Tracing the Dust: Two Decades of Dust Storm Dynamics in Yazd Province from Ground-Based and Satellite Aerosol Observations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data
2.2.1. Synoptic Stations Data
2.2.2. Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) Data
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA)
2.3.2. Kriging Interpolation
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variations of Dust Events Using Station Data
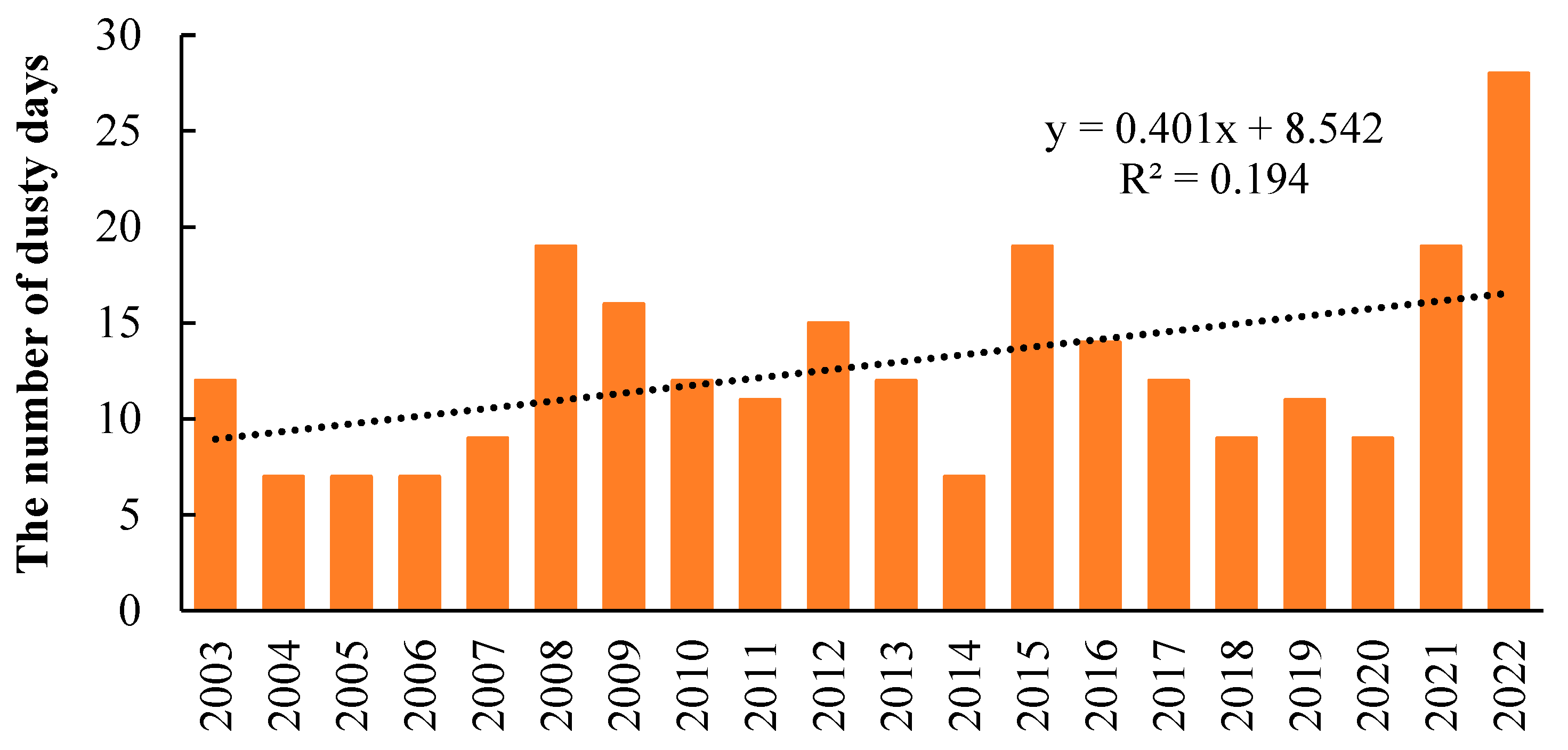
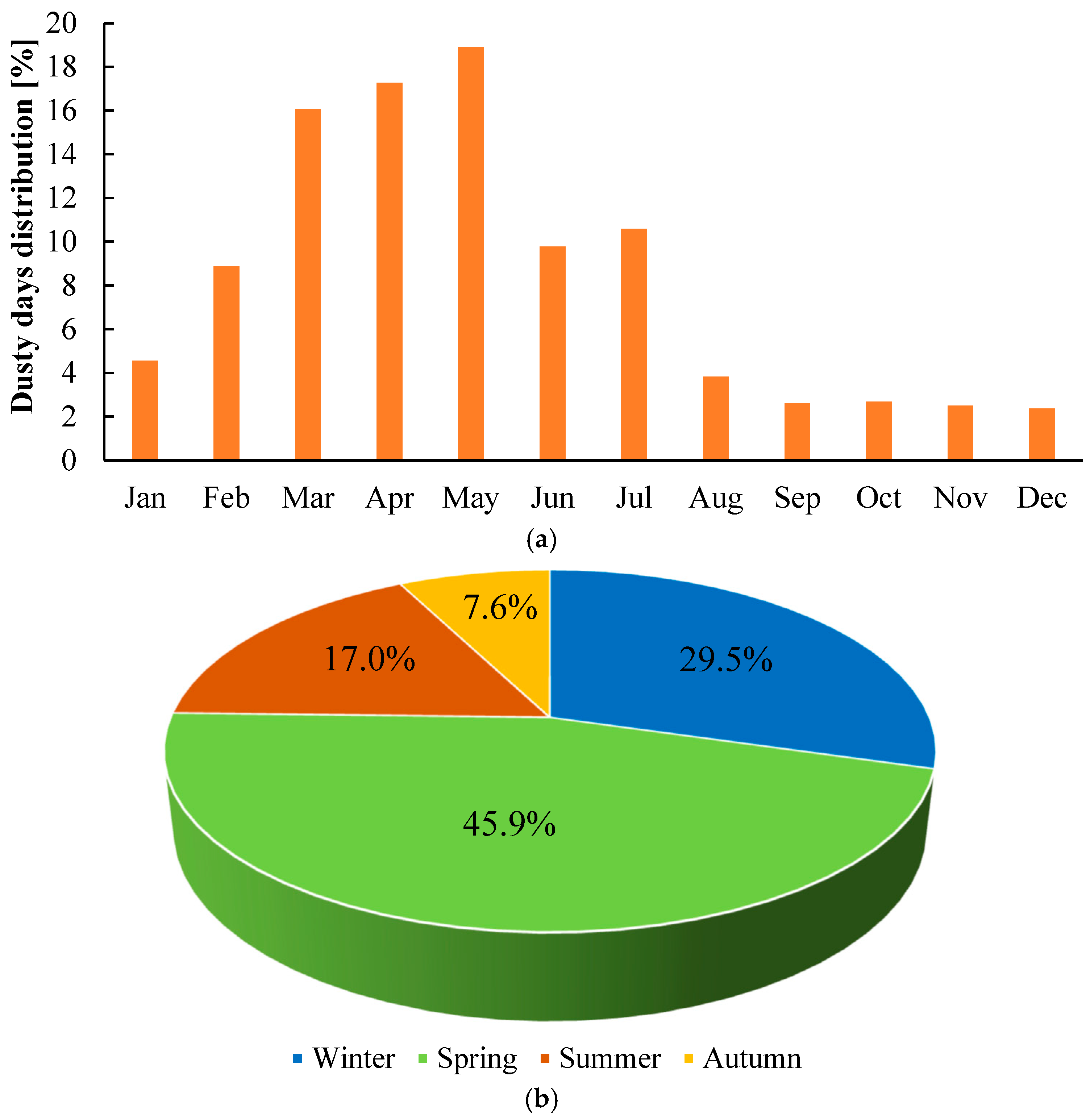
3.1.1. Temporal Distribution of the Frequency of Dust Days
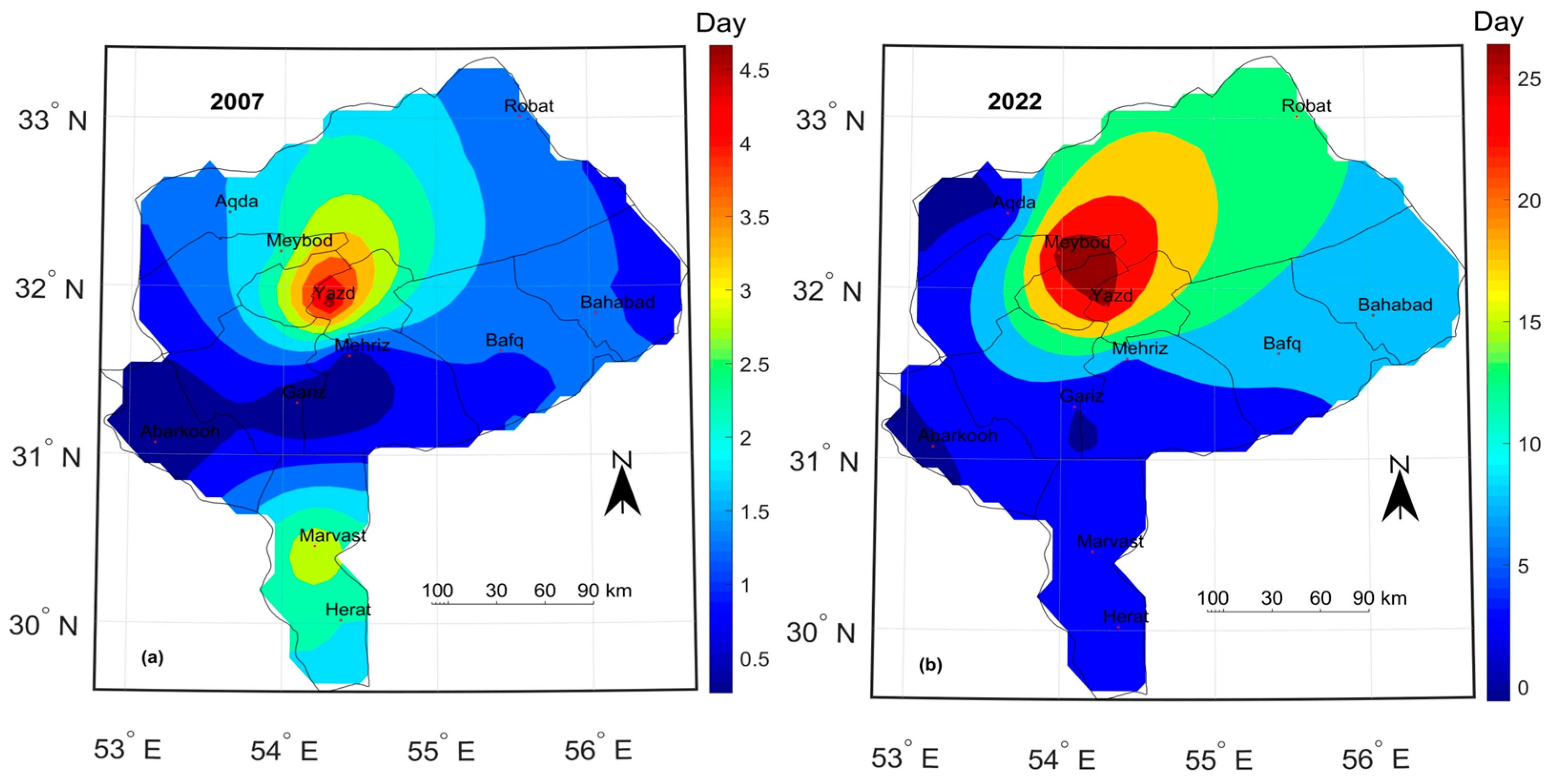
3.1.2. Spatial Distribution of the Frequency of Dust Days
3.2. Spatiotemporal Variations of Dust Events Using Aqua MODIS AOD Data
3.2.1. Temporal Variations of Dust Events Using Aqua MODIS AOD Data
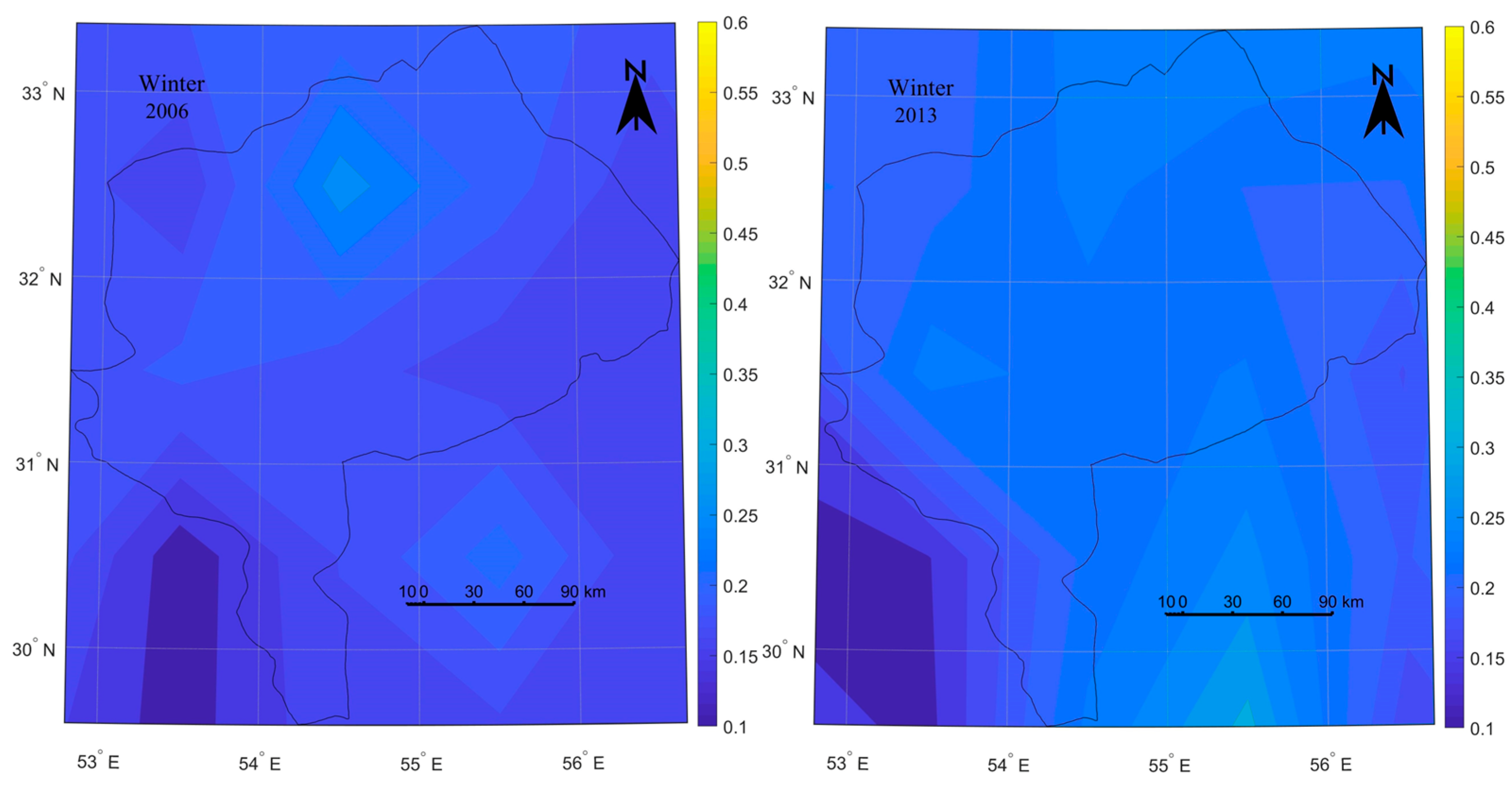
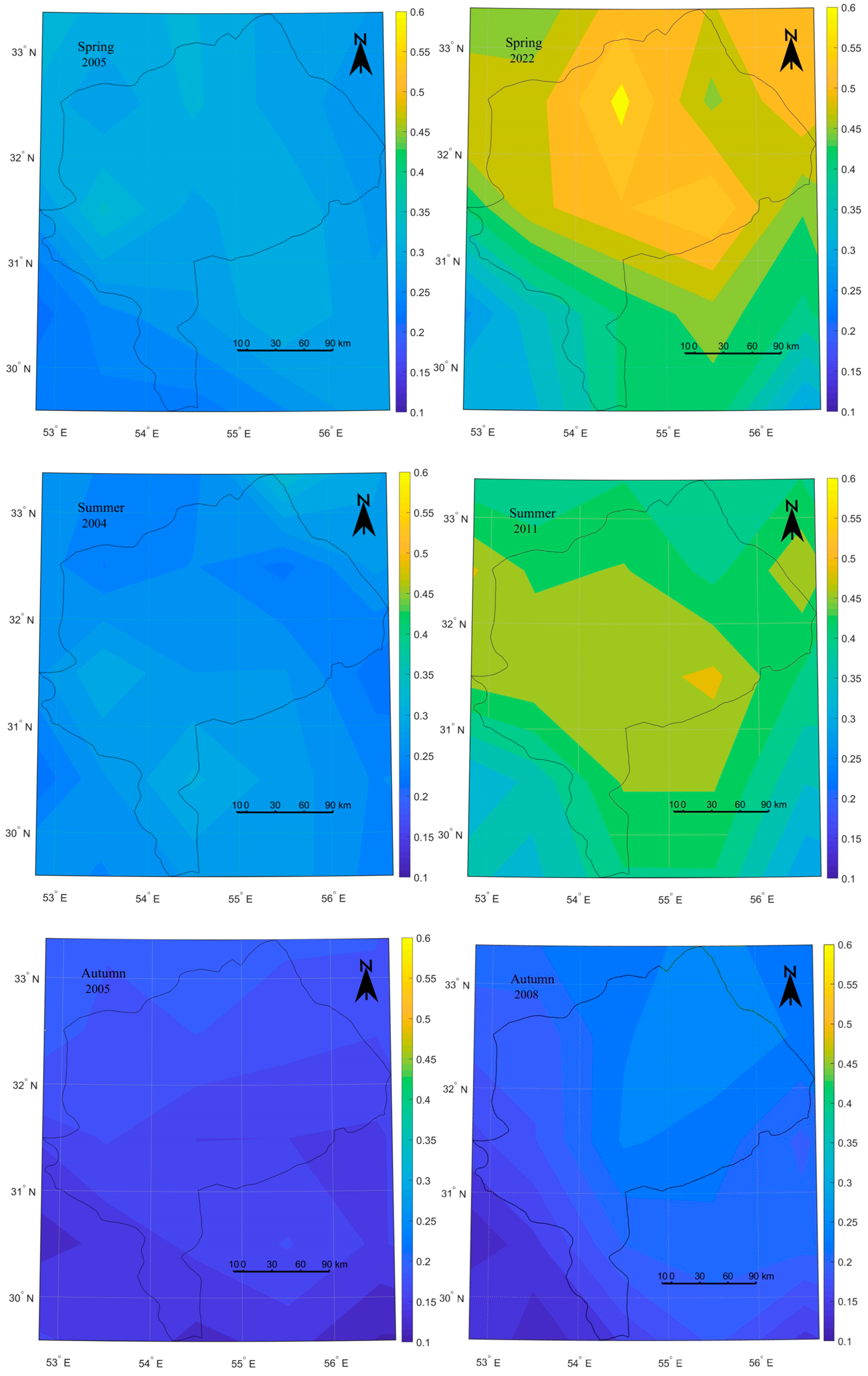
3.2.2. Spatial Variations of Dust Events Using Aqua MODIS AOD Data
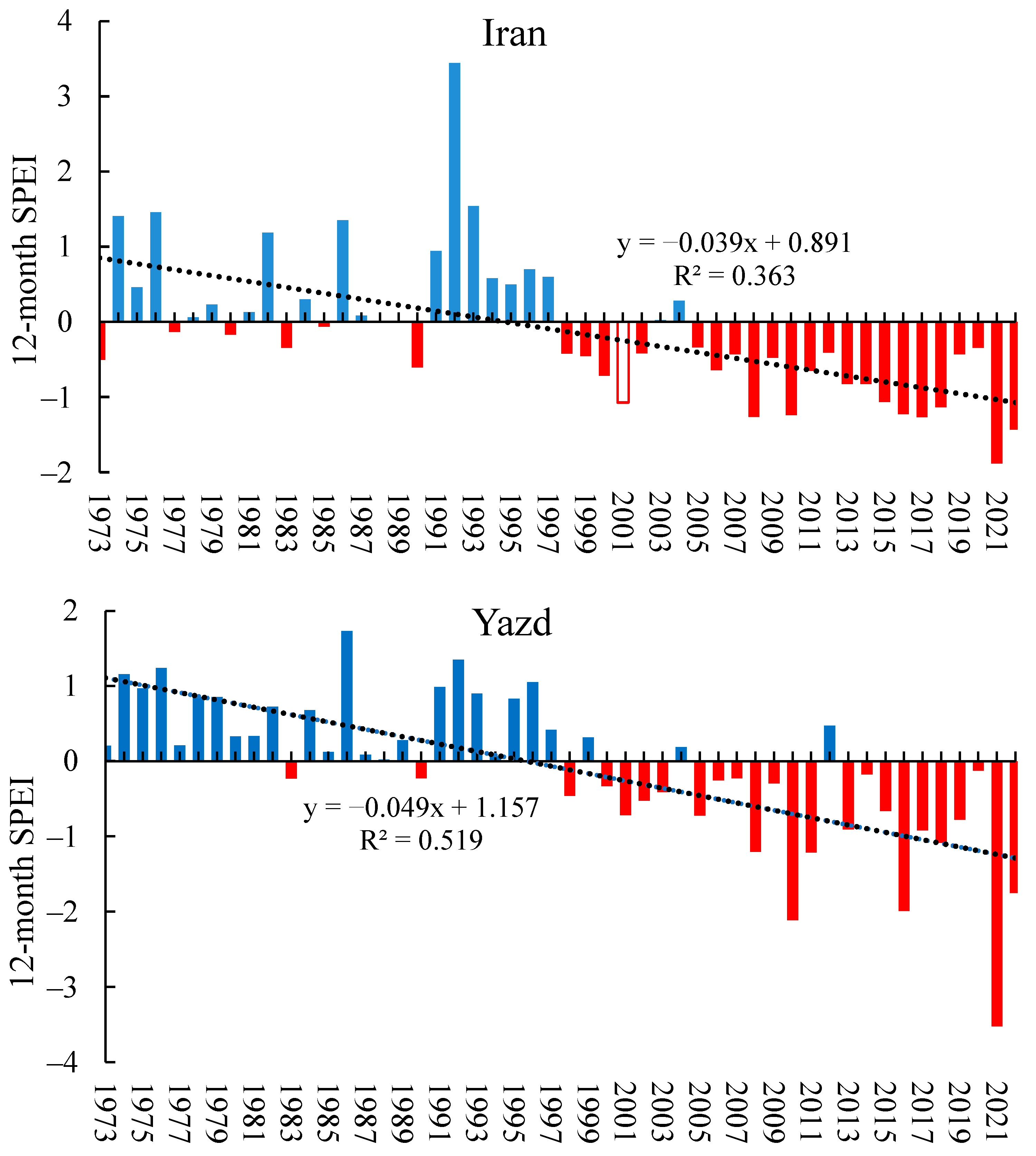
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rap, A.; Scott, C.E.; Spracklen, D.V.; Bellouin, N.; Forster, P.M.; Carslaw, K.S.; Schmidt, A.; Mann, G. Natural aerosol direct and indirect radiative effects. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2013, 40, 3297–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucca, C.; Fleiner, R.; Bonaiuti, E.; Kang, U. Land degradation drivers of anthropogenic sand and dust storms. Catena 2022, 219, 106575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N. Rangeland management and climate hazards in drylands: Dust storms, desertification and the overgrazing debate. Nat. Hazards 2018, 92, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Caballero, E.; Belnap, J.; Büdel, B.; Crutzen, P.J.; Andreae, M.O.; Pöschl, U.; Weber, B. Dryland photoautotrophic soil surface communities endangered by global change. Nat. Geosci. 2018, 11, 185–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudie, A.; Middleton, N. Desert Dust in the Global System; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Attiya, A.A.; Jones, B.G. An extensive dust storm impact on air quality on 22 November 2018 in Sydney, Australia, using satellite remote sensing and ground data. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2022, 194, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Graaf, M. Remote Sensing of UV-Absorbing Aerosols Using Space-Borne Spectrometers. Ph.D. Thesis, Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam, Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2006; 132p. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M.; Westphal, D.L.; Wang, S.; Shimizu, A.; Sugimoto, N.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Y. A high-resolution numerical study of the Asian dust storms of April 2001. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2003, 108, 8653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, S.; Karimi, N.; Sorooshian, A.; Mohammadi, G.; Sehatkashani, S. Impacts of climate and synoptic fluctuations on dust storm activity over the Middle East. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 173, 265–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, Y.J.; Tanré, D.; Boucher, O. A satellite view of aerosols in the climate system. Nature 2002, 419, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.J. Desert dust hazards: A global review. Aeolian Res. 2017, 24, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, J.F.; Ward, D.S.; Mahowald, N.M.; Evan, A.T. Global and regional importance of the direct dust-climate feedback. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Lu, M.; Chen, D.; Zhang, L. Understanding the weakening patterns of inner Tibetan Plateau vortices. Environ. Res. Lett. 2024, 19, 064076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Qiu, C.; Wang, D.; Chen, Z.; Hibiya, T.; Xie, X.; Yu, X. Kinetic energetic exchange between near-inertial waves and mesoscale eddy/diurnal tide during Typhoon Rai. J. Phys. Oceanogr. 2025, 55, 1033–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Wang, J.; Zuo, H.; Fu, Z.; Xiao, W.; Cui, Y.; Zhou, Z. Spatiotemporal distribution and variation characteristics of convective activities in different climate zones in northern China based on 25 years of satellite observations. Int. J. Climatol. 2025, 45, e8908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.F.; Lu, H.L.; Wang, G.Q.; Qiu, J. Long-term capturability of atmospheric water on a global scale. Water Resour. Res. 2024, 60, e2023WR034757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, K.; Shafiepour-Motlagh, M.; Aslemand, A.; Ghader, S. Dust storm simulation over Iran using HYSPLIT. J. Environ. Health Sci. Eng. 2014, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, N. Variability and trends in dust storm frequency on decadal timescales: Climatic drivers and human impacts. Geosciences 2019, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.; Kashani, S.S.; Attarchi, S.; Rahnama, M.; Mosalman, S.T. Synoptic causes and socio-economic consequences of a severe dust storm in the Middle East. Atmosphere 2021, 12, 1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Yu, C.; You, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Xiang, S.; Hao, K.; Chen, J. Bacteriome and mycobiome in ambient PMs during haze episodes and health hazard: A nationwide survey in China. Energy Environ. Sustain. 2025, 1, 100023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, A.; Ali, M.; Israr, M.; Gulzar, S.; Khan, M.I.; Ali, M.A.S.; Majid, A.; Rukh, S. Mapping annual soil loss in the southeast of Peshawar basin, Pakistan, using RUSLE model with geospatial approach. Geol. Ecol. Landsc. 2025, 9, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Bai, F.; Li, X.; Nie, Q.; Jia, X.; Wu, H. The remediation efficiency of heavy metal pollutants in water by industrial red mud particle waste. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2022, 28, 102944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crosbie, E.; Sorooshian, A.; Monfared, N.A.; Shingler, T.; Esmaili, O. A multi-year aerosol characterization for the greater Tehran area using satellite, surface, and modeling data. Atmosphere 2014, 5, 178–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Shi, C.; Wu, B.; Chen, Z.; Nie, S.; He, D.; Zhang, H. Analysis of aerosol characteristics and their relationships with meteorological parameters over Anhui province in China. Atmos. Res. 2012, 109, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippertz, P.; Todd, M.C. Mineral dust aerosols over the Sahara: Meteorological controls on emission and transport and implications for modeling. Rev. Geophys. 2012, 50, RG1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, N.; Kang, U. Sand and dust storms: Impact mitigation. Sustainability 2017, 9, 1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namdari, S.; Valizade, K.; Rasuly, A.; Sari Sarraf, B. Spatio-temporal analysis of MODIS AOD over western part of Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2016, 9, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qor-el-aine, A.; Beres, A.; Geczi, G. Dust storm simulation over the Sahara Desert (Moroccan and Mauritanian regions) using HYSPLIT. Atmos. Sci. Lett. 2022, 23, e1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minder, J.R.; Mote, P.W.; Lundquist, J.D. Surface temperature lapse rates over complex terrain: Lessons from the Cascade Mountains. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2010, 115, D14122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyler, J.W.; Dobrowski, S.Z.; Holden, Z.A.; Running, S.W. Remotely sensed land skin temperature as a spatial predictor of air temperature across the conterminous United States. J. Appl. Meteorol. Climatol. 2016, 55, 1441–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhebsi, K. Spatio-Temporal Variability of Aerosol Optical Depth in the UAE Using MODIS Data. Master’s Thesis, George Mason University, Fairfax, VA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirgholami, M.R.; Masoodian, S.A.; Montazeri, M. Investigation of environmental changes in arid and semi-arid regions based on MODIS LST data (case study: Yazd province, central Iran). Arab. J. Geosci. 2023, 16, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Zhu, C.; Hulugalla, R.; Gu, J.; Di, G. Spatial and temporal characteristics of aerosol optical depth over East Asia and their association with wind fields. Meteorol. Appl. 2008, 15, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, M.J.; Assiri, M.E.; Ali, M.A. Assessment of AOD variability over Saudi Arabia using MODIS Deep Blue products. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 231, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Tang, C.; Wu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F.; Liu, D. The global spatial-temporal distribution and EOF analysis of AOD based on MODIS data during 2003–2021. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 302, 119722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltaci, H. Meteorological characteristics of dust storm events in Turkey. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Rahn, K.A.; Zhuang, G. A mechanism for the increase of pollution elements in dust storms in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2004, 38, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jish Prakash, P.; Stenchikov, G.; Kalenderski, S.; Osipov, S.; Bangalath, H. The impact of dust storms on the Arabian Peninsula and the Red Sea. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2015, 15, 199–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miri, A.; Ahmadi, H.; Ekhtesasi, M.R.; Panjehkeh, N.; Ghanbari, A. Environmental and socio-economic impacts of dust storms in Sistan Region, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Stud. 2009, 66, 343–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashki, A.; Middleton, N.J.; Goudie, A.S. Dust storms in Iran–Distribution, causes, frequencies and impacts. Aeolian Res. 2021, 48, 100655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aili, A.; Oanh, N.T.K.; Abuduwaili, J. Variation trends of dust storms in relation to meteorological conditions and anthropogenic impacts in the northeast edge of the Taklimakan Desert, China. Open J. Air Pollut. 2016, 5, 127–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indoitu, R.; Orlovsky, L.; Orlovsky, N. Dust storms in Central Asia: Spatial and temporal variations. J. Arid Environ. 2012, 85, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Xu, H.; Lan, J.; Goldsmith, Y.; Torfstein, A.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Zhou, K.E.; Tan, L. Dust storms in northern China during the last 500 years. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2021, 64, 813–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, H.; Amiraslani, F.; Liu, J.; Zhou, N. Identification of dust storm source areas in West Asia using multiple environmental datasets. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 502, 224–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarres, R.; Sadeghi, S. Spatial and temporal trends of dust storms across desert regions of Iran. Nat. Hazards 2018, 90, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Yang, W.; Wang, X.; Yin, B.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Gu, C.; Ming, J.; Geng, C.; Bai, Z. A seriously sand storm mixed air-polluted area in the margin of Tarim Basin: Temporal-spatial distribution and potential sources. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 676, 436–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Stein, A.F.; Draxler, R.R.; de la Rosa, J.D.; Zhang, X. Global sand and dust storms in 2008: Observation and HYSPLIT model verification. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 6368–6381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X. Mapping the global dust storm records: Review of dust data sources in supporting modeling/climate study. Curr. Pollut. Rep. 2015, 1, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO Bulletin. WMO Bulletin Spotlights Hazards and Impacts of Sand and Dust Storms; Press Release; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024; Available online: https://public.wmo.int/news/media-centre/wmo-bulletin-spotlights-hazards-and-impacts-of-sand-and-dust-storms (accessed on 3 April 2025).
- Bao, C.; Yong, M.; Bueh, C.; Bao, Y.; Jin, E.; Bao, Y.; Purevjav, G. Analyses of the dust storm sources, affected areas, and moving paths in Mongolia and China in early spring. Remote Sens. 2022, 14, 3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, T.; Xi, G.; Hao, Y.; Chang, I.-S.; Wu, J.; Xue, Z.; Jin, E.; Zhang, W.; Bao, Y. The Transport Path and Vertical Structure of Dust Storms in East Asia and the Impacts on Cities in Northern China. Remote Sens. 2023, 15, 3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notaro, M.; Alkolibi, F.; Fadda, E.; Bakhrjy, F. Trajectory analysis of Saudi Arabian dust storms. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2013, 118, 6028–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hemoud, A.; Al-Dashti, H.; Al-Saleh, A.; Petrov, P.; Malek, M.; Elhamoud, E.; Al-Khafaji, S.; Li, J.; Koutrakis, P.; Doronzo, D. Dust storm ‘hot spots’ and transport pathways affecting the Arabian Peninsula. J. Atmos. Sol.-Terr. Phys. 2022, 238, 105932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, W. Long-Range Transport of a Dust Event and Impact on Marine Chlorophyll-a Concentration in April 2023. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, H.K.H. Dust Storms in the Middle East: Sources of Origin and Their Temporal Characteristics. Indoor Built Environ. 2003, 12, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keramat, A.; Marivani, B.; Samsami, M. Climatic change, drought and dust crisis in Iran. Int. J. Geol. Environ. Eng. 2011, 5, 472–475. [Google Scholar]
- Baghbanan, P.; Ghavidel, Y.; Farajzadeh, M. Temporal long-term variations in the occurrence of dust storm days in Iran. Meteorol. Atmos. Phys. 2020, 132, 885–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papi, R.; Kakroodi, A.; Soleimani, M.; Karami, L.; Amiri, F.; Alavipanah, S.K. Identifying sand and dust storm sources using spatial-temporal analysis of remote sensing data in Central Iran. Ecol. Inform. 2022, 70, 101724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javadnia, E.; Zahedi, N. Investigation impact of massive dust storm on aerosol optical, physical, radiative properties over Southwest Iran. Earth Obs. Geomat. Eng. 2022, 6, 135–149. [Google Scholar]
- Iraji, F.; Memarian, M.H.; Joghataei, M.; Malamiri, H.R.G. Determining the source of dust storms with use of coupling WRF and HYSPLIT models: A case study of Yazd province in central desert of Iran. Dyn. Atmos. Ocean. 2021, 93, 101197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseini Dehshiri, S.S.; Firoozabadi, B.; Afshin, H. A multidisciplinary approach to identify dust storm sources based on measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS): Case of Yazd in Iran. Nat. Hazards 2023, 116, 1663–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, K.; Trautmann, T.; Blaschke, T.; Subhan, F. Changes in aerosol optical properties due to dust storms in the Middle East and Southwest Asia. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 143, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, Y.; Wu, Z.; Liao, K.; Ren, Y. Handling missing data in large-scale MODIS AOD products using a two-step model. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 3786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caido, N.G.; Ong, P.M.; Rempillo, O.; Galvez, M.C.; Vallar, E. Spatiotemporal analysis of MODIS aerosol optical depth data in the Philippines from 2010 to 2020. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirgholami, M.; Masoodian, S.A. Assessment of spatial and temporal variations of land surface temperature (LST) due to elevation changes in Yazd Province, Iran. Arab. J. Geosci. 2022, 15, 1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vancutsem, C.; Ceccato, P.; Dinku, T.; Connor, S.J. Evaluation of MODIS land surface temperature data to estimate air temperature in different ecosystems over Africa. Remote Sens. Environ. 2010, 114, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Wang, P.; Li, X. Using MODIS land surface temperature and normalized difference vegetation index products for monitoring drought in the southern Great Plains, USA. Int. J. Remote Sens. 2004, 25, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Mao, K.; Cai, Y.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Qin, Z.; Meng, X.; Shen, X.; Guo, Z. A combined Terra and Aqua MODIS land surface temperature and meteorological station data product for China from 2003 to 2017. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2020, 12, 2555–2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WMO. Manual on Codes—International Codes, Volume I.1, Annex II to the WMO Technical Regulations: Part A—Alphanumeric Codes; World Meteorological Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Baddock, M.C.; Strong, C.L.; Leys, J.; Heidenreich, S.; Tews, E.; McTainsh, G.H. A visibility and total suspended dust relationship. Atmos. Environ. 2014, 89, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirgholami, M.R. Identifying trajectories and sources of dust events in Yazd Province using HYSPLIT model and remote sensing data. J. Arid Biome 2023, 13, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Box, G.; Jenkins, G. Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control; Holden-Day: San Francisco, CA, USA, 1970. [Google Scholar]
- Mann, H.B. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 1945, 13, 245–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kendall, M.G. Rank Correlation Methods; Griffin: London, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Ljung, G.M.; Box, G.E.P. On a measure of a lack of fit in time series models. Biometrika 1978, 65, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Z.; Zhou, S.; Su, Q.; Yi, H.; Wang, J. Comparison study on the estimation of the spatial distribution of regional soil metal(loids) pollution based on kriging interpolation and BP neural network. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitas, L.; Mitasova, H. Spatial interpolation. In Geographical Information Systems: Principles, Techniques, Management and Applications; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1999; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Tewolde, M.G.; Beza, T.A.; Costa, A.C.; Painho, M. Comparison of different interpolation techniques to map temperature in the southern region of Eritrea. In Geospatial Thinking: Proceedings of the 13th AGILE International Conference on Geographic Information Science, Guimarães, Portugal, 11–14 May 2010; Painho, M., Santos, M.Y., Pundt, H., Eds.; Association of Geographic Information Laboratories for Europe: Warsaw, Poland, 2010; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Awadh, S.M. Impact of North African sand and dust storms on the Middle East using Iraq as an example: Causes, sources, and mitigation. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khusfi, Z.; Vali, A.; Khosroshahi, M.; Ghazavi, R. The role of dried bed of Gavkhooni wetland on the production of the internal dust using remote sensing and storm roses (case study: Isfahan province). Iran. J. Range Desert Res. 2017, 24, 152–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, A.; Hedayati Aghmashhadi, A. Zoning Map of Dust Phenomenon in Markazi Province. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 20, 17–27. [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimikhusfi, Z.; Khosroshahi, M.; Naeimi, M.; Zandifar, S. Evaluating and monitoring of moisture variations in Meyghan wetland using the remote sensing technique and the relation to the meteorological drought indices. J. RS GIS Nat. Resour. 2019, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Mirzaei, R.; Zareie, H.; Talaie, M. Impact assessment of Meighan wetland to create dust phenomenon in Arak city. J. Environ. Sci. Stud. 2021, 6, 3434–3440. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Jiang, N.; Huang, J.; Xu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zang, Z.; Huang, K.; Xu, X.; Wei, Y.; Guan, X.; et al. Quantifying contributions of natural and anthropogenic dust emission from different climatic regions. Atmos. Environ. 2018, 191, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Fan, Y.; Luo, L.; Liao, J.; Li, Z.; Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Xue, X.; Wang, T. Identification of natural and anthropogenic sources and the effects of climatic fluctuations and land use changes on dust emissions variations in the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Agric. For. Meteorol. 2023, 340, 109628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boloorani, A.D.; Papi, R.; Soleimani, M.; Karami, L.; Amiri, F.; Samany, N.N. Water bodies changes in Tigris and Euphrates basin has impacted dust storms phenomena. Aeolian Res. 2021, 50, 100698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, F.; Mesbahzadeh, T.; Zehtabian, G. Drought investigation using SPEI Index and its relationship with dust (Case Study of Khuzestan Province). Iran. J. Range Desert Res. 2021, 28, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoljoodi, M.; Didevarasl, A.; Saadatabadi, A.R. Dust events in the western parts of Iran and the relationship with drought expansion over the dust-source areas in Iraq and Syria. Atmos. Clim. Sci. 2013, 3, 321–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Name | Latitude (N) | Longitude (E) | Altitude (m) | Year of Establishment |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Abarkooh | 31.12 | 53.23 | 1536 | 1997 |
| Aqda | 32.45 | 53.64 | 1150 | 2002 |
| Bafq | 31.63 | 55.42 | 991 | 1992 |
| Gariz | 31.31 | 54.10 | 1985 | 1995 |
| Herat | 30.02 | 54.38 | 1632 | 2003 |
| Marvast | 30.46 | 54.21 | 1547 | 1996 |
| Mehriz | 31.59 | 54.44 | 1487 | 2002 |
| Meybod | 32.22 | 53.98 | 1110 | 1999 |
| Robat | 33.01 | 55.56 | 1234 | 1992 |
| Yazd | 31.90 | 54.29 | 1237 | 1952 |
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| 06 | Widespread dust in suspension in the air |
| 07 | Dust or sand raised by wind at or near the station at the time of observation |
| 08 | Well-developed dust whirls or sand whirls seen at or near the station |
| 09 | Dust storm or sand storm within sight at the time of observation, or at the station during the preceding hour |
| 30 | Slight or moderate dust storm or sand storm has decreased during the preceding hour |
| 31 | Slight or moderate dust storm or sand storm shows no appreciable change during the preceding hour |
| 32 | Slight or moderate dust storm or sand storm has begun or increased during the preceding hour |
| 33 | Severe dust storm or sand storm decreased during the preceding hour |
| 34 | Severe dust storm or sand storm shows no appreciable change during the preceding hour |
| 35 | Severe dust storm or sand storm has begun or increased during the preceding hour |
| 98 | Thunderstorm combined with dust storm or sandstorm at time of observation-thunderstorm at time of observation |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shirgholami, M.; Rousta, I.; Olafsson, H.; Petracchini, F.; Krzyszczak, J. Tracing the Dust: Two Decades of Dust Storm Dynamics in Yazd Province from Ground-Based and Satellite Aerosol Observations. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111242
Shirgholami M, Rousta I, Olafsson H, Petracchini F, Krzyszczak J. Tracing the Dust: Two Decades of Dust Storm Dynamics in Yazd Province from Ground-Based and Satellite Aerosol Observations. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111242
Chicago/Turabian StyleShirgholami, Mohammadreza, Iman Rousta, Haraldur Olafsson, Francesco Petracchini, and Jaromir Krzyszczak. 2025. "Tracing the Dust: Two Decades of Dust Storm Dynamics in Yazd Province from Ground-Based and Satellite Aerosol Observations" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111242
APA StyleShirgholami, M., Rousta, I., Olafsson, H., Petracchini, F., & Krzyszczak, J. (2025). Tracing the Dust: Two Decades of Dust Storm Dynamics in Yazd Province from Ground-Based and Satellite Aerosol Observations. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111242









