Spatiotemporal Trends and Variations in Rainfall Erosivity in the East Qinling Mountains and the Environmental Impacts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
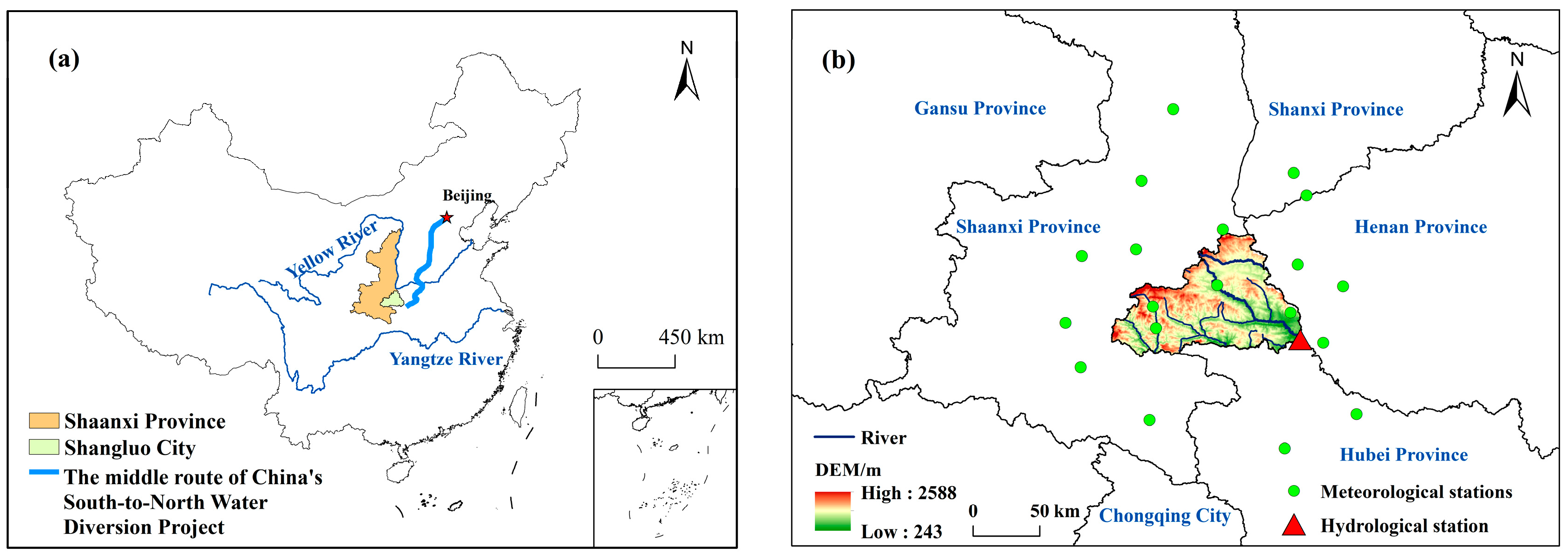
2.1. Study Site
2.2. Data Sources and Processing
2.3. Methods
2.3.1. Calculation of Rainfall Erosivity
2.3.2. Linear Regression Analysis Method
2.3.3. Cumulative Anomaly Method
2.3.4. Double Cumulative Curve Method
2.3.5. Spatial Interpolation Method
3. Results
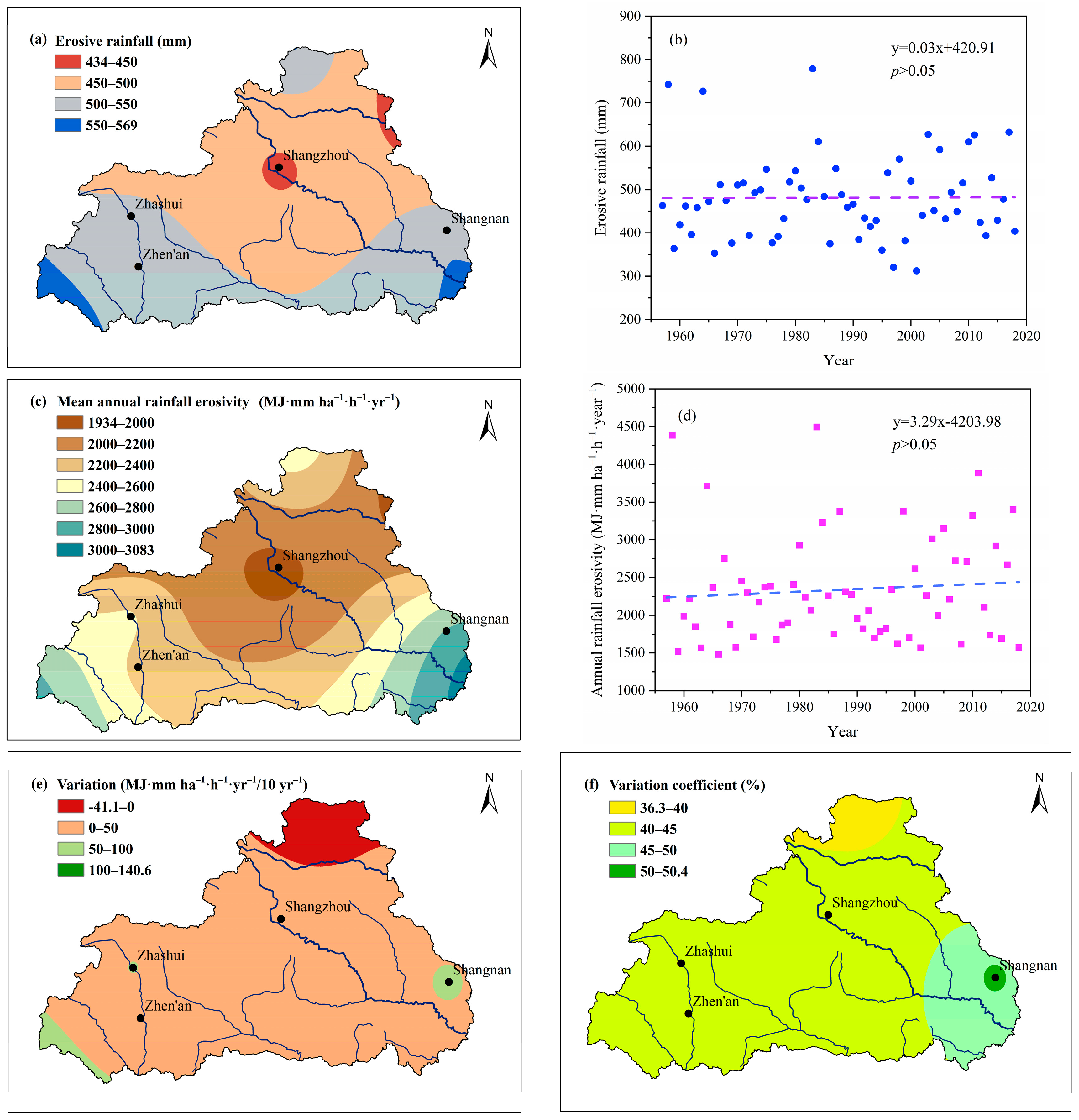
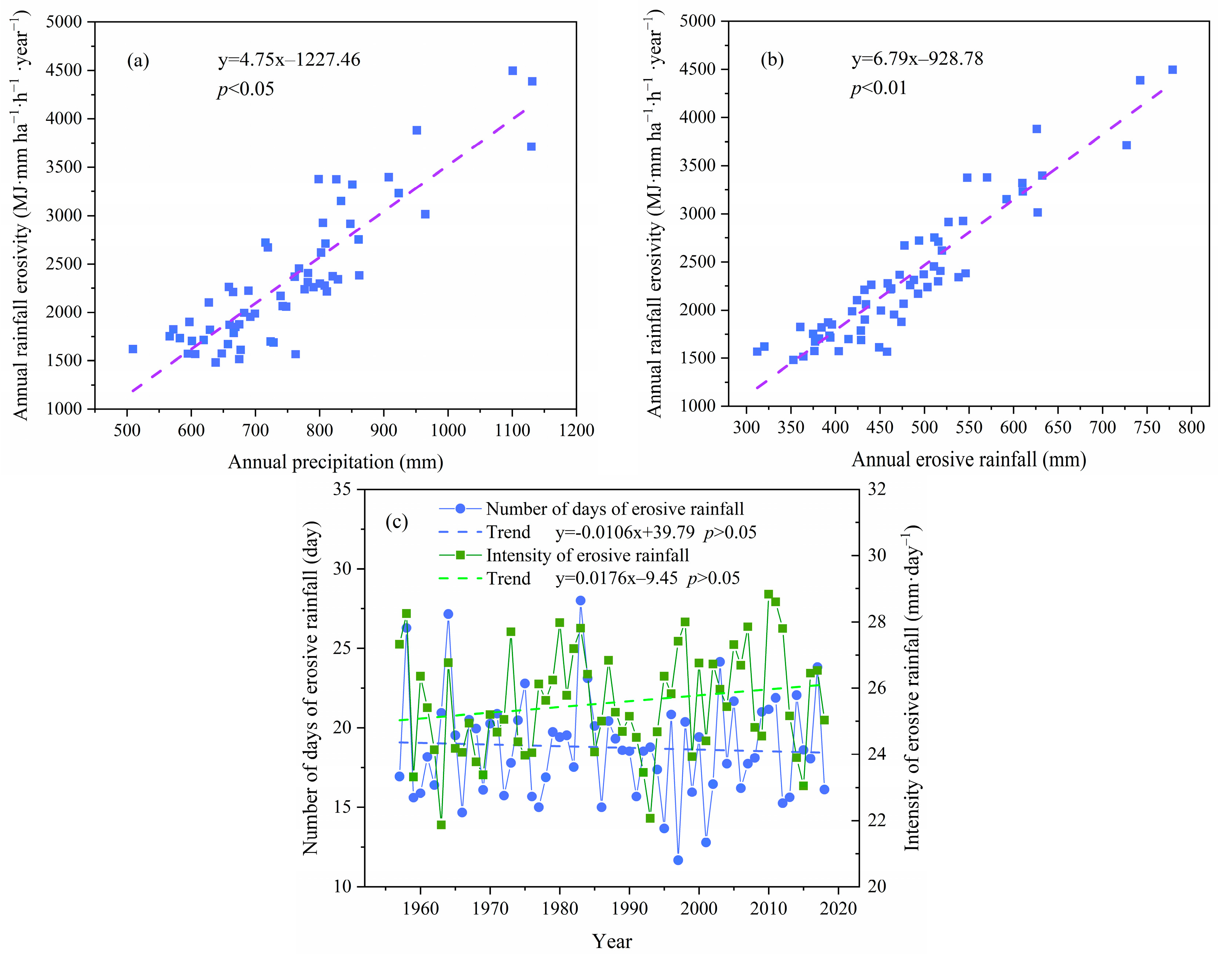
3.1. Interannual Variations in Rainfall Erosivity
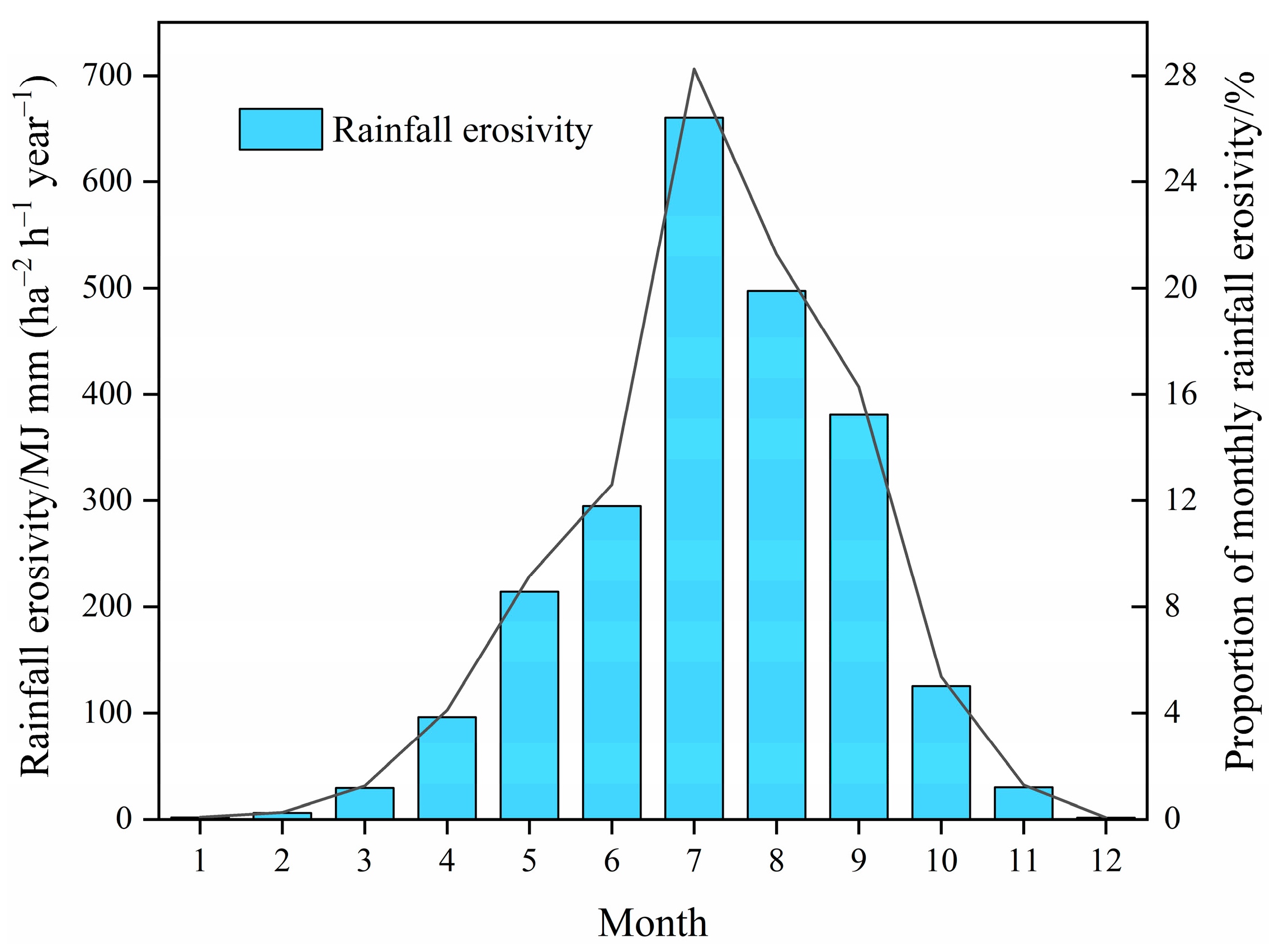
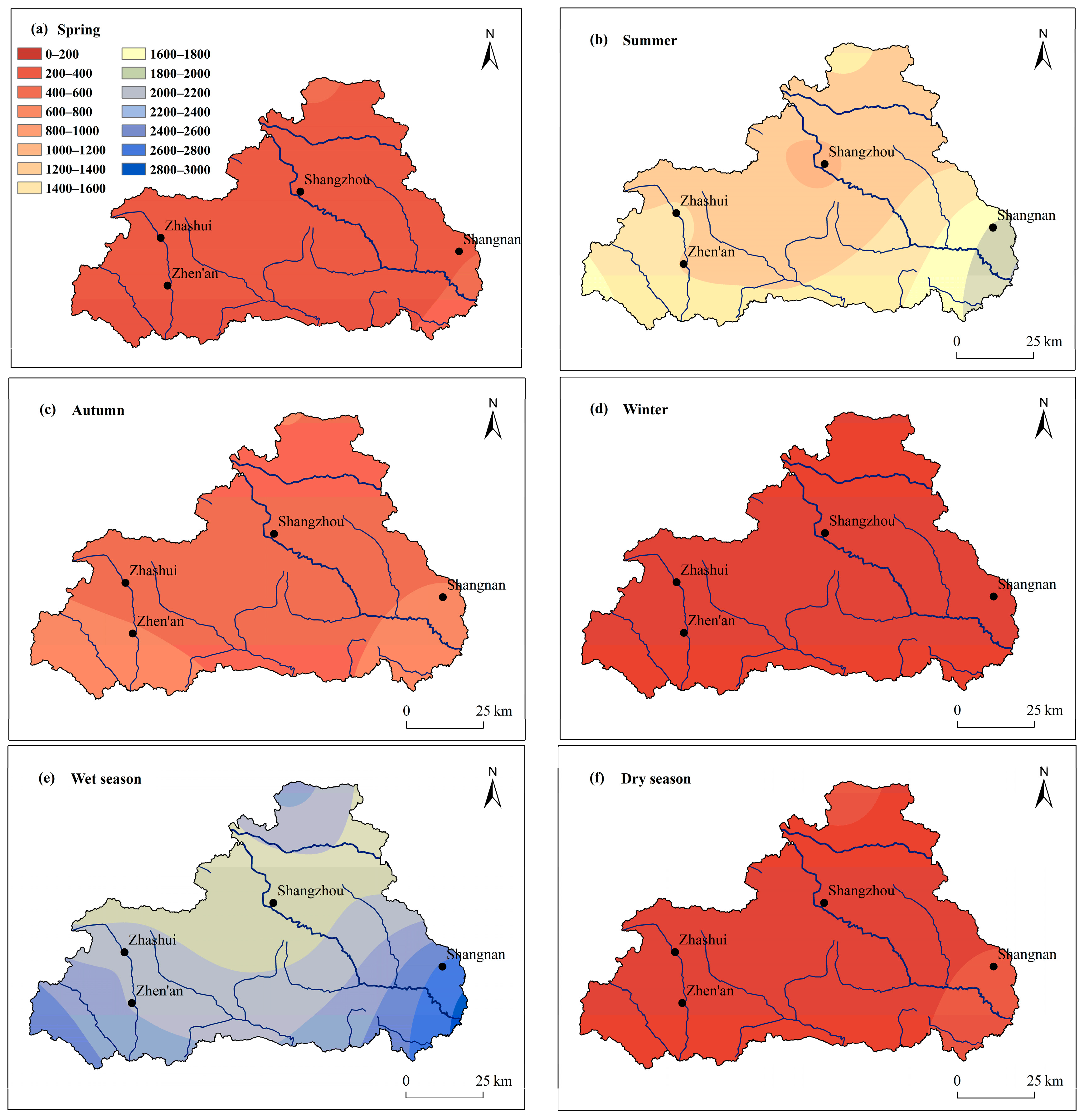
3.2. Seasonal Variations in Rainfall Erosivity
3.3. Relationship between Rainfall Erosivity and Climate Change
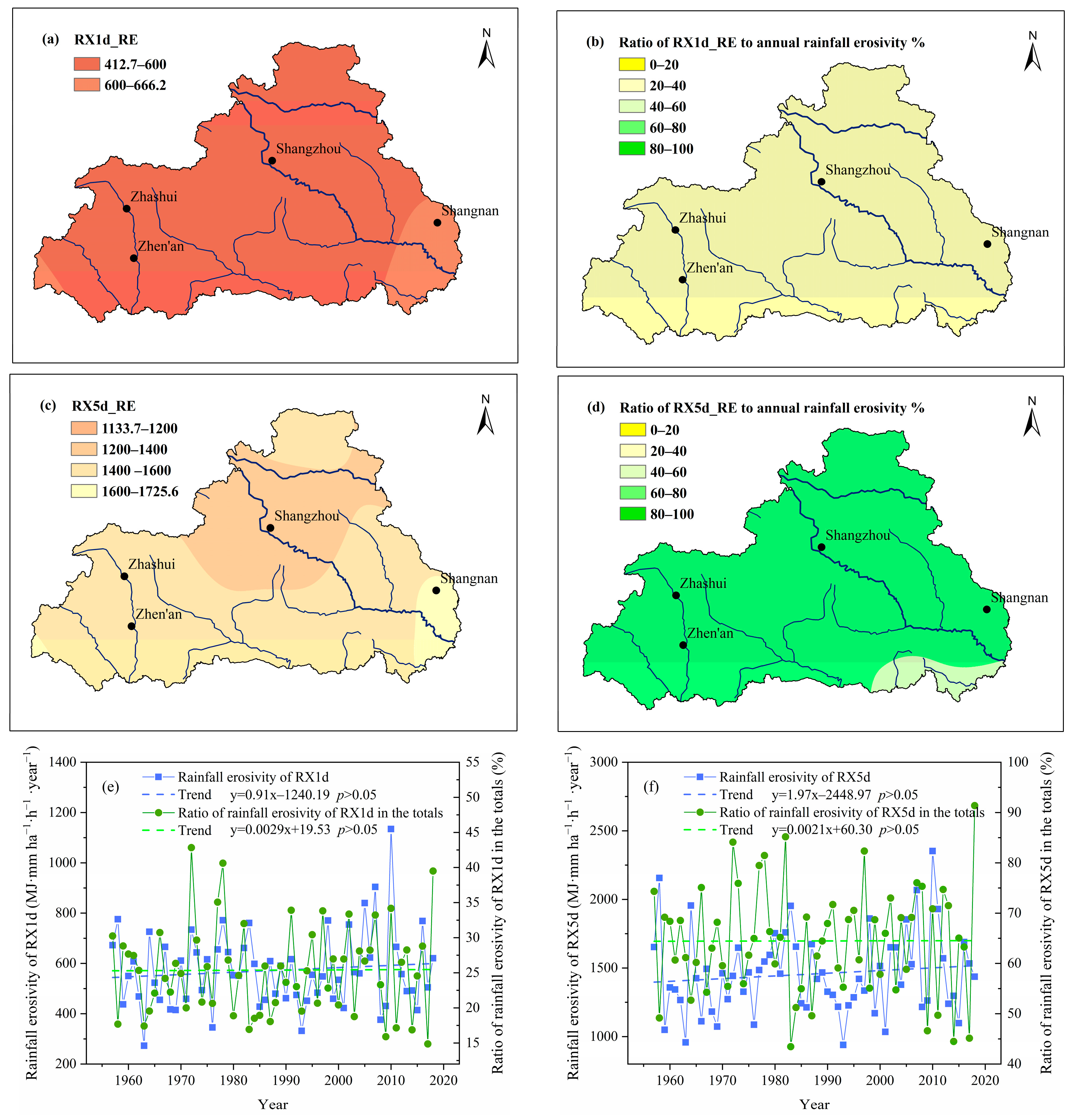
3.4. Variations in Rainfall Erosivity during Extreme Rainfall Events
3.5. Effects of Rainfall Erosivity on Agricultural Management
4. Discussion
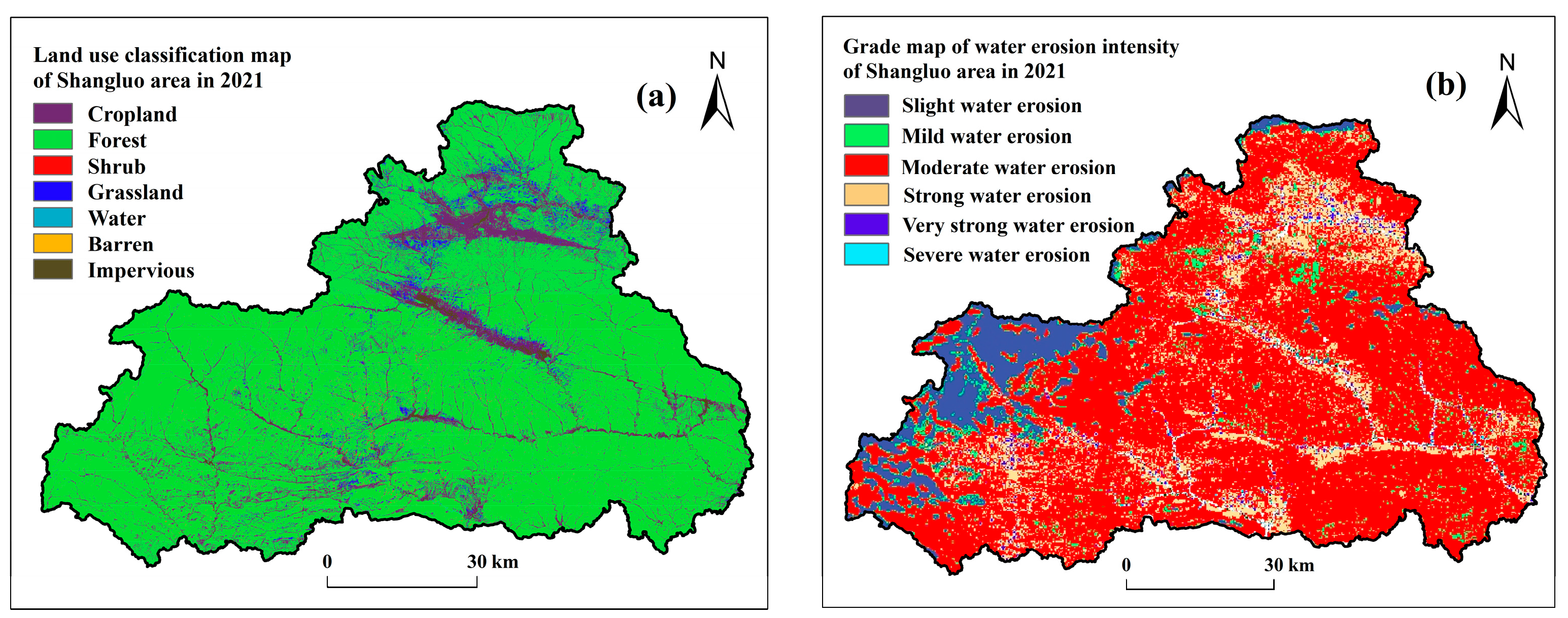
4.1. Effects of Rainfall Erosivity on Soil Erosion
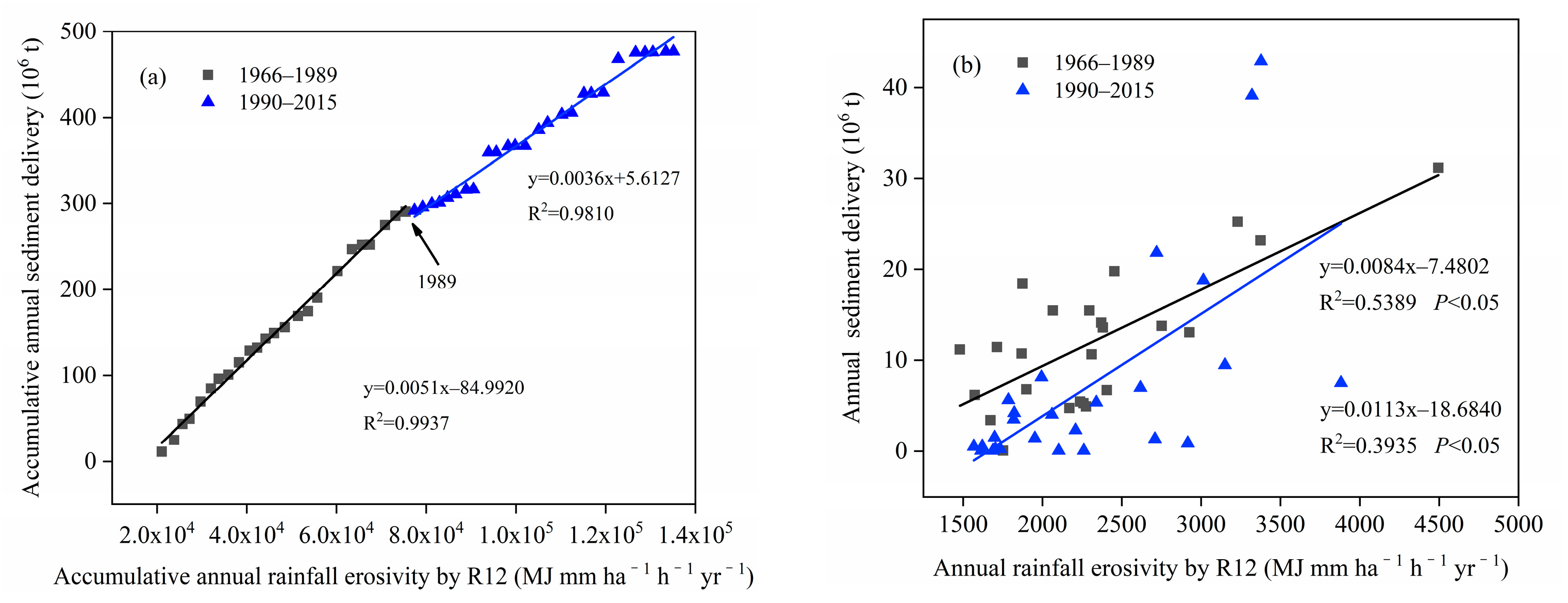
4.2. Responses of River Runoff and Sediment Delivery Due to Rainfall Trends and Human Activities
4.3. Adaptation of Agricultural Activities to Climate Change
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hornbeck, J.W.; Adams, M.B.; Corbett, E.S.; Verry, E.S.; Lynch, J.A. Long-term impacts of forest treatments on water yield: A summary for northeastern USA. J. Hydrol. 1993, 150, 323–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, I.M.; Soden, B.J. Robust responses of the hydrological cycle to global warming. J. Clim. 2006, 19, 5686–5699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, Z.B.; Yu, X.X.; Li, Q.Y.; Lu, X.X. Spatiotemporal variation in rainfall erosivity on the Chinese Loess Plateau during the period 1956–2008. Reg. Environ. Change 2011, 11, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallebona, C.; Pellegrino, E.; Frumento, P.; Bonari, E. Temporal trends in extreme rainfall intensity and erosivity in the Mediterranean region: A case study in southern Tuscany, Italy. Clim. Chang. 2015, 128, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Cui, L.L.; Wang, J.B.; Du, H.Q.; Wen, K.M. Changes in the temperature and precipitation extremes in China during 1961–2015. Quat. Int. 2019, 527, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.D.; Yang, D.; Tanoli, J.I. Variations in extreme precipitation and relation to the Asia summer monsoon over the Qinling-Dabashan Mountains, China. Terr. Atmos. Ocean. Sci. 2022, 32, 1271–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.F.; Lin, Y.H.; Zhao, H.F.; He, H.M. Soil erosion processes and geographical differentiation in Shaanxi during 1980–2015. Sustainability 2022, 14, 10512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Huang, T. Spatiotemporal trends and variation of precipitation over China’s Loess Plateau across 1957–2018. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.H.; Wang, Z.L. A study on rainstorm causing soil erosion in the Loess Plateau. J. Soil Water Conserv. 1992, 6, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, G.J.; Mu, X.M.; Wen, Z.M.; Wang, F.; Gao, P. Soil erosion, conservation, and eco-environment changes in the Loess Plateau of China. Land Degrad. Dev. 2013, 24, 499–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, K.H.; Merwade, V. The effect of land cover change on duration and severity of high and low flows. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 133–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Song, H.M.; An, Z.S.; Sun, C.F.; Trouetf, V.; Cai, Q.F.; Liu, R.S.; Leavittf, S.W.; Song, Y.; Li, Q.; et al. Recent anthropogenic curtailing of Yellow River runoff and sediment load is unprecedented over the past 500 y. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 18251–18257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.H.; Ke, L.H.; Wang, J.D.; Tamlin, M.P.; George, H.A.; Yong, W.S.; Duan, X.J.; Zhu, Y.Q.; Wu, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Satellites reveal hotspots of global river extent change. Nat. Clim. Change 2023, 14, 1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Chen, L.D.; Fu, B.J.; Huang, Z.; Wu, D.P.; Gui, L.D. The effect of land uses and rainfall regimes on runoff and soil erosion in the semi-arid loess hilly area, China. J. Hydrol. 2007, 335, 247–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podlasly, C.; Ren, Y.; Zhang, L.L.; Feger, K.H.; Wang, Y.H.; Kai, S. Separating the effects of changes in land management and climatic conditions on long-term streamflow trends analyzed for a small catchment in the Loess Plateau region, NW China. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 1284–1293. [Google Scholar]
- Wischmeier, W.H.; Smith, D.D. Predicting rainfall erosion losses: A guide to conservation planning. In Agriculture Handbook 537; US Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service: Washington, DC, USA, 1978. [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, C.W.; Foster, G.R.; Wright, D.A. Estimation of erosion index from daily rainfall amount. Trans. ASAE 1983, 26, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yin, S.Q.; Liu, B.Y.; Nearing, M.A.; Zhao, Y. Models for estimating daily rainfall erosivity in China. J. Hydrol. 2016, 535, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCool, D.K.; Foster, G.R.; Yoder, D.C.; Weesies, G.A.; McGregor, K.C.; Bingner, R.L. The revised universal soil loss equation, Version 2. In Proceedings of the International Soil Conservation Organization Conference Proceedings, Brisbane, Australia, 4–8 July 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, L.; Yu, K.; Li, Z.; Li, P.; Xu, G.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Z. The changing pattern of rainfall erosivity and its impact on sediment load in the Loess Plateau, China: A case study of a typical watershed. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2022, 77, 528–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.J.; Zhang, X.P.; He, L.; He, J.; Tian, Q.L.; Zou, Y.D.; An, Z.F. Detecting the impact of the ‘Grain for Green’ program on land use/land cover and hydrological regimes in a watershed of the Chinese Loess Plateau over the next 30 years. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, S.Q.; Zhu, Z.Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.Y.; Xie, Y.; Wang, G.N.; Li, Y.S. Regional soil erosion assessment based on a sample survey and geostatistics. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2016, 22, 1695–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinton, J.N.; Edwards, G.M.; Morgan, R.P.C. The influence of vegetation species and plant properties on runoff and soil erosion: Results from a rainfall simulation study in south east Spain. Soil. Use Manag. 1997, 13, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.E.; Zhang, L.; McMahon, T.A.; Western, A.W.; Vertessy, R.A. A review of paired catchment studies for determining changes in water yield resulting from alterations in vegetation. J. Hydrol. 2005, 310, 28–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, Z.; Wei, X.; McNulty, S.G.; Vose, J.M. Potential water yield reduction due to forestation across China. J. Hydrol. 2006, 328, 548–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo-Martínez, M.; Beguería, S. Estimating rainfall erosivity from daily precipitation records: A comparison among methods using data from the Ebro Basin (NE Spain). J. Hydrol. 2009, 379, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fu, B.J.; Sl, P.; Lv, Y.H.; Ciais, P.; Feng, X.M.; Wang, Y.F. Reduced sediment transport in the Yellow River due to anthropogenic changes. Nat. Geosci. 2016, 9, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.P.; Lin, P.F.; Chen, H.; Yan, R.; Zhang, J.J.; Yu, Y.P.; Liu, E.J.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, W.H.; Lv, D.; et al. Understanding land use and cover change impacts on run-off and sediment load at flood events on the Loess Plateau, China. Hydrol. Process. 2018, 32, 576–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yin, X.; Wang, Z. Effect of soil and water conservation measures on the reduction of runoff and sediment load in a loess hilly-gully region. J. Soil Water Conserv. 2021, 76, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhou, X.; Huang, K.; Hao, G.R.; Li, J.K. Research on optimal control of non-point source pollution: A case study from the Danjiang River basin in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. R. 2022, 29, 15582–15602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.G.; Huang, C.C.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Pang, J.L.; Ma, Y.G. Hydrological reconstruction of extreme palaeoflood events 9000-8500 a BP in the Danjiang River Valley, tributary of the Danjiangkou Reservoir, China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2020, 13, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.W.; Ding, W.F.; Xu, W.T.; Zhu, X.D.; Wang, X.K.; Tang, W.J. Assessment of an Alternative Climate Product for Hydrological Modeling: A Case Study of the Danjiang River Basin, China. Water 2022, 14, 1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; He, Y.; Liu, W.Q. Attribution of runoff changes in the Danjiang River Basin in the Qinba Mountains, China. Front. For. Glob. Chang. 2023, 6, 1187515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Zhang, X.P.; Ma, Q.; Zhang, J.J.; Ma, T.Y.; Sun, Y.P. Spatiotemporal characteristics of precipitation and extreme events on the Loess Plateau of China between 1957 and 2009. Hydrol. Process. 2014, 28, 4971–4983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, X.; Yue, D.P.; Liang, W.; Li, S. Quantitative analysis of impacts of climate change and human activities on sediment discharge in Danjiang River Basin. Acta Agric. Jiangxi 2016, 28, 102–106+118, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.J.; Su, Y. Assessment of soil erosion in the Qinba Mountains of the southern Shaanxi Province in China using the RUSLE Model. Sustainability 2020, 12, 1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.M.; Lyu, D.; Lei, X.J.; Huang, T.; Li, Y.L.; Yi, H.J.; Guo, J.W.; He, L.; He, J.; Yang, X.H.; et al. Variability of extreme precipitation and rainfall erosivity and their attenuated effects on sediment delivery from 1957 to 2018 on the Chinese Loess Plateau. J. Soil Sediment 2021, 21, 3933–3947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.X.; Ding, W.F.; Lin, Q.M. Characteristics analysis of runoff and sediment variation in Danjiang River Watershed. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2019, 28, 1956–1964, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Chao, Y.; Fan, R.R.; Ren, F.E.; Qi, B.; Ji, K.; Xu, B. Spatial-temporal trends of rainfall erosivity and its implication for sustainable agriculture in the Wei River Basin of China. Agric. Water Manag. 2021, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhu, W.B.; Liu, J.J.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, L.Q.; Wang, L.Y.; Chen, C.A.; Ahmed, N.; Gurung, S.B. Study on multidimensional changes of rainfall erosivity during 1970-2017 in the North-South Transition Zone, China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 969522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Yu, K.X.; Li, Z.B.; Li, P.; Zhang, J.Z.; Wang, A.N.; Ma, L.; Xu, G.C.; Zhang, X. Temporal and spatial variation of rainfall erosivity in the Loess Plateau of China and its impact on sediment load. Catena 2022, 210, 105931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marill, K.A. Advanced statistics: Linear regression, Part I: Simple linear regression. Acad. Emerg. Med. 2004, 11, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, L.; Wang, S.; Fan, X. Channel change at Toudaoguai station and its responses to the operation of upstream reservoirs in the upper Yellow River. J. Geogr. Sci. 2010, 20, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Chiueh, Y.W.; Lien, H.C.; Hsu, C.T. Modeling risk analysis for rice production due to agro-climate change in Taiwan. Paddy Water Environ. 2015, 13, 391–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searcy, J.K.; Hardisoni, C.H.; Langbein, W.B. Double mass curves. In Geological Survey Water Supply Paper 1541-B; US Geological Survey: Washington, DC, USA, 1960. [Google Scholar]
- Mu, X.M.; Zhang, X.Q.; Gao, P.; Wang, F. Theory of double mass curves and its applications in hydrology and meteorology. J. China Hydrol. 2010, 30, 47–51, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar]
- Gao, P.; Li, P.F.; Zhao, B.L.; Xu, R.R.; Zhao, G.J.; Sun, W.Y.; Mu, X.M. Use of double mass curves in hydrologic benefit evaluations. Hydrol. Process. 2017, 31, 4639–4646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.Y.; Yin, S.Q.; Xie, Y.; Yu, B.F.; Liu, B.Y. Rainfall erosivity mapping over mainland China based on high-density hourly rainfall records. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2022, 14, 665–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Guo, X.D.; Zhao, W.W.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, X. A Comparative analysis of runoff and soil loss characteristics between “extreme precipitation year” and “normal precipitation year” at the plot scale: A case study in the Loess Plateau in China. Water 2014, 7, 3343–3366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.W.; Xu, X.L.; Zhu, J.X.; Zhong, F.X.; Xu, C.H.; Wang, K.L. Can precipitation extremes explain variability in runoff and sediment yield across heterogeneous karst watersheds? J. Hydrol. 2021, 596, 125698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, W.Z.; Zhang, X.C.; Zheng, F.L. Impacts of land use change and climate variability on hydrology in an agricultural catchment on the Loess Plateau of China. J. Hydrol. 2009, 377, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, X.P.; Abla, M.; Lü, D.; Yan, R.; Ren, Q.F.; Ren, Z.Y.; Yang, Y.H.; Zhao, W.H.; Lin, P.F.; et al. Effects of vegetation and rainfall types on surface runoff and soil erosion on steep slopes on the Loess Plateau, China. Catena 2018, 170, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.H.; Zhang, X.P.; Lv, D.; Yin, S.Q.; Zhang, M.X.; Zhu, Q.G.Z.; Yu, Q. Remote sensing estimation of the soil erosion cover-management factor for China’s Loess Plateau. Land Degrad. Dev. 2020, 31, 1942–1955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.L.; Wang, G.Q.; Yinglan, A.; Liu, T.X. Ecohydrological effects of litter cover on the hillslope-scale infiltration-runoff patterns for layered soil in forest ecosystem. Ecol. Eng. 2020, 155, 105930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustomji, P.; Zhang, X.P.; Hairsinen, P.B.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, J. River sediment load and concentration responses to changes in hydrology and catchment management in the Loess Plateau region of China. Water Resour. Res. 2008, 45, 377–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Y.; Meng, Q.; You, Q.J.; Huang, T.S.; Zhang, X.M. Influence of vegetation filter strip on slope runoff, sediment yield and nutrient loss. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, S.; Goebes, P.; Puerta, V.L.; Pereira, E.I.P.; Wittwer, R.; Six, J.; van der Heijden, M.G.A.; Scholten, T. Conservation tillage and organic farming reduce soil erosion. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2019, 39, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaraman, S.; Dalal, R.C. No-till farming: Prospects, challenges—Productivity, soil health, and ecosystem services. Soil. Res. 2022, 60, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Harche, S.; Chikhaoui, M.; Naimi, M.; Seif-Ennasr, M.; Whalen, J.; Chaaou, A. No-tillage and agroforestry decrease sediment loss from a hilly landscape in northern Morocco. Catena 2023, 223, 106951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, S.; Basche, A.; Traylor, E.; Roy, T. The efficacy of conservation practices in reducing floods and improving water quality. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1136989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwanake, H.; Mehdi-Schulz, B.; Schulz, K.; Kitaka, N.; Olang, L.O.; Lederer, J.; Herrnegger, M. Agricultural Practices and Soil and Water Conservation in the Transboundary Region of Kenya and Uganda: Farmers’ Perspectives of Current Soil Erosion. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, S.; Bhatt, R.; Sharma, V.; Hadda, M.S. Indigenous practices of soil and water conservation for sustainable hill agriculture and improving livelihood security. Environ. Manag. 2023, 72, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, L.S.; Fang, N.F.; Shi, Z.H.; Tan, W.F. Mid-infrared spectroscopy tracing of channel erosion in highly erosive catchments on the Chinese Loess Plateau. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 687, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Peng, J.B.; Zhuang, J.Q.; Feng, L.; Huo, A.D.; Mu, X.M.; Wang, W.L. Gully erosion and expansion mechanisms in loess tablelands and the scientific basis of gully consolidation and tableland protection. Sci. China Earth Sci. 2023, 53, 806–822, (In Chinese with English abstract). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Index Type | Number | Index | Description | Definition | Units |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intensity | 1 | RX1d | Maximum 1-day precipitation | Annual maximum for 1-day precipitation | mm |
| 2 | RX5d | Maximum 5-day precipitation | Annual maximum for 5-day precipitation | mm |
| Period | Mean | Maximum | Minimum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ⅰ (1957–1969) | 2269 | 4387 | 1480 | 0.37 |
| Ⅱ (1970–1979) | 2123 | 2454 | 1673 | 0.14 |
| Ⅲ (1980–1989) | 2595 | 4495 | 1753 | 0.30 |
| Ⅳ (1990–1999) | 2018 | 3378 | 1621 | 0.25 |
| Ⅴ (2000–2009) | 2386 | 3150 | 1568 | 0.22 |
| Ⅵ (2010–2018) | 2587 | 3882 | 1572 | 0.31 |
| Name of Periods | Range of Periods | Rainfall Erosivity | Proportion of Rainfall Erosivity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Spring | March to May | 339.5 | 14.5 |
| Summer | June to August | 1452.5 | 61.8 |
| Autumn | September to November | 536.1 | 23.3 |
| Winter | December to the following February | 9.8 | 0.4 |
| Wet season | May to October | 2172.5 | 93.0 |
| Dry season | November to the following April | 165.3 | 7.0 |
| June–September | June to September | 1833.2 | 78.5 |
| Annual | January to December | 2337.8 | 100 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, X. Spatiotemporal Trends and Variations in Rainfall Erosivity in the East Qinling Mountains and the Environmental Impacts. Atmosphere 2024, 15, 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091050
Xu X. Spatiotemporal Trends and Variations in Rainfall Erosivity in the East Qinling Mountains and the Environmental Impacts. Atmosphere. 2024; 15(9):1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091050
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Xiaoming. 2024. "Spatiotemporal Trends and Variations in Rainfall Erosivity in the East Qinling Mountains and the Environmental Impacts" Atmosphere 15, no. 9: 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091050
APA StyleXu, X. (2024). Spatiotemporal Trends and Variations in Rainfall Erosivity in the East Qinling Mountains and the Environmental Impacts. Atmosphere, 15(9), 1050. https://doi.org/10.3390/atmos15091050





