Vehicle Indoor Air Quality Due to External Pollutant Ingress While Driving
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Test Method Design
2.1. Review of Factors Influencing Vehicle Indoor Air Quality
2.2. Selection of Targets to Be Measured and Measurement Equipment
2.3. On-Road Driving Test Method
2.3.1. On-Road Driving Route
2.3.2. HVAC Mode Setting
2.3.3. Test Procedures and Conditions
2.4. Calculation of Cleaning Efficiency
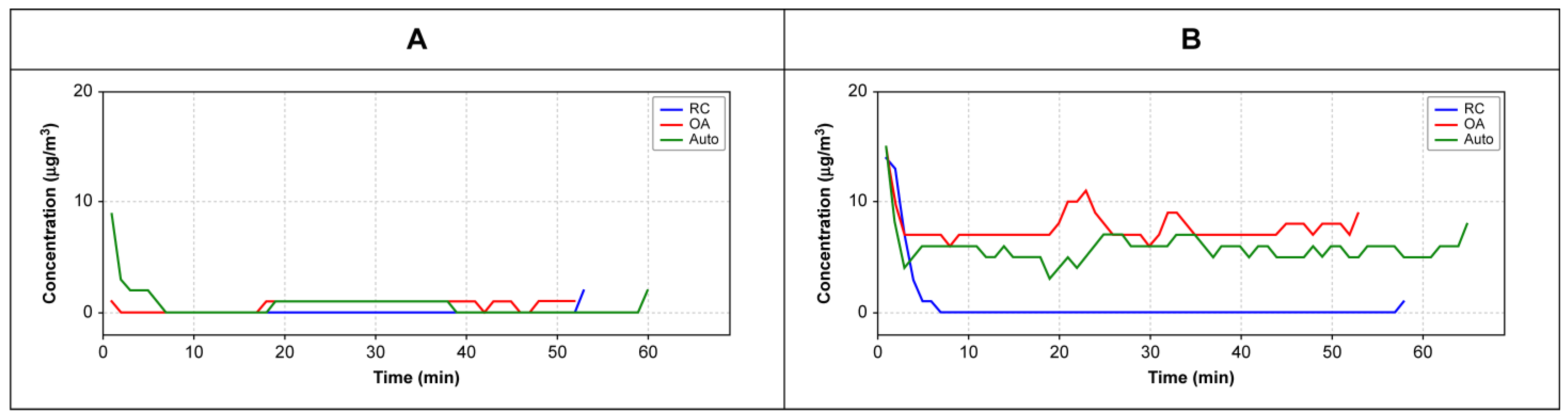
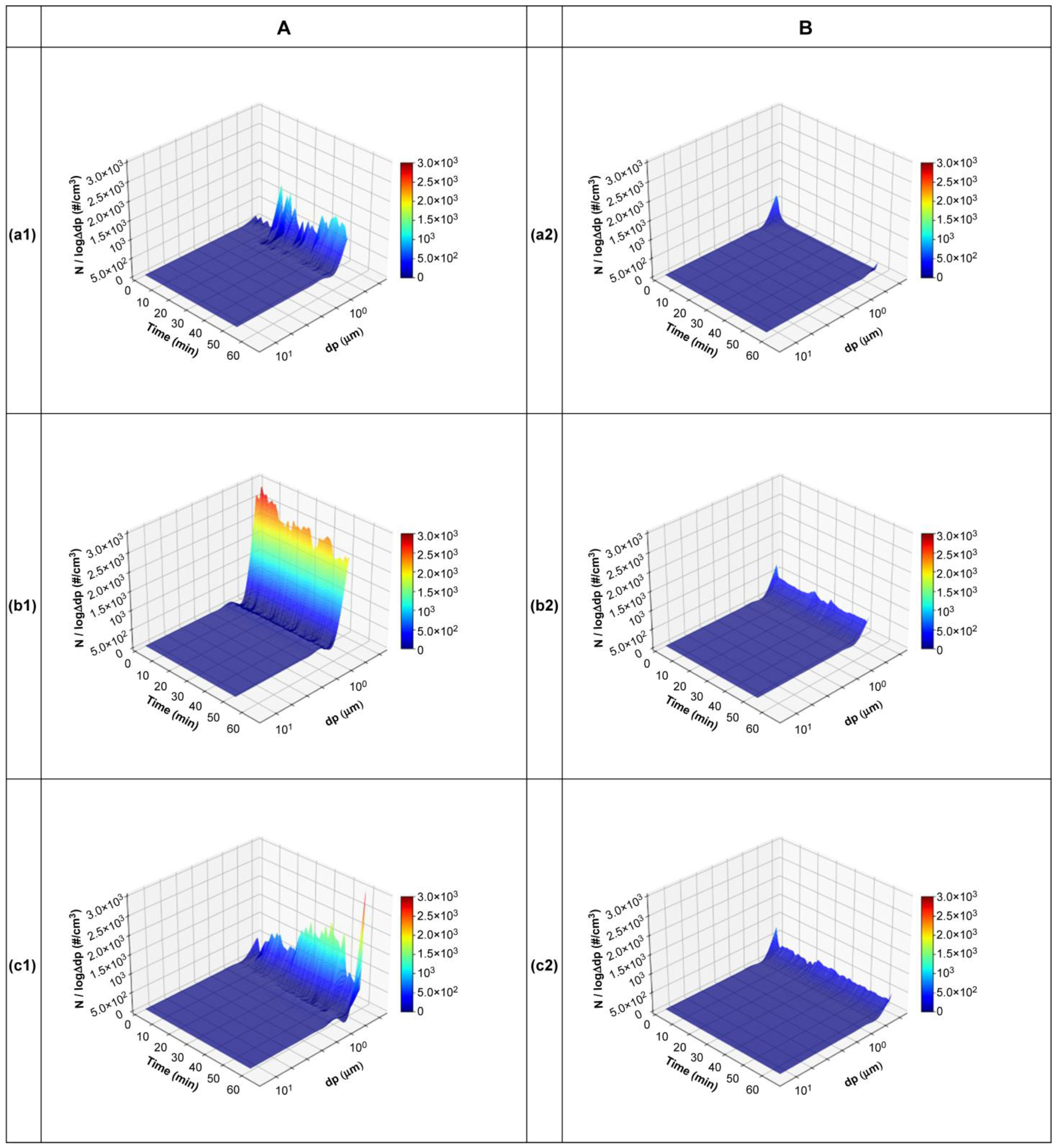
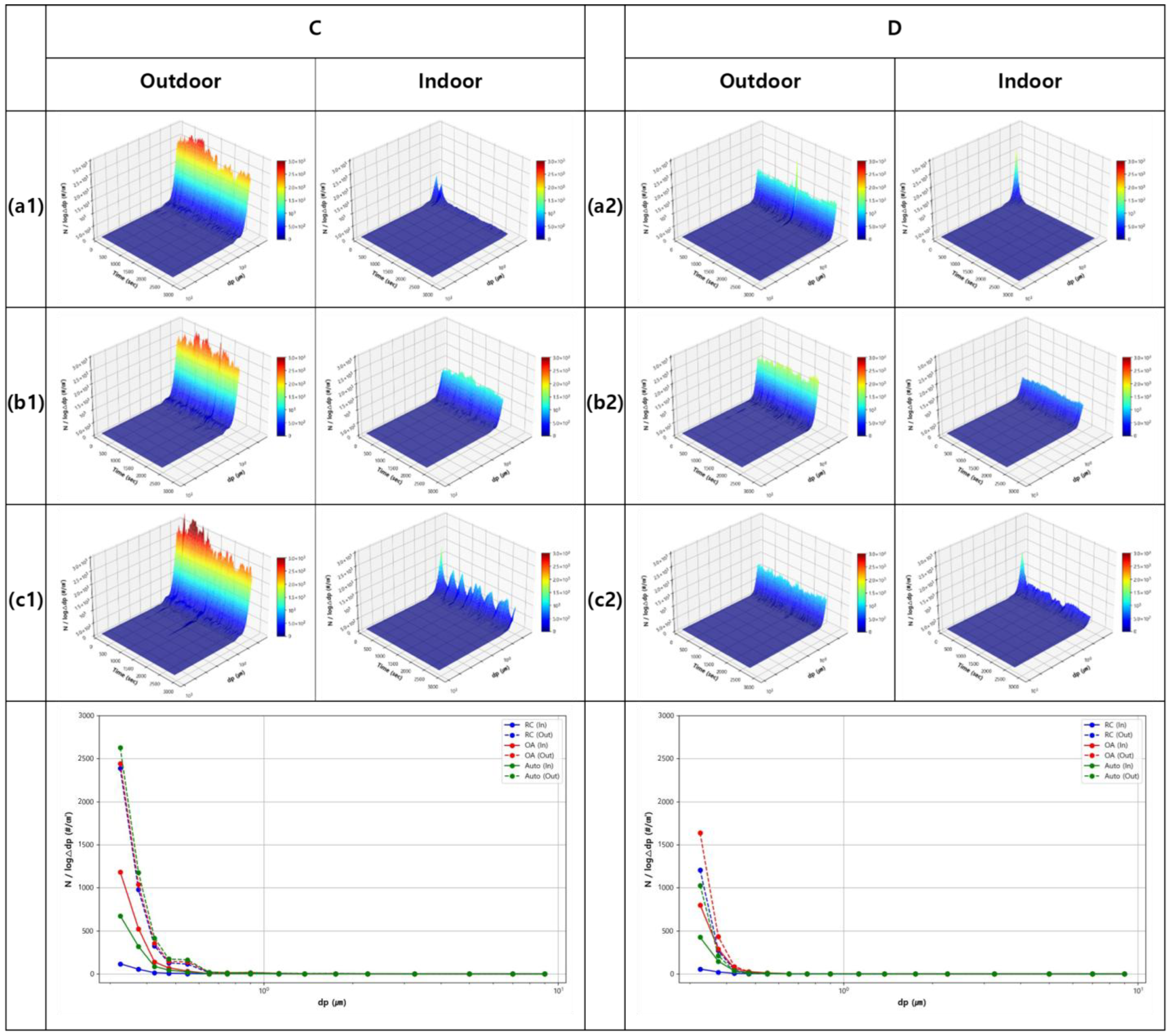
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Exploratory Test
3.2. Definitive Test
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| VIAQ | Vehicle indoor air quality |
| HVAC | Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning |
| IARC | International Agency for Research on Cancer |
| UNECE VIAQ IWG UN | European Economic Commission for Europe Vehicles Interior Air Quality Informal Working Group |
| VOC | Volatile organic compound |
| PN | Particulate number concentration |
| AER | Air exchange rate |
| OA | Outside air ventilation |
| RC | In-vehicle recirculation |
| Auto | Automatic mode |
| GSL | Gasoline |
| DSL | Diesel |
References
- KOSTAT (Statistics Korea). Report on the Time Use Survey Volume 1–2 Time Spent on Activities (6~17); KOSTAT: Daejeon, Republic of Korea, 2020; Available online: https://books.google.com/books?id=9B8OzgEACAAJ (accessed on 19 October 2023)ISBN 978-89-5801-454-6.
- Klepeis, N.; Nelson, W.; Ott, W.; Robinson, J.; Tsang, A.; Switzer, P.; Behar, J.; Hern, S.; Engelmann, W. The National Human Activity Pattern Survey (NHAPS): A resource for assessing exposure to environmental pollutants. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 2001, 11, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- U.S. Energy Information Administration (EIA). EIA Projects Global Conventional Vehicle Fleet will Peak in 2038. Today in Energy 2021. Available online: https://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.php?id=50096 (accessed on 12 October 2025).
- Weisel, C.P.; Lawryk, N.J.; Lioy, P.J. Exposure to emissions from gasoline within automobile cabins. J. Expo. Anal. Environ. Epidemiol. 1992, 2, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dor, F.; Moullec, Y.L.; Festy, B. Exposure of city residents to carbon monoxide and monocyclic aromatic hydrocarbons during commuting trips in the Paris metropolitan area. J. Air Waste Manage. Assoc. 1995, 45, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seaton, A.; Godden, D.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K. Particulate air pollution and acute health effects. Lancet 1995, 345, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flachsbart, P.G. Human exposure to carbon monoxide from mobile sources. Chemosphere Glob. Chang. Sci. 1999, 1, 301–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauer, M.; Hoek, G.; Van Vliet, P.; Meliefste, K.; Fischer, P.H.; Wijga, A.; Koopman, L.P.; Neijens, H.J.; Gerritsen, J.; Kerkhof, M.; et al. Air pollution from traffic and the development of respiratory infections and asthmatic and allergic symptoms in children. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 1092–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, A.; Von Klot, S.; Heier, M.; Trentinaglia, I.; Hörmann, A.; Wichmann, H.E.; Löwel, H. Cooperative Health Research in the Region of Augsburg Study Group. Exposure to traffic and the onset of myocardial infarction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pope III, C.A.; Burnett, R.T.; Thurston, G.D.; Thun, M.J.; Calle, E.E.; Krewski, D.; Godleski, J.J. Cardiovascular mortality and long-term exposure to particulate air pollution: Epidemiological evidence of general pathophysiological pathways of disease. Circulation 2004, 109, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donaldson, K.; Tran, L.; Jimenez, L.A.; Duffin, R.; Newby, D.E.; Mills, N.; MacNee, W.; Stone, V. Combustion-derived nanoparticles: A review of their toxicology following inhalation exposure. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2005, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, N.L.; Törnqvist, H.; Robinson, S.D.; Gonzalez, M.; Darnley, K.; MacNee, W.; Boon, N.A.; Donaldson, K.; Blomberg, A.; Sandstrom, T.; et al. Diesel exhaust inhalation causes vascular dysfunction and impaired endogenous fibrinolysis. Circulation 2005, 112, 3930–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldo, E.; Medina, S.; LeTertre, A.; Hurley, F.; Mücke, H.G.; Ballester, F.; Aguilera, I.; Eilstein, D.; Apheis Group. Apheis: Health impact assessment of long-term exposure to PM2.5 in 23 European cities. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 21, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pope, C.A.; Dockery, D.W. Health Effects of Fine Particulate Air Pollution: Lines that Connect. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2006, 56, 709–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Khazaei, M.; van Eeden, S.F.; Laher, I. The pharmacology of particulate matter air pollution-induced cardiovascular dysfunction. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 113, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Törnqvist, H.; Mills, N.L.; Gonzalez, M.; Miller, M.R.; Robinson, S.D.; Megson, I.L.; MacNee, W.; Donaldson, K.; Söderberg, S.; Newby, D.E.; et al. Persistent endothelial dysfunction in humans after diesel exhaust inhalation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, D.J.; Huang, H.L. Concentrations of volatile organic compounds, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and particulate matter in buses on highways in Taiwan. Atmos. Environ. 2009, 43, 5723–5730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panel on the Health Effects of Traffic-Related Air Pollution. Traffic-Related Air Pollution: A Critical Review of the Literature on Emissions, Exposure, and Health Effects; Health Effects Institute (HEI): Boston, MA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Knibbs, L.D.; Cole-Hunter, T.; Morawska, L.A. review of commuter exposure to ultrafine particles and its health effects. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 2611–2622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Colvile, R.N. Fine particulate matter and carbon monoxide exposure concentrations in urban street transport microenvironments. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 4781–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Fadel, M.; Abi-Esber, L. In-vehicle exposure to carbon monoxide emissions from vehicular exhaust: A critical review. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 39, 585–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Eiguren-Fernandez, A.; Hinds, W.C.; Miguel, A.H. In-Cabin Commuter Exposure to Ultrafine Particles on Los Angeles Freeways. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hinds, W.C.; Krudysz, M.; Kuhn, T.; Froines, J.; Sioutas, C. Penetration of freeway ultrafine particles into indoor environments. J. Aerosol Sci. 2005, 36, 303–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, O.; Tirendi, S.; Barrero-Moreno, J.; Kotzias, D. Investigation of volatile organic compounds and phthalates present in the cabin air of used private cars. Environ. Int. 2009, 35, 1188–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, H. Modeling CO2 Concentrations in Vehicle Cabin; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dons, E.; Int Panis, L.; Van Poppel, M.; Theunis, J.; Willems, H.; Torfs, R.; Wets, G. Impact of time–activity patterns on personal exposure to black carbon. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 3594–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruin, S.; Westerdahl, D.; Sax, T.; Sioutas, C.; Fine, P.M. Measurements and predictors of on-road ultrafine particle concentrations and associated pollutants in Los Angeles. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, H.S.; Nieuwenhuijsen, M.J.; Colvile, R.N.; McMullen, M.; Khandelwal, P. Fine particle (PM2.5) personal exposure levels in transport microenvironments, London, UK. Sci. Total Environ. 2001, 279, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, K.W.; Sarnat, J.A.; Koutrakis, P. Concentrations of PM2.5 mass and components in residential and non-residential indoor microenvironments: The Sources and Composition of Particulate Exposures study. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2012, 22, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molden, N.; Hemming, C.; Leach, F.; Levine, J.G.; Ropkins, K.; Bloss, W. Exposures to Particles and Volatile Organic Compounds across Multiple Transportation Modes. Sustainability 2023, 15, 4005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matthaios, V.N.; Di Marco, M.; Buonanno, G.; Kumar, P. Quantifying the performance of vehicle cabin air filters for exposure mitigation in real driving conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 160395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pöhler, D.; Riedner, S.; Brenner, R.; Gröschel, L.; Bigge, K.; Horbanski, M.; Platt, U. Personal exposure of NO2 for cyclist, car drivers and in indoor environments. In Proceedings of the EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts, Vienna, Austria, 8–13 April 2018; Volume 14529. [Google Scholar]
- Moldanova, J.; Parsmo, R.; Langer, S.; Salberg, H.; Jutterström, S.; Rydström, A. Improving Cabin Air Quality in Road Vehicles; IVL Swedish Environmental Research Institute: Stockholm, Sweden, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Matthaios, V.N.; Di Marco, M.; Järv, O.; Gulliver, J. In-vehicle exposure to traffic air pollution: Contribution of environmental, vehicle and driving factors. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 899, 165537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campagnolo, D.; Cattaneo, A.; Corbella, L.; Borghi, F.; Del Buono, L.; Rovelli, S.; Spinazzé, A.; Cavallo, D.M. In-vehicle airborne fine and ultra-fine particulate matter exposure: The impact of leading vehicle emissions. Environ. Int. 2019, 123, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russi, L.; Guidorzi, P.; Pulvirenti, B.; Aguiari, D.; Pau, G.; Semprini, G. Air Quality and Comfort Characterisation within an Electric Vehicle Cabin in Heating and Cooling Operations. Sensors 2022, 22, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- UN European Economic Commission for Europe Vehicles Interior Air Quality Informal Working Group. Available online: https://wiki.unece.org/pages/viewpage.action?pageId=25266269 (accessed on 7 March 2024).
- Grady, M.L.; Jung, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, J.K.; Lee, B.C. Vehicle Cabin Air Quality with Fractional Air Recirculation; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudda, N.; Kostenidou, E.; Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J.; Fruin, S.A. Vehicle and Driving Characteristics That Influence In-Cabin Particle Number Concentrations. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 8691–8697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruin, S.A.; Hudda, N.; Sioutas, C.; Delfino, R.J. Predictive Model for Vehicle Air Exchange Rates Based on a Large, Representative Sample. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 3569–3575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, L.Y.; Lau, W.L.; Zou, S.C.; Cao, Z.X.; Lai, S.C. Exposure level of carbon monoxide and respirable suspended particulate in public transportation modes while commuting in urban area of Guangzhou, China. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5831–5840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi Esber, L.; El-Fadel, M.; Nuwayhid, I.; Saliba, N. The effect of different ventilation modes on in-vehicle carbon monoxide exposure. Atmos. Environ. 2007, 41, 3644–3657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Stanley, N.; Pui, D.Y.H.; Kuehn, T.H. Laboratory and On-Road Evaluations of Cabin Air Filters Using Number and Surface Area Concentration Monitors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 4128–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Liu, S.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y. Effects of Vehicle Cabin Filter Efficiency on Ultrafine Particle Concentration Ratios Measured In-Cabin and On-Roadway. Aerosol Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knibbs, L.D.; de Dear, R.J.; Morawska, L. Effect of cabin ventilation rate on ultrafine particle exposure inside automobiles. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3546–3551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keita, N.S.; Mehel, A.; Murzyn, F.; Taniere, A.; Arcen, B.; Diourte, B. Numerical study of ultrafine particles dispersion in the wake of a cylinder. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2019, 10, 294–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathur, G. Experimental Investigation to Monitor Indoor Air Quality (IAQ) in Detroit Metropolitan Area; SAE Technical Paper; SAE: Warrendale, PA, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sommer, F.; Dietze, V.; Baum, A.; Sauer, J.; Gilge, S.; Maschowski, C.; Gieré, R. Tire Abrasion as a Major Source of Microplastics in the Environment. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2014–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abi-Esber, L.; El-Fadel, M. Indoor to outdoor air quality associations with self-pollution implications inside passenger car cabins. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 81, 450–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Liu, W.; Gao, H.O.; Li, J. Variations in exposure to in-vehicle particle mass and number concentrations in different road environments. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2019, 69, 988–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwon, O.Y.; An, Y.S. In-vehicle Pollution under Various Driving Conditions. In Proceeding of the 43rd Meeting of KOSAE, Mokpo, Republic of Korea, 26 October 2006; pp. 564–565. [Google Scholar]
- Frey, H.C.; Zhai, H.; Rouphail, N.M.; Colyar, J.D. Fuel Use and Emissions Comparisons for Alternative Routes, Time of Day, Road Grade, and Vehicles Based on In-Use Measurements. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 2483–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ning, Z.; Cheung, C.S.; Lu, Y.; Liu, M.A.; Hung, W.T. Experimental and numerical study of the dispersion of motor vehicle pollutants under idle condition. Atmos. Environ. 2005, 39, 7880–7893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alm, S.; Jantunen, M. Urban commuter exposure to particle matter and carbon monoxide inside an automobile. Atmos. Environ. 1999, 33, 923–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, L.; Molden, N.; Boyle, S.; Johnson, K.; Jung, H. Development of a standard testing method for vehicle cabin air quality index. SAE Int. J. Commer. Veh. 2019, 12, 151–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiss, O.; Barrero-Moreno, J.; Tirendi, S.; Kotzias, D. Exposure to Particulate Matter in Vehicle Cabins of Private Cars. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2010, 10, 581–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallace, L.A.; Wheeler, A.J.; Kearney, J.; Van Ryswyk, K.; You, H.; Kulka, R.H.; Rasmussen, P.E.; Brook, J.R.; Xu, X. Validation of continuous particle monitors for personal, indoor, and outdoor exposures. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Oh, J.; Choi, J.; Ahn, J.; Yoon, G.; Park, J. A study on the correction factor of optic scattering PM2.5 by gravimetric method. J. Kor. Soc. Urban Environ. 2014, 14, 41–47. [Google Scholar]
- Park, D.J.; Lee, K.Y.; Park, K.; Bae, M.S. Diurnal Size Distributions of Black Carbon by Comparison of Optical Particulate Measurements—Part I. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 32, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.J.; Park, S.S. Evaluation of PM10 and PM2.5 Concentrations from Online Light Scattering Dust Monitors Using Gravimetric and Beta-ray Absorption Methods. J. Korean Soc. Atmos. Environ. 2019, 35, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Jimenez, D.; Lakey, P.S.; Shiraiwa, M.; Jung, H. Behavior of carbon monoxide, nitrogen oxides, and ozone in a vehicle cabin with a passenger. Environ. Sci. Processes Impacts 2021, 23, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Standards | Pollutants |
|---|---|
| Comprehensive air-quality index (CAI) | PM10, PM2.5, O3, NO2, CO, SO2 |
| National ambient air quality standard | PM10, PM2.5, O3, NO2, CO, SO2, Pb, Benzene |
| Public buses’ indoor air quality standard | PM2.5, CO2 |
| Indoor parking lot air quality standard | PM10, CO, HCHO, NO2, Rn, TVOC |
| Standards in the tunnel | CO, NOx |
| Green NCAP Clean Air Index | HC, NO2, NO, NH3, CO, PM, PN |
| Test | Exploratory Test | Definitive Test | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vehicle | A | B | C | D |
| Body type | Sedan | SUV | SUV | SUV |
| Powertrain | GSL | DSL | GSL | DSL |
| Model year | 2022 | 2022 | 2022 | 2022 |
| Displacement (cc) | 1999 | 2151 | 2497 | 2151 |
| Curb Weight (kg) | 1415 | 1755 | 1750 | 1820 |
| Odometer Reading (km) | 1046 | 13,755 | 13,038 | 33,961 |
| HVAC | Vehicle A | Vehicle B | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | RC | 0.06 ± 0.30 | 0.69 ± 2.64 |
| OA | 0.63 ± 0.49 | 7.68 ± 1.45 | |
| Auto | 0.68 ± 1.30 | 5.82 ± 1.46 | |
| NO (ppb) | RC | 339.62 ± 277.59 | 472.41 ± 133.50 |
| OA | 675.00 ± 254.28 | 269.81 ± 156.38 | |
| Auto | 1493.33 ± 193.86 | 530.77 ± 93.41 | |
| NO2 (ppb) | RC | 292.45 ± 33.10 | 222.41 ± 46.05 |
| OA | 275.00 ± 51.92 | 220.75 ± 45.40 | |
| Auto | 220.00 ± 48.01 | 192.31 ± 36.69 |
| HVAC | Vehicle C | Vehicle D | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Indoor | Outdoor | Indoor | Outdoor | ||
| PM2.5 (µg/m3) | RC | 3.49 ± 2.68 | 54.83 ± 7.25 | 1.04 ± 5.04 | 38.97 ± 3.50 |
| OA | 23.42 ± 1.94 | 52.96 ± 5.56 | 12.76 ± 0.83 | 45.25 ± 3.33 | |
| Auto | 13.83 ± 5.03 | 58.28 ± 10.30 | 8.16 ± 5.12 | 36.58 ± 4.60 | |
| NO (ppb) | RC | 97.96 ± 27.41 | 141.23 ± 158.24 | 93.15 ± 49.07 | 76.04 ± 190.23 |
| OA | 85.12 ± 91.62 | 101.32 ± 170.84 | 27.34 ± 61.64 | 43.02 ± 111.33 | |
| Auto | 101.63 ± 64.22 | 155.2 ± 256.31 | 51.62 ± 71.01 | 69.84 ± 167.89 | |
| NO2 (ppb) | RC | 6.10 ± 5.74 | 59.04 ± 42.45 | 11.40 ± 5.90 | 17.42 ± 29.94 |
| OA | 46.71 ± 22.37 | 63.26 ± 45.20 | 11.91 ± 9.71 | 13.41 ± 28.12 | |
| Auto | 21.25 ± 9.61 | 58.07 ± 29.05 | 6.45 ± 6.70 | 17.70 ± 34.37 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, H.-H.; Park, I.-J.; Kim, C.-R.; Lee, H.-W.; Kim, H.-H. Vehicle Indoor Air Quality Due to External Pollutant Ingress While Driving. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111238
Yang H-H, Park I-J, Kim C-R, Lee H-W, Kim H-H. Vehicle Indoor Air Quality Due to External Pollutant Ingress While Driving. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(11):1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111238
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Ho-Hyeong, In-Ji Park, Cha-Ryung Kim, Hyun-Woo Lee, and Ho-Hyun Kim. 2025. "Vehicle Indoor Air Quality Due to External Pollutant Ingress While Driving" Atmosphere 16, no. 11: 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111238
APA StyleYang, H.-H., Park, I.-J., Kim, C.-R., Lee, H.-W., & Kim, H.-H. (2025). Vehicle Indoor Air Quality Due to External Pollutant Ingress While Driving. Atmosphere, 16(11), 1238. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16111238





