Relationship between Meteorological Variables and NO x Emission Factors Based on Plume-Chasing Measurements. ACS EST Eng. 2023, 3, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, H.; Hagler, G.; Kimbrough, E.; Williams, R.; Mukerjee, S.; Neas, L. Mobile air monitoring data-processing strategies and effects on spatial air pollution trends. Atmos. Meas. Tech. 2014, 7, 2169–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Wen, Y.; Xiang, S.; Yang, P.; Zheng, X.; You, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wu, Y. Cost-Effective Mapping of Hyperlocal Air Pollution Using Large-Scale Mobile Monitoring and Land-Use Machine Learning. ACS EST Air 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, S.; Zhang, S.; Yu, Y.T.; Wang, H.; Hao, K.; Wu, Y. Significant NO2 Formation in Truck Exhaust Plumes and Its Association with Ambient O3: Evidence from Extensive Plume-Chasing Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Date(mm-dd) | Background | Urban Freeway | Rural Freeway | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNC * | BC # | NOx $ | PNC * | BC # | NOx $ | PNC * | BC # | NOx $ | ||
| Non-holiday | 9-21 | 10,517 | 1561 | 52.6 | 32,366 | 7808 | 303.7 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. |
| 9-22 | 14,507 | 3152 | 104.9 | 33,507 | 10,256 | 328.6 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
| 9-23 | 13,863 | 3611 | 82.8 | 31,579 | 10,804 | 312.6 | 18,665 | 5627 | 127.6 | |
| 9-24 | 10,738 | 3969 | 71.2 | 24,467 | 9138.5 | 244.7 | 27,082 | 8348 | 237.8 | |
| 9-27 | 9353 | 1581 | 45.0 | 30,620 | 8330 | 302.5 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
| 9-28 | 9437 | 2778 | 62.2 | 23,531 | 8196 | 257.3 | n.a. | n.a. | n.a. | |
| 9-29 | 4405 | 820 | 24.7 | 28,861 | 11,929 | 326.3 | 12,199 | 4522 | 96.0 | |
| 9-30 | 10,022 | 3474 | 97.7 | 41,457 | 15,373 | 415.3 | 16,520 | 7407 | 164.9 | |
| 10-9 | 3440 | 1306 | 31.0 | 26,502 | 9847 | 372.3 | 12,525 | 3887 | 145.3 | |
| 10-10 | 6790 | 1066 | 30.1 | 24,300 | 10,059 | 316.7 | 15,492 | 4377 | 116.8 | |
| Holiday | 10-1 | 6552 | 1469 | 39.8 | 12,770 | 4826 | 87.6 | 14,611 | 4984 | 65.8 |
| 10-2 | 6020 | 1546 | 26.8 | 12,193 | 4104 | 85.8 | 11,841 | 2849 | 84.0 | |
| 10-3 | 6258 | 841 | 24.6 | 20,598 | 3063 | 129.4 | 16,391 | 3989 | 146.7 | |
| 10-4 | 4411 | 417 | 19.3 | 15,687 | 3975 | 162.3 | 5261 | 1742 | 47.4 | |
| 10-6 | 7524 | 813 | 40.8 | 18,615 | 4187 | 150.5 | 7780 | 2454 | 74.9 | |
| 10-7 | 3943 | 515 | 17.0 | 14,822 | 5091 | 133.0 | 8816 | 3274 | 99.7 | |
| 10-8 | 3272 | 791 | 14.9 | 17,182 | n.a. | 275.5 | 9543 | 3161 | 84.3 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xiang, S.; Yu, J.; Yu, Y.T.; Zhao, P.; Zheng, T.; Yue, J.; Yang, Y.; Liu, H. Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171
Xiang S, Yu J, Yu YT, Zhao P, Zheng T, Yue J, Yang Y, Liu H. Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(2):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171
Chicago/Turabian StyleXiang, Sheng, Jiaojiao Yu, Yu Ting Yu, Pengbo Zhao, Tie Zheng, Jingsong Yue, Yuanyuan Yang, and Haobing Liu. 2025. "Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 2: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171
APA StyleXiang, S., Yu, J., Yu, Y. T., Zhao, P., Zheng, T., Yue, J., Yang, Y., & Liu, H. (2025). Exploring the Holiday Effect on Elevated Traffic-Related Air Pollution with Hyperlocal Measurements in Chengdu, China. Atmosphere, 16(2), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16020171









