Quantifying the Contribution of Global Precipitation Product Uncertainty to Ensemble Discharge Simulations and Projections: A Case Study in the Liujiang Catchment, Southwest China
Abstract
1. Introduction
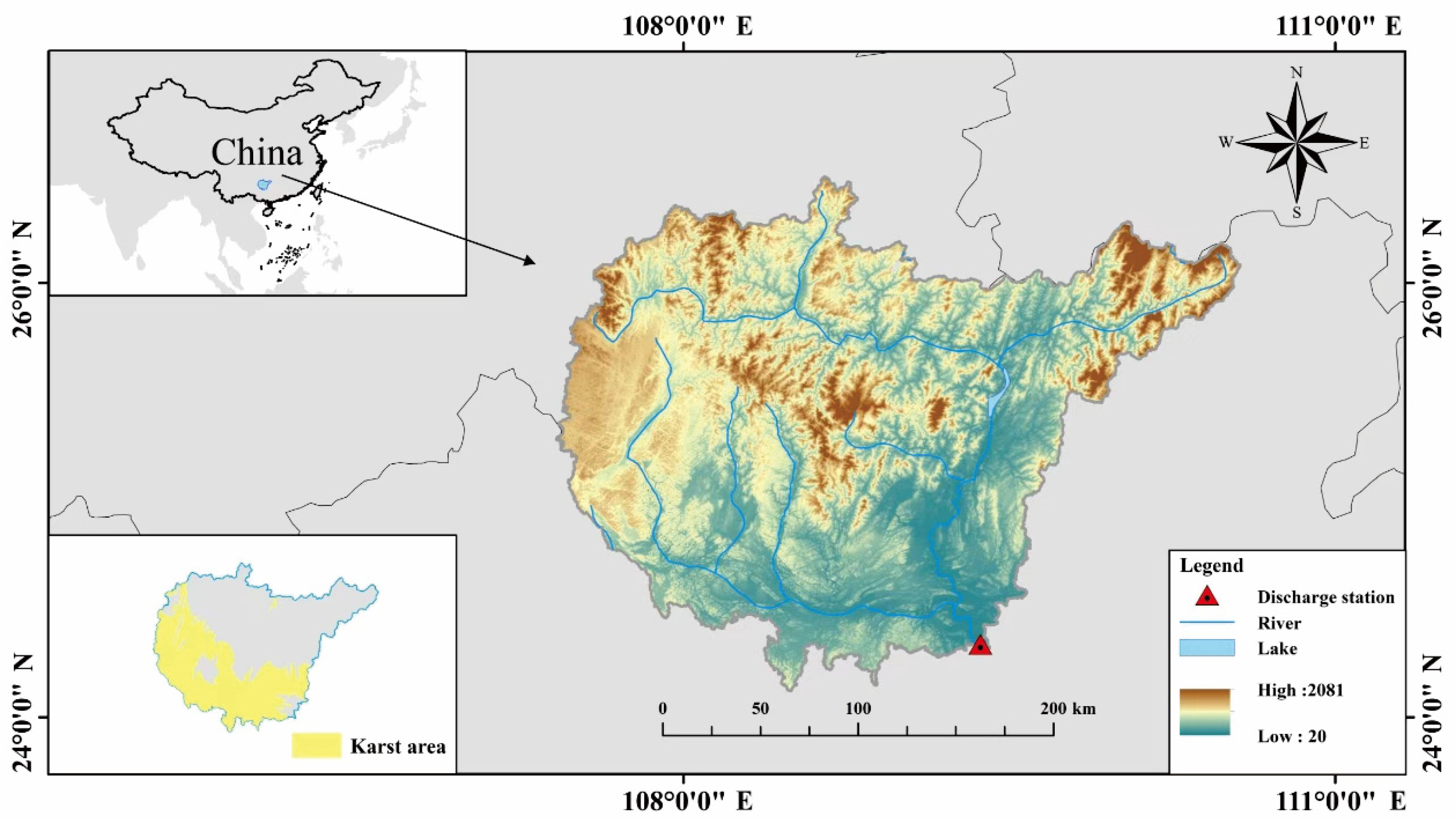
2. Description of Study Site and Datasets
3. Methodology
3.1. Three Different Hydrological Models
3.2. Future Climate Projections
3.3. ANOVA Method
4. Results
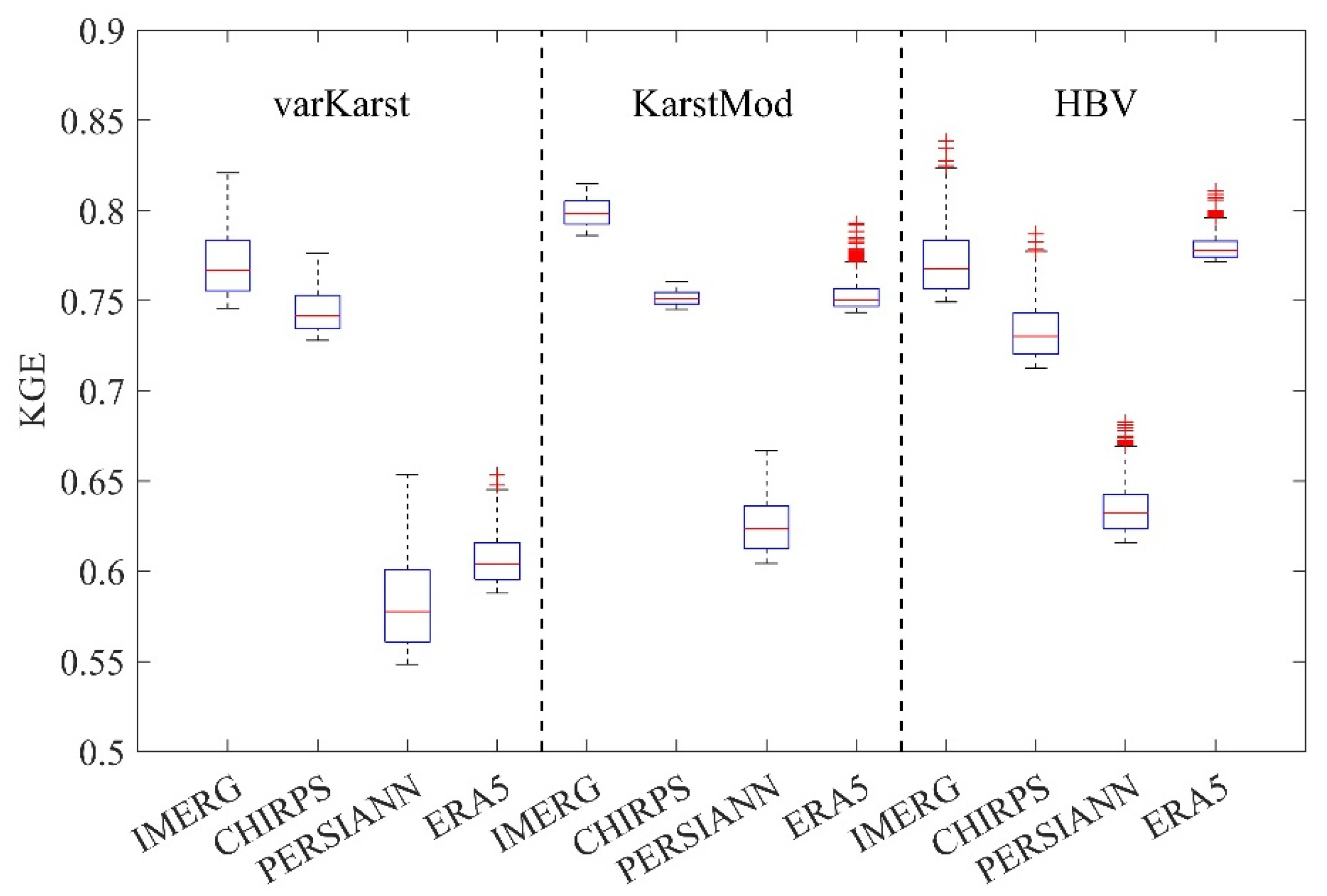
4.1. Calibration Results of Different Precipitation Products
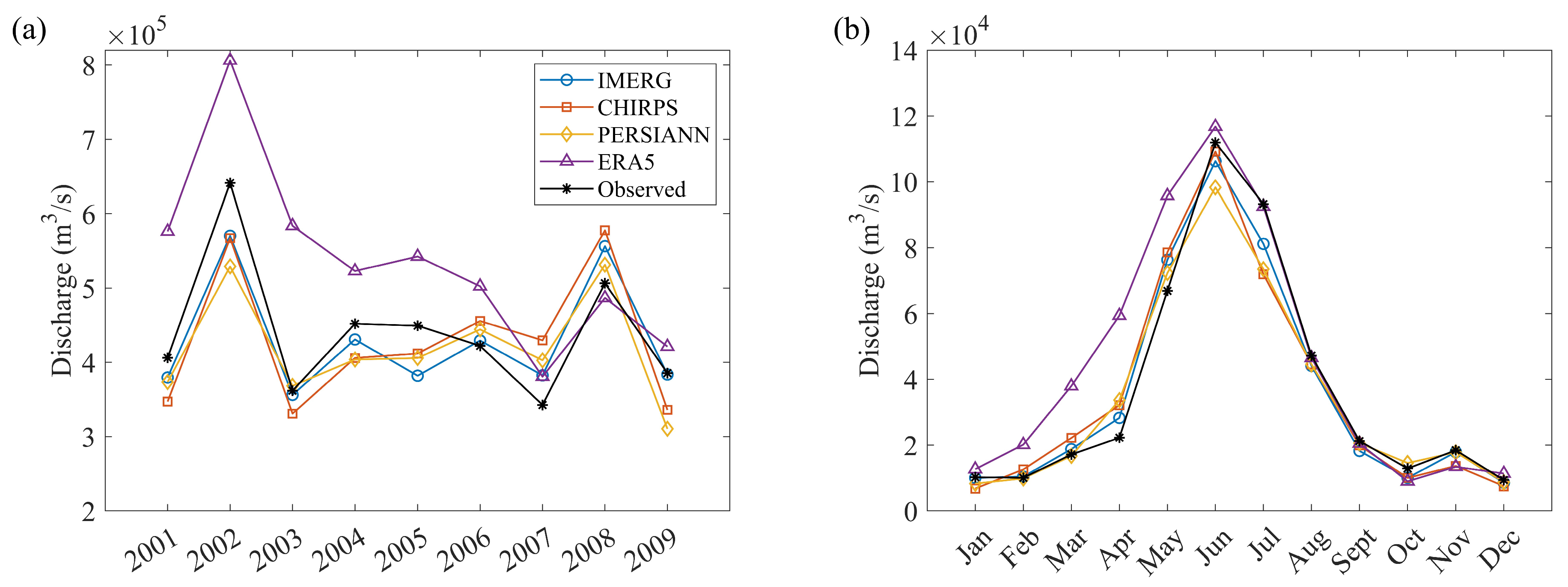
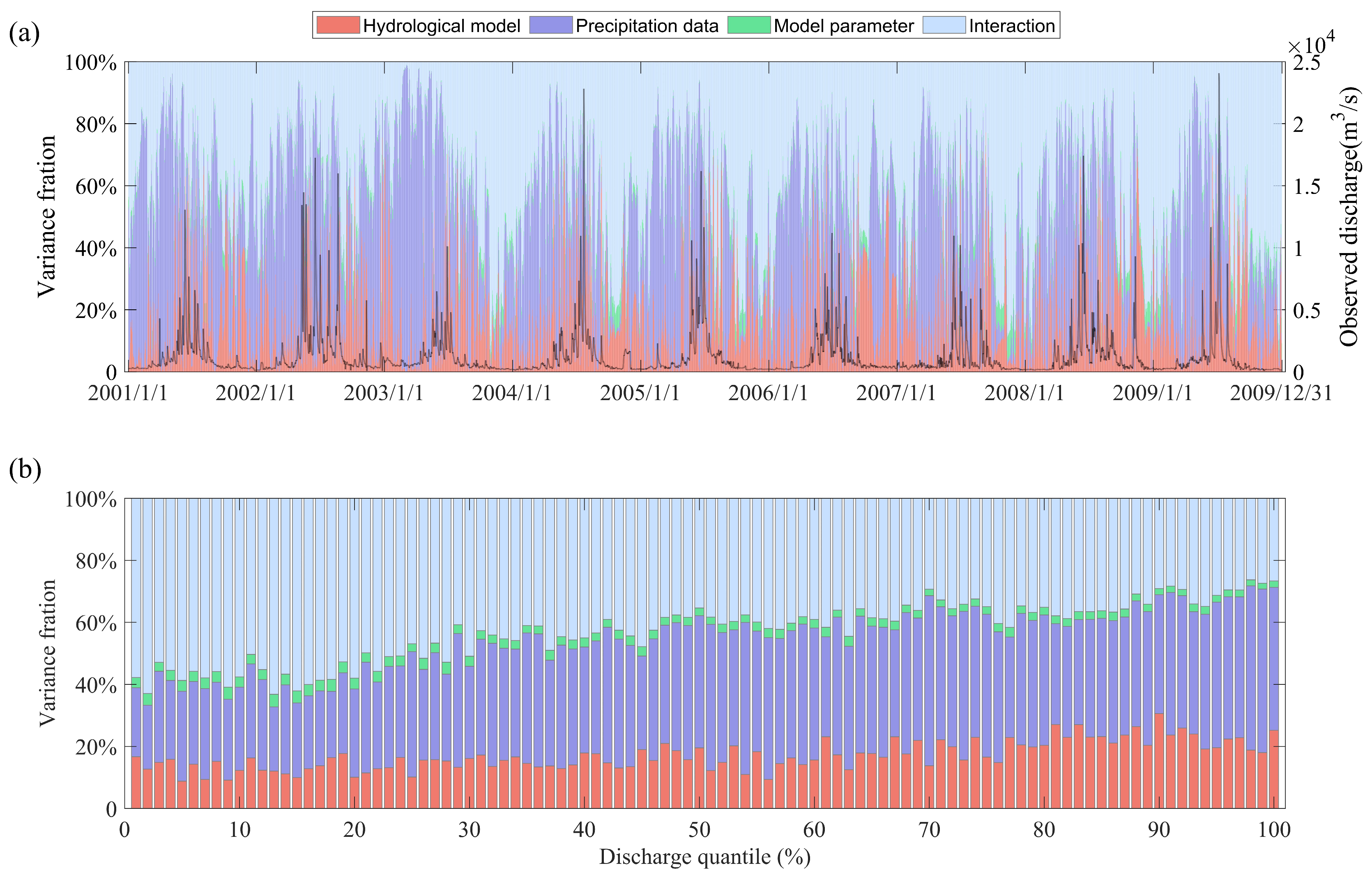
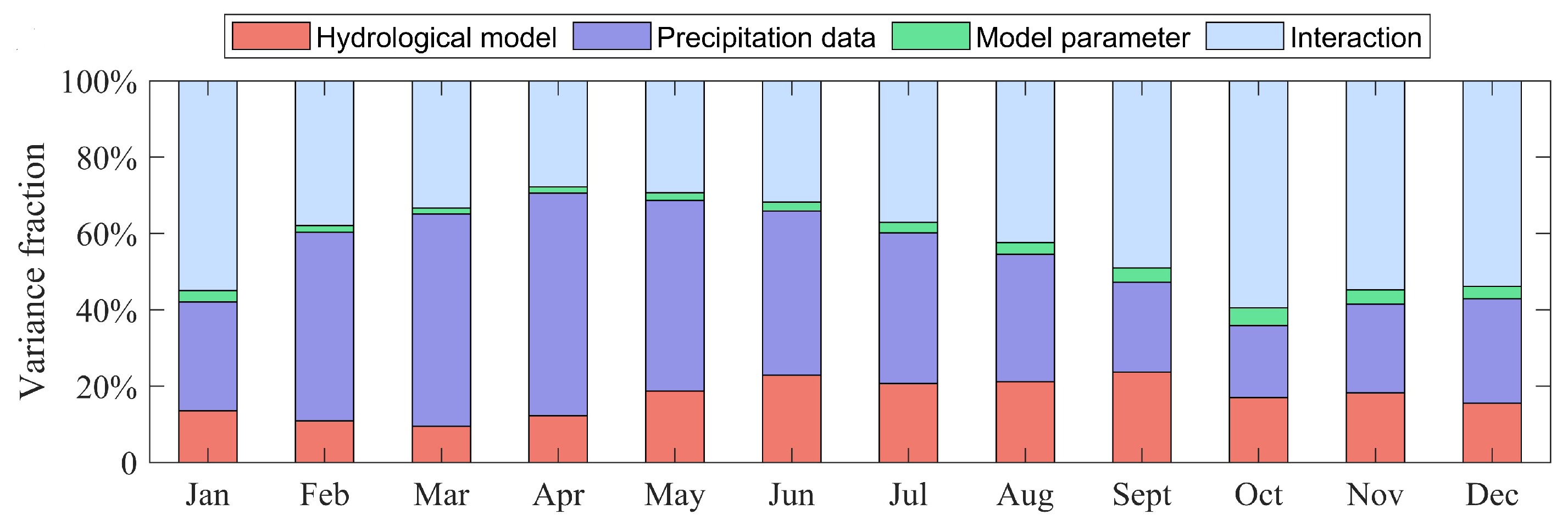
4.2. Uncertainty Analysis in the Calibration Period
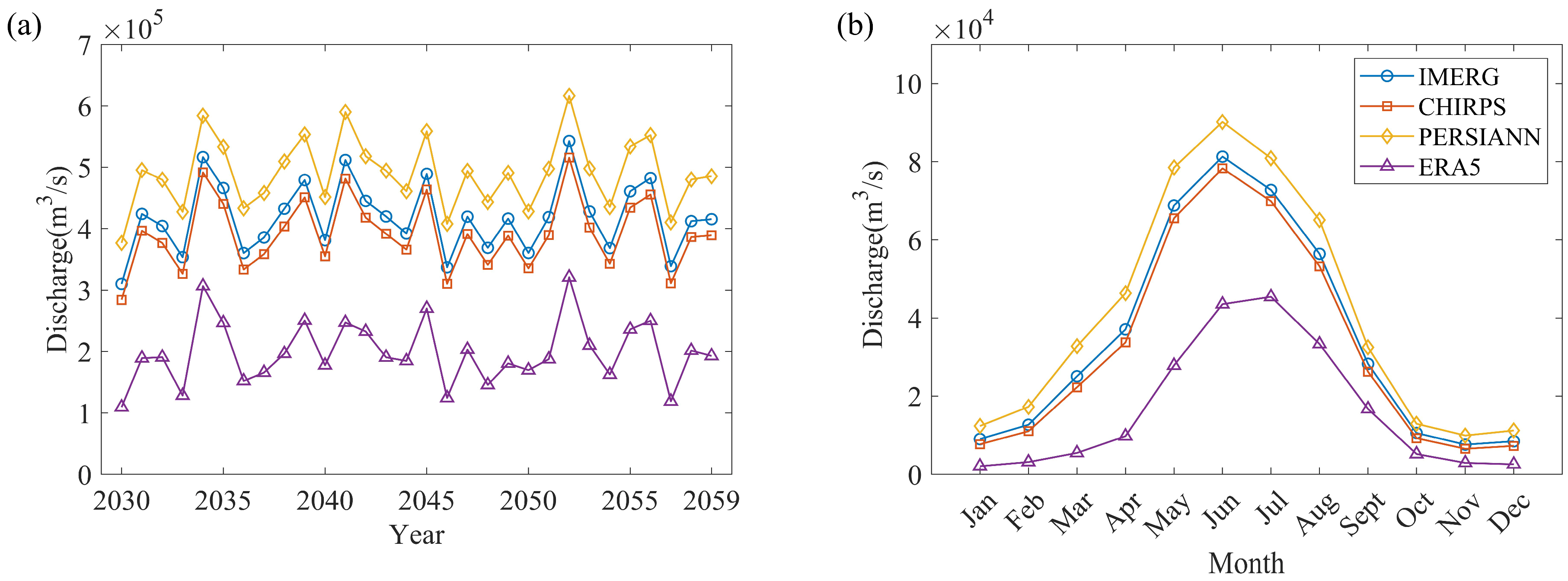
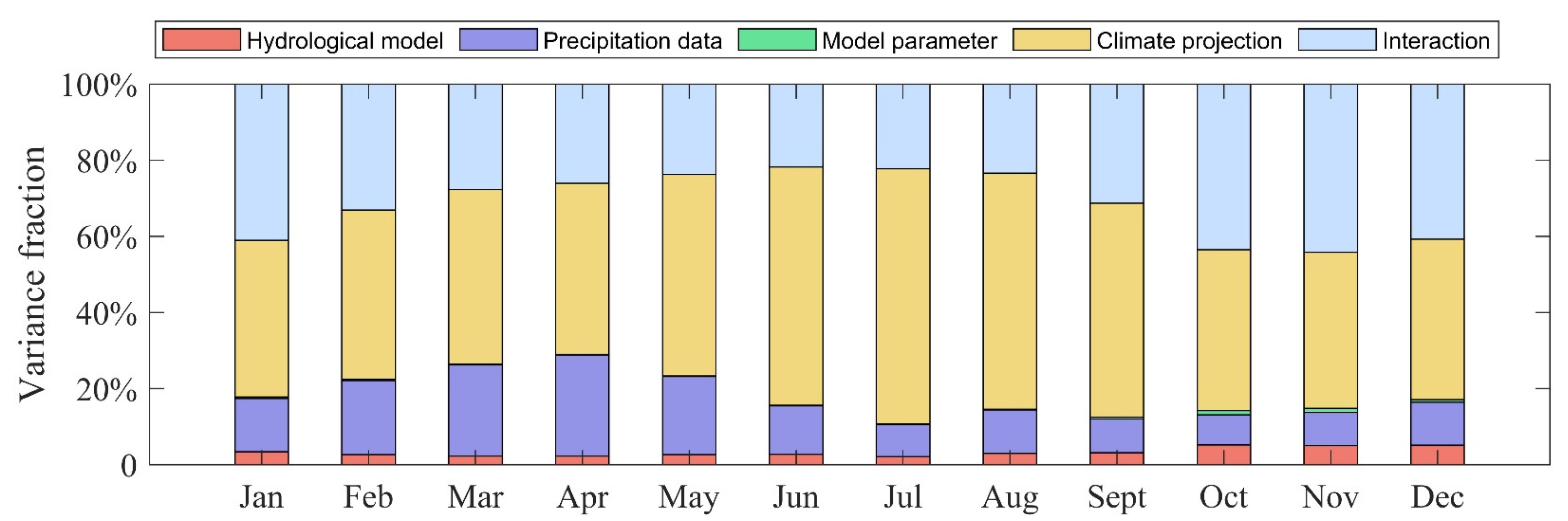
4.3. Uncertainty Analysis in the Future Period
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khatakho, R.; Talchabhadel, R.; Thapa, B.R. Evaluation of Different Precipitation Inputs on Streamflow Simulation in Himalayan River Basin. J. Hydrol. 2021, 599, 126390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauch, M.; Bernhofer, C.; Koide, S.; Volk, M.; Lorz, C.; Makeschin, F. Using Precipitation Data Ensemble for Uncertainty Analysis in SWAT Streamflow Simulation. J. Hydrol. 2012, 414–415, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tudaji, M.; Nan, Y.; Tian, F. Assessing the Value of High-Resolution Rainfall and Streamflow Data for Hydrological Modeling: An Analysis Based on 63 Catchments in Southeast China. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2025, 29, 1919–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidd, C.; Huffman, G. Global Precipitation Measurement. Meteorol. Appl. 2011, 18, 334–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, H. Assessing 10 Satellite Precipitation Products in Capturing the July 2021 Extreme Heavy Rain in Henan, China. J. Meteorol. Res. 2022, 36, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Miao, C.; Duan, Q.; Ashouri, H.; Sorooshian, S.; Hsu, K.-L. A Review of Global Precipitation Data Sets: Data Sources, Estimation, and Intercomparisons. Rev. Geophys. 2018, 56, 79–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Wang, Z. Comprehensive Evaluation of IMERG, ERA5-Land and Their Fusion Products in the Hydrological Simulation of Three Karst Catchments in Southwest China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2024, 52, 101671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaowei, N.; Jie, W.; Juliang, J.; Xiaoyan, X.; Yuliang, Z.; Fan, S.; Linlin, Z. Comprehensive Evaluation of Satellite-Derived Precipitation Products Considering Spatial Distribution Difference of Daily Precipitation over Eastern China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 44, 101242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taye, M.; Mengistu, D.; Sahlu, D. Performance Evaluation of Multiple Satellite Rainfall Data Sets in Central Highlands of Abbay Basin, Ethiopia. Eur. J. Remote Sens. 2023, 56, 2233686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alazzy, A.A.; Lü, H.; Chen, R.; Ali, A.B.; Zhu, Y.; Su, J. Evaluation of Satellite Precipitation Products and Their Potential Influence on Hydrological Modeling over the Ganzi River Basin of the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Meteorol. 2017, 2017, 3695285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dembélé, M.; Schaefli, B.; van de Giesen, N.; Mariéthoz, G. Suitability of 17 Gridded Rainfall and Temperature Datasets for Large-Scale Hydrological Modelling in West Africa. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2020, 24, 5379–5406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laiti, L.; Mallucci, S.; Piccolroaz, S.; Bellin, A.; Zardi, D.; Fiori, A.; Nikulin, G.; Majone, B. Testing the Hydrological Coherence of High-Resolution Gridded Precipitation and Temperature Data Sets. Water Resour. Res. 2018, 54, 1999–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Q.; Li, W.; Fan, Z.; He, X.; Sun, W.; Chen, S.; Wen, J.; Gao, J.; Wang, J. Evaluation of the ERA5 Reanalysis Precipitation Dataset over Chinese Mainland. J. Hydrol. 2021, 595, 125660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, X.; Lyu, J.; Zhao, L. Evaluation of the GPM-IMERG V06 Final Run Products for Monthly/Annual Precipitation under the Complex Climatic and Topographic Conditions of China. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2023, 62, 929–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebrechorkos, S.H.; Leyland, J.; Dadson, S.J.; Cohen, S.; Slater, L.; Wortmann, M.; Ashworth, P.J.; Bennett, G.L.; Boothroyd, R.; Cloke, H.; et al. Global-Scale Evaluation of Precipitation Datasets for Hydrological Modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2024, 28, 3099–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Perrin, C.; Mathevet, T.; Andréassian, V.; Michel, C. Impact of Biased and Randomly Corrupted Inputs on the Efficiency and the Parameters of Watershed Models. J. Hydrol. 2006, 320, 62–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oudin, L.; Andréassian, V.; Perrin, C.; Anctil, F. Locating the Sources of Low-Pass Behavior within Rainfall-Runoff Models. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 3291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, C.M.; Pham, H.T.; Marshall, L.A.; Johnson, F.M. Which Rainfall Errors Can Hydrologic Models Handle? Implications for Using Satellite-Derived Products in Sparsely Gauged Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, 29331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuo, L.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A.; Abdelhalim, A.; Han, D. Interacting Effects of Precipitation and Potential Evapotranspiration Biases on Hydrological Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, 33323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmanuel, I.; Payrastre, O.; Andrieu, H.; Zuber, F. A Method for Assessing the Influence of Rainfall Spatial Variability on Hydrograph Modeling. First Case Study in the Cevennes Region, Southern France. J. Hydrol. 2017, 555, 314–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velásquez, N.; Krajewski, W.F.; Seo, B.-C. Assessing the Impact of Radar-Rainfall Uncertainty on Streamflow Simulation. J. Hydrometeorol. 2025, 26, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A.; Das, T. Influence of Rainfall Observation Network on Model Calibration and Application. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2008, 12, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Xu, C.-Y.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L. Assessing the Influence of Rain Gauge Density and Distribution on Hydrological Model Performance in a Humid Region of China. J. Hydrol. 2013, 505, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Z.; Liao, W.; Lei, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, R. Comparing the Hydrological Responses of Conceptual and Process-Based Models with Varying Rain Gauge Density and Distribution. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Refsgaard, J.C.; Sonnenborg, T.O.; Vejen, F.; Jensen, K.H. Statistical Analysis of the Impact of Radar Rainfall Uncertainties on Water Resources Modeling. Water Resour. Res. 2011, 47, W09526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignal, B.; Galli, G.; Joss, J.; Germann, U. Three Methods to Determine Profiles of Reflectivity from Volumetric Radar Data to Correct Precipitation Estimates. J. Appl. Meteorol. 2000, 39, 1715–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- HABIB, E.; ADUVALA, A.V.; MESELHE, E.A. Analysis of Radar-Rainfall Error Characteristics and Implications for Streamflow Simulation Uncertainty. Hydrol. Sci. J. 2008, 53, 568–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Peng, D.Z.; Cluckie, I.D. Statistical Analysis of Error Propagation from Radar Rainfall to Hydrological Models. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2013, 17, 1445–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fei, K.; Chen, M.; Zhou, Y.; Du, H.; Deng, S.; Gao, L. Streamflow and Surface Soil Moisture Simulation Capacity of High-Resolution Satellite-Derived Precipitation Estimate Datasets: A Case Study in Xijiang River Basin, China. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 2022, 42, 101163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Peng, D.; Gu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Luo, X. Evaluation of Multiple Satellite Precipitation Products and Their Potential Utilities in the Yarlung Zangbo River Basin. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 13334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Wang, G.; Nanding, N.; Chen, W. Hydrological Evaluation of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products in Hunan Province. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.; Xiong, L.; Liu, D.; Xu, C.-Y.; Guo, S. Evaluating the Temporal Dynamics of Uncertainty Contribution from Satellite Precipitation Input in Rainfall-Runoff Modeling Using the Variance Decomposition Method. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Zhang, C.; Fu, G.; Sweetapple, C.; Zhou, H. Evaluation of Global Fine-Resolution Precipitation Products and Their Uncertainty Quantification in Ensemble Discharge Simulations. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 20, 903–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, C.; Peterson, P.; Landsfeld, M.; Pedreros, D.; Verdin, J.; Shukla, S.; Husak, G.; Rowland, J.; Harrison, L.; Hoell, A.; et al. The Climate Hazards Infrared Precipitation with Stations—A New Environmental Record for Monitoring Extremes. Sci. Data 2015, 2, 150066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashouri, H.; Hsu, K.-L.; Sorooshian, S.; Braithwaite, D.K.; Knapp, K.R.; Cecil, L.D.; Nelson, B.R.; Prat, O.P. PERSIANN-CDR: Daily Precipitation Climate Data Record from Multisatellite Observations for Hydrological and Climate Studies. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 2015, 96, 69–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffman, G.J.; Bolvin, D.T.; Braithwaite, D.; Hsu, K.-L.; Joyce, R.J.; Kidd, C.; Nelkin, E.J.; Sorooshian, S.; Stocker, E.F.; Tan, J. Integrated Multi-Satellite Retrievals for the Global Precipitation Measurement (GPM) Mission (IMERG). In Satellite Precipitation Measurement: Volume 1; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2020; pp. 343–353. [Google Scholar]
- Soci, C.; Hersbach, H.; Simmons, A.; Poli, P.; Bell, B.; Berrisford, P.; Horányi, A.; Muñoz-Sabater, J.; Nicolas, J.; Radu, R.; et al. The ERA5 Global Reanalysis from 1940 to 2022. Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2024, 150, 4014–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, A.; Barberá, J.A.; Andreo, B. On the Value of Water Quality Data and Informative Flow States in Karst Modelling. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2017, 21, 5971–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzilli, N.; Guinot, V.; Jourde, H.; Lecoq, N.; Labat, D.; Arfib, B.; Baudement, C.; Danquigny, C.; Dal Soglio, L.; Bertin, D. KarstMod: A Modelling Platform for Rainfall—Discharge Analysis and Modelling Dedicated to Karst Systems. Environ. Model. Softw. 2019, 122, 103927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tritz, S.; Guinot, V.; Jourde, H. Modelling the Behaviour of a Karst System Catchment Using Non-Linear Hysteretic Conceptual Model. J. Hydrol. 2011, 397, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Chen, Z. Applicability of Evapotranspiration Equations for the Pearl River Basin. Trop. Geogr. 2014, 34, 737–745. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Bosshard, T.; Carambia, M.; Goergen, K.; Kotlarski, S.; Krahe, P.; Zappa, M.; Schär, C. Quantifying Uncertainty Sources in an Ensemble of Hydrological Climate-Impact Projections. Water Resour. Res. 2013, 49, 1523–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhuo, L.; Han, D.; Liu, Y.; Rico-Ramirez, M.A. Hydrological Model Adaptability to Rainfall Inputs of Varied Quality. Water Resour. Res. 2023, 59, 32484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Chen, H.; Xu, C.-Y.; Jie, M.-X.; Chen, J.; Guo, S.-L.; Liu, J. The Effect of Rain Gauge Density and Distribution on Runoff Simulation Using a Lumped Hydrological Modelling Approach. J. Hydrol. 2018, 563, 106–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, C.; Gou, J.; Hu, J.; Duan, Q. Impacts of Different Satellite-Based Precipitation Signature Errors on Hydrological Modeling Performance Across China. Earth’s Future 2024, 12, e2024EF004954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bárdossy, A.; Anwar, F. Why Do Our Rainfall–Runoff Models Keep Underestimating the Peak Flows? Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2023, 27, 1987–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayal, D.; Pandey, A.; Gupta, P.K.; Kalura, P. Investigating the Utility of Satellite-Based Precipitation Products for Simulating Extreme Discharge Events: An Exhaustive Model-Driven Approach for a Tropical River Basin in India. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2024, 196, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Kempen, G.; van der Wiel, K.; Melsen, L.A. The Impact of Hydrological Model Structure on the Simulation of Extreme Runoff Events. Nat. Hazards Earth Syst. Sci. 2021, 21, 961–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addor, N.; Rössler, O.; Köplin, N.; Huss, M.; Weingartner, R.; Seibert, J. Robust Changes and Sources of Uncertainty in the Projected Hydrological Regimes of Swiss Catchments. Water Resour. Res. 2014, 50, 7541–7562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Her, Y.; Yoo, S.-H.; Cho, J.; Hwang, S.; Jeong, J.; Seong, C. Uncertainty in Hydrological Analysis of Climate Change: Multi-Parameter vs. Multi-GCM Ensemble Predictions. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kingston, D.G.; Thompson, J.R.; Kite, G. Uncertainty in Climate Change Projections of Discharge for the Mekong River Basin. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2011, 15, 1459–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yuan, F.; Wang, B.; Ren, L.; Zhao, C.; Shi, J.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yang, X.; Chen, T.; et al. Quantifying Uncertainty Sources in Extreme Flow Projections for Three Watersheds with Different Climate Features in China. Atmospheric Res. 2021, 249, 105331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evin, G.; Hingray, B.; Thirel, G.; Ducharne, A.; Strohmenger, L.; Corre, L.; Tramblay, Y.; Vidal, J.-P.; Bonneau, J.; Colleoni, F.; et al. Uncertainty Sources in a Large Ensemble of Hydrological Projections: Regional Climate Models and Internal Variability Matter. EGUsphere 2025, 2025, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, T.; Pokhrel, Y.; Felfelani, F. On the Precipitation-Induced Uncertainties in Process-Based Hydrological Modeling in the Mekong River Basin. Water Resour. Res. 2022, 58, e2021WR030828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhter, M.; Ahanger, M.A. Uncertainty in Evapotranspiration Inputs Impacts Hydrological Modeling. Water Sci. Technol. 2024, 91, 235–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayathilake, D.I.; Smith, T. Assessing the Impact of PET Estimation Methods on Hydrologic Model Performance. Hydrol. Res. 2020, 52, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, Y.; Mu, N.; Qi, Y.; Liu, L. Quantifying the Contribution of Global Precipitation Product Uncertainty to Ensemble Discharge Simulations and Projections: A Case Study in the Liujiang Catchment, Southwest China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111260
Chang Y, Mu N, Qi Y, Liu L. Quantifying the Contribution of Global Precipitation Product Uncertainty to Ensemble Discharge Simulations and Projections: A Case Study in the Liujiang Catchment, Southwest China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111260
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Yong, Nan Mu, Yaoyong Qi, and Ling Liu. 2025. "Quantifying the Contribution of Global Precipitation Product Uncertainty to Ensemble Discharge Simulations and Projections: A Case Study in the Liujiang Catchment, Southwest China" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111260
APA StyleChang, Y., Mu, N., Qi, Y., & Liu, L. (2025). Quantifying the Contribution of Global Precipitation Product Uncertainty to Ensemble Discharge Simulations and Projections: A Case Study in the Liujiang Catchment, Southwest China. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1260. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111260





