Characterization and Atmospheric Drivers of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement in Putian City, China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Data and Methods
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Sources of Observation Data
2.3. Criteria for NOE Events
2.4. WRF-CMAQ Model Configuration
2.5. Evaluation Indicators
3. Results and Discussion
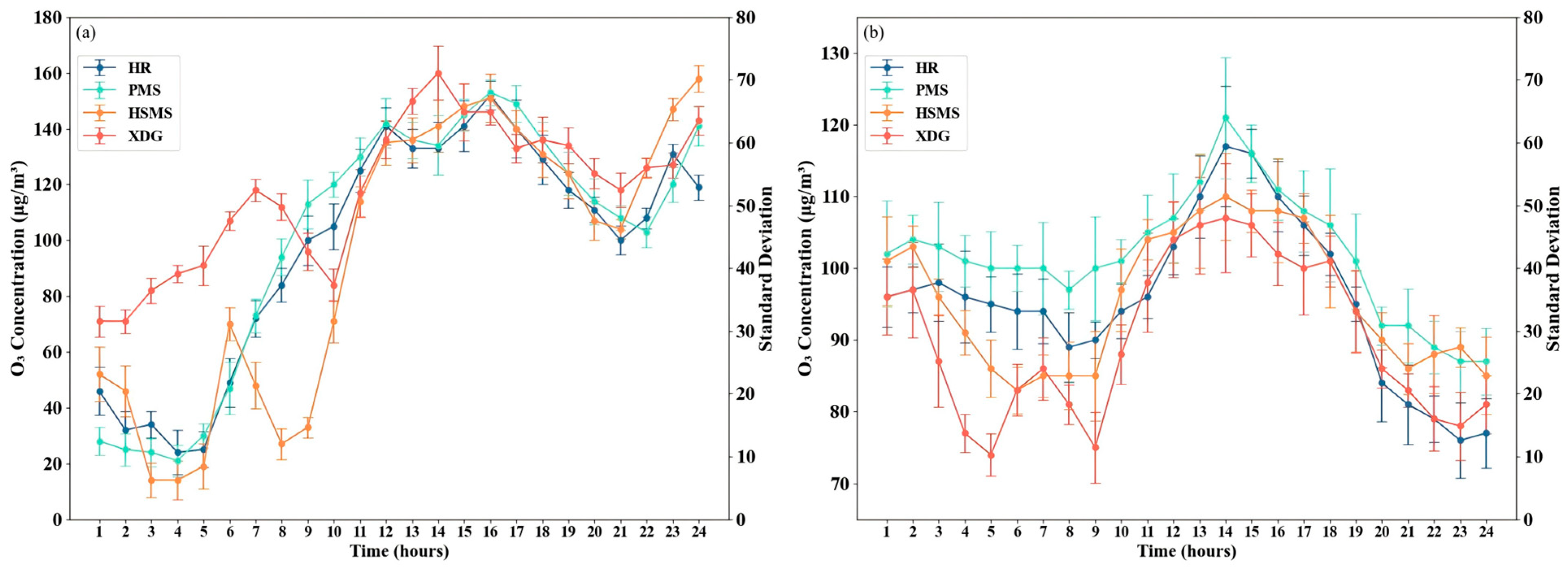
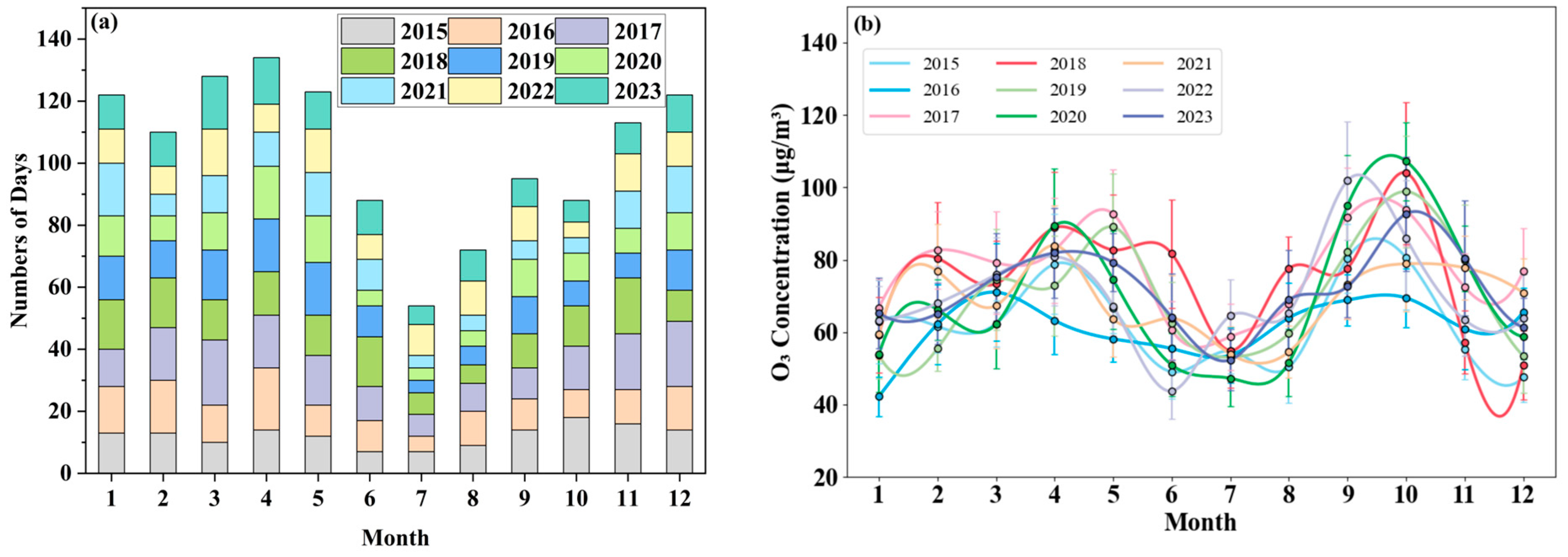
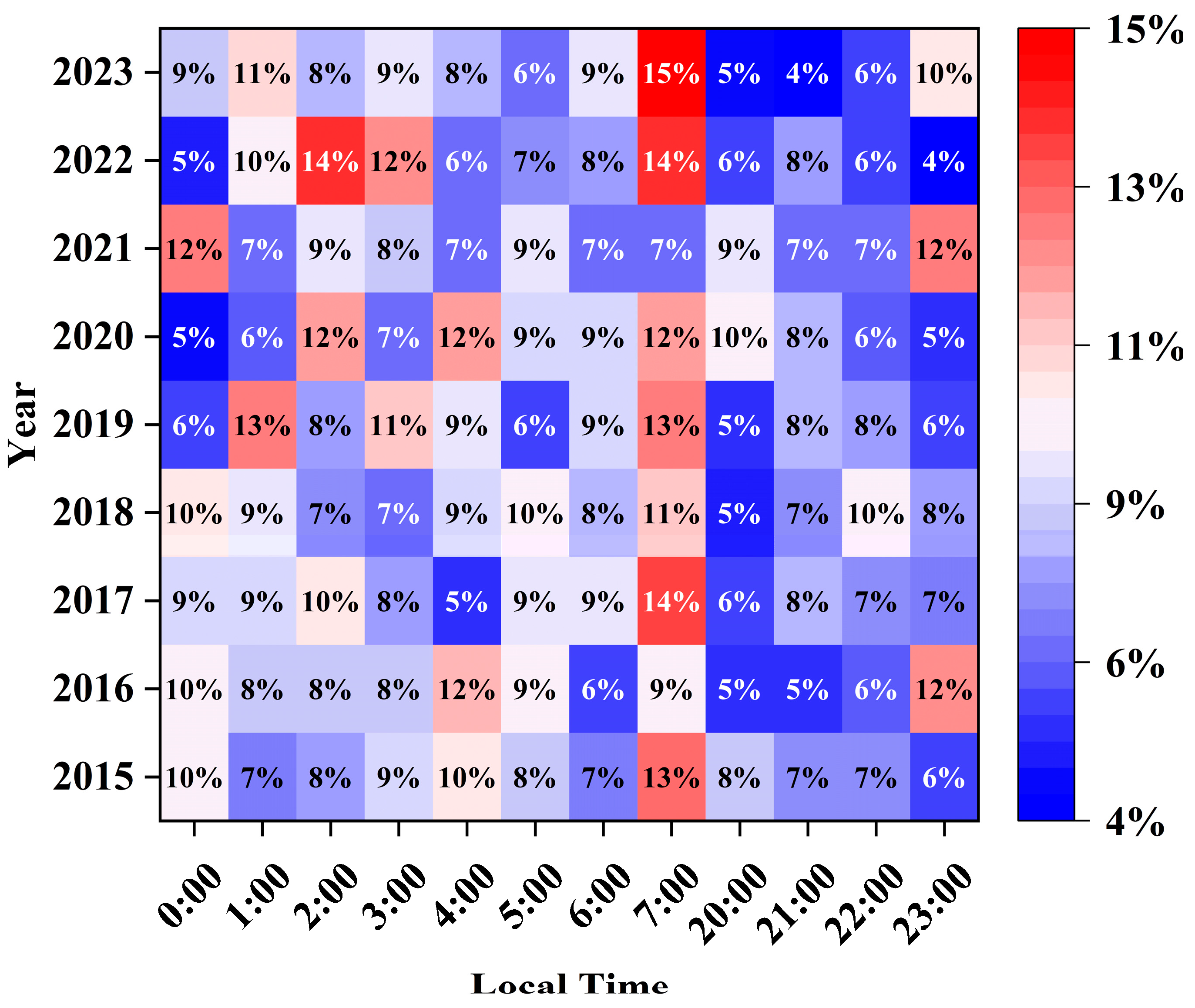
3.1. General Characteristics of the NOE
3.2. Model Analysis
3.2.1. WRF-CMAQ Simulation Validation Assessment
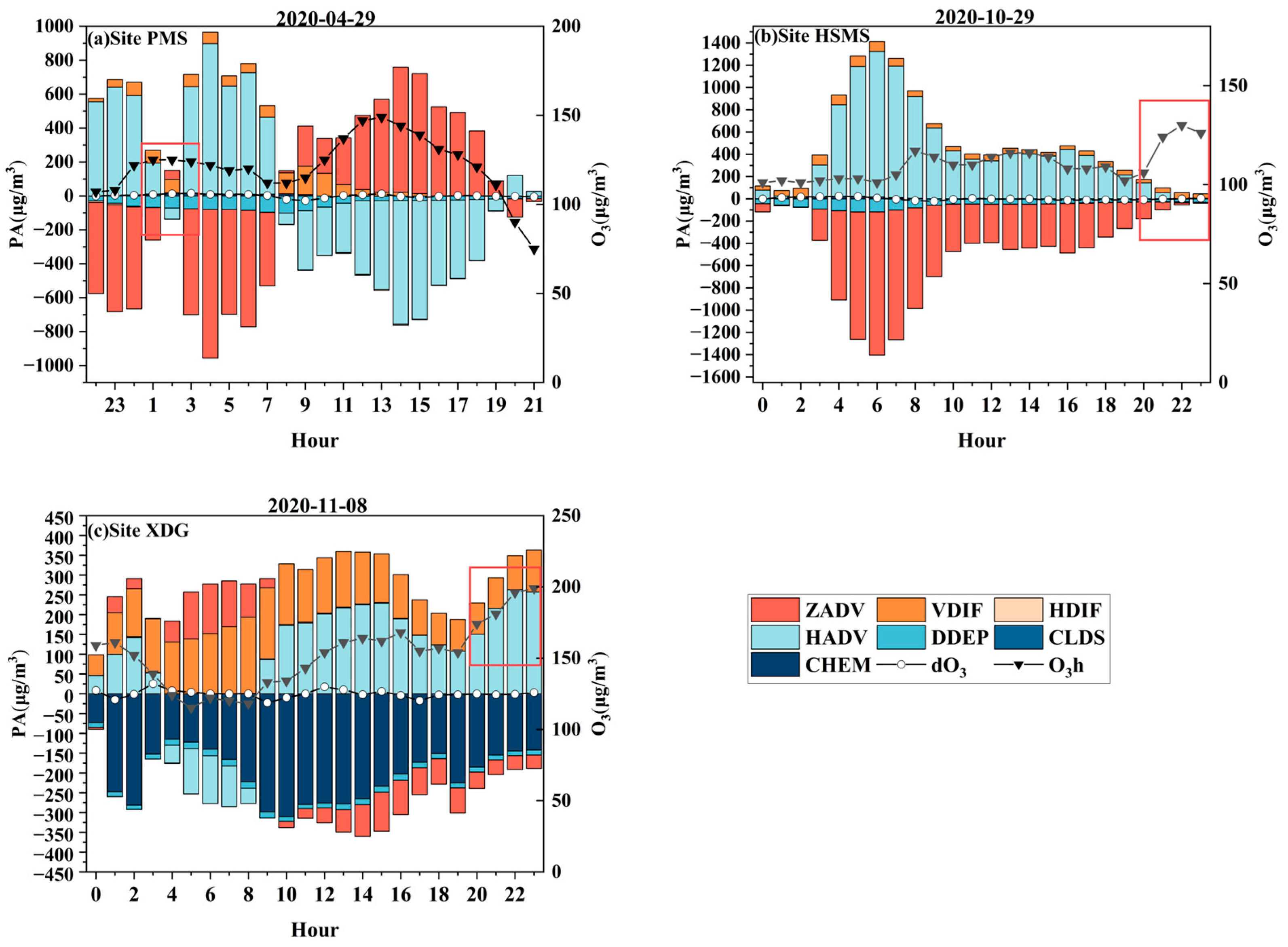
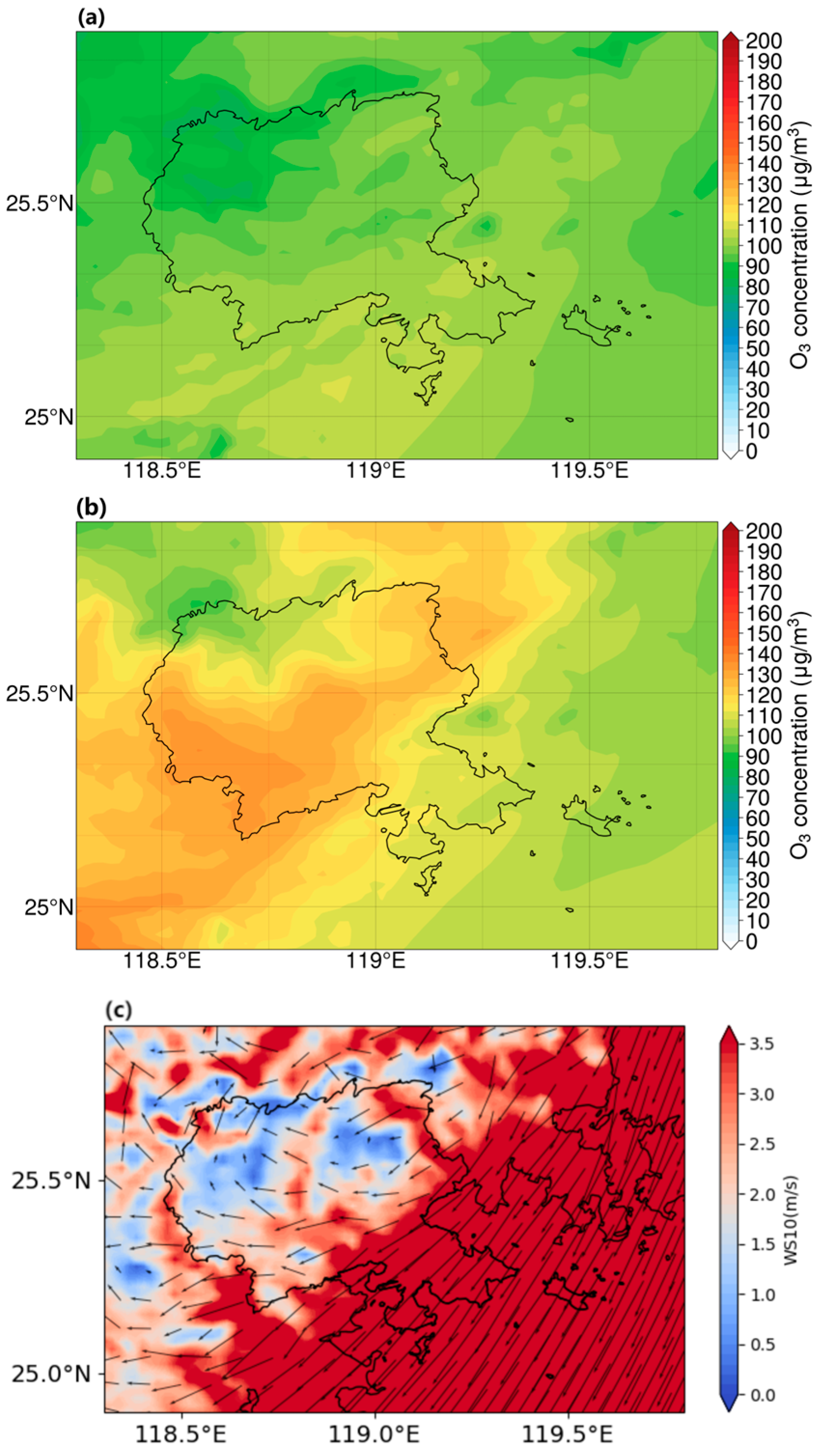
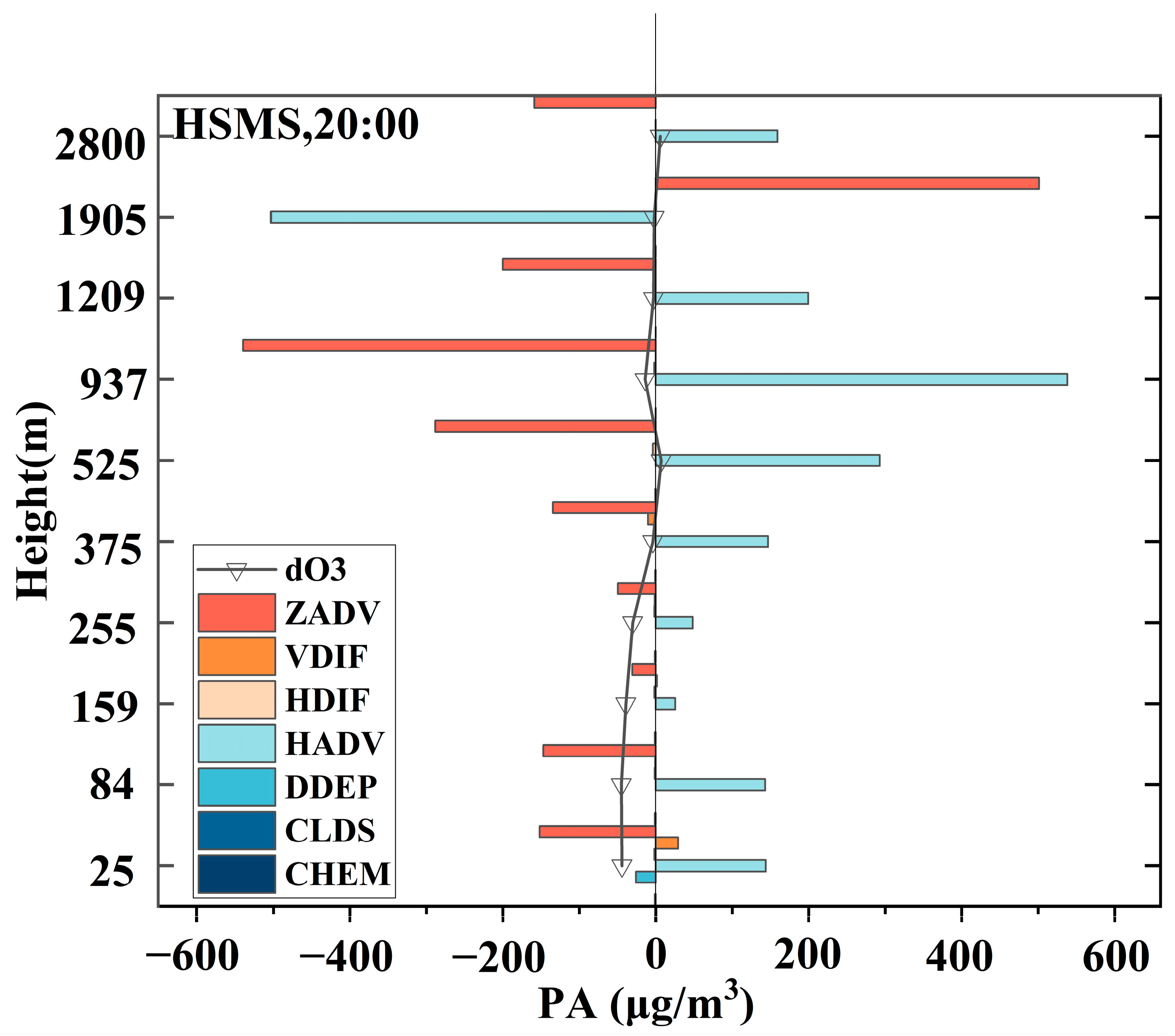
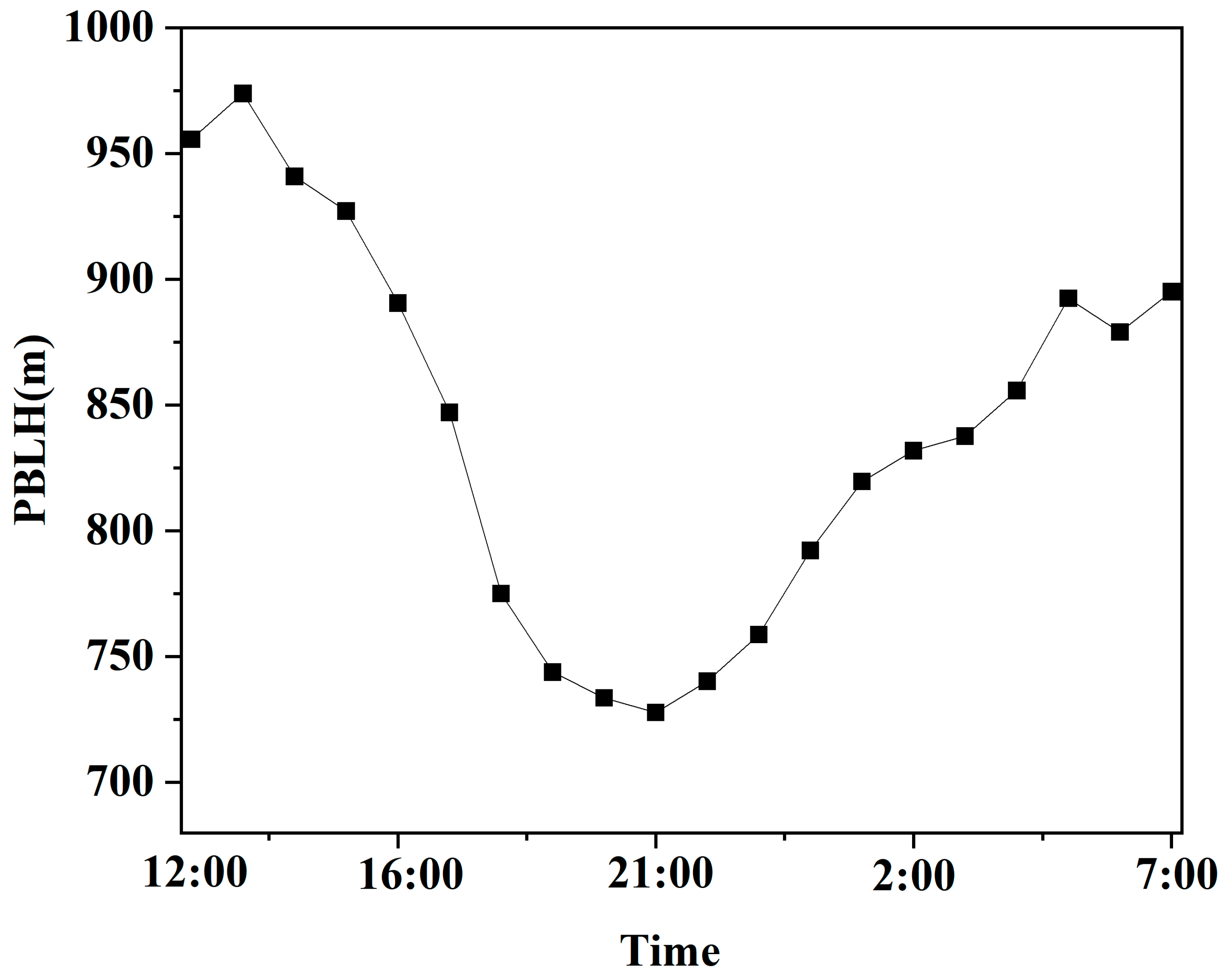
3.2.2. Mechanisms for a Typical NOE Event in Putian City
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Luo, Q.; Ren, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, B.; Yang, S.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Cheng, H. Atmospheric Mercury Pollution Caused by Fluorescent Lamp Manufacturing and the Associated Human Health Risk in a Large Industrial and Commercial City. Environ. Pollut. 2021, 269, 116146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xue, L.; Brimblecombe, P.; Lam, Y.F.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Ozone Pollution in China: A Review of Concentrations, Meteorological Influences, Chemical Precursors, and Effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 1582–1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefohn, A.S.; Malley, C.S.; Smith, L. Tropospheric Ozone Assessment Report: Global Ozone Metrics for Climate Change, Human Health, and Crop/Ecosystem Research. Elementa 2018, 6, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- GB 3095-2012; Ambient Air Quality Standards. China Environmental Science Press: Beijing, China, 2012.
- Bernier, C.; Wang, Y.; Estes, M. Clustering Surface Ozone Diurnal Cycles to Understand the Impact of Circulation Patterns in Houston. J. Geophys. Res. Atmos. 2019, 124, 13457–13474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Huang, X.; Wang, N.; Li, Y.; Ding, A. Understanding Ozone Pollution in the Yangtze River Delta of Eastern China from the Perspective of Diurnal Cycles. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 752, 141928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.-T.; Youn, D.; Liang, X.-Z.; Wuebbles, D.J. Global Model Simulation of Summertime U.S. Ozone Diurnal Cycle and Its Sensitivity to PBL Mixing, Spatial Resolution, and Emissions. Atmos. Environ. 2008, 42, 8470–8483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Bortoli, D.; Silva, A.M.; Reeves, C.E. Enhancements in Nocturnal Surface Ozone at Urban Sites in the UK.8. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2015, 22, 20295–20305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Bortoli, D.; Silva, A.M. Nocturnal Surface Ozone Enhancement and Trend over Urban and Suburban Sites in Portugal. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 71, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliasson, I.; Thorsson, S.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Summer Nocturnal Ozone Maxima in Göteborg, Sweden. Atmos. Environ. 2003, 37, 2615–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Sharma, R.; Nagaveena, S. Summer Time Variation and Unexpected Nocturnal Peak in Precursors Related Surface Ozone Concentration in Air over a Tropical Coastal Region of Southern Tamil Nadu, India. Polym. J. 2016, 2, 433–448. Available online: https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/SUMMER-TIME-VARIATION-AND-UNEXPECTED-NOCTURNAL-PEAK-Sharma-Nagaveena/ba0140ba5bfdaf864d4dbd0785a2573acbfd0769#citing-papers (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Mollinedo, E.M.; Krecl, P.; Targino, A.C.; Moreno, R.C.I. From Lowland Plains to the Altiplano: The Impacts of Regional Transport of Wildfire Smoke on the Air Quality of Bolivian Cities. Atmos. Environ. 2023, 315, 120137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lu, C.; Hu, Y.; Chan, P.-W.; Li, L.; Zhang, L. Effects of Horizontal Transport and Vertical Mixing on Nocturnal Ozone Pollution in the Pearl River Delta. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmond, J.A.; McKendry, I.G. Secondary Ozone Maxima in a Very Stable Nocturnal Boundary Layer: Observations from the Lower Fraser Valley, BC. Atmos. Environ. 2002, 36, 5771–5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Han, X.; Xu, L.; Guan, X.; Gong, A.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M. Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement in Shandong Province, China, in 2020–2022: Spatiotemporal Distribution and Formation Mechanisms. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 925, 171542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, S.I.V.; Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M.; Martins, F.G. Identification and Origin of Nocturnal Ozone Maxima at Urban and Rural Areas of Northern Portugal–Influence of Horizontal Transport. Atmos. Environ. 2011, 45, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, W.; You, Y.; Xie, Q.; Jia, S.; Wang, X. Quantitative Impacts of Vertical Transport on the Long-Term Trend of Nocturnal Ozone Increase over the Pearl River Delta Region during 2006–2019. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2023, 23, 453–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.-M.; Klein, P.M.; Xue, M.; Zhang, F.; Doughty, D.C.; Forkel, R.; Joseph, E.; Fuentes, J.D. Impact of the Vertical Mixing Induced by Low-Level Jets on Boundary Layer Ozone Concentration. Atmos. Environ. 2013, 70, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Wu, J.; Guo, H.; Yin, X.; Ma, X.; Qiao, L. Impacts of Meteorological Conditions on Nocturnal Surface Ozone Enhancement during the Summertime in Beijing. Atmos. Environ. 2020, 225, 117368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim-Ferraz, M.C.M.; Mesquita, M.C.; Ferreira, M.I.; Sousa, S.I.V. Influence of land-sea breezes on nocturnal ozone maxima observed in urban areas. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2010, 6, 293–308. [Google Scholar]
- He, Y.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Xu, X.; Li, Y.; Fan, S. Meteorology and Topographic Influences on Nocturnal Ozone Increase during the Summertime over Shaoguan, China. Atmos. Environ. 2021, 256, 118459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Gu, T.; Wang, C.; Wu, D.; Deng, X.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y. Influence of typhoon Nida process on ozone concentration in Guangzhou. Acta Sci. Circumstantiae 2018, 38, 4565–4572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, C.; Yan, Y.; Gao, X.; Yan, X.; Ji, Y.; Shang, F.; Li, J.; Tan, L.; Gao, R.; Bi, F.; et al. A Comparative Investigation of the Characteristics of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement Events and Their Effects on Ground-Level Ozone and PM2.5 in the Central City of the Yellow River Delta, China, in 2022 and 2023. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, D.; Lal, S.; Sarkar, U. High Nocturnal Ozone Levels at a Surface Site in Kolkata, India: Trade-off between Meteorology and Specific Nocturnal Chemistry. Urban Clim. 2013, 5, 82–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, P.S.; Dasari, H.P.; Sharma, A.; Bortoli, D.; Salgado, R.; Silva, A.M. Nocturnal Surface Ozone Enhancement over Portugal during Winter: Influence of Different Atmospheric Conditions. Atmos. Environ. 2016, 147, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.-P.; Chen, K.-S.; Lou, J.-C.; Hwang, S.-W.; Wang, W.-C.; Lai, C.-H.; Tsai, M.-Y. Measurements and Mesoscale Modeling of Autumnal Vertical Ozone Profiles in Southern Taiwan. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2008, 19, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, C.; Lu, X.; Wang, H.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; He, G.; He, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; et al. The Unexpected High Frequency of Nocturnal Surface Ozone Enhancement Events over China: Characteristics and Mechanisms. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2022, 22, 15243–15261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Q.P.; Wen, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.Y. Effects of the Enso cycle on the variation of near-surface ozone concentration in Fujian Province. J. Trop. Meteorol. 2021, 37, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Sunwoo, Y. Environmental Benefits of Ammonia Reduction in an Agriculture-Dominated Area in South Korea. Atmosphere 2022, 13, 384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jung, J.; Choi, Y.; Mousavinezhad, S.; Pouyaei, A. The Sensitivities of Ozone and PM2.5 Concentrations to the Satellite-Derived Leaf Area Index over East Asia and Its Neighboring Seas in the WRF-CMAQ Modeling System. Environ. Pollut. 2022, 306, 119419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dou, X.; Yu, S.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Song, Z.; Yao, N.; Li, P. The WRF-CMAQ Simulation of a Complex Pollution Episode with High-Level O3 and PM2.5 over the North China Plain: Pollution Characteristics and Causes. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, T.; Yu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Z.; Song, Z.; Li, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Impacts of Chemical Initial Conditions in the WRF-CMAQ Model on the Ozone Forecasts in Eastern China. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2022, 22, 210402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Jiang, F.; Feng, S.; Xia, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Lyu, X.; Zhang, L.; Lou, C. Increased Diurnal Difference of NO2 Concentrations and Its Impact on Recent Ozone Pollution in Eastern China in Summer. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Guo, H.; Jiang, F.; Ling, Z.H.; Wang, T. Simulation of Ozone Formation at Different Elevations in Mountainous Area of Hong Kong Using WRF-CMAQ Model. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 505, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, C.; Wu, K.; Liu, K.; Wang, H.; Dan, M.; Ji, X.; Tong, Q. ISAT v2.0: An Integrated Tool for Nested-Domain Configurations and Model-Ready Emission Inventories for WRF-AQM. Geosci. Model Dev. 2023, 16, 1961–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- André Ronald, V.A. Methane: Its Role in Climate Change and Options for Control. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen University, Wageningen, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, B.; Tong, D.; Li, M.; Liu, F.; Hong, C.; Geng, G.; Li, H.; Li, X.; Peng, L.; Qi, J.; et al. Trends in China’s Anthropogenic Emissions since 2010 as the Consequence of Clean Air Actions. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2018, 18, 14095–14111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qiu, J.; Liu, Y.; Fan, Q.; Lu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, K.; Shen, A.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Y.; et al. MEIAT-CMAQ: A Modular Emission Inventory Allocation Tool for Community Multiscale Air Quality Model. Atmos. Environ. 2024, 331, 120604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emery, C.; Liu, Z.; Russell, A.G.; Odman, M.T.; Yarwood, G.; Kumar, N. Recommendations on Statistics and Benchmarks to Assess Photochemical Model Performance. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2017, 67, 582–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, H.; Baker, K.R.; Phillips, S. Compilation and Interpretation of Photochemical Model Performance Statistics Published between 2006 and 2012. Atmos. Environ. 2012, 61, 124–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boylan, J.W.; Russell, A.G. PM and Light Extinction Model Performance Metrics, Goals, and Criteria for Three-Dimensional Air Quality Models. Atmos. Environ. 2006, 40, 4946–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Huo, G.W.; Liu, C.X. Characterization of nocturnal ozone increase events during the warm season in Guangzhou and analysis of a single case of horizontal transport. J. Membr. Sci. 2023, 43, 76–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Ozone Pollution Characteristics and Typical Pollution Processes in Putian City. Straits Sci. 2019, 6, 24–29. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Chen, J.; Ying, Q.; Zhang, H. One-Year Simulation of Ozone and Particulate Matter in China Using WRF/CMAQ Modeling System. Atmos. Chem. Phys. 2016, 16, 10333–10350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, X.; Hong, S.; Jaffe, D.A. Ozone in China: Spatial Distribution and Leading Meteorological Factors Controlling O3 in 16 Chinese Cities. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2018, 18, 2287–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Number | Name | Abbr. | Longitude (°E) | Latitude (°N) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Houcang Road | HR | 119.0141 | 25.4325 |
| 2 | Putian Monitoring Station | PMS | 119.0015 | 25.4553 |
| 3 | Hanjiang Sixth Middle School | HSMS | 119.1119 | 25.4661 |
| 4 | Xiuyu District Government | XDG | 119.1013 | 25.3215 |
| 5 | Putian | PT | 119.1164 | 25.2782 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fang, C.; Zhou, X.; Cai, Y.; Wang, J. Characterization and Atmospheric Drivers of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement in Putian City, China. Atmosphere 2025, 16, 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010045
Fang C, Zhou X, Cai Y, Wang J. Characterization and Atmospheric Drivers of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement in Putian City, China. Atmosphere. 2025; 16(1):45. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010045
Chicago/Turabian StyleFang, Chunsheng, Xiaowei Zhou, Yuxuan Cai, and Ju Wang. 2025. "Characterization and Atmospheric Drivers of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement in Putian City, China" Atmosphere 16, no. 1: 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010045
APA StyleFang, C., Zhou, X., Cai, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). Characterization and Atmospheric Drivers of Nocturnal Ozone Enhancement in Putian City, China. Atmosphere, 16(1), 45. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos16010045






